Treatment of Parkinson’s disease using focused ultrasound with GDNF retrovirus-loaded microbubbles to open the blood–brain barrier
-
Feng Wang
and Jianping Lu
Abstract
This study aims to prepare ultrasound-targeted glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) retrovirus-loaded microbubbles (M pLXSN-GDNF) to verify the properties of the microbubbles and to study the therapeutic effect of the GDNF retrovirus-loaded microbubbles combined with ultrasound (U) to open the blood–brain barrier (BBB) in a Parkinson’s disease (PD) model in rats, allowing the retrovirus to pass through the BBB and transfect neurons in the substantia nigra of the midbrain, thereby increasing the expression of GDNF. The results of western blot analysis revealed significant differences between U + MpLXSN-EGFP, U + M + pLXSN-GDNF, and M pLXSN-GDNF (P < 0.05) groups. After 8 weeks of treatment, the evaluation of the effect of increased GDNF expression on behavioral deficits in PD model rats was conducted. The rotation symptom was significantly improved in the U + MpLXSN-GDNF group, and the difference before and after treatment was significant (P < 0.05). Also, the content of dopamine and the number of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive (dopaminergic) neurons were found to be higher in the brain of PD rats in the U + M pLXSN-GDNF group than in the control groups. Ultrasound combined with GDNF retrovirus-loaded microbubbles can enhance the transfection efficiency of neurons in vivo and highly express the exogenous GDNF gene to play a therapeutic role in PD model rats.
1 Introduction
The main pathological feature of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the midbrain, leading to decreased dopamine (DA) content in the striatum [1]. Recently, with advances in cell and molecular biology, scientists have begun to pay attention to finding a way to delay and reverse the degeneration process of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) has been shown to specifically promote the survival of dopaminergic neurons and protect neurons from the effect of neurotoxins, and thus represents a potential therapy for PD. It has been confirmed that increasing GDNF protein content in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system can significantly improve PD symptoms in animal models [2,3]. Therefore, it has been proposed that GDNF and the regulation of its signaling pathway may be an effective molecular target for the treatment of PD [4,5,6]. However, due to the relatively large molecular weight of GDNF (24 kDa), it is difficult for it to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB). For example, direct intracerebral injection or direct injection of a viral vector carrying the GDNF gene into the brain will damage the brain tissue. Accordingly, the development of a non-invasive method for GDNF to cross the BBB, leading to an increase in its effective concentration in the central nervous system, is key for the application of GDNF in the treatment of PD [7]. Ultrasound with microbubbles has been demonstrated to open the BBB locally, reversibly, and noninvasively at energy levels that do not cause cellular damage, which provides the possibility of successfully treating brain diseases, such as PD. Some scientists have used focused ultrasound with a microbubble contrast agent to open the BBB and treat central nervous system diseases by targeted release of drugs and biomolecules [8,9,10]. Acoustic microbubbles could be used as gene carriers to treat diseases. Ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction (UTMD) technology uses microbubble contrast agents as carriers to make an adherent surface or to encapsulate target genes [11,12]. UTMD is definitely a promising strategy to improve the efficiency of gene delivery for multiple applications, and it is proven by increasing evidence that organs can be targeted with its high specificity [13]. Targeted acoustic microbubbles containing target genes are injected intravenously to reach target tissues, where the bubbles are broken to release the genes using ultrasonic irradiation.
With the in-depth study of ultrasound drug-loaded microbubbles and application of ultrasound with microbubbles to open the BBB, microbubbles carrying drugs or genes targeted to treat brain diseases provide a new strategy for the treatment of these diseases. In this study, we prepared targeted cationic microbubbles carrying GDNF retrovirus to enhance the transfection efficiency of neurons in vivo and highly express the exogenous GDNF gene to play a therapeutic role in PD model rats.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and equipment
Distearoylphosphatidylcholine (DSPC), polyethylene glycol–distearoyl phosphatidylethanolamine (DSPE-PEG2000), and polyethylenediamine-600 (PEI600) (Avanti Polar Lipids Inc., Alabaster, AL, USA) were used; an automatic dilution AccuSizer particle counter (Particle Sizing Systems, Santa Barbara, CA, USA), Quintessential Stereotaxic Injector (Stoelting, Wood Dale, IL, USA), inverted fluorescence microscope (Olympus Corp., Tokyo, Japan), and centrifuge (Eppendorf, GmbH, Hamburg, Germany) were the instruments used. Retroviral vectors, pLXSN-GDNF and pLXSN-EGFP, were purchased from HanBio Technology Co. Ltd (Shanghai, China). Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were obtained from Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center (Foshan, China). The system used to generate ultrasound energy in all the experiments comprised a function generator (AGF3022B; Tektronix, USA), an RF amplifier (DC2500A; AR, Souderton PA, USA), and a custom-made passive L–C matching circuit. Ultrasound waves were generated using a single-element focused ultrasound transducer (Valpey Fisher, Hopkinton, MA, USA). The subsequent experiments were performed under these conditions as our previous research (frequency, 1 MHz; MB dosage, 0.5 mL; exposure time, 1 min; pressure amplitude, 0.8 MPa; delay time, 60 s) [14].
2.2 Preparation of cationic microbubbles
DSPC, DSPE-PEG2000, and PEI 600 (Avanti Polar Lipids Inc., Alabaster, AL, USA) were added into a tube at a molar ratio of 9:0.5:0.5. A layer of phospholipid film was formed on the tube wall under nitrogen gas flow (0.1 MPa). The tube mouth was sealed with a sealing film with a few holes punched using a needle. The tube was put into a 500 mL suction filter bottle and subjected to a vacuum for 2–3 h. Subsequently, after adding 5 mL of Tris buffer, the tube was oscillated in an ultrasonic oscillator at 55–60°C for 20 min. The phospholipid suspension in the tube was subpackaged into 2.5 mL penicillin vials with 1 mL in each for gas exchange to fill the vial with perfluoropropane [15]. Normal lipid microbubbles and biotinylated lipid microbubbles were prepared by the above methods.
2.3 Preparation of cationic microbubbles loaded with GDNF virus
After the microbubbles were prepared by the mechanical vibration method, they were washed 3–4 times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) by the centrifugal floating method to remove the unreacted phospholipid not incorporated into microbubbles [16]. A total of 4 × 107 microbubbles were added to 1 mL of a pLXSN-GDNF virus solution (4.2 × 109 particles/mL). After incubation at room temperature for 30 min, the microbubbles were washed twice by the floating method to wash off the unbound virus particles and obtain the pLXSN-GDNF microbubble contrast agent. Four sample aliquots were taken from the virus solution, washing the supernatant each time and microbubble solution binding virus, in which the virus quantity was detected by real-time (fluorescence) quantitative PCR, and the adhesion efficiency of the virus and microbubbles was determined [17]. The preparation and detection methods for pLXSN-EGFP microbubbles were the same as those above.
2.4 Establishment of PD rat models
All procedures in the animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines developed by the National Institutes of Health and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Xinxiang Medical University (Permit No. 18-216). Before injection of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), the PD rats with memory impairment were excluded using the Morris water maze test, and those with rotational behavior were excluded using an apomorphine-induced rotation test after intraperitoneal injection of apomorphine (0.5 mg/kg). The rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 10% chloral hydrate (4 mL/kg). A 2 µL volume of 6-OHDA (4 g/L) was injected at two injection sites, namely in the right dense part of the substantia nigra (4.4 mm behind the anterior fontanelle, 1.2 mm to the right of the sagittal suture, and 7.8 mm under the dura) and the ventral tegmental area of the midbrain (4.8 mm behind the anterior fontanelle, 1.0 mm to the right of the sagittal suture, and 7.8 mm under the dura). The 6-OHDA was injected slowly at a rate of 0.5 μL/min, and stopped 10 min after injection, when the needle was slowly withdrawn. Postoperatively, the rats were kept warm and hydrated, and given a daily intraperitoneal injection of penicillin 30,000 U/d for 1 week to prevent infection. On the 21st day postoperatively, the rats were injected with 0.5 mg/kg apomorphine intraperitoneally to induce left rotational behavior. The rats with an average rotation speed of more than 7 rpm on the 21st day were considered as successful PD models.
2.5 Grouping and treatment
The rats were assigned to four groups: (1) control group (normal group), including normal rats that were not treated; (2) ultrasound + pLXSN-EGFP microbubble group (U + MpLXSN-EGFP group), injected with 4 × 107 pLXSN-EGFP microbubbles into the tail vein and sonicated with ultrasound in the damaged brain region; (3) ultrasound + pLXSN-GDNF microbubble group (U + MpLXSN-GDNF group), injected with 4 × 107 pLXSN-GDNF microbubbles into the tail vein and sonicated with ultrasound in the damaged brain region; and (4) ultrasound + microbubbles + pLXSN-GDNF group (U + M + pLXSN-GDNF group), injected with 4 × 107 microbubbles and pLXSN-GDNF virus into the tail vein and sonicated with ultrasound in the damaged brain region.
