Exploring the effect of khat (Catha edulis) chewing on the pharmacokinetics of the antiplatelet drug clopidogrel in rats using the newly developed LC-MS/MS technique
-
Hassan A. Alhazmi
Abstract
Clopidogrel (CLOP) is widely used worldwide for cardiovascular complications. CLOP is highly metabolized in the liver to its active metabolite by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Studies have shown that khat, an addictive substance, is a powerful inhibitor of cytochrome P450 enzymes and can influence the metabolism of drugs that are concomitantly used. Therefore, this study was designed to evaluate the effects of khat on the pharmacokinetics of CLOP in rats. In this study, rats were administered either CLOP alone or CLOP combined with khat and their plasma were obtained at different time intervals and analyzed using the newly developed and validated liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method using foretinib (FTB) as the internal standard. The corresponding peak area of the analyte versus FTB was used for calculating the peak ratio. The validated LC-MS/MS method resulted in the separation of the well-defined quantifiable peaks of CLOP, FTB, and CLOP metabolite within 7 min. Results showed a significant influence of khat on the peak ratio of CLOP metabolite, which was found to be significantly decreased (P < 0.05) in comparison to CLOP alone, suggesting significant decrease in the conversion of CLOP to its active metabolite due to the inhibition of CYP450 enzymes by khat. Therefore, there might be a need for dose adjustment for regular khat chewers using CLOP.
1 Introduction
Khat (Catha edulis [Vahl] Endl) is a plant that is grown in some parts of the South Western Arab Peninsula and East Africa [1]. Generally, the leaves of the khat plant are chewed on a daily basis by more than 20 million people in the South Western Arabian Peninsula and Eastern part of Africa [2,3]. A large number of people chew khat leaves owing to their amphetamine-like properties with a variety of pleasurable and stimulating effects [4]. The stimulating and euphoric effects of khat are due to the presence of alkaloids, cathine and cathinone [5,6]. These alkaloids are categorized as sympathomimetic amines, the category similar to amphetamine [7,8].
Previously, a number of studies have been carried out to establish the effects of khat on the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzyme family [9,10,11]. In one of these studies, the effects of the khat extract on the activity of three in vitro human recombinant cytochrome P450 (CYP)2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 enzymes were checked and compared with that of cathinone, a constituent of khat [12]. Interestingly, the khat extract was observed to inhibit all three subenzymes with IC50 of 42, 62, and 18 µg/mL, whereas cathinone showed negligible inhibition of the tested CYPs [12].
Clopidogrel (CLOP), an antiplatelet thienopyridine-derivative drug, has been implicated as an effective therapeutic strategy against atherosclerosis, is used for both management and prevention of ischemic stroke [13,14], and is widely prescribed to patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in clinical practice. Figure 1 shows the structures of CLOP and foretinib (FTB) along with their molecular weights. CLOP irreversibly inhibits P2Y12 receptor, a subtype of adenosine diphosphate G protein-coupled receptor (P2Y receptor) family [14]. Functioning as a prodrug, CLOP is converted into its active form through two steps by the CYP450 family of enzymes in the liver. CLOP is first converted into 2-oxo-CLOP by CYP2C19, CYP1A2, and CYP2B6 before it is further biotransformed into its active metabolite by CYP3A4, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, and CYP2C9 subenzymes [15].
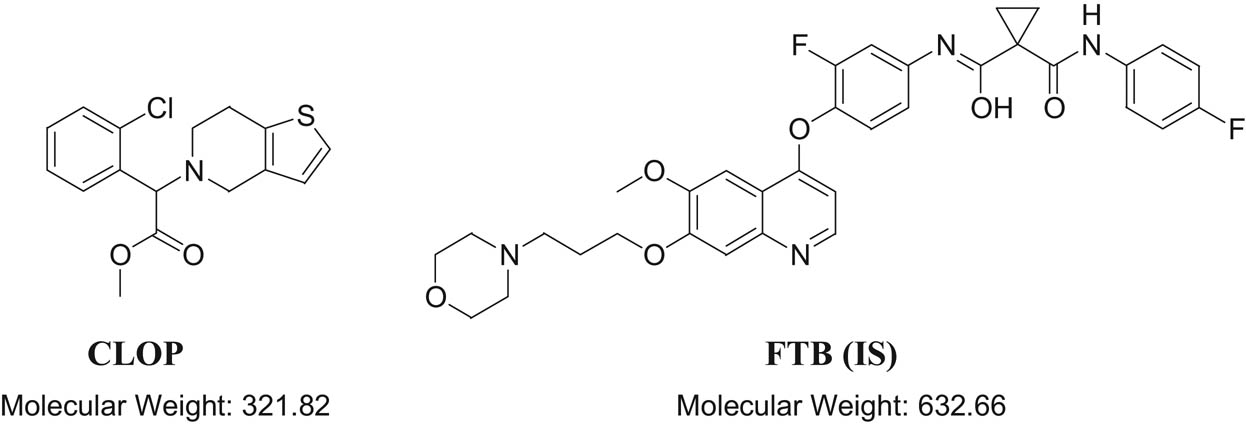
Chemical structures and molecular weights of CLOP and FTB (IS).
As CYP450 regulates the metabolism of a large number of drugs, herbs, and dietary chemicals including CLOP, coadministration of CLOP with inhibitors or inducers of CYP450 might alter the pharmacokinetic profile of CLOP and its conversion to active metabolite, which will eventually influence the efficacy of CLOP [16,17]. For instance, previously it has been reported that the pharmacokinetic profile of CLOP was effectively decreased by coadministration of fluvoxamine, a potent CYP1A2 and CYP2C19 inhibitor [18]. Similarly, the concomitant use of CYP3A4 inhibitors and atorvastatin with CLOP also exhibited a marked reduction in the clinical efficacy of CLOP via inhibition of the CYP3A4-mediated oxidation of CLOP [19]. Moreover, CYP2C19-mediated metabolism of CLOP was also revealed to be decreased by omeprazole, one of the proton pump inhibitors acting as a CYP2C9 inhibitor [20]. Therefore, uncovering the potential alteration in the pharmacokinetics of CLOP by other coadministered drugs is particularly of clinical interest.
Owing to the growing consumption of herbal medicines, the assessment of herb–drug interaction has become an urgent clinical issue, particularly for patients on combination therapy. The interactions of khat with other coadministered chemical drugs including CLOP have never been previously investigated and are particularly important for the patients who regularly chew khat and are on medications. Since khat chewing itself is one of the reasons for cardiovascular diseases, many khat chewers remain on cardiovascular drug therapy. A significant number of khat users are known to have developed some kind of cardiovascular complications due to either khat or some other reason. Cardiovascular drugs are widely prescribed to these patients for the prevention of stroke. Therefore, it is very important to study the effect of khat on these drugs and to establish their interaction. Since khat is a known inhibitor of CYP450 enzymes, it was anticipated that the pharmacokinetic properties of CLOP could be affected by the concomitant use of khat. This study is very important for attracting the attention of physicians and clinical practitioners when prescribing the optimal dose of CLOP for khat-chewing patients. Therefore, we developed a sensitive, rapid, and robust liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) technique to quantify CLOP in plasma samples using FTB (GSK1363089), which is a CYP450-3A subfamily substrate as International Standard (IS) to investigate the potential effect of khat on pharmacokinetics of CLOP and its metabolite.
2 Experimental
2.1 Chemicals and reagents
CLOP and FTB (IS) reference standards were purchased from Med Chem Express (USA). High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-grade acetonitrile (ACN), analytical reagent-grade ammonium formate (HCOONH4), formic acid (HCOOH), and microsomes from human liver (pooled; M0567) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The HPLC-grade water was used throughout the study and was produced in our lab using Milli-Q® plus filtration system (Missouri city, TX, USA).
2.2 Plant material
Khat (C. edulis [Vahl] Endl) leaves were obtained from the Substance Abuse and Toxicology Research Centre of Jazan University. Freshly cultivated khat leaves that were grown at the western border of Jazan province were selected for the study. In order to have more cathinone content, smaller leaves present at the apex of the branch were used. The doses of the khat leaves administered to rats were calculated according to the general human intake of khat on a daily basis.
2.3 LC-MS/MS methodology
2.3.1 Operating parameters
The best chromatographic separation with high resolution was obtained for CLOP and FTB (IS) by optimizing all LC-MS/MS parameters (Table 1). For the analysis of CLOP in plasma samples, FTB was chosen as the IS in the light of the fact that similar extraction technique could effectively be utilized for the two drugs. A triple quadrupole (QqQ) mass spectrometer working in the positive electrospray–ionization interface (ESI) source mode was used for the detection of peaks. In the ESI source, the low-purity nitrogen (12 L/min) was used as the drying gas, whereas high-purity nitrogen (55 psi) was utilized as the collision gas. Moreover, the ESI temperature “T” and the capillary voltage “V” were maintained at 350°C and 4,000 V, respectively. MassHunter software (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used to control the instruments and for data acquisition.
LC-MS/MS analytical parameters
| LC | MS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRLC | Agilent 1200 | MS | Agilent 6410 QqQ | |
| Isocratic mobile phase | 75% ACN | ESI | Positive ESI | |
| 10 mM NH4COOH | 25% | Drying gas: N2 of low purity at 12 L/min | ||
| pH: 4.2 | ||||
| Flow rate: 0.2 mL/min | Pressure (60 psi) | |||
| Injection volume: 5 μL | ||||
| Agilent eclipse plus C18 column | Length: 100 mm | Source temp.: 350°C | ||
| Internal diameter: 2.1 mm | Capillary voltage: 4,000 V | |||
| Particle size: 1.8 μm | Collision cell | N2 gas (highly pure) | ||
| Temp.: 20 ± 2°C | Mode | MRM | ||
| Mass spectra segment | 0.0–4.0 min | CLOP MRM | CLOP | m/z 322 → m/z 212, FV:a 135 V, CE:b 15 eV |
| m/z 322 → m/z 184, FV: 130 V, CE: 20 eV | ||||
| 0.0–4.0 min | CLOP-metabolite | CLOP-metabolite | m/z 308 → m/z 113, FV: 130 V, CE: 20 eV | |
| MRM | ||||
| 4.0–7.0 min | FTB MRM | FTB (IS) | m/z 633 → m/z 128, FV: 145 V, CE: 20 eV | |
- a
Fragmentor voltage.
- b
Collison energy.
