Abstract
Mechanical alloying can be carried out by a method known as friction stir processing, whereby solid Zn particles in a solution are distributed onto an aluminium alloy plate. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of a volume of Zn particles on the mechanical and physical properties of aluminium 1xxx alloy that had been subjected to friction stir processing. The specimens were plates composed of 1xxx series aluminium. A groove, measuring 12 mm in diameter, was pierced to various depths, and the Zn particles in these containers were then subjected to friction stir processing using a pin-less tool with a diameter of 15 mm. The results showed that the highest hardness was found in the uppermost layer of the workpiece, and this gradually decreased with thickness. An increase in the amount of Zn particles caused an increase in material hardness. The highest hardness of 87.1 HV in the friction stir-processed AA1100 was obtained at the highest volume of Zn compared to the hardness of 44.5 HV, which was obtained for the specimen without the addition of Zn.
1 Introduction
The use of aluminium alloy in vehicle components is very important for improving fuel efficiency. Aluminium alloy has mild strength properties and good formability compared to steel [1]. Efforts to improve the mechanical properties of aluminium can be achieved by several methods including heat treatment, mechanical treatment, coating treatment or surface treatment [2]. Generally, the aim of these treatments is to obtain the desired properties by modifying the microstructure of the material [3]. One such effort to improve the mechanical properties of aluminium is surface treatment. This treatment is aimed at increasing the corrosion resistance, wear resistance, electrical resistance, material strength, and good weldability [4] of the material. Generally, the failure of a component starts from the surface and then, develops into a structural failure [5].
One method of surface treatment is friction stir processing (FSP), which can be used to enhance the mechanical properties and modify the micro structure of a material. Investigation on FSP in laboratory scale has been conducted by some researcher. In FSP, a rotating tool, consisting of a shoulder and a pin, is plunged at a certain rotating speed into the surface of the workpiece so that the pin pierces and the shoulder scrapes the surface of the workpiece. The friction between the tool and the surface of the workpiece will give rise to frictional heat, thereby softening the surface of the workpiece [6, 7]. FSP produces a defect-free material with finer grains [8]. In addition, FSP also improves the processing of solid solutions to enhance the mechanical properties of materials [3].
Additional material particles used in improving mechanical properties in the FSP are ceramics particles such as AL2O3, SiC, SiO2, TiO2, TiC or alloying elements such as Cu,Ni, Zn [9, 10]. The role of ceramic particles in increasing mechanical strength is as a nucleation sites of solidification so that the grain size to be finer. Whereas the role of alloying elements is to form solid solution of aluminum alloy which causes grain size refinement [11]. The FSP treatment gives an increase in mechanical strength due to grain size refinement and more evenly distributed of additional material particles, thereby giving rise to the dispersion strengthening and eliminating casting defects. Althoug the result of the investigation on FSP got attractive mechanical properties and modified micro structure of materials, on the other hand it is guite a few succesfull practical use in industrial scope [12]. However, no studies investigated on the effects of the amount of additional Zn particles on the mechanical and physical properties of the friction stir processed aluminum Alloy.
The aim of this research was to investigate the effects of the alloying of Zn particles on the mechanical and physical properties of friction stir-processed AA 1100.
2 Experimental Procedure
AA 1100 aluminium alloy plates, with dimensions of 70 mm × 40 mm × 4 mm, were used in the friction stir processing method. Holes, with a diameter of 12 mm and various depths of 0.2 mm, 0.4 mm, 0.6 mm, and 0.8 mm, were made on the surface of the workpiece to be filled with Zn particles at volumes of 22 mm3 (A1), 45 mm3 (A2), 67 mm3 (A3), and 90 mm3 (A4), respectively. FSP was carried out on the surface of the workpiece.
A pin-less tool made of HSS with a diameter of 15 mm was used to fabricate the specimen with the process parameters of the tool being a plunge depth of 1.2 mm, rotation speed of 1120 rpm and dwell time of 10 seconds. A schematic diagram of the friction stir processing is shown in Figure 1. The friction stir processing parameters are listed in Table 1. An FSP run with the same parameters was conducted, as a reference, on the specimen without the Zn particles. A Vickers micro hardness test was carried out using a Highwood HWMMT X7 with a load of 300 gr and dwell time of 10 s.
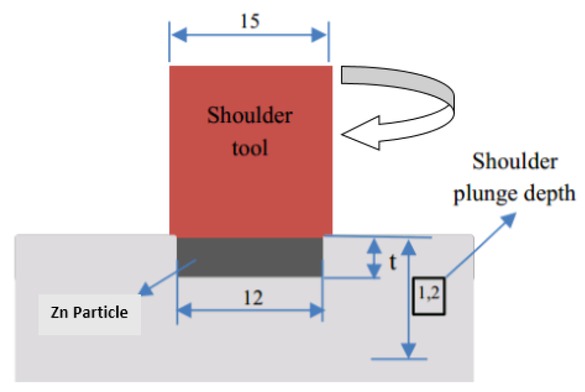
Schematic diagram of friction stir processing of aluminium alloy with the addition of Zn particles
Parameters of friction stir processing.
| No | Specimen | Tool Rotation Speed (RPM) | Hole Thickness (mm) | Tool Diameter (mm) | Volume Zn (mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A1 | 1120 | 0.2 | 15 | 22 |
| 2 | A2 | 1120 | 0.4 | 15 | 45 |
| 3 | A3 | 1120 | 0.6 | 15 | 67 |
| 4 | A4 | 1120 | 0.8 | 15 | 90 |
| 5 | A5 | 1120 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
The microstructure of the friction stir-processed specimen was characterized using scanning electron microscopy and optical microscopy.
