Abstract
Gastric mucosal injury is caused by an imbalance between the mucosal defense and gastro-irritants, leading to gastroenteritis. Diosgenin is a steroidal sapogenin found in the wild Yam plant that has been reported with several pharmacological properties. The aim of this study is to explore the gastroprotective role of diosgenin on gastric mucosal damage caused by HCl/ethanol in rats. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were intragastrically administered with diosgenin (20 mg/kg) before HCl/ethanol (0.15 M HCl in 98 % ethanol) administration. Omeprazole was used as a positive control. Diosgenin-attenuated oxidative stress by enhancing (p < 0.05) antioxidant enzymes, reducing lipid peroxidation (MDA), and modulating nitric oxide (NO) levels. Anti-inflammatory effects of diosgenin were observed by a reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines (p < 0.05), decreased myeloperoxidase (MPO) activities (p < 0.05), and histopathological observation of gastric mucosal damage. Western blot analysis provided evidence on the downregulation of NF-κβ by diosgenin. The findings showed that diosgenin has a significant protective role on gastric injury caused by HCl/ethanol, through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory role, and suppression of NF-κβ and MPO activities.
1 Introduction
Gastric injury or gastroenteritis is a common disease among millions of people around the world [1]. Gastric mucosal lining is linked to various exogenous and endogenous protection and maintenance mechanisms such as alkaline mucus secretion, gastric microcirculation, renin–angiotensin system, antioxidant, and enzymatic barriers against gastro-irritants and toxic substances [2]. The gastric mucosa is vulnerable to toxins excreted by Helicobacter pylori, noxious matters, alcohol/ethanol, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), hydrochloric acid (HCl), bile acids, and pepsin [3]. Alcohol is one of the highly abused substances in the world, which could lead to upper gastrointestinal bleeding and peptic ulcers. An imbalance between the mucosal defense and gastro-irritants/aggressive materials leads to gastric mucosal injury. Untreated conditions could lead to peptic ulcers accompanied by symptoms of abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, loss of weight, poor appetite, and bloating [4]. Oxidative stress and inflammation are often linked with the progression of gastric mucosal damage at the cellular level. During inadequate defense by antioxidants and antioxidant enzymes to scavenge the excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) free radicals, gastric mucosal injury is initiated and is prolonged by infiltration of pro-inflammatory cytokines and neutrophils [5,6].
Natural products are known for their therapeutic potentials against various ailments caused by oxidative stress and have been a choice for research and treatment in recent years due to their effectiveness and safety with less or no side effects [7]. Past researchers have demonstrated the gastroprotective ability of plants extracts and natural active constituents from plants against experimental gastric injury in animal models [8]. A preclinical model of gastric mucosal injury is commonly induced using HCl/ethanol since alcohol abuse is one of the leading causes of gastric injury in humans [9]. Diosgenin is a steroidal sapogenin that could be found as a major bioactive compound in tubers of wild Yam plants (Dioscorea villosa) and several other plants including Costus, Smilax, Dioscorea, and Trigonella [10,11]. Diosgenin has multiple pharmaceutical advantages including anti-inflammatory [12], hepatoprotective [13], anti-hypercholesterolemic [14,15], anti-osteoporotic [16], prevents spinal cord injury [17], prevents testicular damage in diabetic rats [18], attenuates Parkinson’s disease [19], and modulates insulin resistance and anabolic hormones [20]. The anti-hypercholesterolemic studies have reported that diosgenin is safe for consumption and has significant inhibition toward gastrointestinal uptake of dietary cholesterol and also the regulation of bile acids [15,16]. Antioxidant compounds have the tendency to exert gastroprotective effects. Till date, there are no studies on the gastroprotective properties of diosgenin; hence it was selected for this study with relevance to its pharmacological properties. Gastrointestinal tract disorders induced by alcohol consumption are relatively high in common. A study on HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury could give a better understanding of the treatment measures for alcoholic gastroenteritis. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective roles of diosgenin on HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Chemicals
Diosgenin, omeprazole, HCl, and ethanol (98%) were procured from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., USA (Figure 1). Chemicals for biochemical analysis, antigens, and antibodies for the ELISA assay were obtained from Sigma, St. Louis, USA, and Abcam, USA. Diosgenin was dissolved in 0.1% tween 80 for experimental administration.
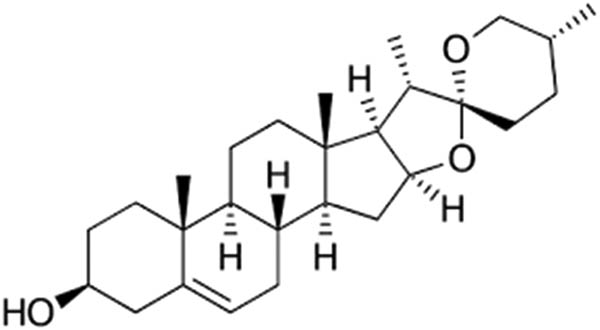
Chemical structure of diosgenin.
2.2 Animals
Male Sprague-Dawley (6–7 weeks) rats (180–200 g) were randomly housed in wire bottom cages for the prevention of coprophagy, in a group of ten (n = 10) at 24 ± 2°C temperature, 60% humidity, 12 h light/dark cycle, supplied with standard rodent feed and water.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to animal use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations and institutional policies for the care and use of animals and was approved by the ethical committee of Xi’an Third Hospital (Ethical No.: XATH20200827).
2.3 Experimental design and HCl/ethanol-induced gastric injury
All animals were fasted for 24 h and allowed free access to water alone before the initiation of the experiment. The experimental protocol was performed following the methods of Yang et al. [21]. Group I (normal control) was treated with intragastric administration of 0.1% tween 80. Group II served as a gastric model group was administered with HCl/ethanol (0.15 M HCl in 98% ethanol) intragastrically. Group III served as an experimental group treated with diosgenin (20 mg/kg b.w.) by intragastric administration. Group IV served as a positive control treated with omeprazole (20 mg/kg b.w.) by intragastric administration. Groups III and IV received intragastric administration of HCl/ethanol (0.15 M HCl in 98% ethanol), 1 h after the drug administration. The dose of diosgenin was selected based on preliminary studies and past research on the animal model study of diosgenin [18] that was able to prevent oxidative stress; hence, the dosage was modified according to the study of treating gastric mucosal damage in rats [22]. One hour after the administration of HCl/ethanol, the rats were sacrificed through cervical dislocation under deep isoflurane anesthesia, the stomach was dissected longitudinally, and it was washed with ice-cold saline. Consequently, gastric mucosal tissues were subjected to histopathological and biochemical analyses.
2.4 Biochemical analysis
The gastric tissues excised from rats were homogenized in cold phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4) and centrifuged at 2,000 ×g for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatants obtained were subjected to biochemical assays for reduced glutathione (GSH), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO) levels, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity. The remaining aliquots were used for the ELISA assay (Sigma, St. Louis, USA) for interleukin 1-beta (IL-1β), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Commercial colorimetric assay kits (Sigma, St. Louis, USA) were used for the determination of CAT, GSH, GPx, SOD, MDA, and NO levels and MPO activity. Protein determination in aliquot was done by Bradford’s assay using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a standard. Briefly, the decomposition rate of H2O2 was observed at 240 nm for CAT determination, formation of 5-thiol-2-nitrobenzoic acid at 412 nm was observed for GSH determination, the oxidation rate of NADPH to NADP+ was observed at 340 nm for GPx determination, inhibition rate of pyrogallol auto-oxidation was observed at 470 nm for SOD determination, formation of thiobarbituric acid (TBA) conjugates was observed at 535 nm for MDA determination, production of stable NO metabolite with Griess reagent was observed at 540 nm for NO determination, and degradation rate of peroxide was observed at 412 nm for MPO determination.
2.5 Histopathological analysis
A portion of the gastric tissue was fixed in formaldehyde (4%) for 24 h. The tissues were then dehydrated and paraffin embedded. Embedded tissues were sliced at 5 µm thickness, deparaffinized, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). The samples were imaged under the light microscope. Histopathological scoring was performed according to the study by Li et al. [23] by a pathologist who was not aware of experimental groups, mucosal edema was given a score range of 0–4, loss of epithelial cells was given a score range of 1–3, infiltration of inflammatory cells was given a score range of 1–3, and hemorrhage was given a score range of 1–4.
2.6 Western blot
Western blot analysis was performed to evaluate the involvement of the NF-κβ pathway in the gastric mucosal injury induced by HCl/ethanol. Gastric tissues were homogenized using lysis buffer with protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail and centrifuged at 4°C for 10 min at 16,000 ×g, and the aliquot was used for western blot analysis. Aliquots with equal amounts of protein were separated through electrophoresis on 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% skimmed milk at room temperature for 2 h in Tris-buffered saline with 0.1% Tween 20. Then, the membranes were incubated overnight with primary antibodies against Ikβα (1:1,000 dilutions; ab32518, Abcam, USA), p-Ikβα (1:1,000 dilutions; ab133462, Abcam, USA), p65 NF-κβ (ab16502, Abcam, USA; 1:1,000 dilutions), p-p65 NF-κβ (1:1,000 dilutions; ab86299, Abcam, USA), and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH; 1:500 dilutions; ab181602, Abcam, USA). The membranes were washed with TBST and further incubated with anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase–conjugated antibody (1:5,000 dilutions; ab97051, Abcam, USA) for 1 h. Immunoreactive protein expressions were detected and quantified with the enhanced chemiluminescence system (Bio-Rad Lab version 6.0, USA).
