Abstract
C36H32Cu2N24Cl4, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 17.6099(4) Å, b = 8.13871(18) Å, c = 14.8084(3) Å, β = 91.6878(19)°, Z = 2, V = 2,121.45(8) Å3, R gt(F) = 0.0549, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1597, T = 293(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Blue block |
| Size: | 0.13 × 0.08 × 0.06 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 4.08 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Xcalibur, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 67.1°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 8,031, 3,769, 0.034 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 3,160 |
| N(param)refined: | 298 |
| Programs: | SHELX 1 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1 | 0.19753 (3) | 0.64048 (7) | 0.64603 (4) | 0.0310 (2) |
| Cl1 | 0.20960 (6) | 0.81935 (15) | 0.76245 (8) | 0.0437 (3) |
| Cl2 | 0.24586 (7) | 0.42454 (14) | 0.73346 (7) | 0.0434 (3) |
| N1 | 0.08430 (18) | 0.7260 (4) | 0.6247 (2) | 0.0305 (7) |
| N2 | 0.02879 (18) | 0.6251 (4) | 0.6407 (2) | 0.0306 (7) |
| N3 | −0.03507 (18) | 0.7139 (4) | 0.6471 (2) | 0.0303 (7) |
| N4 | −0.15391 (18) | 0.6137 (4) | 0.5855 (2) | 0.0270 (7) |
| N5 | −0.13698 (18) | 0.5005 (4) | 0.5235 (2) | 0.0288 (7) |
| N6 | −0.18991 (18) | 0.5129 (4) | 0.4601 (2) | 0.0288 (7) |
| N7 | 0.26887 (19) | 0.7982 (5) | 0.5644 (2) | 0.0341 (8) |
| N8 | 0.2903 (2) | 0.7499 (4) | 0.4841 (2) | 0.0351 (8) |
| N9 | 0.33781 (19) | 0.8650 (4) | 0.4546 (3) | 0.0352 (8) |
| N10 | 0.4401 (2) | 0.7374 (5) | 0.3791 (3) | 0.0375 (8) |
| N11 | 0.5078 (2) | 0.8006 (6) | 0.4077 (3) | 0.0502 (10) |
| N12 | 0.5580 (2) | 0.6844 (6) | 0.4107 (3) | 0.0509 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0913 (3) | 1.0357 (6) | 0.6048 (3) | 0.0384 (10) |
| H1 | 0.1431 | 1.0430 | 0.5950 | 0.046* |
| C2 | 0.0468 (3) | 1.1714 (6) | 0.6048 (3) | 0.0443 (11) |
| H2 | 0.0686 | 1.2734 | 0.5941 | 0.053* |
| C3 | −0.0317 (3) | 1.1624 (6) | 0.6206 (3) | 0.0434 (11) |
| H3 | −0.0600 | 1.2589 | 0.6204 | 0.052* |
| C4 | −0.0673 (2) | 1.0172 (6) | 0.6360 (3) | 0.0365 (9) |
| H4 | −0.1191 | 1.0112 | 0.6464 | 0.044* |
| C5 | −0.0213 (2) | 0.8776 (5) | 0.6352 (3) | 0.0292 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0565 (2) | 0.8838 (5) | 0.6203 (3) | 0.0292 (8) |
| C7 | −0.1059 (2) | 0.6311 (5) | 0.6665 (3) | 0.0301 (8) |
| H7A | −0.1328 | 0.6934 | 0.7113 | 0.036* |
| H7B | −0.0948 | 0.5232 | 0.6914 | 0.036* |
| C8 | −0.2176 (2) | 0.6951 (6) | 0.5618 (3) | 0.0355 (9) |
| H8 | −0.2410 | 0.7780 | 0.5941 | 0.043* |
| C9 | −0.2406 (2) | 0.6316 (6) | 0.4812 (3) | 0.0386 (10) |
| H9 | −0.2831 | 0.6632 | 0.4468 | 0.046* |
| C10 | 0.3027 (3) | 0.9432 (6) | 0.5850 (4) | 0.0427 (11) |
| H10 | 0.2968 | 1.0028 | 0.6379 | 0.051* |
| C11 | 0.3470 (3) | 0.9870 (6) | 0.5149 (4) | 0.0436 (11) |
| H11 | 0.3768 | 1.0806 | 0.5100 | 0.052* |
| C12 | 0.3746 (3) | 0.8408 (6) | 0.3690 (3) | 0.0398 (10) |
| H12A | 0.3388 | 0.7914 | 0.3260 | 0.048* |
| H12B | 0.3897 | 0.9465 | 0.3451 | 0.048* |
| C13 | 0.4466 (2) | 0.5737 (6) | 0.3622 (3) | 0.0342 (9) |
| C14 | 0.5229 (3) | 0.5395 (7) | 0.3831 (3) | 0.0432 (11) |
| C15 | 0.5518 (3) | 0.3799 (7) | 0.3715 (4) | 0.0528 (13) |
| H15 | 0.6025 | 0.3551 | 0.3844 | 0.063* |
| C16 | 0.5017 (3) | 0.2633 (7) | 0.3405 (4) | 0.0573 (14) |
| H16 | 0.5188 | 0.1562 | 0.3330 | 0.069* |
| C17 | 0.4252 (3) | 0.3000 (7) | 0.3195 (4) | 0.0541 (13) |
| H17 | 0.3936 | 0.2168 | 0.2975 | 0.065* |
| C18 | 0.3956 (3) | 0.4541 (6) | 0.3305 (3) | 0.0426 (11) |
| H18 | 0.3447 | 0.4775 | 0.3176 | 0.051* |
1 Source of materials
All starting materials are commercially available without further purification. 1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole (tmbt) was prepared according to the literature method with some modifications. 2 The ligand 1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole (0.03 mmol, 0.0060 g) was dissolved in 2 mL of methanol solution and the solution was slowly add to 2 mL of CuCl2 (0.06 mmol, 0.0103 g) of methanol solution. The prepared solution was placed at room temperature and blue crystals were obtained after eight days.
