Abstract
C18H22N5O2·C7H4ClO2, orthorhombic, P212121 (no. 19), a = 8.9188(2) Å, b = 10.8391(2) Å, c = 25.9295(5) Å, V = 2506.65(9) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt (F) = 0.0357, wRref (F 2) = 0.1085, T = 293(2) K.
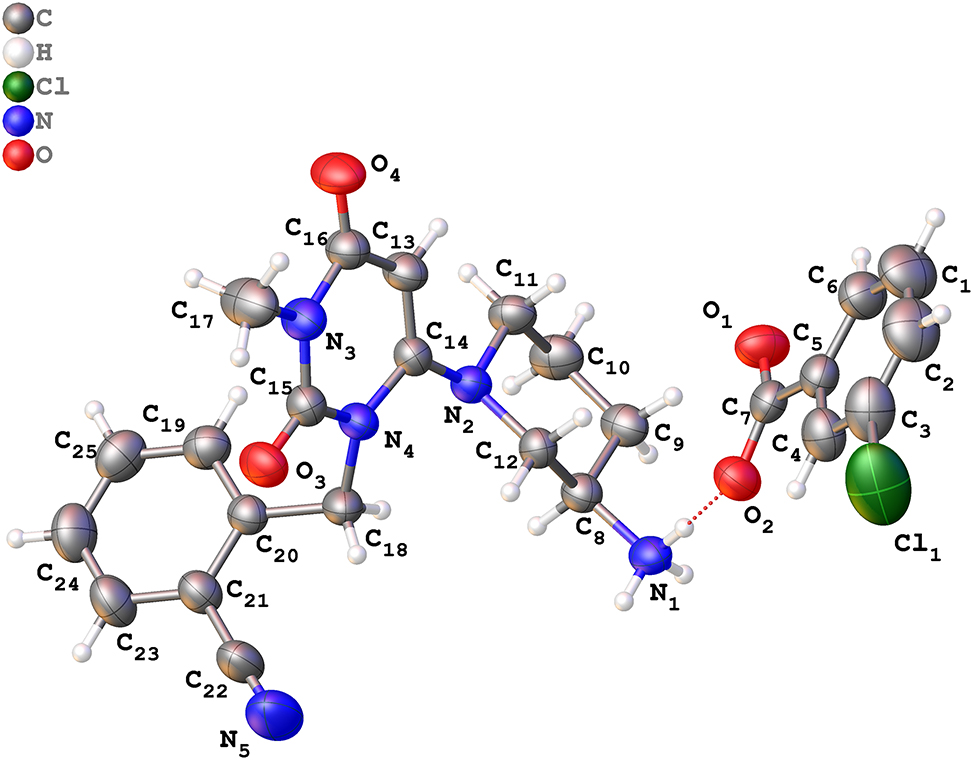
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.40 × 0.37 × 0.34 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 1.69 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 66.6°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 9419, 4279, 0.030 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 3,898 |
| N(param)refined: | 345 |
| Programs: | Olex2, 1 SHELX 2 , 3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.4242 (5) | 0.3274 (4) | 0.61808 (18) | 0.0819 (12) |
| H1 | 0.356699 | 0.331259 | 0.645366 | 0.092 (15)* |
| C2 | 0.4866 (6) | 0.2165 (5) | 0.60452 (18) | 0.0834 (13) |
| H2 | 0.461870 | 0.144956 | 0.622404 | 0.107 (17)* |
| C3 | 0.5853 (5) | 0.2126 (4) | 0.56450 (16) | 0.0734 (11) |
| C4 | 0.6237 (5) | 0.3166 (3) | 0.53667 (13) | 0.0596 (8) |
| H4 | 0.691428 | 0.311803 | 0.509462 | 0.064 (11)* |
| C5 | 0.5591 (3) | 0.4282 (3) | 0.55022 (12) | 0.0480 (7) |
| C6 | 0.4610 (4) | 0.4332 (4) | 0.59151 (14) | 0.0623 (9) |
| H6 | 0.419743 | 0.508365 | 0.601383 | 0.061 (10)* |
| C7 | 0.5989 (3) | 0.5440 (3) | 0.52018 (11) | 0.0457 (7) |
| C8 | 0.6868 (3) | 0.7879 (3) | 0.40523 (11) | 0.0438 (6) |
| H8 | 0.722457 | 0.833441 | 0.374962 | 0.045 (8)* |
| C9 | 0.6339 (3) | 0.8781 (3) | 0.44572 (12) | 0.0507 (7) |
| H9A | 0.713274 | 0.936255 | 0.453619 | 0.073 (12)* |
| H9B | 0.608320 | 0.834164 | 0.477108 | 0.053 (9)* |
| C10 | 0.4980 (4) | 0.9464 (3) | 0.42574 (15) | 0.0571 (8) |
| H10A | 0.527196 | 0.997257 | 0.396661 | 0.069 (11)* |
| H10B | 0.460027 | 1.000352 | 0.452563 | 0.077 (12)* |
| C11 | 0.3747 (3) | 0.8585 (3) | 0.40907 (12) | 0.0486 (7) |
| H11A | 0.340059 | 0.811016 | 0.438441 | 0.059 (10)* |
| H11B | 0.290492 | 0.904859 | 0.395451 | 0.055 (10)* |
| C12 | 0.5605 (3) | 0.7018 (3) | 0.38933 (11) | 0.0406 (6) |
| H12A | 0.595794 | 0.645176 | 0.363022 | 0.050 (9)* |
| H12B | 0.527746 | 0.653794 | 0.418827 | 0.040 (8)* |
| C13 | 0.1842 (3) | 0.6917 (3) | 0.35628 (12) | 0.0478 (7) |
| H13 | 0.148083 | 0.733416 | 0.385056 | 0.062 (10)* |
| C14 | 0.3290 (3) | 0.7069 (3) | 0.34216 (10) | 0.0400 (6) |