2.7 Statistical analysis
All values are displayed as mean ± SEM for 10 rats. Statistical significance was verified with SPSS version 19.0 by performing ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. All p < 0.05 were regarded as significant.
3 Results
3.1 Effects of diosgenin on GSH, GPx, SOD, and CAT activities
Antioxidant enzymes and nonenzymatic GSH in the normal and experimental rats are shown in Figure 2. GSH levels were reduced significantly (approximately 59%) in the gastric model group (p < 0.05) from the control group. Similarly, levels of antioxidant enzymes were decreased (p < 0.05) approximately 54% for GPx, 42.5% for SOD, and 48% for CAT by HCl/ethanol in the gastric model group compared to normal. Compared to the model group, GSH, GPx, SOD, and CAT levels were elevated by the intragastric administration of diosgenin (p < 0.05) and by positive control omeprazole.
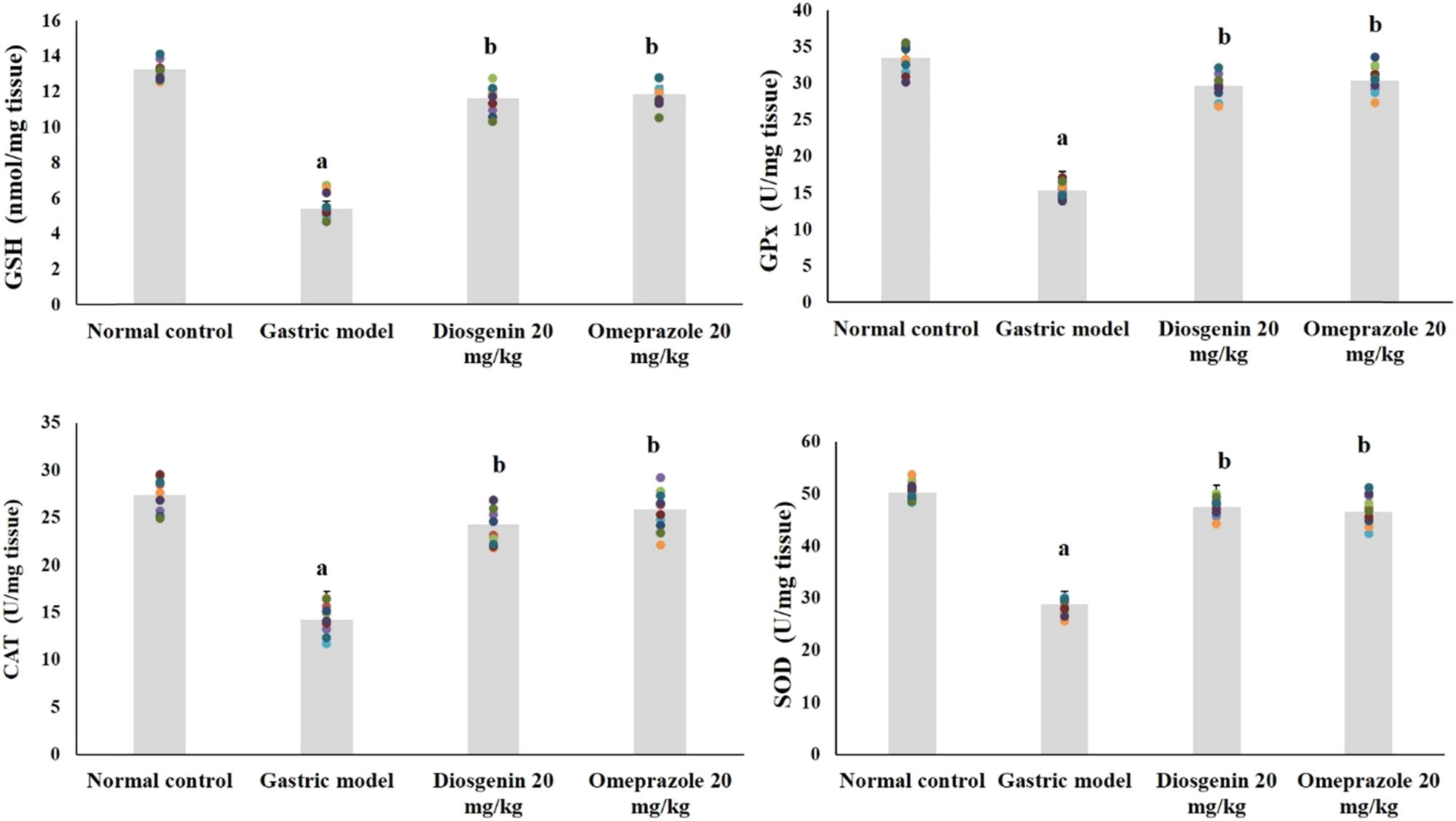
Diosgenin prevents oxidative stress in gastric ulcer-induced rats. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of antioxidant and antioxidant enzymes in rats (n = 10). p(a) < 0.05 compared to the normal control. p(b) < 0.05 compared to the gastric ulcer model. GSH = reduced glutathione; GPx = glutathione peroxidase; SOD = superoxide dismutase; CAT = catalase.
3.2 Effects of diosgenin on MDA and NO levels
Lipid peroxidation indicator MDA and NO levels in the normal and experimental rats are shown in Figure 3. HCl/ethanol-induced gastric model rats showed elevated MDA for about fourfolds from the normal group and suppressed NO by 66% (p < 0.05). Instead, intragastric administration of diosgenin decreased MDA and elevated NO (p < 0.05) against the model group, similar to the positive control group.
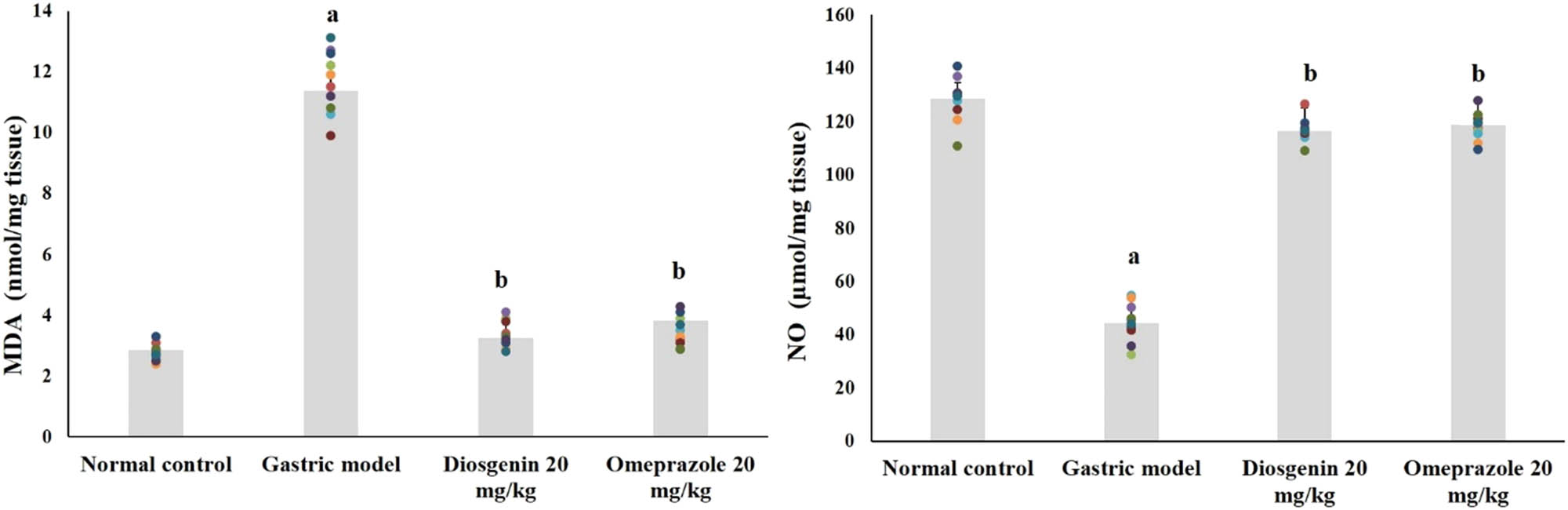
Diosgenin prevents lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide in gastric ulcer-induced rats. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of lipid peroxidation and nitric oxide levels in rats (n = 10). p(a) < 0.05 compared to the normal control. p(b) < 0.05 compared to the gastric ulcer model. MDA = malondialdehyde; NO = nitric oxide.
