Abstract
C30H31N5O6S2, Triclinic,
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
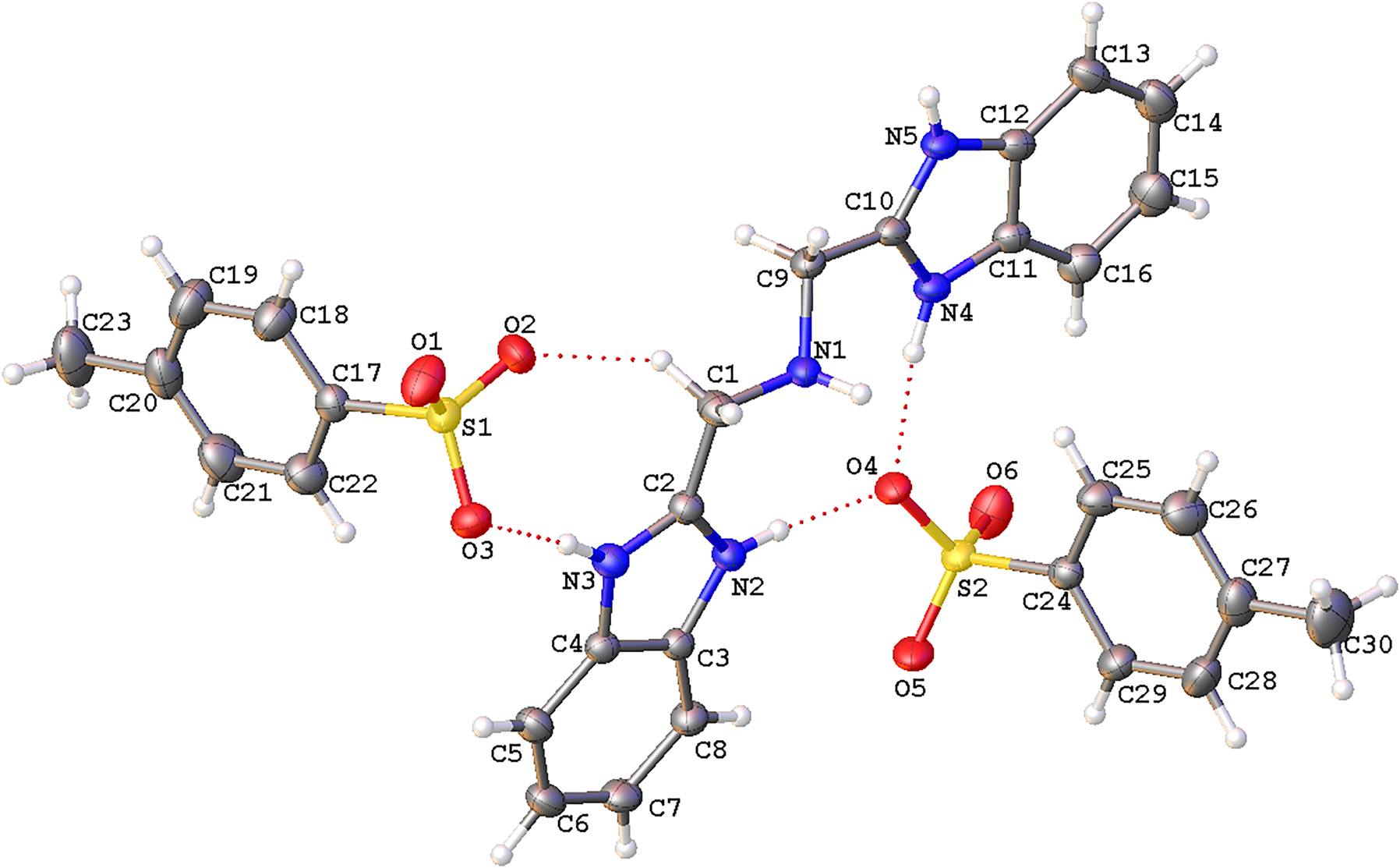
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Ga Kα radiation (1.34139 Å) |
| μ: | 1.37 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 VENTURE, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 72.3°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 49,293, 8,746, 0.050 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ (I obs), 7,915 |
| N(param)refined: | 406 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 , 6 Diamond, 4 Olex2 5 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.60211 (15) | 0.88932 (16) | 0.53249 (12) | 0.0307 (3) |
| H1A | 0.550479 | 0.890108 | 0.589033 | 0.037* |
| H1B | 0.588154 | 0.959022 | 0.502768 | 0.037* |
| C2 | 0.75641 (14) | 0.91684 (14) | 0.56159 (10) | 0.0237 (3) |
| C3 | 0.97162 (14) | 0.89467 (13) | 0.57903 (9) | 0.0220 (2) |
| C4 | 0.97453 (14) | 1.01670 (14) | 0.63286 (10) | 0.0230 (2) |
| C5 | 1.09660 (16) | 1.10286 (15) | 0.68854 (11) | 0.0290 (3) |
| H5 | 1.098151 | 1.186033 | 0.724957 | 0.035* |
| C6 | 1.21561 (16) | 1.05986 (17) | 0.68756 (12) | 0.0321 (3) |
| H6 | 1.301722 | 1.115395 | 0.723924 | 0.038* |
| C7 | 1.21218 (15) | 0.93633 (17) | 0.63419 (12) | 0.0314 (3) |
| H7 | 1.295973 | 0.910450 | 0.636277 | 0.038* |
| C8 | 1.09072 (15) | 0.85065 (15) | 0.57850 (11) | 0.0274 (3) |
| H8 | 1.088918 | 0.767269 | 0.542321 | 0.033* |
| C9 | 0.39273 (14) | 0.70540 (15) | 0.47086 (10) | 0.0260 (3) |
| H9B | 0.338200 | 0.758897 | 0.448656 | 0.031* |
| H9A | 0.375177 | 0.702372 | 0.536784 | 0.031* |
| C10 | 0.34681 (13) | 0.57103 (14) | 0.40996 (10) | 0.0238 (3) |
| C11 | 0.35766 (14) | 0.38260 (14) | 0.32450 (10) | 0.0257 (3) |
| C12 | 0.21648 (14) | 0.38391 (15) | 0.31638 (10) | 0.0260 (3) |
| C13 | 0.10900 (16) | 0.28015 (17) | 0.25994 (12) | 0.0335 (3) |
| H13 | 0.013152 | 0.281011 | 0.254269 | 0.040* |
| C14 | 0.1498 (2) | 0.17572 (17) | 0.21260 (13) | 0.0392 (4) |
| H14 | 0.079766 | 0.102727 | 0.173298 | 0.047* |
