Computational design and in vitro assay of lantadene-based novel inhibitors of NS3 protease of dengue virus
-
Somdutt Mujwar
, Abhishek Tiwari
Abstract
Dengue virus (DENV) infection is one of the diseases for which no drug is available for the treatment. The DENV NS2B-NS3 protease is considered to be the prime target for anti-dengue drug development because of its importance in the development of new virus subunits via DENV poly-protein breakdown. Pentacyclic triterpenoids (Lantadenes) from the weed Lantana camara L. and its semi-synthetic congeners have shown a wide array of biological activities in the last two decades. The virtual screening strategy was used on the library of 78 natural and semi-synthetic lantadenes to predict the potent antagonists for the NS2B-NS3 protease enzyme of DENV and their experimental validation by in vitro assay of lead molecules. In the in silico analysis of 78 triterpenoids, two lead molecules (−10.60 and −9.93 kcal/mol) were predicted to be inhibitors of protease (viral) when compared to its reference ligand 1,8-dihydroxy-4,5-dinitroanthraquinone (−5.377 kcal/mol). At the same time, binding affinity, pharmacokinetic, and toxicity profiling, along with molecular dynamics simulations, were studied. The in vitro viral infection inhibition assay inferred that lead molecule 62 exhibited a 60% and 45% reduction in DENV titers at 10 and 5 µM concentrations, respectively. The lead molecule 62 can further be optimized for its pharmacophore and has the potential to be developed as a drug-like molecule.
1 Introduction
Dengue virus (DENV) is a pathogenic parasitic organism belonging to the disease-causing family of Flaviviruses. The viral genome of DENV is a single-stranded RNA having about 11k nucleotides encoding three major structural proteins of the viral capsid, envelop protein, membrane proteins, as well as seven non-structural proteins, i.e., NS1, NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, and NS,5 which are majorly involved in the biochemical processes of the viral pathogen [1]. The viral genome of DENV encodes for a single polyprotein that further undergoes fragmentation at the surface of the host’s rough ER by the viral NS2B/NS3 protease enzyme. DENV protease enzyme is a serine protease belonging to the chymotrypsin enzyme family having a catalytic triad in the form of Ser-His-Asp [2]. The biochemical functioning of the viral NS3 protease enzyme is regulated via an NS2B cofactor for recognition of the substrate. Eight out of the 13 polyprotein cleavage sites are cleaved by the viral protease for further processing and maturation into the viral particles, making it an appropriate target for developing novel drugs for the treatment of dengue [3].
Natural products offer a wide and complex array of structure and have been responsible for various types of biological activities. Triterpenoids are a class of secondary metabolite plants that have demonstrated different pharmacological properties, including anticancer, antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-viral activities due to their complex and unique structural feature. Triterpenoids from the weed Lantana camara L. called Lantadenes (Figure 1) have attracted a lot of interest in the last two decades, and more than a hundred semi-synthetic congeners have been synthesized by us and have been evaluated for their anticancer activities [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. These diverse libraries of compounds have been screened computationally and lead molecules have been studied for their in vitro dengue inhibition potential.

Chemical structures of lantadenes A and B.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 In silico analysis
2.1.1 Design of the ligand library
A ligand library of lantadene analogues was prepared using a bioisosteric replacement strategy with the intent to increase its affinity for its macromolecular target and increase its permeability across the plasma membrane to optimize pharmacokinetics for increased bioavailability. Initially the 2D structures of all the concerned ligands were prepared by using the ChemDraw-15.0 tool, followed by converting each of the ligands to stabilized conformation having minimum structural energy with optimized spatial geometry by applying MM2 forcefield of Chem3D software [13]. Optimized 3D structure of each ligand was finally saved in protein databank (*.pdb) format as per compatibility with the AutoDock tool.
2.1.2 Selection and preparation of target proteins
The structural protein model of the viral NS3 protease enzyme was selected on the basis of the lowest resolution of X-ray used for the structural determination via the XRD technique for the refined structural model as well as the presence of a complex ligand for the validation of docking protocol. Structural prototype of the NS3 protease enzyme of DENV co-crystallized with coenzyme NS2B was downloaded from the protein databank (PDB code-2FOM) [14,15,16]. The bound peptidyl coenzyme-based ligand was detached from the macromolecular complex by using the Chimera tool to obtain nascent receptor and ligand molecules required for docking analysis [17,18,19]. Macromolecular target was set for docking analysis by removing non-redundant water molecules and assigning Gasteiger charge and addition of polar hydrogens.
2.1.3 Binding site identification
The macromolecular active site was explored by using the DoGSiteScorer module of the Protein Plus webserver by observing the conformational and surface of the target protein. DoGSiteScorer is a grid-based approach that uses Gaussian filters for the identification of pockets and sub-pockets present in the macromolecular structure. The identified macromolecular active site of the viral NS3 protease enzyme was further utilized for finalizing the grid parameters required for performing docking analysis [20,21,22].
2.1.4 Molecular docking
The grid-box prepared by using the prior identified parameters covering the ligand’s extended conformations as well as the active residues incorporated in the ligand binding were later utilized for generating map files for specific atoms with the Autogrid software [23,24,25,26,27,28].
For docking investigations, AutoDock 4.2 software was utilized, which uses the Lamarckian genetic (LG) algorithm for conformational search. The binding energy of each ligand is calculated from a docked atom configuration by utilizing a force field with linear weights as a scoring function. The forcefield estimates the ligand’s free binding energy based on the integration by comparative energetics of intramolecular energies for the bound and unbound states of the reference ligand by using a thermodynamic model. The optimized parameters for the docking of the reference crystallized ligand were saved in the docking parameter file and are utilized for the docking analysis of newer ligands [29,30,31].
2.1.5 In silico screening
The molecular ligand library of 78 lantadene-based ligand molecules was further utilized to execute computational screening against the viral NS3 protease enzyme to predict the potent leads based on their binding affinities (Table S1, supplementary information). The interacting macromolecular residues actively involved in the binding of the concerned ligands were specifically analyzed to predict the affinity of the specific ligand against the viral NS3 protease enzyme. The utilized docking parameters were further evaluated to validate that the executed method based on the resulting binding energy for the reference ligand should fall well within the defined range. The validated parameters were further employed for the docking analysis of the ligands of the prepared library, and the leads were shortlisted for further analysis based on their highest affinity and lowest binding energy against the concerned antiviral target. Lamarckian Genetic algorithm was the scoring function of the AutoDock tool to evaluate their binding affinity for the target receptor [32,33,34,35,36,37,38].
2.1.6 Pharmacokinetic and toxicological profiling
The lead molecules need to have discrete physicochemical properties that facilitate the smooth movement of the drug within the human body to impart long-lasting and potent therapeutic effects. The pharmacokinetics optimization by absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) is a crucial step in developing a new drug molecule. It has been observed that the physicochemical properties of the small chemical moieties play a significant role in controlling their ADME, and their pharmacokinetics can be optimized by making small structural changes. Nowadays, computational modeling is a trending approach for optimizing the pharmacokinetic profile of a small molecule and is considered as highly reliable for predetermining the pharmacokinetic behavior of a newer lead drug development regimen. These computational modeling approaches for pharmacokinetic modeling were proven to be an economical and faster alternative to the experimental methods [39,40,41]. pkCSM webserver was utilized in this study to evaluate critical drug-like characteristics based on the physicochemical and pharmacological features of shortlisted leads based on Lipinski’s rule of five.
2.1.7 Molecular dynamic simulation
Based on the observed docking outcome and their safety profile, lead compound 62 was shortlisted post-computational screening for proceeding further to analyze its thermodynamic stability by executing MD simulation. The nominated lead molecule was first exposed to a simulation for a timeframe of 100 ns to confirm the complex stability with regard to time at a fixed temperature of 300 K. Desmond software by Schrodinger was utilized to simulate the dynamic nature of ligand 62 complexed within the macromolecular target. The ligand–receptor complex was solvated in an explicit water box by employing an OPLS3e force field. The preferred SPC (single point charge) model was inferred for the explicit water molecules by using the OPLS3e force field for the simulation of macromolecular complexes having small ligands for the best repeatable results [42,43,44,45].
The displacement of the residues of the macromolecular receptor and the ligand from their original positions within a specific time period during their binding process was determined using their root mean square deviation (RMSD). The movement of the macromolecular residues from their initial positions in the structural model was calculated as the root mean square fluctuation (RMSF). The structural arrangements of the macromolecular secondary structure elements (SSE), such as α-helices and β-strands, were calculated by considering their consistent residue index during simulation. The chemical interactions existing between the macromolecular target and the bound ligand during the simulation were assessed by hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, and interactions via the formation of water bridges. The ligand’s RMSD value was determined by its relative movement with reference to its initial frame during the simulation. The ligand’s extended length, corresponding to its primary moment of inertia, was determined using rGyr MolSA, which represents van der Waal’s surface area. The contribution of oxygen and nitrogen atoms was considered in estimating the polar surface area (PSA), while rGyr MolSA was calculated using a 1.4 probe radius.
2.2 Methodology for the synthesis of lead compounds
2.2.1 General experimental procedures
The procedure and conditions of synthesis are described in Supplementary information. All the reagents and solvents were purchased from local Indian suppliers (Ranchem, S D Fine) and were used without further purification or distillation unless otherwise stated.
2.2.2 Plant material, extraction, and isolation of lantadenes
Lantana camara L. leaves were collected in July 2022 from Palampur, Himachal Pradesh, India. The plant was authenticated by a qualified botanist and taxonomist, and herbarium sheet (LCL/2022/234) was submitted. The leaves were dried and powdered. Lantadenes A and B were isolated in their pure form, as described in our previous publications, and the purity of Lantadenes A and B was ascertained by spectroscopic studies [4].
2.2.3 Synthesis of lead molecules (62 and 64)
The synthesis was carried out by the procedure as reported by us previously [5,6,7,8]. The detailed scheme and spectral data are provided as supplementary information.
2.2.4 In vitro dengue inhibition assay
The lead molecules identified after computational screening were synthesized and screened for their antiviral activities on A549 cell lines. The cells (∼50,000) were seeded in a 48-well plate and infected with the DENV2 strain at five MOI for 1 h. The infected cultures were incubated for 1 h in the culture media with selected lead molecules at two different concentrations (10 or 5 µM). After 24 h post-infection, viral titers in the supernatants were estimated by a plaque assay, as published previously [46].
3 Results
3.1 Ligand designing
With the intent to increase the affinity against the concerned receptor as well as to optimize the pharmacokinetics of the resulting compound, bioisosteric substitutions have been executed at C-3 and C-22 of the lantadene nucleus. Based on the executed substitutions, a ligand library of 78 energy-minimized lantadene analogues was prepared by using ChemDraw and Chem3D software.
3.2 Macromolecular target selection
The structural model of the NS3 protease enzyme of DENV procured from the PDB database was resolved by XRD at a resolution of 1.50 Å and an Escherichia coli-based expression system. The macromolecular structure of the antiviral drug target has two polypeptide chains: a small polypeptide chain A of the NS2B domain having 62 amino acids and a chain B of the NS3 protease enzyme having 185 amino acids. Chain B of the viral NS3 protease enzyme was used for docking studies by removing the coenzyme structure.
3.3 Molecular docking simulation
The macromolecular target for the current docking protocol was set for docking analysis by adding polar hydrogen atoms, providing equal distribution of Gasteiger charge, and assigning autodock4 atom type to all the macromolecular residues. The grid box was equipped by casing the extended conformations of the reference ligand and interacting residues with the complex ligand. The grid dimensions considered for the current study were x = −5.387, y = −12.72, and z = 13.414, having a size of 40 × 40 × 40 and a spacing of 0.586 Å. The docked reference ligand has identical interactions and is clearly shrouded over biologically active conformation, leading to successful validation of the current docking protocol by chemical resemblance and overlay methods. These validated parameters were further used for performing in silico screening of the prepared ligand library against the viral enzyme.