| C15 | 0.2948 (3) | 0.5670 (3) | 0.27001 (11) | 0.0459 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0863 (3) | 0.6137 (3) | 0.32818 (12) | 0.0483 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0600 (5) | 0.4575 (4) | 0.25911 (17) | 0.0749 (12) |
| H17A | 0.001306 | 0.410487 | 0.283138 | 0.13 (2)* |
| H17B | 0.125139 | 0.403179 | 0.240340 | 0.111 (18)* |
| H17C | −0.005501 | 0.499233 | 0.235456 | 0.18 (3)* |
| C18 | 0.5177 (3) | 0.6949 (3) | 0.27054 (11) | 0.0472 (7) |
| H18A | 0.585385 | 0.625800 | 0.265709 | 0.057 (10)* |
| H18B | 0.567829 | 0.755230 | 0.292111 | 0.060 (10)* |
| C19 | 0.3731 (4) | 0.8412 (3) | 0.21402 (14) | 0.0523 (7) |
| H19 | 0.317810 | 0.864387 | 0.242845 | 0.057 (10)* |
| C20 | 0.4830 (3) | 0.7520 (3) | 0.21886 (11) | 0.0421 (6) |
| C21 | 0.5651 (4) | 0.7196 (3) | 0.17514 (12) | 0.0499 (7) |
| C22 | 0.6770 (4) | 0.6253 (4) | 0.17892 (13) | 0.0620 (9) |
| C23 | 0.5358 (5) | 0.7757 (4) | 0.12763 (13) | 0.0633 (9) |
| H23 | 0.590925 | 0.753546 | 0.098627 | 0.083 (13)* |
| C24 | 0.4254 (5) | 0.8637 (3) | 0.12391 (15) | 0.0653 (9) |
| H24 | 0.405663 | 0.901208 | 0.092371 | 0.078 (12)* |
| C25 | 0.3439 (4) | 0.8963 (3) | 0.16700 (15) | 0.0604 (9) |
| H25 | 0.269062 | 0.955735 | 0.164427 | 0.077 (12)* |
| Cl1 | 0.6700 (2) | 0.07193 (10) | 0.54875 (5) | 0.1116 (5) |
| N1 | 0.8120 (3) | 0.7110 (3) | 0.42644 (9) | 0.0462 (6) |
| H1A | 0.855664 | 0.669541 | 0.400878 | 0.053 (9)* |
| H1B | 0.775610 | 0.657951 | 0.449457 | 0.078 (13)* |
| H1C | 0.879245 | 0.759691 | 0.441569 | 0.085 (14)* |
| N2 | 0.4340 (3) | 0.7750 (2) | 0.36911 (9) | 0.0415 (5) |
| N3 | 0.1499 (3) | 0.5485 (3) | 0.28718 (10) | 0.0512 (6) |
| N4 | 0.3806 (2) | 0.6516 (2) | 0.29682 (9) | 0.0428 (5) |
| N5 | 0.7643 (5) | 0.5491 (4) | 0.18345 (15) | 0.0922 (12) |
| O1 | 0.5343 (3) | 0.6422 (2) | 0.53142 (10) | 0.0608 (6) |
| O2 | 0.6970 (3) | 0.5325 (2) | 0.48583 (8) | 0.0557 (6) |
| O3 | 0.3449 (3) | 0.5131 (2) | 0.23236 (9) | 0.0588 (6) |
| O4 | −0.0470 (2) | 0.5948 (3) | 0.33937 (10) | 0.0645 (7) |
1 Source of material
All chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used as received. The alogliptin (33.9 mg, 0.1 mol) and m chlorobenzoic acid (15.6 mg, 0.1 mol) were dissolved in MeOH (10 mL). The mixture was refluxed for 0.5 h and then filtered and placed in a sample vial, covered with membrane and punctured. The filtrate was slowly evaporated at room temperature to obtain crystals of the title compound.
