Abstract
C21H24CINO4, monoclinic, P21 (no. 14), a = 8.6813(3) Å, b = 7.3821(2) Å, c = 16.0325(6) Å, β = 105.282(2)°, V = 991.13(6) Å3, Z = 2, R gt(F) = 0.0405, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1014, T = 296.15 K.
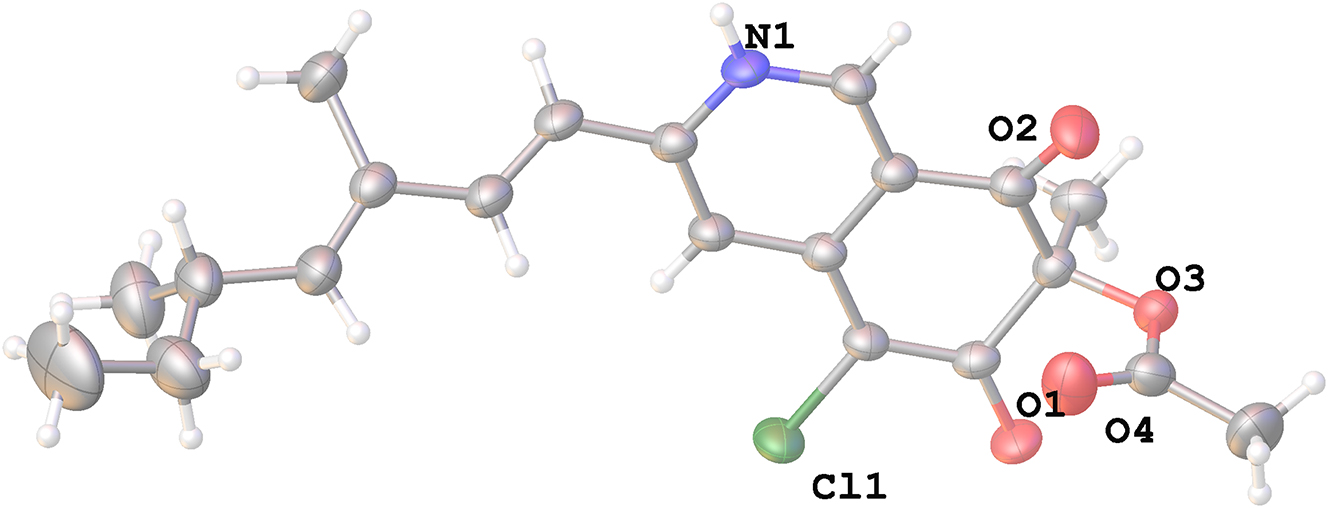
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red needle |
| Size: | 0.28 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | MoKα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.22 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker P4, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 27.9°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 15860, 4621, 0.033 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3735 |
| N(param)refined: | 252 |
| Programs: | Olex2, 1 , 2 SHELX 3 , 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.8155 (3) | 0.3956 (5) | 0.36708 (17) | 0.0336 (6) |
| C3 | 0.8946 (3) | 0.4085 (5) | 0.51986 (16) | 0.0332 (6) |
| C4 | 0.7381 (3) | 0.4134 (5) | 0.52163 (17) | 0.0340 (6) |
| C5 | 0.4504 (3) | 0.4150 (5) | 0.44303 (16) | 0.0328 (6) |
| C6 | 0.3242 (3) | 0.4171 (5) | 0.36775 (16) | 0.0313 (6) |
| C7 | 0.3690 (3) | 0.4414 (4) | 0.28128 (17) | 0.0317 (6) |
| C8 | 0.5378 (3) | 0.3845 (4) | 0.28142 (17) | 0.0337 (6) |
| C9 | 1.0284 (3) | 0.4089 (5) | 0.59771 (17) | 0.0367 (6) |
| C10 | 1.0275 (3) | 0.3142 (4) | 0.66721 (19) | 0.0375 (7) |
| C11 | 1.1521 (3) | 0.3023 (4) | 0.7484 (2) | 0.0367 (7) |
| C12 | 1.1324 (4) | 0.1892 (5) | 0.8089 (2) | 0.0451 (8) |
| C13 | 1.2414 (4) | 0.1551 (6) | 0.8979 (2) | 0.0516 (9) |
| C14 | 1.2179 (5) | −0.0362 (7) | 0.9276 (3) | 0.0710 (12) |
| C15 | 1.3464 (7) | −0.0961 (11) | 1.0063 (4) | 0.115 (2) |
| C16 | 1.2133 (6) | 0.2974 (7) | 0.9604 (3) | 0.0772 (13) |
| C17 | 1.2947 (4) | 0.4251 (6) | 0.7595 (2) | 0.0539 (9) |
| C18 | 0.3543 (4) | 0.6407 (4) | 0.2567 (2) | 0.0435 (8) |
| C19 | 0.2457 (4) | 0.1689 (5) | 0.2252 (2) | 0.0404 (7) |
| C20 | 0.1074 (5) | 0.0876 (6) | 0.1604 (3) | 0.0656 (11) |
| C21 | 0.6103 (3) | 0.4091 (5) | 0.44447 (15) | 0.0301 (5) |
| C22 | 0.6582 (3) | 0.3972 (5) | 0.36516 (16) | 0.0316 (6) |
