Abstract
C21H19BrO3, orthorhombic, P212121 (no. 19), a = 6.011(2) Å, b = 11.630(2) Å, c = 25.165(5) Å, V = 1759.3(7) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt (F) = 0.0163, wRref (F 2) = 0.0420, T = 100(2) K.
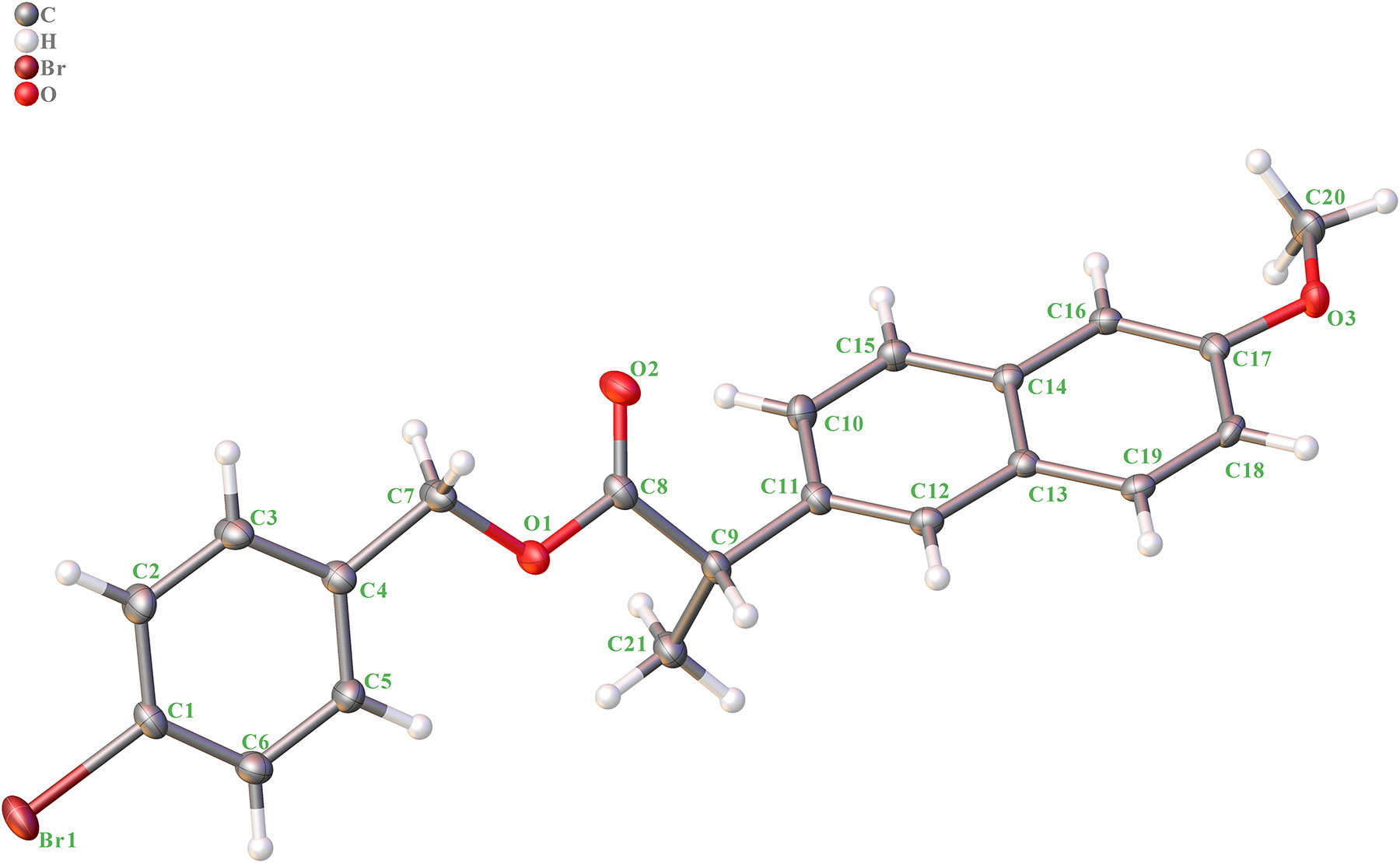
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.12 × 0.11 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.35 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II |
| θ max, completeness: | 27.5°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 84,060, 4,020, 0.037 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3,879 |
| N(param)refined: | 228 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br1 | 0.08234 (3) | −0.15505 (2) | 0.74872 (2) | 0.02566 (6) |
| C1 | 0.2394 (3) | −0.04140 (16) | 0.70911 (7) | 0.0182 (3) |
| C2 | 0.4405 (3) | −0.06943 (16) | 0.68613 (8) | 0.0210 (4) |
| H2 | 0.498387 | −0.145251 | 0.688661 | 0.025* |
| C3 | 0.5568 (3) | 0.01614 (16) | 0.65912 (8) | 0.0203 (4) |
| H3 | 0.695523 | −0.001965 | 0.643087 | 0.024* |
| C4 | 0.4741 (3) | 0.12762 (15) | 0.65511 (7) | 0.0167 (4) |
| C5 | 0.2693 (3) | 0.15291 (16) | 0.67810 (7) | 0.0199 (3) |
| H5 | 0.209888 | 0.228343 | 0.675178 | 0.024* |
| C6 | 0.1503 (3) | 0.06836 (17) | 0.70544 (8) | 0.0202 (4) |
| H6 | 0.010827 | 0.085738 | 0.721251 | 0.024* |
| C7 | 0.6089 (3) | 0.21588 (16) | 0.62514 (8) | 0.0203 (4) |
| H7A | 0.762476 | 0.218253 | 0.639308 | 0.024* |
| H7B | 0.616282 | 0.194859 | 0.587061 | 0.024* |
| C8 | 0.6281 (3) | 0.41768 (16) | 0.61422 (7) | 0.0174 (4) |
| C9 | 0.4976 (3) | 0.52931 (15) | 0.62140 (7) | 0.0160 (3) |
| H9 | 0.362205 | 0.523626 | 0.598465 | 0.019* |
| C10 | 0.8387 (3) | 0.66093 (16) | 0.62498 (7) | 0.0171 (3) |
