Abstract
To eliminate problems caused by gypsum soil in Iraq (due to gypsum salt under building foundations and projects), this study evaluates the effect of using the proposed stabiliser additives (vehicle waste oil and asphalt powder) to produce a composite enhancement material as a novel solution by examining the shear strength of the gypseous soil using the direct shear and constant head permeability tests. Three burned-oil weights were used (3%, 5%, and 7% by dry soil weight), which were mixed with a constant quantity of asphalt powder (10% of the sample weight) to investigate the shear strength of the composite material. Several factors were considered in this study, including soaking time and moisture content.
The main findings reveal that composite material could improve the strength of the gypseous soil. The stabiliser reduces water leakage and percolation by forming an impermeable layer with a very fine texture, causing a significant reduction in the permeability coefficient, which improves the gypseous soil and reduces the collapse phenomenon.
1 Introduction
Collapsible soil or rock is considered a severe problem that faces civil engineers when constructing structures. Excessive settlement may suddenly occur due to water leakage into cracks in the construction during rainfall or the rise of the water table level.
Many researchers have studied the collapsibility behaviour of gypseous soils, which is called the collapse potential. Arid and semi-arid areas contain gypseous soil as a result of storing the rainwater that is needed to wash the gypsum from the soil. It is present in the soil as hydrated calcium sulphate (CaSO4·2H2O), which is crystalline, or as anhydrous calcium sulphate (CaSO4), which is the non-crystalline form [1]. The gypsum percentage can be low or high in rocks and can reach up to 90%. The specific gravity of gypsum is 2.3 [2], and it is a water-soluble salt [3]. Thus, to dissolve gypsum, the temperature and velocity of water flows need to be considered. One of the most complicated engineering problems that face civil engineers is the presence of gypsum in the soil [4] due to several factors, such as temperature, moisture content, and the presence of certain types of salt. Therefore, these factors should be considered and measured before any construction takes place. Gypsum soil has many problems that are challenging for the engineers responsible for projects based on this soil type. Many cases of collapse or cracking are recorded in buildings in different areas of Iraq with gypsum soils, for example, the defects in hotel Samarra due to gypsum exuding from the soil. In addition, the continuous leaching of gypsum from the soil caused the dam of Mosul to be vulnerable to collapse, prompting engineers to inject the dam floor with cement to fill the voids. Another case of collapse occurred in Habbaniyah, a tourist city, which suffered damage and defects due to the presence of gypsum soil [5]. Some researchers have turned to the method of waste recycling which can be considered as one of the measures of sustainable methods forimproving the properties of soil and concrete [6, 7, 8]. Many studies have assessed inexpensive functional materials to improve gypseous soil. Al-Zory [9] studied the treatment of the gypseous soil with lime, [10] and other researchers have used cement or bituminous materials [11], whereas Esho (2004) suggested emulsion asphalt [12]. In addition, both lime and emulsion asphalt were added in another study [13].
These investigations demonstrate that these techniques can facilitate controlling the effects of gypsum. Many studies have focused on increasing the strength, reducing the permeability, and improving the characteristics of the soil [14, 15, 16, 17, 18]. It is worth noting that research efforts to improve the soil were not limited to the practical side only, as there are several researches conducted numerically on improvement [19], this study was carried using finite element software (Plaxis) in studying the Engineering behavior of erodible soil-quarry dust composite at a proportion of 50% quarry dust and 10% cement.
In this work, new economical materials are introduced. These materials are impermeable and can hold structure loads.
The materials contain gypseous soil, which is treated with waste oil (WO). The behaviour of the WO and asphalt powder (AP) in the gypseous composite material is studied using the direct shear and permeability tests.
2 Materials and Methods
2.1 Soil and Stabiliser
The soil used in this study is a mixed sandy clay soil with a high percentage of gypsum at about 50%, which behaves as gypseous soil with high permeability and collapsibility, requiring treatment with a stabiliser. The physical behaviour of gypseous soil is represented by classification tests on the soil using a series of laboratory tests that include particle-size distribution, Atterberg limits, relative density, and compaction characteristics. The results are given in Tables 1 to 4.
Results of the sieve analysis of the untreated gypseous soil [ASTM D422-63, 2007]
| Passing % | Cum % | % Ret | Ret | Sieve. no |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 86.2 | 13.8 | 13.8 | 138 | 4.75 |
| 76.9 | 23.1 | 9.3 | 93 | 2.36 |
| 63.9 | 36.1 | 13 | 130 | 1.18 |
| 55.6 | 44.4 | 8.3 | 83 | 0.6 |
| 33.5 | 66.5 | 22.1 | 221 | 0.3 |
| 12.4 | 87.6 | 21.1 | 211 | 0.15 |
| 1.3 | 98.7 | 11.1 | 111 | 0.075 |
Results of the liquid limit test of the untreated gypseous soil [ASTM D4254-2000]
| Wc% | No. blows | No. |
|---|---|---|
| 12.5 | 60 | 1 |
| 18.8 | 17 | 2 |
| 20.3 | 10 | 3 |
Results of the plastic limit test of the untreated gypseous soil [ASTM D4254-2000]
| P.L = 11.1% | |
|---|---|
| 20 | Weight of wet sample(gm) |
| 18 | Weight of dry sample(gm) |
Results of the compaction test of the untreated gypseous soil [ASTM D1557-00, 2007]
| Density (gm /cm3) | 1660 | 1679 | 1690 | 1654 | 1511 |
| Wc% | 6.33 | 7.48 | 10.5 | 11.715 | 13.558 |
The proposed stabiliser consists of two materials: a WO (brownish-black petroleum fractions consisting mainly of the distilled residues from asphalt-type crude oils, with a relative density of about 0.95 [20, 21, 22]) and AP, which can be obtained from the waste of old asphalt pavement ground to a powder.