3.4 In silico screening
The docking-based computational screening of a designed molecular library comprising 78 lantadene analogues against the viral NS3 protease enzyme was performed to identify potential leads. The validated grid parameters were used for the virtual screening of the ligand library against the active binding site of the target viral receptor. The obtained docking results are tabulated in Table 1.
Binding energies of the shortlisted lantadene-based leads against the viral NS3 protease enzyme
| S. No. | Name/code | Structure | NS3 protease enzyme (PDB id: 2FOM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11 |
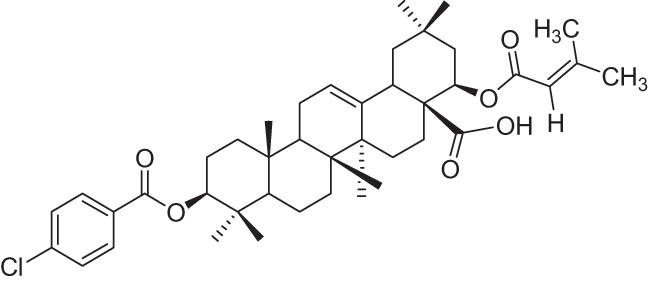 |
−9.27 |
| 2 | 18 |
 |
−9.24 |
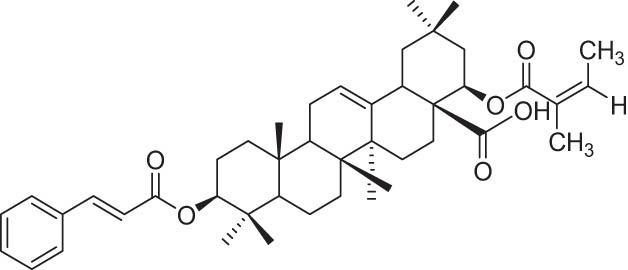
| 3 | 25 |
 |
−9.48 |
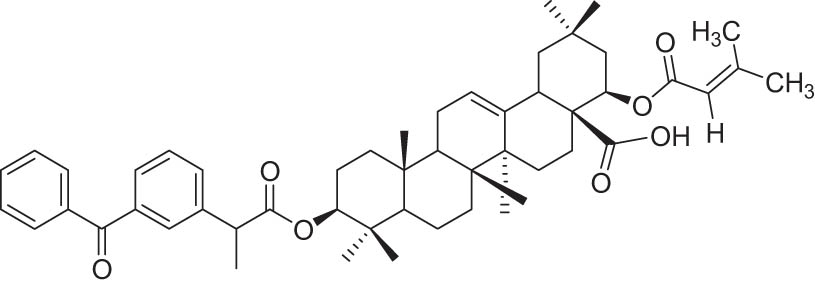
| 4 | 30 |
 |
−9.29 |
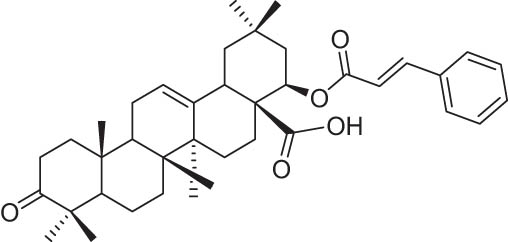
| 5 | 37 |
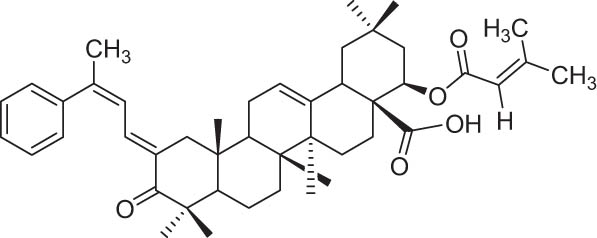 |
−9.24 |
| 6 | 62 |
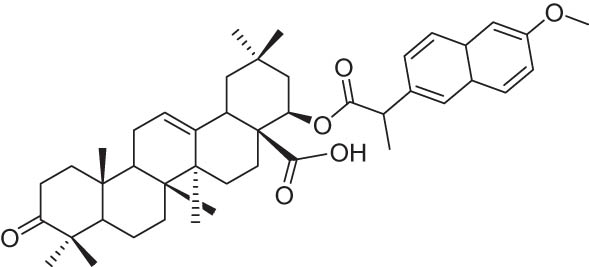 |
−10.60 |
| 7 | 64 |
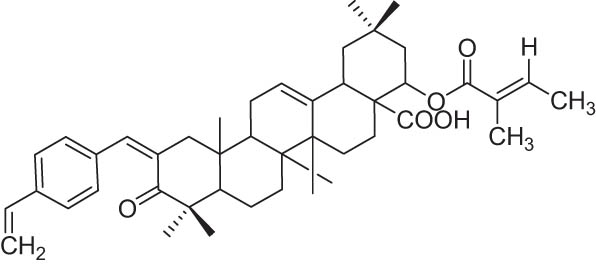 |
−9.93 |
| 8 | 65 |
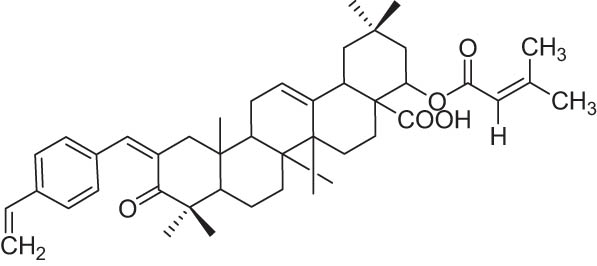 |
−9.85 |
| 9 | Reference |
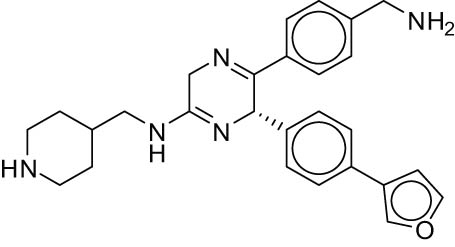 |
−5.84 (i16) |
3.5 Pharmacokinetic and toxicological profiling
Pharmacokinetic factors control how drugs travel through the human body. The physicochemical, ADME, and toxicity characteristics of the lead compounds were predicted using pkCSM webserver. Table 2 lists the proposed lead’s pharmacokinetics and toxicity characteristics. According to Lipinski’s rule of five, all of the studied parameters (MW, HBA, HBD, TPSA, and LogP) of the selected compounds fall within the optimal range. Compound 62 has been recommended with better pharmacokinetic qualities based on the specified physicochemical parameters. P-glycoprotein does not exhibit itself as a substrate for the ligand molecule 62, serving as a physiological barrier for drugs, toxins, and xenobiotics. For most of the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes, except CYP3A4, compound 62 has not shown substrate-like characteristics. The ligand consistently shows a high propensity to be eliminated from the body via a small number of toxicity pathways, such as hERG-I blocking, sensitization of the skin, toxic effects of Tetrahymena pyriformis, hepatotoxicity, and minnow toxicity. The estimated ADME and toxicological parameters of compound 62, which are based on physicochemical factors, match well within the permitted range, making it a better option for therapeutic development.
Physicochemical, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics properties of the selected lead compounds for the viral NS3 protease enzyme
| Property | Descriptor | 11 | 18 | 25 | 30 | 37 | 62 | 64 | 65 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW | (g/mol) | 693.365 | 684.958 | 791.082 | 600.84 | 680.97 | 684.958 | 666.943 | 666.943 | 441.579 |
| LogP | — | 10.2396 | 9.9858 | 11.3071 | 8.6769 | 10.5695 | 9.4283 | 10.2662 | 10.2662 | 3.937 |
| Rotatable bond | — | 5 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| HBA | — | 5 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 6 |
| HBD | — | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| TPSA | (Å)2 | 297.97 | 299.707 | 345.98 | 263.458 | 300.269 | 299.449 | 293.904 | 293.904 | 194.573 |
| Absorption | Water solubility (mol/L) | −3.763 | −3.708 | −3.333 | −3.753 | −3.651 | −3.705 | −3.799 | −3.726 | −3.647 |
| CaCo2 permeability | 0.75 | 0.711 | 0.575 | 0.685 | 0.706 | 0.861 | 0.809 | 0.758 | 0.888 | |
| Intestinal absorption (%) (human) | 95.559 | 98.072 | 100 | 98.289 | 99.122 | 99.958 | 99.719 | 99.286 | 92.131 | |
| Skin Permeability (Log Kp) | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.778 | |
| P-glycoprotein substrate | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| P-glycoprotein I inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | |
| P-glycoprotein II inhibitor | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Distribution | VDss (human) | −0.805 | −0.979 | −1.153 | −0.784 | −1.187 | −0.676 | −1.096 | −1.129 | 1.822 |
| Fraction unbound (human) | 0 | 0 | 0.037 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.131 | |
| BBB permeability | −0.603 | −0.426 | −0.686 | −0.185 | −0.106 | −0.328 | −0.12 | −0.122 | −0.376 | |
| CNS permeability | −1.755 | −1.787 | −1.756 | −0.994 | −0.624 | −1.889 | −0.695 | −0.704 | −2.029 | |
| Metabolism | CYP2D6 substrate | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| CYP3A4 substrate | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| CYP1A2 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | |
| CYP2C19 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| CYP2C9 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| CYP2D6 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | |
| Excretion | Total clearance (log ml/min/kg) | −0.749 | −0.405 | −0.888 | −0.374 | −0.618 | −0.615 | −0.55 | −0.636 | 0.6 |
| Renal OCT2 substrate | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| Toxicity | AMES toxicity | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Max. tolerated dose (human) (log mg/kg/day) | 0.74 | 0.6 | 0.208 | 0.534 | 0.574 | 0.996 | 0.66 | 0.62 | 0.095 | |
| hERG I inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| hERG II inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | |
| Oral rat acute toxicity (LD50) (mol/kg) | 2.774 | 2.684 | 2.617 | 2.662 | 2.681 | 2.877 | 2.732 | 2.726 | 2.744 | |
| Oral rat chronic toxicity (LOAEL) (mg/kg/day) | 0.402 | 0.755 | 0.661 | 0.977 | 0.206 | 1.309 | 0.268 | 0.249 | 1.027 | |
| Hepatotoxicity | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | |
| Skin sensitization | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| T. pyriformis toxicity (mg/L) | 0.285 | 0.285 | 0.285 | 0.285 | 0.285 | 0.285 | 0.285 | 0.285 | 0.416 | |
| Minnow toxicity | −3.594 | −3.664 | −5.087 | −2.384 | −3.222 | −1.751 | −3.139 | −3.055 | 2.099 |
3.6 Molecular dynamics simulation
By running a 100 ns MD simulation using the Schrodinger Desmond program, the macromolecular complex of the NS3 protease with the proposed lantadene-based antagonist compound 62 has been further confirmed for its thermodynamic stability. The macromolecular receptor consists of 150 amino acids, and the ligand contains 50 heavy atoms of 110 atoms in total, along with 7 rotatable bonds. RMSD analysis ensures effective implementation of the simulation procedure for validating the structural integrity during the entire operation. Through the alignment of their heavy metals, the ligand’s RMSD measurement indicates its stability in relation to the active residues of the target enzyme throughout the simulation. RMSD for the macromolecular residues demonstrated consistent vibrations within the range of 1.2–2.0 Å, indicating that the majority of the residues remained unchanged in their initial positions during the complexation of the ligand molecule. Throughout the simulation run, the RMSD value of the ligand molecule remained stable within the range of 4.8–6.4 Å, without significant deviations. Both the backbone of the macromolecule and the ligand based on lantadene exhibited high stability during the simulation, with minimal fluctuations. The RMSD plot in Figure 2 illustrates the macromolecule and ligand’s stability throughout the 100 ns simulation process. RMSF for most of the macromolecular amino acids, except some terminal residues, lies within the range of 0.5–2.0 Å, which was well within the allowed range of 3 Å. Figure 3(a) and (b) displays the RMSF of the NS3 protease enzyme and lantadene-based ligand (Compound 62) during the simulation. RMSF analysis was performed on the ligand complexed within the active site of the target NS3 protease. It was observed that the RMSF values ranged from 2 to 3 Å during the entire 100 ns simulation. This indicates the ligand’s stability within the macromolecular active site with only minor alterations in a few functional groups that are essential for interacting with the target macromolecule.