The mass reactions (parent to fragment ions) from 322 → 212 and 322 → 184 for CLOP, 633 → 128 for FTB, and 308 → 113 for the CLOP metabolite (Figure 2) were observed to quantify the CLOP using the analyzer mode of multiple reaction monitoring (MRM). The fragmentor voltage (FV) was set at 135 and 130 V with collision energy (CE) of 15 and 20 for CLOP and FV of 140 V with a CE of 20 for FTB. The MRM mass analyzer mode was used for CLOP quantification to omit any possible interference caused by the plasma constituents as well as to increase the sensitivity of the method.
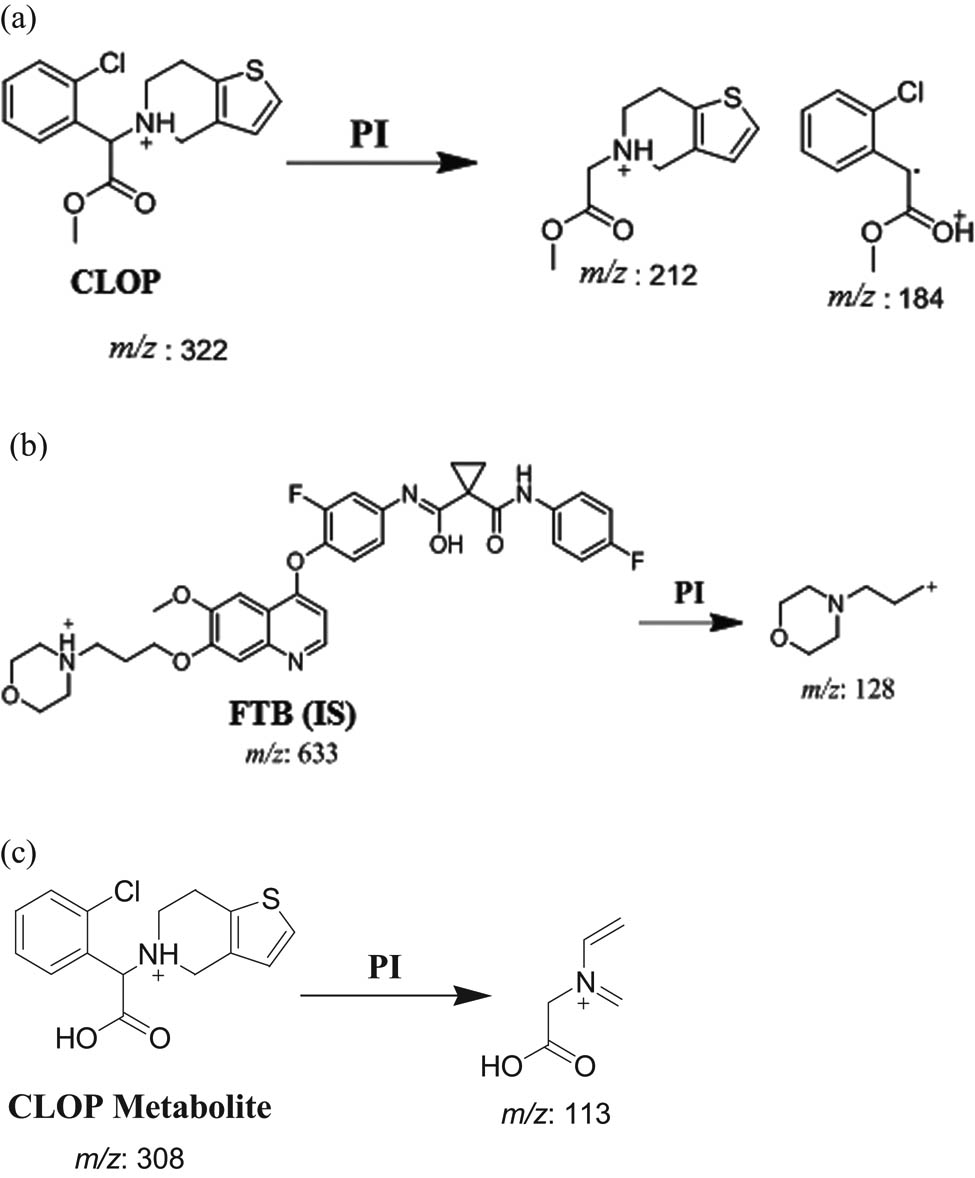
MRM mass spectra of (a) CLOP, (b) FTB, and (c) CLOP metabolite.
2.3.2 CLOP calibration stock solutions
The stock solution of CLOP (1 mg/mL) was prepared in water and was further diluted using the mobile phase to get 100 µg/mL (working solution 1) and 10 µg/mL (working solution 2) solutions. Similarly, the IS stock solution of 100 µg/mL concentration was prepared in DMSO and was further diluted using the mobile phase to obtain the IS working solution of 1 µg/mL.
2.3.3 Preparation of CLOP calibration standards
A calibration plot of 12 points (5, 10, 15, 30, 50, 80, 100, 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500 ng/mL) was constructed by spiking CLOP working solution 2 into rat plasma. For quality control study, four calibration levels were selected, namely, lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of concentration 5 ng/mL, low limit (LQC) of 15 ng/mL, medium limit (MQC) of 150 ng/mL, and high limit (HQC) of 400 ng/mL quality control samples. A fixed volume of IS working solution (100 µL) was added to all samples followed immediately by the addition of ACN to precipitate the protein. The resulting solution was vortexed and then followed by centrifugation at 1,000 rpm for 4 min. The supernatant was siphoned off and injected into the LC-MS system. All the LC-MS analyses were performed in triplicate.
2.3.4 Method validation
Various parameters used for the validation of the newly proposed LC-MS/MS method for CLOP assay were per the guidelines provided by Food and Drug Administration [21]. All the parameters including linearity, sensitivity, assay recovery, specificity, reproducibility, limit of detection (LOD), and limit of quantification (LOQ) were calculated. The least-squares statistical method was used to compute the calibration curve equation (y = ax + b), and a linear fit was confirmed by r2, which showed linearity in the range of 5–500 ng/mL.
2.3.5 Dose selection and corresponding calculations
The homogenate of khat leaves was prepared by mincing fresh khat leaves in 100% distilled water. The estimated amount of khat leaves consumed daily by an adult human was used to calculate the corresponding dose to be administered orally to rats. The daily use of khat in Yemen, Saudi Arabia, and some African countries has been reported earlier [2,22,23]. This was also established by additional research on the average content of fresh leaves of khat from cathinone, cathine, and norephedrine. A psychoactive dose of fresh khat leaves should contain about 0.8 mg cathinone per kg body weight [24]. The chewing dose of fresh khat leaves is estimated to be ∼5 g/kg per chewing session [23]. Therefore, the current study uses the daily use rate of fresh khat rather than the extracted khat. This will provide a more practical conclusion on the pharmacokinetic effects of the whole khat leaves.
2.3.6 Pharmacokinetic study
Male Wistar rats of 200–300 g were used in this study. The study was conducted following the ethical guidelines of the Jazan University ethical committee. Rats were placed individually in cages, allowed to recover, and kept on fasting for 12 h prior to the pharmacokinetic study. Eighteen rats were randomized into three equal groups. The first group served as the control and received the control vehicle (0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose) only. The second group (CK) rats were orally administered with khat (12.4 g/kg dose) first and CLOP (7.75 mg/kg dose) after 15 min. The third group (CA) received oral dose of CLOP alone (7.75 mg/kg dose). Blood samples (250 μL) were collected into heparinized tubes before the start of the study (0 h) and at the following times: 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 , and 4.0 h. All the blood samples obtained were immediately centrifuged at 1,000 rpm at 4°C, and the plasma separated was siphoned off and stored at −80°C till further analyses.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 LC-MS/MS methodology
The mass spectral transitions obtained in MRM mode of CLOP, FTB (IS), and CLOP metabolite are presented in Figure 3. The total run time taken for complete elution of CLOP and FTB was 7 min and the peaks showed good resolution. Also, no carryover peaks were observed in the blank rat plasma matrix sample. Figure 4 represents the MRM mode chromatogram of CLOP standard (500 ng/mL) and FTB (50 ng/mL). CLOP metabolite has been eluted before CLOP prodrug as shown in Figure 5.
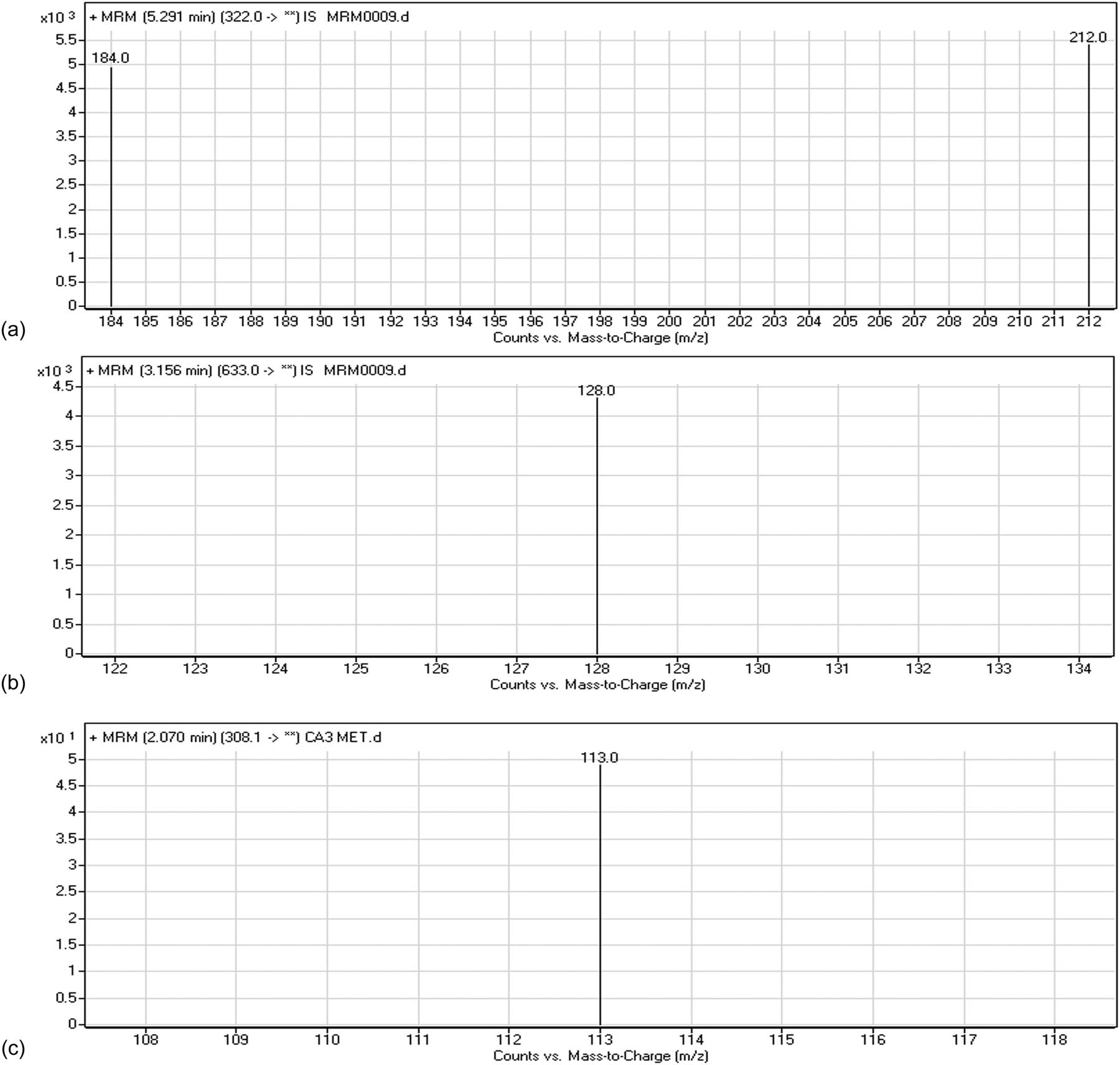
MRM mass spectral transitions of (a) CLOP, (b) FTB (IS), and (c) CLOP metabolite.
