Abstract
C25H29Br2N3O3, orthorhombic, Pbca (61), a = 20.109(5) Å, b = 10.754(5) Å, c = 24.321(5) Å, V = 5,259(3) Å3, Z = 8, R gt(F) = 0.0464, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1156, T = 295 K.
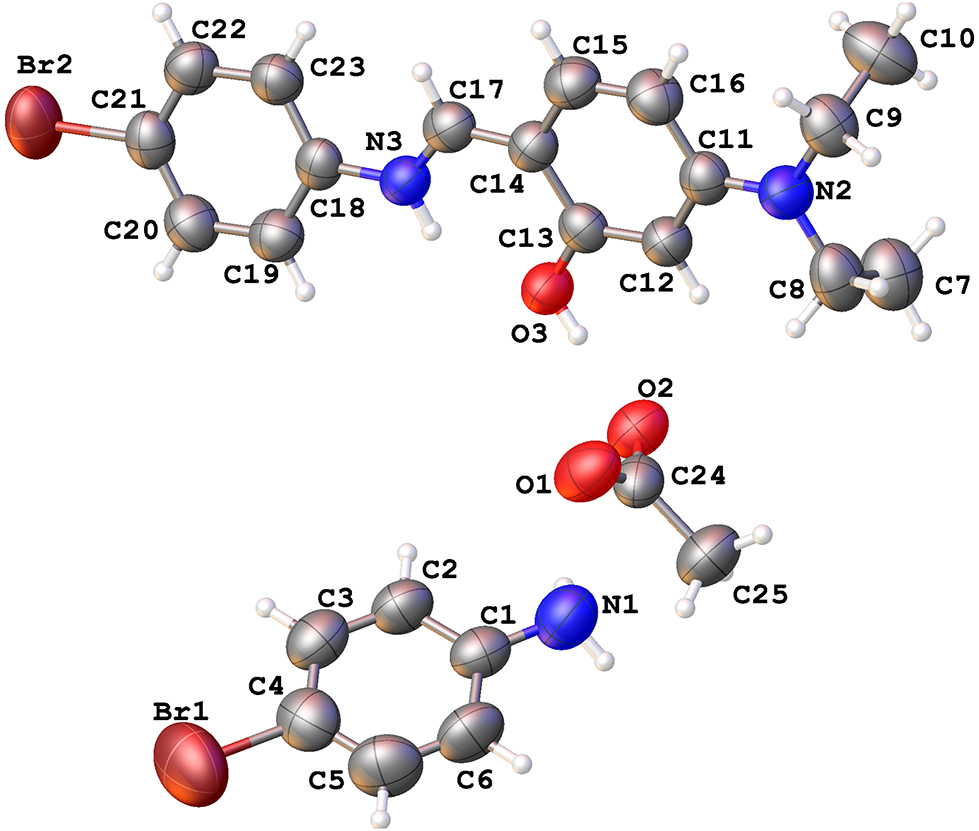
A part of the molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Orange needle |
| Size: | 0.26 × 0.18 × 0.13 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 3.11 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 26.0°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 62,620, 5,175, 0.068 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 2,802 |
| N(param)refined: | 353 |
| Programs: | Olex2, 1 , 2 SHELX, 3 Mercury 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br1 | 0.48429 (8) | 0.74278 (14) | 0.40079 (6) | 0.1522 (8) |
| N1 | 0.52520 (18) | 0.7484 (3) | 0.64863 (13) | 0.1010 (12) |
| H1a | 0.4922 (7) | 0.784 (2) | 0.6646 (2) | 0.1211 (14)* |
| H1b | 0.5290 (14) | 0.6736 (4) | 0.66070 (17) | 0.1211 (14)* |
| C1 | 0.51439 (19) | 0.7463 (4) | 0.59187 (18) | 0.0731 (10) |
| C2 | 0.54121 (19) | 0.6535 (4) | 0.55945 (18) | 0.0798 (11) |
| H2 | 0.56544 (19) | 0.5899 (4) | 0.57586 (18) | 0.0958 (13)* |
| C3 | 0.5327 (2) | 0.6536 (4) | 0.5032 (2) | 0.0863 (12) |
| H3b | 0.5516 (2) | 0.5906 (4) | 0.4821 (2) | 0.1035 (14)* |
| C4 | 0.4966 (2) | 0.7462 (5) | 0.47801 (19) | 0.0904 (13) |
| C5 | 0.4696 (2) | 0.8396 (4) | 0.5098 (2) | 0.1039 (15) |
| H5 | 0.4453 (2) | 0.9029 (4) | 0.4933 (2) | 0.1246 (18)* |
| C6 | 0.4787 (2) | 0.8395 (4) | 0.5661 (2) | 0.0920 (13) |
| H6 | 0.4605 (2) | 0.9034 (4) | 0.5870 (2) | 0.1104 (16)* |
| Br2 | 0.73770 (6) | −0.30466 (9) | 0.50363 (4) | 0.0980 (6) |
| O1 | 0.57549 (14) | 0.5268 (3) | 0.70577 (12) | 0.0967 (9) |
| O2 | 0.55573 (12) | 0.3728 (2) | 0.76409 (10) | 0.0772 (7) |
| O3 | 0.65715 (12) | 0.2657 (2) | 0.73219 (10) | 0.0677 (7) |
| H3 | 0.62489 (17) | 0.306 (2) | 0.7424 (14) | 0.1016 (10)* |
| N2 | 0.76822 (15) | 0.5675 (3) | 0.84425 (13) | 0.0741 (9) |
| N3 | 0.73015 (14) | 0.1122 (3) | 0.67233 (10) | 0.0612 (7) |
| H3a | 0.69096 (14) | 0.1349 (3) | 0.68230 (10) | 0.0735 (9)* |
| C7 | 0.6750 (2) | 0.5462 (4) | 0.90902 (17) | 0.0999 (14) |
| H7a | 0.6687 (14) | 0.4619 (8) | 0.8971 (4) | 0.150 (2)* |
| H7b | 0.7044 (7) | 0.548 (2) | 0.9401 (5) | 0.150 (2)* |
| H7c | 0.6328 (7) | 0.5813 (17) | 0.9192 (9) | 0.150 (2)* |
| C8 | 0.7044 (2) | 0.6202 (4) | 0.86348 (16) | 0.0866 (12) |
| H8a | 0.7116 (2) | 0.7049 (4) | 0.87595 (16) | 0.1039 (15)* |
| H8b | 0.6733 (2) | 0.6229 (4) | 0.83300 (16) | 0.1039 (15)* |
| C9 | 0.8286 (2) | 0.6246 (3) | 0.86756 (15) | 0.0792 (11) |