2 Experimental details
H atoms were generated geometrically and refined as riding atoms with C–H = 0.93 Å and the and U iso(H) = 1.2 times U eq(C) for aromatic H atoms, with C–H = 0.97 Å and U iso(H) = 1.2 times U eq(C) for methylene H atoms.
3 Comment
Heterocyclic compounds, as a class of organic compounds, have been widely concerned by researchers because of their properties. For example, the isatin heterocyclic compounds synthesized by the Altamimi, M team have anti-cancer and antibacterial properties. 3 The heterocyclic compounds studied by Zhou M’s team can be applied as fluorescent anticancer drugs, 4 and the robust leishmanicidal upshot of some new diphenyl triazine-based molecules synthesized by Singh A’s team. 5 Among them, benzotriazole and triazole compounds, as nitrogen heterocyclic thick ring compounds, have abundant electrons and can be coordinated with transition metals to synthesize metal complexes with stable structure and different properties. And widely used in medicine fields. For example, Ricardo A Murcia-Galan’s team synthesized Co(II) and Cu(II) complexes containing 1,3-bis(benzotriazol-1-yl)-propan-2-ol and studied their antibacterial activities. 6 Czylkowska and Agnieszka synthesized five metal complexes from triazole derivatives, and found that the anticancer activity of the synthesized metal complexes was significantly stronger than that of the ligands. 7 Zhao Wanling and colleagues studied the synthesis of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone-copper metal complex (CAM–DHF) from flavonoid compounds such as 7,8-dihydroxyflavone found in traditional Chinese medicine and other natural medicines with copper ions. The formation of the complex with flavonoids can reduce the reproductive toxicity of copper ions, and it is speculated to have good biosafety. 8
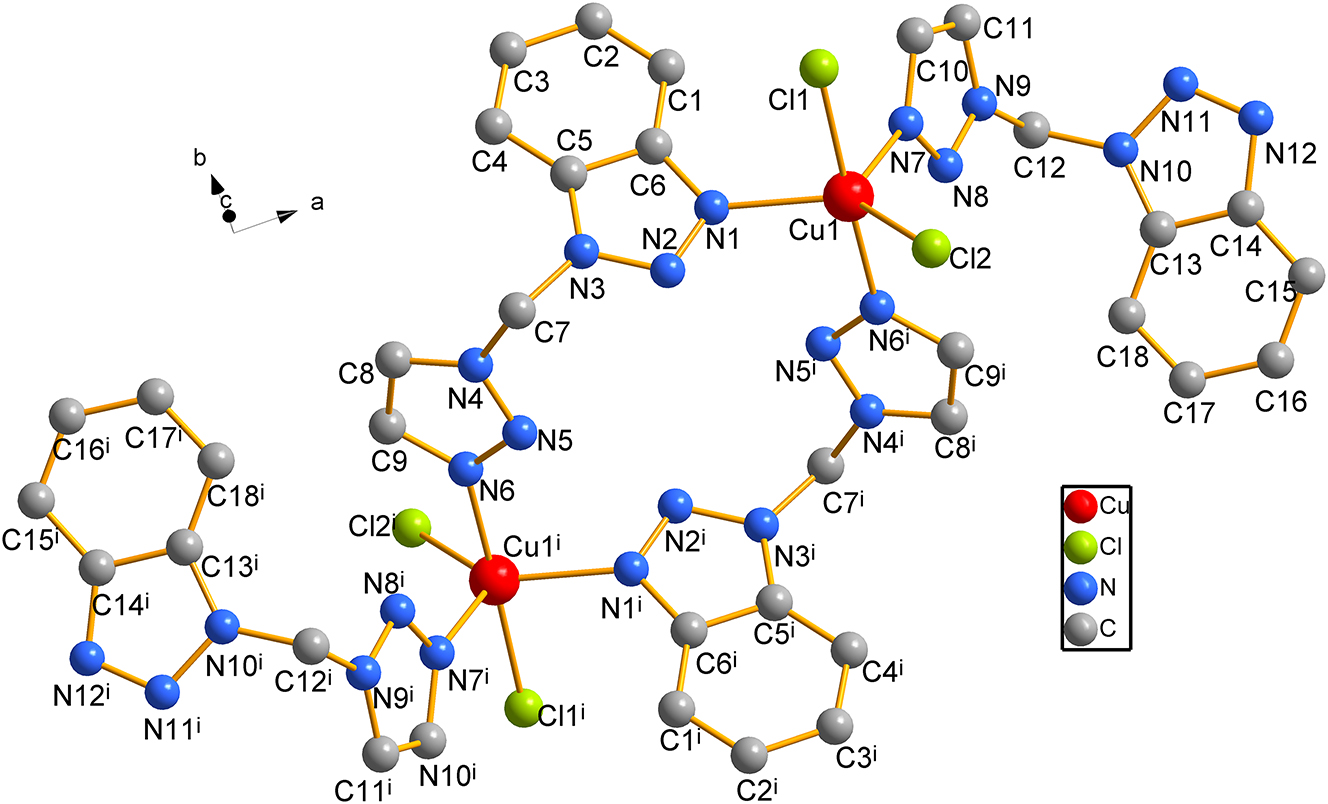
X-ray crystallographic analysis shows that the title complex has a binuclear structure and crystallized in a monoclinic P21/c space group. As shown in figure, the central atom Cu(II) is coordinated with two Cl ions (Cl1, and Cl2) and three N atoms (N1, N6i and N7 from three tmbt ligands, respectively). The Cu–Cl and Cu–N bonds around Cu1 are of length: Cu1–Cl1: 2.2616(12) Å; Cu1–Cl2: 2.3291(12) Å; Cu1–N1: 2.127(3) Å; Cu1–N6i: 2.008(3) Å; Cu1–N7:2.185(4) Å. The range of bond angles around the metal center Cu(II) is 88.23(10)°–130.93(11)°. In each tmbt ligand, the angle between the benzotriazole ring and the triazole ring is 71.973(137)° and 72.026(116)°, the distance between the benzotriazole rings in two adjacent monodentate coordinated tmbt ligands is 3.982 Å, so it can be inferred that there may be one kind of π–π conjugation between the two adjacent molecules, which makes the centrosymmetric unit extend into a more stable one-dimensional chain structure.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: None declared.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
