Abstract
This article was designed to explore the effects and mechanisms of miR-185-5p on the replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV). Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed for detecting the abundance of miR-185-5p and HCV RNA in HCV-infected primary hepatocytes and Huh7.5 cells. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay was used for exploring the interaction between miR-185-5p and GALNT8. Western blot analyzed protein expression of GALNT8, NS3, and NS5A. miR-185-5p was remarkably downregulated in HCV-infected primary hepatocytes and Huh7.5 cells. miR-185-5p upregulation inhibited HCV RNA expression, while its inhibition promoted HCV replication. miR-185-5p induced accumulation of NS3 and NS5A in the cells. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay verified the targeted relationship between miR-185-5p and GALNT8. In addition, the effects of overexpressing or knocking down miR-185-5p on HCV replication could be correspondingly eliminated by the overexpression or knockdown of GALNT8. miR-185-5p may target GALNT8 in JFH1-infected Huh7.5 cells and then inhibit HCV replication. miR-185-5p may be a potential target for treating HCV.
1 Introduction
Hepatitis C virus (HCV), belonging to Flaviviridae and including one single open reading frame, is a RNA virus (single positive-strand) with envelopes, with its frame-encoding polyproteins of 3,000 amino acids [1,2]. After translation, polyproteins are processed into viral structural proteins and nonstructural proteins (NS3, NS5A) [3]. HCV core protein, considered to be a pathogenic factor, induces fatty degeneration, hepatocellular carcinoma, and oxidative stress [4]. However, currently, there is no effective vaccine to prevent HCV infection, which is mainly treated by ribavirin-based antiviral therapy in clinical practice, and only some patients can produce sustained immune responses [5,6].
As small noncoding RNAs (single stranded, about 22 nucleotides long), microRNAs (miRNAs) can inhibit the expression of target genes by imperfectly pairing with miRNA response elements in 3′-untranslated regions (UTRs) [7]. As one of them, miR-185-5p is mainly considered a regulatory factor for cancer progression [8]. Based on the latest research, miR-185-5p is involved in how HCV core protein regulates SREBP2 [9]. As reported by previous studies, HCV can induce the fatty degeneration of the liver to enhance its replication [10], and the host’s cholesterol metabolism is essential for the complete life cycle of HCV [11]. Accordingly, miR-185-5p may have a regulatory effect on HCV replication, which has been rarely studied.
Herein, we explored the effects of miR-185-5p on HCV replication and the possible mechanisms. Our findings may provide potential therapeutic targets for HCV treatment.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Cell culture
Primary human hepatocytes and human Huh7.5 cells were purchased from ATCC. By using MEGAscript RNAi kits, HCV genotype 2a (JFH1) RNA was prepared and then seeded into the cells with Lipofectamine 2000. The cells were cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (a humidified incubator, 5% CO2, 37°C).
2.2 Cell transfection
For upregulating or inhibiting miR-185-5p expression, miR-185-5p mimics (miR-185-5p) or miR-185-5p inhibitor (anti-miR-185-5p) and its negative control (miR-NC) were transfected into Huh7.5 cells. For overexpressing GALNT8, pcDNA3.1-GALNT8 (GALNT8) was introduced into Huh7.5.1 cells, and pcDNA3.1 empty vector (Vector) was used as a control. For downregulating GALNT8, siRNA targeting GALNT8 (si-GALNT8) was transfected into the cells and siRNA (si-NC) was also used as a control. According to the manufacturer’s instruction, Lipofectamine 2000 was applied to transfection.
2.3 Reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
With reference to the TRIzol reagents manufacturer’s instruction, total RNA was extracted from the cells, and then, the NanoDrop spectrophotometer was adopted to determine its concentration and purity. Then, based on the instruction of reverse transcription kits, the mRNA or the miRNA was used for the synthesis of the first-strand cDNA. The quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed with SYBR Green. The amplification steps were as follows: 95°C for 60 s, 95°C for 15 s, and 60°C for 1 min, which were cycled 40 times. The 2−ΔΔCt was used for analyzing the results, with β-Actin and U6 as control genes. The following primers (Invitrogen) were designed: forward and reverse primers for HCV were 5′-TCTGCGGAACCGGTGAGTA-3′ and 5′-TCAGGCACTACCACAAGGC-3′, respectively. Those for β-Actin were 5′-AGCAGCATCGCCCCAAAGTT-3′ and 5′-GGGCACGAAGGCTCATCATT-3′, respectively. Those for miR-185-5p were 5′-CGCTGGAGAGAAAGGCAGT-3′ and 5′-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3′, respectively. Those for U6 were 5′-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3′ and 5′ -AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3′, respectively. All measurements were repeated in triplicate.
2.4 Western blot
The cultured cells in each group were collected and subjected to RIPA (Thermo Scientific, USA) lysis for extracting the total protein. The BCA (Thermo Scientific, USA) method was used to detect its concentration. After the protein concentration was adjusted to 4 μg/μL, separation with 12% SDS-PAGE was performed. Subsequently, proteins were transferred to a PVDF membrane. Next, Ponceau S working solution was used for staining the membrane, which was immersed in PBST (5 min). After being cleaned and sealed (2 h) with 5% skimmed milk, the membrane was sealed (4°C) overnight with GALNT8 (1:500), NS3 (1:500), NS5A (1:500), and β-actin (1:500; Cell Signaling Technology). After being washed to remove the primary antibodies, a horseradish peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody (goat anti-rabbit (1:1,000)) was added, and the membranes were incubated at 37°C for 1 h, and rinsed with PBS (5 min) three times. Finally, it was developed with the ECL luminescence reagent. The gray values were analyzed.
2.5 Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay (DLRGA)
Dual-luciferase reporter plasmids (WT and MUT) of GALNT8 3′-UTR were constructed through RiboBio and co-transfected with miR-185-5p or miR-NC into the cells using Lipofectamine 2000. After 48 h, based on the manufacturer’s instruction, luciferase activities were detected through the dual-luciferase reporter assay system.
2.6 Statistical analysis
In this study, SPSS 19.0 was adopted for data analysis and GraphPad Prism 6 for plotting relevant figures. Results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD ± means), and measurement data were compared by the t test. The comparison between groups was conducted by the independent samples t test and represented by t. The comparison between multiple groups was conducted by one-way analysis of variance, and the LSD-t test was used for post hoc pairwise comparison. Bonferroni was applied to the post hoc test, and Pearson was applied to the correlation analysis. When P < 0.05, the difference was statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 HCV infection could inhibit miR-185-5p in hepatocytes
Compared with untreated primary hepatocytes, the expression of miR-185-5p was downregulated in HCV-infected primary human hepatocytes (Figure 1a). Compared with Huh7.5 cells, the expression of miR-185-5p was downregulated in Huh7.5 cells transfected with JFH1 (Figure 1b). Accordingly, HCV infection could inhibit miR-185-5p in hepatocytes.