Figure 2 shows the measurement point for the Vickers hardness on a cross section of the friction stir-processed specimen with various volumes of Zn particles. The hardness testing was conducted on three rows to determine the effect of the FSP treatment on the hardness along the thickness of the workpiece.

Mapping the measurement point of the Vickers hardness test
3 Results and Discussion
Cross-sectional images of the FSP specimen with variations in the volume of Zn particles can be seen in Figure 3. The distribution of the Zn particles can be observed by the brighter colour compared to the surrounding area.
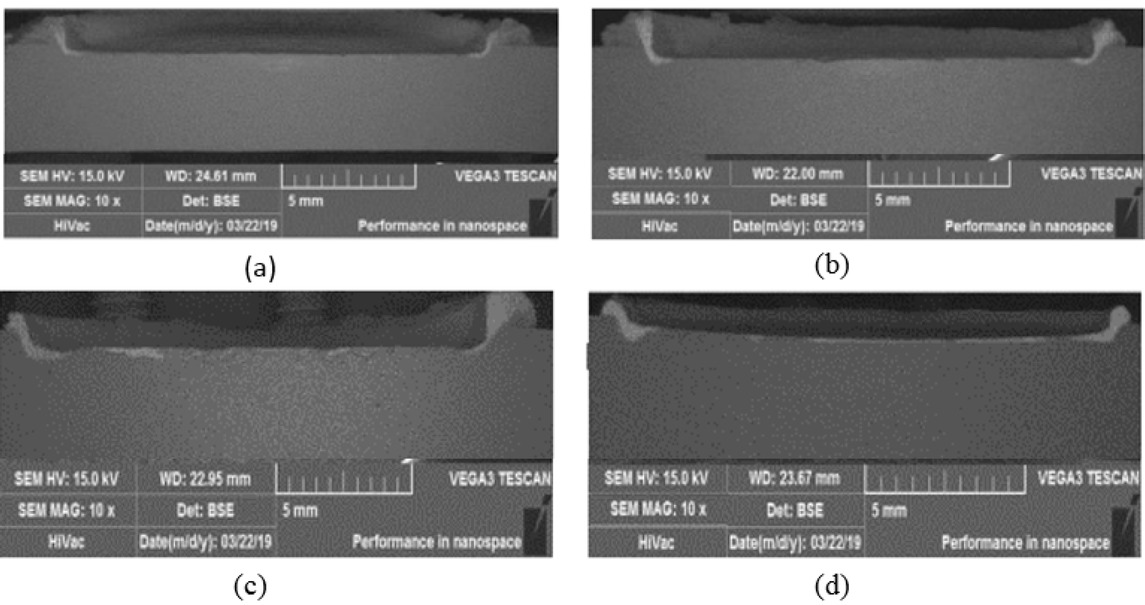
Cross sections of friction stir-processed AA1100 with various Zn particle volumes of (a) 22 mm3, (b) 45 mm3, (c) 67 mm3, and (d) 90 mm3
Most of the Zn particles moved to the outer diameter of the FSP tool. This could be explained by the fact that the rotating tool on the workpiece generated heat on the material beneath the tool [12], thereby softening both the aluminium and the Zn particles. The rotating action of the tool tended to draw the Zn particles to the edge of the FSP region [13]. The amount of Zn particles that accumulated at the edge of the friction stir-processed zone varied. This was attributed to the differences in the volume of Zn particles used during the FSP process. Increasing the volume of Zn particles meant that there were more Zn particles. However, this had no significant effect on the distribution of Zn particles in the area beneath the tool.
The microstructure of the shoulder affected zone (SAZ) under various volumes of Zn particles is shown in Figure 4. The SAZ had a finer grain size compared to the other regions due to both the dynamic recrystallization and severe plastic deformation generated by the stirring action between the tool surface and workpiece [4]. It was observed that increasing the Zn particle volume resulted in finer grains in the SAZ. This was consistent with the results of a previous research, which stated that the addition of Zn particles led to the production of finer grains [11].