2.2 Design of Soil – Stabiliser Material Preparation
To prepare the tested specimens, the soil passing sieve No. 4 was oven-dried at a temperature of 105∘. For the test, the prepared specimens were divided into two groups as shown in Figure 1. For the first group, to calculate the maximum dry unit weight or density and the optimum moisture content and dry density of the soil, the standard compaction test was used, resulting in 16.9 kN/m3, which was selected as a reference in the compaction process. Next, the prepared soil was placed into square moulds (60 × 60 mm × 20 mm) to calculate the shear strength using the direct shear test. Finally, the rest of the specimen was tested for permeability at different immersion times (3, 10, 30, and 55 days), applying a water height of 2.0 m. The permeability tests were measured daily and then weekly until the soil collapsed [ASTM D434], as shown in Figure 2.
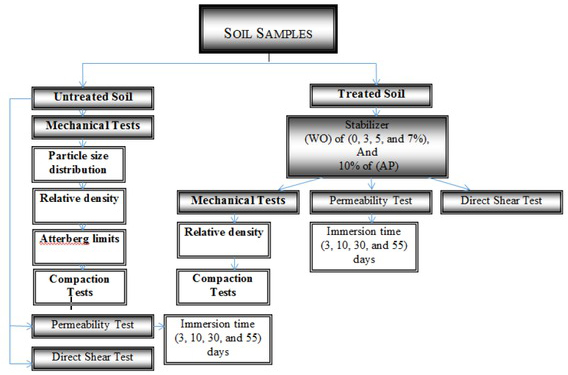
Flowchart of the research methodology
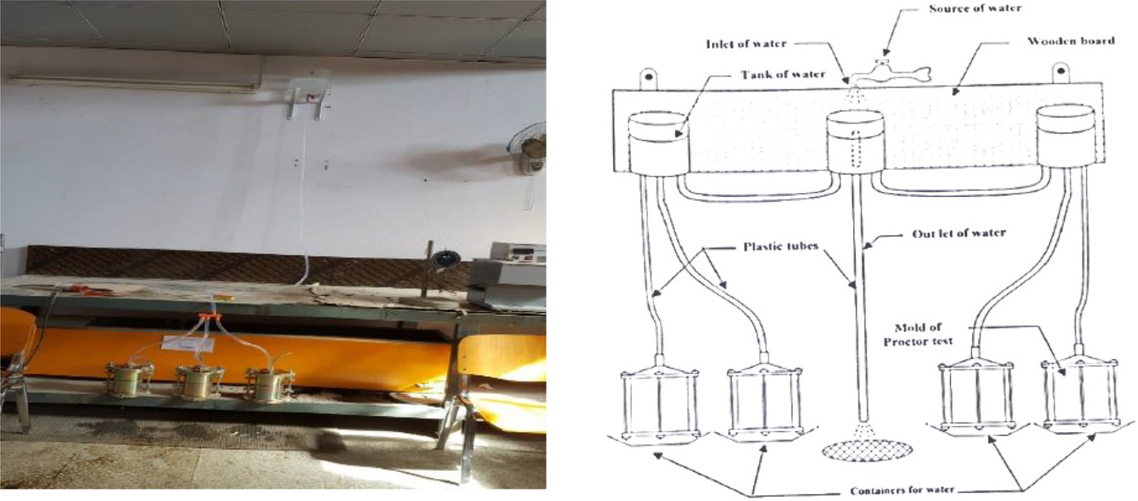
Model setup for the permeability and durability test
The second group included the treated specimens prepared by compacting the gypseous soil with different WOs at 0%, 3%, 5%, and 7% with 10% AP at the corresponding optimum moisture content for different WO percentages.
The specimen was mixed with WOs at different weight ratios (i.e., Wr = (Wa /WS) x 100% = 0%, 3%, 5%, 7%). First, the stabiliser and distilled water were added to the container and stirred to obtain an evenly viscous solution. Then, this solution was added to the prepared soil and mixed to obtain soil-stabiliser material.
The second group included the treated specimens prepared by compacting the gypseous soil with different WOs at 0%, 3%, 5%, and 7% with 10% AP at the corresponding optimum moisture content for different WO percentages.
The specimen was mixed with WOs at different weight ratios (i.e., Wr = (Wa /WS) x 100% = 0%, 3%, 5%, 7%). First, the stabiliser and distilled water were added to the container and stirred to obtain an evenly viscous solution. Then, this solution was added to the prepared soil and mixed to obtain soil-stabiliser material. Next, the treated specimens were exposed to the same test that was applied to the untreated group.
2.3 Laboratory Shear Test
The shear strength behaviour of the soil-stabiliser material after curing was studied using the direct shear test. The shear stress-displacement curve is pictured separately under the normal stress (σ) of 14, 27 and 40 kPa at a shear rated speed of 0.4 mm/min.
The model of the test was untrained to show the effect of consolidation in the soil within the process of loading over time [ASTM D3080]. The mixed materials were carefully transferred to the shear box in three layers with compaction to achieve the corresponding maximum unit weight. Three normal stresses of 14, 27 and 40 kPa were used to consider the stress range in the field applications.
The shear strength parameters, including cohesion (c) and the internal friction angle (φ), are calculated using Coulomb’s law of shear strength, as shown in Formula (1):
where τ is the shear strength of the soil equal to shear force to an area at S/A, c denotes the cohesion of the soil mass, φ represents the angle of the shear resistance for the soil, and σ is the normal stress equal to normal force to area soil mass at N/A.
3 Results
3.1 Effect of Compaction
Mixed gypseous soils with AP and different percentages of WO were used to study the effect of the proposed stabiliser on the compaction characteristics (i.e. maximising the optimum moisture content and dry density). The compaction test was conducted according to [12]. The maximum dry density was obtained according to the WO percentage,which is considered the corresponding water content. To prepare all tested samples, the standard proctor mould with a diameter of 4 in and a height of 4.6 in and a 5.5 lb standard hammer were used, and the samples were compacted in three successive layers using 25 blows for each layer.