3.3 Effects of diosgenin on IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels
The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in normal and experimental rats are shown in Figure 4. Compared to the normal group, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were significantly elevated due to HCl/ethanol in the model group (p < 0.05). Remarkably, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were reduced (p < 0.05) due to intragastric administration of diosgenin from the HCl/ethanol-induced model group. Omeprazole administration exerted similar results as diosgenin.
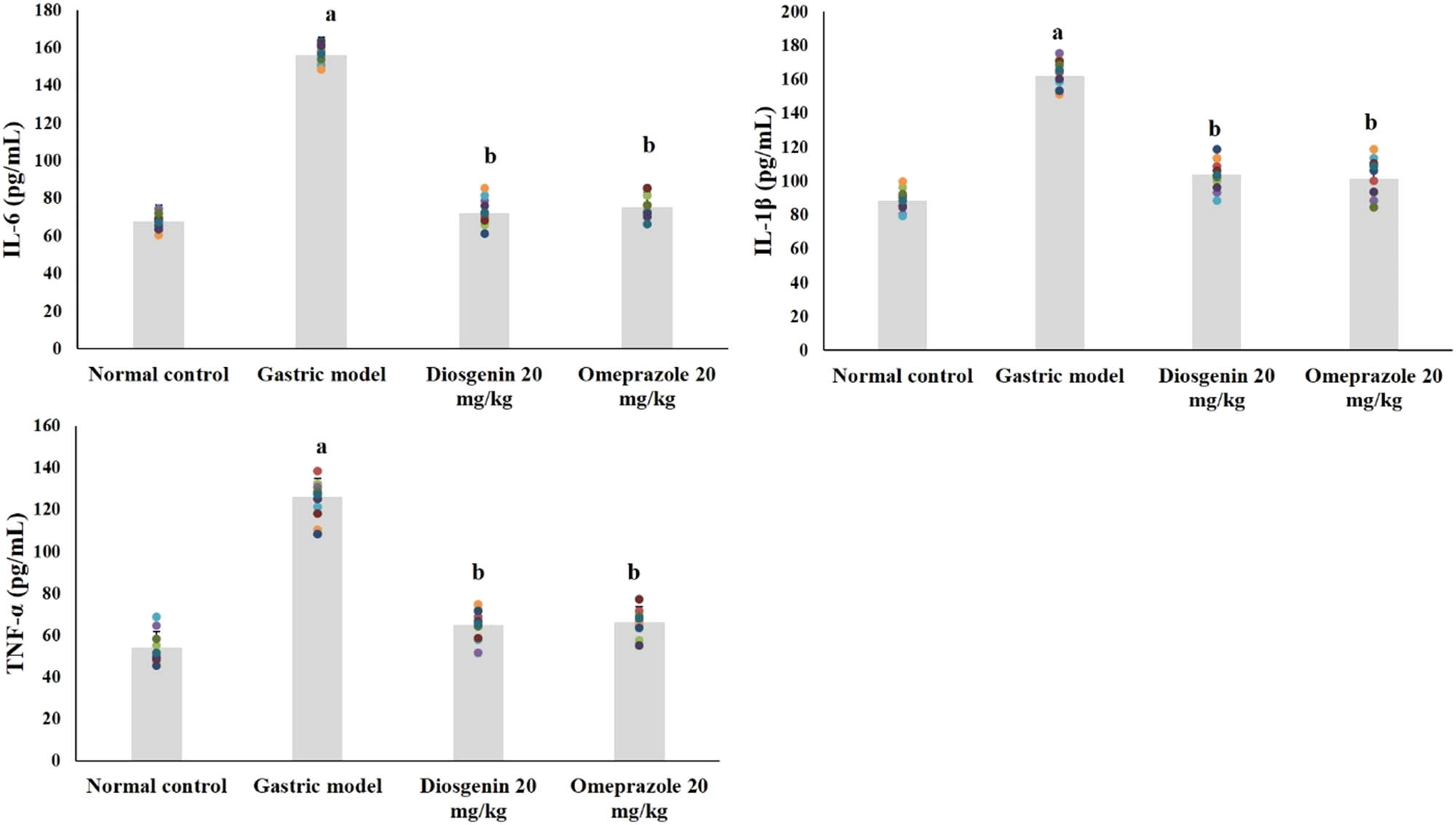
Diosgenin prevents pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) in gastric ulcer-induced rats. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in rats (n = 10). p(a) < 0.05 compared to the normal control. p(b) < 0.05 compared to the gastric ulcer model.
3.4 Effects of diosgenin on MPO activities
MPO activities of the normal and experimental rats are shown in Figure 5. The activities of MPO in HCl/ethanol-induced model rats were high (p < 0.05) up to 40% from the normal group. Compared to the model group, intragastric administration of diosgenin significantly reduced MPO activities (p < 0.05) similar to the positive control group.
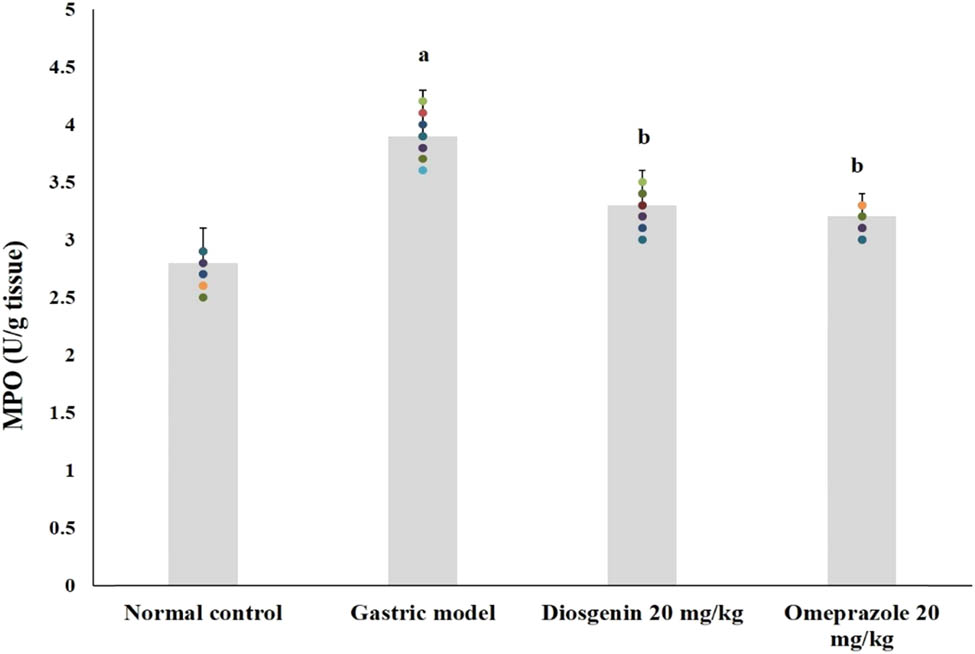
Effects of diosgenin on MPO activities in rat gastric tissue. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of MPO activities in rats (n = 10). p(a) < 0.05 compared to the normal control. p(b) < 0.05 compared to the gastric ulcer model.
3.5 Effects of diosgenin on histopathological changes
Histopathological observations of the normal and experimental rats are shown in Figure 6. The histopathology of the HCl/ethanol-induced gastric injury model showed signs of epithelial cell loss, submucosal edema, hemorrhage, and infiltration of inflammatory cells, indicating mucosal injury compared to the normal rats, which showed normal arrangements and glandular structure of the gastric mucosa. The histopathological scores indicate the mucosal damage caused by HCl/ethanol and the protective measure by diosgenin. Diosgenin administration prevented the changes in rat gastric mucosa by reducing the damage caused by HCl/ethanol, which was comparable to the results of the omeprazole-treated group.