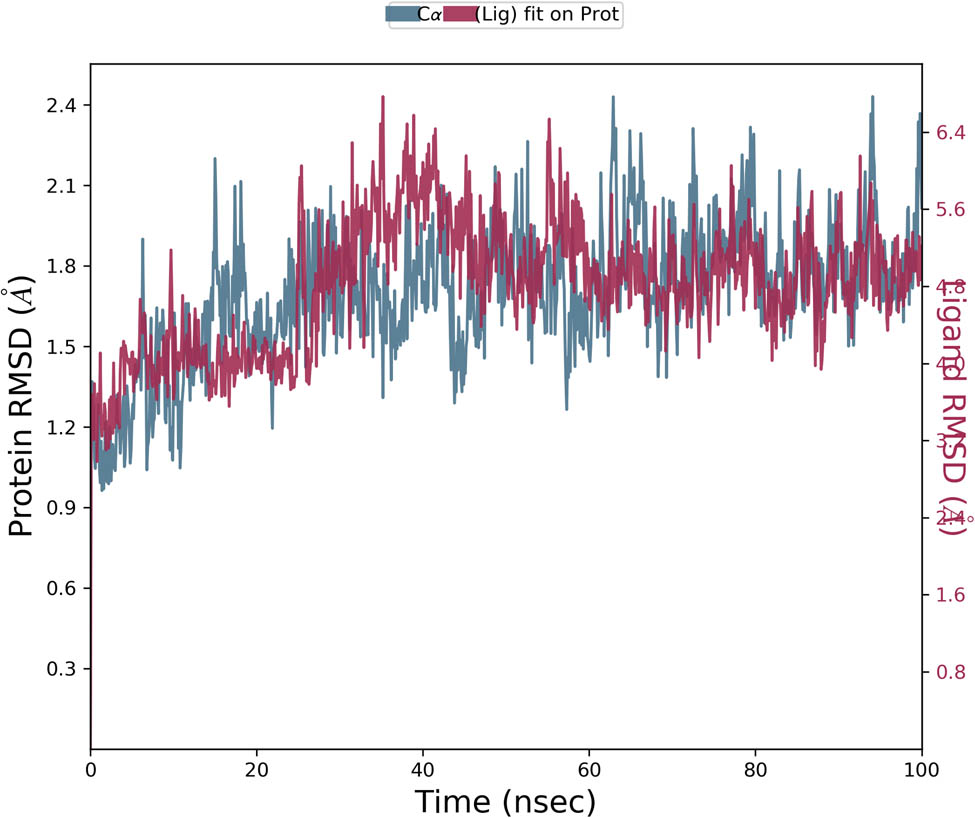
RMSD of the Cα backbones of the viral NS3 protease enzyme and compound 62 observed via MD simulation analysis.
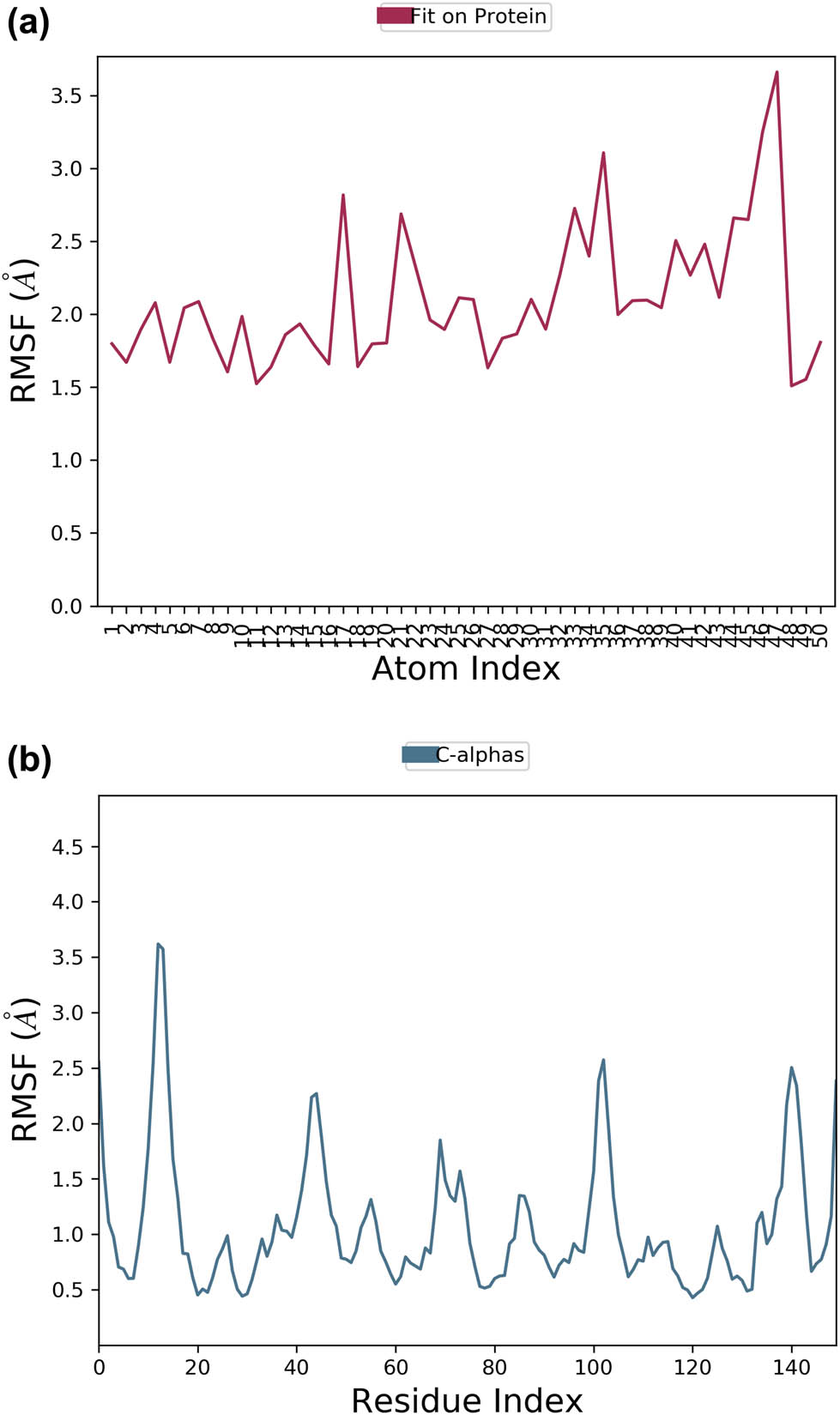
RMSF of the bound lantadene-based compound 62 (a) and the Cα backbone of the viral NS3 protease enzyme (b) observed via MD simulation analysis.
Throughout the simulation, the SSE analysis showed that approximately 2% of the structure consisted of α helices, while about 43% consisted of β strands, resulting in a combined contribution of 45% from SSE, which remained relatively consistent for most of the simulation duration. The investigation of the interactions between the macromolecule and the ligand revealed specific residues, including His51, Lys73, Leu128, Pro132, Ser135, Gly151, Asn152, Gly153, and Tyr161, that interacted with the ligand during the entire 100 ns simulation. A detailed representation of the protein–ligand connections observed during the entire simulation period is shown in Figure 4. Additionally, Figure 5 illustrates the two-dimensional binding interaction between the viral NS3 protease enzyme and the designed lantadene-based inhibitor compound 62.
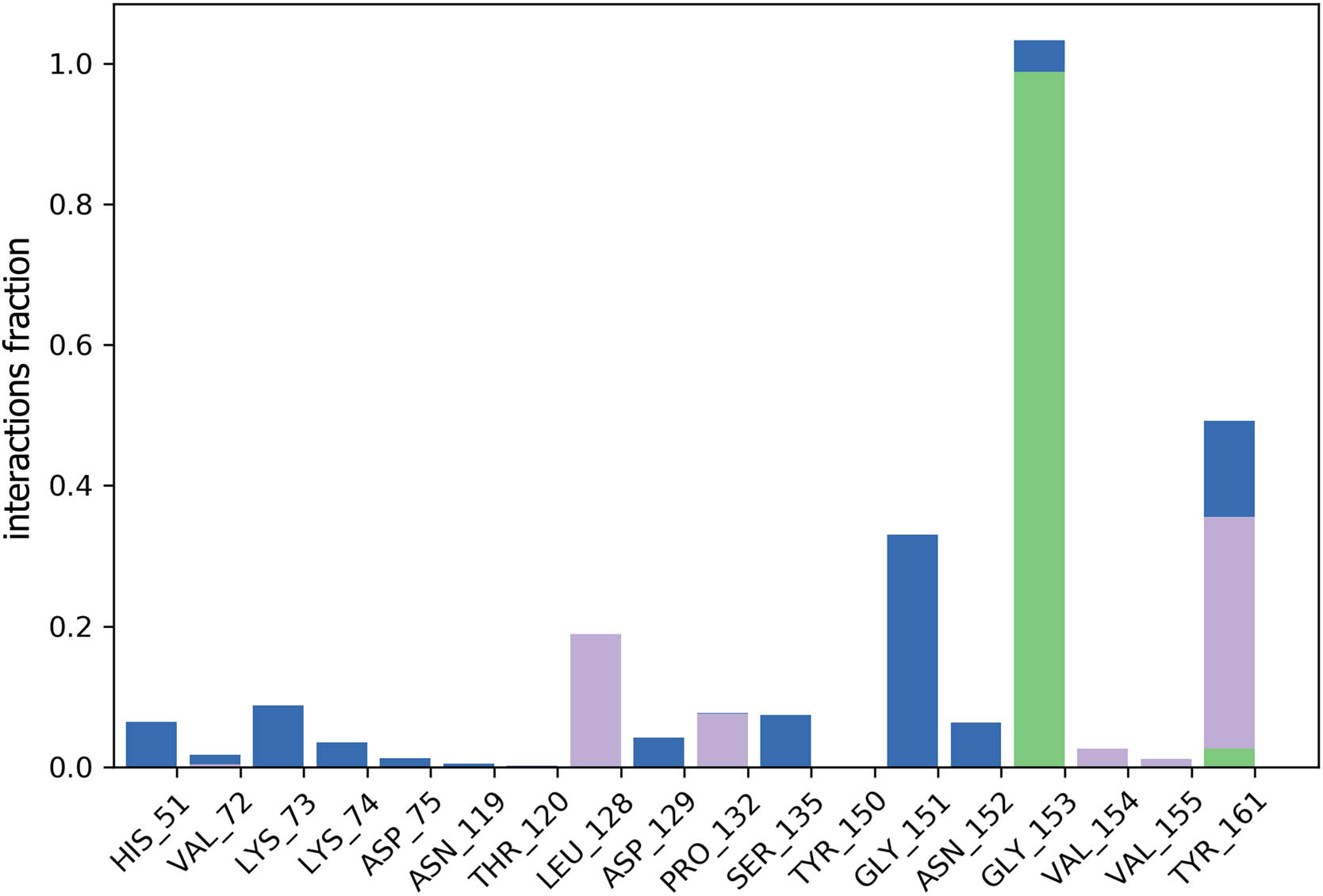
Interactions observed between compound 62 and the macromolecular target during the MD simulation analysis. Water bridges are depicted in blue, H-bonds are depicted in green, and hydrophobic interactions are shown in magenta.