| H10 | 0.904670 | 0.609787 | 0.649839 | 0.021* |
| C11 | 0.6264 (3) | 0.63434 (15) | 0.60312 (7) | 0.0156 (3) |
| C12 | 0.5334 (3) | 0.70879 (15) | 0.56694 (7) | 0.0142 (3) |
| H12 | 0.392398 | 0.691113 | 0.552002 | 0.017* |
| C13 | 0.6437 (3) | 0.81172 (15) | 0.55137 (7) | 0.0132 (3) |
| C14 | 0.8556 (3) | 0.83769 (15) | 0.57347 (6) | 0.0133 (3) |
| C15 | 0.9494 (3) | 0.75952 (15) | 0.61064 (7) | 0.0155 (3) |
| H15 | 1.090752 | 0.775661 | 0.625788 | 0.019* |
| C16 | 0.9659 (3) | 0.94206 (15) | 0.55873 (7) | 0.0138 (3) |
| H16 | 1.106488 | 0.960738 | 0.573638 | 0.017* |
| C17 | 0.8666 (3) | 1.01518 (15) | 0.52280 (7) | 0.0143 (3) |
| C18 | 0.6562 (3) | 0.98877 (15) | 0.50027 (7) | 0.0152 (3) |
| H18 | 0.590593 | 1.039986 | 0.475384 | 0.018* |
| C19 | 0.5473 (3) | 0.88988 (15) | 0.51424 (7) | 0.0142 (3) |
| H19 | 0.406282 | 0.873161 | 0.499054 | 0.017* |
| C20 | 1.1470 (3) | 1.15938 (17) | 0.53247 (8) | 0.0209 (4) |
| H20A | 1.189780 | 1.234095 | 0.517645 | 0.031* |
| H20B | 1.269563 | 1.104703 | 0.527902 | 0.031* |
| H20C | 1.113889 | 1.168001 | 0.570394 | 0.031* |
| C21 | 0.4167 (3) | 0.54378 (16) | 0.67891 (7) | 0.0207 (4) |
| H21A | 0.326793 | 0.477016 | 0.689058 | 0.031* |
| H21B | 0.326442 | 0.613693 | 0.681681 | 0.031* |
| H21C | 0.545311 | 0.549880 | 0.702678 | 0.031* |
| O1 | 0.5056 (2) | 0.32711 (11) | 0.63099 (5) | 0.0200 (3) |
| O2 | 0.8126 (2) | 0.40755 (12) | 0.59612 (6) | 0.0247 (3) |
| O3 | 0.9537 (2) | 1.11748 (11) | 0.50539 (5) | 0.0187 (3) |
1 Source of materials
The compound was obtained commercially (Bide Pharmatech Co., Ltd). Crystals suitable for the diffraction study were taken directly from the provided product.
