Abstract
C12H15NO9Cu, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 7.3596(3) Å, b = 8.1735(2) Å, c = 12.0982(4) Å, α = 85.754(3)°, β = 80.318(3)°, γ = 84.852(2)°, V = 702.61(5) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0494, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1463, T = 298 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Pink block |
| Size: | 0.28 × 0.26 × 0.22 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) 1.61 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θ max, completeness: |
XtaLAB AFC12 (RINC), 25.3°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 17674, 2564, 0.036 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 2489 |
| N(param)refined: | 228 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX, 3 Diamond 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1 | 0.69719 (8) | 0.72438 (7) | 0.14864 (5) | 0.0285 (2) |
| O1 | 0.2107 (5) | 0.4914 (5) | 0.1937 (3) | 0.0426 (9) |
| O2 | 0.4692 (5) | 0.6120 (4) | 0.1209 (3) | 0.0322 (8) |
| O3 | 1.1907 (5) | 0.9957 (5) | 0.1490 (3) | 0.0419 (9) |
| O4 | 0.9665 (5) | 0.8446 (4) | 0.1205 (3) | 0.0331 (8) |
| O5 | 0.5716 (5) | 0.9547 (5) | 0.1303 (4) | 0.0393 (9) |
| H5A | 0.456769 | 0.968792 | 0.123955 | 0.059* |
| H5B | 0.610948 | 1.049945 | 0.116167 | 0.059* |
| O6 | 0.8352 (5) | 0.5007 (4) | 0.1823 (3) | 0.0315 (8) |
| H6A | 0.952960 | 0.511117 | 0.179111 | 0.047* |
| H6B | 0.833077 | 0.435526 | 0.129494 | 0.047* |
| O7 | 0.7923 (7) | 0.7118 (5) | −0.0229 (3) | 0.0445 (10) |
| H7A | 0.793041 | 0.802046 | −0.063067 | 0.067* |
| H7B | 0.756373 | 0.644107 | −0.062950 | 0.067* |
| N1 | 0.5163 (5) | 0.6921 (4) | 0.3211 (3) | 0.0224 (7) |
| C1 | 0.3464 (6) | 0.5689 (6) | 0.2017 (4) | 0.0275 (9) |
| C2 | 0.3652 (6) | 0.6186 (5) | 0.3171 (4) | 0.0246 (9) |
| C3 | 0.2297 (7) | 0.5877 (6) | 0.4139 (4) | 0.0329 (10) |
| H3 | 0.123806 | 0.536308 | 0.407750 | 0.040* |
| C4 | 0.2542 (7) | 0.6332 (6) | 0.5160 (4) | 0.0342 (11) |
| H4 | 0.164941 | 0.612958 | 0.579844 | 0.041* |
| C5 | 0.4134 (6) | 0.7105 (5) | 0.5252 (4) | 0.0250 (9) |
| C6 | 0.5430 (6) | 0.7371 (5) | 0.4233 (4) | 0.0234 (9) |
| C7 | 0.7072 (7) | 0.8122 (7) | 0.4275 (4) | 0.0335 (11) |
| C8 | 0.7421 (8) | 0.8612 (7) | 0.5275 (4) | 0.0393 (12) |
| H8 | 0.850036 | 0.912678 | 0.529019 | 0.047* |
| C9 | 0.6149 (8) | 0.8336 (7) | 0.6272 (4) | 0.0358 (11) |
| H9 | 0.640291 | 0.865659 | 0.694945 | 0.043* |
| C10 | 0.4546 (7) | 0.7608 (6) | 0.6271 (4) | 0.0321 (10) |
| H10 | 0.371740 | 0.743983 | 0.694448 | 0.039* |
| C11 | 0.9639 (7) | 0.9289 (6) | 0.3043 (4) | 0.0316 (11) |
| H11A | 1.061518 | 0.907845 | 0.350063 | 0.038* |
| H11B | 0.900246 | 1.036242 | 0.319517 | 0.038* |
| H11C | 1.044331 | 0.863874 | 0.350113 | 0.038* |
| H11D | 0.950139 | 1.041444 | 0.326268 | 0.038* |
| C12 | 1.0454 (6) | 0.9222 (6) | 0.1808 (4) | 0.0268 (9) |
| O9 | 0.835 (2) | 0.805 (2) | 0.3290 (9) | 0.034 (3) |
| O9A | 0.788 (3) | 0.864 (5) | 0.3189 (10) | 0.028 (4) |
| O8 | 0.7405 (5) | 0.2571 (5) | 0.0574 (3) | 0.0337 (8) |
| H8A | 0.829357 | 0.210581 | 0.012400 | 0.051* |
| H8B | 0.666147 | 0.302194 | 0.015025 | 0.051* |
1 Source of materials
The title Cu(II) complex has been synthesized by the following method: 0.1336 g 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid (0.5 mmol), 0.1011 g 2-(2-methyl-imidazol-1-yl)benzoic acid (0.5 mmol), 0.040 g NaOH (1.0 mmol) were added to the solution of 15 ml water-ethanol (v:v = 2:1) with stirring. After dissolution, 0.0998 g cupric acetate monohydrate (0.5 mmol) solid was added to the above solution with stirring. Then the mixture solution was stirred for 4 h at 75 °C and for another 3 h at room temperature. Blue block crystals were obtained after 10 days.