After locally opening the BBB by using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided low-frequency focused ultrasound with microbubbles (with or without virus), the transfection efficiency of neurons in the striatum of each group was determined. The level of GDNF in the brain was detected by western blot analysis, and the behavioral changes of PD rats were evaluated.
2.6 Detection of GDNF expression in the brain
Western blot analysis was used to detect the expression of GDNF in the substantia nigra in each group. Total proteins in the substantia nigra were extracted using conventional methods and separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. After transferring to a membrane, 5% bovine serum albumin was used to block the membrane overnight at 4°C, and rabbit anti-rat GDNF protein primary antibodies were added. Glass dishes with the membranes were placed on a shaking table and gently shaken at room temperature for 1 h. Secondary antibodies were added and shaken gently at room temperature for 45 min, and then the membrane was rinsed three times with TBS-T, with gentle shaking at room temperature for 5 min each time. The expression of GDNF was measured after exposure, development, and fixation using an ECL kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA).
2.7 Detection of dopaminergic neurons
Immunohistochemistry analysis was used to detect the changes in the number of dopaminergic neurons by determining the number of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive neurons in each group. Paraffin-embedded sections of rat brain tissues were prepared on microscope slides. The sections were then immersed in 0.5% hydrogen peroxide for 20 min at room temperature and incubated with goat serum for 30 min to block specific antigens. Rabbit anti-TH antibodies were added, and the slides were incubated at 4°C overnight. Afterward, the slides were washed three times with PBS, then secondary sheep anti-rabbit IgG was added and incubated in a dark box at room temperature for 1 h. After washing three times with PBS, the slides were sealed, observed under a microscope, and photographed. ImagePro image analysis software was used to analyze and count the number of TH-positive neurons in the ultrasound-irradiated area from three slices of each rat.
2.8 Effects of different treatments on the content of DA in brain
For measuring the content of DA, samples were prepared with the substantia nigra. The striatum was dissected in accordance with the rat brain atlas. The brain tissues were homogenized in 0.20 M HClO4. Homogenates were centrifuged for 10 min at 4°C and 12,000 g. The supernatant was filtered using a 0.20 µm membrane filter and injected into the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The levels of AD were expressed as ng per μg of brain tissues.
2.9 Statistical analysis
Our normality test indicated that the data belong to normal distribution, and so the measurement data were expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t test for two-group comparisons, and one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc tests for multiple comparisons among more than two groups. All data analyses were performed with SPSS 19.0 statistical software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Detection of ultrasound microbubbles
The average size of the cationic microbubbles was 1.02 ± 0.4 µm, and the concentration was (1.2 ± 0.3) × 1010 bubbles/mL. After loading the virus, the particle size was 1.06 ± 0.4 µm and the concentration was (1.0 ± 0.2) × 1010 bubbles/mL. The average surface potential of the cationic microbubbles was 32.0 ± 2.0 mV measured with a Malvern laser potentiometer, and it changed to −8.67 ± 1.52 mV after adding the virus. The adhesion efficiency of the microbubbles, measured by real-time (fluorescence) quantitative PCR, was 37.2 ± 2.2% (Figure 1).
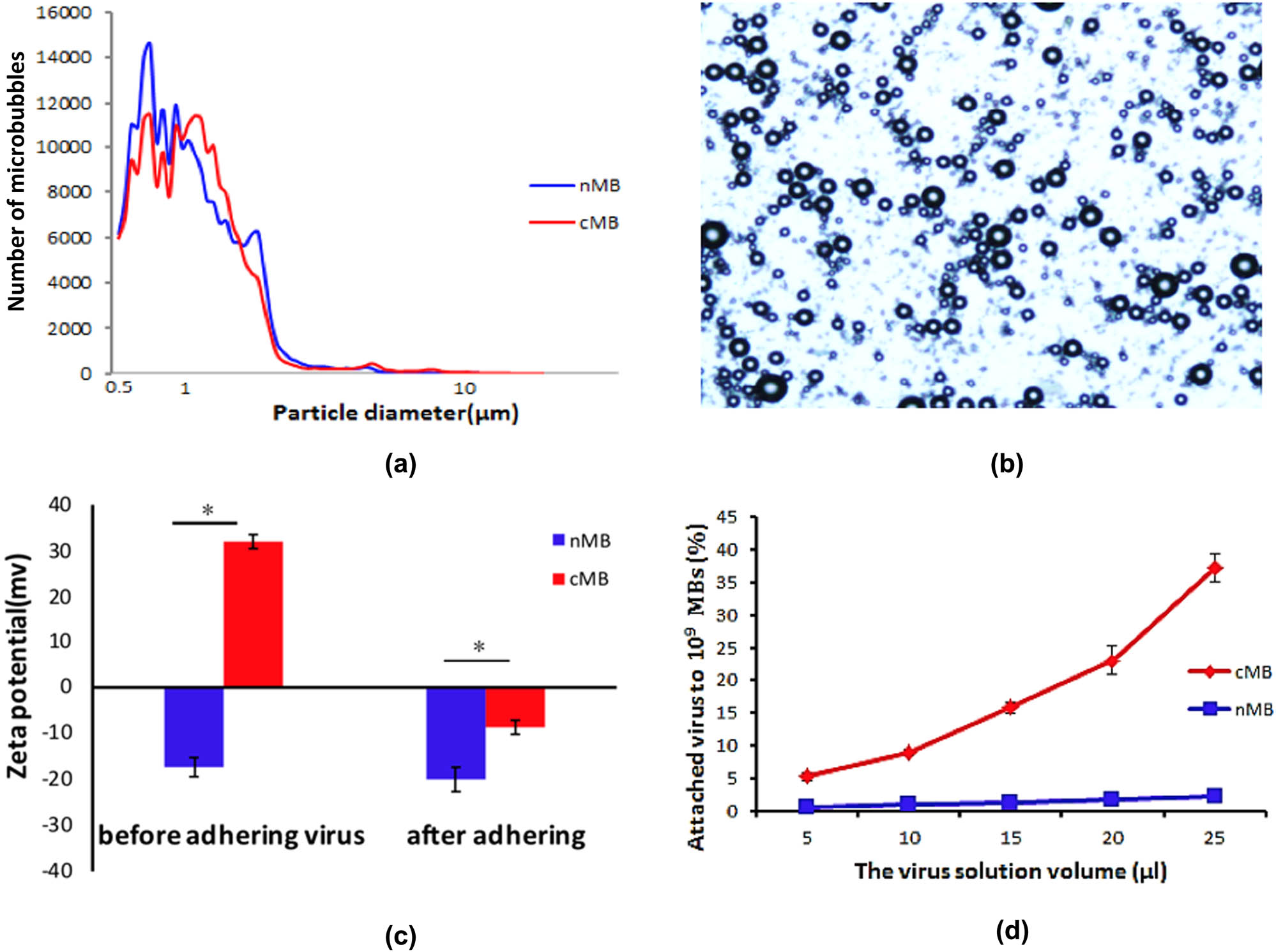
Characterization of virus-loaded microbubbles. (a) Particle size distribution of nMB (normal microbubbles) and cMB (cationic microbubbles); (b) observation of microbubbles in a light field; (c) potential change in microbubbles after adding virus, nMB, and cMB; and (d) percentage of virus adhering to microbubbles.
3.2 Detection of GDNF expression in the brain
After 48 h of ultrasonic irradiation, the rats in each group were sacrificed. The brain tissue from the irradiated area was harvested, and total protein was extracted. The content of GDNF protein in the ultrasound-irradiated area was determined by western blot analysis. The results showed significant difference between the U+MpLXSN-EGFP group and U+M+pLXSN-GDNF group (P < 0.05) (Figure 2).