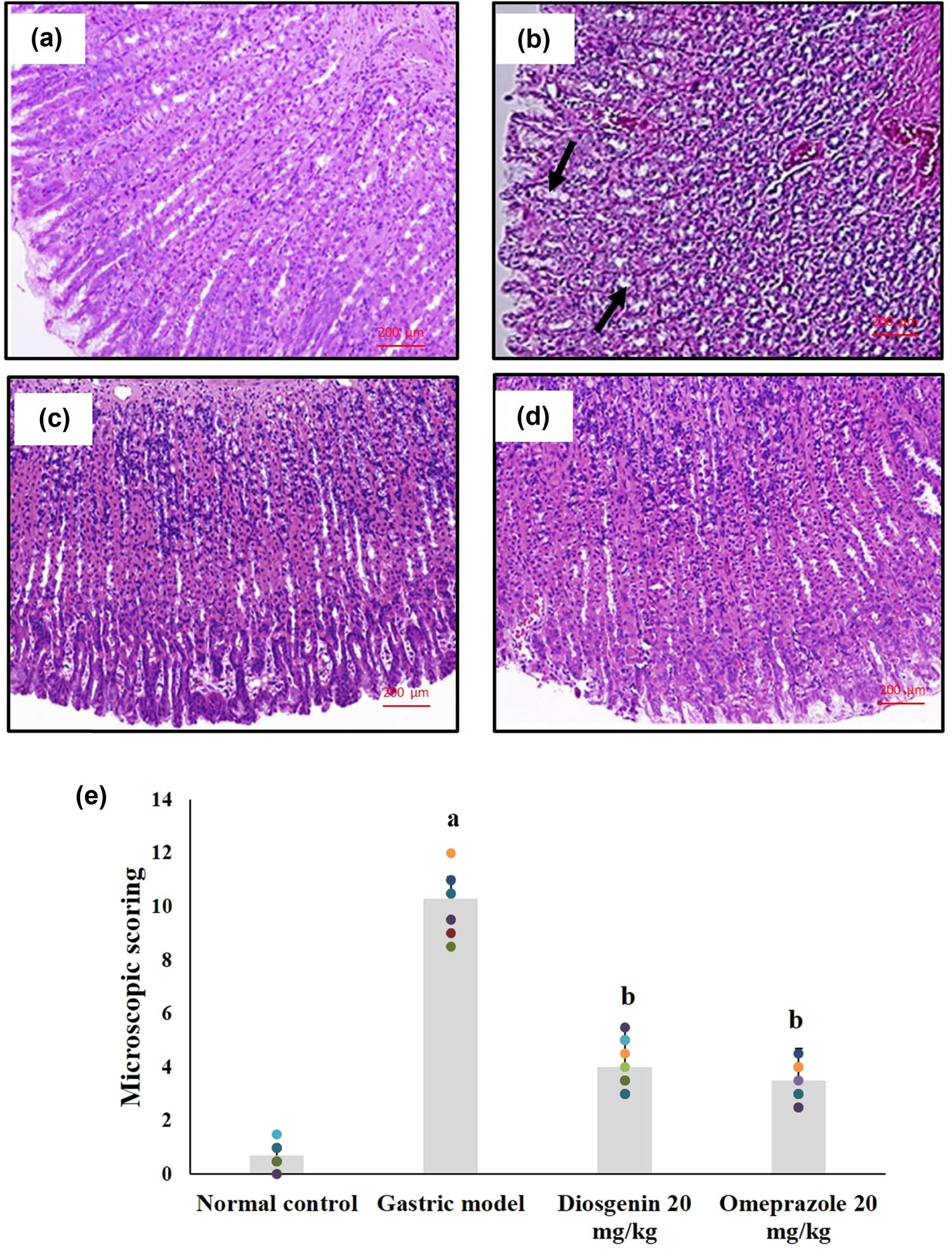
Histopathological changes due to HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury and the protective effects of diosgenin. (a) Normal control; (b) gastric model with prominent mucosal injury; (c) diosgenin 20 mg/kg treated gastric tissue with mild mucosal injury; and (d) omeprazole 20 mg/kg treated gastric tissue with very mild mucosal injury. Magnification at 100×. (e) Histopathological scoring of gastric mucosal injury. p(a) < 0.05 compared to the normal control. p(b) < 0.05 compared to the gastric ulcer model.
3.6 Effects of diosgenin on NF-κβ activation
Western blot analysis on the HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury-related NF-κβ pathway provided evidence that NF-κβ was activated in the gastric model group by phosphorylation of the subunits as demonstrated by the ratio of phosphorylation in Figure 7. HCl/ethanol administration induced the expression of phosphorylated p65 NF-κβ and Iκβα in the gastric model group compared to the normal control group. Diosgenin significantly suppressed the expressions of phosphorylated Iκβα and p65 NF-κβ compared to the gastric model group.
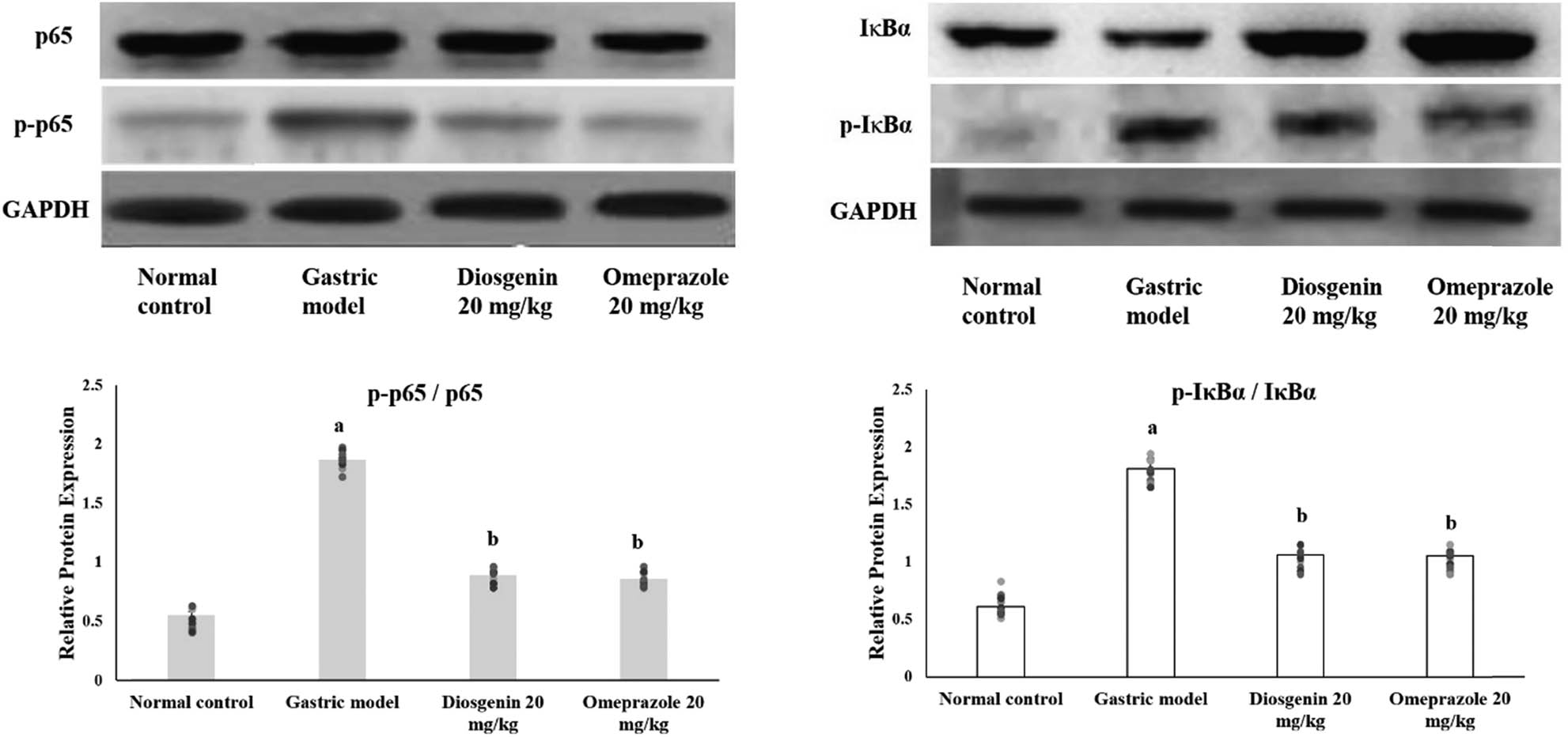
Western blot analysis on NF-κβ in HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury and the protective effects of diosgenin. Phosphorylation ratio of p65 NF-κβ and IκBα was quantified and displayed as bar graphs. The bar graphs are the demonstration of three independent results of the western blot analysis, expressed as mean ± SEM. p(a) < 0.05 compared to the normal control. p(b) < 0.05 compared to the gastric ulcer model. GAPDH was used as the internal standard.
4 Discussion
The present study demonstrated gastroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of diosgenin against gastric mucosal damage due to HCl/ethanol in rats for the first time. Similar to the previous studies, HCl/ethanol administration caused severe gastric mucosal damage that was observed through gastric ulcer index and histopathological changes with signs of epithelial cell loss, submucosal edema, and hemorrhage [23,24]. Intragastric administration of diosgenin significantly reversed the HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage as demonstrated in the results. The gastroprotective effects of diosgenin have similar findings with other bioactive compounds tested in past studies against chemically induced gastric injury in animal models [23,24,25,26,27]. The gastroprotective results of the reported bioactive compounds are associated with their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. In this study, diosgenin was able to increase antioxidant GSH and enzymatic CAT, GPx, and SOD in HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in a similar style to the reference drug omeprazole. Antioxidant enzymes and GSH are regulators of ROS and other free radicals by maintaining the equilibrium of concentration of free radicals formed and scavenged to prevent oxidative stress [8]. Lipid peroxidation is a process of oxidation of lipids forming the cellular membrane by excessive free radicals formed during oxidative stress conditions [3]. The gastric injury model rats were in a state of oxidative stress due to the increased levels of MDA, suppressed NO levels, and diminished GSH, GPx, SOD, and CAT activities. Oxidative stress often leads to the pathophysiology of many diseases including gastric mucosal injury and ulcer [26]. The levels of MDA were incisively reduced, and the NO levels were replenished by intragastric administration of diosgenin. HCl/ethanol administration triggers endogenous inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) enzyme, causing the suppression of NO production. It has been reported that the increased NO levels help the healing of gastric mucosal injury [8]. Therefore, the antioxidant activity of diosgenin was prevailing in the results through prevention of oxidative stress and prevention of the inhibition of NOS.