Figure 3 shows the dry density moisture content relationship curves of the soil-stabiliser material. From these relationships, the values of the maximum mixture dry density and optimum moisture content can be obtained. The compaction curve shapes for the treated soil are similar to that of the untreated sample. The maximum dry unit weight or density of the soil-stabiliser mixtures increases with an increase in the WO. The figure illustrates the considerable effect of the WO percentage on the moisture content value.
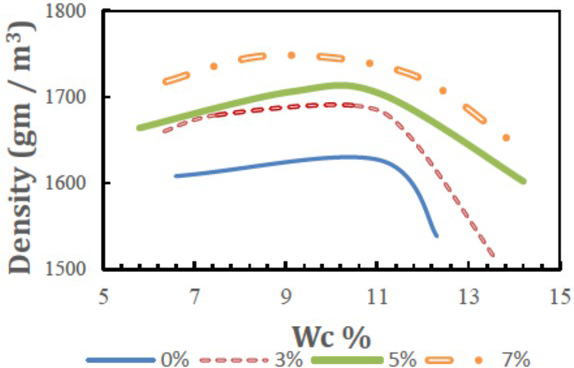
Effect of stabiliser percentage on moisture content and dry density curves
3.2 Failure Mode Results
All untreated and treated specimens were sheared alone first with the direct shear box to determine their frictional characteristics.
The two groups of soil specimens reached their ultimate shear strength in the untreated state under the normal stresses of 13, 27, and 40 kPa, as shown in Figure 4.
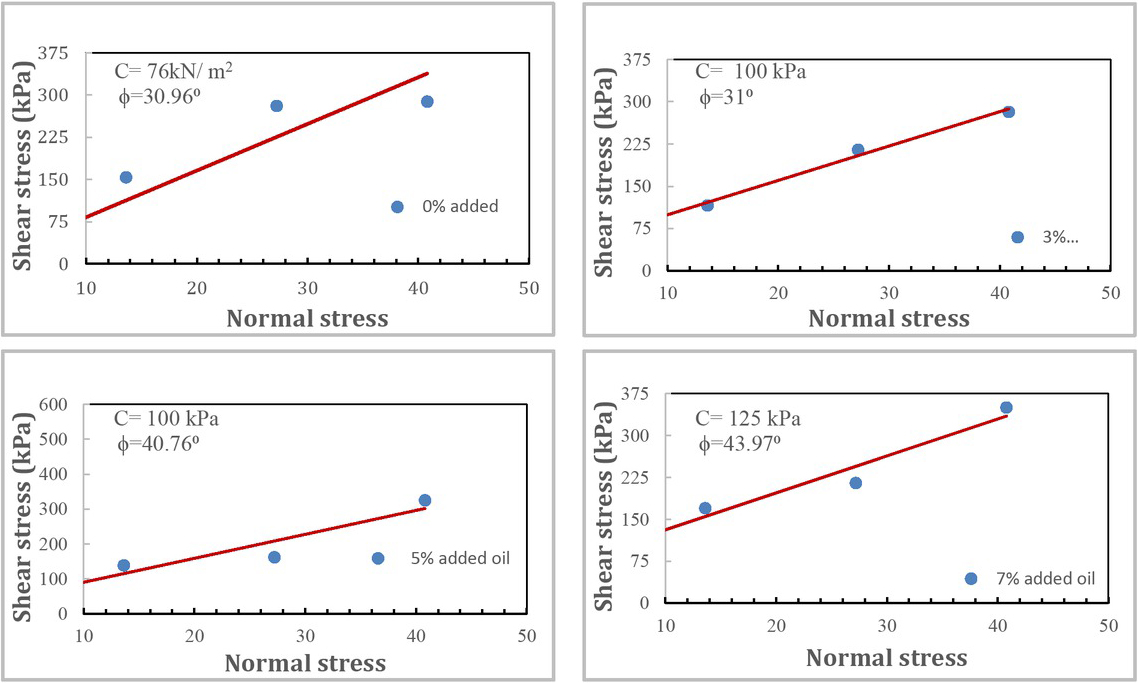
Shear stress versus normal stress values (failure envelope)
The figure demonstrates that the cohesion (c) and angle of shear resistance (φ) increased with an increase in the stabiliser percentage. The untreated soil specimens clearly have a low cohesive value due to the small volume of soil particles passing from sieve No. 0.075.
The increase in cohesiveness is attributed to the stabiliser, which affords the soil the property of fine minerals and fills the voids of the sandy soil, making it more cohesive. In addition, the increment in the angle of friction (φ) was very small for a stabiliser of 3%WO. From these test trials, the effective percentage of stabiliser that can be used with gypseous soil is 7%.
3.3 Peak Shear Strength
The maximum shear strength is reported in Figure 5. The direct shear tests for the untreated soil and soil-stabiliser specimens were conducted under the same normal loading and testing protocol for the sake of comparison. To discuss the effects of adding stabiliser on the stress-deformation behaviour of the tested specimens, the results of the direct shear tests under 40 kPa (as an example) are presented in Figure 5. The results show that a well-defined peak shear strength is not observed for the soil stabiliser. Generally, the yield shear stress is reached at a small horizontal displacement of less than 1.0 mm.