| C15 | 0.2918 (2) | 0.17379 (17) | 0.22060 (14) | 0.0394 (4) |
| H15 | 0.314694 | 0.099645 | 0.186837 | 0.047* |
| C16 | 0.39889 (18) | 0.27743 (16) | 0.27654 (12) | 0.0333 (3) |
| H16 | 0.494858 | 0.276857 | 0.281909 | 0.040* |
| N1 | 0.54421 (12) | 0.76341 (13) | 0.46645 (9) | 0.0260 (2) |
| H1 | 0.555 (2) | 0.773 (2) | 0.4056 (15) | 0.031* |
| N2 | 0.83250 (12) | 0.83517 (12) | 0.53554 (8) | 0.0230 (2) |
| H2 | 0.796 (2) | 0.760 (2) | 0.4986 (15) | 0.028* |
| N3 | 0.83836 (12) | 1.02692 (12) | 0.61950 (9) | 0.0249 (2) |
| H3 | 0.812 (2) | 1.096 (2) | 0.6501 (15) | 0.030* |
| N4 | 0.43484 (12) | 0.50080 (12) | 0.38439 (9) | 0.0245 (2) |
| H4 | 0.532 (2) | 0.530 (2) | 0.3997 (15) | 0.029* |
| N5 | 0.21481 (12) | 0.50303 (13) | 0.37166 (9) | 0.0260 (2) |
| H5A | 0.141 (2) | 0.527 (2) | 0.3764 (15) | 0.031* |
| C17 | 0.66183 (16) | 1.19534 (14) | 0.87118 (10) | 0.0274 (3) |
| C18 | 0.5537 (2) | 1.1999 (2) | 0.92812 (13) | 0.0411 (4) |
| H18 | 0.470233 | 1.215630 | 0.904885 | 0.049* |
| C19 | 0.5682 (2) | 1.1814 (2) | 1.01915 (14) | 0.0479 (5) |
| H19 | 0.494262 | 1.184923 | 1.057914 | 0.058* |
| C20 | 0.6889 (2) | 1.15793 (18) | 1.05433 (13) | 0.0411 (4) |
| C21 | 0.7962 (2) | 1.1548 (2) | 0.99695 (14) | 0.0457 (4) |
| H21 | 0.879834 | 1.139578 | 1.020396 | 0.055* |
| C22 | 0.78387 (19) | 1.17358 (19) | 0.90542 (13) | 0.0372 (4) |
| H22 | 0.858472 | 1.171440 | 0.867005 | 0.045* |
| C23 | 0.7022 (3) | 1.1355 (2) | 1.15307 (15) | 0.0565 (6) |
| H23A | 0.774235 | 1.090980 | 1.158526 | 0.085* |
| H23B | 0.610566 | 1.081177 | 1.165488 | 0.085* |
| H23C | 0.730411 | 1.219975 | 1.199099 | 0.085* |
| O1 | 0.56683 (15) | 1.30587 (14) | 0.75218 (9) | 0.0413 (3) |
| O2 | 0.54799 (12) | 1.07599 (13) | 0.70167 (9) | 0.0396 (3) |
| O3 | 0.77714 (11) | 1.23848 (11) | 0.72020 (8) | 0.0309 (2) |
| S1 | 0.63572 (3) | 1.20569 (4) | 0.75266 (2) | 0.02644 (11) |
| C24 | 0.80725 (14) | 0.53929 (13) | 0.24491 (10) | 0.0244 (3) |
| C25 | 0.67968 (16) | 0.54733 (18) | 0.20599 (12) | 0.0342 (3) |
| H25 | 0.601686 | 0.542454 | 0.242139 | 0.041* |