2 Experimental details
X-ray intensity data of the crystal of dimensions 0.40 × 0.37 × 0.34 mm were collected on Rigaku HyPix detector diffractometer. Using Olex2, 1 the structure was solved with the XT 2 structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL 3 refinement package. All H atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with the d(C–H) = 0.93 Å and d(N–H) = 0.89 Å, U iso(H) = 1.2 times U iso(C) and U iso(H) = 1.5 times U iso(O).
3 Comment
Alogliptin is a novel dipeptide peptidase-4 inhibitor approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetic mellitus. 4 Because of its low water solubility, alogliptin was commercialized orally in its benzoate salt form (Nesina), which was developed by Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., LTD. and has been approved for marketing in the United States in January 2013. 5 , 6 Salt formation is one of the most common used methods to improve the solubility and dissolution rates of insoluble drugs. 7
The asymmetric unit of the title structure contains one alogliptin cation and one m chlorobenzoic acid anion (see the figure). Bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges. The title molecule has an approximately ladder-like structure. 8 It indicates that three types of hydrogen bonds play an important role in maintaining the crystal structure, including, N1–H1A⋯O4 (1 + X, +Y, +Z) [length 2.875(3) Å, angle 173.5°], N1–H1B⋯O2 [length 2.677(3) Å, angle 169.4°], N1–H1C⋯O1 (1/2 + X, 3/2 – Y, 1 − Z) [length 2.768(3) Å, angle 174.5°]. 9 The carboxylate group forms two hydrogen bonds by interacting with an aminium group of alogliptinium in the unit cell and in an expanded unit cell. Another hydrogen bond comes from the additionally interacting between carbonyl group of alogliptin and an aminium group of another alogliptinium in an expanded unit cell. There are no specific interactions formed by the Cl atoms.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: New engineering research and reform practice project (2021xgk10); Chuzhou University college students innovation and entrepreneurship training program (No. 2024CXXL021); Anhui University Natural Science Foundation (No. KJ2021B16).
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122, https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wallace, M. B.; Stafford, J. A.; Kaldor, S. W.; Kassel, D. B.; Navre, M.; Shi, L.; Skene, R. J.; Asakawa, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Xu, R.; Webb, D. R.; Gwaltney, S. L. Discovery of Alogliptin: A Potent, Selective, Bioavailable, and Efficacious Inhibitor of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2297–2300; https://doi.org/10.1021/jm070104l.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Gelbrich, T.; Kahlenberg, V.; Griesser, U. J. Alogliptin and Its Benzoate Salt. J. Acta Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 674–678; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108270113012560.Search in Google Scholar
6. Scott, L. J. Alogliptin: A Review of Its Use in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Drugs 2010, 70, 2051–2072; https://doi.org/10.2165/11205080-000000000-00000.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Serajudidin, A. T. M. Salt Formation to Improve Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 613–616.10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. James, T. P. M.; Sebusi, O.; Ofentse, M.; Lebogang, G. J.; Thuto, M.; Florence, N. Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Pyridin-4-Ylmethyl 4-Aminobenzoate, C13H12N2O2. Crystallogr. Rep. 2022, 67, 1203–1206; https://doi.org/10.1134/s1063774522070094.Search in Google Scholar
9. Murthy Bandaru, S. S.; Bhilare, S.; Chrysochos, N.; Gayakhe, V.; Trentin, I.; Schulzke, C.; Kapdi, A. R. Pd/PTABS: Catalyst for Room Temperature Amination of Heteroarenes. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 473–476; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03854.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