Anti-inflammatory effects of diosgenin were proven in the results of the ELISA assay on IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, where diosgenin suppressed activities of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The gastric injury model rats were having severe inflammation at the site of gastric mucosal injury evidenced by the ELISA assay results on pro-inflammatory cytokines and the histopathological findings of inflammatory cells infiltration. TNF-α and IL-6 are predominantly involved in the inflammatory reaction in gastric mucosal injury by recruiting other inflammatory mediators to the site of injury and also triggers oxidative stress [27]. Accumulation of these pro-inflammatory cytokines increases the damage to surrounding gastric cells. Suppressing these pro-inflammatory cytokines could be a potent therapeutic approach to cure gastric mucosal damage. The activity of MPO is directly related to the inflammatory process during gastric mucosal damage. Increased MPO activity is an indicator for high neutrophil infiltration to the site of gastric mucosal damage since MPOs are released by stimulated neutrophils [28]. The MPO activity of the HCl/ethanol-initiated gastric mucosal damage model group indicated the high rate of neutrophil infiltration. Diosgenin administration significantly reduced the MPO activities. NF-κβ is an important factor in triggering inflammatory reactions, which has control over genes of inflammatory mediators. Translocation of NF-κβ into the nucleus initiates the transcription of TNF-α, IL-6, and other inflammatory markers. Previous studies on the involvement of NF-κβ in gastric mucosal injuries make it an important target for the therapeutic effect of gastric injuries [29,30]. Diosgenin significantly prevented the translocation of NF-κβ as evidenced by the western blot results. Therefore, the anti-inflammatory role of diosgenin and gastroprotective effects might be due to the downregulation of NF-κβ and inhibition of MPO activities through the prevention of inflammatory cells infiltration.
5 Conclusion
Overall, this study finds that diosgenin has significant gastroprotective and anti-inflammatory roles against HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. The antioxidant effects of diosgenin significantly attenuated oxidative stress by improving the antioxidant enzyme activities, reducing MDA and NO formations. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory role of diosgenin was exerted by downregulation of NF-κβ and MPO in the stomach of HCl/ethanol-induced rats comparable to the action of the commercial drug omeprazole. Therefore, diosgenin can be promoted as an important food ingredient to prevent gastric injury. Further researches are needed to determine the safe dose and toxicity levels of the compound before be included as an essential food additive.
-
Author contributions: H.Z. wrote the manuscript, performed the experiments, and analyzed the data; X.Z. and B.Z. wrote the manuscript and analyzed the data statistically; X.Q. prepared the experimental design, conducted the experiment, and edited the manuscript.
-
Funding information: The authors state no funding involved.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Koc K, Cerig S, Ucar S, Colak S, Bakir M, Erol HS, et al. Gastroprotective effects of oleuropein and thymol on indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in Sprague-Dawley rats. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2020;43:441–53. 10.1080/01480545.2018.1530261.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Amirshahrokhi K, Khalili AR. Gastroprotective effect of 2-mercaptoethane sulfonate against acute gastric mucosal damage induced by ethanol. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;34:183–8. 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.03.006.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Chatterjee A, Chattopadhyay S, Bandyopadhyay SK. Biphasic effect of Phyllanthus emblica L. extract on NSAID-induced ulcer: an antioxidative trail weaved with immunomodulatory effect. Evid-Based Compl Alt Med. 2011;2011:146808. 10.1155/2011/146808.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Song H, Hou X, Zeng M, Chen X, Chen X, Yang T, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine Li-Zhong-Tang accelerates the healing of indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers in rats by affecting TLR-2/MyD88 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;259:112979. 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112979.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Paturi G, Butts CA, Bentley-Hewitt KL, Mcghie TK, Saleh ZS, Mcleod A. Apple polyphenol extracts protect against aspirin-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. Phytother Res. 2014;28:1846–54. 10.1002/ptr.5210.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Rozza AL, Meira de Faria F, Souza Brito AR, Pellizzon CH. The gastroprotective effect of menthol: involvement of anti-apoptotic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e86686. 10.1371/journal.pone.0086686.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Hamza AA, Ahmed MM, Elwey HM, Amin A. Melissa officinalis protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats and potentiates its anticancer activity on MCF-7 cells. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0167049. 10.1371/journal.pone.0167049.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Karampour NS, Arzi A, Rezaie A, Pashmforoosh M, Kordi F. Gastroprotective effect of zingerone on ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in rats. Medicina. 2019;55:64. 10.3390/medicina55030064.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Li W, Wang X, Zhang H, He Z, Zhi W, Liu F, et al. Anti-ulcerogenic effect of cavidine against ethanol-induced acute gastric ulcer in mice and possible underlying mechanism. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;38:450–9. 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.06.016.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Binic I, Lazarevic V, Ljubenovic M, Mojsa J, Sokolovic D. Skin ageing: natural weapons and strategies. Evid-Based Compl Alt Med. 2013;2013:827248. 10.1155/2013/827248.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Jesus M, Martins AP, Gallardo E, Silvestre S. Diosgenin: recent highlights on pharmacology and analytical methodology. J Anal Method Chem. 2016;2016:4156293. 10.1155/2016/4156293.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Zhang L, Li S, Ma D, Du X, Zhou S, Song Y. Protective effects of diosgenin against ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation-induced inflammation in human dermal fibroblasts. Int J Pharmacol. 2019;15:623–8. 10.3923/ijp.2019.623.628.Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Chen Z, Xu J, Wu Y, Lei S, Liu H, Meng Q, et al. Diosgenin inhibited the expression of TAZ in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 2018;503:1181–5. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.022.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Li R, Liu Y, Shi J, Yu Y, Lu H, Yu L, et al. Diosgenin regulates cholesterol metabolism in hypercholesterolemic rats by inhibiting NPC1L1 and enhancing ABCG5 and ABCG8. BBA – Mol Cell Biol Lipid. 2019;1864:1124–33. 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.04.010.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Marín-Medina A, Ruíz-Hidalgo G, Blé-Castillo J, Zetina-Esquivel A, Zamora R, Juárez-Rojop I, et al. Combined effect of diosgenin along with ezetimibe or atorvastatin on the fate of labelled bile acid and cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic rats. Int J Env Res Pub Health. 2019;16:627. 10.3390/ijerph16040627.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Zhang Z, Chen Y, Xiang L, Wang Z, Xiao G, Ju D. Diosgenin protects against alveolar bone loss in ovariectomized rats via regulating long non-coding RNAs. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16:3939–50. 10.3892/etm.2018.6681.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Chen XB, Wang ZL, Yang QY, Zhao FY, Qin XL, Tang XE, et al. Diosgenin glucoside protects against spinal cord injury by regulating autophagy and alleviating apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:2274. 10.3390/ijms19082274.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Khosravi Z, Sedaghat R, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M. Diosgenin ameliorates testicular damage in streptozotocin-diabetic rats through attenuation of apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;70:37–46. 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.01.047.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Li B, Xu P, Wu S, Jiang Z, Huang Z, Li Q, et al. Diosgenin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced Parkinson’s disease by inhibiting the TLR/NF-κB pathway. J Alzh Dis. 2018;64:943–55. 10.3233/jad-180330.Suche in Google Scholar
[20] Kiss R, Pesti-Asbóth G, Szarvas MM, Stündl L, Cziáky Z, Hegedűs C, et al. Diosgenin and its fenugreek based biological matrix affect insulin resistance and anabolic hormones in a rat based insulin resistance model. BioMed Res Int. 2019;2019:7213913. 10.1155/2019/7213913.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Yang Y, Yin B, Lv L, Wang Z, He J, Chen Z, et al. Gastroprotective effect of aucubin against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice. Life Sci. 2017;189:44–51. 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.09.016.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] El-Maraghy SA, Rizk SM, Shahin NN. Gastroprotective effect of crocin in ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats. Chem-Biol Inter. 2015;229:26–35. 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.01.015.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Li W, Wang X, Zhi W, Zhang H, He Z, Wang Y, et al. The gastroprotective effect of nobiletin against ethanol-induced acute gastric lesions in mice: impact on oxidative stress and inflammation. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2017;39:354–63. 10.1080/08923973.2017.1379088.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Karaboğa I, Ovalı MA, Yılmaz A, Alpaslan M. Gastroprotective effect of apricot kernel oil in ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. Biotech Histochem. 2018;93:601–7. 10.1080/10520295.2018.1511064.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Katary MA, Salahuddin A. Gastroprotective effect of punicalagin against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer: The possible underlying mechanisms. Biomark J. 2017;3:3. 10.21767/2472-1646.100025.Suche in Google Scholar