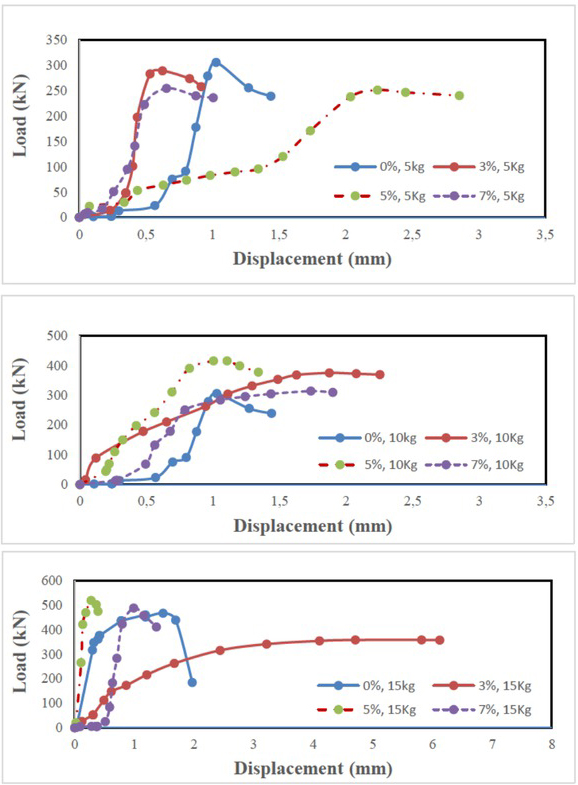
Horizontal deformation versus shear stress under 40 kPa of normal loading
It became constant after a displacement of 1.0 mm. The percentages of 0%, 3%and7%were used because the soils show more shear strength than the other case of 5% stabiliser.
There is no effect on moisture content, which produces a higher dry density value, and it is not necessary to show a higher shear resistance than for the other specimens.
By calculating the shear strength, which depends on the angle of internal friction of the soil and the cohesion, whether the soil strength is increased or decreased with treatment can be estimated. Therefore, a foundation with the dimensions of 2.0 × 2.0 m as single footing with a depth of 1.5 m was taken as an example to calculate the bearing capacity using the Terzagi method depending on the angle of internal friction and the cohesion.
The results were as follows:
Q (0%) = 9172.3 kN/m2
Q (3%) = 15390.5 kN/m2
Q (5%) = 19351.671 kN/m2
Q (7%) = 28131.8 kN/m2
From the above results, the bearing capacity increased by increasing the percentage of treatment despite that the cohesion values decreased. This might be attributed to the increase in the values of the angle of internal friction, which counteracts the lower cohesion values.
3.4 Constant Head Permeability Test
Figure 6 shows the relationship between the flow of water in a pipe for the constant head permeability test and the duration of time. From the figure, the head of water is reduced over time until reaching zero within 1.5 hours, which means that the soil has high permeability.
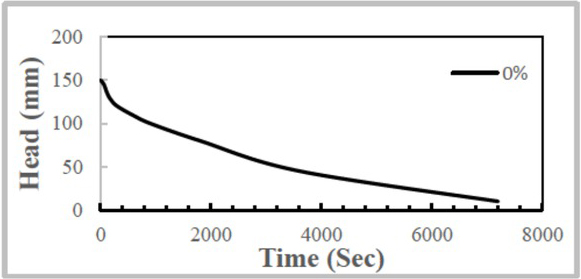
Relationship between falling water in a pipe for the constant head permeability test and the duration of time for untreated soil (0%) at 3 days of soaking
This sample will fail (collapse within 1 day after 3 days of applying a head of 1.35 m. The results are shown in Figures 7 to 10.
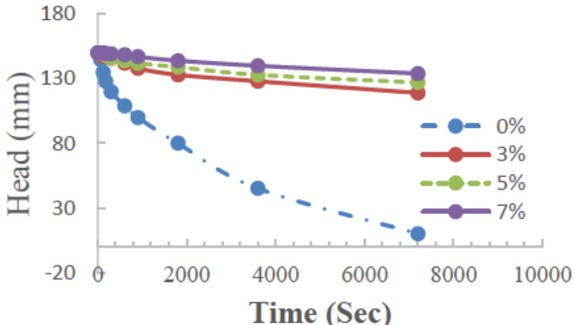
Relationship between falling water in a pipe for the constant head permeability test and the duration of time for untreated and 3%, 5%, and 7% stabiliser-treated soil after 3 days of soaking
Relationship between falling water in a pipe for the constant head permeability test and the duration of time for untreated and 3%, 5%, and 7% stabiliser-treated soil after 3 days of soaking
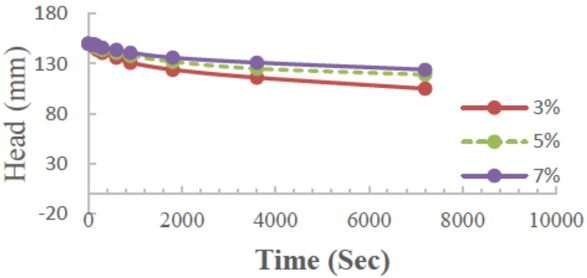
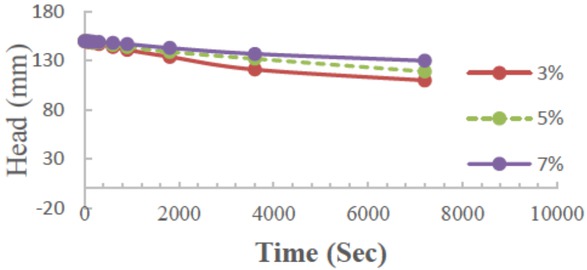
Relationship between falling water in a pipe for the constant head permeability test and the duration of time for 3%, 5%, and 7% stabiliser-treated soil after 30 days of soaking
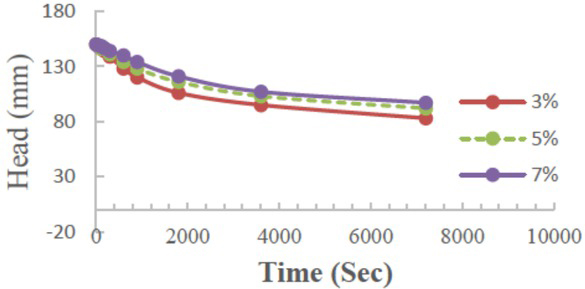
Relationship between falling water in a pipe for the constant head permeability test and the duration of time for 3%, 5%, and 7% stabiliser-treated soil after 55 days of soaking
The effect of treatment with 3%, 5%, and 7% of WO on permeability is shown in Figures 7 to 10.
