Abstract
C38H38O8Ni, orthorhombic, Cmc21 (no. 36), a = 19.0266(4) Å, b = 8.2409(2) Å, c = 21.4315(5) Å, V = 3,360.38(13) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt (F) = 0.0406, wRref (F 2) = 0.1058, T = 293 K.
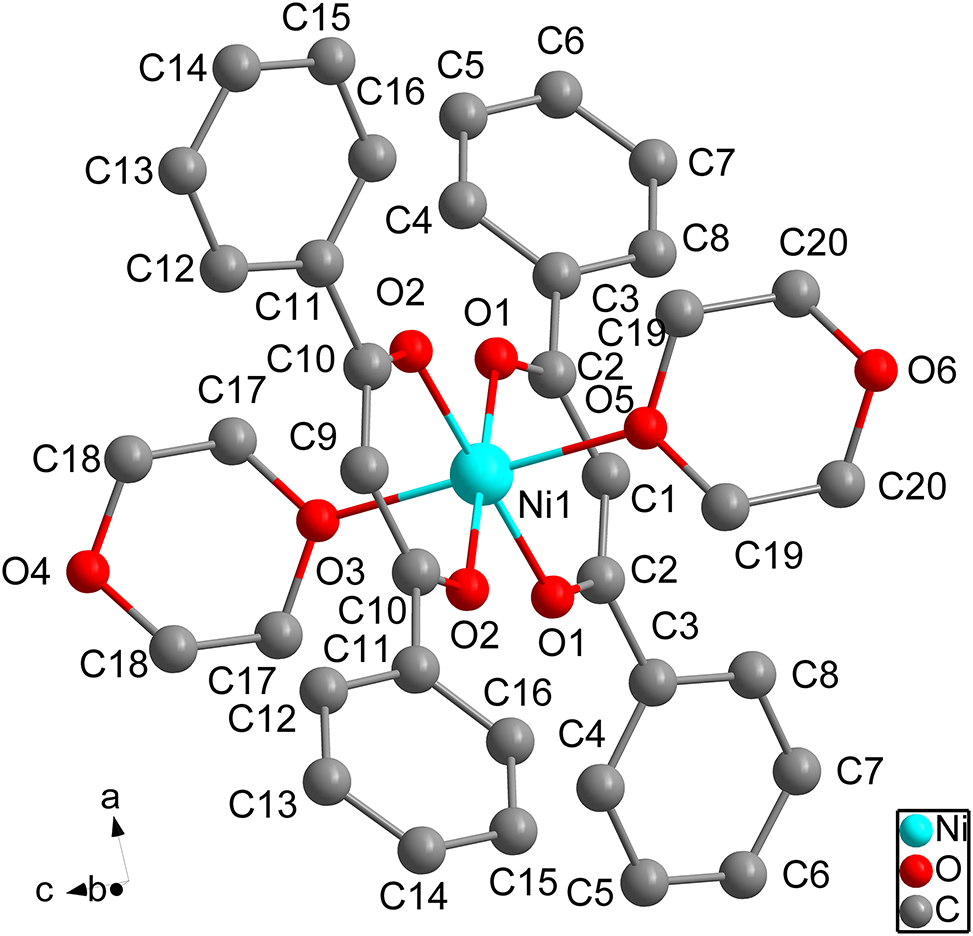
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless needle |
| Size: | 0.16 × 0.06 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 1.27 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 73.8°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 15,013, 3,348, 0.071 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 3,133 |
| N(param)refined: | 223 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 , 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.500000 | 0.6348 (5) | 0.3927 (2) | 0.0429 (10) |
| H1 | 0.500000 | 0.708002 | 0.359638 | 0.051* |
| C2 | 0.56557 (16) | 0.5844 (4) | 0.41536 (15) | 0.0387 (7) |
| C3 | 0.62979 (16) | 0.6661 (3) | 0.38993 (16) | 0.0395 (6) |
| C4 | 0.68599 (18) | 0.6977 (4) | 0.42930 (19) | 0.0487 (7) |
| H4 | 0.684163 | 0.664307 | 0.470718 | 0.058* |
| C5 | 0.74455 (19) | 0.7783 (6) | 0.4075 (2) | 0.0603 (10) |
| H5 | 0.781390 | 0.801260 | 0.434585 | 0.072* |
| C6 | 0.7490 (2) | 0.8251 (5) | 0.3459 (3) | 0.0619 (12) |
| H6 | 0.788757 | 0.878914 | 0.331384 | 0.074* |
| C7 | 0.6942 (2) | 0.7914 (5) | 0.3061 (2) | 0.0582 (9) |
| H7 | 0.697130 | 0.821415 | 0.264319 | 0.070* |
| C8 | 0.63444 (18) | 0.7129 (5) | 0.32792 (18) | 0.0499 (8) |
| H8 | 0.597393 | 0.691593 | 0.300824 | 0.060* |
| C9 | 0.500000 | 0.0504 (6) | 0.5974 (2) | 0.0422 (9) |
| H9 | 0.500001 | −0.026990 | 0.628960 | 0.051* |
| C10 | 0.43437 (16) | 0.1036 (4) | 0.57561 (15) | 0.0372 (6) |
| C11 | 0.37038 (15) | 0.0180 (3) | 0.59904 (15) | 0.0378 (6) |
| C12 | 0.36529 (17) | −0.0382 (5) | 0.65994 (17) | 0.0468 (7) |
| H12 | 0.402406 | −0.022596 | 0.687534 | 0.056* |
| C13 | 0.3050 (2) | −0.1174 (6) | 0.67972 (19) | 0.0578 (9) |
| H13 | 0.301527 | −0.153223 | 0.720755 | 0.069* |
| C14 | 0.2504 (2) | −0.1432 (6) | 0.6390 (2) | 0.0598 (11) |
| H14 | 0.210574 | −0.198902 | 0.652337 | 0.072* |
| C15 | 0.25422 (18) | −0.0871 (5) | 0.5785 (2) | 0.0574 (9) |
| H15 | 0.216916 | −0.103690 | 0.551219 | 0.069* |
| C16 | 0.31385 (16) | −0.0059 (4) | 0.55856 (18) | 0.0478 (7) |
| H16 | 0.316241 | 0.033071 | 0.517886 | 0.057* |
| C17 | 0.5619 (3) | 0.5603 (6) | 0.6056 (3) | 0.0713 (12) |
| H17A | 0.563937 | 0.677699 | 0.602844 | 0.086* |