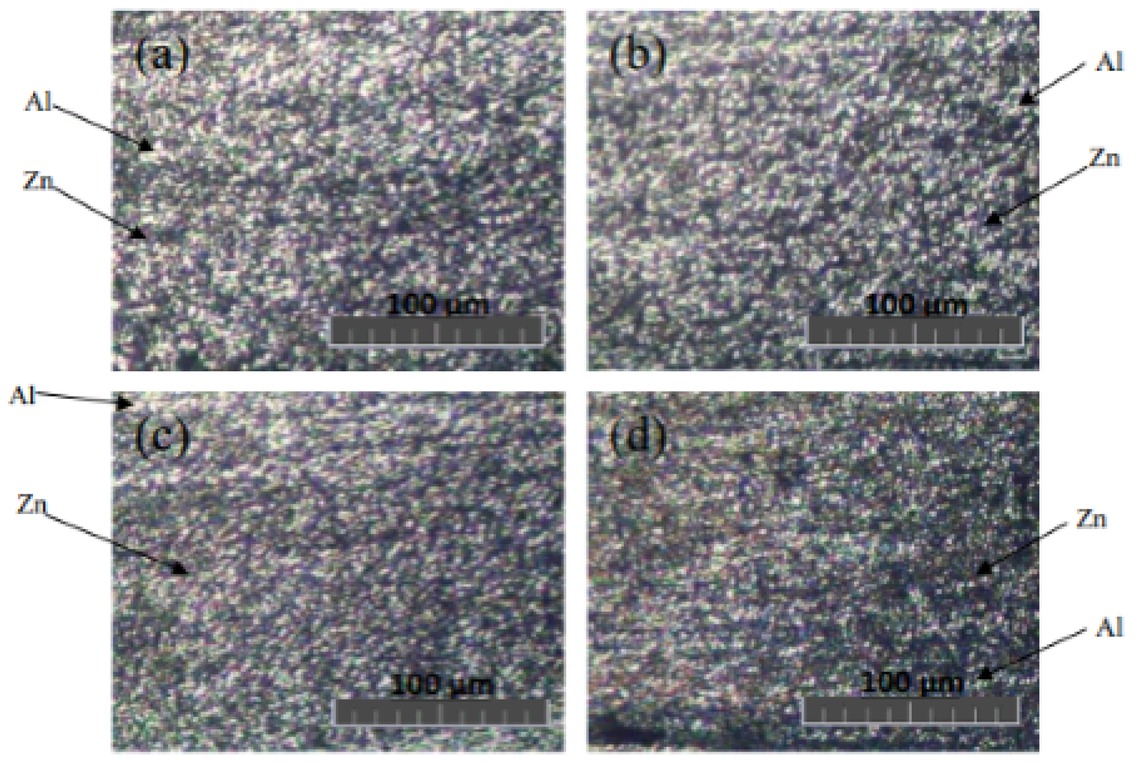
Microstructure of friction stir-welded specimen under various Zn Particle volumes of (a) 22 mm3, (b) 45 mm3, (c) 67 mm3, and (d) 90 mm3
The distribution of various volumes of Zn particles on the cross section of the workpiece was tested using energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS mapping), as shown in Figure 5. It could be discerned that the distribution of Zn particles across the processing zone was in line with the macro-graph shown in Figure 3, where the Zn particles were concentrated at the edge of the processing zone, as indicated by the high concentration of purple dots. An increase in the volume of Zn caused the Zn particles to become more visible. It could be seen that the increased volume of Zn particles caused them to penetrate in the direction of thickness, making it more significant.
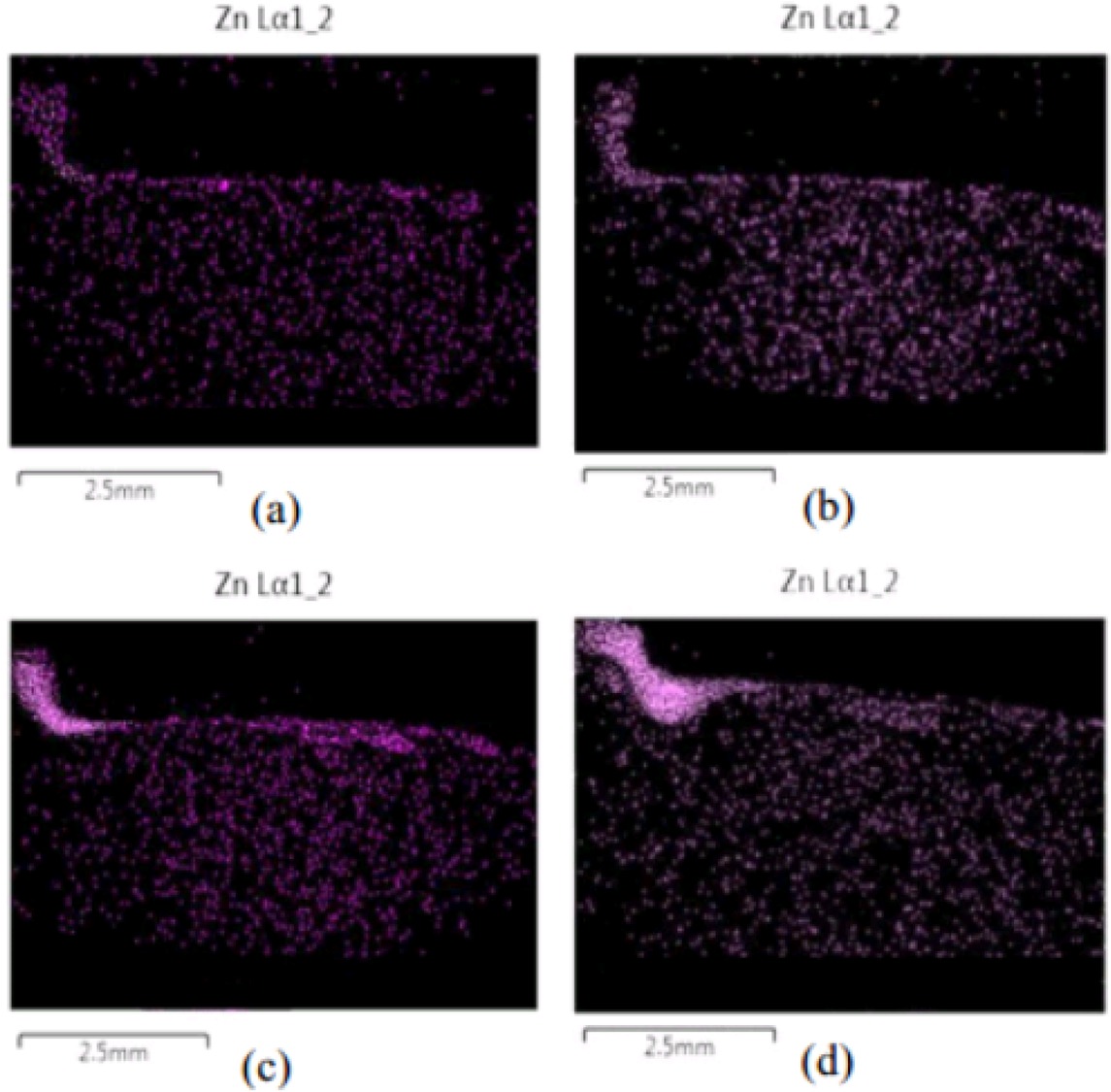
EDS mapping of friction stir-processed specimen under various Zn Particle volumes of (a) 22 mm3, (b) 45 mm3, (c) 67 mm3, and (d) 90 mm3
The results of the EDS test, as shown in Figure 6, proved that a Zn particle content of 0.2% was obtained at the centre of the friction processing zone, whereas the content was 4.2% at the edge. Increasing the Zn particle volume from 22 mm3 to 45 mm3 caused the Zn content to rise at both the centre and edge of the friction stir processing zone by 0.5% and 7.8%, respectively. The largest Zn particle content at the centre of the friction stir processing zone was 1.7%, while a Zn particle content of 11.4% was obtained at the edge of the friction processing zone at a Zn particle volume of 95 mm3.
