Abstract
C32H30ClCoN5O8S, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 14.5008(9) Å, b = 13.6648(9) Å, c = 17.9741(12) Å, β = 113.086(2)°, V = 3276.4(4) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0620, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1696, T = 293(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Green block |
| Size: | 0.27 × 0.15 × 0.14 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) 0.73 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θ max, completeness: |
Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω
27.5°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 51,167, 7520, 0.057 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 5061 |
| N(param) refined: | 452 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 , 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.3588 (3) | 0.2079 (3) | 0.4876 (2) | 0.0530 (10) |
| H1 | 0.347188 | 0.273553 | 0.473215 | 0.064* |
| C2 | 0.4032 (4) | 0.1843 (4) | 0.5698 (3) | 0.0656 (12) |
| H2 | 0.421054 | 0.232823 | 0.609226 | 0.079* |
| C3 | 0.4193 (4) | 0.0881 (4) | 0.5902 (3) | 0.0697 (12) |
| H3 | 0.447468 | 0.070681 | 0.644581 | 0.084* |
| C4 | 0.3501 (3) | 0.0468 (3) | 0.4509 (2) | 0.0447 (8) |
| C5 | 0.3949 (3) | 0.0163 (3) | 0.5324 (3) | 0.0557 (10) |
| C6 | 0.4122 (4) | −0.0868 (4) | 0.5484 (4) | 0.0767 (16) |
| H6 | 0.440360 | −0.108344 | 0.601663 | 0.092* |
| C7 | 0.3887 (4) | −0.1526 (4) | 0.4883 (4) | 0.0828 (18) |
| H7 | 0.401893 | −0.218381 | 0.501209 | 0.099* |
| C8 | 0.3244 (3) | −0.0242 (3) | 0.3873 (2) | 0.0484 (9) |
| C9 | 0.3441 (3) | −0.1247 (3) | 0.4053 (3) | 0.0628 (13) |
| C10 | 0.3201 (4) | −0.1894 (3) | 0.3400 (4) | 0.0759 (16) |
| H10 | 0.333129 | −0.255861 | 0.349340 | 0.091* |
| C11 | 0.2778 (4) | −0.1552 (3) | 0.2631 (4) | 0.0759 (15) |
| H11 | 0.261148 | −0.197875 | 0.219481 | 0.091* |
| C12 | 0.2597 (3) | −0.0558 (3) | 0.2506 (3) | 0.0608 (11) |
| H12 | 0.230649 | −0.033218 | 0.197573 | 0.073* |
| C13 | 0.0867 (3) | 0.1718 (3) | 0.3572 (2) | 0.0466 (9) |
| H13 | 0.134923 | 0.180679 | 0.409218 | 0.056* |
| C14 | −0.0128 (3) | 0.1661 (3) | 0.3473 (3) | 0.0528 (10) |
| H14 | −0.030089 | 0.171396 | 0.391822 | 0.063* |
| C15 | −0.0846 (3) | 0.1526 (3) | 0.2727 (3) | 0.0521 (10) |
| H15 | −0.151519 | 0.147618 | 0.265511 | 0.063* |
| C16 | −0.0576 (3) | 0.1462 (2) | 0.2058 (2) | 0.0435 (8) |
| C17 | −0.1279 (3) | 0.1344 (3) | 0.1246 (3) | 0.0571 (11) |
| H17 | −0.195831 | 0.129700 | 0.114107 | 0.068* |
| C18 | −0.0978 (3) | 0.1300 (3) | 0.0629 (3) | 0.0615 (12) |
| H18 | −0.145469 | 0.123127 | 0.010372 | 0.074* |
| C19 | 0.0055 (3) | 0.1358 (3) | 0.0762 (2) | 0.0499 (9) |
| C20 | 0.0776 (3) | 0.1473 (2) | 0.1556 (2) | 0.0366 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0448 (2) | 0.1526 (2) | 0.2215 (2) | 0.0346 (7) |
| C22 | 0.0426 (4) | 0.1304 (4) | 0.0150 (3) | 0.0660 (12) |