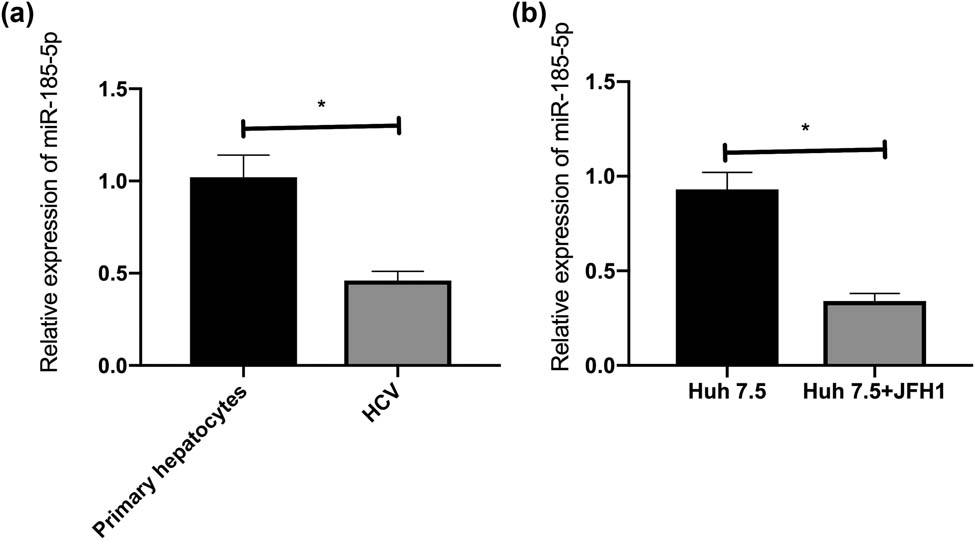
HCV infection led to miR-185-5p downregulation. (a) miR-185-5p expression in HCV-infected primary hepatocytes. (b) miR-185-5p expression in HCV-infected Huh7.5 cells. *P < 0.05.
3.2 miR-185-5p inhibited HCV replication
To determine the effects of miR-185-5p on HCV replication, miR-185-5p or anti-miR-185-5p was transfected into JFH1-infected Huh7.5 cells, and transfection efficiency was confirmed by the qRT-PCR. Among them, miR-185-5p was overexpressed by its mimics and inhibited by its inhibitor successfully (Figure 2a). In addition, in JFH1-infected Huh7.5 cells, the overexpression of miR-185-5p inhibited HCV RNA expression, while the inhibition of miR-185-5p promoted HCV RNA expression (Figure 2b). According to the western blot, the miR-185-5p overexpression inhibited the accumulation of NS3 and NS5A in the cells (Figure 2c and d), suggesting that miR-185-5p can inhibit HCV replication while inhibiting miR-185-5p has an opposite effect. Accordingly, miR-185-5p is involved in the progression of HCV infection.
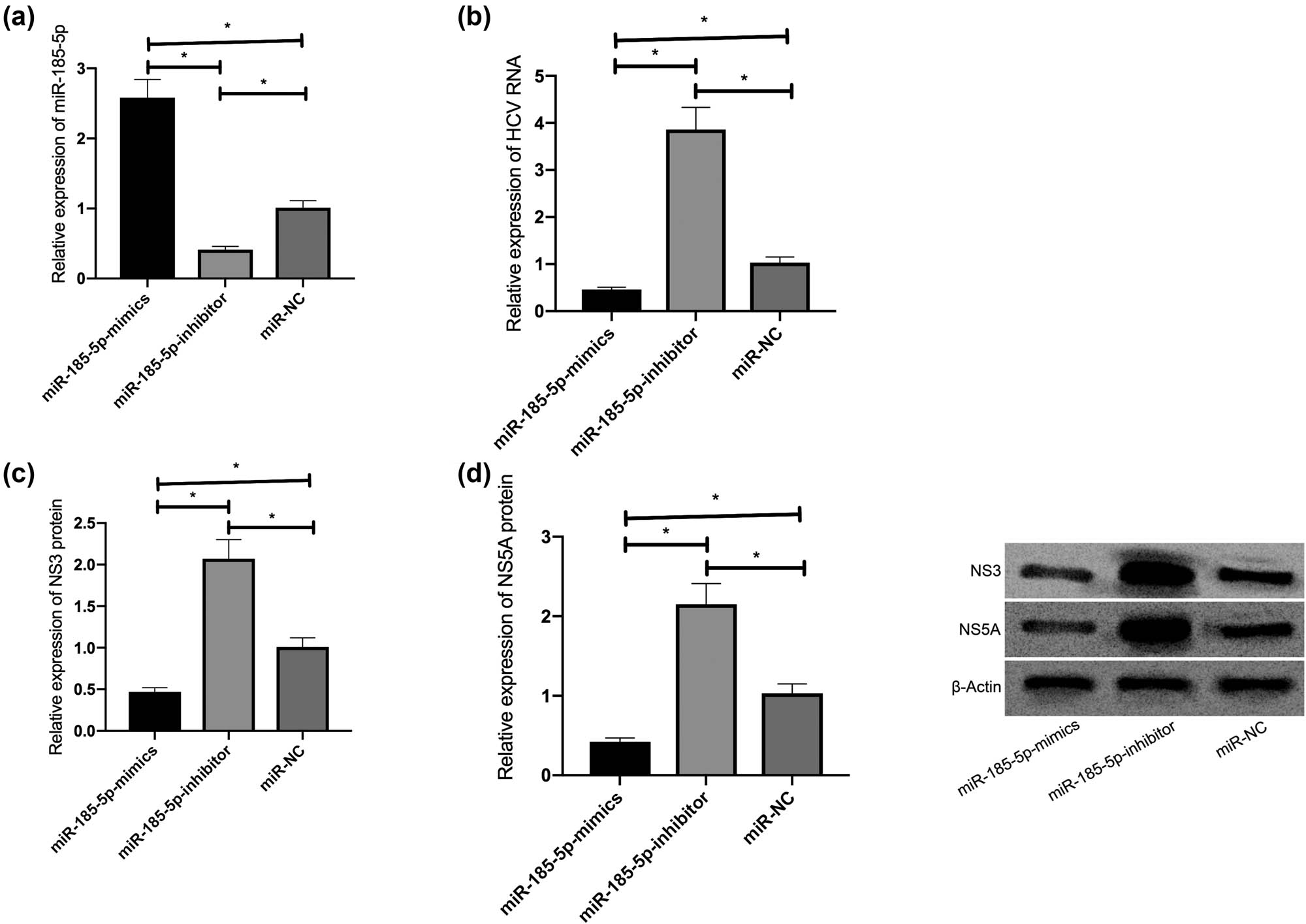
miR-185-5p inhibited HCV replication. (a) The transfection efficiency of miR-185-5p in Huh7.5 cells. (b) The effects of miR-185-5p on HCV RNA replication in cells. (c) The effects of miR-185-5p on NS3 in cells. (d) The effects of miR-185-5p on NS5A in cells. *P < 0.05.
3.3 DLRGA
After confirming that miR-185-5p can inhibit HCV replication, we tried to determine whether this miR interacts with GALNT8. According to the bioinformatics analysis, the online tool TargetScan predicted the putative binding sites between the two, which indicates that GALNT8 may be the direct target gene of miR-185-5p (Figure 3a). DLRGA confirmed that miR-185-5p directly targeted GALNT8 (Figure 3a). When this miR was overexpressed in Huh7.5 cells, the luciferase activity of GALNT8-wt declined remarkably. Western blot was also performed to detect GALNT8 in the JFH1-infected Huh7.5 cells transfected with miR-185-5p or anti-miR-185-5p. miR-185-5p overexpression could inhibit GALNT8 expression, while the inhibition of this miR could enhance the expression (Figure 3b).