[26] Allam MM, El-Gohary OA. Gastroprotective effect of ghrelin against indomethacin-induced gastric injury in rats: possible role of heme oxygenase-1 pathway. Gen physiol biophys. 2017;36:321–30. 10.4149/gpb_2016056.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Song JW, Seo CS, Kim TI, Moon OS, Won YS, Son HY, et al. Protective effects of Manassantin A against ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2016;39(2):221–9. 10.1248/bpb.b15-00642.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Yang J, Zhou W, Gu Y, Dai J, Li X, Tai P, et al. Protective effect of Pu-erh tea extracts against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. Biomed Rep. 2018;8:335–42. 10.3892/br.2018.1068.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Li WF, Hao DJ, Fan T, Huang HM, Yao H, Niu XF. Protective effect of chelerythrine against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in mice. Chem-Biol Inter. 2014;208:18–27. 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.11.011.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Li W, Huang H, Niu X, Fan T, Mu Q, Li H. Protective effect of tetrahydrocoptisine against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013;272:21–9. 10.1016/j.taap.2013.05.035.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2021 Hengfang Zhao et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Biomedical Sciences
- Research progress on the mechanism of orexin in pain regulation in different brain regions
- Adriamycin-resistant cells are significantly less fit than adriamycin-sensitive cells in cervical cancer
- Exogenous spermidine affects polyamine metabolism in the mouse hypothalamus
- Iris metastasis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma misdiagnosed as primary angle-closure glaucoma: A case report and review of the literature
- LncRNA PVT1 promotes cervical cancer progression by sponging miR-503 to upregulate ARL2 expression
- Two new inflammatory markers related to the CURB-65 score for disease severity in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: The hypersensitive C-reactive protein to albumin ratio and fibrinogen to albumin ratio
- Circ_0091579 enhances the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma via miR-1287/PDK2 axis
- Silencing XIST mitigated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory injury in human lung fibroblast WI-38 cells through modulating miR-30b-5p/CCL16 axis and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats
- ABCB1 polymorphism in clopidogrel-treated Montenegrin patients
- Metabolic profiling of fatty acids in Tripterygium wilfordii multiglucoside- and triptolide-induced liver-injured rats
- miR-338-3p inhibits cell growth, invasion, and EMT process in neuroblastoma through targeting MMP-2
- Verification of neuroprotective effects of alpha-lipoic acid on chronic neuropathic pain in a chronic constriction injury rat model
- Circ_WWC3 overexpression decelerates the progression of osteosarcoma by regulating miR-421/PDE7B axis
- Knockdown of TUG1 rescues cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through targeting the miR-497/MEF2C axis
- MiR-146b-3p protects against AR42J cell injury in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis model through targeting Anxa2
- miR-299-3p suppresses cell progression and induces apoptosis by downregulating PAX3 in gastric cancer
- Diabetes and COVID-19
- Discovery of novel potential KIT inhibitors for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- TEAD4 is a novel independent predictor of prognosis in LGG patients with IDH mutation
- circTLK1 facilitates the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating miR-495-3p/CBL axis
- microRNA-9-5p protects liver sinusoidal endothelial cell against oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury
- Long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-320c/MMP-13 axis in osteoarthritis
- Duodenal adenocarcinoma with skin metastasis as initial manifestation: A case report
- Effects of Loofah cylindrica extract on learning and memory ability, brain tissue morphology, and immune function of aging mice
- Recombinant Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin-1 (rBFT-1) promotes proliferation of colorectal cancer via CCL3-related molecular pathways
- Blocking circ_UBR4 suppressed proliferation, migration, and cell cycle progression of human vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis
- Gene therapy in PIDs, hemoglobin, ocular, neurodegenerative, and hemophilia B disorders
- Downregulation of circ_0037655 impedes glioma formation and metastasis via the regulation of miR-1229-3p/ITGB8 axis
- Vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes population
- Circ_0013359 facilitates the tumorigenicity of melanoma by regulating miR-136-5p/RAB9A axis
- Mechanisms of circular RNA circ_0066147 on pancreatic cancer progression
- lncRNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) knockdown alleviates LPS-induced chondrocytes inflammatory injury via regulating miR-488-3p/sex determining region Y-related HMG-box 11 (SOX11) axis
- Identification of circRNA circ-CSPP1 as a potent driver of colorectal cancer by directly targeting the miR-431/LASP1 axis
- Hyperhomocysteinemia exacerbates ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced acute kidney injury by mediating oxidative stress, DNA damage, JNK pathway, and apoptosis
- Potential prognostic markers and significant lncRNA–mRNA co-expression pairs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Gamma irradiation-mediated inactivation of enveloped viruses with conservation of genome integrity: Potential application for SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine development
- ADHFE1 is a correlative factor of patient survival in cancer
- The association of transcription factor Prox1 with the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer
- Is there a relationship between the prevalence of autoimmune thyroid disease and diabetic kidney disease?
- Immunoregulatory function of Dictyophora echinovolvata spore polysaccharides in immunocompromised mice induced by cyclophosphamide
- T cell epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and conserved surface protein of Plasmodium malariae share sequence homology
- Anti-obesity effect and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells influence on obese mice
- Long noncoding RNA HULC contributes to paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer via miR-137/ITGB8 axis
- Glucocorticoids protect HEI-OC1 cells from tunicamycin-induced cell damage via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning
- Gastroprotective effects of diosgenin against HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury through suppression of NF-κβ and myeloperoxidase activities
- Silencing of LINC00707 suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by modulating miR-338-3p/AHSA1 axis
- Successful extracorporeal membrane oxygenation resuscitation of patient with cardiogenic shock induced by phaeochromocytoma crisis mimicking hyperthyroidism: A case report
- Effects of miR-185-5p on replication of hepatitis C virus
- Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis
- Primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis presenting as lymphatic malformation: A case report
- Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging analysis in the characteristics of Wilson’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Therapeutic potential of anticoagulant therapy in association with cytokine storm inhibition in severe cases of COVID-19: A case report
- Neoadjuvant immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy for locally advanced squamous cell lung carcinoma: A case report and literature review
- Rufinamide (RUF) suppresses inflammation and maintains the integrity of the blood–brain barrier during kainic acid-induced brain damage
- Inhibition of ADAM10 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiac remodeling by suppressing N-cadherin cleavage
- Invasive ductal carcinoma and small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia manifesting as a collision breast tumor: A case report and literature review
- Clonal diversity of the B cell receptor repertoire in patients with coronary in-stent restenosis and type 2 diabetes
- CTLA-4 promotes lymphoma progression through tumor stem cell enrichment and immunosuppression
- WDR74 promotes proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Down-regulation of IGHG1 enhances Protoporphyrin IX accumulation and inhibits hemin biosynthesis in colorectal cancer by suppressing the MEK-FECH axis
- Curcumin suppresses the progression of gastric cancer by regulating circ_0056618/miR-194-5p axis
- Scutellarin-induced A549 cell apoptosis depends on activation of the transforming growth factor-β1/smad2/ROS/caspase-3 pathway
- lncRNA NEAT1 regulates CYP1A2 and influences steroid-induced necrosis
- A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer
- Isolation of microglia from retinas of chronic ocular hypertensive rats
- Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study
- Calcineurin Aβ gene knockdown inhibits transient outward potassium current ion channel remodeling in hypertrophic ventricular myocyte
- Aberrant expression of PI3K/AKT signaling is involved in apoptosis resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Clinical significance of activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling in apoptosis inhibition of oral cancer
- circ_CHFR regulates ox-LDL-mediated cell proliferation, apoptosis, and EndoMT by miR-15a-5p/EGFR axis in human brain microvessel endothelial cells
- Resveratrol pretreatment mitigates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating conventional dendritic cells’ maturation and function
- Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T promotes tumor stem cell characteristics and migration of cervical cancer cells by regulating the GRP78/FAK pathway
- Carriage of HLA-DRB1*11 and 1*12 alleles and risk factors in patients with breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- Protective effect of Lactobacillus-containing probiotics on intestinal mucosa of rats experiencing traumatic hemorrhagic shock
- Glucocorticoids induce osteonecrosis of the femoral head through the Hippo signaling pathway
- Endothelial cell-derived SSAO can increase MLC20 phosphorylation in VSMCs
- Downregulation of STOX1 is a novel prognostic biomarker for glioma patients
- miR-378a-3p regulates glioma cell chemosensitivity to cisplatin through IGF1R
- The molecular mechanisms underlying arecoline-induced cardiac fibrosis in rats
- TGF-β1-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate Th17/Treg cells by regulating the expression of IFN-γ
- The influence of MTHFR genetic polymorphisms on methotrexate therapy in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Red blood cell distribution width-standard deviation but not red blood cell distribution width-coefficient of variation as a potential index for the diagnosis of iron-deficiency anemia in mid-pregnancy women
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma expressing alpha fetoprotein in the endometrium
- Superoxide dismutase and the sigma1 receptor as key elements of the antioxidant system in human gastrointestinal tract cancers