2 Experimental details
The hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically (C–H = 0.93–0.97 Å, O–H = 0.85–0.86 Å). Their U iso values were set to 1.2 U eq or 1.5 U eq of the parent atoms.
3 Comment
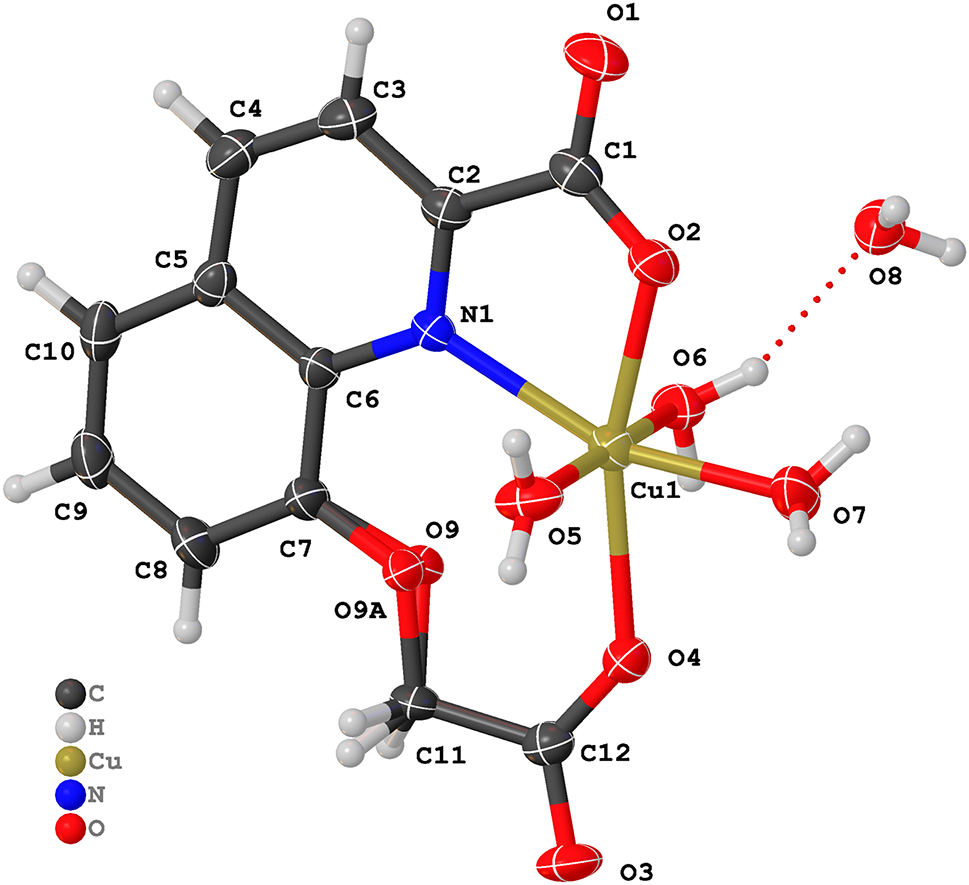
The Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II), and Mn(II) complexes constructed by 8-carboxymethoxyquinoline-2-carboxylate ligand have showed multiple coordination modes and potential applications such as magnetic property, DNA/BSA binding and DNA cleavage ability. 5 , 6 Our group has also synthesized and structurally characterized Cu(II), Ni(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) complexes using 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid ligand. 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 According to the above studies, it was found that the synthesis conditions and pH could affect the structure of the complex, for example, under the same hydrothermal conditions, nickel(II) acetate tetrahydrate and nickel (II) nitrate hexahydrate respectively form six-coordinated complexes with different structures with 8-carboxymethoxyquinoline-2-carboxylic acid ligand. 6 However, under ordinary pressure conditions, nickel(II) acetate tetrahydrate forms seven-coordinated complex with 8-carboxymethoxyquinoline-2-carboxylic acid ligand. 10 To further explore the effect of the synthesis conditions on the structure of metal complexes with the 8-carboxymethoxyquinoline-2-carboxylic acid, in this paper, we synthesized and structurally characterized a new Cu(II) complex using nickel(II) acetate tetrahydrate, 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid, 2-(2-methyl-imidazol-1-yl)benzoic acid, and NaOH. The molecular structure of Cu(II) complex is shown in Figure. The Cu(II) complex contains one central Cu(II) ion, one completely deprotonated 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate ligand, three coordinated water molecules, and one uncoordinated water molecule. The Cu(II) ion is six-coordinated by two carboxylic O atoms (O2 and O4) and one N atom (N1) from 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate ligand, three O atoms from three coordinated water molecules, adopting a distorted octahedral coordination geometry. Unfortunately, the 2-(2-methyl-imidazol-1-yl)benzoic acid ligand does not take part in coordination with Cu(II) ion. The bond angle of O5–Cu1–O6 is 173.52(15)°, indicating that the O5 and O6 of coordinated water molecules occupy the axial positions. And the N1, O2, O4 and O7 atoms from the basal plane. The angles around the Cu(II) ion within the basal plane vary from 74.88(13) to 122.87(13)°, and the sum of bond angles is 360.02°. The bond lengths of Cu–O and Cu–N are 2.031(4)–2.239(3) Å and 2.264(4) Å, respectively, which is consistent with other Cu(II) complexes reported in the literature. 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 The Cu(II) complex molecules form 1D chained structure by intermolecular O–H·O hydrogen bonds.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21171132, https://doi.org/10.13039/501100001809), and Science and Technology Development Plan Project of Weifang.
References
1. Bruker. Saint and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Brandenburg, K. Diamond. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 3.2; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