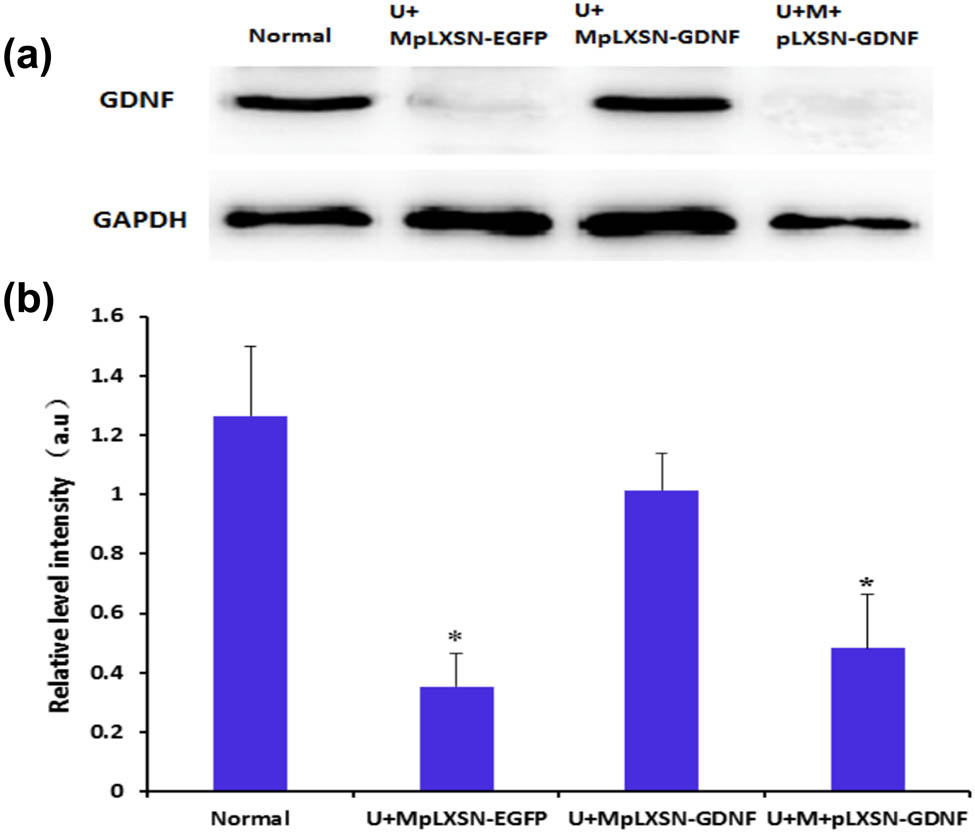
Detection of GDNF protein expression in the substantia nigra of rats from each group by western blot analysis. (a) Expression of GDNF protein in the substantia nigra of rats from each group; (b) relative optical density analysis; compared with the normal group and U + MpLXSN-EGFP group, *P < 0.05.
3.3 Behavioral tests
After 8 weeks of treatment, the rats were subjected to an apomorphine-induced rotation test. The rotation test results demonstrated that after 8 weeks of treatment, the difference between before and after treatment in the U + M + pLXSN-GDNF group was statistically significant (P < 0.05), and in other groups before and after treatment, it was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). Moreover, there was significant rotational behavior (>7 rpm) (Figure 3).
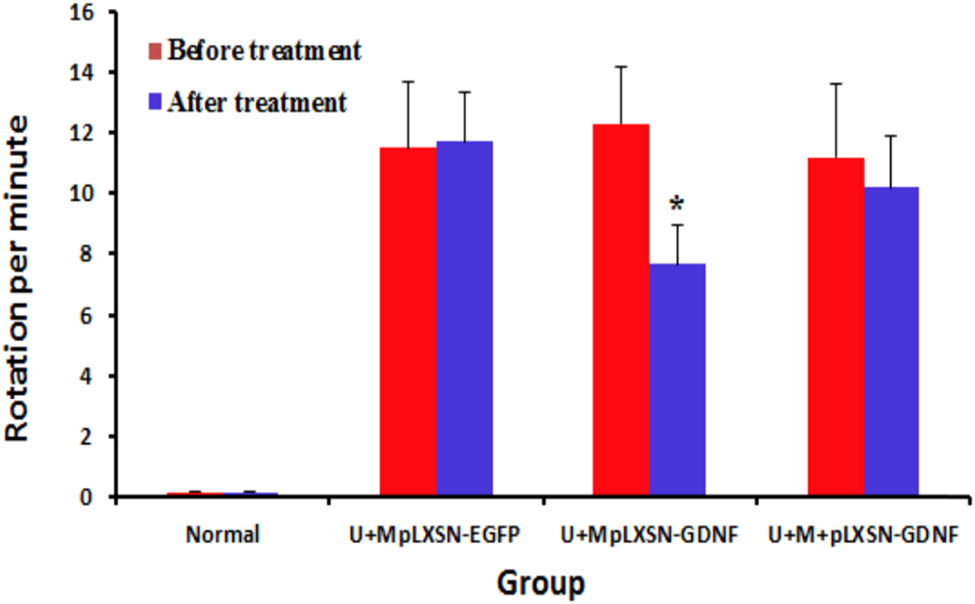
Rotation test after 8 weeks of treatment; the rats were subjected to an apomorphine-induced rotation test to the left by intraperitoneal injection of 0.5 mg/kg apomorphine. The U + M + pLXSN-GDNF group showed a significant difference between before and after treatment, *P < 0.05.
3.4 Quantification of the number of TH-positive neurons
Targeted opening of the BBB promotes the release of pLXSN-GDNF into the lesion area, and the virus transfects the cells in this area. Immunohistochemistry analysis was used to determine the number of TH-positive cells in the substantia nigra of rats from each group, and the protective effect on dopaminergic neurons in the targeted transfection area was assessed. Compared with the control group, the number of TH-positive neurons in the U + MpLXSN-EGFP group and the U + M + pLXSN-GDNF group decreased significantly (P < 0.01). Additionally, the number of dopaminergic TH-positive neurons was significantly increased in the U + MpLXSN-GDNF group compared with the U + MpLXSN-EGFP group and the U + M + pLXSN-GDNF group (P < 0.05) (Figure 4).
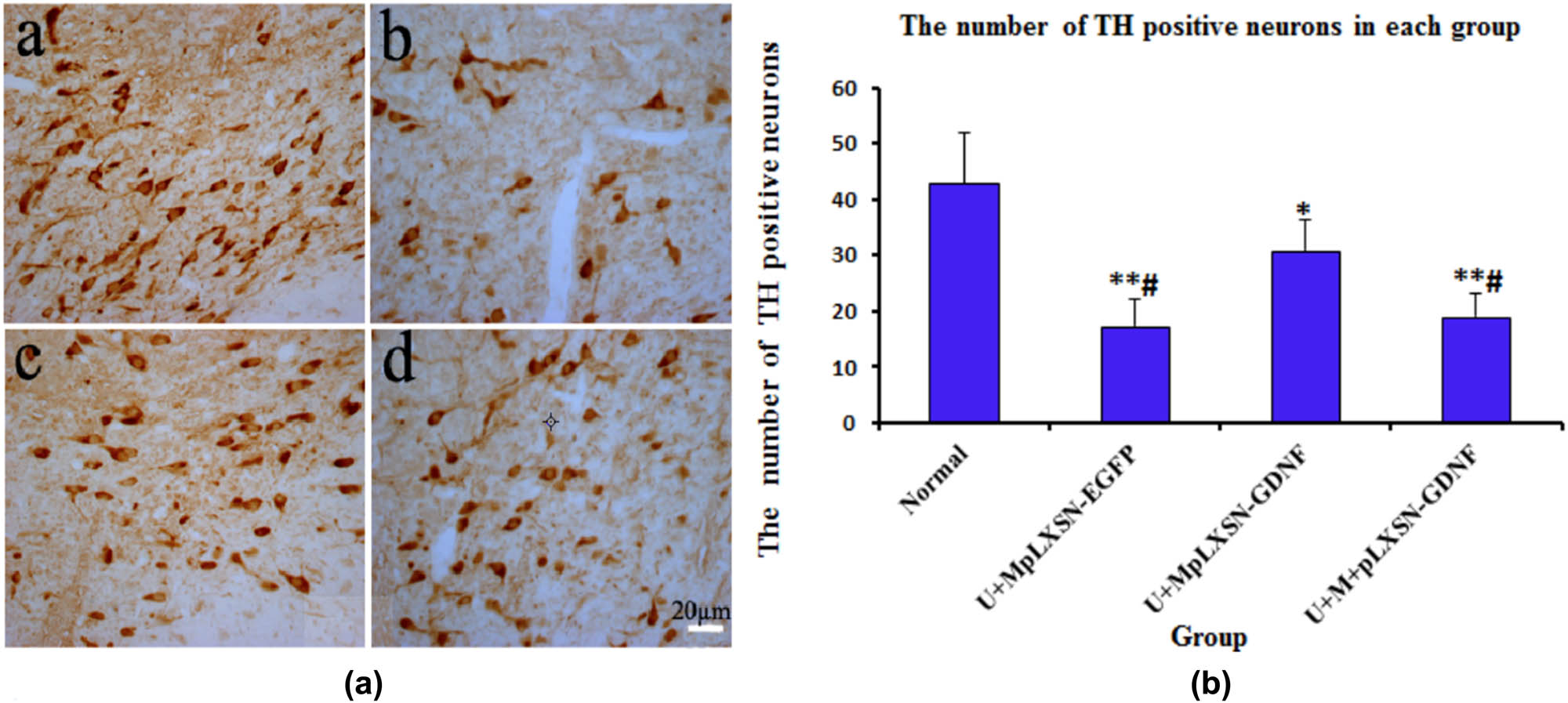
Quantification of the number of TH-positive neurons by immunohistochemistry analysis. (a) Determination of TH-positive neurons in each group; a: normal group; b: U + MpLXSN-EGFP group; c: U + MpLXSN-GDNF group; d: U + M + pLXSN-GDNF group; (b) analysis of TH-positive neurons in each group using ImagePro analysis software; compared with the normal group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; compared with the U + MpLXSN-EGFP group and U + MpLXSN-GDNF group, #P < 0.05.