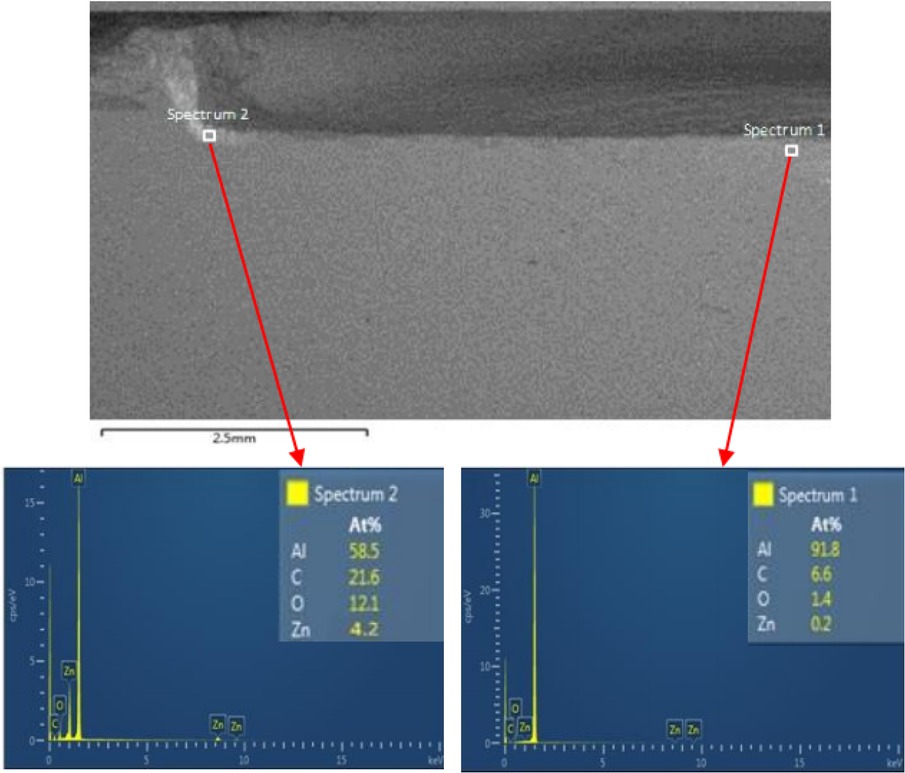
Atomic percentage of Zn at the edge and centre of the friction stir processing zone
The Vickers hardness values of the friction stir-processed AA1100 under various Zn particle volumes at the uppermost surface are shown in Figure 7. The mechanical behaviour of the specimens produced by friction stir processing under various volumes of Zn particles showed that an increase in the Zn particle volume led to an increase in the hardness. The shoulder affected zone (SAZ) experienced an increase in hardness when the Zn particle volume was increased. An increase in Zn particle volume to 22 mm3 (A1), 45 mm3 (A2), 67 mm3 (A3), and 90 mm3 (A4) showed an increase in the Vickers hardness numbers to 35.5 HV, 36.1 HV, 40.7HV, and 46.1 HV, respectively at the centre of the friction stir processing zone, and an increase to 65.6 HV, 74.6 HV, 80.4 HV, and 87.1 HV, respectively at the edge of the zone.
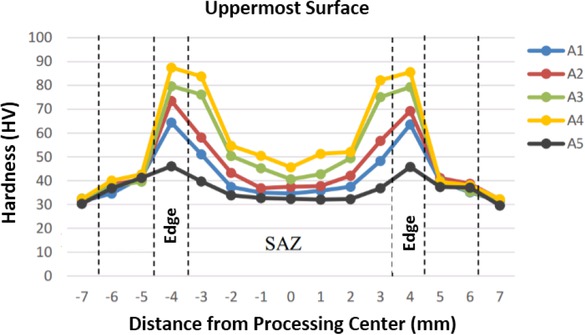
Vickers micro hardness at uppermost surface of friction stir-processed specimen under various Zn particle volumes of 22 mm3 (A1), 45 mm3 (A2), 67 mm3 (A3), 90 mm3 (A4) and 0 mm3
A gradual increase in hardness could be observed from the centre to the edge of the friction stir processing zone. When the Zn particle volume was 90 mm3 (A4), the hardness value was 46.1 HV at the centre of the friction stir processing zone, and it gradually increased to 87.1 HV at the edge of the friction stir processing zone.