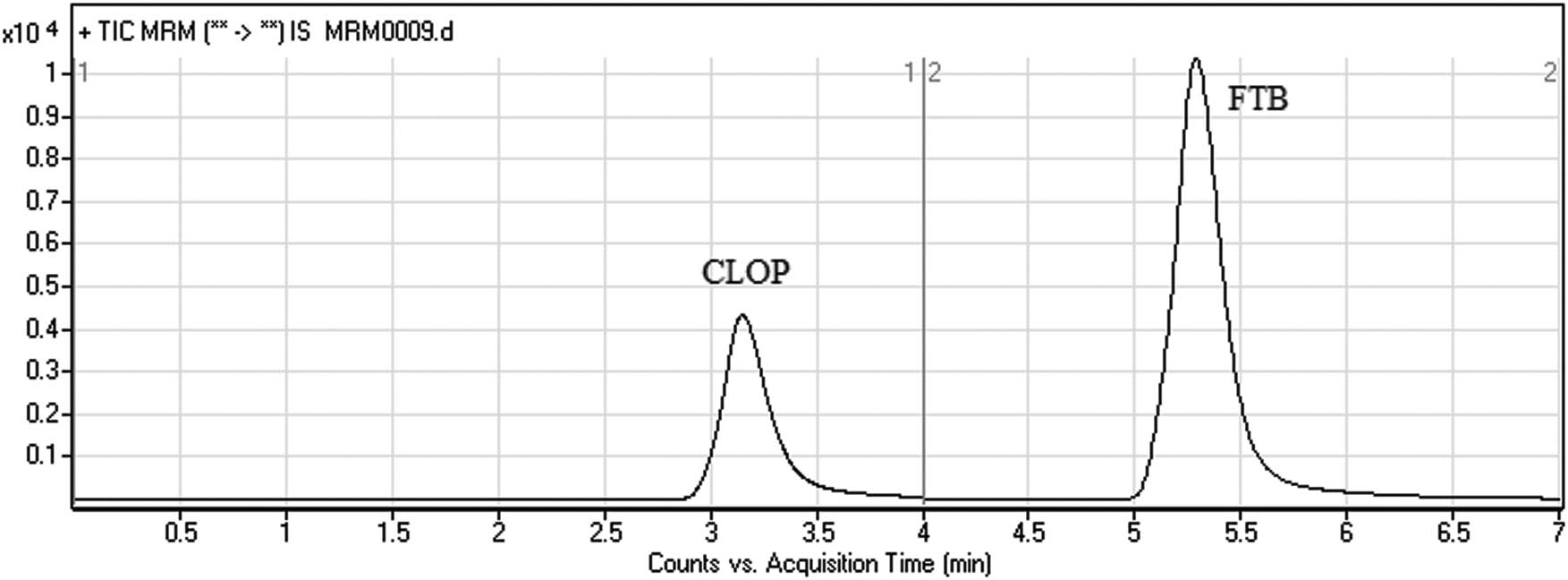
MRM chromatograms of CLOP standard (500 ng/mL) and FTB (50 ng/mL).
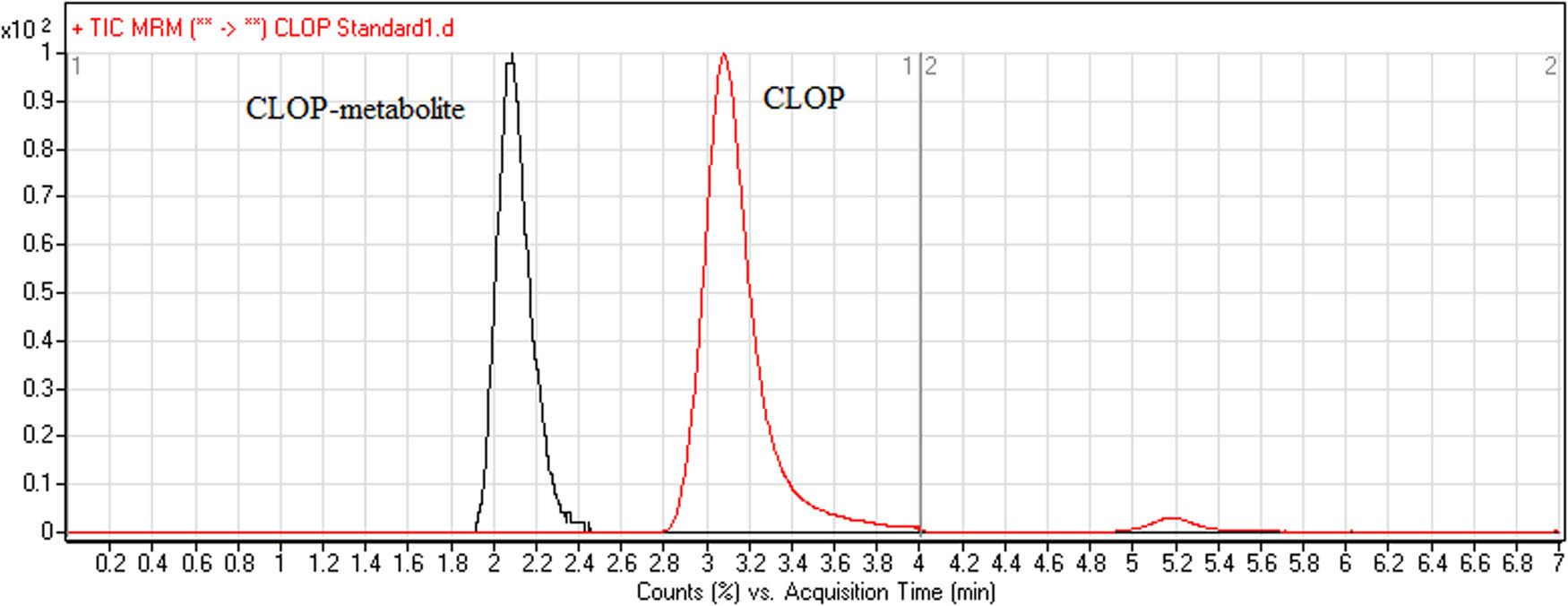
MRM chromatograms of CLOP prodrug (red line, RT: 3.1 min) and its metabolite (black line, RT: 2.1 min).
3.2 Validation of the established LC-MS/MS method
The HPLC-MS/MS was developed to determine the remaining amount of CLOP prodrug, which could not metabolize due to the influence of khat. As evident in Figure 6, optimum separation of CLOP and FTB peaks was obtained in the absence of any peak in the blank CLOP matrix at their elution times, which confirmed the specificity of the newly established method. Moreover, no carryover effect of CLOP and FTB was observed in the MS chromatograms.
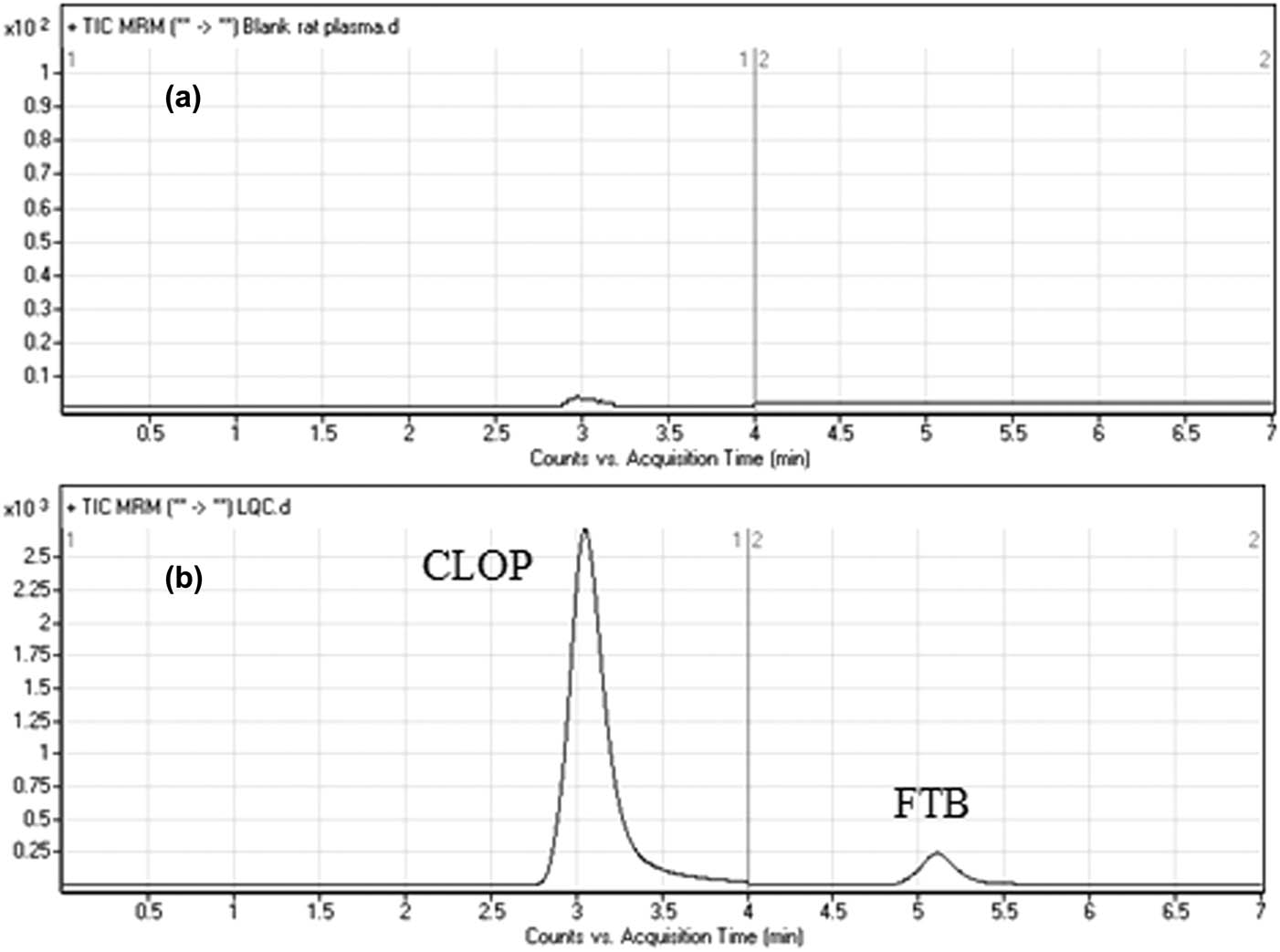
MRM chromatograms of (a) blank rat plasma and (b) CLOP (15 ng/mL; LQC). The blank rat plasma did not reveal any matrix interference.