3.5 Effects of the treatment with GDNF on DA concentration in the substantia nigra of rats
The DA content in the substantia nigra of rats was determined by HPLC, and the data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA test. The results showed that compared with the normal group, there were significant differences in the other groups (U + MpLXSN-EGFP and U + M + pLXSN-GDNF groups, P < 0.01; U + MpLXSN-GDNF group, P < 0.05). Additionally, compared with the U + MpLXSN-EGFP and the U + M + pLXSN-GDNF groups, the DA concentration in the substantia nigra of rats from the U + MpLXSN-GDNF group was significantly increased (P < 0.05) (Figure 5).
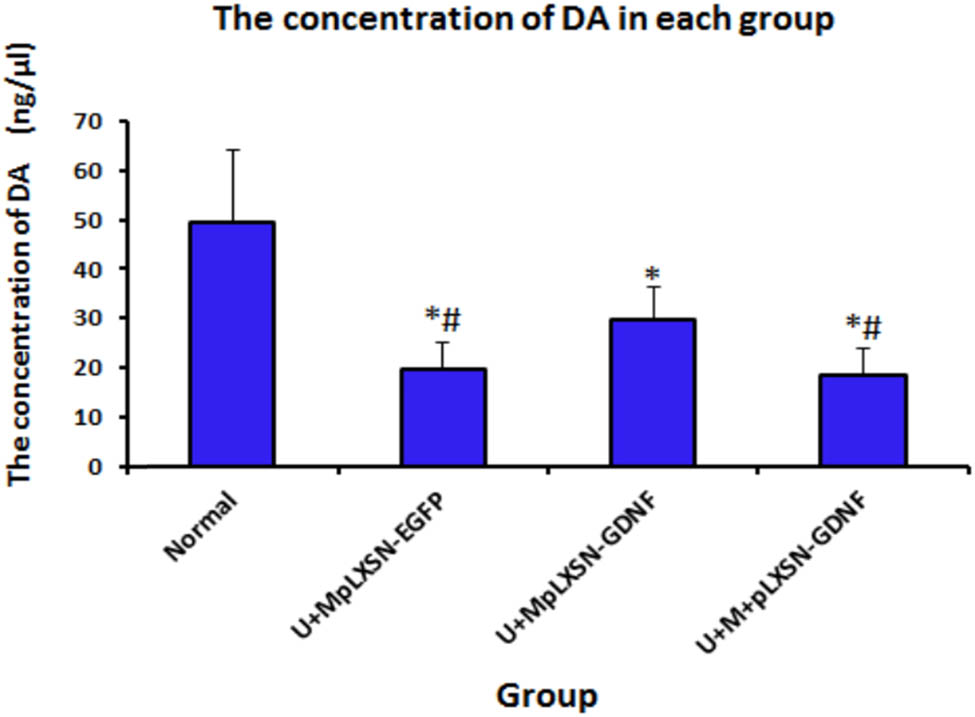
Determination of DA concentration in each group by HPLC. Compared with the normal group **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, compared with the U + MpLXSN-GDNF group #P < 0.05.
4 Discussion
The main pathological feature of PD is the progressive decrease in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons in the midbrain, leading to reduced DA content in the striatum [18,19]. With recent advances in cell and molecular biology, scientists have started to pay attention to finding a way to delay and reverse the degeneration process of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. GDNF has been shown to protect neurons from the effect of neurotoxins, and specifically promote survival of dopaminergic neurons, thereby representing a potential therapeutic approach for patients with PD [20,21,22].
However, due to the relatively large molecular weight of GDNF, it is difficult for it to cross the BBB. Direct intracerebral injection of GDNF or direct injection of viral vectors carrying the GDNF gene into the brain will damage the brain tissue. Thus, getting GDNF non-invasively across the BBB, increasing its effective concentration in the central nervous system, is key for the successful treatment of PD with GDNF [23,24]. Combining ultrasound with microbubbles has been shown to open the BBB locally, reversibly, and noninvasively, thereby offering the possibility for the effective treatment of brain diseases.
In this study, real-time MRI-guided focused ultrasound with microbubbles carrying a retrovirus containing the GDNF gene was used to irradiate the substantia nigra of rats to open the BBB, allow the retrovirus to cross the BBB, transfect dopaminergic neurons in this area, and increase the expression of GDNF in these neurons. The expression of GDNF in the brain was analyzed by western blotting. The difference between the U + MpLXSN-EGFP group, the U + M + pLXSN-GDNF group, and the normal group was statistically significant (P < 0.05) and that between the U + MpLXSN-GDNF group and the normal group was not (P > 0.05). The effect of the increased GDNF content on 6-OHDA PD rats was evaluated by behavioral tests. After 8 weeks of treatment, the rats in each group were subjected to an apomorphine-induced left rotation test. Compared with the behavior before treatment, the rotational behavior of rats in the U + M + pLXSN-GDNF group was significantly improved (P < 0.05), while that in other groups was not (P > 0.05). In addition, immunohistochemistry analysis of the number of TH-positive neurons in the rat brain revealed that after the BBB was partially opened, retrovirus entered the brain to transfect neurons specifically in the substantia nigra, thereby increasing the expression of GDNF and affecting the number of central dopaminergic neurons in this brain region. The results showed significantly increased (P < 0.05) TH-positive neurons in the U + MpLXSN-EGFP group and the U + M + pLXSN-GDNF group. Moreover, U + MpLXSN-GDNF showed a significant therapeutic effect on PD model rats. Therefore, it is confirmed that ultrasound with GDNF virus microbubbles can increase the transfection efficiency of nerve cells in targeted regions of the brain and result in high expression of the exogenous gene GDNF, demonstrating its potential for application as a therapeutic approach to treat PD.
In addition, the mechanism of the GDNF effect on PD was also examined in this study. The pharmacological study of the long-term expression of the target gene in the brain after non-invasive and reversible opening of the BBB by low-frequency focused ultrasound with microbubbles and gene transfection will contribute to applying the advantages of GDNF in the treatment of brain diseases, and provide scientific basis for the use of GDNF in the treatment of PD.
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. U1804187), the Shenzhen Science and Technology Planning Project (grant no. JCYJ20170413100222613, JCYJ20170306154931588), the Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen SZSM201612079, and the Shenzhen Double Chain Grant [2018]256.