| Cl1 | 0.39620 (8) | 0.41451 (13) | 0.54013 (4) | 0.0456 (2) |
| H1 | 1.023 (4) | 0.408 (6) | 0.4420 (19) | 0.043* |
| H7 | 0.714105 | 0.419778 | 0.574764 | 0.041* |
| H9 | 0.844461 | 0.388791 | 0.315300 | 0.040* |
| H10 | 1.117772 | 0.478740 | 0.598111 | 0.044* |
| H11 | 0.935853 | 0.246350 | 0.664171 | 0.045* |
| H13 | 1.038800 | 0.121459 | 0.794599 | 0.054* |
| H14 | 1.351979 | 0.166268 | 0.894354 | 0.062* |
| H15A | 1.115170 | −0.042867 | 0.940769 | 0.085* |
| H15B | 1.215475 | −0.119588 | 0.880576 | 0.085* |
| H16A | 1.306118 | −0.192321 | 1.034882 | 0.173* |
| H16B | 1.377033 | 0.004212 | 1.045210 | 0.173* |
| H16C | 1.437546 | −0.138294 | 0.988604 | 0.173* |
| H17A | 1.371654 | 0.397295 | 0.812935 | 0.081* |
| H17B | 1.261343 | 0.548981 | 0.760272 | 0.081* |
| H17C | 1.341920 | 0.407420 | 0.712265 | 0.081* |
| H18A | 1.233217 | 0.415402 | 0.940354 | 0.116* |
| H18B | 1.284197 | 0.276321 | 1.016557 | 0.116* |
| H18C | 1.104755 | 0.290498 | 0.963866 | 0.116* |
| H20A | 0.125220 | −0.039885 | 0.155616 | 0.098* |
| H20B | 0.096197 | 0.144363 | 0.105278 | 0.098* |
| H20C | 0.011777 | 0.105937 | 0.178691 | 0.098* |
| H21A | 0.373926 | 0.656168 | 0.200940 | 0.065* |
| H21B | 0.431065 | 0.709387 | 0.298927 | 0.065* |
| H21C | 0.248674 | 0.682383 | 0.254724 | 0.065* |
| N1 | 0.9305 (3) | 0.4036 (4) | 0.44192 (14) | 0.0360 (5) |
| O1 | 0.18009 (19) | 0.4126 (4) | 0.36458 (12) | 0.0441 (5) |
| O2 | 0.5699 (2) | 0.3456 (4) | 0.21459 (14) | 0.0495 (7) |
| O3 | 0.2532 (2) | 0.3499 (3) | 0.21400 (13) | 0.0357 (5) |
| O4 | 0.3378 (3) | 0.0903 (3) | 0.28234 (17) | 0.0552 (6) |
1 Source of material
The title compound is a natural product, which has been totally synthesized in 2011. 5 We got it by extraction and isolation from fungal fermentation products. 6
2 Experimental details
The structure was treated with the Olex2 crystallographic software package, 1 , 2 solved with the SHELXT structure solution program and refined with the SHELXL refinement package. 3 , 4 Carbon-bound hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined with riding coordinates, with U iso (H) fixed at 1.2 times of U eq (C) (Tables 1 and 2).