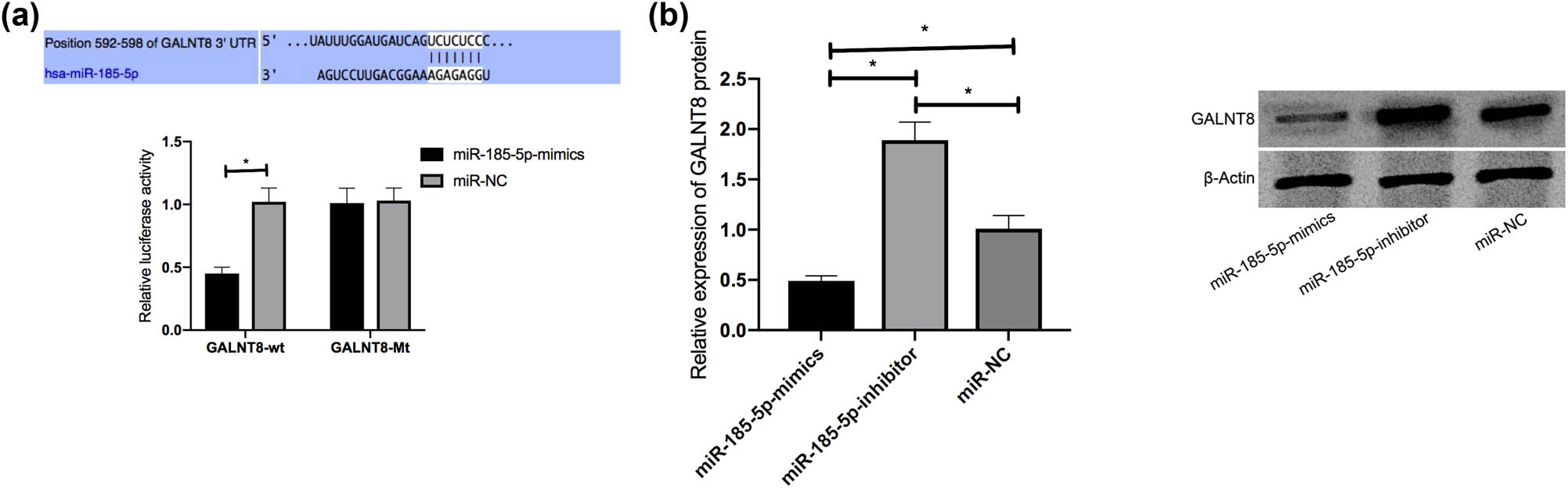
DLRGA. (a) The effects of miR-185-5p on luciferase activities of GALNT8. (b) The effects of miR-185-5p on GALNT8 in Huh7.5 cells. *P < 0.05.
3.4 GALNT8 could reverse the inhibitory effect of miR-185-5p on HCV replication
For further exploring whether GALNT8 could eliminate the inhibitory effect of miR-185-5p on HCV replication, miR-185-5p, miR-185-5p + pcDNA3.1-GALNT8, and anti-miR-185-5p or anti-miR-185-5p + si-GALNT8 were transfected into JFH1-infected Huh7.5 cells. Compared with miR-185-5p alone, the addition of GALNT8 remarkably enhanced HCV replication in the cells (Figure 4a). On the contrary, the depletion of GALNT8 reversed the effects, which were mediated by anti-miR-185-5p, on promoting HCV replication, thereby reducing HCV RNA (Figure 4d). Compared with the pcDNA treatment group, GALNT8 could remarkably increase NS3 and NS5A in the cells transfected with miR-185-5p (Figure 4b and c), while inhibiting this protein had an opposite effect (Figure 4e and f). These findings suggest that GALNT8 can reverse the inhibitory effect of miR-185-5p on HCV replication in JFH1-infected Huh7.5 cells.
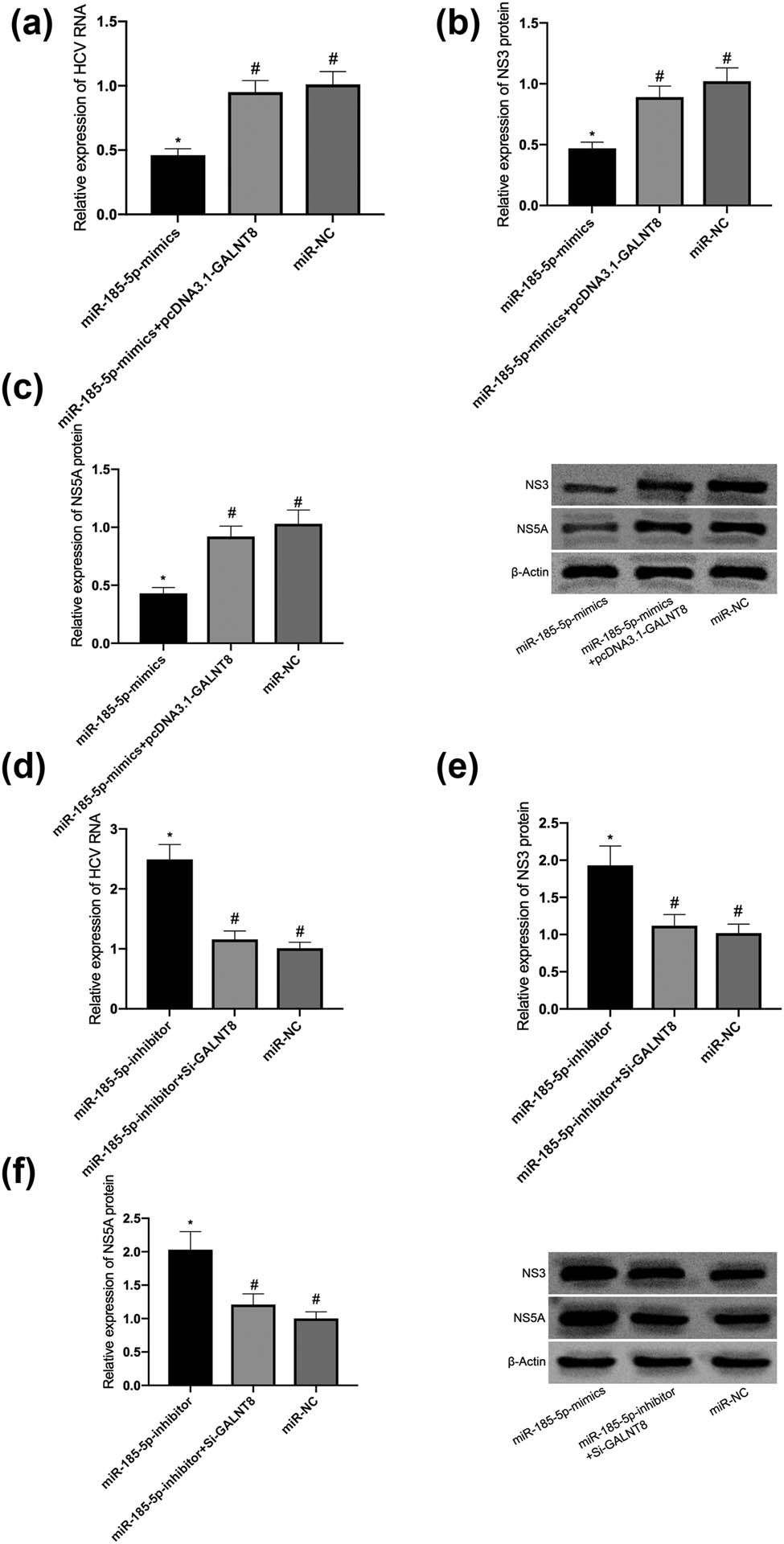
GALNT8 could reverse the inhibitory effect of miR-185-5p on HCV replication. (a) The effects of pcDNA3.1-GALNT8 on HCV RNA replication after miR-185-5p transfection. (b) The effects of pcDNA3.1-GALNT8 on NS3 after miR-185-5p transfection. (c) The effects of pcDNA3.1-GALNT8 on NS5A after miR-185-5p transfection. (d) The effects of si-GALNT8 on HCV RNA replication after anti-miR-185-5p transfection. (e) The effects of si-GALNT8 on NS3 after anti-miR-185-5p transfection. (f) The effects of si-GALNT8 on NS5A after anti-miR-185-5p transfection. * was compared with #, P < 0.05.