The variation in hardness along the cross section of the specimen was due to the uneven distribution of Zn particles along the cross section. When the stirring process occurred, the heat energy that was generated softened the Al and the rotational motion of the tool blended it with the Zn particles. The higher hardness was the result of the refined grain size and the presence of a solid solution of Zn particles. This was due to the rotating tool, which rubbed the surface of the workpiece, thereby generating the heat that led to the recrystallization of the grains. The severe plastic deformation caused by the stirring action of the tool resulted in dynamic recrystallization, which led to the production of very fine grains [8, 15].
Figure 8 shows the Vickers micro hardness value at the middle thickness of the specimen. Generally, the hardness at the middle thickness will be lower than that of the uppermost surface. This is because the Zn particle distribution along the thickness will gradually decrease, as seen in Figure 5.
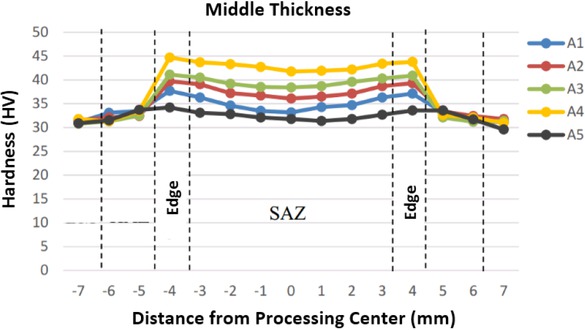
Vickers micro hardness values at middle thickness of friction stir-processed specimen under various Zn particle volumes of 22 mm3 (A1), 45 mm3 (A2), 67 mm3 (A3), 90 mm3 (A4) and 0 mm3
4 Conclusions
Surface hardening by the friction stir process method on AA 1100 aluminium under various Zn particle volumes was investigated, and the following conclusions were drawn:
In the microstructure of the shoulder affected zone (SAZ), the grains were finer than the base metal due to recrystallization and severe plastic deformation. The SAZ region contained more Zn particles when the volume of Zn particles was increased. The existence of Zn in the AA1100 aluminium caused the AA1100 material to be stronger.
Increasing the volume of Zn particles caused the AA1100 friction stir-processed specimen to have a higher hardness. The highest hardness of 87.5 HV was found at the edge of the friction stir-processed specimen with the highest Zn particle volume of 90 mm3. The highest hardness of 46.1 HV was found at the centre of the friction stir-processed specimen with the highest Zn particle volume of 90 mm3, while the lowest hardness of 35.5 HV was found at the lowest Zn particle volume of 22 mm3. The increasing volume of Zn particles was effective in increasing the hardness of the material.
References
[1] Aurich, J.C.,Mayer, P., Kirsch, B., Eifler, D., Smaga, M., Skorupski, R. Characterization of deformation induced surface hardening during cryogenic turning of AISI 347. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol. 2014; 63(1): 65-410.1016/j.cirp.2014.03.079Search in Google Scholar
[2] Ebnesajjad, S. Surface Treatment ofMaterials for Adhesive Bonding. 2nd Ed. Oxford; 2014.10.1016/B978-0-323-26435-8.00016-2Search in Google Scholar
[3] Ma, Z.Y., Sharma S.R., Mishra, R.S. Microstructural modification of as-cast AlSi-Mg alloy by friction stir processing. Met Mater Trans. 2006; A 37: 3323-1310.1007/BF02586167Search in Google Scholar
[4] Charit, I., and Mishra, R.S. Effect of friction stir processed microstructure on tensile properties of an Al-Zn-Mg-Sc alloy upon subsequent aging heat treatment. J Mater Sci Technol. 2018; 34(1): 214-5.10.1016/j.jmst.2017.10.021Search in Google Scholar
[5] Cho, K.T., Song, K., Oh, S.H., Lee Y.K., Lim K.M., Lee,W. B. Surface hardening of aluminum alloy by shot peening treatment with Zn based ball. Mater Sci Eng. 2012; A 543: 44-610.1016/j.msea.2012.02.043Search in Google Scholar
[6] Darras, B. M. Experimental and Analytical Study of Friction Stir Processing [Master’s Theses]: University of Kentucky; 2005.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Muhayat, N., Triyono, Kusharjanta, B., Handika, R.T. Effect of Preheat Temperature on Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloy 5052 Joints. Applied Mechanics and Materials. 2014: 597; 253-410.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.597.253Search in Google Scholar
[8] Kianezhad, M., and Raouf, A.H. Effect of nano-Al2O3 particles and friction stir processing on 5083 TIG welding properties. J Mater Process Technol. 2019: 263; 356-10.10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.08.010Search in Google Scholar
[9] Węglowski, M.S. Friction stir processing – State of the art. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering. 2018: 18; 114-1610.1016/j.acme.2017.06.002Search in Google Scholar
[10] Bauri, R., Yadav, D., Suhas, G. Effect of friction stir processing (FSP) on microstructure and properties of Al-TiC in situ composite. Mater Sci Eng. 2011: A528; 4732-8.10.1016/j.msea.2011.02.085Search in Google Scholar
[11] Yadav, D., Bauri, R., Chawake, N. Fabrication of Al-Zn solid solution via friction stir processing. Mater Charact. 2018: 136. Dec 2017; 221-810.1016/j.matchar.2017.12.022Search in Google Scholar
[12] Mishra, R.S., and Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater Sci Eng. 2005: R 50; pp. 1-7810.1007/978-3-319-07043-8Search in Google Scholar
[13] Muhayat, N., Triyono., Rahmanto, R.D. Effect of Tool Plunge Depth and Pin Profile on Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Spot Welded AA 5052 Joints. Journal of Mechanical Engineering. 2018: SI 5(1); 181-11.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Liu, Z., Cui, H., Ji, S., Xu, M., and Meng, X.: Improving Joint Features and Mechanical Properties of Pinless Fiction Stir Welding of Alcald 2A12-T4 Aluminum Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., vol. 32, pp. 1372-1377, (2016).10.1016/j.jmst.2016.07.003Search in Google Scholar
[15] Shettigar, A. K., Salian, G., Herbert, M., Rao, S. Microstructural Characterization and Hardness Evaluation of Friction Stir Welded Composite AA6061 -4.5Cu-5SiC (Wt .%). Defence science Journal. 2013: 63 (4); 429-5.10.14429/dsj.63.4869Search in Google Scholar
© 2020 N. Muhayat et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Fabrication of aluminium covetic casts under different voltages and amperages of direct current