The linearity range and r2 for the proposed method were found to be 5–500 ng/mL and ≥0.9994, respectively, in the rat plasma matrix, and the linear regression equation for the CLOP calibration plot was y = 0.5942x − 1.264. The LOD and LOQ values were calculated from the slope of the curve and were found to be 1.12 and 3.39 ng/mL, respectively. The lower limit quality control (LLQC) chromatogram displayed a peak with good shape and high signal to noise (S/N) ratio, indicating good sensitivity of the established LC-MS/MS method.
The precision (percentage of relative standard deviation [%RSD]) and the accuracy of the developed method were tested on different quality control samples. The concentrations of CLOP obtained from rat plasma matrix were back calculated and the results are summarized in Table 2. Different LLQC, LQC, MQC, and HQC samples were used for the study and the %RSD and %accuracy were calculated.
CLOP back-calculated calibration standard concentrations from rat plasma matrix
| Samples | CLOP nominal concentrations (ng/mL) | Meana | SD | RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLQC | 5 | 5.25 | 0.06 | 1.18 | 5.03 |
| 10 | 9.82 | 0.41 | 4.21 | −1.85 | |
| LQC | 15 | 14.79 | 0.19 | 1.29 | −1.42 |
| 30 | 32.25 | 0.36 | 1.13 | 7.49 | |
| 50 | 51.56 | 1.54 | 2.99 | 3.12 | |
| 80 | 77.02 | 1.34 | 1.74 | −3.72 | |
| 100 | 97.17 | 1.85 | 1.91 | −2.83 | |
| MQC | 150 | 147.35 | 2.06 | 1.40 | −1.77 |
| 200 | 197.52 | 2.42 | 1.22 | −1.24 | |
| 300 | 295.67 | 3.19 | 1.08 | −1.44 | |
| HQC | 400 | 386.53 | 4.52 | 1.17 | −3.37 |
| 500 | 498.21 | 5.78 | 1.16 | −0.36 |
- a
Mean of six replicates; RSD: relative standard deviation
The three quality control samples, namely, LQC, MQC, and HQC, were also analyzed interday as well as intraday to see the interference and deviation, if any. The %RSD values and %accuracy were calculated for LQC, MQC, and HQC samples. The results for interday and intraday samples are shown in Table 3. All the values obtained were acceptable per the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines Q2R1.
Intraday and interday (accuracy and precision) of the established method
| Rat plasma matrix | LQC (15 ng/mL) | MQC (150 ng/mL) | HQC (400 ng/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraday assay | Interday assay | Intraday assay | Interday assay | Intraday assay | Interday assay | |
| Mean | 14.79* | 14.90** | 147.35 | 148.43 | 386.53 | 384.74 |
| SD | 0.19 | 0.19 | 2.06 | 3.11 | 4.52 | 3.54 |
| Precision (%RSD) | 1.29 | 1.27 | 1.40 | 2.09 | 1.17 | 1.05 |
| % accuracy | −1.42 | −0.65 | −1.77 | −1.05 | −3.37 | −1.34 |
*Mean of 12 replicates on the same day. **Mean of six replicates for 3 days.
LQC: low-quality control; MQC: medium-quality control; HQC: high-quality control.
3.3 Pharmacokinetic study
The developed LC-MS/MS method was applied to study the effect of khat on the pharmacokinetics of CLOP in plasma following their oral administration in rats. Plasma samples obtained from the rats at different time points were brought to room temperature and spiked with IS FTB before injecting into the LC-MS/MS system. Control, CLOP alone, and CLOP + khat groups of samples were analyzed at different times) 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 h) and the analyte to IS peak area ratio was calculated. Values obtained are shown in Table 4 and represented in Figure 7. As evident from Table 4, the peak corresponding to the CLOP disappeared in both CLOP alone and CLOP with khat samples. This is due to the fact that CLOP gets highly metabolized by CYP450 enzymes present in the blood and is converted to its different metabolites. Another peak corresponding to CLOP metabolite was observed from which the peak ratio was calculated and used for comparison. The CLOP metabolite powder was utilized for the MS/MS optimization.
Concentration of CLOP and its metabolite at different time intervals
| Sample | CLOP | Metabolite |
|---|---|---|
| CA* 0 h | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| CA 0.5 h | 0.0 | 128.67 |
| CA 1 h | 0.0 | 141.33 |
| CA 2 h | 0.0 | 360.67 |
| CA 3 h | 0.0 | 194.67 |
| CA 4 h | 0.0 | 125.33 |
| **CK 0 h | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| CK 0.5 h | 0.0 | 0.00 |
| CK 1 h | 0.0 | 28.00 |
| CK 2 h | 0.0 | 117.33 |
| CK 3 h | 0.0 | 126.43 |
| CK 4 h | 0.0 | 48.00 |
| Control 0 h | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Control 0.5 h | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Control 1 h | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Control 2 h | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Control 3 h | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Control 4 h | 0.0 | 0.0 |
*CA = CLOP alone. **CK = CLOP + khat.
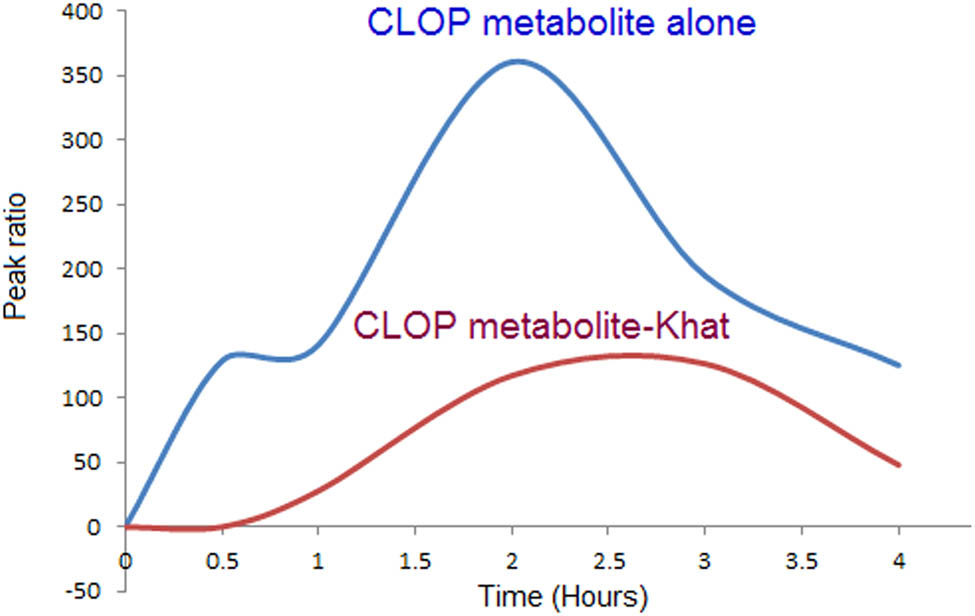
Influence of khat on the level of CLOP active metabolite over time in rat plasm.
As shown in Table 4 and Figure 7, the decreased peak ratios of CLOP metabolite and khat samples indicate the significant influence of khat on CLOP metabolism. In CLOP only samples, the metabolite appeared at 0.5 h interval which increased at 1 and 2 h of the administration and decreased thereafter. The highest peak area was observed at 2 h. On the other hand, CLOP with khat samples showed the appearance of a metabolite peak at 1 h, instead of 0.5 h as observed in the case of CLOP alone. The metabolite peak area at 1 h for CLOP with khat was also observed to be far less than the CLOP alone. It increased at 2 and 3 h under the influence of khat but was still lesser than CLOP alone. The highest peak area was obtained at 3 h which decreased thereafter at 4 h. It was clear from the results that the highest peak area of CLOP with khat which was obtained at 3 h was almost equal to the peak area of CLOP only at 0.5 h. It shows that the concentration of CLOP metabolite decreased under the influence of khat and less CLOP metabolite was available in the blood when compared to CLOP only. This is because of the fact that khat has potentially inhibited the CYP450 enzymes which are responsible for the metabolism of CLOP to its active metabolite. However, the CLOP prodrug peak in the presence of khat did not appear, and this probably was due to the fact that khat could not influence the first step of CLOP prodrug metabolism and could not inhibit the enzymes that convert the CLOP prodrug to its metabolites.