2. Katritzky, A.-R.; Drewniak-Deyrup, M.; Lan, X.-F.; Brunner, F. Chemistry of Benzotriazole. Preparation, Lithiation and Transformation of N-(Benzotriazol-1-ylmethyl) Heterocycles. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1989, 26, 829–836; https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.5570260359.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Altamimi, M.; Syed, S. A.; Tuzun, B.; Alhazani, M. R.; Alnemer, O.; Bari, A. Synthesis Biological Evaluation and Molecular Docking of Isatin Hybrids as Anti-cancer and Anti-microbial Agents. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2024, 39, 2288548; https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2023.2288548.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Zhou, M.; Duan, X.; Jin, T.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Feng, J.; Zhang, M.; Chai, T.; Mao, B.; Shao, S.; Jin, G. Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of BF3-O, M, P-Phenylenediamine Bridged with Pyrimidine-Indole BF3 Adduction Derivatives. Mol. Divers. 2024, 7; https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-024-10863-3.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Singh, A.; Beg, M. A.; Jamal, S.; Khan, A.; Rahman, A.; Selvapandiyan, A.; Shafi, S.; Hoda, N. Robust Leishmanicidal Upshot of Some New Diphenyl Triazine-Based Molecules. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 22587–22597; https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ra01904k.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Murcia-Galán, R. A.; Durán, S. M.; Leal-Pinto, S. M.; Roa-Cordero, M. V.; Vargas, J. D.; Herrera, L. V.; Muñoz-Castro, A.; MacLeod-Carey, D.; Naranjo, T. W.; Rodríguez-Kessler, P. L.; Hurtado, J. J. Antifungal Activity of Co(II) and Cu(II) Complexes Containing 1,3-Bis(benzotriazol-1-Yl)-Propan-2-Ol on the Growth and Virulence Traits of Fluconazole-Resistant Candida Species: Synthesis, DFT Calculations, and Biological Activity. BMC Chem. 2023, 17, 135; https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-023-01037-7.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
7. Czylkowska, A.; Pitucha, M.; Lanka, S.; Raducka, A.; Rogalewicz, B.; Szczesio, M.; Swiatkowski, M.; Zarczynski, A.; Klepacz-Smółka, A.; Szczytko, J.; Camargo, B.; Drabinska, A.; Szymanski, P. Triazole-based Mn(II), Fe(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) Complexes as Potential Anticancer Agents – Physicochemical Properties, In Silico Predictions and In Vitro Activity. Polyhedron 2024, 261, 117106; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2024.117106.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Zhao, W. L. Reproductive Toxicity of 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone-Copper Metal Complexes in Mice. Master’s Thesis, Guangzhou Univ. Chin. Med., Guangzhou, China, 2021.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3