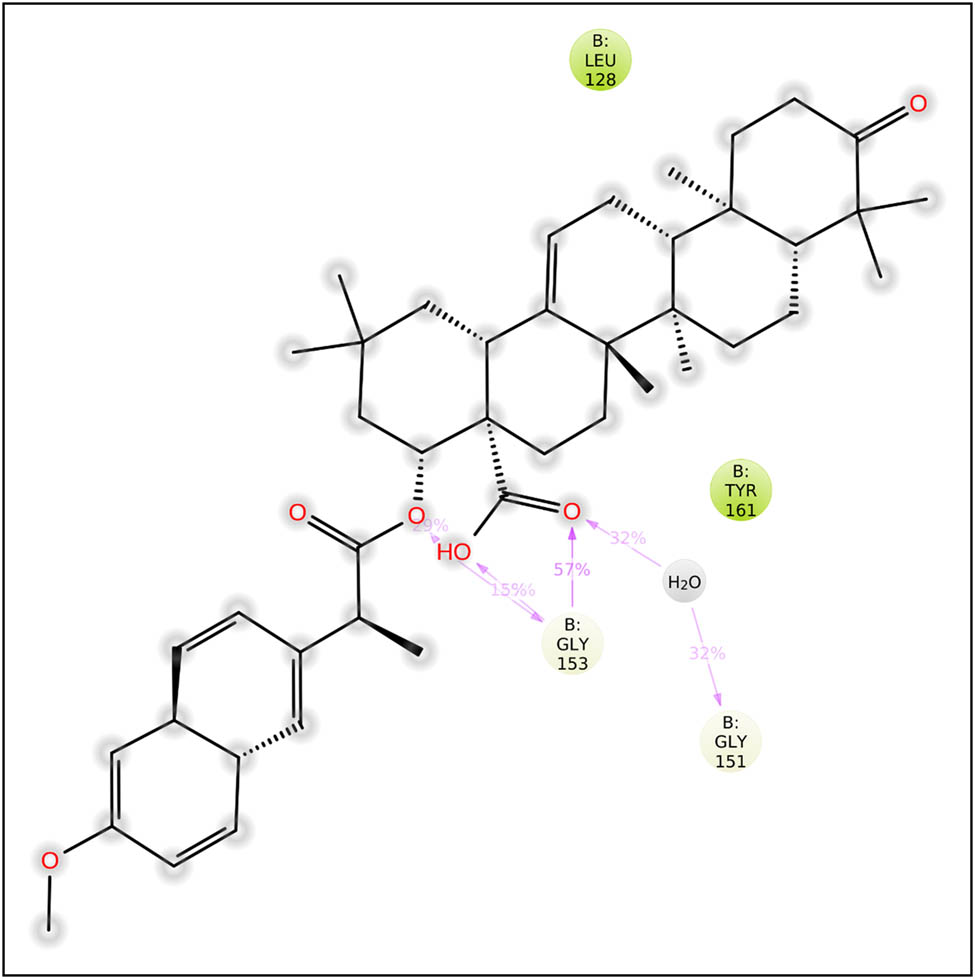
Two-dimensional ligand interactions of compound 62 with the viral NS3 protease enzyme.
3.7 In vitro dengue inhibition activity
The two lead molecules (62, 64) were identified by computational screening of 78 lantadene congeners. The lead molecules were screened for inhibitory assay of dengue in vitro. The results showed that compound 62 reduced DENV titers by 60% and 45% at 10 and 5 µM concentrations, respectively (Figure 6a). However, compound 64 exhibited a 40% and 15% reduction in the DENV titers at 10 and 5 µM concentrations, respectively (Figure 6b). Compound 62 has been previously developed by us as NF kappa B inhibitors in various cancer cell lines. In docking studies against the viral NF kappa B receptor, compound 62 showed maximum efficacy. The results indicate that compound 62 can be a promising candidate for the development of DENV infection. Further, optimization of the pharmacophore and ADME studies are vital to developing lead molecule 62 as a promising NCE against DENV.
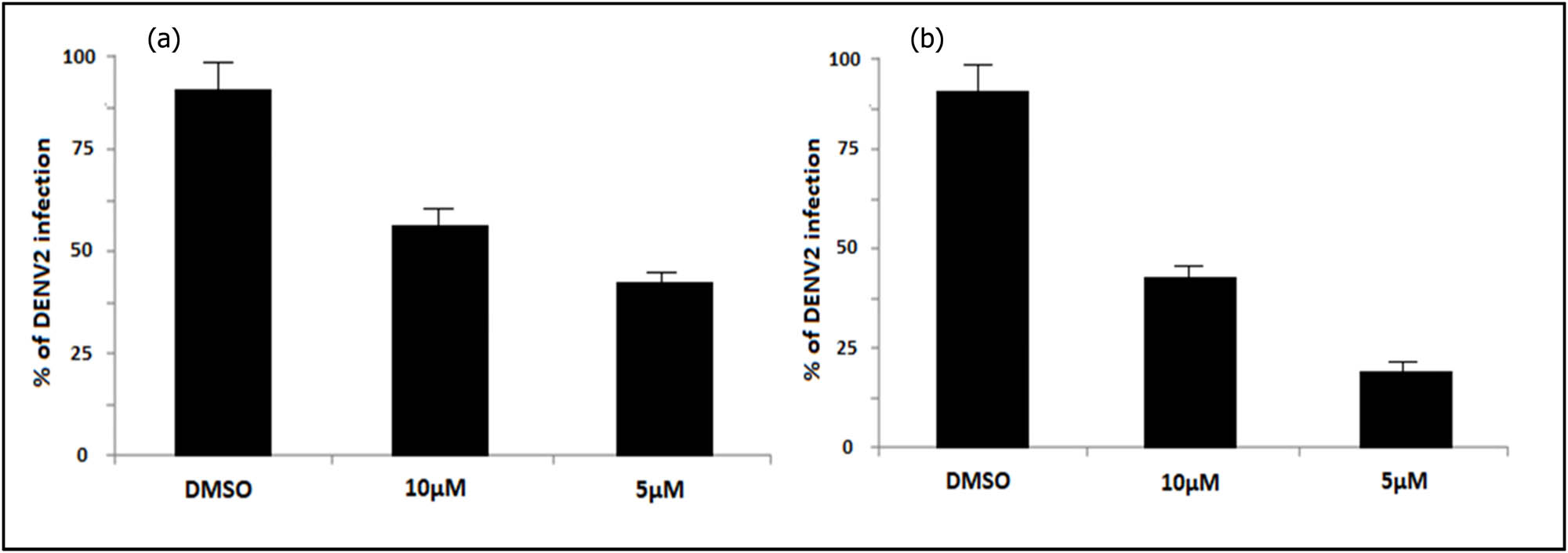
DENV2 strain inhibition by (a) compound 62 and (b) compound 64 at 10 and 5 µM. The 95% confidence intervals of geometric means were used for error bars.
4 Discussion
Computational designing methods, including docking and dynamic simulation, are highly reliable approaches to predicting the molecular behavior of ligands within the macromolecular cavity. The predicted molecular behavior of the newer ligands based on the chemical laws helps determine the binding affinity toward the specific target receptor. The computational techniques are very fast, economical, and multitasking in nature, which fastens the drug discovery process with reduced economic burden and a higher rate of success [47].
Lantadenes are a group of compounds having pentacyclic triterpenoid oleanane nucleus, which was first obtained from the plant Lantana camara and exhibited diverse therapeutic potential including anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiulcer, insecticidal, antihyperglycaemic, antihypertensive, anti-urolithiatic, and wound healing [48]. Reported for multiple therapeutic potentials of lantadene derivatives, a series of lantadene analogues were designed by considering diverse functionalities based on the bioisosteric replacements to evaluate their therapeutic potential against DENV. The NS3 protease enzyme is a vital component of the DENV involved in the vital process of replication and processing of viral polyproteins required for the execution of the viral life cycle and causing infection within the human body. Thus, the NS3 protease enzyme can be a crucial therapeutic target to be considered in the current study to develop lantadene-based antiviral agents targeting DENV.
The three-dimensional structural model of the NS3 protease enzyme was selected from the PDB database based on the minimum resolution of X-ray used for determination of their structural model, as the lowest resolution of X-ray used in X-ray crystallography results in a more refined structural model of the protein. The procured structure model is then explored to identify the binding cavity in the macromolecular structure by using the DoGSiteScorer module of Protein Plus webserver, which observes the conformational surface of the protein for the presence of cavity or furrow-like structure suitable for strong binding of ligand by using Gaussian filters. Later, the macromolecular structure is prepared for docking by the addition of polar hydrogens and equal distribution of Gasteiger charge. Later, the energy-minimized ligand library was computationally screened against the concerned antiviral target to shortlist the potential leads having strong binding affinity for the viral drug target and compared with the reference inhibitor 1,8-dihydroxy-4,5-dinitroanthraquinone. The shortlisted leads for the viral NS3 protease enzyme were further screened for their pharmacokinetic profiling based on their physicochemical characteristics, as the considered physicochemical properties govern the rate-limiting steps of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, which regulates the bioavailability of the proposed molecule at the target site. Compound 62 was proposed as a lantadene-based optimized lead molecule having good binding affinity as well as an optimized pharmacokinetic profile to proceed for MD simulation of 100 ns using the Desmond tool by Schrodinger for evaluating its thermodynamic stability within the binding cavity of the viral NS3 protease enzyme.
Later, the lantadene was isolated from the L. camara plant and was further utilized for the chemical synthesis of the desired lantadene analogue, i.e., compound 62. The synthesized compound 62 was characterized by using diverse spectroscopic techniques and further evaluated for their therapeutic potential against DENV by using in vitro cell line-based inhibition assay using A549 cell lines at two different concentrations of 10 or 5 µM and it shows 60 and 45% reduction in DENV titers, respectively.
5 Conclusions
The 78 pentacyclic triterpenoids (Lantadenes) from weed Lantana camara L. and their semi-synthetic congeners were virtually screened to predict the potent inhibitors of DENV NS2B-NS3 protease with an in vitro assay of lead molecules. In the in silico analysis of 78 triterpenoids, two lead molecules (−10.60 and −9.93 kcal/mol) were found to be a viral protease antagonist when compared with the reference ligand 1,8-dihydroxy-4,5-dinitroanthraquinone (−5.377 kcal/mol). At the same time, the lead molecules were studied for binding affinity, pharmacokinetic, and toxicity profiling, along with molecular dynamics simulations. The in vitro viral infection inhibition assay indicated that lead molecule 62 leads to a 60 and 45% reduction in DENV titers at 10 and 5 µM concentrations, respectively. The lead molecule 62 can further be optimized for its pharmacophore, and based on the in silico and in vitro observation for molecule 62, we are planning for the in vivo preclinical studies to confirm the therapeutic efficiency of molecule 62 against DENV followed by clinical trials based on the observed preclinical manifestations.
-
Funding information: The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research through the project number IFP-IMSIU-2023097. The authors also appreciate the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) for supporting and supervising this project.