5. Zhang, Y. P.; Yang, J. J.; Lu, J. Y.; Gao, C. Y.; Zhao, J. Z. Syntheses, Structures, DNA/BSA Binding and DNA Cleavage of Mononuclear Manganese(II) and Cobalt(II) Complexes with N,O-chelating Quinoline Derivative Ligand. Chinese J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 32, 2172–2182.Search in Google Scholar
6. Lou, H. D.; Yin, L.; Zhang, B. Q.; Ouyang, Z. W.; Li, B.; Wang, Z. X. Series of Single-Ion and 1D Chain Complexes Based on Quinolinic Derivative: Synthesis, Crystal Structures, HF-EPR, and Magnetic Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 7757–7762; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b00812.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Zhao, Z. B.; Yang, S. C.; Yang, B. Q.; Cheng, L. X.; Tai, X. S. The Crystal Structure of [(8-Carboxymethoxy-Quinoline-2-Carboxylate-κ4 N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N-Copper(II)]tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 1115–1117; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0347.Search in Google Scholar
8. Wang, L. H.; Yan, X. H.; Wang, Y. F.; Tai, X. S. Crystal Structure of [triaqua-(8-Carboxymethoxy-Quinoline-2-Carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)Cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15N1O9Cd. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 29–31.Search in Google Scholar
9. Wang, L. H.; Yan, X. H.; Wang, Y. F.; Tai, X. S. The Crystal Structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-Zinc(II)] Monohydrate, C12H15NO9Zn. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 205–206; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0483.Search in Google Scholar
10. Tai, X. S.; Yan, X. H.; Wang, Y. F.; Wang, L. H. The Crystal Structure of Triaqua-(8-Carboxymethoxy-Quinoline-2-Carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)Nickel(II) Monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 133–135; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0476.Search in Google Scholar
11. Wang, L. H.; Azam, M.; Yan, X. H.; Tai, X. S. Synthesis, Structural Characterization, and Hirschfeld Surface Analysis of a New Cu(II) Complex and its Role in Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. Molecules 2024, 29, 1957; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29091957.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
12. Cao, S. H.; Li, K. X.; Gao, Y.; Li, F. H.; Cao, X. X.; Dai, Y. W.; Mao, L. R.; Wang, S. S.; Tai, X. S. A Simultaneously GSH-Depleted Bimetallic Cu(II) Complex for Enhanced Chemodynamic Cancer Therapy. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 11851–11858; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0dt01742f.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Cao, S. H.; Li, F. H.; Xu, Q.; Yao, M.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. J.; Cui, X. T.; Man, R. L.; Li, K. X.; Tai, X. S. Synthesis, Crystal Structure of a Novel Tetranuclear Cu(II) Complex and Its Application in GSH-Triggered Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species for Chemodynamic Therpy. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101372; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2021.101372.Search in Google Scholar
14. Feng, Y. M.; Tai, X. S.; Xia, Y. P. The Crystal Structure of [(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2N,O)Copper(II)], C34H24N4O4Cu. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 285–287.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