Khat intake is a major problem associated with a number of people worldwide particularly in the Gulf region. Generally, the leaves of khat are chewed on a daily basis by more than 20 million people on the Arabian Peninsula and Eastern part of Africa [25,26]. A large number of people chew khat leaves due to their amphetamine-like properties involving a variety of pleasurable and stimulating effects [27]. It is expected that around 500 g of fresh khat leaves are chewed by the user per day depending upon the variety of khat, nature of the user, and the availability in market. This amount usually increases on certain occasions such as cultural/social festivals and ceremonies [28]. More than 60 phytochemicals have been isolated and identified from khat [25]. Our previous research using GC-MS has also identified a number of constituents of khat plants including cathine and cathinone alkaloids [26,27]. The stimulating and euphoric effects of khat are due to the presence of these alkaloids in the plants. These alkaloids are categorized as sympathomimetic amines, the category similar to amphetamine. They result in the feeling of well-being and mental alertness as well as excitement in users, but they have a number of untoward effects as well, which is why their use is banned in many countries. As aforementioned, the previous research shows neither cathine nor cathinone appears to be responsible for the inhibition of cytochrome subenzymes [9,10,12,28]. Therefore, investigating the molecular mechanism of cytochrome subenzymes’ inhibition by khat is still very much needed.
Khat has been used by millions of people around the world, but the effect of khat use on the metabolism of various drugs has not been addressed. Khat has a clear influence on the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of various drugs administered concomitantly including CLOP, as evident from this study. The activity and toxicity of any drug depend upon the concentration that reaches the site of action, and generally, the drug concentration in plasma is related to its pharmacological response. Like other drugs, dosing of CLOP is based on the assumption that a particular dose will produce a predefined blood concentration and, thereby, create the anticipated therapeutic effect. Therefore, this study emphasizes that physicians need to be cautious when prescribing CLOP to khat using patients who should be monitored to determine the optimal dose of CLOP.
4 Conclusions
A sensitive, newly developed, and validated LC-MS/MS method was successfully used to evaluate the effects of khat, a known inhibitor of CYP group of enzymes, on the pharmacokinetics of CLOP, on rats. The use of khat is prevalent in Middle-Eastern countries; and many people, who are suffering from cardiovascular disorders, use CLOP as an antiplatelet drug. Therefore, in khat users, the dose of CLOP should be monitored to achieve the optimal dose. Meanwhile, the physicians and pharmacists should educate the patient about the consequences of the use of khat on the efficiency of drugs prescribed for the chronic diseases.
Author contributions
HAA was involved with LC-MS/MS and manuscript writing; AAK contributed to LC-MS/MS and study design; MWA was involved in LC-MS/MS and study design; WA performed the pharmacokinetic study; MMET contributed to pharmacokinetic study and manuscript writing; and AK contributed to study design and manuscript writing.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Deanship of Scientific Research, Jazan University for providing the financial support (Research initiative project No. SARC/001).
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Haile D, Lakew Y. Khat chewing practice and associated factors among adults in ethiopia: further analysis using the 2011 demographic and health survey. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0130460.10.1371/journal.pone.0130460Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Al-Motarreb A, Baker K, Broadley KJ. Khat: pharmacological and medical aspects and its social use in yemen. Phytother Res. 2002;16(5):403–13.10.1002/ptr.1106Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Meulman T, Bakker J, van den Bos E. Ischemic cardiomyopathy and cerebral infarction in a young patient associated with khat chewing. Case Rep Radiol. 2015;2015:893176.10.1155/2015/893176Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Sallam MA, Sheikh KA, Baxendale R, Azam MN, Hossain AM, El-Setouhy M. The physiological and ergogenic effects of khat (catha edulis forsk) extract. Subst Use Misuse. 2018;53(1):94–100.10.1080/10826084.2017.1325375Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Al Bratty M, Ahsan W, Alhazmi HA, Attafi IM, Khardali IA, Abdelwahab SI. Determination of trace metal concentrations in different parts of the khat varieties (catha edulis) using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy technique and their human exposure assessment. Pharmacogn Mag. 2019;15(63):449.10.4103/pm.pm_658_18Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Nigatu A, Libsu S. Studies on the effects of extracts of fresh khat/catha edulis leaves on the oxidation of niger seed oil. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019;7:421–8.Suche in Google Scholar
[7] Feng L-Y, Battulga A, Han E, Chung H, Li J-H. New psychoactive substances of natural origin: a brief review. J Food Drug Anal. 2017;25(3):461–71.10.1016/j.jfda.2017.04.001Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Gonçalves JL, Alves VL, Aguiar J, Teixeira HM, Câmara JS. Synthetic cathinones: an evolving class of new psychoactive substances. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2019;49(7):549–66.10.1080/10408444.2019.1679087Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Bedada W, de Andrés F, Engidawork E, Hussein J, LLerena A, Aklillu E. Effects of khat (catha edulis) use on catalytic activities of major drug-metabolizing cytochrome p450 enzymes and implication of pharmacogenetic variations. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):12726.10.1038/s41598-018-31191-1Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Bedada W, de Andres F, Engidawork E, Pohanka A, Beck O, Bertilsson L, et al. The psychostimulant khat (catha edulis) inhibits cyp2d6 enzyme activity in humans. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;35(6):694–9.10.1097/JCP.0000000000000413Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Pantano F, Tittarelli R, Mannocchi G, Zaami S, Ricci S, Giorgetti R, et al. Hepatotoxicity induced by “the 3ks”: Kava, kratom and khat. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(4):580.10.3390/ijms17040580Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Lim SYM, Azidin ARB, Ung YT, Al-Shagga M, Alshawsh MA, Mohamed Z, et al. Effect of 95% ethanol khat extract and cathinone on in vitro human recombinant cytochrome p450 (cyp) 2c9, cyp2d6, and cyp3a4 activity. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2019;44(3):423–31.10.1007/s13318-018-0518-2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Johnston SC, Easton JD, Farrant M, Barsan W, Conwit RA, Elm JJ, et al. Clopidogrel and aspirin in acute ischemic stroke and high-risk tia. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(3):215–25.10.1056/NEJMoa1800410Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Liu F, Tantry US, Gurbel PA. P2y12 receptor inhibitors for secondary prevention of ischemic stroke. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16(8):1149–65.10.1517/14656566.2015.1035256Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Zhu Y, Zhou J. In vitro biotransformation studies of 2-oxo-clopidogrel: multiple thiolactone ring-opening pathways further attenuate prodrug activation. Chem Res Toxicol. 2012;26(1):179–90.10.1021/tx300460kSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Bath PM, May J, Heptinstall S. Clinical utility of remote platelet function measurement using p-selectin: assessment of aspirin, clopidogrel, and prasugrel and bleeding disorders. Platelets. 2018;29(5):425–30.10.1080/09537104.2018.1445839Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Saiz-Rodríguez M, Belmonte C, Caniego JL, Koller D, Zubiaur P, Bárcena E, et al. Influence of cyp450 enzymes, ces1, pon1, abcb1, and p2ry12 polymorphisms on clopidogrel response in patients subjected to a percutaneous neurointervention. Clin Ther. 2019;41(6):1199–212.10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.04.037Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Chen F, Yang Y, Fang C, Zhao J, Han M, Zhu Q, et al. Effect of fluvoxamine on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of clopidogrel in rats. Xenobiotica. 2015;45(12):1122–8.10.3109/00498254.2015.1045570Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Tirkkonen T, Heikkilä P, Vahlberg T, Huupponen R, Laine K. Epidemiology of cyp 3a4-mediated clopidogrel drug–drug interactions and their clinical consequences. Cardiovasc Ther. 2013;31(6):344–51.10.1111/1755-5922.12028Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Scott SA, Owusu Obeng A, Hulot J-S. Antiplatelet drug interactions with proton pump inhibitors. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2014;10(2):175–89.10.1517/17425255.2014.856883Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] U.S. Department of Health and Human Services FaDA, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Veterinary Medicine (CMV), Guidance for Industry, Bioanalytical Method Validation, May 2018. Document available at https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm070107.pdf.Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Brenneisen R, Fisch H, Koelbing U, Geisshusler S, Kalix P. Amphetamine-like effects in humans of the khat alkaloid cathinone. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30(6):825–8.10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb05447.xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Toennes SW, Harder S, Schramm M, Niess C, Kauert GF. Pharmacokinetics of cathinone, cathine and norephedrine after the chewing of khat leaves. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;56(1):125–30.10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01834.xSuche in Google Scholar
[24] Halket J, Karasu Z, Murray-Lyon I. Plasma cathinone levels following chewing khat leaves (catha edulis forsk.). J Ethnopharmacol. 1995;49(2):111–3.10.1016/0378-8741(95)90038-1Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Getasetegn M. Chemical composition of catha edulis (khat): a review. Phytochem Rev. 2016;15(5):907–20.10.1007/s11101-015-9435-zSuche in Google Scholar
[26] Abdelwahab SI, Hassan A, Mariod A, Al-Sheraji S, Namrima P, Taha M, et al. Catha edulis forsk.(khat): antioxidative activities and chemical diversities using hplc-dad-ms/ms analysis of some ethiopian and yemenis varieties. Ciência e Técnica Vitivinícola. 2015;2015:299–323.Suche in Google Scholar
[27] Alsanosy R, Alhazmi HA, Sultana S, Abdalla AN, Ibrahim Y, AlBratty M, et al. Phytochemical screening and cytotoxic properties of ethanolic extract of young and mature khat leaves. J Chem. 2020, Article ID 7897435. 10.1155/2020/7897435Suche in Google Scholar
[28] Bedada W. Phenotypic and genotypic evaluation of catha edulis f.(khat) effect on cytochrome p450 mediated drug metabolism. Ph.D. Thesis. Addis Ababa University; 2016.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2020 Hassan A. Alhazmi et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Electrochemical antioxidant screening and evaluation based on guanine and chitosan immobilized MoS2 nanosheet modified glassy carbon electrode (guanine/CS/MoS2/GCE)
- Kinetic models of the extraction of vanillic acid from pumpkin seeds
- On the maximum ABC index of bipartite graphs without pendent vertices
- Estimation of the total antioxidant potential in the meat samples using thin-layer chromatography
- Molecular dynamics simulation of sI methane hydrate under compression and tension
- Spatial distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of some trace elements in sediments and grey mangrove (Avicennia marina) along the Arabian Gulf coast, Saudi Arabia
- Amino-functionalized graphene oxide for Cr(VI), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from industrial wastewater
- Chemical composition and in vitro activity of Origanum vulgare L., Satureja hortensis L., Thymus serpyllum L. and Thymus vulgaris L. essential oils towards oral isolates of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata
- Effect of excess Fluoride consumption on Urine-Serum Fluorides, Dental state and Thyroid Hormones among children in “Talab Sarai” Punjab Pakistan
- Design, Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Isoxazole Tagged Indole Hybrid Compounds
- Comparison of kinetic and enzymatic properties of intracellular phosphoserine aminotransferases from alkaliphilic and neutralophilic bacteria
- Green Organic Solvent-Free Oxidation of Alkylarenes with tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Water-Soluble Copper Complex
- Ducrosia ismaelis Asch. essential oil: chemical composition profile and anticancer, antimicrobial and antioxidant potential assessment