| H22 | −0.001519 | 0.122160 | −0.038534 | 0.079* |
| C23 | 0.1419 (4) | 0.1371 (4) | 0.0335 (3) | 0.0679 (13) |
| H23 | 0.166230 | 0.133373 | −0.007216 | 0.082* |
| C24 | 0.2083 (3) | 0.1498 (3) | 0.1140 (2) | 0.0535 (10) |
| H24 | 0.276507 | 0.155173 | 0.125850 | 0.064* |
| C25 | −0.0442 (3) | 0.3980 (3) | 0.0829 (2) | 0.0487 (9) |
| C26 | −0.0548 (3) | 0.3946 (3) | 0.1556 (3) | 0.0504 (10) |
| H26 | −0.118299 | 0.391451 | 0.156755 | 0.060* |
| C27 | 0.0293 (3) | 0.3961 (3) | 0.2268 (2) | 0.0443 (9) |
| H27 | 0.022621 | 0.393241 | 0.276169 | 0.053* |
| C28 | 0.1331 (3) | 0.4070 (3) | 0.1518 (2) | 0.0441 (9) |
| H28 | 0.196465 | 0.411718 | 0.150636 | 0.053* |
| C29 | 0.0493 (3) | 0.4053 (3) | 0.0803 (2) | 0.0509 (10) |
| H29 | 0.055847 | 0.409052 | 0.030915 | 0.061* |
| C30 | 0.1236 (2) | 0.4017 (2) | 0.2248 (2) | 0.0353 (7) |
| C31 | 0.4471 (3) | 0.2491 (3) | 0.2928 (2) | 0.0446 (9) |
| C32 | 0.3967 (3) | 0.3382 (3) | 0.3093 (4) | 0.0691 (14) |
| H32A | 0.438877 | 0.365609 | 0.361362 | 0.083* |
| H32B | 0.388943 | 0.387339 | 0.268271 | 0.083* |
| Cl1 | −0.14930 (8) | 0.39317 (10) | −0.00707 (8) | 0.0761 (4) |
| Co1 | 0.26804 (3) | 0.16814 (3) | 0.30081 (3) | 0.03432 (15) |
| N1 | 0.2816 (2) | 0.0092 (2) | 0.3101 (2) | 0.0474 (8) |
| N2 | 0.3327 (2) | 0.1422 (2) | 0.42965 (18) | 0.0448 (7) |
| N3 | 0.1173 (2) | 0.1655 (2) | 0.29682 (16) | 0.0361 (6) |
| N4 | 0.1766 (2) | 0.1544 (2) | 0.17391 (17) | 0.0399 (7) |
| N5 | 0.2996 (2) | 0.3148 (2) | 0.30930 (17) | 0.0371 (6) |
| O1 | 0.28102 (19) | 0.49502 (18) | 0.31874 (16) | 0.0514 (7) |
| O2 | 0.1963 (2) | 0.3847 (2) | 0.37872 (15) | 0.0559 (7) |
| O3 | 0.40152 (19) | 0.16917 (19) | 0.28193 (17) | 0.0481 (6) |
| O4 | 0.5322 (2) | 0.2591 (2) | 0.2929 (2) | 0.0702 (9) |
| O5 | 0.3105 (3) | 0.6232 (3) | 0.1980 (3) | 0.0983 (12) |
| H5A | 0.347048 | 0.666098 | 0.188612 | 0.147* |
| H5B | 0.258118 | 0.613758 | 0.155492 | 0.147* |
| O6 | 0.3351 (4) | 0.8969 (3) | 0.0997 (3) | 0.1259 (17) |
| H6A | 0.376116 | 0.937335 | 0.131724 | 0.189* |
| H6B | 0.357366 | 0.877645 | 0.064874 | 0.189* |
| O7Aa | 0.4063 (6) | 0.5759 (5) | 0.4692 (5) | 0.108 (3) |
| H7AAa | 0.371085 | 0.584915 | 0.496824 | 0.163* |
| H7ABa | 0.454505 | 0.537395 | 0.494454 | 0.163* |
| O7Bb | 0.4614 (12) | 0.5853 (10) | 0.4370 (9) | 0.146 (6) |
| H7BAb | 0.507441 | 0.607708 | 0.423668 | 0.219* |
| H7BBb | 0.425621 | 0.632318 | 0.441668 | 0.219* |
| O8Aa | 0.5302 (6) | 0.5306 (7) | 0.2911 (6) | 0.118 (3) |
| H8AAa | 0.579273 | 0.567926 | 0.316685 | 0.176* |
| H8ABa | 0.477073 | 0.564506 | 0.270094 | 0.176* |
| O8Bb | 0.5483 (10) | 0.5755 (10) | 0.3449 (10) | 0.128 (5) |
| H8BAb | 0.523108 | 0.617531 | 0.366272 | 0.192* |
| H8BBb | 0.565908 | 0.525171 | 0.375012 | 0.192* |
| S2 | 0.23263 (7) | 0.40128 (6) | 0.31590 (5) | 0.0367 (2) |
-
aOccupancy: 0.597 (10), bOccupancy: 0.403 (10).