The values of permeability are represented with the coefficient of permeability (k). The figures show that the coefficient of permeability is reduced over time with an increasing percentage of treatment. This leads to an increase in the density and reduces the voids between particles,which leads to reducing the permeability and reducing the effects of leaching and collapsibility. From the above results, the treatment with the proposed stabiliser is useful to modify the soil properties represented by the density and permeability, which are the main problems in gypseous soils, as illustrated in Figure 11.
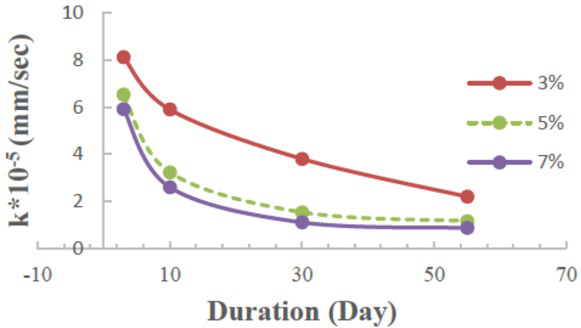
Comparison between (k*10−5) coefficients of permeability with 3%, 5%, and 7% stabiliser applied to the soil
4 Discussion
By treating the gypseous soil with a stabiliser (i.e. 3%, 5%, and 7% WO and 10% AP), the properties of the gypseous soil and its behaviours can be summarised as follows. For the treated soil, permeability and leaching decreased because the void ratio was reduced and caused lubrication between the soil particles, which reduced the voids and rearranged the particles.
The treatment of soil with a 5% stabiliser increased the durability compared to untreated soil. The 7% stabiliser was beneficial for all periods of the tests and may still be durable for a long time in the structure. The aim of this study was achieved by enhancing the permeability of the stabilised soil because this is the most important factor for soil failure, and it was solved using material available in Iraq. The soil properties for gypsum soil particles were improved by coating with WO and AP, which prevented collapse by reducing the dissolution of the gypsum. The cohesion was increased, and a suitable bearing capacity was maintained for carrying the loads.
To avoid the collapsibility of gypseous soil, a mixture of 3% WO and AP was used for sandy soils to create a suitable solution. In addition, the bearing capacity value was maintained to handle structure loads. The use of AP and WO was successful in improving the properties of the gypseous soils and may be considered the proposed method to provide the fullest advantage to modify the soil, compared with previous studies. This method of treatment using WO mixed with AP is considered the first method to treat the lack of cohesion and to increase the shear strength and bearing capacity of the soil.
References
[1] Buringh P. Soils and conditions in Iraq. Baghdad, Iraq: Ministry of Agriculture; 1960.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Blyth FG. A geology for engineers. 5th ed. London: Edward Arnold Ltd.; 1971.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Barazanji AF. (1973). Gypsiferous soils of Iraq. PhD thesis, University of Ghent, BelgiumSearch in Google Scholar
[4] Al-Saoudi NK. (2013). ‘Challenging problems of gypseous soils in Iraq’. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, ParisSearch in Google Scholar
[5] Al-Zory EA. (1993). The effect of leaching on lime stabilized gypseous soil. MSc thesis, Mosul UniversitySearch in Google Scholar
[6] Hamdan RK, Sarsam SI. Impact of Rejuvenators Type on Physical Properties of Aged Asphalt Cement. Civil Engineering Journal. 2019;5(9):2058–69.10.28991/cej-2019-03091393Search in Google Scholar
[7] Jajin MG, Hamedi GH. Examining the Effect of Dry Resin on Moisture Sensitivity of Asphaltic Mixtures. Civil Engineering Journal. 2018;4(7):1714–27.10.28991/cej-03091107Search in Google Scholar
[8] Gamil, Y., Bakar, I., & Ahmed, K. (2017). Simulation and development of instrumental setup to be used for cement grouting of sand soil. Emerging Science Journal, 1(1), 16-27. https://doi.org/10.28991/esj-2017-01112.https://doi.org/10.28991/esj-2017-01112Search in Google Scholar
[9] O’Flaherty CA. (1988). Highways: Volume 1 highway engineering. 3rd ed., Edward Arnold, LondonSearch in Google Scholar
[10] Al-Morshedy AD. (2001). The use of cut-back MC-30 for controlling the collapsibility of gypseous soils. MSc thesis, Building and Construction Department, University of TechnologySearch in Google Scholar
[11] Al-Alawee AB. (2001). Treatment of Al-Therthar gypseous soil by emulsified asphalt using mold test. MSc thesis, Building and Construction Department University of Technology, BaghdadSearch in Google Scholar
[12] Esho BG. (2004). Stabilization of gypseous soils by lime and emulsified asphalt. MSc thesis, College of Engineering, University of MosulSearch in Google Scholar
[13] Bushra S. ‘Treatment of gypsum soil breakdown’ [in Arabic]. J Eng (Stevenage). 2008;14(3):444–57.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Liu, J. et al. (2018). ‘An experimental study on the shear behaviors of polymer-sand compositematerials after immersion’. Polymers 10.8: 924, https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080924.https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080924Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Fattah MY, Al-Ani MM, Al-LamyMT. ‘Studying collapse potential of gypseous soil treated by grouting’. Soil Found. 2014;54(3):396–404.10.1016/j.sandf.2014.04.008Search in Google Scholar
[16] Fattah MY, al-Musawi HH, Salman FA. ‘Treatment of collapsibility of gypseous soils by dynamic compaction’. Geotech Geol Eng. 2012;30(6):1369–87.10.1007/s10706-012-9552-zSearch in Google Scholar
[17] Al-Taie AJ, Al-Shakarchi YJ. ‘Shear strength, collapsibility and compressibility characteristics of compacted Baiji Dune soils’. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology. 2017;12(3):767–79.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Aziz HY, Ma J. ‘Gypseous soil improvement using fuel oil’. World Acad Sci Eng Technol. 2011;51:299–303.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Emeka AE, Chukwuemeka AJ, Okwudili MB. Deformation behaviour of erodible soil stabilized with cement and quarry dust. Emerging Science Journal. 2018;2(6):383–7.10.28991/esj-2018-01157Search in Google Scholar
[20] Al-Otaibi FA. (2006). Assessment of the possibility of stabilising Sabkha soils using oil lake residue: Reuse of waste materials. Dissertation. Cardiff UniversitySearch in Google Scholar