- DFT calculations as an efficient tool for prediction of Raman and infra-red spectra and activities of newly synthesized cathinones
- Influence of Chemical Osmosis on Solute Transport and Fluid Velocity in Clay Soils
- A New fatty acid and some triterpenoids from propolis of Nkambe (North-West Region, Cameroon) and evaluation of the antiradical scavenging activity of their extracts
- Antiplasmodial Activity of Stigmastane Steroids from Dryobalanops oblongifolia Stem Bark
- Rapid identification of direct-acting pancreatic protectants from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves tea by the method of serum pharmacochemistry combined with target cell extraction
- Immobilization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa static biomass on eggshell powder for on-line preconcentration and determination of Cr (VI)
- Assessment of methyl 2-({[(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)carbamoyl] sulfamoyl}methyl)benzoate through biotic and abiotic degradation modes
- Stability of natural polyphenol fisetin in eye drops Stability of fisetin in eye drops
- Production of a bioflocculant by using activated sludge and its application in Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
- Molecular Properties of Carbon Crystal Cubic Structures
- Synthesis and characterization of calcium carbonate whisker from yellow phosphorus slag
- Study on the interaction between catechin and cholesterol by the density functional theory
- Analysis of some pharmaceuticals in the presence of their synthetic impurities by applying hybrid micelle liquid chromatography
- Two mixed-ligand coordination polymers based on 2,5-thiophenedicarboxylic acid and flexible N-donor ligands: the protective effect on periodontitis via reducing the release of IL-1β and TNF-α
- Incorporation of silver stearate nanoparticles in methacrylate polymeric monoliths for hemeprotein isolation
- Development of ultrasound-assisted dispersive solid-phase microextraction based on mesoporous carbon coated with silica@iron oxide nanocomposite for preconcentration of Te and Tl in natural water systems
- N,N′-Bis[2-hydroxynaphthylidene]/[2-methoxybenzylidene]amino]oxamides and their divalent manganese complexes: Isolation, spectral characterization, morphology, antibacterial and cytotoxicity against leukemia cells
- Determination of the content of selected trace elements in Polish commercial fruit juices and health risk assessment
- Diorganotin(iv) benzyldithiocarbamate complexes: synthesis, characterization, and thermal and cytotoxicity study
- Keratin 17 is induced in prurigo nodularis lesions
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and acute toxicity studies of a Saudi polyherbal formulation, PHF5
- LaCoO3 perovskite-type catalysts in syngas conversion
- Comparative studies of two vegetal extracts from Stokesia laevis and Geranium pratense: polyphenol profile, cytotoxic effect and antiproliferative activity
- Fragmentation pattern of certain isatin–indole antiproliferative conjugates with application to identify their in vitro metabolic profiles in rat liver microsomes by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- Investigation of polyphenol profile, antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective potential of Aconogonon alpinum (All.) Schur roots
- Lead discovery of a guanidinyl tryptophan derivative on amyloid cascade inhibition
- Physicochemical evaluation of the fruit pulp of Opuntia spp growing in the Mediterranean area under hard climate conditions
- Electronic structural properties of amino/hydroxyl functionalized imidazolium-based bromide ionic liquids
- New Schiff bases of 2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetohydrazide and their Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) metal complexes: their in vitro antimicrobial potentials and in silico physicochemical and pharmacokinetics properties
- Treatment of adhesions after Achilles tendon injury using focused ultrasound with targeted bFGF plasmid-loaded cationic microbubbles
- Synthesis of orotic acid derivatives and their effects on stem cell proliferation
- Chirality of β2-agonists. An overview of pharmacological activity, stereoselective analysis, and synthesis
- Fe3O4@urea/HITh-SO3H as an efficient and reusable catalyst for the solvent-free synthesis of 7-aryl-8H-benzo[h]indeno[1,2-b]quinoline-8-one and indeno[2′,1′:5,6]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives
- Adsorption kinetic characteristics of molybdenum in yellow-brown soil in response to pH and phosphate
- Enhancement of thermal properties of bio-based microcapsules intended for textile applications
- Exploring the effect of khat (Catha edulis) chewing on the pharmacokinetics of the antiplatelet drug clopidogrel in rats using the newly developed LC-MS/MS technique
- A green strategy for obtaining anthraquinones from Rheum tanguticum by subcritical water
- Cadmium (Cd) chloride affects the nutrient uptake and Cd-resistant bacterium reduces the adsorption of Cd in muskmelon plants
- Removal of H2S by vermicompost biofilter and analysis on bacterial community
- Structural cytotoxicity relationship of 2-phenoxy(thiomethyl)pyridotriazolopyrimidines: Quantum chemical calculations and statistical analysis
- A self-breaking supramolecular plugging system as lost circulation material in oilfield
- Synthesis, characterization, and pharmacological evaluation of thiourea derivatives
- Application of drug–metal ion interaction principle in conductometric determination of imatinib, sorafenib, gefitinib and bosutinib
- Synthesis and characterization of a novel chitosan-grafted-polyorthoethylaniline biocomposite and utilization for dye removal from water
- Optimisation of urine sample preparation for shotgun proteomics
- DFT investigations on arylsulphonyl pyrazole derivatives as potential ligands of selected kinases
- Treatment of Parkinson’s disease using focused ultrasound with GDNF retrovirus-loaded microbubbles to open the blood–brain barrier
- New derivatives of a natural nordentatin
- Fluorescence biomarkers of malignant melanoma detectable in urine
- Study of the remediation effects of passivation materials on Pb-contaminated soil
- Saliva proteomic analysis reveals possible biomarkers of renal cell carcinoma
- Withania frutescens: Chemical characterization, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and healing activities
- Design, synthesis and pharmacological profile of (−)-verbenone hydrazones
- Synthesis of magnesium carbonate hydrate from natural talc
- Stability-indicating HPLC-DAD assay for simultaneous quantification of hydrocortisone 21 acetate, dexamethasone, and fluocinolone acetonide in cosmetics
- A novel lactose biosensor based on electrochemically synthesized 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene/thiophene (EDOT/Th) copolymer
- Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: Chemical characterization, scavenging and cytotoxic activities
- Development and validation of a high performance liquid chromatography/diode array detection method for estrogen determination: Application to residual analysis in meat products
- PCSK9 concentrations in different stages of subclinical atherosclerosis and their relationship with inflammation
- Development of trace analysis for alkyl methanesulfonates in the delgocitinib drug substance using GC-FID and liquid–liquid extraction with ionic liquid
- Electrochemical evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of natural compounds on glassy carbon electrode modified with guanine-, polythionine-, and nitrogen-doped graphene
- A Dy(iii)–organic framework as a fluorescent probe for highly selective detection of picric acid and treatment activity on human lung cancer cells
- A Zn(ii)–organic cage with semirigid ligand for solvent-free cyanosilylation and inhibitory effect on ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion ability via regulating mi-RNA16 expression
- Polyphenol content and antioxidant activities of Prunus padus L. and Prunus serotina L. leaves: Electrochemical and spectrophotometric approach and their antimicrobial properties
- The combined use of GC, PDSC and FT-IR techniques to characterize fat extracted from commercial complete dry pet food for adult cats
- MALDI-TOF MS profiling in the discovery and identification of salivary proteomic patterns of temporomandibular joint disorders
- Concentrations of dioxins, furans and dioxin-like PCBs in natural animal feed additives
- Structure and some physicochemical and functional properties of water treated under ammonia with low-temperature low-pressure glow plasma of low frequency
- Mesoscale nanoparticles encapsulated with emodin for targeting antifibrosis in animal models
- Amine-functionalized magnetic activated carbon as an adsorbent for preconcentration and determination of acidic drugs in environmental water samples using HPLC-DAD
- Antioxidant activity as a response to cadmium pollution in three durum wheat genotypes differing in salt-tolerance
- A promising naphthoquinone [8-hydroxy-2-(2-thienylcarbonyl)naphtho[2,3-b]thiophene-4,9-dione] exerts anti-colorectal cancer activity through ferroptosis and inhibition of MAPK signaling pathway based on RNA sequencing
- Synthesis and efficacy of herbicidal ionic liquids with chlorsulfuron as the anion
- Effect of isovalent substitution on the crystal structure and properties of two-slab indates BaLa2−xSmxIn2O7
- Synthesis, spectral and thermo-kinetics explorations of Schiff-base derived metal complexes
- An improved reduction method for phase stability testing in the single-phase region
- Comparative analysis of chemical composition of some commercially important fishes with an emphasis on various Malaysian diets
- Development of a solventless stir bar sorptive extraction/thermal desorption large volume injection capillary gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric method for ultra-trace determination of pyrethroids pesticides in river and tap water samples
- A turbidity sensor development based on NL-PI observers: Experimental application to the control of a Sinaloa’s River Spirulina maxima cultivation
- Deep desulfurization of sintering flue gas in iron and steel works based on low-temperature oxidation
- Investigations of metallic elements and phenolics in Chinese medicinal plants
- Influence of site-classification approach on geochemical background values
- Effects of ageing on the surface characteristics and Cu(ii) adsorption behaviour of rice husk biochar in soil
- Adsorption and sugarcane-bagasse-derived activated carbon-based mitigation of 1-[2-(2-chloroethoxy)phenyl]sulfonyl-3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl) urea-contaminated soils
- Antimicrobial and antifungal activities of bifunctional cooper(ii) complexes with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, flufenamic, mefenamic and tolfenamic acids and 1,10-phenanthroline
- Application of selenium and silicon to alleviate short-term drought stress in French marigold (Tagetes patula L.) as a model plant species
- Screening and analysis of xanthine oxidase inhibitors in jute leaves and their protective effects against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in cells
- Synthesis and physicochemical studies of a series of mixed-ligand transition metal complexes and their molecular docking investigations against Coronavirus main protease
- A study of in vitro metabolism and cytotoxicity of mephedrone and methoxetamine in human and pig liver models using GC/MS and LC/MS analyses
- A new phenyl alkyl ester and a new combretin triterpene derivative from Combretum fragrans F. Hoffm (Combretaceae) and antiproliferative activity
- Erratum
- Erratum to: A one-step incubation ELISA kit for rapid determination of dibutyl phthalate in water, beverage and liquor
- Review Articles
- Sinoporphyrin sodium, a novel sensitizer for photodynamic and sonodynamic therapy
- Natural products isolated from Casimiroa
- Plant description, phytochemical constituents and bioactivities of Syzygium genus: A review
- Evaluation of elastomeric heat shielding materials as insulators for solid propellant rocket motors: A short review
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2019
- An overview of Monascus fermentation processes for monacolin K production
- Study on online soft sensor method of total sugar content in chlorotetracycline fermentation tank
- Studies on the Anti-Gouty Arthritis and Anti-hyperuricemia Properties of Astilbin in Animal Models
- Effects of organic fertilizer on water use, photosynthetic characteristics, and fruit quality of pear jujube in northern Shaanxi
- Characteristics of the root exudate release system of typical plants in plateau lakeside wetland under phosphorus stress conditions
- Characterization of soil water by the means of hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratio at dry-wet season under different soil layers in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha River
- Composition and diurnal variation of floral scent emission in Rosa rugosa Thunb. and Tulipa gesneriana L.