-
Author contributions: Somdutt Mujwar: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing – original draft preparation. Jyoti Pal: methodology, visualization. Manu Sharma: methodology, supervision. Abhishek Tiwari: methodology, validation. Varsha Tiwari: validation. Manish Kumar: validation, writing – review and editing, supervision. Shivani Verma: validation, formal analysis, writing – review and editing. Ashraf Ahmed Qurtam: writing – review and editing. Fahd A. Nasr: writing – review and editing. Mohammed Al-Zharani: methodology, writing – review and editing, funding acquisition. Abdulsalam Alhalmi: formal analysis, writing – review and editing.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
-
Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animal use.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Lim SP. Dengue drug discovery: Progress, challenges and outlook. Antivir Res. 2019 Mar;163:156–78.10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.12.016Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Kumar S, Bajrai LH, Faizo AA, Khateb AM, Alkhaldy AA, Rana R, et al.Pharmacophore-model-based drug repurposing for the identification of the potential inhibitors targeting the allosteric site in dengue virus NS5 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Viruses. 2022 Aug;14(8):14081827.10.3390/v14081827Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Chitranshi N, Gupta S, Tripathi PK, Seth PK. New molecular scaffolds for the design of Alzheimer’s acetylcholinesterase inhibitors identified using ligand- and receptor-based virtual screening. Med Chem Res. 2013;22(5):2328–45.10.1007/s00044-012-0227-3Search in Google Scholar
[4] Kumar SS, Tailor N, Lee HB, Sharma M. Reduced lantadenes A and B: semi-synthetic synthesis, selective cytotoxicity, apoptosis induction and inhibition of NO, TNF-α production in HL-60 cells. Med Chem Res. 2013;22(7):3379–88.10.1007/s00044-012-0354-xSearch in Google Scholar
[5] Tailor NK, Jaiswal V, Lan SS, Lee HB, Sharma M. Synthesis, selective cancer cytotoxicity and mechanistic studies of novel analogs of lantadenes. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Jul;13(6):957–66.10.2174/18715206113139990127Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Tailor NK, Boon HL, Sharma M. Synthesis and in vitro anticancer studies of novel C-2 arylidene congeners of lantadenes. Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Jun;64:285–91.10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.04.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Suthar SK, Lee HB, Sharma M. The synthesis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)–lantadene prodrugs as novel lung adenocarcinoma inhibitors via the inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2){,} cyclin D1 and TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation. RSC Adv. 2014;4(37):19283–93. 10.1039/C4RA00280F.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Suthar SK, Sharma N, Lee HB, Nongalleima K, Sharma M. Novel dual inhibitors of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and cyclooxygenase- 2 (COX-2): synthesis, in vitro anticancer activity and stability studies of lantadene-non steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) conjugates. Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14(8):991–1004.10.2174/1568026614666140324120503Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Monika Sharma A, Suthar SK, Aggarwal V, Lee HB, Sharma M. Synthesis of lantadene analogs with marked in vitro inhibition of lung adenocarcinoma and TNF-α induced nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Aug;24(16):3814–8.10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.06.068Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Sharma M, Sharma PD, Bansal MP, Singh J. Lantadene A-induced apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Indian J Pharmacol. 2007;39(3):140–4.10.4103/0253-7613.33433Search in Google Scholar
[11] Sharma M, Sharma PD, Bansal MP, Singh J. Synthesis, cytotoxicity, and antitumor activity of lantadene-A congeners. Chem Biodivers. 2007 May;4(5):932–9.10.1002/cbdv.200790082Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Sharma M, Dev Sharma P, Pal Bansal M, Singh J. Synthesis and antitumor activity of novel pentacyclic triterpenoid lantadene D. Lett Drug Des Discovery. 2007;4:201–6.10.2174/157018007780077471Search in Google Scholar
[13] Cousins KR. Computer review of ChemDraw Ultra 12.0. J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Jun;133(21):8388.10.1021/ja204075sSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Berman HM, Battistuz T, Bhat TN, Bluhm WF, Bourne PE, Burkhardt K, et al. The protein data bank. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002 Jun;58(Pt 6 No 1):899–907.10.1107/S0907444902003451Search in Google Scholar
[15] Mujwar S, Pardasani KR. Prediction of riboswitch as a potential drug target and design of its optimal inhibitors for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int J Comput Biol Drug Des. 2015 Jan;8(4):326–47.10.1504/IJCBDD.2015.073671Search in Google Scholar
[16] Mujwar S, Shah K, Gupta JK, Gour A. Docking based screening of curcumin derivatives: a novel approach in the inhibition of tubercular DHFR. Int J Comput Biol Drug Des. 2021 Jan;14(4):297–314. https://www.inderscienceonline.com/doi/abs/10.1504/IJCBDD.2021.118830.10.1504/IJCBDD.2021.118830Search in Google Scholar
[17] Rani I, Goyal A, Sharma M. Computational design of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2022 Oct;20(7):317–37.10.1089/adt.2022.057Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, et al.UCSF Chimera-A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem. 2004 Oct;25(13):1605–12.10.1002/jcc.20084Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Rani I, Goyal A. Role of GSK3 (glycogen synthase kinase 3) as tumor promoter and tumor suppressor - A review. Plant Arch. 2019;19:1360–5.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Kaur A, Mujwar S, Adlakha N. In-silico analysis of riboswitch of Nocardia farcinica for design of its inhibitors and pharmacophores. Int J Comput Biol Drug Des. 2016 Jan;9(3):261–76.10.1504/IJCBDD.2016.078278Search in Google Scholar
[21] Sharma KK, Singh B, Mujwar S, Bisen PS. Molecular docking based analysis to elucidate the DNA topoisomerase IIβ as the potential target for the ganoderic acid; a natural therapeutic agent in cancer therapy. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2020;16(2):176–89.10.2174/1573409915666190820144759Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Minaz N, Razdan R, Hammock BD, Mujwar S, Goswami SK. Impact of diabetes on male sexual function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Protective role of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jul;115:108897.10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108897Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Mujwar S, Kumar V. Computational drug repurposing approach to identify potential fatty acid-binding protein-4 Inhibitors to develop novel antiobesity therapy. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2020 Oct;18(7):318–27.10.1089/adt.2020.976Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Jain R, Mujwar S. Repurposing metocurine as main protease inhibitor to develop novel antiviral therapy for COVID-19. Struct Chem. 2020;31(6):2487–99.10.1007/s11224-020-01605-wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Shah K, Mujwar S. Delineation of a novel non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs derivative using molecular docking and pharmacological assessment. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2022;84(3):642–53.10.36468/pharmaceutical-sciences.959Search in Google Scholar
[26] Mujwar S, Tripathi A. Repurposing benzbromarone as antifolate to develop novel antifungal therapy for Candida albicans. J Mol Model. 2022 Jun;28(7):193.10.1007/s00894-022-05185-wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Mujwar S, Harwansh RK. In silico bioprospecting of taraxerol as a main protease inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 to develop therapy against COVID-19. Struct Chem. 2022;33(5):1517–28.10.1007/s11224-022-01943-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Mujwar S, Pardasani KR. Prediction of riboswitch as a potential drug target for infectious diseases: An insilico case study of anthrax. J Med Imaging Heal Inform. 2015;5(1):7–16.10.1166/jmihi.2015.1358Search in Google Scholar
[29] Behl T, Kumar K, Brisc C, Rus M, Nistor-Cseppento DC, Bustea C, et al. Exploring the multifocal role of phytochemicals as immunomodulators. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jan;133:110959.10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110959Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Mujwar S, Sun L, Fidan O. In silico evaluation of food-derived carotenoids against SARS-CoV-2 drug targets: Crocin is a promising dietary supplement candidate for COVID-19. J Food Biochem. 2022;46(9):e14219. 10.1111/jfbc.14219.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Fidan O, Mujwar S, Kciuk M. Discovery of adapalene and dihydrotachysterol as antiviral agents for the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 through computational drug repurposing. Mol Divers. 2023 Feb;27(1):463–75.10.1007/s11030-022-10440-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Ika M, Sharma A, Aggarwal V, Sharma M, Dhingra N. Lantadenes targeting NF-KB in cancer: Molecular docking and ADMET predictions. Int J Life Sci Pharma Res. 2021;11(2):114–22.10.22376/ijpbs/lpr.2021.11.2.P114-122Search in Google Scholar
[33] Suthar SK, Hooda A, Sharma A, Bansal S, Monga J, Chauhan M, et al. Isolation optimisation, synthesis, molecular docking and in silico ADMET studies of lantadene a and its derivatives. Nat Prod Res. 2021 Nov;35(21):3939–44.10.1080/14786419.2020.1752204Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Mujwar S. Computational bioprospecting of andrographolide derivatives as potent cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Biomed Biotechnol Res J. 2021 Oct;5(4):446–50.10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_56_21Search in Google Scholar
[35] Agrawal N, Upadhyay PK, Mujwar S, Mishra P. Analgesic, anti-inflammatory activity and docking study of 2-(substituted phenyl)-3-(naphthalen-1-yl)thiazolidin-4-ones. J Indian Chem Soc. 2020;97(1):39–46.Search in Google Scholar
[36] Shah K, Mujwar S, Krishna G, Gupta JK. Computational design and biological depiction of novel naproxen derivative. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2020 Oct;18(7):308–17.10.1089/adt.2020.977Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Pradhan P, Soni NK, Chaudhary L, Mujwar S, Pardasani KR. In-silico prediction of riboswitches and design of their potent inhibitors for H1N1, H2N2 and H3N2 strains of influenza virus. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia. 2015;12(3):2173–86.10.13005/bbra/1889Search in Google Scholar
[38] Mujwar S, Deshmukh R, Harwansh RK, Gupta JK, Gour A. Drug repurposing approach for developing novel therapy against mupirocin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2019 Oct;17(7):298–309.10.1089/adt.2019.944Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[39] Arora A, Behl T, Sehgal A, Singh S, Sharma N, Bhatia S, et al. Unravelling the involvement of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Life Sci. 2021 May;273:119311.10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119311Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Gielecińska A, Kciuk M, Mujwar S, Celik I, Kołat D, Kałuzińska-Kołat Ż, et al. Substances of Natural origin in medicine: plants vs. Cancer Cell. 2023;12(7):12070986.10.3390/cells12070986Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Kareem SM, Al-Kadmy IMS, Kazaal SS, Mohammed Ali AN, Aziz SN, Makharita RR, et al.Detection of gyra and parC mutations and prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Drug Resist. 2021;14:555–63.10.2147/IDR.S275852Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Mujwar S. Computational repurposing of tamibarotene against triple mutant variant of SARS-CoV-2. Comput Biol Med. 2021 Sep;136:104748.10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104748Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[43] Kciuk M, Mujwar S, Szymanowska A, Marciniak B, Bukowski K, Mojzych M, et al. Preparation of novel pyrazolo[4,3-e]tetrazolo[1,5-b][1,2,4]triazine sulfonamides and their experimental and computational biological studies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May;23(11):23115892.10.3390/ijms23115892Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Shinu P, Sharma M, Gupta GL, Mujwar S, Kandeel M, Kumar M, et al. Computational design, synthesis, and pharmacological evaluation of naproxen-guaiacol chimera for gastro-sparing anti-inflammatory response by selective COX2 inhibition. Molecules. 2022;27(20):27206905.10.3390/molecules27206905Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[45] Kciuk M, Mujwar S, Rani I, Munjal K, Gielecińska A, Kontek R, et al. Computational bioprospecting guggulsterone against ADP ribose phosphatase of SARS-CoV-2. Molecules. 2022 Nov;27(23):27238287.10.3390/molecules27238287Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] Medigeshi GR, Kumar R, Dhamija E, Agrawal T, Kar M. N-desmethylclozapine, fluoxetine, and salmeterol inhibit postentry stages of the dengue virus life cycle. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Nov;60(11):6709–18.10.1128/AAC.01367-16Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Tăuţan A-M, Ionescu B, Santarnecchi E. Artificial intelligence in neurodegenerative diseases: A review of available tools with a focus on machine learning techniques. Artif Intell Med. 2021 Jul;117:102081.10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102081Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Chauhan M, Dhar ZA, Gorki V, Sharma S, Koul A, Bala S, et al. Exploration of anticancer potential of Lantadenes from weed Lantana camara: Synthesis, in silico, in vitro and in vivo studies. Phytochemistry. 2023;206:113525.10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113525Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Porous silicon nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and their antifungal activity
- Biochar from de-oiled Chlorella vulgaris and its adsorption on antibiotics
- Phytochemicals profiling, in vitro and in vivo antidiabetic activity, and in silico studies on Ajuga iva (L.) Schreb.: A comprehensive approach