- Molecular characterization and phylogenetic studies of Echinococcus granulosus and Taenia multiceps coenurus cysts in slaughtered sheep in Saudi Arabia
- ITGB5 mutation discovered in a Chinese family with blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome
- ACTB and GAPDH appear at multiple SDS-PAGE positions, thus not suitable as reference genes for determining protein loading in techniques like Western blotting
- Facilitation of mouse skin-derived precursor growth and yield by optimizing plating density
- 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethanol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiac injury in a murine model
- Downregulation of PITX2 inhibits the proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells and induces cell apoptosis
- Expression of CDK9 in endometrial cancer tissues and its effect on the proliferation of HEC-1B
- Novel predictor of the occurrence of DKA in T1DM patients without infection: A combination of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and white blood cells
- Investigation of molecular regulation mechanism under the pathophysiology of subarachnoid hemorrhage
- miR-25-3p protects renal tubular epithelial cells from apoptosis induced by renal IRI by targeting DKK3
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Green fabrication of Co and Co3O4 nanoparticles and their biomedical applications: A review
- Agriculture
- Effects of inorganic and organic selenium sources on the growth performance of broilers in China: A meta-analysis
- Crop-livestock integration practices, knowledge, and attitudes among smallholder farmers: Hedging against climate change-induced shocks in semi-arid Zimbabwe
- Food Science and Nutrition
- Effect of food processing on the antioxidant activity of flavones from Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce
- Vitamin D and iodine status was associated with the risk and complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China
- Diversity of microbiota in Slovak summer ewes’ cheese “Bryndza”
- Comparison between voltammetric detection methods for abalone-flavoring liquid
- Composition of low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and their effects on the rheological properties of dough
- Application of culture, PCR, and PacBio sequencing for determination of microbial composition of milk from subclinical mastitis dairy cows of smallholder farms
- Investigating microplastics and potentially toxic elements contamination in canned Tuna, Salmon, and Sardine fishes from Taif markets, KSA
- From bench to bar side: Evaluating the red wine storage lesion
- Establishment of an iodine model for prevention of iodine-excess-induced thyroid dysfunction in pregnant women
- Plant Sciences
- Characterization of GMPP from Dendrobium huoshanense yielding GDP-D-mannose
- Comparative analysis of the SPL gene family in five Rosaceae species: Fragaria vesca, Malus domestica, Prunus persica, Rubus occidentalis, and Pyrus pyrifolia
- Identification of leaf rust resistance genes Lr34 and Lr46 in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ssp. aestivum) lines of different origin using multiplex PCR
- Investigation of bioactivities of Taxus chinensis, Taxus cuspidata, and Taxus × media by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Morphological structures and histochemistry of roots and shoots in Myricaria laxiflora (Tamaricaceae)
- Transcriptome analysis of resistance mechanism to potato wart disease
- In silico analysis of glycosyltransferase 2 family genes in duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) and its role in salt stress tolerance
- Comparative study on growth traits and ions regulation of zoysiagrasses under varied salinity treatments
- Role of MS1 homolog Ntms1 gene of tobacco infertility
- Biological characteristics and fungicide sensitivity of Pyricularia variabilis
- In silico/computational analysis of mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase gene families in Campanulids
- Identification of novel drought-responsive miRNA regulatory network of drought stress response in common vetch (Vicia sativa)
- How photoautotrophy, photomixotrophy, and ventilation affect the stomata and fluorescence emission of pistachios rootstock?
- Apoplastic histochemical features of plant root walls that may facilitate ion uptake and retention
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- The impact of sewage sludge on the fungal communities in the rhizosphere and roots of barley and on barley yield
- Domestication of wild animals may provide a springboard for rapid variation of coronavirus
- Response of benthic invertebrate assemblages to seasonal and habitat condition in the Wewe River, Ashanti region (Ghana)
- Molecular record for the first authentication of Isaria cicadae from Vietnam
- Twig biomass allocation of Betula platyphylla in different habitats in Wudalianchi Volcano, northeast China
- Animal Sciences
- Supplementation of probiotics in water beneficial growth performance, carcass traits, immune function, and antioxidant capacity in broiler chickens
- Predators of the giant pine scale, Marchalina hellenica (Gennadius 1883; Hemiptera: Marchalinidae), out of its natural range in Turkey
- Honey in wound healing: An updated review
- NONMMUT140591.1 may serve as a ceRNA to regulate Gata5 in UT-B knockout-induced cardiac conduction block
- Radiotherapy for the treatment of pulmonary hydatidosis in sheep
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Long non-coding RNA TUG1 knockdown hinders the tumorigenesis of multiple myeloma by regulating microRNA-34a-5p/NOTCH1 signaling pathway”
- Special Issue on Reuse of Agro-Industrial By-Products
- An effect of positional isomerism of benzoic acid derivatives on antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli
- Special Issue on Computing and Artificial Techniques for Life Science Applications - Part II
- Relationship of Gensini score with retinal vessel diameter and arteriovenous ratio in senile CHD
- Effects of different enantiomers of amlodipine on lipid profiles and vasomotor factors in atherosclerotic rabbits
- Establishment of the New Zealand white rabbit animal model of fatty keratopathy associated with corneal neovascularization
- lncRNA MALAT1/miR-143 axis is a potential biomarker for in-stent restenosis and is involved in the multiplication of vascular smooth muscle cells
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Biomedical Sciences
- Research progress on the mechanism of orexin in pain regulation in different brain regions
- Adriamycin-resistant cells are significantly less fit than adriamycin-sensitive cells in cervical cancer
- Exogenous spermidine affects polyamine metabolism in the mouse hypothalamus
- Iris metastasis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma misdiagnosed as primary angle-closure glaucoma: A case report and review of the literature
- LncRNA PVT1 promotes cervical cancer progression by sponging miR-503 to upregulate ARL2 expression
- Two new inflammatory markers related to the CURB-65 score for disease severity in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: The hypersensitive C-reactive protein to albumin ratio and fibrinogen to albumin ratio
- Circ_0091579 enhances the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma via miR-1287/PDK2 axis
- Silencing XIST mitigated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory injury in human lung fibroblast WI-38 cells through modulating miR-30b-5p/CCL16 axis and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats
- ABCB1 polymorphism in clopidogrel-treated Montenegrin patients
- Metabolic profiling of fatty acids in Tripterygium wilfordii multiglucoside- and triptolide-induced liver-injured rats
- miR-338-3p inhibits cell growth, invasion, and EMT process in neuroblastoma through targeting MMP-2
- Verification of neuroprotective effects of alpha-lipoic acid on chronic neuropathic pain in a chronic constriction injury rat model
- Circ_WWC3 overexpression decelerates the progression of osteosarcoma by regulating miR-421/PDE7B axis
- Knockdown of TUG1 rescues cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through targeting the miR-497/MEF2C axis
- MiR-146b-3p protects against AR42J cell injury in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis model through targeting Anxa2
- miR-299-3p suppresses cell progression and induces apoptosis by downregulating PAX3 in gastric cancer
- Diabetes and COVID-19
- Discovery of novel potential KIT inhibitors for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- TEAD4 is a novel independent predictor of prognosis in LGG patients with IDH mutation
- circTLK1 facilitates the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating miR-495-3p/CBL axis
- microRNA-9-5p protects liver sinusoidal endothelial cell against oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury
- Long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-320c/MMP-13 axis in osteoarthritis
- Duodenal adenocarcinoma with skin metastasis as initial manifestation: A case report
- Effects of Loofah cylindrica extract on learning and memory ability, brain tissue morphology, and immune function of aging mice
- Recombinant Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin-1 (rBFT-1) promotes proliferation of colorectal cancer via CCL3-related molecular pathways
- Blocking circ_UBR4 suppressed proliferation, migration, and cell cycle progression of human vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis
- Gene therapy in PIDs, hemoglobin, ocular, neurodegenerative, and hemophilia B disorders
- Downregulation of circ_0037655 impedes glioma formation and metastasis via the regulation of miR-1229-3p/ITGB8 axis
- Vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes population
- Circ_0013359 facilitates the tumorigenicity of melanoma by regulating miR-136-5p/RAB9A axis
- Mechanisms of circular RNA circ_0066147 on pancreatic cancer progression
- lncRNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) knockdown alleviates LPS-induced chondrocytes inflammatory injury via regulating miR-488-3p/sex determining region Y-related HMG-box 11 (SOX11) axis
- Identification of circRNA circ-CSPP1 as a potent driver of colorectal cancer by directly targeting the miR-431/LASP1 axis
- Hyperhomocysteinemia exacerbates ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced acute kidney injury by mediating oxidative stress, DNA damage, JNK pathway, and apoptosis
- Potential prognostic markers and significant lncRNA–mRNA co-expression pairs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Gamma irradiation-mediated inactivation of enveloped viruses with conservation of genome integrity: Potential application for SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine development
- ADHFE1 is a correlative factor of patient survival in cancer
- The association of transcription factor Prox1 with the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer
- Is there a relationship between the prevalence of autoimmune thyroid disease and diabetic kidney disease?