- Preparation of a novel ginkgolide B niosomal composite drug
- The degradation, biodegradability and toxicity evaluation of sulfamethazine antibiotics by gamma radiation
- Special issue on Monitoring, Risk Assessment and Sustainable Management for the Exposure to Environmental Toxins
- Insight into the cadmium and zinc binding potential of humic acids derived from composts by EEM spectra combined with PARAFAC analysis
- Source apportionment of soil contamination based on multivariate receptor and robust geostatistics in a typical rural–urban area, Wuhan city, middle China
- Special Issue on 13th JCC 2018
- The Role of H2C2O4 and Na2CO3 as Precipitating Agents on The Physichochemical Properties and Photocatalytic Activity of Bismuth Oxide
- Preparation of magnetite-silica–cetyltrimethylammonium for phenol removal based on adsolubilization
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Size-dependent growth kinetics of struvite crystals in wastewater with calcium ions
- The effect of silica-calcite sedimentary rock contained in the chicken broiler diet on the overall quality of chicken muscles
- Physicochemical properties of selected herbicidal products containing nicosulfuron as an active ingredient
- Lycopene in tomatoes and tomato products
- Fluorescence in the assessment of the share of a key component in the mixing of feed
- Sulfur application alleviates chromium stress in maize and wheat
- Effectiveness of removal of sulphur compounds from the air after 3 years of biofiltration with a mixture of compost soil, peat, coconut fibre and oak bark
- Special Issue on the 4th Green Chemistry 2018
- Study and fire test of banana fibre reinforced composites with flame retardance properties
- Special Issue on the International conference CosCI 2018
- Disintegration, In vitro Dissolution, and Drug Release Kinetics Profiles of k-Carrageenan-based Nutraceutical Hard-shell Capsules Containing Salicylamide
- Synthesis of amorphous aluminosilicate from impure Indonesian kaolin
- Special Issue on the International Conf on Science, Applied Science, Teaching and Education 2019
- Functionalization of Congo red dye as a light harvester on solar cell
- The effect of nitrite food preservatives added to se’i meat on the expression of wild-type p53 protein
- Biocompatibility and osteoconductivity of scaffold porous composite collagen–hydroxyapatite based coral for bone regeneration
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Effect of natural boron mineral use on the essential oil ratio and components of Musk Sage (Salvia sclarea L.)
- A theoretical and experimental study of the adsorptive removal of hexavalent chromium ions using graphene oxide as an adsorbent
- A study on the bacterial adhesion of Streptococcus mutans in various dental ceramics: In vitro study
- Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study
- Special Issue on Chemistry Today for Tomorrow 2019
- Diabetes mellitus type 2: Exploratory data analysis based on clinical reading
- Multivariate analysis for the classification of copper–lead and copper–zinc glasses
- Special Issue on Advances in Chemistry and Polymers
- The spatial and temporal distribution of cationic and anionic radicals in early embryo implantation
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Magnetic iron oxide/clay nanocomposites for adsorption and catalytic oxidation in water treatment applications
- Special Issue on IC3PE 2018/2019 Conference
- Exergy analysis of conventional and hydrothermal liquefaction–esterification processes of microalgae for biodiesel production
- Advancing biodiesel production from microalgae Spirulina sp. by a simultaneous extraction–transesterification process using palm oil as a co-solvent of methanol
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Omega and the related counting polynomials of some chemical structures
- M-polynomial and topological indices of zigzag edge coronoid fused by starphene
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Electrochemical antioxidant screening and evaluation based on guanine and chitosan immobilized MoS2 nanosheet modified glassy carbon electrode (guanine/CS/MoS2/GCE)
- Kinetic models of the extraction of vanillic acid from pumpkin seeds
- On the maximum ABC index of bipartite graphs without pendent vertices
- Estimation of the total antioxidant potential in the meat samples using thin-layer chromatography
- Molecular dynamics simulation of sI methane hydrate under compression and tension
- Spatial distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of some trace elements in sediments and grey mangrove (Avicennia marina) along the Arabian Gulf coast, Saudi Arabia
- Amino-functionalized graphene oxide for Cr(VI), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from industrial wastewater
- Chemical composition and in vitro activity of Origanum vulgare L., Satureja hortensis L., Thymus serpyllum L. and Thymus vulgaris L. essential oils towards oral isolates of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata
- Effect of excess Fluoride consumption on Urine-Serum Fluorides, Dental state and Thyroid Hormones among children in “Talab Sarai” Punjab Pakistan
- Design, Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Isoxazole Tagged Indole Hybrid Compounds
- Comparison of kinetic and enzymatic properties of intracellular phosphoserine aminotransferases from alkaliphilic and neutralophilic bacteria
- Green Organic Solvent-Free Oxidation of Alkylarenes with tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Water-Soluble Copper Complex
- Ducrosia ismaelis Asch. essential oil: chemical composition profile and anticancer, antimicrobial and antioxidant potential assessment
- DFT calculations as an efficient tool for prediction of Raman and infra-red spectra and activities of newly synthesized cathinones
- Influence of Chemical Osmosis on Solute Transport and Fluid Velocity in Clay Soils
- A New fatty acid and some triterpenoids from propolis of Nkambe (North-West Region, Cameroon) and evaluation of the antiradical scavenging activity of their extracts
- Antiplasmodial Activity of Stigmastane Steroids from Dryobalanops oblongifolia Stem Bark
- Rapid identification of direct-acting pancreatic protectants from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves tea by the method of serum pharmacochemistry combined with target cell extraction
- Immobilization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa static biomass on eggshell powder for on-line preconcentration and determination of Cr (VI)
- Assessment of methyl 2-({[(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)carbamoyl] sulfamoyl}methyl)benzoate through biotic and abiotic degradation modes
- Stability of natural polyphenol fisetin in eye drops Stability of fisetin in eye drops
- Production of a bioflocculant by using activated sludge and its application in Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
- Molecular Properties of Carbon Crystal Cubic Structures
- Synthesis and characterization of calcium carbonate whisker from yellow phosphorus slag
- Study on the interaction between catechin and cholesterol by the density functional theory
- Analysis of some pharmaceuticals in the presence of their synthetic impurities by applying hybrid micelle liquid chromatography
- Two mixed-ligand coordination polymers based on 2,5-thiophenedicarboxylic acid and flexible N-donor ligands: the protective effect on periodontitis via reducing the release of IL-1β and TNF-α
- Incorporation of silver stearate nanoparticles in methacrylate polymeric monoliths for hemeprotein isolation
- Development of ultrasound-assisted dispersive solid-phase microextraction based on mesoporous carbon coated with silica@iron oxide nanocomposite for preconcentration of Te and Tl in natural water systems
- N,N′-Bis[2-hydroxynaphthylidene]/[2-methoxybenzylidene]amino]oxamides and their divalent manganese complexes: Isolation, spectral characterization, morphology, antibacterial and cytotoxicity against leukemia cells
- Determination of the content of selected trace elements in Polish commercial fruit juices and health risk assessment
- Diorganotin(iv) benzyldithiocarbamate complexes: synthesis, characterization, and thermal and cytotoxicity study
- Keratin 17 is induced in prurigo nodularis lesions
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and acute toxicity studies of a Saudi polyherbal formulation, PHF5
- LaCoO3 perovskite-type catalysts in syngas conversion
- Comparative studies of two vegetal extracts from Stokesia laevis and Geranium pratense: polyphenol profile, cytotoxic effect and antiproliferative activity
- Fragmentation pattern of certain isatin–indole antiproliferative conjugates with application to identify their in vitro metabolic profiles in rat liver microsomes by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- Investigation of polyphenol profile, antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective potential of Aconogonon alpinum (All.) Schur roots
- Lead discovery of a guanidinyl tryptophan derivative on amyloid cascade inhibition
- Physicochemical evaluation of the fruit pulp of Opuntia spp growing in the Mediterranean area under hard climate conditions
- Electronic structural properties of amino/hydroxyl functionalized imidazolium-based bromide ionic liquids
- New Schiff bases of 2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetohydrazide and their Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) metal complexes: their in vitro antimicrobial potentials and in silico physicochemical and pharmacokinetics properties
- Treatment of adhesions after Achilles tendon injury using focused ultrasound with targeted bFGF plasmid-loaded cationic microbubbles
- Synthesis of orotic acid derivatives and their effects on stem cell proliferation
- Chirality of β2-agonists. An overview of pharmacological activity, stereoselective analysis, and synthesis
- Fe3O4@urea/HITh-SO3H as an efficient and reusable catalyst for the solvent-free synthesis of 7-aryl-8H-benzo[h]indeno[1,2-b]quinoline-8-one and indeno[2′,1′:5,6]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives
- Adsorption kinetic characteristics of molybdenum in yellow-brown soil in response to pH and phosphate
- Enhancement of thermal properties of bio-based microcapsules intended for textile applications
- Exploring the effect of khat (Catha edulis) chewing on the pharmacokinetics of the antiplatelet drug clopidogrel in rats using the newly developed LC-MS/MS technique
- A green strategy for obtaining anthraquinones from Rheum tanguticum by subcritical water
- Cadmium (Cd) chloride affects the nutrient uptake and Cd-resistant bacterium reduces the adsorption of Cd in muskmelon plants
- Removal of H2S by vermicompost biofilter and analysis on bacterial community
- Structural cytotoxicity relationship of 2-phenoxy(thiomethyl)pyridotriazolopyrimidines: Quantum chemical calculations and statistical analysis
- A self-breaking supramolecular plugging system as lost circulation material in oilfield
- Synthesis, characterization, and pharmacological evaluation of thiourea derivatives
- Application of drug–metal ion interaction principle in conductometric determination of imatinib, sorafenib, gefitinib and bosutinib
- Synthesis and characterization of a novel chitosan-grafted-polyorthoethylaniline biocomposite and utilization for dye removal from water