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Beal MF. Experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:325–34.10.1038/35072550Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Bohlhalter S. Update on parkinson disease. Rev Med Suisse. 2013;9:247–8.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Bjorklund A, Lindvall O. Parkinson disease gene therapy moves toward the clinic. Nat Med. 2000;6:1207–8.10.1038/81291Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Penttinen AM, Parkkinen I, Voutilainen MH, Koskela M, Back S, Their A, et al. Pre-alpha-pro-GDNF and pre-beta-pro-GDNF isoforms are neuroprotective in the 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurol. 2018;9:457.10.3389/fneur.2018.00457Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Sun S, Zhang Q, Li M, Gao P, Huang K, Beejadhursing R, et al. GDNF promotes survival and therapeutic efficacy of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Transplant. 2020;29:963689720908512.10.1177/0963689720908512Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Kirik D, Cederfjäll E, Halliday G, Petersén Å. Gene therapy for Parkinson’s disease: disease modification by GDNF family of ligands. Neurobiol Dis. 2017;97:179–88.10.1016/j.nbd.2016.09.008Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Biju K, Zhou Q, Li G, Imam SZ, Roberts JL, Morgan WW, et al. Macrophage-mediated GDNF delivery protects against dopaminergic neurodegeneration: a therapeutic strategy for Parkinson’s disease. Mol Ther. 2010;18:1536–44.10.1038/mt.2010.107Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Kobus T, Zervantonakis IK, Zhang YZ, McDannold NJ. Growth inhibition in a brain metastasis model by antibody delivery using focused ultrasound-mediated blood–brain barrier disruption. J Controlled Release. 2016;238:281–8.10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.08.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Alli S, Figueiredo CA, Golbourn B, Sabha N, Wu MY, Bondoc A, et al. Brainstem blood brain barrier disruption using focused ultrasound: a demonstration of feasibility and enhanced doxorubicin delivery. J Controlled Release. 2018;281:29–41.10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.05.005Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Zhao GJ, Huang Q, Wang F, Zhang X, Hu JG, Tan Y, et al. Targeted shRNA-loaded liposome complex combined with focused ultrasound for blood brain barrier disruption and suppressing glioma growth. Cancer Lett. 2018;418:147–58.10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.035Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Tan JK, Pham B, Zong Y, Perez C, Maris DO, Hemphill A, et al. Microbubbles and ultrasound increase intraventricular polyplex gene transfer to the brain. J Controlled Release. 2016;231:86–93.10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.02.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Chang EL, Ting CY, Hsu PH, Lin YC, Liao EC, Huang CY, et al. Angiogenesis-targeting microbubbles combined with ultrasound-mediated gene therapy in brain tumors. J Controlled Release. 2017;255:164–75.10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.04.010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Danialou G, Comtois AS, Dudley RWR, Nalbantoglu J, Gilbert R, Karpati G, et al. Ultrasound increases plasmid-mediated gene transfer to dystrophic muscles without collateral damage. Mol Ther. 2002;6:687–93.10.1016/S1525-0016(02)90723-9Search in Google Scholar
[14] Wang F, Shi Y, Lu L, Liu L, Cai Y, Zheng H, et al. Targeted delivery of GDNF through the blood–brain barrier by MRI-guided focused ultrasound. PLoS One. 2012;7:e52925.10.1371/journal.pone.0052925Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Chang EL, Ting CY, Hsu PH, Lin YC, Liao EC, Huang CY, et al. Angiogenesis-targeting microbubbles combined with ultrasound-mediated gene therapy in brain tumors. J Controlled Release. 2017;255:164–75.10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.04.010Search in Google Scholar
[16] Jin Q, Wang Z, Yan F, Deng Z, Ni F, Wu J, et al. A novel cationic microbubble coated with stearic acid-modified polyethylenimine to enhance DNA loading and gene delivery by ultrasound. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e76544.10.1371/journal.pone.0076544Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Zhu J, Yang L, Zhang Q, Meng J, Lu ZL, Rong R. Autophagy induced by Simian Retrovirus infection controls viral replication and apoptosis of Jurkat T lymphocytes. Viruses. 2020;12(4):381.10.3390/v12040381Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Xu G, Xiong Z, Yong Y, Wang Z, Ke Z, Xia Z, et al. Catalpol attenuates Mptp induced neuronal degeneration of Nigral-Striatal dopaminergic pathway in mice through elevating Glial cell derived neurotrophic factor in striatum. Neuroscience. 2010;167:174–84.10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.01.048Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Sonntag KC, Simantov R, Isacson O. Stem cells may reshape the prospect of Parkinson’s disease therapy. Mol Brain Res. 2005;134:34–51.10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.09.002Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Whone AL, Boca M, Luz M, Woolley M, Mooney L, Dharia S, et al. Extended treatment with Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2019;9:301–13.10.3233/JPD-191576Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Salvatore MF, Zhang JL, Large DM, Wilson PE, Gash CR, Thomas TC, et al. Striatal GDNF administration increases tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation in the rat striatum and substantia nigra. J Neurochem. 2004;90:245–54.10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02496.xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Wu SS, Frucht SJ. Treatment of Parkinson’s disease: what’s on the horizon? CNS Drugs. 2005;19:723–43.10.2165/00023210-200519090-00001Search in Google Scholar
[23] Whone A, Luz M, Boca M, Woolley M, Mooney L, Dharia S, et al. Randomized trial of intermittent intraputamenal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2019;142:512–25.10.1093/brain/awz023Search in Google Scholar
[24] Bohn MC, Kozlowski DA, Connor B. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) as a defensive molecule for neurodegenerative disease: a tribute to the studies of Antonia Vernadakis on neuronal-glial interactions. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2000;18:679–84.10.1016/S0736-5748(00)00036-8Search in Google Scholar
© 2020 Feng Wang et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Electrochemical antioxidant screening and evaluation based on guanine and chitosan immobilized MoS2 nanosheet modified glassy carbon electrode (guanine/CS/MoS2/GCE)
- Kinetic models of the extraction of vanillic acid from pumpkin seeds
- On the maximum ABC index of bipartite graphs without pendent vertices
- Estimation of the total antioxidant potential in the meat samples using thin-layer chromatography
- Molecular dynamics simulation of sI methane hydrate under compression and tension
- Spatial distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of some trace elements in sediments and grey mangrove (Avicennia marina) along the Arabian Gulf coast, Saudi Arabia
- Amino-functionalized graphene oxide for Cr(VI), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from industrial wastewater
- Chemical composition and in vitro activity of Origanum vulgare L., Satureja hortensis L., Thymus serpyllum L. and Thymus vulgaris L. essential oils towards oral isolates of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata
- Effect of excess Fluoride consumption on Urine-Serum Fluorides, Dental state and Thyroid Hormones among children in “Talab Sarai” Punjab Pakistan
- Design, Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Isoxazole Tagged Indole Hybrid Compounds
- Comparison of kinetic and enzymatic properties of intracellular phosphoserine aminotransferases from alkaliphilic and neutralophilic bacteria
- Green Organic Solvent-Free Oxidation of Alkylarenes with tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Water-Soluble Copper Complex
- Ducrosia ismaelis Asch. essential oil: chemical composition profile and anticancer, antimicrobial and antioxidant potential assessment
- DFT calculations as an efficient tool for prediction of Raman and infra-red spectra and activities of newly synthesized cathinones
- Influence of Chemical Osmosis on Solute Transport and Fluid Velocity in Clay Soils
- A New fatty acid and some triterpenoids from propolis of Nkambe (North-West Region, Cameroon) and evaluation of the antiradical scavenging activity of their extracts
- Antiplasmodial Activity of Stigmastane Steroids from Dryobalanops oblongifolia Stem Bark
- Rapid identification of direct-acting pancreatic protectants from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves tea by the method of serum pharmacochemistry combined with target cell extraction
- Immobilization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa static biomass on eggshell powder for on-line preconcentration and determination of Cr (VI)
- Assessment of methyl 2-({[(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)carbamoyl] sulfamoyl}methyl)benzoate through biotic and abiotic degradation modes
- Stability of natural polyphenol fisetin in eye drops Stability of fisetin in eye drops
- Production of a bioflocculant by using activated sludge and its application in Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
- Molecular Properties of Carbon Crystal Cubic Structures
- Synthesis and characterization of calcium carbonate whisker from yellow phosphorus slag
- Study on the interaction between catechin and cholesterol by the density functional theory
- Analysis of some pharmaceuticals in the presence of their synthetic impurities by applying hybrid micelle liquid chromatography
- Two mixed-ligand coordination polymers based on 2,5-thiophenedicarboxylic acid and flexible N-donor ligands: the protective effect on periodontitis via reducing the release of IL-1β and TNF-α
- Incorporation of silver stearate nanoparticles in methacrylate polymeric monoliths for hemeprotein isolation
- Development of ultrasound-assisted dispersive solid-phase microextraction based on mesoporous carbon coated with silica@iron oxide nanocomposite for preconcentration of Te and Tl in natural water systems
- N,N′-Bis[2-hydroxynaphthylidene]/[2-methoxybenzylidene]amino]oxamides and their divalent manganese complexes: Isolation, spectral characterization, morphology, antibacterial and cytotoxicity against leukemia cells
- Determination of the content of selected trace elements in Polish commercial fruit juices and health risk assessment
- Diorganotin(iv) benzyldithiocarbamate complexes: synthesis, characterization, and thermal and cytotoxicity study
- Keratin 17 is induced in prurigo nodularis lesions
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and acute toxicity studies of a Saudi polyherbal formulation, PHF5
- LaCoO3 perovskite-type catalysts in syngas conversion
- Comparative studies of two vegetal extracts from Stokesia laevis and Geranium pratense: polyphenol profile, cytotoxic effect and antiproliferative activity
- Fragmentation pattern of certain isatin–indole antiproliferative conjugates with application to identify their in vitro metabolic profiles in rat liver microsomes by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- Investigation of polyphenol profile, antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective potential of Aconogonon alpinum (All.) Schur roots
- Lead discovery of a guanidinyl tryptophan derivative on amyloid cascade inhibition
- Physicochemical evaluation of the fruit pulp of Opuntia spp growing in the Mediterranean area under hard climate conditions
- Electronic structural properties of amino/hydroxyl functionalized imidazolium-based bromide ionic liquids