4 Discussion
In recent years, there has been more evidence that miRNAs exert a significant function in regulating HCV pathogenesis [12]. It has been previously reported that miR-122 is a promising candidate for anti-HCV therapy because its inhibitory effect reduces the richness of HCV RNA [13,14]. In this study, we have confirmed that miR-185-5p inhibits HCV replication by targeting GALNT8.
According to previous studies, miR-185-5p has a significant effect on virus-related liver cancer. For instance, it can reduce the activity of HBV S1p by targeting ELK1, thus inhibiting the progression of HBV-related liver cancer [15]. In our study, miR-185-5p was remarkably reduced in HCV-infected human liver cells and liver cancer cells, suggesting that the miR might be related to the activities of HCV viruses. Some researchers identified miRNA expression profiles in the serum of patients with HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma, finding that miR-185-5p remarkably declined in the serum [16]. That is consistent with our results. Then, for observing influences of miR-185-5p on HCV replication, we overexpressed and inhibited it in JFH1-infected Huh7.5 cells because JFH1 is the first HCV strain producing HCV particles and has a significant effect on the progression of HCV [17]. Subsequently, we observed that the overexpression could remarkably inhibit the richness of HCV, but the inhibition could promote HCV replication, which was confirmed by the increase in HCV RNA and NS3 and NS5A levels. According to a previous study, miR-185-5p can promote HCV replication [18], in which our experiments have further revealed the role of miRNAs.
Next, we further discussed the possible molecular basis of HCV replication induced by miR-185-5p. According to the bioinformatics analysis and the DLRGA, GALNT8 was identified as the direct target of miR-185-5p. As we all know, miRNA has multiple targets. According to relevant references, GALNT8 is a miR-185-5p target related to HCV replication, so we chose GALNT8 as the research target. As a member of the O-linked UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (GalNAc) glycosyltransferase family, GALNT8 transfers GalNAc to serine and threonine residues on target proteins in the Golgi apparatus, thus taking part in the biosynthesis of mucin-type O-glycans [19,20].
Moreover, single nucleotide polymorphism in GALNT8 is related to the responses of HCV to interferon therapy [21]. In our study, knocking down GALNT8 could inhibit HCV replication in Huh7.5 cells, which was manifested by the decrease in HCV RNA and levels of NS3 and NS5A. In addition, the miR-185-5p-induced inhibition of HCV replication was destroyed by GALNT8 upregulation in Huh7.5 cells, which suggests that miR-185-5p inhibits HCV replication by inhibiting GALNT8. The results of the rescue experiment also confirmed that miR-185-5p inhibited HCV replication through a specific molecular mechanism, and this study has initially verified the targeted relationship between the two markers in HCV infection.
5 Conclusion
To sum up, in this study, first, the interaction between miR-185-5p and HCV infection has been primarily explored based on fundamental research. HCV infection inhibits miR-185-5p, and overexpressing the miR inhibits the replication by inhibiting GALNT8 in JFH1-infected Huh7.5 cells. This demonstrates that this miR has a potential targeting effect and is conducive to formulating targeted therapeutic schemes for HCV infection. However, this study also has some limitations. For example, we have not yet verified the effect of miR-185-5p on HCV replication in vivo. Second, the downstream pathway mechanism of GALNT8 still needs to be further explored. However, this study has provided a certain experimental basis for inhibiting HCV replication based on a primary research, and we will conduct further research on this to get more data support for finding possible targets for inhibiting HCV.
-
Funding information: The authors state no funding involved.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Rossetti B, Bai F, Tavelli A, Galli M, Antinori A, Castelli F, et al. Evolution of the prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection and hepatitis C virus genotype distribution in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in Italy between 1997 and 2015. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018;24:422–7.10.1016/j.cmi.2017.07.021Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Khan M, Jahan S, Khaliq S, Ijaz B, Ahmad W, Samreen B, et al. The interaction of the core of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and cellular genes in the development of steatosis induced by HCV. Arch Virus. 2010;155:1735–53.10.1007/s00705-010-0797-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Reed KE, Rice CM. An overview of hepatitis C virus genome structure, multi-protein processing and protein properties. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000;242:55–84.10.1007/978-3-642-59605-6_4Search in Google Scholar
[4] Moriya K, Nakagawa K, Santa T, Shinya Y, Rich Sister H, Miyoshi H, et al. In a mouse model of hepatitis C virus-related liver cancer development, there is oxidative stress in the absence of inflammation. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4365–70.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Kao JH, Tung SY, Lee Y, Thongsawat S, Tanwandee T, Sheen IS, et al. Ritonavir-boosted danoprevir plus peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin in Asian chronic hepatitis C patients with or without cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:1757–65.10.1111/jgh.13374Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Erickson AK, Seiwert S, Gale M. Antiviral potency analysis and functional comparison of consensus interferon, interferon-alpha2a and pegylated interferon-alpha2b against hepatitis C virus infection. Antivir Ther (Lond). 2008;13:851–62.10.1177/135965350801300706Search in Google Scholar
[7] Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. The mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation of microRNA: is the answer right now? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–14.10.1038/nrg2290Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Değerli E, Torun V, Cansaran-Duman D. miR-185-5p response to usnic acid suppresses proliferation and regulating apoptosis in breast cancer cell by targeting Bcl2. Biol Res. 2020;53:19.10.1186/s40659-020-00285-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Li M, Wang Q, Liu SA, Zhang JQ, Ju W, Quan M, et al. microRNA-185-5p mediates the regulation of SREBP2 expression through the hepatitis C virus core protein. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(15):4517–25.10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4517Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Kapadia SB, Barth H, Baumert T, McKeating JA, Chisari FV. The onset of hepatitis C virus infection depends on cholesterol and the synergy between CD81 and the type I scavenger receptor B. J Virol. 2007;81:374–83.10.1128/JVI.01134-06Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Sidorkiewicz M, Józwiak B, Durys B, Majda-Stanislawska E, Piekarska A, Kosciuk N, et al. The regulation of the mevalonate pathway is related to the presence of hepatitis C virus RNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Virus Database. 2009;145:141–4.10.1016/j.virusres.2009.06.001Search in Google Scholar