1 Source of material
In a 250 ml round-bottom flask, a solution was prepared by dissolving glycine (7.51 g, 100 mmol), sodium hydroxide (8.00 g, 200 mmol), and 100 ml of deionized water with thorough stirring to ensure complete solubilization. Subsequently, 4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl chloride (21.11 g, 100 mmol) was introduced into the mixture, which was then stirred continuously at ambient temperature for a duration of 10 h to facilitate the sulfonylation reaction. Upon completion of the reaction, the pH of the reaction mixture was carefully adjusted to 1 using a 6 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution, prompting the precipitation of a white solid. The precipitate was isolated via filtration, rinsed with deionized water to remove any residual impurities, and then dried to yield the desired product, ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine.
A mixture of ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine (124.8 mg, 0.5 mmol), Co(CH3COO)2⋅4H2O (124.5 mg, 0.5 mmol), and 1,10-phenanthroline (180.2 mg, 1.0 mmol) was dissolved in a 50 ml volume of a 50 % methanolic solution at ambient temperature. The pH of the resulting solution was meticulously adjusted to neutral (pH 7) using a 2 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was subjected to thermal processing at 80 °C for 12 h within a Teflon-lined autoclave and then filtered. The filtrate was then allowed to undergo slow evaporation at room temperature, leading to the crystallization of colorless, block crystals of the title compound over a period of two weeks.
2 Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were added using riding models. Their U iso values were set to 1.2U eq of the parent atoms. The structure was solved with the ShelXT 3 structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL. 4
3 Comment
The acquisition of single crystals for peptide metal complexes often presents a formidable challenge, prompting the exploration of ligands with structural analogies to peptides to elucidate the intricate interactions between these biomolecules and metal ions. 5 , 6 , 7 Sulfonamide moieties are renowned for their diverse biological activities. 