- Synthesis, characterization, in silico and in vitro studies of novel glycoconjugates as potential antibacterial, antifungal, and antileishmanial agents
- Sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by potato starch: Its performance in the treatment of esophageal cancer
- Computational study of ADME-Tox prediction of selected phytochemicals from Punica granatum peels
- Phytochemical analysis, in vitro antioxidant and antifungal activities of extracts and essential oil derived from Artemisia herba-alba Asso
- Two triazole-based coordination polymers: Synthesis and crystal structure characterization
- Phytochemical and physicochemical studies of different apple varieties grown in Morocco
- Synthesis of multi-template molecularly imprinted polymers (MT-MIPs) for isolating ethyl para-methoxycinnamate and ethyl cinnamate from Kaempferia galanga L., extract with methacrylic acid as functional monomer
- Nutraceutical potential of Mesembryanthemum forsskaolii Hochst. ex Bioss.: Insights into its nutritional composition, phytochemical contents, and antioxidant activity
- Evaluation of influence of Butea monosperma floral extract on inflammatory biomarkers
- Cannabis sativa L. essential oil: Chemical composition, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial properties, and acute toxicity: In vitro, in vivo, and in silico study
- The effect of gamma radiation on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural conversion in water and dimethyl sulfoxide
- Hollow mushroom nanomaterials for potentiometric sensing of Pb2+ ions in water via the intercalation of iodide ions into the polypyrrole matrix
- Determination of essential oil and chemical composition of St. John’s Wort
- Computational design and in vitro assay of lantadene-based novel inhibitors of NS3 protease of dengue virus
- Anti-parasitic activity and computational studies on a novel labdane diterpene from the roots of Vachellia nilotica
- Microbial dynamics and dehydrogenase activity in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) rhizospheres: Impacts on growth and soil health across different soil types
- Correlation between in vitro anti-urease activity and in silico molecular modeling approach of novel imidazopyridine–oxadiazole hybrids derivatives
- Spatial mapping of indoor air quality in a light metro system using the geographic information system method
- Iron indices and hemogram in renal anemia and the improvement with Tribulus terrestris green-formulated silver nanoparticles applied on rat model
- Integrated track of nano-informatics coupling with the enrichment concept in developing a novel nanoparticle targeting ERK protein in Naegleria fowleri
- Cytotoxic and phytochemical screening of Solanum lycopersicum–Daucus carota hydro-ethanolic extract and in silico evaluation of its lycopene content as anticancer agent
- Protective activities of silver nanoparticles containing Panax japonicus on apoptotic, inflammatory, and oxidative alterations in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity
- pH-based colorimetric detection of monofunctional aldehydes in liquid and gas phases
- Investigating the effect of resveratrol on apoptosis and regulation of gene expression of Caco-2 cells: Unravelling potential implications for colorectal cancer treatment
- Metformin inhibits knee osteoarthritis induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats: S100A8/9 and S100A12 as players and therapeutic targets
- Effect of silver nanoparticles formulated by Silybum marianum on menopausal urinary incontinence in ovariectomized rats
- Synthesis of new analogs of N-substituted(benzoylamino)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridines
- Response of yield and quality of Japonica rice to different gradients of moisture deficit at grain-filling stage in cold regions
- Preparation of an inclusion complex of nickel-based β-cyclodextrin: Characterization and accelerating the osteoarthritis articular cartilage repair
- Empagliflozin-loaded nanomicelles responsive to reactive oxygen species for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury protection
- Preparation and pharmacodynamic evaluation of sodium aescinate solid lipid nanoparticles
- Assessment of potentially toxic elements and health risks of agricultural soil in Southwest Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Theoretical investigation of hydrogen-rich fuel production through ammonia decomposition
- Biosynthesis and screening of cobalt nanoparticles using citrus species for antimicrobial activity
- Investigating the interplay of genetic variations, MCP-1 polymorphism, and docking with phytochemical inhibitors for combatting dengue virus pathogenicity through in silico analysis
- Ultrasound induced biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles embedded into chitosan polymers: Investigation of its anti-cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma effects
- Copper oxide nanoparticles-mediated Heliotropium bacciferum leaf extract: Antifungal activity and molecular docking assays against strawberry pathogens
- Sprouted wheat flour for improving physical, chemical, rheological, microbial load, and quality properties of fino bread
- Comparative toxicity assessment of fisetin-aided artificial intelligence-assisted drug design targeting epibulbar dermoid through phytochemicals
- Acute toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity of bis-thiourea derivatives
- Anti-diabetic activity-guided isolation of α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory terpenes from Capsella bursa-pastoris Linn.
- GC–MS analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 metabolites and its computational analysis on familial pulmonary fibrosis hub genes
- Green formulation of copper nanoparticles by Pistacia khinjuk leaf aqueous extract: Introducing a novel chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of prostate cancer
- Improved photocatalytic properties of WO3 nanoparticles for Malachite green dye degradation under visible light irradiation: An effect of La doping
- One-pot synthesis of a network of Mn2O3–MnO2–poly(m-methylaniline) composite nanorods on a polypyrrole film presents a promising and efficient optoelectronic and solar cell device
- Groundwater quality and health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride in Al Qaseem area, Saudi Arabia
- A comparative study of the antifungal efficacy and phytochemical composition of date palm leaflet extracts
- Processing of alcohol pomelo beverage (Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck) using saccharomyces yeast: Optimization, physicochemical quality, and sensory characteristics
- Specialized compounds of four Cameroonian spices: Isolation, characterization, and in silico evaluation as prospective SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Identification of a novel drug target in Porphyromonas gingivalis by a computational genome analysis approach
- Physico-chemical properties and durability of a fly-ash-based geopolymer
- FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitory potentials of some phytochemicals from anti-leukemic plants using computational chemical methodologies
- Wild Thymus zygis L. ssp. gracilis and Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh.: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of essential oils
- 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, ADMET, simulation dynamic, and retrosynthesis studies on new styrylquinolines derivatives against breast cancer
- Deciphering the influenza neuraminidase inhibitory potential of naturally occurring biflavonoids: An in silico approach
- Determination of heavy elements in agricultural regions, Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis and characterization of antioxidant-enriched Moringa oil-based edible oleogel
- Ameliorative effects of thistle and thyme honeys on cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity in mice
- Study of phytochemical compound and antipyretic activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. fractions
- Investigating the adsorption mechanism of zinc chloride-modified porous carbon for sulfadiazine removal from water
- Performance repair of building materials using alumina and silica composite nanomaterials with electrodynamic properties
- Effects of nanoparticles on the activity and resistance genes of anaerobic digestion enzymes in livestock and poultry manure containing the antibiotic tetracycline
- Effect of copper nanoparticles green-synthesized using Ocimum basilicum against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice lung infection model
- Cardioprotective effects of nanoparticles green formulated by Spinacia oleracea extract on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in mice by the determination of PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway
- Anti-OTC antibody-conjugated fluorescent magnetic/silica and fluorescent hybrid silica nanoparticles for oxytetracycline detection
- Curcumin conjugated zinc nanoparticles for the treatment of myocardial infarction
- Identification and in silico screening of natural phloroglucinols as potential PI3Kα inhibitors: A computational approach for drug discovery
- Exploring the phytochemical profile and antioxidant evaluation: Molecular docking and ADMET analysis of main compounds from three Solanum species in Saudi Arabia
- Unveiling the molecular composition and biological properties of essential oil derived from the leaves of wild Mentha aquatica L.: A comprehensive in vitro and in silico exploration
- Analysis of bioactive compounds present in Boerhavia elegans seeds by GC-MS
- Homology modeling and molecular docking study of corticotrophin-releasing hormone: An approach to treat stress-related diseases
- LncRNA MIR17HG alleviates heart failure via targeting MIR17HG/miR-153-3p/SIRT1 axis in in vitro model
- Development and validation of a stability indicating UPLC-DAD method coupled with MS-TQD for ramipril and thymoquinone in bioactive SNEDDS with in silico toxicity analysis of ramipril degradation products
- Biosynthesis of Ag/Cu nanocomposite mediated by Curcuma longa: Evaluation of its antibacterial properties against oral pathogens
- Development of AMBER-compliant transferable force field parameters for polytetrafluoroethylene
- Treatment of gestational diabetes by Acroptilon repens leaf aqueous extract green-formulated iron nanoparticles in rats
- Development and characterization of new ecological adsorbents based on cardoon wastes: Application to brilliant green adsorption
- A fast, sensitive, greener, and stability-indicating HPLC method for the standardization and quantitative determination of chlorhexidine acetate in commercial products
- Assessment of Se, As, Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb content status in Ankang tea plantations of China
- Effect of transition metal chloride (ZnCl2) on low-temperature pyrolysis of high ash bituminous coal
- Evaluating polyphenol and ascorbic acid contents, tannin removal ability, and physical properties during hydrolysis and convective hot-air drying of cashew apple powder
- Development and characterization of functional low-fat frozen dairy dessert enhanced with dried lemongrass powder
- Scrutinizing the effect of additive and synergistic antibiotics against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Preparation, characterization, and determination of the therapeutic effects of copper nanoparticles green-formulated by Pistacia atlantica in diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction in rat
- Antioxidant and antidiabetic potentials of methoxy-substituted Schiff bases using in vitro, in vivo, and molecular simulation approaches
- Anti-melanoma cancer activity and chemical profile of the essential oil of Seseli yunnanense Franch
- Molecular docking analysis of subtilisin-like alkaline serine protease (SLASP) and laccase with natural biopolymers
- Overcoming methicillin resistance by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Computational evaluation of napthyridine and oxadiazoles compounds for potential dual inhibition of PBP-2a and FemA proteins
- Exploring novel antitubercular agents: Innovative design of 2,3-diaryl-quinoxalines targeting DprE1 for effective tuberculosis treatment
- Drimia maritima flowers as a source of biologically potent components: Optimization of bioactive compound extractions, isolation, UPLC–ESI–MS/MS, and pharmacological properties
- Estimating molecular properties, drug-likeness, cardiotoxic risk, liability profile, and molecular docking study to characterize binding process of key phyto-compounds against serotonin 5-HT2A receptor
- Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin-based microgels for enhancing solubility of Terbinafine: An in-vitro and in-vivo toxicological evaluation
- Phyto-mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of cationic and anionic dyes
- Monosodium glutamate induces hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis hyperactivation, glucocorticoid receptors down-regulation, and systemic inflammatory response in young male rats: Impact on miR-155 and miR-218
- Quality control analyses of selected honey samples from Serbia based on their mineral and flavonoid profiles, and the invertase activity
- Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus niruri leaf extract: Assessment of antimicrobial activity, effectiveness on tropical neglected mosquito vector control, and biocompatibility using a fibroblast cell line model
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles containing Cichorium intybus to treat the sepsis-induced DNA damage in the liver of Wistar albino rats
- Quality changes of durian pulp (Durio ziberhinus Murr.) in cold storage
- Study on recrystallization process of nitroguanidine by directly adding cold water to control temperature
- Determination of heavy metals and health risk assessment in drinking water in Bukayriyah City, Saudi Arabia
- Larvicidal properties of essential oils of three Artemisia species against the chemically insecticide-resistant Nile fever vector Culex pipiens (L.) (Diptera: Culicidae): In vitro and in silico studies
- Design, synthesis, characterization, and theoretical calculations, along with in silico and in vitro antimicrobial proprieties of new isoxazole-amide conjugates
- The impact of drying and extraction methods on total lipid, fatty acid profile, and cytotoxicity of Tenebrio molitor larvae
- A zinc oxide–tin oxide–nerolidol hybrid nanomaterial: Efficacy against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Research on technological process for production of muskmelon juice (Cucumis melo L.)
