Abstract
C16H14BrN3O2Pd, triclinic,
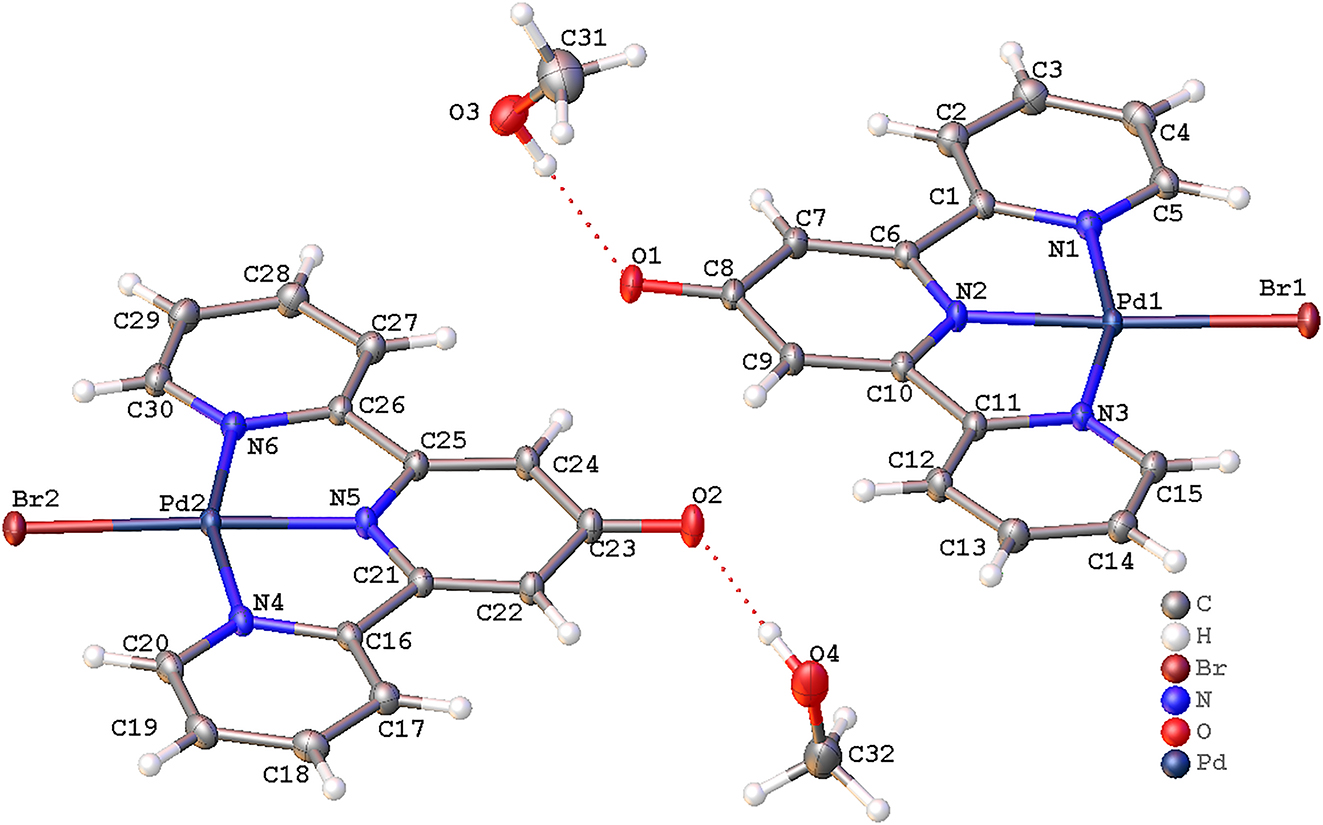
A part of the molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Green block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.10 × 0.06 mm |
| Wavelength: | Ga Kα radiation (1.34139 Å) |
| μ: | 8.72 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 venture, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 72.5°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 48198, 9168, 0.032 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 8,873 |
| N(param)refined: | 420 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 , 4 Diamond, 5 Olex2 6 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br1 | 0.24570 (2) | 1.13961 (2) | 0.87041 (2) | 0.01838 (4) |
| C1 | 0.1297 (2) | 1.04707 (13) | 0.64470 (9) | 0.0147 (2) |
| C2 | 0.0441 (2) | 1.10615 (14) | 0.57444 (9) | 0.0187 (3) |
| H2 | 0.031369 | 1.065222 | 0.538906 | 0.022* |
| C3 | −0.0229 (2) | 1.22528 (14) | 0.55636 (9) | 0.0210 (3) |
| H3 | −0.080644 | 1.266530 | 0.508296 | 0.025* |
| C4 | −0.0041 (2) | 1.28330 (14) | 0.60954 (10) | 0.0211 (3) |
| H4 | −0.048393 | 1.364763 | 0.598231 | 0.025* |
| C5 | 0.0804 (2) | 1.22031 (13) | 0.67953 (9) | 0.0176 (3) |
| H5 | 0.091899 | 1.259802 | 0.716178 | 0.021* |
| C6 | 0.2074 (2) | 0.92083 (12) | 0.66960 (8) | 0.0141 (2) |
| C7 | 0.2008 (2) | 0.84113 (13) | 0.63102 (9) | 0.0163 (3) |
| H7 | 0.145498 | 0.866451 | 0.581727 | 0.020* |
| C8 | 0.2770 (2) | 0.71995 (13) | 0.66485 (9) | 0.0163 (3) |
| C9 | 0.3609 (2) | 0.68971 (13) | 0.73914 (9) | 0.0167 (3) |
| H9 | 0.415415 | 0.611265 | 0.764201 | 0.020* |
| C10 | 0.3617 (2) | 0.77500 (12) | 0.77380 (9) | 0.0146 (2) |
| C11 | 0.4348 (2) | 0.75792 (12) | 0.85067 (8) | 0.0144 (2) |
| C12 | 0.5187 (2) | 0.65065 (13) | 0.89824 (9) | 0.0182 (3) |
| H12 | 0.534672 | 0.582952 | 0.881507 | 0.022* |
| C13 | 0.5788 (2) | 0.64349 (13) | 0.97049 (9) | 0.0191 (3) |
| H13 | 0.635167 | 0.570723 | 1.004032 | 0.023* |
| C14 | 0.5558 (2) | 0.74373 (14) | 0.99329 (9) | 0.0187 (3) |
| H14 | 0.597218 | 0.740489 | 1.042333 | 0.022* |
| C15 | 0.4716 (2) | 0.84844 (13) | 0.94355 (9) | 0.0169 (3) |
| H15 | 0.456392 | 0.916966 | 0.959148 | 0.020* |