| C26 | 0.6670 (2) | 0.5625 (2) | 0.11411 (14) | 0.0417 (4) |
| H26 | 0.579270 | 0.567093 | 0.087679 | 0.050* |
| C27 | 0.7797 (2) | 0.57117 (19) | 0.05978 (13) | 0.0406 (4) |
| C28 | 0.9067 (2) | 0.56505 (19) | 0.10041 (13) | 0.0405 (4) |
| H28 | 0.985452 | 0.572643 | 0.064819 | 0.049* |
| C29 | 0.92167 (17) | 0.54806 (17) | 0.19196 (12) | 0.0334 (3) |
| H29 | 1.009072 | 0.542492 | 0.218067 | 0.040* |
| C30 | 0.7651 (3) | 0.5883 (3) | −0.04041 (16) | 0.0623 (6) |
| H30A | 0.859581 | 0.624009 | −0.059089 | 0.093* |
| H30B | 0.709446 | 0.648653 | −0.043823 | 0.093* |
| H30C | 0.716696 | 0.503214 | −0.083120 | 0.093* |
| O4 | 0.73325 (10) | 0.58172 (11) | 0.41444 (8) | 0.0284 (2) |
| O5 | 0.97546 (11) | 0.58327 (14) | 0.39779 (9) | 0.0385 (3) |
| O6 | 0.78284 (16) | 0.37789 (12) | 0.35497 (9) | 0.0409 (3) |
| S2 | 0.82679 (3) | 0.51735 (3) | 0.36129 (2) | 0.02405 (10) |
1 Source of materials
All the reagents and solvents were used as obtained without further purification. Bis((benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl) amine (IDB) was prepared according to a slightly modified method described by Adams et al. 7 The ligand IDB (27.7 mg, 0.1 mmol) and p-toluenesulfonic acid (34.4 g, 0.2 mmol) were thoroughly mixed and dissolved in 10.0 mL methanol solution. The resulting clear solution was kept at ambient condition. Colorless block crystals were obtained five days later at the bottom of the vessel. For a better X-ray data collection crystals selected have been immersed into perfluoroalkylether, which was then cooled down to −73 °C during the measurement.
2 Experimental details
H atoms bound to carbon atoms were placed at their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C–H = 0.95 Å (aromatic), 0.99 Å (methylene), 0.98 Å (methyl), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq (aromatic and methylene) and 1.5U eq (methyl). Those H atoms bound with N1–N5 atoms were found initially from the difference maps with N–H distances being refined freely, and the U iso values being set 1.2 times of their respective parent atoms.