- New Schiff bases of 2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetohydrazide and their Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) metal complexes: their in vitro antimicrobial potentials and in silico physicochemical and pharmacokinetics properties
- Treatment of adhesions after Achilles tendon injury using focused ultrasound with targeted bFGF plasmid-loaded cationic microbubbles
- Synthesis of orotic acid derivatives and their effects on stem cell proliferation
- Chirality of β2-agonists. An overview of pharmacological activity, stereoselective analysis, and synthesis
- Fe3O4@urea/HITh-SO3H as an efficient and reusable catalyst for the solvent-free synthesis of 7-aryl-8H-benzo[h]indeno[1,2-b]quinoline-8-one and indeno[2′,1′:5,6]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives
- Adsorption kinetic characteristics of molybdenum in yellow-brown soil in response to pH and phosphate
- Enhancement of thermal properties of bio-based microcapsules intended for textile applications
- Exploring the effect of khat (Catha edulis) chewing on the pharmacokinetics of the antiplatelet drug clopidogrel in rats using the newly developed LC-MS/MS technique
- A green strategy for obtaining anthraquinones from Rheum tanguticum by subcritical water
- Cadmium (Cd) chloride affects the nutrient uptake and Cd-resistant bacterium reduces the adsorption of Cd in muskmelon plants
- Removal of H2S by vermicompost biofilter and analysis on bacterial community
- Structural cytotoxicity relationship of 2-phenoxy(thiomethyl)pyridotriazolopyrimidines: Quantum chemical calculations and statistical analysis
- A self-breaking supramolecular plugging system as lost circulation material in oilfield
- Synthesis, characterization, and pharmacological evaluation of thiourea derivatives
- Application of drug–metal ion interaction principle in conductometric determination of imatinib, sorafenib, gefitinib and bosutinib
- Synthesis and characterization of a novel chitosan-grafted-polyorthoethylaniline biocomposite and utilization for dye removal from water
- Optimisation of urine sample preparation for shotgun proteomics
- DFT investigations on arylsulphonyl pyrazole derivatives as potential ligands of selected kinases
- Treatment of Parkinson’s disease using focused ultrasound with GDNF retrovirus-loaded microbubbles to open the blood–brain barrier
- New derivatives of a natural nordentatin
- Fluorescence biomarkers of malignant melanoma detectable in urine
- Study of the remediation effects of passivation materials on Pb-contaminated soil
- Saliva proteomic analysis reveals possible biomarkers of renal cell carcinoma
- Withania frutescens: Chemical characterization, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and healing activities
- Design, synthesis and pharmacological profile of (−)-verbenone hydrazones
- Synthesis of magnesium carbonate hydrate from natural talc
- Stability-indicating HPLC-DAD assay for simultaneous quantification of hydrocortisone 21 acetate, dexamethasone, and fluocinolone acetonide in cosmetics
- A novel lactose biosensor based on electrochemically synthesized 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene/thiophene (EDOT/Th) copolymer
- Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: Chemical characterization, scavenging and cytotoxic activities
- Development and validation of a high performance liquid chromatography/diode array detection method for estrogen determination: Application to residual analysis in meat products
- PCSK9 concentrations in different stages of subclinical atherosclerosis and their relationship with inflammation
- Development of trace analysis for alkyl methanesulfonates in the delgocitinib drug substance using GC-FID and liquid–liquid extraction with ionic liquid
- Electrochemical evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of natural compounds on glassy carbon electrode modified with guanine-, polythionine-, and nitrogen-doped graphene
- A Dy(iii)–organic framework as a fluorescent probe for highly selective detection of picric acid and treatment activity on human lung cancer cells
- A Zn(ii)–organic cage with semirigid ligand for solvent-free cyanosilylation and inhibitory effect on ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion ability via regulating mi-RNA16 expression
- Polyphenol content and antioxidant activities of Prunus padus L. and Prunus serotina L. leaves: Electrochemical and spectrophotometric approach and their antimicrobial properties
- The combined use of GC, PDSC and FT-IR techniques to characterize fat extracted from commercial complete dry pet food for adult cats
- MALDI-TOF MS profiling in the discovery and identification of salivary proteomic patterns of temporomandibular joint disorders
- Concentrations of dioxins, furans and dioxin-like PCBs in natural animal feed additives
- Structure and some physicochemical and functional properties of water treated under ammonia with low-temperature low-pressure glow plasma of low frequency
- Mesoscale nanoparticles encapsulated with emodin for targeting antifibrosis in animal models
- Amine-functionalized magnetic activated carbon as an adsorbent for preconcentration and determination of acidic drugs in environmental water samples using HPLC-DAD
- Antioxidant activity as a response to cadmium pollution in three durum wheat genotypes differing in salt-tolerance
- A promising naphthoquinone [8-hydroxy-2-(2-thienylcarbonyl)naphtho[2,3-b]thiophene-4,9-dione] exerts anti-colorectal cancer activity through ferroptosis and inhibition of MAPK signaling pathway based on RNA sequencing
- Synthesis and efficacy of herbicidal ionic liquids with chlorsulfuron as the anion
- Effect of isovalent substitution on the crystal structure and properties of two-slab indates BaLa2−xSmxIn2O7
- Synthesis, spectral and thermo-kinetics explorations of Schiff-base derived metal complexes
- An improved reduction method for phase stability testing in the single-phase region
- Comparative analysis of chemical composition of some commercially important fishes with an emphasis on various Malaysian diets
- Development of a solventless stir bar sorptive extraction/thermal desorption large volume injection capillary gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric method for ultra-trace determination of pyrethroids pesticides in river and tap water samples
- A turbidity sensor development based on NL-PI observers: Experimental application to the control of a Sinaloa’s River Spirulina maxima cultivation
- Deep desulfurization of sintering flue gas in iron and steel works based on low-temperature oxidation
- Investigations of metallic elements and phenolics in Chinese medicinal plants
- Influence of site-classification approach on geochemical background values
- Effects of ageing on the surface characteristics and Cu(ii) adsorption behaviour of rice husk biochar in soil
- Adsorption and sugarcane-bagasse-derived activated carbon-based mitigation of 1-[2-(2-chloroethoxy)phenyl]sulfonyl-3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl) urea-contaminated soils
- Antimicrobial and antifungal activities of bifunctional cooper(ii) complexes with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, flufenamic, mefenamic and tolfenamic acids and 1,10-phenanthroline
- Application of selenium and silicon to alleviate short-term drought stress in French marigold (Tagetes patula L.) as a model plant species
- Screening and analysis of xanthine oxidase inhibitors in jute leaves and their protective effects against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in cells
- Synthesis and physicochemical studies of a series of mixed-ligand transition metal complexes and their molecular docking investigations against Coronavirus main protease
- A study of in vitro metabolism and cytotoxicity of mephedrone and methoxetamine in human and pig liver models using GC/MS and LC/MS analyses
- A new phenyl alkyl ester and a new combretin triterpene derivative from Combretum fragrans F. Hoffm (Combretaceae) and antiproliferative activity
- Erratum
- Erratum to: A one-step incubation ELISA kit for rapid determination of dibutyl phthalate in water, beverage and liquor
- Review Articles
- Sinoporphyrin sodium, a novel sensitizer for photodynamic and sonodynamic therapy
- Natural products isolated from Casimiroa
- Plant description, phytochemical constituents and bioactivities of Syzygium genus: A review
- Evaluation of elastomeric heat shielding materials as insulators for solid propellant rocket motors: A short review
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2019
- An overview of Monascus fermentation processes for monacolin K production
- Study on online soft sensor method of total sugar content in chlorotetracycline fermentation tank
- Studies on the Anti-Gouty Arthritis and Anti-hyperuricemia Properties of Astilbin in Animal Models
- Effects of organic fertilizer on water use, photosynthetic characteristics, and fruit quality of pear jujube in northern Shaanxi
- Characteristics of the root exudate release system of typical plants in plateau lakeside wetland under phosphorus stress conditions
- Characterization of soil water by the means of hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratio at dry-wet season under different soil layers in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha River
- Composition and diurnal variation of floral scent emission in Rosa rugosa Thunb. and Tulipa gesneriana L.
- Preparation of a novel ginkgolide B niosomal composite drug
- The degradation, biodegradability and toxicity evaluation of sulfamethazine antibiotics by gamma radiation
- Special issue on Monitoring, Risk Assessment and Sustainable Management for the Exposure to Environmental Toxins
- Insight into the cadmium and zinc binding potential of humic acids derived from composts by EEM spectra combined with PARAFAC analysis
- Source apportionment of soil contamination based on multivariate receptor and robust geostatistics in a typical rural–urban area, Wuhan city, middle China
- Special Issue on 13th JCC 2018
- The Role of H2C2O4 and Na2CO3 as Precipitating Agents on The Physichochemical Properties and Photocatalytic Activity of Bismuth Oxide
- Preparation of magnetite-silica–cetyltrimethylammonium for phenol removal based on adsolubilization
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Size-dependent growth kinetics of struvite crystals in wastewater with calcium ions
- The effect of silica-calcite sedimentary rock contained in the chicken broiler diet on the overall quality of chicken muscles
- Physicochemical properties of selected herbicidal products containing nicosulfuron as an active ingredient
- Lycopene in tomatoes and tomato products
- Fluorescence in the assessment of the share of a key component in the mixing of feed
- Sulfur application alleviates chromium stress in maize and wheat
- Effectiveness of removal of sulphur compounds from the air after 3 years of biofiltration with a mixture of compost soil, peat, coconut fibre and oak bark
- Special Issue on the 4th Green Chemistry 2018
- Study and fire test of banana fibre reinforced composites with flame retardance properties
- Special Issue on the International conference CosCI 2018
- Disintegration, In vitro Dissolution, and Drug Release Kinetics Profiles of k-Carrageenan-based Nutraceutical Hard-shell Capsules Containing Salicylamide
- Synthesis of amorphous aluminosilicate from impure Indonesian kaolin
- Special Issue on the International Conf on Science, Applied Science, Teaching and Education 2019
- Functionalization of Congo red dye as a light harvester on solar cell
- The effect of nitrite food preservatives added to se’i meat on the expression of wild-type p53 protein
- Biocompatibility and osteoconductivity of scaffold porous composite collagen–hydroxyapatite based coral for bone regeneration
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Effect of natural boron mineral use on the essential oil ratio and components of Musk Sage (Salvia sclarea L.)