- Physicochemical components, antioxidant activity, and predictive models for quality of soursop tea (Annona muricata L.) during heat pump drying
- Characterization and application of Fe1−xCoxFe2O4 nanoparticles in Direct Red 79 adsorption
- Torilis arvensis ethanolic extract: Phytochemical analysis, antifungal efficacy, and cytotoxicity properties
- Magnetite–poly-1H pyrrole dendritic nanocomposite seeded on poly-1H pyrrole: A promising photocathode for green hydrogen generation from sanitation water without using external sacrificing agent
- HPLC and GC–MS analyses of phytochemical compounds in Haloxylon salicornicum extract: Antibacterial and antifungal activity assessment of phytopathogens
- Efficient and stable to coking catalysts of ethanol steam reforming comprised of Ni + Ru loaded on MgAl2O4 + LnFe0.7Ni0.3O3 (Ln = La, Pr) nanocomposites prepared via cost-effective procedure with Pluronic P123 copolymer
- Nitrogen and boron co-doped carbon dots probe for selectively detecting Hg2+ in water samples and the detection mechanism
- Heavy metals in road dust from typical old industrial areas of Wuhan: Seasonal distribution and bioaccessibility-based health risk assessment
- Phytochemical profiling and bioactivity evaluation of CBD- and THC-enriched Cannabis sativa extracts: In vitro and in silico investigation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
- Investigating dye adsorption: The role of surface-modified montmorillonite nanoclay in kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics
- Antimicrobial activity, induction of ROS generation in HepG2 liver cancer cells, and chemical composition of Pterospermum heterophyllum
- Study on the performance of nanoparticle-modified PVDF membrane in delaying membrane aging
- Impact of cholesterol in encapsulated vitamin E acetate within cocoliposomes
- Review Articles
- Structural aspects of Pt(η3-X1N1X2)(PL) (X1,2 = O, C, or Se) and Pt(η3-N1N2X1)(PL) (X1 = C, S, or Se) derivatives
- Biosurfactants in biocorrosion and corrosion mitigation of metals: An overview
- Stimulus-responsive MOF–hydrogel composites: Classification, preparation, characterization, and their advancement in medical treatments
- Electrochemical dissolution of titanium under alternating current polarization to obtain its dioxide
- Special Issue on Recent Trends in Green Chemistry
- Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of Vitex agnus-castus L.
- Phytochemical study, antioxidant activity, and dermoprotective activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.)
- Exploitation of mangliculous marine fungi, Amarenographium solium, for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against multiple drug-resistant bacteria
- Study of the phytotoxicity of margines on Pistia stratiotes L.
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part III
- Impact of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, development, and antioxidant system of high protein content crop (Lablab purpureus L.) sweet
- Green synthesis, characterization, and application of iron and molybdenum nanoparticles and their composites for enhancing the growth of Solanum lycopersicum
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Olea europaea L. extracted polysaccharides, characterization, and its assessment as an antimicrobial agent against multiple pathogenic microbes
- Photocatalytic treatment of organic dyes using metal oxides and nanocomposites: A quantitative study
- Antifungal, antioxidant, and photocatalytic activities of greenly synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles
- Special Issue on Phytochemical and Pharmacological Scrutinization of Medicinal Plants
- Hepatoprotective effects of safranal on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
- Chemical composition and biological properties of Thymus capitatus plants from Algerian high plains: A comparative and analytical study
- Chemical composition and bioactivities of the methanol root extracts of Saussurea costus
- In vivo protective effects of vitamin C against cyto-genotoxicity induced by Dysphania ambrosioides aqueous extract
- Insights about the deleterious impact of a carbamate pesticide on some metabolic immune and antioxidant functions and a focus on the protective ability of a Saharan shrub and its anti-edematous property
- A comprehensive review uncovering the anticancerous potential of genkwanin (plant-derived compound) in several human carcinomas
- A study to investigate the anticancer potential of carvacrol via targeting Notch signaling in breast cancer
- Assessment of anti-diabetic properties of Ziziphus oenopolia (L.) wild edible fruit extract: In vitro and in silico investigations through molecular docking analysis
- Optimization of polyphenol extraction, phenolic profile by LC-ESI-MS/MS, antioxidant, anti-enzymatic, and cytotoxic activities of Physalis acutifolia
- Phytochemical screening, antioxidant properties, and photo-protective activities of Salvia balansae de Noé ex Coss
- Antihyperglycemic, antiglycation, anti-hypercholesteremic, and toxicity evaluation with gas chromatography mass spectrometry profiling for Aloe armatissima leaves
- Phyto-fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles by using Timur (Zanthoxylum armatum DC) and their effect on wound healing
- Does Erodium trifolium (Cav.) Guitt exhibit medicinal properties? Response elements from phytochemical profiling, enzyme-inhibiting, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities
- Integrative in silico evaluation of the antiviral potential of terpenoids and its metal complexes derived from Homalomena aromatica based on main protease of SARS-CoV-2
- 6-Methoxyflavone improves anxiety, depression, and memory by increasing monoamines in mice brain: HPLC analysis and in silico studies
- Simultaneous extraction and quantification of hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants in Solanum lycopersicum L. varieties marketed in Saudi Arabia
- Biological evaluation of CH3OH and C2H5OH of Berberis vulgaris for in vivo antileishmanial potential against Leishmania tropica in murine models
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Porous silicon nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and their antifungal activity
- Biochar from de-oiled Chlorella vulgaris and its adsorption on antibiotics
- Phytochemicals profiling, in vitro and in vivo antidiabetic activity, and in silico studies on Ajuga iva (L.) Schreb.: A comprehensive approach
- Synthesis, characterization, in silico and in vitro studies of novel glycoconjugates as potential antibacterial, antifungal, and antileishmanial agents
- Sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by potato starch: Its performance in the treatment of esophageal cancer
- Computational study of ADME-Tox prediction of selected phytochemicals from Punica granatum peels
- Phytochemical analysis, in vitro antioxidant and antifungal activities of extracts and essential oil derived from Artemisia herba-alba Asso
- Two triazole-based coordination polymers: Synthesis and crystal structure characterization
- Phytochemical and physicochemical studies of different apple varieties grown in Morocco
- Synthesis of multi-template molecularly imprinted polymers (MT-MIPs) for isolating ethyl para-methoxycinnamate and ethyl cinnamate from Kaempferia galanga L., extract with methacrylic acid as functional monomer
- Nutraceutical potential of Mesembryanthemum forsskaolii Hochst. ex Bioss.: Insights into its nutritional composition, phytochemical contents, and antioxidant activity
- Evaluation of influence of Butea monosperma floral extract on inflammatory biomarkers
- Cannabis sativa L. essential oil: Chemical composition, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial properties, and acute toxicity: In vitro, in vivo, and in silico study
- The effect of gamma radiation on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural conversion in water and dimethyl sulfoxide
- Hollow mushroom nanomaterials for potentiometric sensing of Pb2+ ions in water via the intercalation of iodide ions into the polypyrrole matrix
- Determination of essential oil and chemical composition of St. John’s Wort
- Computational design and in vitro assay of lantadene-based novel inhibitors of NS3 protease of dengue virus
- Anti-parasitic activity and computational studies on a novel labdane diterpene from the roots of Vachellia nilotica
- Microbial dynamics and dehydrogenase activity in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) rhizospheres: Impacts on growth and soil health across different soil types
- Correlation between in vitro anti-urease activity and in silico molecular modeling approach of novel imidazopyridine–oxadiazole hybrids derivatives
- Spatial mapping of indoor air quality in a light metro system using the geographic information system method
- Iron indices and hemogram in renal anemia and the improvement with Tribulus terrestris green-formulated silver nanoparticles applied on rat model
- Integrated track of nano-informatics coupling with the enrichment concept in developing a novel nanoparticle targeting ERK protein in Naegleria fowleri
- Cytotoxic and phytochemical screening of Solanum lycopersicum–Daucus carota hydro-ethanolic extract and in silico evaluation of its lycopene content as anticancer agent
- Protective activities of silver nanoparticles containing Panax japonicus on apoptotic, inflammatory, and oxidative alterations in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity
- pH-based colorimetric detection of monofunctional aldehydes in liquid and gas phases
- Investigating the effect of resveratrol on apoptosis and regulation of gene expression of Caco-2 cells: Unravelling potential implications for colorectal cancer treatment
- Metformin inhibits knee osteoarthritis induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats: S100A8/9 and S100A12 as players and therapeutic targets
- Effect of silver nanoparticles formulated by Silybum marianum on menopausal urinary incontinence in ovariectomized rats
- Synthesis of new analogs of N-substituted(benzoylamino)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridines
- Response of yield and quality of Japonica rice to different gradients of moisture deficit at grain-filling stage in cold regions
- Preparation of an inclusion complex of nickel-based β-cyclodextrin: Characterization and accelerating the osteoarthritis articular cartilage repair
- Empagliflozin-loaded nanomicelles responsive to reactive oxygen species for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury protection
- Preparation and pharmacodynamic evaluation of sodium aescinate solid lipid nanoparticles
- Assessment of potentially toxic elements and health risks of agricultural soil in Southwest Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Theoretical investigation of hydrogen-rich fuel production through ammonia decomposition
- Biosynthesis and screening of cobalt nanoparticles using citrus species for antimicrobial activity
- Investigating the interplay of genetic variations, MCP-1 polymorphism, and docking with phytochemical inhibitors for combatting dengue virus pathogenicity through in silico analysis
- Ultrasound induced biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles embedded into chitosan polymers: Investigation of its anti-cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma effects
- Copper oxide nanoparticles-mediated Heliotropium bacciferum leaf extract: Antifungal activity and molecular docking assays against strawberry pathogens
- Sprouted wheat flour for improving physical, chemical, rheological, microbial load, and quality properties of fino bread
- Comparative toxicity assessment of fisetin-aided artificial intelligence-assisted drug design targeting epibulbar dermoid through phytochemicals
- Acute toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity of bis-thiourea derivatives
- Anti-diabetic activity-guided isolation of α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory terpenes from Capsella bursa-pastoris Linn.