| H9a | 0.8623 (2) | 0.6298 (3) | 0.83908 (15) | 0.0951 (13)* |
| H9b | 0.8183 (2) | 0.7087 (3) | 0.87926 (15) | 0.0951 (13)* |
| C10 | 0.8564 (2) | 0.5540 (4) | 0.91539 (18) | 0.1021 (14) |
| H10a | 0.8674 (14) | 0.4711 (10) | 0.9040 (3) | 0.153 (2)* |
| H10b | 0.8957 (9) | 0.5950 (17) | 0.9286 (8) | 0.153 (2)* |
| H10c | 0.8238 (6) | 0.551 (2) | 0.9443 (5) | 0.153 (2)* |
| C11 | 0.76977 (18) | 0.4710 (3) | 0.80829 (14) | 0.0632 (9) |
| C12 | 0.71136 (18) | 0.4148 (3) | 0.78867 (13) | 0.0620 (9) |
| H12 | 0.67052 (18) | 0.4436 (3) | 0.80127 (13) | 0.0744 (11)* |
| C13 | 0.71250 (18) | 0.3177 (3) | 0.75118 (13) | 0.0571 (8) |
| C14 | 0.77492 (17) | 0.2709 (3) | 0.73180 (14) | 0.0589 (9) |
| C15 | 0.83348 (19) | 0.3282 (3) | 0.75223 (15) | 0.0713 (10) |
| H15 | 0.87455 (19) | 0.2996 (3) | 0.74002 (15) | 0.0855 (12)* |
| C16 | 0.83181 (19) | 0.4235 (3) | 0.78904 (15) | 0.0721 (10) |
| H16 | 0.87136 (19) | 0.4580 (3) | 0.80173 (15) | 0.0865 (12)* |
| C17 | 0.78055 (18) | 0.1729 (3) | 0.69465 (14) | 0.0628 (9) |
| H17 | 0.82321 (18) | 0.1482 (3) | 0.68473 (14) | 0.0754 (11)* |
| C18 | 0.73383 (18) | 0.0136 (3) | 0.63366 (13) | 0.0566 (9) |
| C19 | 0.67542 (18) | −0.0229 (3) | 0.60745 (14) | 0.0688 (10) |
| H19 | 0.63552 (18) | 0.0163 (3) | 0.61599 (14) | 0.0826 (12)* |
| C20 | 0.6765 (2) | −0.1173 (3) | 0.56875 (15) | 0.0730 (10) |
| H20 | 0.6375 (2) | −0.1414 (3) | 0.55113 (15) | 0.0875 (12)* |
| C21 | 0.7356 (2) | −0.1747 (3) | 0.55667 (13) | 0.0656 (9) |
| C22 | 0.7937 (2) | −0.1410 (3) | 0.58246 (15) | 0.0692 (10) |
| H22 | 0.8333 (2) | −0.1808 (3) | 0.57360 (15) | 0.0831 (12)* |
| C23 | 0.79310 (19) | −0.0472 (3) | 0.62183 (14) | 0.0656 (10) |
| H23 | 0.83203 (19) | −0.0253 (3) | 0.64007 (14) | 0.0787 (11)* |
| C24 | 0.54435 (18) | 0.4819 (4) | 0.74432 (15) | 0.0666 (10) |
| C25 | 0.4910 (2) | 0.5558 (4) | 0.77283 (19) | 0.0969 (14) |
| H25a | 0.4598 (8) | 0.5001 (4) | 0.7896 (10) | 0.145 (2)* |
| H25b | 0.5109 (3) | 0.607 (2) | 0.8006 (8) | 0.145 (2)* |
| H25c | 0.4684 (10) | 0.607 (2) | 0.7465 (3) | 0.145 (2)* |
1 Source of material
The titled compound was prepared by adding 6–7 drops of glacial acetic acid to methanolic solution of 4-(diethylamino)salicylaldehyde (0.3 g, 1.5 mmol) and 4-bromoaniline (0.27 g, 1.5 mmol) and the resultant mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Rotary evaporator was used to remove methanol from the solution to afford an orange crude product. Slow evaporation of dichloromethane solution of the compound yielded mainly yellow block-like crystals of (E)-2-((4-bromophenylimino)methyl)-5-(diethylamino)phenol and few orange needle crystals of the title compound.
2 Experimental details
