Abstract
C19H17FINO4, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 7.1158(2) Å, b = 11.1914(3) Å, c = 12.4974(3) Å, α = 73.015(2)°, β = 87.945(2)°, γ = 78.137(2)°, V = 931.19(4) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0563, wRref (F 2) = 0.1639, T = 293(2) K.
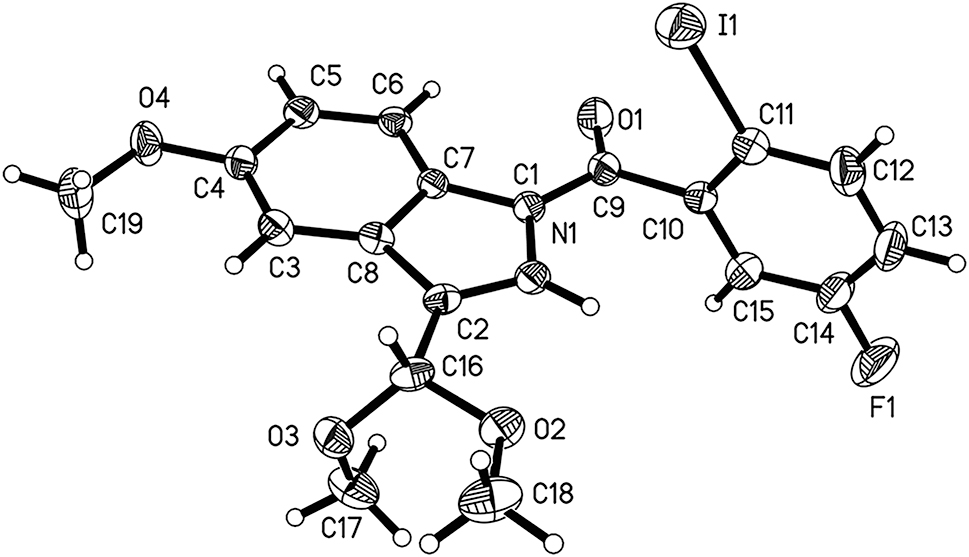
The crystal structure is shown in figure. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30 % probability level.
Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 13.8 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB synergy R, four-circle diffractometer |
| θ max, completeness: | 74.0°, 97 % |
| N(hkl)measured , N(hkl)unique, R int: | 9895, 3519, 0.066 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3042 |
| N(param)refined: | 239 |
| Programs: | Rigaku, 1 SHELX 2 , 3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | X | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | −0.0486 (7) | 0.6884 (4) | 0.7243 (4) | 0.0399 (10) |
| H1 | −0.112865 | 0.764732 | 0.675566 | 0.048* |
| C2 | −0.0532 (6) | 0.5729 (4) | 0.7163 (4) | 0.0368 (9) |
| C3 | 0.1171 (7) | 0.3466 (4) | 0.8385 (4) | 0.0416 (10) |
| H3 | 0.069593 | 0.299897 | 0.799122 | 0.050* |
| C4 | 0.2405 (7) | 0.2865 (4) | 0.9298 (4) | 0.0411 (10) |
| C5 | 0.3096 (7) | 0.3570 (5) | 0.9910 (4) | 0.0427 (11) |
| H5 | 0.390470 | 0.314069 | 1.053136 | 0.051* |
| C6 | 0.2601 (7) | 0.4872 (4) | 0.9609 (4) | 0.0380 (9) |
| H6 | 0.306944 | 0.533507 | 1.000957 | 0.046* |
| C7 | 0.1381 (6) | 0.5475 (4) | 0.8690 (4) | 0.0335 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0660 (7) | 0.4793 (4) | 0.8071 (3) | 0.0354 (9) |
| C9 | 0.1071 (7) | 0.7797 (4) | 0.8472 (4) | 0.0429 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0311 (7) | 0.9098 (4) | 0.7680 (4) | 0.0419 (10) |
| C11 | 0.1382 (8) | 0.9640 (5) | 0.6785 (5) | 0.0480 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0715 (11) | 1.0861 (5) | 0.6101 (5) | 0.0633 (16) |
| H12 | 0.143458 | 1.120901 | 0.549773 | 0.076* |
| C13 | −0.1002 (12) | 1.1564 (5) | 0.6307 (7) | 0.0726 (19) |
| H13 | −0.145211 | 1.239528 | 0.586172 | 0.087* |
| C14 | −0.2029 (10) | 1.1008 (5) | 0.7184 (6) | 0.0643 (16) |
| C15 | −0.1450 (9) | 0.9802 (5) | 0.7885 (5) | 0.0548 (13) |
| H15 | −0.220139 | 0.946272 | 0.847535 | 0.066* |
| C16 | −0.1543 (7) | 0.5433 (5) | 0.6271 (4) | 0.0433 (10) |
| H16 | −0.055819 | 0.514220 | 0.578276 | 0.052* |
| C17 | −0.4007 (10) | 0.4698 (7) | 0.7447 (6) | 0.0672 (16) |
| H17A | −0.345003 | 0.493644 | 0.802218 | 0.101* |