| N1 | 0.14632 (17) | 1.10498 (11) | 0.69686 (7) | 0.0147 (2) |
| N2 | 0.28703 (18) | 0.88698 (11) | 0.73915 (7) | 0.0141 (2) |
| N3 | 0.41064 (17) | 0.85628 (10) | 0.87369 (7) | 0.0136 (2) |
| O1 | 0.27118 (17) | 0.64407 (10) | 0.63150 (7) | 0.0211 (2) |
| Pd1 | 0.27793 (2) | 1.00028 (2) | 0.79471 (2) | 0.01240 (4) |
| Br2 | 0.69846 (2) | −0.09628 (2) | 0.61552 (2) | 0.01836 (4) |
| C16 | 0.8032 (2) | 0.01556 (12) | 0.83456 (9) | 0.0145 (2) |
| C17 | 0.8835 (2) | −0.03799 (13) | 0.90644 (9) | 0.0177 (3) |
| H17 | 0.887367 | 0.006101 | 0.941319 | 0.021* |
| C18 | 0.9582 (2) | −0.15653 (13) | 0.92696 (9) | 0.0196 (3) |
| H18 | 1.012809 | −0.194337 | 0.976116 | 0.023* |
| C19 | 0.9522 (2) | −0.21915 (13) | 0.87490 (10) | 0.0197 (3) |
| H19 | 1.004755 | −0.300062 | 0.887568 | 0.024* |
| C20 | 0.8681 (2) | −0.16203 (13) | 0.80383 (9) | 0.0177 (3) |
| H20 | 0.862355 | −0.205116 | 0.768563 | 0.021* |
| C21 | 0.7211 (2) | 0.14060 (12) | 0.80652 (8) | 0.0140 (2) |
| C22 | 0.7170 (2) | 0.22341 (12) | 0.84376 (9) | 0.0159 (3) |
| H22 | 0.777002 | 0.202436 | 0.891645 | 0.019* |
| C23 | 0.6221 (2) | 0.34179 (13) | 0.81038 (9) | 0.0168 (3) |
| C24 | 0.5415 (2) | 0.36717 (12) | 0.73609 (9) | 0.0169 (3) |
| H24 | 0.477086 | 0.443808 | 0.711278 | 0.020* |
| C25 | 0.5583 (2) | 0.27964 (12) | 0.70117 (8) | 0.0144 (2) |
| C26 | 0.4923 (2) | 0.29155 (12) | 0.62387 (9) | 0.0147 (2) |
| C27 | 0.4026 (2) | 0.39598 (13) | 0.57487 (9) | 0.0176 (3) |
| H27 | 0.380004 | 0.465450 | 0.590135 | 0.021* |
| C28 | 0.3464 (2) | 0.39722 (14) | 0.50301 (9) | 0.0204 (3) |
| H28 | 0.283549 | 0.467623 | 0.468869 | 0.024* |
| C29 | 0.3828 (2) | 0.29488 (14) | 0.48165 (9) | 0.0199 (3) |
| H29 | 0.345932 | 0.294580 | 0.432622 | 0.024* |
| C30 | 0.4736 (2) | 0.19299 (14) | 0.53257 (9) | 0.0174 (3) |
| H30 | 0.498388 | 0.122992 | 0.517792 | 0.021* |
| N4 | 0.79476 (17) | −0.04715 (11) | 0.78396 (7) | 0.0145 (2) |
| N5 | 0.64389 (18) | 0.16958 (11) | 0.73660 (7) | 0.0141 (2) |
| N6 | 0.52755 (17) | 0.19071 (11) | 0.60248 (7) | 0.0144 (2) |
| O2 | 0.60970 (18) | 0.42002 (10) | 0.84444 (7) | 0.0221 (2) |
| Pd2 | 0.66287 (2) | 0.05112 (2) | 0.68439 (2) | 0.01267 (4) |
| C31 | −0.1127 (3) | 0.5446 (2) | 0.69386 (13) | 0.0401 (5) |