Using Olex2, 1 the structure was solved with the SHELXT 3 structure solution program and refined with the olex2.refine 2 refinement package using Gauss–Newton minimisation. The visual crystal structure information was performed using Mercury 4 system software.
3 Comment
A renowned German scientist and a Nobel Prize awardee, Hugo Schiff, firstly discovered Schiff bases in 1864 5 and till date, these compounds are being explored by researchers in various fields. 6 In coordination chemistry, Schiff bases are regarded as one of the major class of ligands due to their ability to coordinate with almost all transition metal ions via imine nitrogen to form complexes. 7 Aside their great coordinating progress, they are also readily available due to their simple method of preparation. 8 Schiff bases are often prepared by the condensation reaction of primary amines with carbonyl compounds (aldehyde or ketones) at appropriate reaction conditions. 9 They have been tested as anticancer, antioxidants, antidiabetics and antimicrobial agents. 10 , 11
The crystal structure of the title compound includes three distinct molecular species in the asymmetric unit: a cationic (E)-4-bromo–N-(4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)benzenaminium, an acetate counterion, and 4-bromoaniline. The solid-state conformation of this protonated Schiff base is nearly planar, as indicated by the dihedral angle of 11.7(1)° between the two phenyl rings. This angle is significantly narrower than those observed in the neutral Schiff bases (E)-2-((4-bromophenylimino)methyl)-5-(diethylamino)phenol (30.31(6)°–32.44(6)°) 12 and (E)-4-(((4-bromophenyl)imino)methyl)–N,N-diethylaniline (60.4(2)°–61.1(1)°). 13 The reduced dihedral angle in the title compound may be attributed to intramolecular N–H⋯O hydrogen bonding between the iminium group’s H3a atom and the adjacent hydroxyl group’s O36 atom. Nonetheless, other intramolecular bond parameters in both the protonated (this work) and neutral Schiff bases remain similar. 12 , 13 , 14 An analysis of intermolecular interactions in the crystal packing of the title compound reveals that the H1a and H1b atoms of the 4-bromoaniline’s amino group interact with the O2 and O1 atoms of the neighbouring acetate molecule via N1–H1a⋯O2 and N1–H2a⋯O1 hydrogen bonds, respectively. Additionally, intermolecular O–H⋯O hydrogen bonds form between the H3 atom of the protonated Schiff base’s hydroxyl group and the O2 atom of the acetate molecule. These intermolecular hydrogen bonding patterns result in a one-dimensional, zigzag supramolecular structure extending along the crystallographic b axis.