[12] Waldron PR, Holodniy M. microRNA and hepatitis C virus – challenges for research and translation: a literature review. Diagn Microb Infect. 2014;80:1–12.10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2014.05.024Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Israelow B, Mullohandov G, Agudo J, Sourisseau M, Bashir A, Maldonado AY, et al. The genetics of the hepatitis C virus affect the demand for miR-122 and the response to miR-122 inhibitors. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5408.10.1038/ncomms6408Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Bandiera S, Pfeffer S, Baumert TF, Zeisel MB. miR-122-Key factors and therapeutic targets of liver disease. J Heparin. 2015;62:448–57.10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.004Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Fan HX, Feng YJ, Zhao XP, He YZ, Tang H. miR-185-5p suppresses HBV gene expression by targeting ELK1 in hepatoma carcinoma cells. Life Sci. 2018;213:9–17.10.1016/j.lfs.2018.10.016Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Li J, Jin B, Wang T, Li W, Wang Z, Zhang H, et al. Serum microRNA expression profiling identifies serum biomarkers for HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2019;26:501–12.10.3233/CBM-181970Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Wakita T. Isolation of JFH-1 strain and development of HCV infection system. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;510:305–27.10.1007/978-1-59745-394-3_23Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Ishida H, Sun T, Feng Shui A, Nava T, Kodama T, Shimizu S, et al. Changes in microRNA expression profiles in HCV-infected liver cancer cells: miR-491 is involved in the regulation of HCV replication through the PI3 kinase/Akt pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;412:92–7.10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.049Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Hussain MR, Nasir J, Al‐Aama JY. Clinically significant missense variants in human GALNT3, GALNT8, GALNT12, and GALNT13 genes: intriguing in silico findings. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118:3520.10.1002/jcb.25675Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Imran M, Manzoor S, Parvaiz F. Predictive potential of IL-18 -607 and osteopontin -442 polymorphism in interferon-based therapy of HCV infection in the Pakistani population. Viral Immunol. 2014;27:404–11.10.1089/vim.2014.0044Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Nakano R, Maekawa T, Abe H, Hayashida Y, Ochi H, Tsunoda T, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in GALNT8 are associated with the response to interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Gen Virol. 2013;94:81–9.10.1099/vir.0.044396-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2021 Wei Huang et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Research progress on the mechanism of orexin in pain regulation in different brain regions
- Adriamycin-resistant cells are significantly less fit than adriamycin-sensitive cells in cervical cancer
- Exogenous spermidine affects polyamine metabolism in the mouse hypothalamus
- Iris metastasis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma misdiagnosed as primary angle-closure glaucoma: A case report and review of the literature
- LncRNA PVT1 promotes cervical cancer progression by sponging miR-503 to upregulate ARL2 expression
- Two new inflammatory markers related to the CURB-65 score for disease severity in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: The hypersensitive C-reactive protein to albumin ratio and fibrinogen to albumin ratio
- Circ_0091579 enhances the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma via miR-1287/PDK2 axis
- Silencing XIST mitigated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory injury in human lung fibroblast WI-38 cells through modulating miR-30b-5p/CCL16 axis and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats
- ABCB1 polymorphism in clopidogrel-treated Montenegrin patients
- Metabolic profiling of fatty acids in Tripterygium wilfordii multiglucoside- and triptolide-induced liver-injured rats
- miR-338-3p inhibits cell growth, invasion, and EMT process in neuroblastoma through targeting MMP-2
- Verification of neuroprotective effects of alpha-lipoic acid on chronic neuropathic pain in a chronic constriction injury rat model
- Circ_WWC3 overexpression decelerates the progression of osteosarcoma by regulating miR-421/PDE7B axis
- Knockdown of TUG1 rescues cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through targeting the miR-497/MEF2C axis
- MiR-146b-3p protects against AR42J cell injury in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis model through targeting Anxa2
- miR-299-3p suppresses cell progression and induces apoptosis by downregulating PAX3 in gastric cancer
- Diabetes and COVID-19
- Discovery of novel potential KIT inhibitors for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- TEAD4 is a novel independent predictor of prognosis in LGG patients with IDH mutation
- circTLK1 facilitates the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating miR-495-3p/CBL axis
- microRNA-9-5p protects liver sinusoidal endothelial cell against oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury
- Long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-320c/MMP-13 axis in osteoarthritis
- Duodenal adenocarcinoma with skin metastasis as initial manifestation: A case report
- Effects of Loofah cylindrica extract on learning and memory ability, brain tissue morphology, and immune function of aging mice
- Recombinant Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin-1 (rBFT-1) promotes proliferation of colorectal cancer via CCL3-related molecular pathways
- Blocking circ_UBR4 suppressed proliferation, migration, and cell cycle progression of human vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis
- Gene therapy in PIDs, hemoglobin, ocular, neurodegenerative, and hemophilia B disorders
- Downregulation of circ_0037655 impedes glioma formation and metastasis via the regulation of miR-1229-3p/ITGB8 axis
- Vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes population
- Circ_0013359 facilitates the tumorigenicity of melanoma by regulating miR-136-5p/RAB9A axis
- Mechanisms of circular RNA circ_0066147 on pancreatic cancer progression
- lncRNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) knockdown alleviates LPS-induced chondrocytes inflammatory injury via regulating miR-488-3p/sex determining region Y-related HMG-box 11 (SOX11) axis
- Identification of circRNA circ-CSPP1 as a potent driver of colorectal cancer by directly targeting the miR-431/LASP1 axis
- Hyperhomocysteinemia exacerbates ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced acute kidney injury by mediating oxidative stress, DNA damage, JNK pathway, and apoptosis
- Potential prognostic markers and significant lncRNA–mRNA co-expression pairs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Gamma irradiation-mediated inactivation of enveloped viruses with conservation of genome integrity: Potential application for SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine development
- ADHFE1 is a correlative factor of patient survival in cancer
- The association of transcription factor Prox1 with the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer
- Is there a relationship between the prevalence of autoimmune thyroid disease and diabetic kidney disease?