2 Experimental details
Coordinates of hydrogen atoms were refined without any constraints or restraints. The U iso values were set to be 1.5U eq of the carrier atom for methyl H atoms and 1.2U eq for the remaining H atoms.
3 Comment
Naproxen, a potent non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), blocks the activity of both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, which are key components of the cyclooxygenase pathway. Naproxen commonly causes gastrointestinal reactions, such as gastrointestinal bleeding. 1 These side effects may be linked to the carboxyl group present in naproxen. Esterifying the carboxyl group has been shown to reduce these side effects. Esterifying the carboxyl group has been shown to reduce these side effects. 2 , 3 Currently, naproxen is used clinically to treat or alleviate inflammation and pain caused by various conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis 4 and gout. 5 Additionally, naproxen has been found to exhibit anticancer activity against bladder 6 and prostate cancer. 7 Furthermore, studies have shown that naproxen acts against type A influenza viruses by binding to the viral nucleoprotein. 8 Therefore, the development of naproxen derivatives with fewer side effects is of significant importance.
The title compound contains one naphthyl ring and one phenyl ring. The bond distances of C–O are 1.372(2) Å (C17–O3), 1.433(2) Å (C20–O3), 1.353(2) Å (C8–O1), 1.442(2) Å (C7–O1) and 1.205(2) Å (C8–O2). The bond distance of C8–O2 are shorter than others, indicating a double bond. The bond of C–Br is 1.9057(19) Å (C1–Br1). The dihedral angels of ring 1 (C1–C2–C3–C4–C5–C6) and ring 2 (C10–C11–C12–C13–C14–C15), ring 1 (C1–C2–C3–C4–C5–C6) and ring 3 (C13–C14–C16–C17–C18–C19), and ring 2 (C10–C11–C12–C13–C14–C15) and ring 3 (C13–C14–C16–C17–C18–C19) are 56.58(5)°, 56.71(5)° and 0.78(5)°. The other bond distances and angles are in their normal ranges according to the previously reported compounds. 9 , 10 , 11 , 12
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement With SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Huang, Z.; Vel’azquez, C. A.; Abdellatif, K. R. A.; Chowdhury, M. A.; Reisz, J. A.; DuMond, J. F.; King, S. B.; Knaus, E. E. Ethanesulfohydroxamic Acid Ester Prodrugs of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Synthesis, Nitric Oxide and Nitroxyl Release, Cyclooxygenase Inhibition, Anti-Inflammatory, and Ulcerogenicity Index Studies. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1356–1364; https://doi.org/10.1021/jm101403g.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Han, M. I.; Kucukguzel, S. G. Anticancer and Antimicrobial Activities of Naproxen and Naproxen Derivatives. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1300–1310; https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557520666200505124922.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Srinivas, S.; Feldman, D. A Phase II Trial of Calcitriol and Naproxen in Recurrent Porstate Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 3605–3610.Search in Google Scholar
7. Kim, M. S.; Kim, J. E.; Lim, D. Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Langfald, A.; Lubet, R. A.; Grubbs, C. J.; Dong, Z.; Bode, A. M. Naproxen Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Urinary Bladder Cancer Cell Lines and Chemically Induced Cancers by Targeting P13–K. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 236–245; https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.capr-13-0288.Search in Google Scholar
8. Wang, L. L.; Xue, D. D. Crystal Structure of 3-Phenylpropyl 2-(6-Methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)Propanoate, C23H24O3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 517–519; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0114.Search in Google Scholar
9. Liang, D.; Yang, X. H.; Sun, W.; Wang, W. N.; Yang, J. Z.; Liu, Y. Y.; Wang, G. S. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Biological Activities of Naproxen-Eugenol Ester Progrug. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2013, 29, 245–248; https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-013-2266-9.Search in Google Scholar
10. Li, F. R.; Zhang, Y. J.; Guo, F. G.; Duan, G. Y., Ge, Y. Q. 3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-(4-Chlorobenzyl)-1H-Pyrazole-5-Carbaldehyde. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, E68, o2203.10.1107/S1600536812027298Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Liu, Y.-L.; Zhang, H.-J.; Luo, J.; Chen, S.-X.; Zhang, J. Crystal Structure of Crystal Structure of N-(4-Bromobenzyl)-3-(Difluoromethyl)-1-Methyl-N-(Pyridin-2-yl)-1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxamide, C18H15BrF2N4O.” Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 257–259. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0513.Search in Google Scholar
12. Jiang, J.; Jiang, H. Crystal Structure of (4-Bromobenzyl)Triphenylphosphonium Bromide Ethanol Solvate, C52H48Br4OP2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239 (3), 495–496. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0060.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