| H31A | −0.221004 | 0.516160 | 0.693016 | 0.060* |
| H31B | −0.153793 | 0.618795 | 0.707019 | 0.060* |
| H31C | −0.029826 | 0.488955 | 0.733546 | 0.060* |
| O3 | −0.01756 (19) | 0.55873 (12) | 0.61951 (8) | 0.0286 (3) |
| H3A | 0.069984 | 0.588316 | 0.619104 | 0.043* |
| C32 | 0.9852 (3) | 0.43833 (18) | 0.91231 (13) | 0.0355 (4) |
| H32A | 1.063576 | 0.449045 | 0.947956 | 0.053* |
| H32B | 0.931692 | 0.512805 | 0.875945 | 0.053* |
| H32C | 1.060618 | 0.385311 | 0.882188 | 0.053* |
| O4 | 0.8411 (2) | 0.39201 (11) | 0.95671 (8) | 0.0320 (3) |
| H4A | 0.765095 | 0.391983 | 0.926121 | 0.048* |
1 Source of materials
All the reagents and solvents were used as obtained without further purification. The ligand 2,6-bis(2-pyridyl)-4(1H)-pyridone (25.0 mg, 0.1 mmol) and palladium bromide (27.0 mg, 0.1 mmol) were thoroughly mixed and dissolved in 20.0 mL a mixed solution of methanol and acetonitrile (v:v = 1:1). The yellow solution was stirred vigorously at 333 K for 2 h and then filtered to remove some precipitate. The final resulting solution was kept at ambient condition. Yellow-brown block crystals were obtained seven days later at bottom of the vessel.
2 Experimental details
All the H atoms bound to carbon atoms were placed at their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C–H = 0.95 Å (aromatic) and 0.98 Å (methyl), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq (aromatic) and 1.5U eq (methyl). These two H atoms bound with O3 and O4 oxygen atoms were initially found from the difference maps and then constrained to be at their ideal positions with O–H = 0.84 Å and the U iso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O).
3 Comment
In recent years, terpyridine-based palladium metal complexes have been widely designed and applied in many fields such as medicine, materials science, chemical sensors, and catalysis. 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 Along with the various structural features, 4′-substituted terpyridine derivatives have interesting photophysical and electrochemical properties. 11 In this work, we have used 2,6-bis(2-pyridyl)-4(1H)-pyridone (TPD) and palladium bromide as the raw material.