| H17B | 0.603186 | 0.516165 | 0.585230 | 0.086* |
| C18 | 0.5606 (4) | 0.5095 (11) | 0.6723 (3) | 0.102 (2) |
| H18A | 0.562238 | 0.391990 | 0.674648 | 0.122* |
| H18B | 0.601921 | 0.551708 | 0.693248 | 0.122* |
| C19 | 0.4382 (2) | 0.1224 (6) | 0.3919 (2) | 0.0628 (10) |
| H19A | 0.396838 | 0.176140 | 0.408461 | 0.075* |
| H19B | 0.436073 | 0.008797 | 0.403577 | 0.075* |
| C20 | 0.4393 (3) | 0.1375 (8) | 0.3226 (3) | 0.0808 (14) |
| H20A | 0.397283 | 0.088154 | 0.305269 | 0.097* |
| H20B | 0.439436 | 0.251296 | 0.311029 | 0.097* |
| Ni1 | 0.500000 | 0.34709 (8) | 0.49657 (4) | 0.0366 (2) |
| O1 | 0.57604 (11) | 0.4791 (3) | 0.45726 (11) | 0.0449 (5) |
| O2 | 0.42402 (11) | 0.2140 (3) | 0.53588 (11) | 0.0435 (5) |
| O3 | 0.500000 | 0.5024 (5) | 0.5755 (2) | 0.0607 (10) |
| O4 | 0.500000 | 0.5655 (12) | 0.7030 (3) | 0.128 (3) |
| O5 | 0.500000 | 0.1946 (5) | 0.41744 (19) | 0.0568 (10) |
| O6 | 0.500000 | 0.0599 (8) | 0.2973 (3) | 0.0931 (17) |
1 Source of materials
1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dione (0.02 mol, 4.485 g) was dissolved in hot ethanol (48 ml) and nickel(II) acetate tetrahydrate (0.01 mol, 2.488 g) were mixed with ethanol (16 ml). Aqueous solution of 1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dione solution was fleetingly added to the ethanol mixture of nickel(II) acetate tetrahydrate, and stirred about 48 h at 78 °C. Followed by cooling in an ice bath, the formation of a light green precipitate results. The precipitate was filtered, washed with distilled hot water and ethanol, dried in an oven (90 °C). Subsequently, single crystals of nickel complexes were crystallized by slow evaporation from a mixture of 1,4-dioxane and ethanol.
2 Experimental details
Absorption corrections were performed by using multi-scan program. 1 The structure was solved with Olex2 and SHELX. 2 , 3 , 4 Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions. Hydrogen atoms were constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
3 Comment
Nickel compounds are widely used in batteries due to their safety advantages. 5 , 6 The study of nickel-containing complexes in the field of batteries is challenging but also extremely prospective. 7 , 8 Nickel-containing complex Ni(acac)2 with β-diketone derivatives as ligands are also widely used in battery research. 9 In this paper, a β-diketone derivative nickel complex was successfully synthesized for further study of its application in the field of battery materials.