- Immunoregulatory function of Dictyophora echinovolvata spore polysaccharides in immunocompromised mice induced by cyclophosphamide
- T cell epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and conserved surface protein of Plasmodium malariae share sequence homology
- Anti-obesity effect and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells influence on obese mice
- Long noncoding RNA HULC contributes to paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer via miR-137/ITGB8 axis
- Glucocorticoids protect HEI-OC1 cells from tunicamycin-induced cell damage via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning
- Gastroprotective effects of diosgenin against HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury through suppression of NF-κβ and myeloperoxidase activities
- Silencing of LINC00707 suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by modulating miR-338-3p/AHSA1 axis
- Successful extracorporeal membrane oxygenation resuscitation of patient with cardiogenic shock induced by phaeochromocytoma crisis mimicking hyperthyroidism: A case report
- Effects of miR-185-5p on replication of hepatitis C virus
- Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis
- Primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis presenting as lymphatic malformation: A case report
- Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging analysis in the characteristics of Wilson’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Therapeutic potential of anticoagulant therapy in association with cytokine storm inhibition in severe cases of COVID-19: A case report
- Neoadjuvant immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy for locally advanced squamous cell lung carcinoma: A case report and literature review
- Rufinamide (RUF) suppresses inflammation and maintains the integrity of the blood–brain barrier during kainic acid-induced brain damage
- Inhibition of ADAM10 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiac remodeling by suppressing N-cadherin cleavage
- Invasive ductal carcinoma and small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia manifesting as a collision breast tumor: A case report and literature review
- Clonal diversity of the B cell receptor repertoire in patients with coronary in-stent restenosis and type 2 diabetes
- CTLA-4 promotes lymphoma progression through tumor stem cell enrichment and immunosuppression
- WDR74 promotes proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Down-regulation of IGHG1 enhances Protoporphyrin IX accumulation and inhibits hemin biosynthesis in colorectal cancer by suppressing the MEK-FECH axis
- Curcumin suppresses the progression of gastric cancer by regulating circ_0056618/miR-194-5p axis
- Scutellarin-induced A549 cell apoptosis depends on activation of the transforming growth factor-β1/smad2/ROS/caspase-3 pathway
- lncRNA NEAT1 regulates CYP1A2 and influences steroid-induced necrosis
- A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer
- Isolation of microglia from retinas of chronic ocular hypertensive rats
- Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study
- Calcineurin Aβ gene knockdown inhibits transient outward potassium current ion channel remodeling in hypertrophic ventricular myocyte
- Aberrant expression of PI3K/AKT signaling is involved in apoptosis resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Clinical significance of activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling in apoptosis inhibition of oral cancer
- circ_CHFR regulates ox-LDL-mediated cell proliferation, apoptosis, and EndoMT by miR-15a-5p/EGFR axis in human brain microvessel endothelial cells
- Resveratrol pretreatment mitigates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating conventional dendritic cells’ maturation and function
- Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T promotes tumor stem cell characteristics and migration of cervical cancer cells by regulating the GRP78/FAK pathway
- Carriage of HLA-DRB1*11 and 1*12 alleles and risk factors in patients with breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- Protective effect of Lactobacillus-containing probiotics on intestinal mucosa of rats experiencing traumatic hemorrhagic shock
- Glucocorticoids induce osteonecrosis of the femoral head through the Hippo signaling pathway
- Endothelial cell-derived SSAO can increase MLC20 phosphorylation in VSMCs
- Downregulation of STOX1 is a novel prognostic biomarker for glioma patients
- miR-378a-3p regulates glioma cell chemosensitivity to cisplatin through IGF1R
- The molecular mechanisms underlying arecoline-induced cardiac fibrosis in rats
- TGF-β1-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate Th17/Treg cells by regulating the expression of IFN-γ
- The influence of MTHFR genetic polymorphisms on methotrexate therapy in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Red blood cell distribution width-standard deviation but not red blood cell distribution width-coefficient of variation as a potential index for the diagnosis of iron-deficiency anemia in mid-pregnancy women
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma expressing alpha fetoprotein in the endometrium
- Superoxide dismutase and the sigma1 receptor as key elements of the antioxidant system in human gastrointestinal tract cancers
- Molecular characterization and phylogenetic studies of Echinococcus granulosus and Taenia multiceps coenurus cysts in slaughtered sheep in Saudi Arabia
- ITGB5 mutation discovered in a Chinese family with blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome
- ACTB and GAPDH appear at multiple SDS-PAGE positions, thus not suitable as reference genes for determining protein loading in techniques like Western blotting
- Facilitation of mouse skin-derived precursor growth and yield by optimizing plating density
- 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethanol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiac injury in a murine model
- Downregulation of PITX2 inhibits the proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells and induces cell apoptosis
- Expression of CDK9 in endometrial cancer tissues and its effect on the proliferation of HEC-1B
- Novel predictor of the occurrence of DKA in T1DM patients without infection: A combination of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and white blood cells
- Investigation of molecular regulation mechanism under the pathophysiology of subarachnoid hemorrhage
- miR-25-3p protects renal tubular epithelial cells from apoptosis induced by renal IRI by targeting DKK3
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Green fabrication of Co and Co3O4 nanoparticles and their biomedical applications: A review
- Agriculture
- Effects of inorganic and organic selenium sources on the growth performance of broilers in China: A meta-analysis
- Crop-livestock integration practices, knowledge, and attitudes among smallholder farmers: Hedging against climate change-induced shocks in semi-arid Zimbabwe
- Food Science and Nutrition
- Effect of food processing on the antioxidant activity of flavones from Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce
- Vitamin D and iodine status was associated with the risk and complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China
- Diversity of microbiota in Slovak summer ewes’ cheese “Bryndza”
- Comparison between voltammetric detection methods for abalone-flavoring liquid
- Composition of low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and their effects on the rheological properties of dough
- Application of culture, PCR, and PacBio sequencing for determination of microbial composition of milk from subclinical mastitis dairy cows of smallholder farms
- Investigating microplastics and potentially toxic elements contamination in canned Tuna, Salmon, and Sardine fishes from Taif markets, KSA
- From bench to bar side: Evaluating the red wine storage lesion
- Establishment of an iodine model for prevention of iodine-excess-induced thyroid dysfunction in pregnant women
- Plant Sciences
- Characterization of GMPP from Dendrobium huoshanense yielding GDP-D-mannose
- Comparative analysis of the SPL gene family in five Rosaceae species: Fragaria vesca, Malus domestica, Prunus persica, Rubus occidentalis, and Pyrus pyrifolia
- Identification of leaf rust resistance genes Lr34 and Lr46 in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ssp. aestivum) lines of different origin using multiplex PCR
- Investigation of bioactivities of Taxus chinensis, Taxus cuspidata, and Taxus × media by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Morphological structures and histochemistry of roots and shoots in Myricaria laxiflora (Tamaricaceae)
- Transcriptome analysis of resistance mechanism to potato wart disease
- In silico analysis of glycosyltransferase 2 family genes in duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) and its role in salt stress tolerance
- Comparative study on growth traits and ions regulation of zoysiagrasses under varied salinity treatments
- Role of MS1 homolog Ntms1 gene of tobacco infertility
- Biological characteristics and fungicide sensitivity of Pyricularia variabilis
- In silico/computational analysis of mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase gene families in Campanulids
- Identification of novel drought-responsive miRNA regulatory network of drought stress response in common vetch (Vicia sativa)
- How photoautotrophy, photomixotrophy, and ventilation affect the stomata and fluorescence emission of pistachios rootstock?
- Apoplastic histochemical features of plant root walls that may facilitate ion uptake and retention
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- The impact of sewage sludge on the fungal communities in the rhizosphere and roots of barley and on barley yield
- Domestication of wild animals may provide a springboard for rapid variation of coronavirus
- Response of benthic invertebrate assemblages to seasonal and habitat condition in the Wewe River, Ashanti region (Ghana)
- Molecular record for the first authentication of Isaria cicadae from Vietnam
- Twig biomass allocation of Betula platyphylla in different habitats in Wudalianchi Volcano, northeast China
- Animal Sciences
- Supplementation of probiotics in water beneficial growth performance, carcass traits, immune function, and antioxidant capacity in broiler chickens
- Predators of the giant pine scale, Marchalina hellenica (Gennadius 1883; Hemiptera: Marchalinidae), out of its natural range in Turkey
- Honey in wound healing: An updated review
- NONMMUT140591.1 may serve as a ceRNA to regulate Gata5 in UT-B knockout-induced cardiac conduction block
- Radiotherapy for the treatment of pulmonary hydatidosis in sheep
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Long non-coding RNA TUG1 knockdown hinders the tumorigenesis of multiple myeloma by regulating microRNA-34a-5p/NOTCH1 signaling pathway”
- Special Issue on Reuse of Agro-Industrial By-Products
- An effect of positional isomerism of benzoic acid derivatives on antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli
- Special Issue on Computing and Artificial Techniques for Life Science Applications - Part II
- Relationship of Gensini score with retinal vessel diameter and arteriovenous ratio in senile CHD
- Effects of different enantiomers of amlodipine on lipid profiles and vasomotor factors in atherosclerotic rabbits
- Establishment of the New Zealand white rabbit animal model of fatty keratopathy associated with corneal neovascularization
- lncRNA MALAT1/miR-143 axis is a potential biomarker for in-stent restenosis and is involved in the multiplication of vascular smooth muscle cells