- Immunoregulatory function of Dictyophora echinovolvata spore polysaccharides in immunocompromised mice induced by cyclophosphamide
- T cell epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and conserved surface protein of Plasmodium malariae share sequence homology
- Anti-obesity effect and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells influence on obese mice
- Long noncoding RNA HULC contributes to paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer via miR-137/ITGB8 axis
- Glucocorticoids protect HEI-OC1 cells from tunicamycin-induced cell damage via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning
- Gastroprotective effects of diosgenin against HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury through suppression of NF-κβ and myeloperoxidase activities
- Silencing of LINC00707 suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by modulating miR-338-3p/AHSA1 axis
- Successful extracorporeal membrane oxygenation resuscitation of patient with cardiogenic shock induced by phaeochromocytoma crisis mimicking hyperthyroidism: A case report
- Effects of miR-185-5p on replication of hepatitis C virus
- Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis
- Primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis presenting as lymphatic malformation: A case report
- Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging analysis in the characteristics of Wilson’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Therapeutic potential of anticoagulant therapy in association with cytokine storm inhibition in severe cases of COVID-19: A case report
- Neoadjuvant immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy for locally advanced squamous cell lung carcinoma: A case report and literature review
- Rufinamide (RUF) suppresses inflammation and maintains the integrity of the blood–brain barrier during kainic acid-induced brain damage
- Inhibition of ADAM10 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiac remodeling by suppressing N-cadherin cleavage
- Invasive ductal carcinoma and small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia manifesting as a collision breast tumor: A case report and literature review
- Clonal diversity of the B cell receptor repertoire in patients with coronary in-stent restenosis and type 2 diabetes
- CTLA-4 promotes lymphoma progression through tumor stem cell enrichment and immunosuppression
- WDR74 promotes proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Down-regulation of IGHG1 enhances Protoporphyrin IX accumulation and inhibits hemin biosynthesis in colorectal cancer by suppressing the MEK-FECH axis
- Curcumin suppresses the progression of gastric cancer by regulating circ_0056618/miR-194-5p axis
- Scutellarin-induced A549 cell apoptosis depends on activation of the transforming growth factor-β1/smad2/ROS/caspase-3 pathway
- lncRNA NEAT1 regulates CYP1A2 and influences steroid-induced necrosis
- A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer
- Isolation of microglia from retinas of chronic ocular hypertensive rats
- Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study
- Calcineurin Aβ gene knockdown inhibits transient outward potassium current ion channel remodeling in hypertrophic ventricular myocyte
- Aberrant expression of PI3K/AKT signaling is involved in apoptosis resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Clinical significance of activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling in apoptosis inhibition of oral cancer
- circ_CHFR regulates ox-LDL-mediated cell proliferation, apoptosis, and EndoMT by miR-15a-5p/EGFR axis in human brain microvessel endothelial cells
- Resveratrol pretreatment mitigates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating conventional dendritic cells’ maturation and function
- Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T promotes tumor stem cell characteristics and migration of cervical cancer cells by regulating the GRP78/FAK pathway
- Carriage of HLA-DRB1*11 and 1*12 alleles and risk factors in patients with breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- Protective effect of Lactobacillus-containing probiotics on intestinal mucosa of rats experiencing traumatic hemorrhagic shock
- Glucocorticoids induce osteonecrosis of the femoral head through the Hippo signaling pathway
- Endothelial cell-derived SSAO can increase MLC20 phosphorylation in VSMCs
- Downregulation of STOX1 is a novel prognostic biomarker for glioma patients
- miR-378a-3p regulates glioma cell chemosensitivity to cisplatin through IGF1R
- The molecular mechanisms underlying arecoline-induced cardiac fibrosis in rats
- TGF-β1-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate Th17/Treg cells by regulating the expression of IFN-γ
- The influence of MTHFR genetic polymorphisms on methotrexate therapy in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Red blood cell distribution width-standard deviation but not red blood cell distribution width-coefficient of variation as a potential index for the diagnosis of iron-deficiency anemia in mid-pregnancy women
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma expressing alpha fetoprotein in the endometrium
- Superoxide dismutase and the sigma1 receptor as key elements of the antioxidant system in human gastrointestinal tract cancers
- Molecular characterization and phylogenetic studies of Echinococcus granulosus and Taenia multiceps coenurus cysts in slaughtered sheep in Saudi Arabia
- ITGB5 mutation discovered in a Chinese family with blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome
- ACTB and GAPDH appear at multiple SDS-PAGE positions, thus not suitable as reference genes for determining protein loading in techniques like Western blotting
- Facilitation of mouse skin-derived precursor growth and yield by optimizing plating density
- 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethanol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiac injury in a murine model
- Downregulation of PITX2 inhibits the proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells and induces cell apoptosis
- Expression of CDK9 in endometrial cancer tissues and its effect on the proliferation of HEC-1B
- Novel predictor of the occurrence of DKA in T1DM patients without infection: A combination of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and white blood cells
- Investigation of molecular regulation mechanism under the pathophysiology of subarachnoid hemorrhage
- miR-25-3p protects renal tubular epithelial cells from apoptosis induced by renal IRI by targeting DKK3
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Green fabrication of Co and Co3O4 nanoparticles and their biomedical applications: A review
- Agriculture
- Effects of inorganic and organic selenium sources on the growth performance of broilers in China: A meta-analysis
- Crop-livestock integration practices, knowledge, and attitudes among smallholder farmers: Hedging against climate change-induced shocks in semi-arid Zimbabwe
- Food Science and Nutrition
- Effect of food processing on the antioxidant activity of flavones from Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce
- Vitamin D and iodine status was associated with the risk and complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China
- Diversity of microbiota in Slovak summer ewes’ cheese “Bryndza”
- Comparison between voltammetric detection methods for abalone-flavoring liquid
- Composition of low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and their effects on the rheological properties of dough
- Application of culture, PCR, and PacBio sequencing for determination of microbial composition of milk from subclinical mastitis dairy cows of smallholder farms
- Investigating microplastics and potentially toxic elements contamination in canned Tuna, Salmon, and Sardine fishes from Taif markets, KSA
- From bench to bar side: Evaluating the red wine storage lesion
- Establishment of an iodine model for prevention of iodine-excess-induced thyroid dysfunction in pregnant women
- Plant Sciences
- Characterization of GMPP from Dendrobium huoshanense yielding GDP-D-mannose
- Comparative analysis of the SPL gene family in five Rosaceae species: Fragaria vesca, Malus domestica, Prunus persica, Rubus occidentalis, and Pyrus pyrifolia
- Identification of leaf rust resistance genes Lr34 and Lr46 in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ssp. aestivum) lines of different origin using multiplex PCR
- Investigation of bioactivities of Taxus chinensis, Taxus cuspidata, and Taxus × media by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Morphological structures and histochemistry of roots and shoots in Myricaria laxiflora (Tamaricaceae)
- Transcriptome analysis of resistance mechanism to potato wart disease
- In silico analysis of glycosyltransferase 2 family genes in duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) and its role in salt stress tolerance
- Comparative study on growth traits and ions regulation of zoysiagrasses under varied salinity treatments
- Role of MS1 homolog Ntms1 gene of tobacco infertility
- Biological characteristics and fungicide sensitivity of Pyricularia variabilis
- In silico/computational analysis of mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase gene families in Campanulids
- Identification of novel drought-responsive miRNA regulatory network of drought stress response in common vetch (Vicia sativa)
- How photoautotrophy, photomixotrophy, and ventilation affect the stomata and fluorescence emission of pistachios rootstock?