3 Comment
Bis(2-benzimidazylmethyl)amine (IDB) is a type of multi-benzimidazole ligands which have been often used in the synthesis of various metal-organic complexes used as functional materials. 7 For instance, by employing a tripodal bis(benzimidazole) ligand bis((benzimidazol-2-yl) methyl)amine(IDB) and its derivative as the main ligand, a series of nickel and copper complexes were synthesized which allow a systematic investigation of a biomimetic chemistry. 8 By using multi- or poly-benzimidazole derivatives, we can improve the properties of a fiber such as reducing flame shrinkage and oxidative resistance. 9 In order to study the flame retardancy of ligands with two benzimidazole, we synthesized a new organic ligand and successfully obtained its p-methylbenzene sulfonate. By introducing a wide variety of anions, we expect to be able to improve the ignition point of the compound as a flame retardant material.
The titled compound was crystallized in the triclinic
In the crystal packing, the ions are linked into a three-dimensional network. In order to simplify the analysis of the crystal packing, it can be introduced in terms of three aspects. Firstly, the IDB cations and p-toluenesulfonate anions are linked together via four N–H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming the one-dimensional chain running along the [100] axis. Meanwhile, one π⃛π stacking interaction was observed between symmetry-related benzene ring (C3–C8) and imidazole ring (N2/N3/C2/C3/C4) with the centroid-to-centroid distance of 3.511(1) Å. Secondly, these adjacent [100] hydrogen chains are linked by one other π⃛π stacking interaction between symmetry-related benzene ring (C11–C16) and imidazole ring (N2/N3/C2/C3/C4) with the centroid-to-centroid distance of 3.523(1) Å, forming a two-dimensional layer structure parallel to the (001) plane. Finally, by analysis using PLATON 14 those neighboring two-dimensional (001) layer structures are linked by weak C–H⃛π interaction originating from the methyl group (C23) and benzene ring (C4–C8) with the nearest C⋯C distance being 3.475(1) Å, giving the final three-dimensional network.
Funding source: R&D Center, Yunnan YunTianHua CO. LTD
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was financially supported by the R&D Center, Yunnan YunTianHua CO. LTD.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX 3 and SAINT V8.40B; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2003.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Refinement with SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND; Crystal Impact GbR: Bonn Germany, 2006.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Tomov, A. K.; Nobbs, J. D.; Chirinos, J. J.; Saini, P. K.; Malinowski, R.; Ho, S. K. Y.; Young, C. T.; McGuinness, D. S.; White, A. J. P.; Elsegood, M. R. J.; Britovsek, G. J. P. Alternating Alpha–Olefin Distributions via Single and Double Insertions in Chromium–Catalyzed Ethylene Oligomerizatio. Organometallics 2017, 36, 510–522. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.organomet.6b00671.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Casella, L.; Carugo, O.; Gullotti, M.; Doldi, S.; Frassoni, M. Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity of Model Complexes of Copper Nitrite Reductase. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 1101–1113. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic950392o.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Coffin, D. R.; Serad, G. A.; Hicks, H. L.; Montgomery, R. T. Properties and Applications of Celanese PBI – Polybenzimidazole Fiber. Text. Res. J. 1982, 52, 466–472. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051758205200706.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Wang, K. Y.; Weber, M.; Chung, T. S. Polybenzimidazoles (PBIs) and State-of-the-Art PBI Hollow Fiber Membranes for Water, Organic Solvent and Gas Separations: A Review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 8687–8718. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TA00422D.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Ji, B.; Deng, D.; Ma, N.; Miao, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Network Formation of Bis(2-Benzimidazylmethyl)amine in Salts with Carboxylic Acids: The Structures Based on the Interplay of Strong and Weak Intermolecular Interactions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 4090–4100. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg2006748.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Zheng, S. R.; Cai, Y. P.; Zhang, X. L.; Su, C. Y. 2,2′-(Iminodimethylene)bis(1H-benzimidazolium)(1+) Chloride. Acta Crystallogr. 2005, C61, o642–o644. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108270105021992.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Zhou, C.-S.; Huang, X.-Y.; Meng, X.-G. 2,2′-(Iminodimethylene)dibenzimidazolium Bis(perchlorate) Methanol Solvate. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, E64, o791–o792. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536808008519.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
14. Spek, A. L. Structure Validation in Chemical Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155. https://doi.org/10.1107/S090744490804362X.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3