[21] Mahdi TA, Al-Otaibi F, Thomas HR. (2006). ‘Sabkha soils mixed with oil lake residues: Reuse of a waste material’. 5th ICEG Environmental Geotechnics: Opportunities, Challenges and Responsibilities for Environmental Geotechnics: Proceedings of the ISSMGE 5th International Congress organized by the Geo-environmental Research Centre, Cardiff University, Cardiff City Hall 26–30th June 2006. Thomas Telford PublishingSearch in Google Scholar
[22] Goodger EM. Hydrocarbon fuels. Volume 87. Macmillan International Higher Education; 1975. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-02652-4.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-02652-4Search in Google Scholar
© 2020 H. Yousif Aziz et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Fabrication of aluminium covetic casts under different voltages and amperages of direct current
- Inhibition effect of the synergistic properties of 4-methyl-norvalin and 2-methoxy-4-formylphenol on the electrochemical deterioration of P4 low carbon mold steel
- Logistic regression in modeling and assessment of transport services
- Design and development of ultra-light front and rear axle of experimental vehicle
- Enhancement of cured cement using environmental waste: particleboards incorporating nano slag
- Evaluating ERP System Merging Success In Chemical Companies: System Quality, Information Quality, And Service Quality
- Accuracy of boundary layer treatments at different Reynolds scales
- Evaluation of stabiliser material using a waste additive mixture
- Optimisation of stress distribution in a highly loaded radial-axial gas microturbine using FEM
- Analysis of modern approaches for the prediction of electric energy consumption
- Surface Hardening of Aluminium Alloy with Addition of Zinc Particles by Friction Stir Processing
- Development and refinement of the Variational Method based on Polynomial Solutions of Schrödinger Equation
- Comparison of two methods for determining Q95 reference flow in the mouth of the surface catchment basin of the Meia Ponte river, state of Goiás, Brazil
- Applying Intelligent Portfolio Management to the Evaluation of Stalled Construction Projects
- Disjoint Sum of Products by Orthogonalizing Difference-Building ⴱ
- The Development of Information System with Strategic Planning for Integrated System in the Indonesian Pharmaceutical Company
- Simulation for Design and Material Selection of a Deep Placement Fertilizer Applicator for Soybean Cultivation
- Modeling transportation routes of the pick-up system using location problem: a case study
- Pinless friction stir spot welding of aluminium alloy with copper interlayer
- Roof Geometry in Building Design
- Review Articles
- Silicon-Germanium Dioxide and Aluminum Indium Gallium Arsenide-Based Acoustic Optic Modulators
- RZ Line Coding Scheme With Direct Laser Modulation for Upgrading Optical Transmission Systems
- LOGI Conference 2019
- Autonomous vans - the planning process of transport tasks
- Drivers ’reaction time research in the conditions in the real traffic
- Design and evaluation of a new intersection model to minimize congestions using VISSIM software
- Mathematical approaches for improving the efficiency of railway transport
- An experimental analysis of the driver’s attention during train driving
- Risks associated with Logistics 4.0 and their minimization using Blockchain
- Service quality of the urban public transport companies and sustainable city logistics
- Charging electric cars as a way to increase the use of energy produced from RES
- The impact of the truck loads on the braking efficiency assessment
- Application of virtual and augmented reality in automotive
- Dispatching policy evaluation for transport of ready mixed concrete
- Use of mathematical models and computer software for analysis of traffic noise
- New developments on EDR (Event Data Recorder) for automated vehicles
- General Application of Multiple Criteria Decision Making Methods for Finding the Optimal Solution in City Logistics
- The influence of the cargo weight and its position on the braking characteristics of light commercial vehicles
- Modeling the Delivery Routes Carried out by Automated Guided Vehicles when Using the Specific Mathematical Optimization Method
- Modelling of the system “driver - automation - autonomous vehicle - road”
- Limitations of the effectiveness of Weigh in Motion systems
- Long-term urban traffic monitoring based on wireless multi-sensor network
- The issue of addressing the lack of parking spaces for road freight transport in cities - a case study
- Simulation of the Use of the Material Handling Equipment in the Operation Process
- The use of simulation modelling for determining the capacity of railway lines in the Czech conditions
- Proposals for Using the NFC Technology in Regional Passenger Transport in the Slovak Republic
- Optimisation of Transport Capacity of a Railway Siding Through Construction-Reconstruction Measures
- Proposal of Methodology to Calculate Necessary Number of Autonomous Trucks for Trolleys and Efficiency Evaluation
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland
- 5G Based Machine Remote Operation Development Utilizing Digital Twin
- On-line moisture content estimation of saw dust via machine vision
- Data analysis of a paste thickener
- Programming and control for skill-based robots
- Using Digital Twin Technology in Engineering Education – Course Concept to Explore Benefits and Barriers
- Intelligent methods for root cause analysis behind the center line deviation of the steel strip
- Engaging Building Automation Data Visualisation Using Building Information Modelling and Progressive Web Application
- Real-time measurement system for determining metal concentrations in water-intensive processes
- A tool for finding inclusion clusters in steel SEM specimens
- An overview of current safety requirements for autonomous machines – review of standards
- Expertise and Uncertainty Processing with Nonlinear Scaling and Fuzzy Systems for Automation
- Towards online adaptation of digital twins
- Special Issue: ICE-SEAM 2019
- Fatigue Strength Analysis of S34MnV Steel by Accelerated Staircase Test
- The Effect of Discharge Current and Pulse-On Time on Biocompatible Zr-based BMG Sinking-EDM