- Inhibition effect of the synergistic properties of 4-methyl-norvalin and 2-methoxy-4-formylphenol on the electrochemical deterioration of P4 low carbon mold steel
- Logistic regression in modeling and assessment of transport services
- Design and development of ultra-light front and rear axle of experimental vehicle
- Enhancement of cured cement using environmental waste: particleboards incorporating nano slag
- Evaluating ERP System Merging Success In Chemical Companies: System Quality, Information Quality, And Service Quality
- Accuracy of boundary layer treatments at different Reynolds scales
- Evaluation of stabiliser material using a waste additive mixture
- Optimisation of stress distribution in a highly loaded radial-axial gas microturbine using FEM
- Analysis of modern approaches for the prediction of electric energy consumption
- Surface Hardening of Aluminium Alloy with Addition of Zinc Particles by Friction Stir Processing
- Development and refinement of the Variational Method based on Polynomial Solutions of Schrödinger Equation
- Comparison of two methods for determining Q95 reference flow in the mouth of the surface catchment basin of the Meia Ponte river, state of Goiás, Brazil
- Applying Intelligent Portfolio Management to the Evaluation of Stalled Construction Projects
- Disjoint Sum of Products by Orthogonalizing Difference-Building ⴱ
- The Development of Information System with Strategic Planning for Integrated System in the Indonesian Pharmaceutical Company
- Simulation for Design and Material Selection of a Deep Placement Fertilizer Applicator for Soybean Cultivation
- Modeling transportation routes of the pick-up system using location problem: a case study
- Pinless friction stir spot welding of aluminium alloy with copper interlayer
- Roof Geometry in Building Design
- Review Articles
- Silicon-Germanium Dioxide and Aluminum Indium Gallium Arsenide-Based Acoustic Optic Modulators
- RZ Line Coding Scheme With Direct Laser Modulation for Upgrading Optical Transmission Systems
- LOGI Conference 2019
- Autonomous vans - the planning process of transport tasks
- Drivers ’reaction time research in the conditions in the real traffic
- Design and evaluation of a new intersection model to minimize congestions using VISSIM software
- Mathematical approaches for improving the efficiency of railway transport
- An experimental analysis of the driver’s attention during train driving
- Risks associated with Logistics 4.0 and their minimization using Blockchain
- Service quality of the urban public transport companies and sustainable city logistics
- Charging electric cars as a way to increase the use of energy produced from RES
- The impact of the truck loads on the braking efficiency assessment
- Application of virtual and augmented reality in automotive
- Dispatching policy evaluation for transport of ready mixed concrete
- Use of mathematical models and computer software for analysis of traffic noise
- New developments on EDR (Event Data Recorder) for automated vehicles
- General Application of Multiple Criteria Decision Making Methods for Finding the Optimal Solution in City Logistics
- The influence of the cargo weight and its position on the braking characteristics of light commercial vehicles
- Modeling the Delivery Routes Carried out by Automated Guided Vehicles when Using the Specific Mathematical Optimization Method
- Modelling of the system “driver - automation - autonomous vehicle - road”
- Limitations of the effectiveness of Weigh in Motion systems
- Long-term urban traffic monitoring based on wireless multi-sensor network
- The issue of addressing the lack of parking spaces for road freight transport in cities - a case study
- Simulation of the Use of the Material Handling Equipment in the Operation Process
- The use of simulation modelling for determining the capacity of railway lines in the Czech conditions
- Proposals for Using the NFC Technology in Regional Passenger Transport in the Slovak Republic
- Optimisation of Transport Capacity of a Railway Siding Through Construction-Reconstruction Measures
- Proposal of Methodology to Calculate Necessary Number of Autonomous Trucks for Trolleys and Efficiency Evaluation
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland
- 5G Based Machine Remote Operation Development Utilizing Digital Twin
- On-line moisture content estimation of saw dust via machine vision
- Data analysis of a paste thickener
- Programming and control for skill-based robots
- Using Digital Twin Technology in Engineering Education – Course Concept to Explore Benefits and Barriers
- Intelligent methods for root cause analysis behind the center line deviation of the steel strip
- Engaging Building Automation Data Visualisation Using Building Information Modelling and Progressive Web Application
- Real-time measurement system for determining metal concentrations in water-intensive processes
- A tool for finding inclusion clusters in steel SEM specimens
- An overview of current safety requirements for autonomous machines – review of standards
- Expertise and Uncertainty Processing with Nonlinear Scaling and Fuzzy Systems for Automation
- Towards online adaptation of digital twins
- Special Issue: ICE-SEAM 2019
- Fatigue Strength Analysis of S34MnV Steel by Accelerated Staircase Test
- The Effect of Discharge Current and Pulse-On Time on Biocompatible Zr-based BMG Sinking-EDM
- Dynamic characteristic of partially debonded sandwich of ferry ro-ro’s car deck: a numerical modeling
- Vibration-based damage identification for ship sandwich plate using finite element method
- Investigation of post-weld heat treatment (T6) and welding orientation on the strength of TIG-welded AL6061
- The effect of nozzle hole diameter of 3D printing on porosity and tensile strength parts using polylactic acid material
- Investigation of Meshing Strategy on Mechanical Behaviour of Hip Stem Implant Design Using FEA