| H17B | −0.449026 | 0.393511 | 0.777574 | 0.101* |
| H17C | −0.504170 | 0.537432 | 0.707337 | 0.101* |
| C18 | −0.3503 (11) | 0.6503 (8) | 0.4649 (5) | 0.077 (2) |
| H18A | −0.251511 | 0.636458 | 0.412944 | 0.116* |
| H18B | −0.440228 | 0.728164 | 0.431259 | 0.116* |
| H18C | −0.415862 | 0.580285 | 0.484269 | 0.116* |
| C19 | 0.2430 (12) | 0.0786 (5) | 0.9120 (6) | 0.0721 (19) |
| H19A | 0.105483 | 0.091404 | 0.913661 | 0.108* |
| H19B | 0.297998 | −0.009381 | 0.948136 | 0.108* |
| H19C | 0.282640 | 0.101152 | 0.835659 | 0.108* |
| F1 | −0.3745 (7) | 1.1691 (4) | 0.7407 (5) | 0.0983 (15) |
| I1 | 0.40179 (6) | 0.85710 (4) | 0.64563 (4) | 0.0756 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0660 (6) | 0.6790 (4) | 0.8160 (3) | 0.0373 (8) |
| O1 | 0.1957 (7) | 0.7661 (4) | 0.9313 (4) | 0.0613 (11) |
| O2 | −0.2666 (6) | 0.6592 (4) | 0.5628 (3) | 0.0556 (9) |
| O3 | −0.2595 (6) | 0.4475 (3) | 0.6665 (3) | 0.0522 (9) |
| O4 | 0.3068 (7) | 0.1568 (3) | 0.9689 (3) | 0.0581 (10) |
1 Source of material
The target compound (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl) (5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone could be synthesized by acylation of 3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indole with corresponding acyl chloride. Firstly, sodium hydride (1.1 g, 27 mmol) and anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF, 12 mL) were added into a 100 mL round bottom flask, and stirred for 5 min in an ice water bath. Secondly, a solution of 3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indole (1.7 g, 7.5 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (10 mL) was added dropwise to the reaction solution, and after the addition was complete, continued stirring for another 5 min. Subsequently, a solution prepared by 5-fluoro-2-iodobenzoyl chloride (3.8 g, 13.5 mmol) and anhydrous DMF (10 mL) was added dropwise. After addition, the reaction mixture was slowly raised to room temperature, and stirred for 4 h. TLC (UV, 254 nm) was used to monitor the reaction process. After the end of reaction, this solution was quenched by saturated ammonium chloride solution carefully, then the crude product precipitated from the mixture. The crude product was homogenized with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (2:1, v/v), followed by filtration and washing to obtain pure product (3.0 g, yield 85 %). Single crystals were obtained from the n-hexane/ethyl acetate (1:1, v/v) solution.