- Dynamic characteristic of partially debonded sandwich of ferry ro-ro’s car deck: a numerical modeling
- Vibration-based damage identification for ship sandwich plate using finite element method
- Investigation of post-weld heat treatment (T6) and welding orientation on the strength of TIG-welded AL6061
- The effect of nozzle hole diameter of 3D printing on porosity and tensile strength parts using polylactic acid material
- Investigation of Meshing Strategy on Mechanical Behaviour of Hip Stem Implant Design Using FEA
- The effect of multi-stage modification on the performance of Savonius water turbines under the horizontal axis condition
- Special Issue: Recent Advances in Civil Engineering
- The effects of various parameters on the strengths of adhesives layer in a lightweight floor system
- Analysis of reliability of compressed masonry structures
- Estimation of Sport Facilities by Means of Technical-Economic Indicator
- Integral bridge and culvert design, Designer’s experience
- A FEM analysis of the settlement of a tall building situated on loess subsoil
- Behaviour of steel sheeting connections with self-drilling screws under variable loading
- Resistance of plug & play N type RHS truss connections
- Comparison of strength and stiffness parameters of purlins with different cross-sections of profiles
- Bearing capacity of floating geosynthetic encased columns (GEC) determined on the basis of CPTU penetration tests
- The effect of the stress distribution of anchorage and stress in the textured layer on the durability of new anchorages
- Analysis of tender procedure phases parameters for railroad construction works
- Special Issue: Terotechnology 2019
- The Use of Statistical Functions for the Selection of Laser Texturing Parameters
- Properties of Laser Additive Deposited Metallic Powder of Inconel 625
- Numerical Simulation of Laser Welding Dissimilar Low Carbon and Austenitic Steel Joint
- Assessment of Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings on the Ti13Nb13Zr Alloy
- Characteristics of selected measures of stress triaxiality near the crack tip for 145Cr6 steel - 3D issues for stationary cracks
- Assessment of technical risk in maintenance and improvement of a manufacturing process
- Experimental studies on the possibility of using a pulsed laser for spot welding of thin metallic foils
- Angular position control system of pneumatic artificial muscles
- The properties of lubricated friction pairs with diamond-like carbon coatings
- Effect of laser beam trajectory on pocket geometry in laser micromachining
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference
- The Employability Skills Needed To Face the Demands of Work in the Future: Systematic Literature Reviews
- Enhancing Higher-Order Thinking Skills in Vocational Education through Scaffolding-Problem Based Learning
- Technology-Integrated Project-Based Learning for Pre-Service Teacher Education: A Systematic Literature Review
- A Study on Water Absorption and Mechanical Properties in Epoxy-Bamboo Laminate Composite with Varying Immersion Temperatures
- Enhancing Students’ Ability in Learning Process of Programming Language using Adaptive Learning Systems: A Literature Review
- Topical Issue on Mathematical Modelling in Applied Sciences, III
- An innovative learning approach for solar power forecasting using genetic algorithm and artificial neural network
- Hands-on Learning In STEM: Revisiting Educational Robotics as a Learning Style Precursor
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Fabrication of aluminium covetic casts under different voltages and amperages of direct current
- Inhibition effect of the synergistic properties of 4-methyl-norvalin and 2-methoxy-4-formylphenol on the electrochemical deterioration of P4 low carbon mold steel
- Logistic regression in modeling and assessment of transport services
- Design and development of ultra-light front and rear axle of experimental vehicle
- Enhancement of cured cement using environmental waste: particleboards incorporating nano slag
- Evaluating ERP System Merging Success In Chemical Companies: System Quality, Information Quality, And Service Quality
- Accuracy of boundary layer treatments at different Reynolds scales
- Evaluation of stabiliser material using a waste additive mixture
- Optimisation of stress distribution in a highly loaded radial-axial gas microturbine using FEM
- Analysis of modern approaches for the prediction of electric energy consumption
- Surface Hardening of Aluminium Alloy with Addition of Zinc Particles by Friction Stir Processing
- Development and refinement of the Variational Method based on Polynomial Solutions of Schrödinger Equation
- Comparison of two methods for determining Q95 reference flow in the mouth of the surface catchment basin of the Meia Ponte river, state of Goiás, Brazil
- Applying Intelligent Portfolio Management to the Evaluation of Stalled Construction Projects
- Disjoint Sum of Products by Orthogonalizing Difference-Building ⴱ
- The Development of Information System with Strategic Planning for Integrated System in the Indonesian Pharmaceutical Company
- Simulation for Design and Material Selection of a Deep Placement Fertilizer Applicator for Soybean Cultivation
- Modeling transportation routes of the pick-up system using location problem: a case study
- Pinless friction stir spot welding of aluminium alloy with copper interlayer
- Roof Geometry in Building Design
- Review Articles
- Silicon-Germanium Dioxide and Aluminum Indium Gallium Arsenide-Based Acoustic Optic Modulators
- RZ Line Coding Scheme With Direct Laser Modulation for Upgrading Optical Transmission Systems
- LOGI Conference 2019
- Autonomous vans - the planning process of transport tasks
- Drivers ’reaction time research in the conditions in the real traffic
- Design and evaluation of a new intersection model to minimize congestions using VISSIM software
- Mathematical approaches for improving the efficiency of railway transport
- An experimental analysis of the driver’s attention during train driving
- Risks associated with Logistics 4.0 and their minimization using Blockchain
- Service quality of the urban public transport companies and sustainable city logistics
- Charging electric cars as a way to increase the use of energy produced from RES