- The effect of multi-stage modification on the performance of Savonius water turbines under the horizontal axis condition
- Special Issue: Recent Advances in Civil Engineering
- The effects of various parameters on the strengths of adhesives layer in a lightweight floor system
- Analysis of reliability of compressed masonry structures
- Estimation of Sport Facilities by Means of Technical-Economic Indicator
- Integral bridge and culvert design, Designer’s experience
- A FEM analysis of the settlement of a tall building situated on loess subsoil
- Behaviour of steel sheeting connections with self-drilling screws under variable loading
- Resistance of plug & play N type RHS truss connections
- Comparison of strength and stiffness parameters of purlins with different cross-sections of profiles
- Bearing capacity of floating geosynthetic encased columns (GEC) determined on the basis of CPTU penetration tests
- The effect of the stress distribution of anchorage and stress in the textured layer on the durability of new anchorages
- Analysis of tender procedure phases parameters for railroad construction works
- Special Issue: Terotechnology 2019
- The Use of Statistical Functions for the Selection of Laser Texturing Parameters
- Properties of Laser Additive Deposited Metallic Powder of Inconel 625
- Numerical Simulation of Laser Welding Dissimilar Low Carbon and Austenitic Steel Joint
- Assessment of Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings on the Ti13Nb13Zr Alloy
- Characteristics of selected measures of stress triaxiality near the crack tip for 145Cr6 steel - 3D issues for stationary cracks
- Assessment of technical risk in maintenance and improvement of a manufacturing process
- Experimental studies on the possibility of using a pulsed laser for spot welding of thin metallic foils
- Angular position control system of pneumatic artificial muscles
- The properties of lubricated friction pairs with diamond-like carbon coatings
- Effect of laser beam trajectory on pocket geometry in laser micromachining
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference
- The Employability Skills Needed To Face the Demands of Work in the Future: Systematic Literature Reviews
- Enhancing Higher-Order Thinking Skills in Vocational Education through Scaffolding-Problem Based Learning
- Technology-Integrated Project-Based Learning for Pre-Service Teacher Education: A Systematic Literature Review
- A Study on Water Absorption and Mechanical Properties in Epoxy-Bamboo Laminate Composite with Varying Immersion Temperatures
- Enhancing Students’ Ability in Learning Process of Programming Language using Adaptive Learning Systems: A Literature Review
- Topical Issue on Mathematical Modelling in Applied Sciences, III
- An innovative learning approach for solar power forecasting using genetic algorithm and artificial neural network
- Hands-on Learning In STEM: Revisiting Educational Robotics as a Learning Style Precursor
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Fabrication of aluminium covetic casts under different voltages and amperages of direct current
- Inhibition effect of the synergistic properties of 4-methyl-norvalin and 2-methoxy-4-formylphenol on the electrochemical deterioration of P4 low carbon mold steel
- Logistic regression in modeling and assessment of transport services
- Design and development of ultra-light front and rear axle of experimental vehicle
- Enhancement of cured cement using environmental waste: particleboards incorporating nano slag
- Evaluating ERP System Merging Success In Chemical Companies: System Quality, Information Quality, And Service Quality
- Accuracy of boundary layer treatments at different Reynolds scales
- Evaluation of stabiliser material using a waste additive mixture
- Optimisation of stress distribution in a highly loaded radial-axial gas microturbine using FEM
- Analysis of modern approaches for the prediction of electric energy consumption
- Surface Hardening of Aluminium Alloy with Addition of Zinc Particles by Friction Stir Processing
- Development and refinement of the Variational Method based on Polynomial Solutions of Schrödinger Equation
- Comparison of two methods for determining Q95 reference flow in the mouth of the surface catchment basin of the Meia Ponte river, state of Goiás, Brazil
- Applying Intelligent Portfolio Management to the Evaluation of Stalled Construction Projects
- Disjoint Sum of Products by Orthogonalizing Difference-Building ⴱ
- The Development of Information System with Strategic Planning for Integrated System in the Indonesian Pharmaceutical Company
- Simulation for Design and Material Selection of a Deep Placement Fertilizer Applicator for Soybean Cultivation
- Modeling transportation routes of the pick-up system using location problem: a case study
- Pinless friction stir spot welding of aluminium alloy with copper interlayer
- Roof Geometry in Building Design
- Review Articles
- Silicon-Germanium Dioxide and Aluminum Indium Gallium Arsenide-Based Acoustic Optic Modulators
- RZ Line Coding Scheme With Direct Laser Modulation for Upgrading Optical Transmission Systems
- LOGI Conference 2019
- Autonomous vans - the planning process of transport tasks
- Drivers ’reaction time research in the conditions in the real traffic
- Design and evaluation of a new intersection model to minimize congestions using VISSIM software
- Mathematical approaches for improving the efficiency of railway transport
- An experimental analysis of the driver’s attention during train driving
- Risks associated with Logistics 4.0 and their minimization using Blockchain
- Service quality of the urban public transport companies and sustainable city logistics
- Charging electric cars as a way to increase the use of energy produced from RES
- The impact of the truck loads on the braking efficiency assessment
- Application of virtual and augmented reality in automotive
- Dispatching policy evaluation for transport of ready mixed concrete