- A theoretical and experimental study of the adsorptive removal of hexavalent chromium ions using graphene oxide as an adsorbent
- A study on the bacterial adhesion of Streptococcus mutans in various dental ceramics: In vitro study
- Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study
- Special Issue on Chemistry Today for Tomorrow 2019
- Diabetes mellitus type 2: Exploratory data analysis based on clinical reading
- Multivariate analysis for the classification of copper–lead and copper–zinc glasses
- Special Issue on Advances in Chemistry and Polymers
- The spatial and temporal distribution of cationic and anionic radicals in early embryo implantation
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Magnetic iron oxide/clay nanocomposites for adsorption and catalytic oxidation in water treatment applications
- Special Issue on IC3PE 2018/2019 Conference
- Exergy analysis of conventional and hydrothermal liquefaction–esterification processes of microalgae for biodiesel production
- Advancing biodiesel production from microalgae Spirulina sp. by a simultaneous extraction–transesterification process using palm oil as a co-solvent of methanol
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Omega and the related counting polynomials of some chemical structures
- M-polynomial and topological indices of zigzag edge coronoid fused by starphene
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Electrochemical antioxidant screening and evaluation based on guanine and chitosan immobilized MoS2 nanosheet modified glassy carbon electrode (guanine/CS/MoS2/GCE)
- Kinetic models of the extraction of vanillic acid from pumpkin seeds
- On the maximum ABC index of bipartite graphs without pendent vertices
- Estimation of the total antioxidant potential in the meat samples using thin-layer chromatography
- Molecular dynamics simulation of sI methane hydrate under compression and tension
- Spatial distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of some trace elements in sediments and grey mangrove (Avicennia marina) along the Arabian Gulf coast, Saudi Arabia
- Amino-functionalized graphene oxide for Cr(VI), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from industrial wastewater
- Chemical composition and in vitro activity of Origanum vulgare L., Satureja hortensis L., Thymus serpyllum L. and Thymus vulgaris L. essential oils towards oral isolates of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata
- Effect of excess Fluoride consumption on Urine-Serum Fluorides, Dental state and Thyroid Hormones among children in “Talab Sarai” Punjab Pakistan
- Design, Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Isoxazole Tagged Indole Hybrid Compounds
- Comparison of kinetic and enzymatic properties of intracellular phosphoserine aminotransferases from alkaliphilic and neutralophilic bacteria
- Green Organic Solvent-Free Oxidation of Alkylarenes with tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Water-Soluble Copper Complex
- Ducrosia ismaelis Asch. essential oil: chemical composition profile and anticancer, antimicrobial and antioxidant potential assessment
- DFT calculations as an efficient tool for prediction of Raman and infra-red spectra and activities of newly synthesized cathinones
- Influence of Chemical Osmosis on Solute Transport and Fluid Velocity in Clay Soils
- A New fatty acid and some triterpenoids from propolis of Nkambe (North-West Region, Cameroon) and evaluation of the antiradical scavenging activity of their extracts
- Antiplasmodial Activity of Stigmastane Steroids from Dryobalanops oblongifolia Stem Bark
- Rapid identification of direct-acting pancreatic protectants from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves tea by the method of serum pharmacochemistry combined with target cell extraction
- Immobilization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa static biomass on eggshell powder for on-line preconcentration and determination of Cr (VI)
- Assessment of methyl 2-({[(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)carbamoyl] sulfamoyl}methyl)benzoate through biotic and abiotic degradation modes
- Stability of natural polyphenol fisetin in eye drops Stability of fisetin in eye drops
- Production of a bioflocculant by using activated sludge and its application in Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
- Molecular Properties of Carbon Crystal Cubic Structures
- Synthesis and characterization of calcium carbonate whisker from yellow phosphorus slag
- Study on the interaction between catechin and cholesterol by the density functional theory
- Analysis of some pharmaceuticals in the presence of their synthetic impurities by applying hybrid micelle liquid chromatography
- Two mixed-ligand coordination polymers based on 2,5-thiophenedicarboxylic acid and flexible N-donor ligands: the protective effect on periodontitis via reducing the release of IL-1β and TNF-α
- Incorporation of silver stearate nanoparticles in methacrylate polymeric monoliths for hemeprotein isolation
- Development of ultrasound-assisted dispersive solid-phase microextraction based on mesoporous carbon coated with silica@iron oxide nanocomposite for preconcentration of Te and Tl in natural water systems
- N,N′-Bis[2-hydroxynaphthylidene]/[2-methoxybenzylidene]amino]oxamides and their divalent manganese complexes: Isolation, spectral characterization, morphology, antibacterial and cytotoxicity against leukemia cells
- Determination of the content of selected trace elements in Polish commercial fruit juices and health risk assessment
- Diorganotin(iv) benzyldithiocarbamate complexes: synthesis, characterization, and thermal and cytotoxicity study
- Keratin 17 is induced in prurigo nodularis lesions
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and acute toxicity studies of a Saudi polyherbal formulation, PHF5
- LaCoO3 perovskite-type catalysts in syngas conversion
- Comparative studies of two vegetal extracts from Stokesia laevis and Geranium pratense: polyphenol profile, cytotoxic effect and antiproliferative activity
- Fragmentation pattern of certain isatin–indole antiproliferative conjugates with application to identify their in vitro metabolic profiles in rat liver microsomes by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- Investigation of polyphenol profile, antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective potential of Aconogonon alpinum (All.) Schur roots
- Lead discovery of a guanidinyl tryptophan derivative on amyloid cascade inhibition
- Physicochemical evaluation of the fruit pulp of Opuntia spp growing in the Mediterranean area under hard climate conditions
- Electronic structural properties of amino/hydroxyl functionalized imidazolium-based bromide ionic liquids
- New Schiff bases of 2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetohydrazide and their Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) metal complexes: their in vitro antimicrobial potentials and in silico physicochemical and pharmacokinetics properties
- Treatment of adhesions after Achilles tendon injury using focused ultrasound with targeted bFGF plasmid-loaded cationic microbubbles
- Synthesis of orotic acid derivatives and their effects on stem cell proliferation
- Chirality of β2-agonists. An overview of pharmacological activity, stereoselective analysis, and synthesis
- Fe3O4@urea/HITh-SO3H as an efficient and reusable catalyst for the solvent-free synthesis of 7-aryl-8H-benzo[h]indeno[1,2-b]quinoline-8-one and indeno[2′,1′:5,6]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives
- Adsorption kinetic characteristics of molybdenum in yellow-brown soil in response to pH and phosphate
- Enhancement of thermal properties of bio-based microcapsules intended for textile applications
- Exploring the effect of khat (Catha edulis) chewing on the pharmacokinetics of the antiplatelet drug clopidogrel in rats using the newly developed LC-MS/MS technique
- A green strategy for obtaining anthraquinones from Rheum tanguticum by subcritical water
- Cadmium (Cd) chloride affects the nutrient uptake and Cd-resistant bacterium reduces the adsorption of Cd in muskmelon plants
- Removal of H2S by vermicompost biofilter and analysis on bacterial community
- Structural cytotoxicity relationship of 2-phenoxy(thiomethyl)pyridotriazolopyrimidines: Quantum chemical calculations and statistical analysis
- A self-breaking supramolecular plugging system as lost circulation material in oilfield
- Synthesis, characterization, and pharmacological evaluation of thiourea derivatives
- Application of drug–metal ion interaction principle in conductometric determination of imatinib, sorafenib, gefitinib and bosutinib
- Synthesis and characterization of a novel chitosan-grafted-polyorthoethylaniline biocomposite and utilization for dye removal from water
- Optimisation of urine sample preparation for shotgun proteomics
- DFT investigations on arylsulphonyl pyrazole derivatives as potential ligands of selected kinases
- Treatment of Parkinson’s disease using focused ultrasound with GDNF retrovirus-loaded microbubbles to open the blood–brain barrier
- New derivatives of a natural nordentatin
- Fluorescence biomarkers of malignant melanoma detectable in urine
- Study of the remediation effects of passivation materials on Pb-contaminated soil
- Saliva proteomic analysis reveals possible biomarkers of renal cell carcinoma
- Withania frutescens: Chemical characterization, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and healing activities
- Design, synthesis and pharmacological profile of (−)-verbenone hydrazones
- Synthesis of magnesium carbonate hydrate from natural talc
- Stability-indicating HPLC-DAD assay for simultaneous quantification of hydrocortisone 21 acetate, dexamethasone, and fluocinolone acetonide in cosmetics
- A novel lactose biosensor based on electrochemically synthesized 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene/thiophene (EDOT/Th) copolymer
- Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: Chemical characterization, scavenging and cytotoxic activities