- Apoplastic histochemical features of plant root walls that may facilitate ion uptake and retention
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- The impact of sewage sludge on the fungal communities in the rhizosphere and roots of barley and on barley yield
- Domestication of wild animals may provide a springboard for rapid variation of coronavirus
- Response of benthic invertebrate assemblages to seasonal and habitat condition in the Wewe River, Ashanti region (Ghana)
- Molecular record for the first authentication of Isaria cicadae from Vietnam
- Twig biomass allocation of Betula platyphylla in different habitats in Wudalianchi Volcano, northeast China
- Animal Sciences
- Supplementation of probiotics in water beneficial growth performance, carcass traits, immune function, and antioxidant capacity in broiler chickens
- Predators of the giant pine scale, Marchalina hellenica (Gennadius 1883; Hemiptera: Marchalinidae), out of its natural range in Turkey
- Honey in wound healing: An updated review
- NONMMUT140591.1 may serve as a ceRNA to regulate Gata5 in UT-B knockout-induced cardiac conduction block
- Radiotherapy for the treatment of pulmonary hydatidosis in sheep
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Long non-coding RNA TUG1 knockdown hinders the tumorigenesis of multiple myeloma by regulating microRNA-34a-5p/NOTCH1 signaling pathway”
- Special Issue on Reuse of Agro-Industrial By-Products
- An effect of positional isomerism of benzoic acid derivatives on antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli
- Special Issue on Computing and Artificial Techniques for Life Science Applications - Part II
- Relationship of Gensini score with retinal vessel diameter and arteriovenous ratio in senile CHD
- Effects of different enantiomers of amlodipine on lipid profiles and vasomotor factors in atherosclerotic rabbits
- Establishment of the New Zealand white rabbit animal model of fatty keratopathy associated with corneal neovascularization
- lncRNA MALAT1/miR-143 axis is a potential biomarker for in-stent restenosis and is involved in the multiplication of vascular smooth muscle cells
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Research progress on the mechanism of orexin in pain regulation in different brain regions
- Adriamycin-resistant cells are significantly less fit than adriamycin-sensitive cells in cervical cancer
- Exogenous spermidine affects polyamine metabolism in the mouse hypothalamus
- Iris metastasis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma misdiagnosed as primary angle-closure glaucoma: A case report and review of the literature
- LncRNA PVT1 promotes cervical cancer progression by sponging miR-503 to upregulate ARL2 expression
- Two new inflammatory markers related to the CURB-65 score for disease severity in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: The hypersensitive C-reactive protein to albumin ratio and fibrinogen to albumin ratio
- Circ_0091579 enhances the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma via miR-1287/PDK2 axis
- Silencing XIST mitigated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory injury in human lung fibroblast WI-38 cells through modulating miR-30b-5p/CCL16 axis and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats
- ABCB1 polymorphism in clopidogrel-treated Montenegrin patients
- Metabolic profiling of fatty acids in Tripterygium wilfordii multiglucoside- and triptolide-induced liver-injured rats
- miR-338-3p inhibits cell growth, invasion, and EMT process in neuroblastoma through targeting MMP-2
- Verification of neuroprotective effects of alpha-lipoic acid on chronic neuropathic pain in a chronic constriction injury rat model
- Circ_WWC3 overexpression decelerates the progression of osteosarcoma by regulating miR-421/PDE7B axis
- Knockdown of TUG1 rescues cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through targeting the miR-497/MEF2C axis
- MiR-146b-3p protects against AR42J cell injury in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis model through targeting Anxa2
- miR-299-3p suppresses cell progression and induces apoptosis by downregulating PAX3 in gastric cancer
- Diabetes and COVID-19
- Discovery of novel potential KIT inhibitors for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- TEAD4 is a novel independent predictor of prognosis in LGG patients with IDH mutation
- circTLK1 facilitates the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating miR-495-3p/CBL axis
- microRNA-9-5p protects liver sinusoidal endothelial cell against oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury
- Long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates degradation of chondrocyte extracellular matrix via miR-320c/MMP-13 axis in osteoarthritis
- Duodenal adenocarcinoma with skin metastasis as initial manifestation: A case report
- Effects of Loofah cylindrica extract on learning and memory ability, brain tissue morphology, and immune function of aging mice
- Recombinant Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin-1 (rBFT-1) promotes proliferation of colorectal cancer via CCL3-related molecular pathways
- Blocking circ_UBR4 suppressed proliferation, migration, and cell cycle progression of human vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis
- Gene therapy in PIDs, hemoglobin, ocular, neurodegenerative, and hemophilia B disorders
- Downregulation of circ_0037655 impedes glioma formation and metastasis via the regulation of miR-1229-3p/ITGB8 axis
- Vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes population
- Circ_0013359 facilitates the tumorigenicity of melanoma by regulating miR-136-5p/RAB9A axis
- Mechanisms of circular RNA circ_0066147 on pancreatic cancer progression
- lncRNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) knockdown alleviates LPS-induced chondrocytes inflammatory injury via regulating miR-488-3p/sex determining region Y-related HMG-box 11 (SOX11) axis
- Identification of circRNA circ-CSPP1 as a potent driver of colorectal cancer by directly targeting the miR-431/LASP1 axis
- Hyperhomocysteinemia exacerbates ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced acute kidney injury by mediating oxidative stress, DNA damage, JNK pathway, and apoptosis
- Potential prognostic markers and significant lncRNA–mRNA co-expression pairs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Gamma irradiation-mediated inactivation of enveloped viruses with conservation of genome integrity: Potential application for SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine development
- ADHFE1 is a correlative factor of patient survival in cancer
- The association of transcription factor Prox1 with the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer
- Is there a relationship between the prevalence of autoimmune thyroid disease and diabetic kidney disease?
- Immunoregulatory function of Dictyophora echinovolvata spore polysaccharides in immunocompromised mice induced by cyclophosphamide
- T cell epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and conserved surface protein of Plasmodium malariae share sequence homology
- Anti-obesity effect and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells influence on obese mice
- Long noncoding RNA HULC contributes to paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer via miR-137/ITGB8 axis
- Glucocorticoids protect HEI-OC1 cells from tunicamycin-induced cell damage via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning
- Gastroprotective effects of diosgenin against HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury through suppression of NF-κβ and myeloperoxidase activities
- Silencing of LINC00707 suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by modulating miR-338-3p/AHSA1 axis
- Successful extracorporeal membrane oxygenation resuscitation of patient with cardiogenic shock induced by phaeochromocytoma crisis mimicking hyperthyroidism: A case report
- Effects of miR-185-5p on replication of hepatitis C virus
- Lidocaine has antitumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma via the circ_DYNC1H1/miR-520a-3p/USP14 axis
- Primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis presenting as lymphatic malformation: A case report
- Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging analysis in the characteristics of Wilson’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Therapeutic potential of anticoagulant therapy in association with cytokine storm inhibition in severe cases of COVID-19: A case report
- Neoadjuvant immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy for locally advanced squamous cell lung carcinoma: A case report and literature review
- Rufinamide (RUF) suppresses inflammation and maintains the integrity of the blood–brain barrier during kainic acid-induced brain damage
- Inhibition of ADAM10 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiac remodeling by suppressing N-cadherin cleavage
- Invasive ductal carcinoma and small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia manifesting as a collision breast tumor: A case report and literature review
- Clonal diversity of the B cell receptor repertoire in patients with coronary in-stent restenosis and type 2 diabetes
- CTLA-4 promotes lymphoma progression through tumor stem cell enrichment and immunosuppression