2 Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d (C–H) = 0.96 Å (methyl), U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.98 Å (methyne), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.93 Å (aromatic), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C).
3 Comment
The research on nitrogen heterocycle compositions has always been a hot topic in organic chemistry and medicinal chemistry. 4 Among the 1086 small molecule drugs approved by the U. S. FDA, 640 drugs (approximately 59 %) contained nitrogen heterocycles in their structures, and indole was the most common fused heterocyclic ring, with 17 new drugs containing this structure, ranking 9th among all heterocycles. 5 In the above context, the synthesis and structural modification of indole skeletons have become significant topics in organic chemistry. 6 The classic strategies for sodium indole synthesis included Bischler–Mohlau (1881), 7 Fischer (1883), 8 Reisset (1897), 9 Nenitzescu (1929) 10 reactions. In addition, Batcho–Leimgruber (1971), 11 Gassman (1974), 12 Hegedus (1976), 13 Mori–Ban (1977), 14 Bartoli (1978), 15 and other named reactions represented new methods in this field. On the other hand, N-acylation reactions, Vilsmeier–Haack reactions, Friedel–Crafts reactions, and diverse transition-metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions were sodium the most used methods for structure modification of indoles. 16 , 17 Based on the previous research on the synthesis methodology and activity evaluation of indole derivatives, we designed and synthesized a series of N-acyl indole skeletons with methoxy and halogen substituents, which could be utilized as key intermediates for the synthesis of diverse anti-inflammatory or anti-tumor compounds. 18
Single-crystal structure analysis reveals that there is one molecule in the asymmetric unit (cf. the Figure). Bond lengths and angles are within a reasonable range. 19 , 20 , 21 In the title molecule, the halogen substituted benzene ring and indole ring are bridged by a carbonyl group. Due to the conjugation effect between the N(1) atom of indole and the carbonyl group, the bond length of C(9)–N(1) (1.382(6) Å) is significantly shortened compared to normal C–N single bonds, which is similar to C(1)–N(1) (1.397(6) Å) and C(7)–N(1) (1.419(6) Å) of the indole ring. The torsion angles of O(1)–C(9)–N(1)–C(1) and O(1)–C(9)–N(1)–C(7) are 174.7(5)° and −7.6(8)°, respectively, indicating that the amide moiety and indole ring are nearly coplanar. The above phenomenon may be due to conjugation effects and smaller steric hindrance. On the contrary, the torsion angles of O(1)–C(9)–C(10)–C(11) and O(1)–C(9)–C(10)–C(15) are 91.9(7)° and −84.4(7)°, respectively, indicating that the carbonyl group and the benzene ring are almost in a vertical conformation, which may be caused by steric hindrance between the carbonyl oxygen atom and the iodine atom. In summary, due to the above two effects, the indole and the halogen substituted benzene ring are nearly perpendicular, with a dihedral angle of 87.85(2)°. Geometric parameters are all in the expected ranges. 22
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: National Science Foundation of China (No. 21702018), a Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (No. 2019GSF108031).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Xing, Q.; Chandrachud, P. P.; Tillett, K.; Lopchuk, J. M. Regioselective Hydroamination of Unactivated Olefins with Diazirines as a Diversifiable Nitrogen Source. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6049; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-50254-8.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Vitaku, E.; Smith, D. T.; Njardarson, J. T. Analysis of the Structural Diversity, Substitution Patterns, and Frequency of Nitrogen Heterocycles Among U. S. FDA Approved Pharmaceuticals. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 57, 10257–10274; https://doi.org/10.1021/jm501100b.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Gavadia, R.; Rasgania, J.; Sahu, N.; Varma–Basil, M.; Chauhan, V.; Kumar, S.; Jakhar, K.; Singh, D. Synthesis of Indole-Functionalized Isoniazid Conjugates with Potent Antimycobacterial and Antioxidant Efficacy. Future Med. Chem. 2024, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/17568919.2024.2379240.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