The title compound is a complex with nickel(II) as the central metal. The coordination sites of the compound was occupied by six oxygen atoms. 10 Four oxygen atoms are derived from the bidentate ligand 1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dione, the other oxygen atoms are derived from monodentate ligand 1,4-dioxane. 11
In the title molecule, the distances of Ni1–O1 and Ni1–O11 bonds both are 1.997(2) Å, the distances of Ni1–O2 and Ni1–O21 bonds both are 2.001(2) Å, the distance of Ni1–O3 bond is 2.121(4) Å, the distance of Ni1–O31 bond is 2.111(4) Å. 12
In addition, the O21–Ni1–O3 angle is 89.72(12)°, the O2–Ni1–O3 angle is 89.72(12)°, the O2–Ni1–O21 angle is 92.53(13)°, the O2–Ni1–O5 angle is 90.68(12)°, the O21–Ni1–O5 angle is 90.68(12)°, the O1–Ni1–O3 angle is 90.44(12)°, the O11–Ni1–O3 angle is 90.44(12)°, the O1–Ni1–O2 angle is 179.77(13)°, the O1–Ni1–O21 angle is 87.30(8)°, the O11–Ni1–O2 angle is 87.30(8)°, the O11–Ni1–O21 angle is 179.77(13)°, the O1–Ni1–O1 angle is 92.86(13)°, the O1–Ni1–O5 angle is 89.16(12)°, the O11–Ni1–O5 angle is 89.16(12)°, and the O5–Ni1–O3 angle is 179.4(2)°. 13
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: None declared.
References
1. Rigaku, OD. CrysAlisPro Software System. Version 1.171.40.84a, 2020.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT: Integrating Space Group Determination and Structure Solution. Acta Crystallogr. 2014, A70, C1437.10.1107/S2053273314085623Suche in Google Scholar
5. Yilin, Z.; Yuqing, C.; Qiu, H.; Jinlong, K.; Wei, W.; Jian-Fang, W.; Peng, G.; Yanhua, L.; Jilei, L. Interface Engineering Strategy via Electron-Defect Trimethyl Borate Additive toward 4.7 V Ultrahigh-Nickel LiNi0.9Co0.05Mn0.05O2 Battery. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 92, 639–647; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2024.02.004.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Jing, H.; Xinliang, W.; Qinjun, X.; Qingyun, C.; Di, C.; Chengjie, L.; Yingchao, Z.; Guofu, L.; Renhong, S.; Qianqiu, T.; Anpeng, G. Facile Synthesis of Ni Anchored on N-Doped Carbon Nanotube as Cathodic Electronic Conductive Agent for Thermal Battery. Mater. Lett. 2024, 360, 136041; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2024.136041.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Si-Wen, K.; Wei, L.; Yuming, G.; Jian, S.; Yifan, L.; Shuai, Y.; Jing–Lin, Z.; Jing, M.; Ping, H. Covalent Organic Frameworks with Ni-Bis(dithiolene) and Co-porphyrin Units as Bifunctional Catalysts for Li–O2 Batteries. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf2398; https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adf2398.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Seon, Y. P.; Sewon, P.; Hyeong, Y. L.; Moonsu, Y.; Jeong–Hee, C.; Sang, K. K.; Sung, Y. H.; Nam–Soon, C. Ni–Ion–Chelating Strategy for Mitigating the Deterioration of Li–Ion Batteries with Nickel–Rich Cathodes. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2205918; https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202205918.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Shujin, H.; Xiaoli, S.; Fei, X.; Meng, S.; Feiyu, D.; Yiqian, W. Electrospun Carbon Nanofibers Embedded with Heterostructured NiFe2O4/Fe0.64Ni0.36 Nanoparticles as an Anode for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Battery. J. Energy Storage 2024, 92, 639–647.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Mladen, B.; Ivan, K.; Marijana, Đ. Predicting Supramolecular Connectivity of Metalcontaining Solid-State Assemblies Using Calculated Molecular Electrostatic Potential Surfaces. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 1985–1995; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.8b01930.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Maria, C.; Leonarda, V.; Goran, M.; Marina, J. K.; Pier, C. R.; Ivan, H.; Francesco, D. Mechanochemical Reactions from Individual Impacts to Global Transformation Kinetics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202308046; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202308046.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Chien, T. P.; Thu, T. P.; Hung, H. N.; Thi, N. T. Syntheses, Structures, and Bioactivities Evaluation of Some Transition Metal Complexes with 4,4′–Diacetylcurcumin. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2020, 646, 495–499; https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.202000088.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Hema, M. K.; Karthik, C. S.; Mahesha; Pampa, K. J.; Mallu, P.; Lokanath, N. K. 4,4,4-Trifluoro-1-phenylbutane-1,3-dione Metal [Cu(II) and Ni(II)] Complexes as an Superlative Antibacterial Agent against MRSA: Synthesis, Structural Quantum-Chemical and Molecular Docking Studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1243, 130774; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130774.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