- GC–MS analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 metabolites and its computational analysis on familial pulmonary fibrosis hub genes
- Green formulation of copper nanoparticles by Pistacia khinjuk leaf aqueous extract: Introducing a novel chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of prostate cancer
- Improved photocatalytic properties of WO3 nanoparticles for Malachite green dye degradation under visible light irradiation: An effect of La doping
- One-pot synthesis of a network of Mn2O3–MnO2–poly(m-methylaniline) composite nanorods on a polypyrrole film presents a promising and efficient optoelectronic and solar cell device
- Groundwater quality and health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride in Al Qaseem area, Saudi Arabia
- A comparative study of the antifungal efficacy and phytochemical composition of date palm leaflet extracts
- Processing of alcohol pomelo beverage (Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck) using saccharomyces yeast: Optimization, physicochemical quality, and sensory characteristics
- Specialized compounds of four Cameroonian spices: Isolation, characterization, and in silico evaluation as prospective SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Identification of a novel drug target in Porphyromonas gingivalis by a computational genome analysis approach
- Physico-chemical properties and durability of a fly-ash-based geopolymer
- FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitory potentials of some phytochemicals from anti-leukemic plants using computational chemical methodologies
- Wild Thymus zygis L. ssp. gracilis and Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh.: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of essential oils
- 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, ADMET, simulation dynamic, and retrosynthesis studies on new styrylquinolines derivatives against breast cancer
- Deciphering the influenza neuraminidase inhibitory potential of naturally occurring biflavonoids: An in silico approach
- Determination of heavy elements in agricultural regions, Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis and characterization of antioxidant-enriched Moringa oil-based edible oleogel
- Ameliorative effects of thistle and thyme honeys on cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity in mice
- Study of phytochemical compound and antipyretic activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. fractions
- Investigating the adsorption mechanism of zinc chloride-modified porous carbon for sulfadiazine removal from water
- Performance repair of building materials using alumina and silica composite nanomaterials with electrodynamic properties
- Effects of nanoparticles on the activity and resistance genes of anaerobic digestion enzymes in livestock and poultry manure containing the antibiotic tetracycline
- Effect of copper nanoparticles green-synthesized using Ocimum basilicum against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice lung infection model
- Cardioprotective effects of nanoparticles green formulated by Spinacia oleracea extract on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in mice by the determination of PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway
- Anti-OTC antibody-conjugated fluorescent magnetic/silica and fluorescent hybrid silica nanoparticles for oxytetracycline detection
- Curcumin conjugated zinc nanoparticles for the treatment of myocardial infarction
- Identification and in silico screening of natural phloroglucinols as potential PI3Kα inhibitors: A computational approach for drug discovery
- Exploring the phytochemical profile and antioxidant evaluation: Molecular docking and ADMET analysis of main compounds from three Solanum species in Saudi Arabia
- Unveiling the molecular composition and biological properties of essential oil derived from the leaves of wild Mentha aquatica L.: A comprehensive in vitro and in silico exploration
- Analysis of bioactive compounds present in Boerhavia elegans seeds by GC-MS
- Homology modeling and molecular docking study of corticotrophin-releasing hormone: An approach to treat stress-related diseases
- LncRNA MIR17HG alleviates heart failure via targeting MIR17HG/miR-153-3p/SIRT1 axis in in vitro model
- Development and validation of a stability indicating UPLC-DAD method coupled with MS-TQD for ramipril and thymoquinone in bioactive SNEDDS with in silico toxicity analysis of ramipril degradation products
- Biosynthesis of Ag/Cu nanocomposite mediated by Curcuma longa: Evaluation of its antibacterial properties against oral pathogens
- Development of AMBER-compliant transferable force field parameters for polytetrafluoroethylene
- Treatment of gestational diabetes by Acroptilon repens leaf aqueous extract green-formulated iron nanoparticles in rats
- Development and characterization of new ecological adsorbents based on cardoon wastes: Application to brilliant green adsorption
- A fast, sensitive, greener, and stability-indicating HPLC method for the standardization and quantitative determination of chlorhexidine acetate in commercial products
- Assessment of Se, As, Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb content status in Ankang tea plantations of China
- Effect of transition metal chloride (ZnCl2) on low-temperature pyrolysis of high ash bituminous coal
- Evaluating polyphenol and ascorbic acid contents, tannin removal ability, and physical properties during hydrolysis and convective hot-air drying of cashew apple powder
- Development and characterization of functional low-fat frozen dairy dessert enhanced with dried lemongrass powder
- Scrutinizing the effect of additive and synergistic antibiotics against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Preparation, characterization, and determination of the therapeutic effects of copper nanoparticles green-formulated by Pistacia atlantica in diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction in rat
- Antioxidant and antidiabetic potentials of methoxy-substituted Schiff bases using in vitro, in vivo, and molecular simulation approaches
- Anti-melanoma cancer activity and chemical profile of the essential oil of Seseli yunnanense Franch
- Molecular docking analysis of subtilisin-like alkaline serine protease (SLASP) and laccase with natural biopolymers
- Overcoming methicillin resistance by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Computational evaluation of napthyridine and oxadiazoles compounds for potential dual inhibition of PBP-2a and FemA proteins
- Exploring novel antitubercular agents: Innovative design of 2,3-diaryl-quinoxalines targeting DprE1 for effective tuberculosis treatment
- Drimia maritima flowers as a source of biologically potent components: Optimization of bioactive compound extractions, isolation, UPLC–ESI–MS/MS, and pharmacological properties
- Estimating molecular properties, drug-likeness, cardiotoxic risk, liability profile, and molecular docking study to characterize binding process of key phyto-compounds against serotonin 5-HT2A receptor
- Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin-based microgels for enhancing solubility of Terbinafine: An in-vitro and in-vivo toxicological evaluation
- Phyto-mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of cationic and anionic dyes
- Monosodium glutamate induces hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis hyperactivation, glucocorticoid receptors down-regulation, and systemic inflammatory response in young male rats: Impact on miR-155 and miR-218
- Quality control analyses of selected honey samples from Serbia based on their mineral and flavonoid profiles, and the invertase activity
- Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus niruri leaf extract: Assessment of antimicrobial activity, effectiveness on tropical neglected mosquito vector control, and biocompatibility using a fibroblast cell line model
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles containing Cichorium intybus to treat the sepsis-induced DNA damage in the liver of Wistar albino rats
- Quality changes of durian pulp (Durio ziberhinus Murr.) in cold storage
- Study on recrystallization process of nitroguanidine by directly adding cold water to control temperature
- Determination of heavy metals and health risk assessment in drinking water in Bukayriyah City, Saudi Arabia
- Larvicidal properties of essential oils of three Artemisia species against the chemically insecticide-resistant Nile fever vector Culex pipiens (L.) (Diptera: Culicidae): In vitro and in silico studies
- Design, synthesis, characterization, and theoretical calculations, along with in silico and in vitro antimicrobial proprieties of new isoxazole-amide conjugates
- The impact of drying and extraction methods on total lipid, fatty acid profile, and cytotoxicity of Tenebrio molitor larvae
- A zinc oxide–tin oxide–nerolidol hybrid nanomaterial: Efficacy against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Research on technological process for production of muskmelon juice (Cucumis melo L.)
- Physicochemical components, antioxidant activity, and predictive models for quality of soursop tea (Annona muricata L.) during heat pump drying
- Characterization and application of Fe1−xCoxFe2O4 nanoparticles in Direct Red 79 adsorption
- Torilis arvensis ethanolic extract: Phytochemical analysis, antifungal efficacy, and cytotoxicity properties
- Magnetite–poly-1H pyrrole dendritic nanocomposite seeded on poly-1H pyrrole: A promising photocathode for green hydrogen generation from sanitation water without using external sacrificing agent
- HPLC and GC–MS analyses of phytochemical compounds in Haloxylon salicornicum extract: Antibacterial and antifungal activity assessment of phytopathogens
- Efficient and stable to coking catalysts of ethanol steam reforming comprised of Ni + Ru loaded on MgAl2O4 + LnFe0.7Ni0.3O3 (Ln = La, Pr) nanocomposites prepared via cost-effective procedure with Pluronic P123 copolymer
- Nitrogen and boron co-doped carbon dots probe for selectively detecting Hg2+ in water samples and the detection mechanism
- Heavy metals in road dust from typical old industrial areas of Wuhan: Seasonal distribution and bioaccessibility-based health risk assessment
- Phytochemical profiling and bioactivity evaluation of CBD- and THC-enriched Cannabis sativa extracts: In vitro and in silico investigation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
- Investigating dye adsorption: The role of surface-modified montmorillonite nanoclay in kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics
- Antimicrobial activity, induction of ROS generation in HepG2 liver cancer cells, and chemical composition of Pterospermum heterophyllum
- Study on the performance of nanoparticle-modified PVDF membrane in delaying membrane aging
- Impact of cholesterol in encapsulated vitamin E acetate within cocoliposomes
- Review Articles
- Structural aspects of Pt(η3-X1N1X2)(PL) (X1,2 = O, C, or Se) and Pt(η3-N1N2X1)(PL) (X1 = C, S, or Se) derivatives
- Biosurfactants in biocorrosion and corrosion mitigation of metals: An overview
- Stimulus-responsive MOF–hydrogel composites: Classification, preparation, characterization, and their advancement in medical treatments
- Electrochemical dissolution of titanium under alternating current polarization to obtain its dioxide
- Special Issue on Recent Trends in Green Chemistry
- Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of Vitex agnus-castus L.
- Phytochemical study, antioxidant activity, and dermoprotective activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.)
- Exploitation of mangliculous marine fungi, Amarenographium solium, for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against multiple drug-resistant bacteria
- Study of the phytotoxicity of margines on Pistia stratiotes L.
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part III
- Impact of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, development, and antioxidant system of high protein content crop (Lablab purpureus L.) sweet
- Green synthesis, characterization, and application of iron and molybdenum nanoparticles and their composites for enhancing the growth of Solanum lycopersicum
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Olea europaea L. extracted polysaccharides, characterization, and its assessment as an antimicrobial agent against multiple pathogenic microbes
- Photocatalytic treatment of organic dyes using metal oxides and nanocomposites: A quantitative study
- Antifungal, antioxidant, and photocatalytic activities of greenly synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles
- Special Issue on Phytochemical and Pharmacological Scrutinization of Medicinal Plants
- Hepatoprotective effects of safranal on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
- Chemical composition and biological properties of Thymus capitatus plants from Algerian high plains: A comparative and analytical study
- Chemical composition and bioactivities of the methanol root extracts of Saussurea costus
- In vivo protective effects of vitamin C against cyto-genotoxicity induced by Dysphania ambrosioides aqueous extract
- Insights about the deleterious impact of a carbamate pesticide on some metabolic immune and antioxidant functions and a focus on the protective ability of a Saharan shrub and its anti-edematous property
- A comprehensive review uncovering the anticancerous potential of genkwanin (plant-derived compound) in several human carcinomas
- A study to investigate the anticancer potential of carvacrol via targeting Notch signaling in breast cancer
- Assessment of anti-diabetic properties of Ziziphus oenopolia (L.) wild edible fruit extract: In vitro and in silico investigations through molecular docking analysis
- Optimization of polyphenol extraction, phenolic profile by LC-ESI-MS/MS, antioxidant, anti-enzymatic, and cytotoxic activities of Physalis acutifolia
- Phytochemical screening, antioxidant properties, and photo-protective activities of Salvia balansae de Noé ex Coss
- Antihyperglycemic, antiglycation, anti-hypercholesteremic, and toxicity evaluation with gas chromatography mass spectrometry profiling for Aloe armatissima leaves
- Phyto-fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles by using Timur (Zanthoxylum armatum DC) and their effect on wound healing
- Does Erodium trifolium (Cav.) Guitt exhibit medicinal properties? Response elements from phytochemical profiling, enzyme-inhibiting, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities
- Integrative in silico evaluation of the antiviral potential of terpenoids and its metal complexes derived from Homalomena aromatica based on main protease of SARS-CoV-2
- 6-Methoxyflavone improves anxiety, depression, and memory by increasing monoamines in mice brain: HPLC analysis and in silico studies
- Simultaneous extraction and quantification of hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants in Solanum lycopersicum L. varieties marketed in Saudi Arabia
- Biological evaluation of CH3OH and C2H5OH of Berberis vulgaris for in vivo antileishmanial potential against Leishmania tropica in murine models