- Optimisation of urine sample preparation for shotgun proteomics
- DFT investigations on arylsulphonyl pyrazole derivatives as potential ligands of selected kinases
- Treatment of Parkinson’s disease using focused ultrasound with GDNF retrovirus-loaded microbubbles to open the blood–brain barrier
- New derivatives of a natural nordentatin
- Fluorescence biomarkers of malignant melanoma detectable in urine
- Study of the remediation effects of passivation materials on Pb-contaminated soil
- Saliva proteomic analysis reveals possible biomarkers of renal cell carcinoma
- Withania frutescens: Chemical characterization, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and healing activities
- Design, synthesis and pharmacological profile of (−)-verbenone hydrazones
- Synthesis of magnesium carbonate hydrate from natural talc
- Stability-indicating HPLC-DAD assay for simultaneous quantification of hydrocortisone 21 acetate, dexamethasone, and fluocinolone acetonide in cosmetics
- A novel lactose biosensor based on electrochemically synthesized 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene/thiophene (EDOT/Th) copolymer
- Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: Chemical characterization, scavenging and cytotoxic activities
- Development and validation of a high performance liquid chromatography/diode array detection method for estrogen determination: Application to residual analysis in meat products
- PCSK9 concentrations in different stages of subclinical atherosclerosis and their relationship with inflammation
- Development of trace analysis for alkyl methanesulfonates in the delgocitinib drug substance using GC-FID and liquid–liquid extraction with ionic liquid
- Electrochemical evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of natural compounds on glassy carbon electrode modified with guanine-, polythionine-, and nitrogen-doped graphene
- A Dy(iii)–organic framework as a fluorescent probe for highly selective detection of picric acid and treatment activity on human lung cancer cells
- A Zn(ii)–organic cage with semirigid ligand for solvent-free cyanosilylation and inhibitory effect on ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion ability via regulating mi-RNA16 expression
- Polyphenol content and antioxidant activities of Prunus padus L. and Prunus serotina L. leaves: Electrochemical and spectrophotometric approach and their antimicrobial properties
- The combined use of GC, PDSC and FT-IR techniques to characterize fat extracted from commercial complete dry pet food for adult cats
- MALDI-TOF MS profiling in the discovery and identification of salivary proteomic patterns of temporomandibular joint disorders
- Concentrations of dioxins, furans and dioxin-like PCBs in natural animal feed additives
- Structure and some physicochemical and functional properties of water treated under ammonia with low-temperature low-pressure glow plasma of low frequency
- Mesoscale nanoparticles encapsulated with emodin for targeting antifibrosis in animal models
- Amine-functionalized magnetic activated carbon as an adsorbent for preconcentration and determination of acidic drugs in environmental water samples using HPLC-DAD
- Antioxidant activity as a response to cadmium pollution in three durum wheat genotypes differing in salt-tolerance
- A promising naphthoquinone [8-hydroxy-2-(2-thienylcarbonyl)naphtho[2,3-b]thiophene-4,9-dione] exerts anti-colorectal cancer activity through ferroptosis and inhibition of MAPK signaling pathway based on RNA sequencing
- Synthesis and efficacy of herbicidal ionic liquids with chlorsulfuron as the anion
- Effect of isovalent substitution on the crystal structure and properties of two-slab indates BaLa2−xSmxIn2O7
- Synthesis, spectral and thermo-kinetics explorations of Schiff-base derived metal complexes
- An improved reduction method for phase stability testing in the single-phase region
- Comparative analysis of chemical composition of some commercially important fishes with an emphasis on various Malaysian diets
- Development of a solventless stir bar sorptive extraction/thermal desorption large volume injection capillary gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric method for ultra-trace determination of pyrethroids pesticides in river and tap water samples
- A turbidity sensor development based on NL-PI observers: Experimental application to the control of a Sinaloa’s River Spirulina maxima cultivation
- Deep desulfurization of sintering flue gas in iron and steel works based on low-temperature oxidation
- Investigations of metallic elements and phenolics in Chinese medicinal plants
- Influence of site-classification approach on geochemical background values
- Effects of ageing on the surface characteristics and Cu(ii) adsorption behaviour of rice husk biochar in soil
- Adsorption and sugarcane-bagasse-derived activated carbon-based mitigation of 1-[2-(2-chloroethoxy)phenyl]sulfonyl-3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl) urea-contaminated soils
- Antimicrobial and antifungal activities of bifunctional cooper(ii) complexes with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, flufenamic, mefenamic and tolfenamic acids and 1,10-phenanthroline
- Application of selenium and silicon to alleviate short-term drought stress in French marigold (Tagetes patula L.) as a model plant species
- Screening and analysis of xanthine oxidase inhibitors in jute leaves and their protective effects against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in cells
- Synthesis and physicochemical studies of a series of mixed-ligand transition metal complexes and their molecular docking investigations against Coronavirus main protease
- A study of in vitro metabolism and cytotoxicity of mephedrone and methoxetamine in human and pig liver models using GC/MS and LC/MS analyses
- A new phenyl alkyl ester and a new combretin triterpene derivative from Combretum fragrans F. Hoffm (Combretaceae) and antiproliferative activity
- Erratum
- Erratum to: A one-step incubation ELISA kit for rapid determination of dibutyl phthalate in water, beverage and liquor
- Review Articles
- Sinoporphyrin sodium, a novel sensitizer for photodynamic and sonodynamic therapy
- Natural products isolated from Casimiroa
- Plant description, phytochemical constituents and bioactivities of Syzygium genus: A review
- Evaluation of elastomeric heat shielding materials as insulators for solid propellant rocket motors: A short review
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2019
- An overview of Monascus fermentation processes for monacolin K production
- Study on online soft sensor method of total sugar content in chlorotetracycline fermentation tank
- Studies on the Anti-Gouty Arthritis and Anti-hyperuricemia Properties of Astilbin in Animal Models
- Effects of organic fertilizer on water use, photosynthetic characteristics, and fruit quality of pear jujube in northern Shaanxi
- Characteristics of the root exudate release system of typical plants in plateau lakeside wetland under phosphorus stress conditions
- Characterization of soil water by the means of hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratio at dry-wet season under different soil layers in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha River
- Composition and diurnal variation of floral scent emission in Rosa rugosa Thunb. and Tulipa gesneriana L.
- Preparation of a novel ginkgolide B niosomal composite drug
- The degradation, biodegradability and toxicity evaluation of sulfamethazine antibiotics by gamma radiation
- Special issue on Monitoring, Risk Assessment and Sustainable Management for the Exposure to Environmental Toxins
- Insight into the cadmium and zinc binding potential of humic acids derived from composts by EEM spectra combined with PARAFAC analysis
- Source apportionment of soil contamination based on multivariate receptor and robust geostatistics in a typical rural–urban area, Wuhan city, middle China
- Special Issue on 13th JCC 2018
- The Role of H2C2O4 and Na2CO3 as Precipitating Agents on The Physichochemical Properties and Photocatalytic Activity of Bismuth Oxide
- Preparation of magnetite-silica–cetyltrimethylammonium for phenol removal based on adsolubilization
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Size-dependent growth kinetics of struvite crystals in wastewater with calcium ions
- The effect of silica-calcite sedimentary rock contained in the chicken broiler diet on the overall quality of chicken muscles
- Physicochemical properties of selected herbicidal products containing nicosulfuron as an active ingredient
- Lycopene in tomatoes and tomato products
- Fluorescence in the assessment of the share of a key component in the mixing of feed
- Sulfur application alleviates chromium stress in maize and wheat
- Effectiveness of removal of sulphur compounds from the air after 3 years of biofiltration with a mixture of compost soil, peat, coconut fibre and oak bark
- Special Issue on the 4th Green Chemistry 2018
- Study and fire test of banana fibre reinforced composites with flame retardance properties
- Special Issue on the International conference CosCI 2018
- Disintegration, In vitro Dissolution, and Drug Release Kinetics Profiles of k-Carrageenan-based Nutraceutical Hard-shell Capsules Containing Salicylamide
- Synthesis of amorphous aluminosilicate from impure Indonesian kaolin
- Special Issue on the International Conf on Science, Applied Science, Teaching and Education 2019
- Functionalization of Congo red dye as a light harvester on solar cell
- The effect of nitrite food preservatives added to se’i meat on the expression of wild-type p53 protein
- Biocompatibility and osteoconductivity of scaffold porous composite collagen–hydroxyapatite based coral for bone regeneration
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Effect of natural boron mineral use on the essential oil ratio and components of Musk Sage (Salvia sclarea L.)
- A theoretical and experimental study of the adsorptive removal of hexavalent chromium ions using graphene oxide as an adsorbent
- A study on the bacterial adhesion of Streptococcus mutans in various dental ceramics: In vitro study
- Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study
- Special Issue on Chemistry Today for Tomorrow 2019
- Diabetes mellitus type 2: Exploratory data analysis based on clinical reading
- Multivariate analysis for the classification of copper–lead and copper–zinc glasses
- Special Issue on Advances in Chemistry and Polymers
- The spatial and temporal distribution of cationic and anionic radicals in early embryo implantation
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Magnetic iron oxide/clay nanocomposites for adsorption and catalytic oxidation in water treatment applications
- Special Issue on IC3PE 2018/2019 Conference
- Exergy analysis of conventional and hydrothermal liquefaction–esterification processes of microalgae for biodiesel production
- Advancing biodiesel production from microalgae Spirulina sp. by a simultaneous extraction–transesterification process using palm oil as a co-solvent of methanol
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Omega and the related counting polynomials of some chemical structures
- M-polynomial and topological indices of zigzag edge coronoid fused by starphene