Funding source: National Research Foundation (N. R. F), Stellenbosch University
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledged the funding from the National Research Foundation (N. R. F.), Stellenbosch University, Matieland, 7602, South Africa. The first author is a recipient of the postdoctoral fellowship award of the N. R. F. at Stellenbosch University, Matieland, South Africa.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: This work was funded by National Research Foundation (N. R. F), Stellenbosch University.
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
2. Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. The Anatomy of a Comprehensive Constrained, Restrained Refinement Program for the Modern Computing Environment – Olex2 Dissected. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 59–75; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Macrae, C. F.; Bruno, I. J.; Chisholm, J. A.; Edgington, P. R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van de Streek, J.; Wood, P. A. Mercury CSD 2.0 – New Features for the Visualization and Investigation of Crystal Structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889807067908.Search in Google Scholar
5. Schiff, H. Mittheilungen aus dem Universitätslaboratorium in Pisa: eine neue Reihe organischer Basen. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1864, 131, 118–119; https://doi.org/10.1002/jlac.18641310113.Search in Google Scholar
6. Oladipo, S. D.; Luckay, R. C.; Olofinsan, K. A.; Obakachi, V. A.; Zamisa, S. J.; Adeleke, A. A.; Badeji, A. A.; Ogundare, S. A.; George, B. P. Antidiabetes and Antioxidant Potential of Schiff Bases Derived from 2-Naphthaldehye and Substituted Aromatic Amines: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Hirshfeld Surface Analysis, Computational, and In Vitro Studies. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23174; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23174.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
7. Yusuf, T. L.; Oladipo, S. D.; Zamisa, S.; Kumalo, H. M.; Lawal, I. A.; Lawal, M. M.; Mabuba, N. Design of New Schiff–Base Copper (II) Complexes: Synthesis, Crystal Structures, DFT Study, and Binding Potency Toward Cytochrome P450 3A4. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 13704–13718; https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00906.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Olagboye, S. A.; Yusuf, T. L.; Oladipo, S. D.; Zamisa, S. J. Crystal Structure of (E)-1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-N-(o-Tolyl) Methanimine, C14H12N2O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 833–836; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0034.Search in Google Scholar
9. Oladipo, S. D.; Yusuf, T. L.; Zamisa, S. J.; Shapi, M.; Ajayi, T. J. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Hirshfeld Surface Analysis and DFT Studies of N-(2, 6-Diisopropylphenyl)-1-(4-Methoxyphenyl) Methanimine. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1241, 130620; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130620.Search in Google Scholar
10. Adeleke, A. A.; Oladipo, S. D.; Luckay, R. C.; Akintemi, E. O.; Olofinsan, K. A.; Babatunde Onajobi, I.; Yussuf, S. T.; Ogundare, S. A.; Adeleke, O. M.; Babalola, K. I. Synthesis and Therapeutic Potential of Selected Schiff Bases: In Vitro Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Computational Studies. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202304967; https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202304967.Search in Google Scholar
11. Adeleke, A. A.; Oladipo, S. D.; Zamisa, S. J.; Sanusi, I. A.; Omondi, B. DNA/BSA Binding Studies and In Vitro Anticancer and Antibacterial Studies of Isoelectronic Cu (I)- and Ag (I)-Pyridinyl Schiff Base Complexes Incorporating Triphenylphosphine as Co-Ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2023, 558, 121760; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2023.121760.Search in Google Scholar
12. Albayrak, Ç.; Kaştaş, G.; Odabaşoğlu, M.; Frank, R. Survey of Conformational Isomerism in (E)-2-[(4-Bromophenylimino)Methyl]-5-(Diethylamino)Phenol Compound from Structural and Thermochemical Points of View. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2012, 95, 664–669; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.04.074.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Li, X.-F. 4–Bromo-N-[4-(Diethylamino)Benzylidene]Aniline. Acta Crystallogr. 2010, E66, o2417; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536810033726.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
14. Basu Baul, T. S.; Singh, K. S.; Holǎpek, M.; Jirásko, R.; Rivarola, E.; Linden, A. Synthesis, Characterization and Crystal Structures of Polymeric and Dimeric Triphenyltin(IV) Complexes of 4-[((E)-1-{2-Hydroxy-5-[(E)-2-(2-Carboxyphenyl)-1-Diazenyl]Phenyl}Methylidene)Amino]Aryls. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 4232–4242.10.1016/j.jorganchem.2005.06.030Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