- Use of mathematical models and computer software for analysis of traffic noise
- New developments on EDR (Event Data Recorder) for automated vehicles
- General Application of Multiple Criteria Decision Making Methods for Finding the Optimal Solution in City Logistics
- The influence of the cargo weight and its position on the braking characteristics of light commercial vehicles
- Modeling the Delivery Routes Carried out by Automated Guided Vehicles when Using the Specific Mathematical Optimization Method
- Modelling of the system “driver - automation - autonomous vehicle - road”
- Limitations of the effectiveness of Weigh in Motion systems
- Long-term urban traffic monitoring based on wireless multi-sensor network
- The issue of addressing the lack of parking spaces for road freight transport in cities - a case study
- Simulation of the Use of the Material Handling Equipment in the Operation Process
- The use of simulation modelling for determining the capacity of railway lines in the Czech conditions
- Proposals for Using the NFC Technology in Regional Passenger Transport in the Slovak Republic
- Optimisation of Transport Capacity of a Railway Siding Through Construction-Reconstruction Measures
- Proposal of Methodology to Calculate Necessary Number of Autonomous Trucks for Trolleys and Efficiency Evaluation
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland
- 5G Based Machine Remote Operation Development Utilizing Digital Twin
- On-line moisture content estimation of saw dust via machine vision
- Data analysis of a paste thickener
- Programming and control for skill-based robots
- Using Digital Twin Technology in Engineering Education – Course Concept to Explore Benefits and Barriers
- Intelligent methods for root cause analysis behind the center line deviation of the steel strip
- Engaging Building Automation Data Visualisation Using Building Information Modelling and Progressive Web Application
- Real-time measurement system for determining metal concentrations in water-intensive processes
- A tool for finding inclusion clusters in steel SEM specimens
- An overview of current safety requirements for autonomous machines – review of standards
- Expertise and Uncertainty Processing with Nonlinear Scaling and Fuzzy Systems for Automation
- Towards online adaptation of digital twins
- Special Issue: ICE-SEAM 2019
- Fatigue Strength Analysis of S34MnV Steel by Accelerated Staircase Test
- The Effect of Discharge Current and Pulse-On Time on Biocompatible Zr-based BMG Sinking-EDM
- Dynamic characteristic of partially debonded sandwich of ferry ro-ro’s car deck: a numerical modeling
- Vibration-based damage identification for ship sandwich plate using finite element method
- Investigation of post-weld heat treatment (T6) and welding orientation on the strength of TIG-welded AL6061
- The effect of nozzle hole diameter of 3D printing on porosity and tensile strength parts using polylactic acid material
- Investigation of Meshing Strategy on Mechanical Behaviour of Hip Stem Implant Design Using FEA
- The effect of multi-stage modification on the performance of Savonius water turbines under the horizontal axis condition
- Special Issue: Recent Advances in Civil Engineering
- The effects of various parameters on the strengths of adhesives layer in a lightweight floor system
- Analysis of reliability of compressed masonry structures
- Estimation of Sport Facilities by Means of Technical-Economic Indicator
- Integral bridge and culvert design, Designer’s experience
- A FEM analysis of the settlement of a tall building situated on loess subsoil
- Behaviour of steel sheeting connections with self-drilling screws under variable loading
- Resistance of plug & play N type RHS truss connections
- Comparison of strength and stiffness parameters of purlins with different cross-sections of profiles
- Bearing capacity of floating geosynthetic encased columns (GEC) determined on the basis of CPTU penetration tests
- The effect of the stress distribution of anchorage and stress in the textured layer on the durability of new anchorages
- Analysis of tender procedure phases parameters for railroad construction works
- Special Issue: Terotechnology 2019
- The Use of Statistical Functions for the Selection of Laser Texturing Parameters
- Properties of Laser Additive Deposited Metallic Powder of Inconel 625
- Numerical Simulation of Laser Welding Dissimilar Low Carbon and Austenitic Steel Joint
- Assessment of Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings on the Ti13Nb13Zr Alloy
- Characteristics of selected measures of stress triaxiality near the crack tip for 145Cr6 steel - 3D issues for stationary cracks
- Assessment of technical risk in maintenance and improvement of a manufacturing process
- Experimental studies on the possibility of using a pulsed laser for spot welding of thin metallic foils
- Angular position control system of pneumatic artificial muscles
- The properties of lubricated friction pairs with diamond-like carbon coatings
- Effect of laser beam trajectory on pocket geometry in laser micromachining
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference
- The Employability Skills Needed To Face the Demands of Work in the Future: Systematic Literature Reviews
- Enhancing Higher-Order Thinking Skills in Vocational Education through Scaffolding-Problem Based Learning
- Technology-Integrated Project-Based Learning for Pre-Service Teacher Education: A Systematic Literature Review
- A Study on Water Absorption and Mechanical Properties in Epoxy-Bamboo Laminate Composite with Varying Immersion Temperatures
- Enhancing Students’ Ability in Learning Process of Programming Language using Adaptive Learning Systems: A Literature Review
- Topical Issue on Mathematical Modelling in Applied Sciences, III
- An innovative learning approach for solar power forecasting using genetic algorithm and artificial neural network
- Hands-on Learning In STEM: Revisiting Educational Robotics as a Learning Style Precursor