8 , 9 , 10 When amino acids are shielded by sulfonamide groups, they exhibit the versatility to function as monodentate ligands through the oxygen of the carboxyl group, or as bidentate ligands by engaging both the carboxyl oxygen and the amino nitrogen. Intriguingly, the –SO2- group has been observed to partake in coordination as well. 11 , 12 , 13 Our research group has successfully synthesized a range of ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-glycine complexes, 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 and this study contributes to our ongoing investigation.
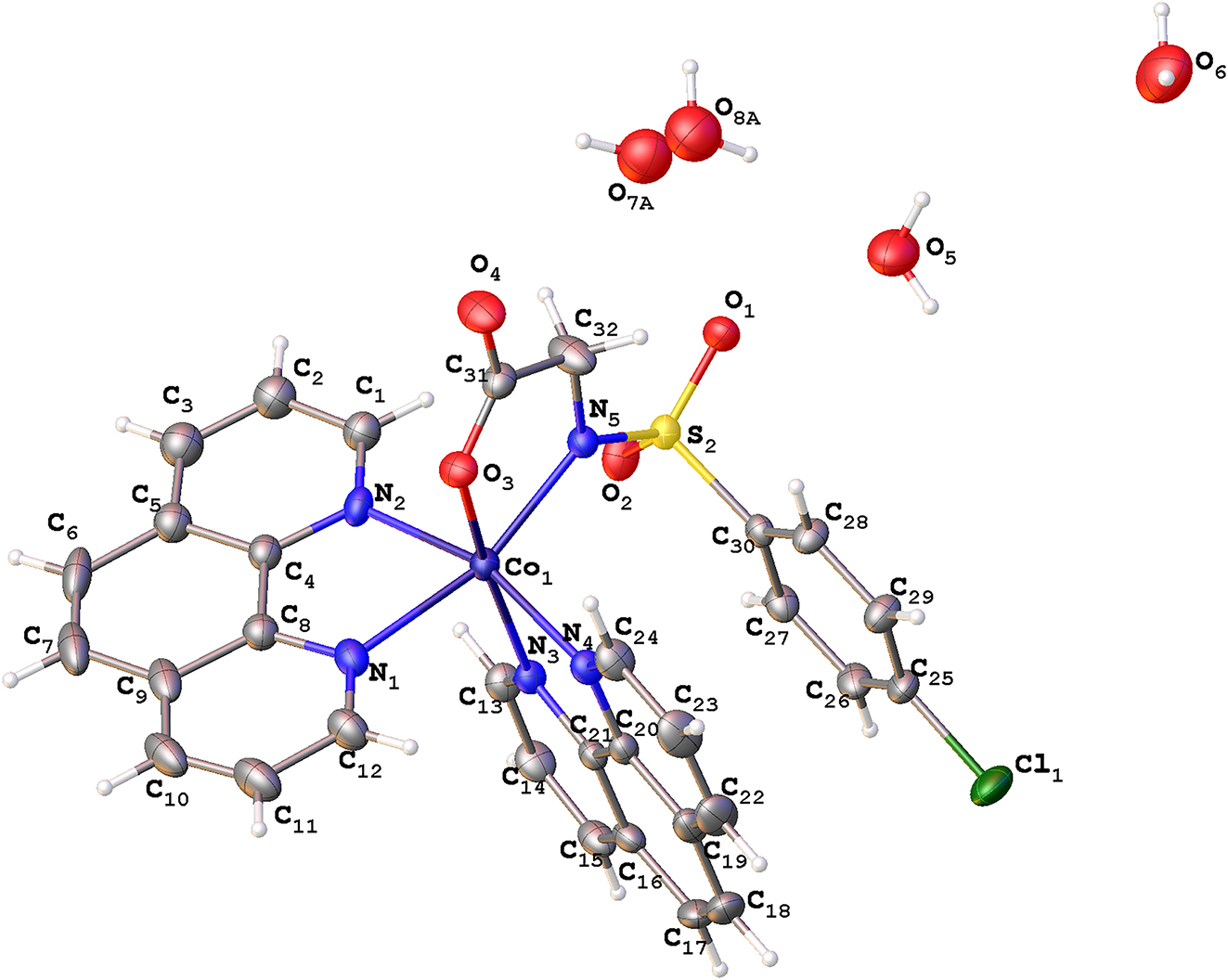
In this paper, the synthesis and crystal structure of a new cobalt(II) complex with ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-glycine and 1,10-phenanthroline were reported. Single crystal X-ray structure analysis reveals that the title complex crystallizes in the monoclinic system with space group P21/c. The asymmetric unit is composed of an independent Co(II) ion, one ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine ligand, two 1,10-phenanthroline ligands, and four lattice water molecules. The crystallographically unique Co(II) ion of the title complex is six-coordinated by four N atoms (N1, N2, N3, N4) from two 1,10-phenanthroline groups, one O atom (O3) and one N atom (N5) from ((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycine group, giving rise to a octahedron geometry. Co–N bond lengths fall in the range 2.0443(18)–2.185(2) Å, and Co–O bond length is 2.0872(16) Å. The bond lengths observed fall within the expected range and align closely with those documented for analogous complexes in prior studies. 16 , 17 The extended 3D supramolecular network is formed through hydrogen bonds of lattice water molecules.
Funding source: Doctoral Fund of Anshun University
Award Identifier / Grant number: asxybsjj202314
Funding source: Key Laboratory of Agricultural Resources and Environment in High Education Institute of Guizhou Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: Qianjiaoji[2023]025
Funding source: Porous Materials and Green Catalysis Innovation Team in High Education Institute of Guizhou Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: Qianjiaoji[2023]086
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: Doctoral Fund of Anshun University (asxybsjj202314), Key Laboratory of Agricultural Resources and Environment in High Education Institute of Guizhou Province (Qianjiaoji[2023]025), and Porous Materials and Green Catalysis Innovation Team in High Education Institute of Guizhou Province (Qianjiaoji[2023]086).