3 Comment
The title compound of C21H24CINO4 has been reported with various biological activities, such as neuroprotective effects, and cytotoxic against hepatoma cells. 7 , 8 The structure of C21H24CINO4 is composed of 4,6-dimethylocta-2,4-diene, pyridine ring, and m-benzoquinone ring moiety. 9 The geometry of title structure was characterized with the bond angles and lengths. In particular, the bond angles for C6⋯C7⋯C8, C5⋯C6⋯C7, C6⋯C5⋯CI1 and C1⋯N1⋯C3 are 115.8(2)°, 116.7 (2)°, 115.85(17)° and 121.5(2)°, respectively. For another, the bond lengths of CI1⋯C5, O1⋯C6, O2⋯C8, C5⋯C6 and C1⋯N1, are 1.741(2) Å, 1.239(3) Å, 1.435(3) Å, 1.400(4) Å, 1.345(3) Å. Furthermore, the molecules are connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonds N1-H1⋯O1, C9-H10⋯CI1, C10-H11⋯O1, which are 2.07 Å/145°, 2.85 Å/133°, 2.66 Å/142°, respectively. These bond lengths are within the normal range. 9 , 10 , 11 In the structure, the pyridine ring and benzoquinone formed a rare isoquinoline quinone skeleton, and it was further unequivocally secured that the stereo configurations of C-7 and C-13 are 7R and 13S (coincident with the reported). 9
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by the Huangshan University school-enterprise cooperation project (hxkt2024095, hxkt2020118), Natural Science Foundation for Colleges and Universities of Jiangsu Province (No. 20KLB350007).
-
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. The Anatomy of a Comprehensive Constrained, Restrained Refinement Program for the Modern Computing Environment–Olex2 Dissected. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 59–75; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of Shelx. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, 64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Germain, A. R.; Bruggemeyer, D. M.; Zhu, J. l.; Genet, C.; Brien, P. O.; Porco Jr, J. A. Synthesis of the Azaphilones (+)-Sclerotiorin and (+)-8-O-Methylsclerotiorinamine Utilizing (+)-Sparteine Surrogates in Copper-Mediated Oxidative Dearomatization. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 2577–2584; https://doi.org/10.1021/jo102448n.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Li, J.; Yang, X.; Lin, Y. Y.; Yun, J.; Lu, Y. J.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Li, M. F.; Lin, Y. C.; He, J. G.; Liu, L. Meroterpenes and Azaphilones from Marine Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Penicillium 303#. Fitoterapia 2014, 97, 241–246; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2014.06.011.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Li, J. L.; Li, Z. X.; Chen, T.; Ye, G. T.; Qiu, L. Y.; Long, Y. H. New Azaphilones from Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Penicillium Sclerotiorin SCNU-F0040. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 296–304; https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2021.1959580.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Guo, Q. F.; Dong, L. L.; Zang, X. Y.; Gu, Z. J.; He, X. Y.; Yao, L. D.; Cao, L.; Qiu, J. Z.; Guan, X. A New Azaphilone from the Entomopathogenic Fungus Hypocrella sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1–7; https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2015.1023199.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Yang, W. C.; Yuan, J.; Tan, Q.; Gu, Z. J.; He, X. Y.; Yao, L. D.; Cao, L. P.; Qiu, J. Z.; Guan, X. Peniazaphilones A–I, Produced by Co-Culturing of Mangrove Endophytic Fungi, Penicillium sclerotiorum THSH-4 and Penicillium sclerotiorum ZJHJJ-18. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 3404–3412; https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.202100542.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Whalley, W. B.; Ferguson, G.; Marsh, W. C.; Restivo, R. J. The Chemistry of Fungi. Part LXVIII. The Absolute Configuration of (+)-sclerotiorin and of the Azaphilones. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1976, 1, 1366–1369; https://doi.org/10.1039/p19760001366.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Hebra, T.; Elie, N.; Poyer, S.; Van Elslande, E.; Touboul, D.; Eparvier, V. Dereplication, Annotation, and Characterization of 74 Potential Antimicrobial Metabolites from Penicillium Sclerotiorum Using t-SNE Molecular Networks. Metabolites 2021, 11, 444; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11070444.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