- WDR74 promotes proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Down-regulation of IGHG1 enhances Protoporphyrin IX accumulation and inhibits hemin biosynthesis in colorectal cancer by suppressing the MEK-FECH axis
- Curcumin suppresses the progression of gastric cancer by regulating circ_0056618/miR-194-5p axis
- Scutellarin-induced A549 cell apoptosis depends on activation of the transforming growth factor-β1/smad2/ROS/caspase-3 pathway
- lncRNA NEAT1 regulates CYP1A2 and influences steroid-induced necrosis
- A two-microRNA signature predicts the progression of male thyroid cancer
- Isolation of microglia from retinas of chronic ocular hypertensive rats
- Changes of immune cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by radiofrequency ablation and hepatectomy, a pilot study
- Calcineurin Aβ gene knockdown inhibits transient outward potassium current ion channel remodeling in hypertrophic ventricular myocyte
- Aberrant expression of PI3K/AKT signaling is involved in apoptosis resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Clinical significance of activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling in apoptosis inhibition of oral cancer
- circ_CHFR regulates ox-LDL-mediated cell proliferation, apoptosis, and EndoMT by miR-15a-5p/EGFR axis in human brain microvessel endothelial cells
- Resveratrol pretreatment mitigates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating conventional dendritic cells’ maturation and function
- Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T promotes tumor stem cell characteristics and migration of cervical cancer cells by regulating the GRP78/FAK pathway
- Carriage of HLA-DRB1*11 and 1*12 alleles and risk factors in patients with breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- Protective effect of Lactobacillus-containing probiotics on intestinal mucosa of rats experiencing traumatic hemorrhagic shock
- Glucocorticoids induce osteonecrosis of the femoral head through the Hippo signaling pathway
- Endothelial cell-derived SSAO can increase MLC20 phosphorylation in VSMCs
- Downregulation of STOX1 is a novel prognostic biomarker for glioma patients
- miR-378a-3p regulates glioma cell chemosensitivity to cisplatin through IGF1R
- The molecular mechanisms underlying arecoline-induced cardiac fibrosis in rats
- TGF-β1-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells reciprocally regulate Th17/Treg cells by regulating the expression of IFN-γ
- The influence of MTHFR genetic polymorphisms on methotrexate therapy in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Red blood cell distribution width-standard deviation but not red blood cell distribution width-coefficient of variation as a potential index for the diagnosis of iron-deficiency anemia in mid-pregnancy women
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma expressing alpha fetoprotein in the endometrium
- Superoxide dismutase and the sigma1 receptor as key elements of the antioxidant system in human gastrointestinal tract cancers
- Molecular characterization and phylogenetic studies of Echinococcus granulosus and Taenia multiceps coenurus cysts in slaughtered sheep in Saudi Arabia
- ITGB5 mutation discovered in a Chinese family with blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome
- ACTB and GAPDH appear at multiple SDS-PAGE positions, thus not suitable as reference genes for determining protein loading in techniques like Western blotting
- Facilitation of mouse skin-derived precursor growth and yield by optimizing plating density
- 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethanol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiac injury in a murine model
- Downregulation of PITX2 inhibits the proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells and induces cell apoptosis
- Expression of CDK9 in endometrial cancer tissues and its effect on the proliferation of HEC-1B
- Novel predictor of the occurrence of DKA in T1DM patients without infection: A combination of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and white blood cells
- Investigation of molecular regulation mechanism under the pathophysiology of subarachnoid hemorrhage
- miR-25-3p protects renal tubular epithelial cells from apoptosis induced by renal IRI by targeting DKK3
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Green fabrication of Co and Co3O4 nanoparticles and their biomedical applications: A review
- Agriculture
- Effects of inorganic and organic selenium sources on the growth performance of broilers in China: A meta-analysis
- Crop-livestock integration practices, knowledge, and attitudes among smallholder farmers: Hedging against climate change-induced shocks in semi-arid Zimbabwe
- Food Science and Nutrition
- Effect of food processing on the antioxidant activity of flavones from Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce
- Vitamin D and iodine status was associated with the risk and complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China
- Diversity of microbiota in Slovak summer ewes’ cheese “Bryndza”
- Comparison between voltammetric detection methods for abalone-flavoring liquid
- Composition of low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and their effects on the rheological properties of dough
- Application of culture, PCR, and PacBio sequencing for determination of microbial composition of milk from subclinical mastitis dairy cows of smallholder farms
- Investigating microplastics and potentially toxic elements contamination in canned Tuna, Salmon, and Sardine fishes from Taif markets, KSA
- From bench to bar side: Evaluating the red wine storage lesion
- Establishment of an iodine model for prevention of iodine-excess-induced thyroid dysfunction in pregnant women
- Plant Sciences
- Characterization of GMPP from Dendrobium huoshanense yielding GDP-D-mannose
- Comparative analysis of the SPL gene family in five Rosaceae species: Fragaria vesca, Malus domestica, Prunus persica, Rubus occidentalis, and Pyrus pyrifolia
- Identification of leaf rust resistance genes Lr34 and Lr46 in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ssp. aestivum) lines of different origin using multiplex PCR
- Investigation of bioactivities of Taxus chinensis, Taxus cuspidata, and Taxus × media by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Morphological structures and histochemistry of roots and shoots in Myricaria laxiflora (Tamaricaceae)
- Transcriptome analysis of resistance mechanism to potato wart disease
- In silico analysis of glycosyltransferase 2 family genes in duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) and its role in salt stress tolerance
- Comparative study on growth traits and ions regulation of zoysiagrasses under varied salinity treatments
- Role of MS1 homolog Ntms1 gene of tobacco infertility
- Biological characteristics and fungicide sensitivity of Pyricularia variabilis
- In silico/computational analysis of mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase gene families in Campanulids
- Identification of novel drought-responsive miRNA regulatory network of drought stress response in common vetch (Vicia sativa)
- How photoautotrophy, photomixotrophy, and ventilation affect the stomata and fluorescence emission of pistachios rootstock?
- Apoplastic histochemical features of plant root walls that may facilitate ion uptake and retention
- Ecology and Environmental Sciences
- The impact of sewage sludge on the fungal communities in the rhizosphere and roots of barley and on barley yield
- Domestication of wild animals may provide a springboard for rapid variation of coronavirus
- Response of benthic invertebrate assemblages to seasonal and habitat condition in the Wewe River, Ashanti region (Ghana)
- Molecular record for the first authentication of Isaria cicadae from Vietnam
- Twig biomass allocation of Betula platyphylla in different habitats in Wudalianchi Volcano, northeast China
- Animal Sciences
- Supplementation of probiotics in water beneficial growth performance, carcass traits, immune function, and antioxidant capacity in broiler chickens
- Predators of the giant pine scale, Marchalina hellenica (Gennadius 1883; Hemiptera: Marchalinidae), out of its natural range in Turkey
- Honey in wound healing: An updated review
- NONMMUT140591.1 may serve as a ceRNA to regulate Gata5 in UT-B knockout-induced cardiac conduction block
- Radiotherapy for the treatment of pulmonary hydatidosis in sheep
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Long non-coding RNA TUG1 knockdown hinders the tumorigenesis of multiple myeloma by regulating microRNA-34a-5p/NOTCH1 signaling pathway”
- Special Issue on Reuse of Agro-Industrial By-Products
- An effect of positional isomerism of benzoic acid derivatives on antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli
- Special Issue on Computing and Artificial Techniques for Life Science Applications - Part II
- Relationship of Gensini score with retinal vessel diameter and arteriovenous ratio in senile CHD
- Effects of different enantiomers of amlodipine on lipid profiles and vasomotor factors in atherosclerotic rabbits
- Establishment of the New Zealand white rabbit animal model of fatty keratopathy associated with corneal neovascularization
- lncRNA MALAT1/miR-143 axis is a potential biomarker for in-stent restenosis and is involved in the multiplication of vascular smooth muscle cells