7. Pchalek, K.; Jones, A. W.; Wekking, M. M. T.; Black, D. S. C. Synthesis of Activated 3-Substituted Indoles: An Optimised One-Pot Procedure. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 77–82; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2004.10.060.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Robinson, B. The Fischer Indole Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 1963, 63, 373–401; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr60224a003.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Frydman, B.; Despuy, M. E.; Rapoport, H. Pyrroles from Azaindoles. A Synthesis of Porphobilinogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965, 87, 3530–3531; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01093a061.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Nenitzescu, C. D. Derivatives of 2-Methyl-5-Hydroxyindole. Bull. Soc. Chim. Romania 1929, 11, 37–43.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Batcho, A. D.; Leimgruber, W. Indoles from 2-Methylnitrobenzenes by Condensation with Formamide Acetals Followed by Reduction: 4-Benzyloxyindole. Org. Synth. 1985, 63, 214–225.10.15227/orgsyn.063.0214Suche in Google Scholar
12. Gassman, P. G.; Van Bergen, T. J.; Gilbert, D. P.; Cue, B. W.Jr. General Method for the Synthesis of Indoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 5495–5508; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00824a028.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Hegedus, L. S.; Allen, G. F.; Waterman, E. L. Palladium Assisted Intramolecular Amination of Olefins. A New Synthesis of Indoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 2674–2676; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00425a051.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Mori, M.; Ban, Y. Reactions and Syntheses with Organometallic Compounds. X. The Intramolecular Cyclization Using Arylpalladium Complexes for Generation of Nitrogen-Heterocycles. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 1133–1136; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-4039(01)86083-4.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Bartoli, G.; Palmieri, G.; Bosco, M.; Dalpozzo, R. The Reaction of Vinyl Grignard Reagents with 2-Substituted Nitroarenes: a New Approach to the Synthesis of 7-Substituted Indoles. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 2129–2132; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-4039(01)93730-x.Suche in Google Scholar
16. Ahmad, T.; Khan, S.; Ullah, N. Recent Advances in the Catalytic Asymmetric Friedel–Crafts Reactions of Indoles. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 35446–35485; https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c05022.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
17. Leitch, J.; Bhonoah, Y.; Frost, C. Beyond C2 and C3: Transition-Metal-Catalyzed C–H Functionalization of Indole. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5618–5627; https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b01785.Suche in Google Scholar
18. Cong, W.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Yao, H. Facile Construction of Pyrrolophenanthridone Skeleton via a One-Pot Intramolecular Heck Reaction and Oxidation. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 312–317; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2013.11.053.Suche in Google Scholar
19. Almutairi, M. S.; Ghabbour, H. A.; Attia, M. I. Crystal Structure of Methyl 1H-Indole-2-Carboxylate, C10H9NO2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2017, 232, 431–432; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2016-0303.Suche in Google Scholar
20. Sun, Y. F.; Tang, Q. Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y. J.; Cong, W. Crystal Structure of 1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-6-Methoxy- 1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C17H12INO3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 299–301; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0599.Suche in Google Scholar
21. Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q. Q.; Yuan, J. C.; Sheng, C. S.; Cong, W. Crystal Structure of 5-Bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-Indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 73–75; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0447.Suche in Google Scholar
22. Kalinowska–Tłuścik, J.; Staroń, J.; Krawczuk, A.; Mordalski, S.; Warszycki, D.; Satała, G.; Hogendorf, A. S.; Bojarski, A. J. The Effect of the Intramolecular C—H⃛O Interactions on the Conformational Preferences of Bis -arylsulfones – 5–HT6 Receptor Antagonists and beyond. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 18672–18681; https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra03107j.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