- The impact of the truck loads on the braking efficiency assessment
- Application of virtual and augmented reality in automotive
- Dispatching policy evaluation for transport of ready mixed concrete
- Use of mathematical models and computer software for analysis of traffic noise
- New developments on EDR (Event Data Recorder) for automated vehicles
- General Application of Multiple Criteria Decision Making Methods for Finding the Optimal Solution in City Logistics
- The influence of the cargo weight and its position on the braking characteristics of light commercial vehicles
- Modeling the Delivery Routes Carried out by Automated Guided Vehicles when Using the Specific Mathematical Optimization Method
- Modelling of the system “driver - automation - autonomous vehicle - road”
- Limitations of the effectiveness of Weigh in Motion systems
- Long-term urban traffic monitoring based on wireless multi-sensor network
- The issue of addressing the lack of parking spaces for road freight transport in cities - a case study
- Simulation of the Use of the Material Handling Equipment in the Operation Process
- The use of simulation modelling for determining the capacity of railway lines in the Czech conditions
- Proposals for Using the NFC Technology in Regional Passenger Transport in the Slovak Republic
- Optimisation of Transport Capacity of a Railway Siding Through Construction-Reconstruction Measures
- Proposal of Methodology to Calculate Necessary Number of Autonomous Trucks for Trolleys and Efficiency Evaluation
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland
- 5G Based Machine Remote Operation Development Utilizing Digital Twin
- On-line moisture content estimation of saw dust via machine vision
- Data analysis of a paste thickener
- Programming and control for skill-based robots
- Using Digital Twin Technology in Engineering Education – Course Concept to Explore Benefits and Barriers
- Intelligent methods for root cause analysis behind the center line deviation of the steel strip
- Engaging Building Automation Data Visualisation Using Building Information Modelling and Progressive Web Application
- Real-time measurement system for determining metal concentrations in water-intensive processes
- A tool for finding inclusion clusters in steel SEM specimens
- An overview of current safety requirements for autonomous machines – review of standards
- Expertise and Uncertainty Processing with Nonlinear Scaling and Fuzzy Systems for Automation
- Towards online adaptation of digital twins
- Special Issue: ICE-SEAM 2019
- Fatigue Strength Analysis of S34MnV Steel by Accelerated Staircase Test
- The Effect of Discharge Current and Pulse-On Time on Biocompatible Zr-based BMG Sinking-EDM
- Dynamic characteristic of partially debonded sandwich of ferry ro-ro’s car deck: a numerical modeling
- Vibration-based damage identification for ship sandwich plate using finite element method
- Investigation of post-weld heat treatment (T6) and welding orientation on the strength of TIG-welded AL6061
- The effect of nozzle hole diameter of 3D printing on porosity and tensile strength parts using polylactic acid material
- Investigation of Meshing Strategy on Mechanical Behaviour of Hip Stem Implant Design Using FEA
- The effect of multi-stage modification on the performance of Savonius water turbines under the horizontal axis condition
- Special Issue: Recent Advances in Civil Engineering
- The effects of various parameters on the strengths of adhesives layer in a lightweight floor system
- Analysis of reliability of compressed masonry structures
- Estimation of Sport Facilities by Means of Technical-Economic Indicator
- Integral bridge and culvert design, Designer’s experience
- A FEM analysis of the settlement of a tall building situated on loess subsoil
- Behaviour of steel sheeting connections with self-drilling screws under variable loading
- Resistance of plug & play N type RHS truss connections
- Comparison of strength and stiffness parameters of purlins with different cross-sections of profiles
- Bearing capacity of floating geosynthetic encased columns (GEC) determined on the basis of CPTU penetration tests
- The effect of the stress distribution of anchorage and stress in the textured layer on the durability of new anchorages
- Analysis of tender procedure phases parameters for railroad construction works
- Special Issue: Terotechnology 2019
- The Use of Statistical Functions for the Selection of Laser Texturing Parameters
- Properties of Laser Additive Deposited Metallic Powder of Inconel 625
- Numerical Simulation of Laser Welding Dissimilar Low Carbon and Austenitic Steel Joint
- Assessment of Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings on the Ti13Nb13Zr Alloy
- Characteristics of selected measures of stress triaxiality near the crack tip for 145Cr6 steel - 3D issues for stationary cracks
- Assessment of technical risk in maintenance and improvement of a manufacturing process
- Experimental studies on the possibility of using a pulsed laser for spot welding of thin metallic foils
- Angular position control system of pneumatic artificial muscles
- The properties of lubricated friction pairs with diamond-like carbon coatings
- Effect of laser beam trajectory on pocket geometry in laser micromachining
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference
- The Employability Skills Needed To Face the Demands of Work in the Future: Systematic Literature Reviews
- Enhancing Higher-Order Thinking Skills in Vocational Education through Scaffolding-Problem Based Learning
- Technology-Integrated Project-Based Learning for Pre-Service Teacher Education: A Systematic Literature Review
- A Study on Water Absorption and Mechanical Properties in Epoxy-Bamboo Laminate Composite with Varying Immersion Temperatures
- Enhancing Students’ Ability in Learning Process of Programming Language using Adaptive Learning Systems: A Literature Review
- Topical Issue on Mathematical Modelling in Applied Sciences, III
- An innovative learning approach for solar power forecasting using genetic algorithm and artificial neural network
- Hands-on Learning In STEM: Revisiting Educational Robotics as a Learning Style Precursor