The titled compound was crystallized in the triclinic
In the crystal packing, the component ions are linked into a three-dimensional network by a combination of O–H⋯O, C–H⋯O, C–H⋯Br and π⋯π stacking interactions. In more details, these two methanol molecules are respectively anchored to the host Pd(II) coordination unit by means of O–H⋯O hydrogen bonds (d 01···03 = 2.733(2) Å, d 02···04 = 2.704(2) Å). The atomic distances d H14···Br1(1 − x, 2 − y, 2 − z) = 2.984(2) Å and d H29···Br2(1 − x, −y, 1 − z) = 2.968(2) Å are slightly shorter than the sum of their van der Waal’s radii, 3.05 Å, indicating weak intermolecular forces between the symmetrically related molecules and forming dimers between molecules of these same type. Further, these dimers are linked into two-dimensional layer structure parallel to the (-2-12) plane by C–H⋯O interactions (C12–H12⋯O2 and C27–H27⋯O1). Finally, those neighboring two-dimensional (-2-12) layer structures are linked into the whole three-dimensional structure via two weak π⋯π interactions. For instances, the centroid-to-centroid distances between symmetry-related pyridine rings (N1-related-pyridie/N6-related-pyridine (x, 1 + y, z)) and (N3-related-pyridine/N4-related-pyridine (1 + x, y − 1, z)) are 3.557(2) and 3.731(2) Å by a calculation using PLATON, 14 showing a moderate π⋯π interaction.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Kashi University.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Kashi University.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX 3 and SAINT V8.40B; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA. 2003.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Refinement with SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
5. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND; Crystal Impact GbR: Bonn Germany, 2006.Search in Google Scholar
6. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, A42, 339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
7. Ramakrishnan, A.; Kuppan, M.; Agarwal, A.; Sivin, V. Advances in the Biological Studies of Metal–Terpyridine Complexes: An Overview from 2012 to 2022. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 496, 215380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215380.Search in Google Scholar
8. Tian, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Uvdal, K.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Du, W.; Huang, B.; Wu, J.; Tian, Y. Probe for Simultaneous Membrane and Nucleus Labeling in Living Cells and In Vivo Bioimaging Using a Two-Photon Absorption Water-Soluble Zn(II) Terpyridine Complex with a Reduced π-conjugation System. Chem. Sci. 2016, 8, 142–149. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6sc02342h.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Manikandamathavan, V. M.; Thangaraj, M.; Weyhermuller, T.; Parameswari, R. P.; Punitha, V.; Narasimha Murthy, N.; Unni Nair, B. Novel Mononuclear Cu (II) Terpyridine Complexes: Impact of Fused Ring Thiophene and Thiazole Head Groups towards DNA/BSA Interaction, Cleavage and Antiproliferative Activity on HepG2 and Triple Negative CAL-51 Cell Line. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 135, 434–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.04.030.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Wang, K. Y.; Weber, M.; Chung, T. S. P.; Zheng, J.; Yan, W.; Wu, W.; Jiang, H. B2pin2 Mediated Palladium–Catalyzed Diacetoxylation of Aryl Alkenes with O2 as Oxygen Source and Sole Oxidant. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 5090–5093. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01806.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Maskus, M.; Abruna, H. D. Synthesis and Characterization of Redox–Active Metal Complexes Sequentially Self-Assembled onto Gold Electrodes via a New Thiol–Terpyridine Ligand. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4455–4462. https://doi.org/10.1021/la960308x.Search in Google Scholar
12. Ha, K. Redetermination of Crystal Structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl) Amine-κ3 N, N′, N″]Chloridopalladium(II) Chloride Monohydrate. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023. 228, 467–469. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023–0037.10.1515/ncrs-2023-0037Search in Google Scholar
13. Broring, M.; Brandt, C. D. One Compound, Two Structures: Synthesis, Structures and Reactivity of a Novel (Tripyrrinato)Palladium(II) Trifluoracetate Complex TrpyPdOAcf. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 2002, 1391–1395. https://doi.org/10.1039/B109510M.Search in Google Scholar
14. Spek, A. L. Structure Validation in Chemical Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155. https://doi.org/10.1107/S090744490804362X.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