References
1. Bruker. SAINT Apex2 and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: a Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT-integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Lillo, V.; Galán-Mascarós, J. R. Transition Metal Complexes with Oligopeptides: Single Crystals and Crystal Structures. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 9821–9833; https://doi.org/10.1039/c4dt00650j.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Battistuzzi, G.; Borsari, M.; Menabue, L.; Saladini, M.; Sola, M. Amide Group Coordination to the Pb2+ Ion. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 4239–4247; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic950599h.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Sigel, H.; Martin, R. B. Coordinating Properties of the Amide Bond. Stability and Structure of Metal Ion Complexes of Peptides and Related Ligands. Chem. Rev. 1982, 82, 385–426; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00050a003.Search in Google Scholar
8. Si, Y.; Basak, S.; Li, Y.; Merino, J.; Iuliano, J. N.; Walker, S. G.; Tonge, P. J. Antibacterial Activity and Mode of Action of a Sulfonamide-Based Class of Oxaborole Leucyl-tRNA-Synthetase Inhibitors. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1231–1238; https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00071.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Naaz, F.; Srivastava, R.; Singh, A.; Singh, N.; Verma, R.; Singh, V. K.; Singh, R. K. Molecular Modeling, Synthesis, Antibacterial and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Sulfonamide Derivatives of Benzimidazole, Indazole, Benzothiazole and Thiazole. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 3414–3428; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2018.05.015.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Ghorab, M. M.; Ragab, F. A.; Heiba, H. I.; El-Gazzar, M. G.; Zahran, S. S. Synthesis, Anticancer and Radiosensitizing Evaluation of Some Novel Sulfonamide Derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 682–692; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.01.036.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Hou, H. W.; Chen, S. H.; Wang, L. Y.; Ma, L. F. Syntheses, Structures and Luminescence of Three New Supramolecular Complexes Containing N-P-Acetamidobenzenesulfonyl-glycine Acid. J. Coord. Chem. 2008, 61, 2690–2702; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958970801975539.Search in Google Scholar
12. Menabue, L.; Saladini, M. N-(arylsulfonyl)glycines as Cyclometalating Ligands. Crystal and Molecular Structures of Disodium bis(μ-chloro)bis[μ-N-(phenylsulfonyl)glycinato-O,N,C]bis[μ-N-(phenylsulfonyl)glycinato-O, O′]Tetrapalladate(II) Hexahydrate and Disodium bis(μ-chloro)bis(μ-N-tosylglycinato-O,N,C) bis(μ-N-Tosylglycinato-O, O′)Tetrapalladate(II)-4.5-Water-2-N-Tosylglycine. Inorg. Chem. 1991, 30, 1651–1655; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic00007a042.Search in Google Scholar
13. Chen, X. M.; Liu, Z. J.; Zhao, R. F.; Cheng, J.-S.; Qin, L.; Long, Z.-D. Crystal Structure of Aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N″)(((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl) glycine-κ2 N,O)copper(II) Dihydrate, C18H20CuN4O9S. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 1141–1143; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0206.Search in Google Scholar
14. Liu, Z. J.; Chen, X. M.; Hao, S. Y.; Cheng, M. Q. Syntheses, Crystal Structures, and Thermal Properties of Two Transition Metal Complexes with 4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl-glycine Acid Ligand. Synth. React. Inorg., Met.-Org., Nano-Met. Chem. 2016, 46, 529–533; https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2014.988810.Search in Google Scholar
15. Cheng, M. Q.; Chen, X. M.; Liu, Z. J.; Feng, C. Q. Syntheses, Structures, and Thermal Properties of Two New Mn(II) and Ni(II) Complexes of 3-Nitrobenzenesulfonyl-Glycine Acid and 4-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl-Glycine Acid Ligands. Synth. React. Inorg., Met.-Org., Nano-Met. Chem. 2013, 44, 27–32; https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2013.763278.Search in Google Scholar
16. Liu, Z. J.; Chen, X. M.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Zhou, W.-C.; Wei, L.; Zhao, Y.-X. Crystal Structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) Dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 1149–1151; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0370.Search in Google Scholar
17. Chen, X. M.; Liu, Z. J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.-T.; He, X.; Deng, Y. Crystal Structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N: N′)cobalt(II)} Dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 1141–1143; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0364.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