- Development and validation of a high performance liquid chromatography/diode array detection method for estrogen determination: Application to residual analysis in meat products
- PCSK9 concentrations in different stages of subclinical atherosclerosis and their relationship with inflammation
- Development of trace analysis for alkyl methanesulfonates in the delgocitinib drug substance using GC-FID and liquid–liquid extraction with ionic liquid
- Electrochemical evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of natural compounds on glassy carbon electrode modified with guanine-, polythionine-, and nitrogen-doped graphene
- A Dy(iii)–organic framework as a fluorescent probe for highly selective detection of picric acid and treatment activity on human lung cancer cells
- A Zn(ii)–organic cage with semirigid ligand for solvent-free cyanosilylation and inhibitory effect on ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion ability via regulating mi-RNA16 expression
- Polyphenol content and antioxidant activities of Prunus padus L. and Prunus serotina L. leaves: Electrochemical and spectrophotometric approach and their antimicrobial properties
- The combined use of GC, PDSC and FT-IR techniques to characterize fat extracted from commercial complete dry pet food for adult cats
- MALDI-TOF MS profiling in the discovery and identification of salivary proteomic patterns of temporomandibular joint disorders
- Concentrations of dioxins, furans and dioxin-like PCBs in natural animal feed additives
- Structure and some physicochemical and functional properties of water treated under ammonia with low-temperature low-pressure glow plasma of low frequency
- Mesoscale nanoparticles encapsulated with emodin for targeting antifibrosis in animal models
- Amine-functionalized magnetic activated carbon as an adsorbent for preconcentration and determination of acidic drugs in environmental water samples using HPLC-DAD
- Antioxidant activity as a response to cadmium pollution in three durum wheat genotypes differing in salt-tolerance
- A promising naphthoquinone [8-hydroxy-2-(2-thienylcarbonyl)naphtho[2,3-b]thiophene-4,9-dione] exerts anti-colorectal cancer activity through ferroptosis and inhibition of MAPK signaling pathway based on RNA sequencing
- Synthesis and efficacy of herbicidal ionic liquids with chlorsulfuron as the anion
- Effect of isovalent substitution on the crystal structure and properties of two-slab indates BaLa2−xSmxIn2O7
- Synthesis, spectral and thermo-kinetics explorations of Schiff-base derived metal complexes
- An improved reduction method for phase stability testing in the single-phase region
- Comparative analysis of chemical composition of some commercially important fishes with an emphasis on various Malaysian diets
- Development of a solventless stir bar sorptive extraction/thermal desorption large volume injection capillary gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric method for ultra-trace determination of pyrethroids pesticides in river and tap water samples
- A turbidity sensor development based on NL-PI observers: Experimental application to the control of a Sinaloa’s River Spirulina maxima cultivation
- Deep desulfurization of sintering flue gas in iron and steel works based on low-temperature oxidation
- Investigations of metallic elements and phenolics in Chinese medicinal plants
- Influence of site-classification approach on geochemical background values
- Effects of ageing on the surface characteristics and Cu(ii) adsorption behaviour of rice husk biochar in soil
- Adsorption and sugarcane-bagasse-derived activated carbon-based mitigation of 1-[2-(2-chloroethoxy)phenyl]sulfonyl-3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl) urea-contaminated soils
- Antimicrobial and antifungal activities of bifunctional cooper(ii) complexes with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, flufenamic, mefenamic and tolfenamic acids and 1,10-phenanthroline
- Application of selenium and silicon to alleviate short-term drought stress in French marigold (Tagetes patula L.) as a model plant species
- Screening and analysis of xanthine oxidase inhibitors in jute leaves and their protective effects against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in cells
- Synthesis and physicochemical studies of a series of mixed-ligand transition metal complexes and their molecular docking investigations against Coronavirus main protease
- A study of in vitro metabolism and cytotoxicity of mephedrone and methoxetamine in human and pig liver models using GC/MS and LC/MS analyses
- A new phenyl alkyl ester and a new combretin triterpene derivative from Combretum fragrans F. Hoffm (Combretaceae) and antiproliferative activity
- Erratum
- Erratum to: A one-step incubation ELISA kit for rapid determination of dibutyl phthalate in water, beverage and liquor
- Review Articles
- Sinoporphyrin sodium, a novel sensitizer for photodynamic and sonodynamic therapy
- Natural products isolated from Casimiroa
- Plant description, phytochemical constituents and bioactivities of Syzygium genus: A review
- Evaluation of elastomeric heat shielding materials as insulators for solid propellant rocket motors: A short review
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2019
- An overview of Monascus fermentation processes for monacolin K production
- Study on online soft sensor method of total sugar content in chlorotetracycline fermentation tank
- Studies on the Anti-Gouty Arthritis and Anti-hyperuricemia Properties of Astilbin in Animal Models
- Effects of organic fertilizer on water use, photosynthetic characteristics, and fruit quality of pear jujube in northern Shaanxi
- Characteristics of the root exudate release system of typical plants in plateau lakeside wetland under phosphorus stress conditions
- Characterization of soil water by the means of hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratio at dry-wet season under different soil layers in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha River
- Composition and diurnal variation of floral scent emission in Rosa rugosa Thunb. and Tulipa gesneriana L.
- Preparation of a novel ginkgolide B niosomal composite drug
- The degradation, biodegradability and toxicity evaluation of sulfamethazine antibiotics by gamma radiation
- Special issue on Monitoring, Risk Assessment and Sustainable Management for the Exposure to Environmental Toxins
- Insight into the cadmium and zinc binding potential of humic acids derived from composts by EEM spectra combined with PARAFAC analysis
- Source apportionment of soil contamination based on multivariate receptor and robust geostatistics in a typical rural–urban area, Wuhan city, middle China
- Special Issue on 13th JCC 2018
- The Role of H2C2O4 and Na2CO3 as Precipitating Agents on The Physichochemical Properties and Photocatalytic Activity of Bismuth Oxide
- Preparation of magnetite-silica–cetyltrimethylammonium for phenol removal based on adsolubilization
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Size-dependent growth kinetics of struvite crystals in wastewater with calcium ions
- The effect of silica-calcite sedimentary rock contained in the chicken broiler diet on the overall quality of chicken muscles
- Physicochemical properties of selected herbicidal products containing nicosulfuron as an active ingredient
- Lycopene in tomatoes and tomato products
- Fluorescence in the assessment of the share of a key component in the mixing of feed
- Sulfur application alleviates chromium stress in maize and wheat
- Effectiveness of removal of sulphur compounds from the air after 3 years of biofiltration with a mixture of compost soil, peat, coconut fibre and oak bark
- Special Issue on the 4th Green Chemistry 2018
- Study and fire test of banana fibre reinforced composites with flame retardance properties
- Special Issue on the International conference CosCI 2018
- Disintegration, In vitro Dissolution, and Drug Release Kinetics Profiles of k-Carrageenan-based Nutraceutical Hard-shell Capsules Containing Salicylamide
- Synthesis of amorphous aluminosilicate from impure Indonesian kaolin
- Special Issue on the International Conf on Science, Applied Science, Teaching and Education 2019
- Functionalization of Congo red dye as a light harvester on solar cell
- The effect of nitrite food preservatives added to se’i meat on the expression of wild-type p53 protein
- Biocompatibility and osteoconductivity of scaffold porous composite collagen–hydroxyapatite based coral for bone regeneration
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Effect of natural boron mineral use on the essential oil ratio and components of Musk Sage (Salvia sclarea L.)
- A theoretical and experimental study of the adsorptive removal of hexavalent chromium ions using graphene oxide as an adsorbent
- A study on the bacterial adhesion of Streptococcus mutans in various dental ceramics: In vitro study
- Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study
- Special Issue on Chemistry Today for Tomorrow 2019
- Diabetes mellitus type 2: Exploratory data analysis based on clinical reading
- Multivariate analysis for the classification of copper–lead and copper–zinc glasses
- Special Issue on Advances in Chemistry and Polymers
- The spatial and temporal distribution of cationic and anionic radicals in early embryo implantation
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Magnetic iron oxide/clay nanocomposites for adsorption and catalytic oxidation in water treatment applications
- Special Issue on IC3PE 2018/2019 Conference
- Exergy analysis of conventional and hydrothermal liquefaction–esterification processes of microalgae for biodiesel production
- Advancing biodiesel production from microalgae Spirulina sp. by a simultaneous extraction–transesterification process using palm oil as a co-solvent of methanol
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Omega and the related counting polynomials of some chemical structures
- M-polynomial and topological indices of zigzag edge coronoid fused by starphene

