Abstract
A modern cardioprotective drug was created by utilizing zinc nanoparticles (ZnNPs) containing curcumin to address isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in mice, with a specific focus on the PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway. During the in vivo study, mice were subjected to myocardial infarction by subcutaneously administering isoproterenol at a dosage of 40 mg/kg every 12 h for a total of three administrations. The mice were randomly divided into five groups: (I, II) isoproterenol + ZnNPs at different concentrations (10, 40 μg/mL) and time intervals, (III) isoproterenol alone, and (IV) control group. Various physicochemical methods, including FT-IR, field emission scanning electron microscopy, X-Ray diffraction analysis, fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, were utilized to analyze and characterize the ZnNPs. The real-time PCR and western blot methods were used to examine the PPAR-γ/NF-κB activation by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and the subsequent cytokine release. This research focused on investigating the inflammatory responses and cell apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells treated with LPS. After the therapy, cardiac function was checked using an electrocardiogram, along with biochemical and histochemical analysis. The introduction of ZnNPs leads to a decrease in the inflammatory conditions present in the hearts of mice suffering from myocardial infarction. The use of ZnNPs not only enhances ventricular wall infarction but also reduces mortality rates and suppresses levels of myocardial injury markers. The usual ST segment depression observed in mice with myocardial infarction is markedly reduced when treated with ZnNPs. The mice with myocardial infarction in the pre + post-isoproterenol group seemed to experience more pronounced cardioprotective effects from the treatment with ZnNPs compared to those in the post-isoproterenol group. In an in vitro experiment, the use of ZnNPs resulted in a significant reduction in cell death and inhibition of inflammation cytokine expression. The gene expression normalization for PPAR-γ/NF-κB/IκB-α/IKKα/β and the phosphorylation of PPAR-γ could potentially be associated with the beneficial effects of ZnNPs. The rise in inflammatory responses was effectively prevented. The results of this study indicate that ZnNPs have cardioprotective efficacies on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction. This positive impact could be linked to the PPAR-γ activation and the NF-κB signaling inhibition.
1 Introduction
Ischemic heart disease poses a significant public health concern due to its increasing burden. Acute myocardial infarction results in tissue loss and compromised heart function, contributing to 40% of deaths in China [1]. Timely revascularization following a heart attack, such as bypass surgery, thrombolytic therapy, and percutaneous coronary intervention, plays a crucial role in enhancing heart function and averting post-heart attack physiological changes [2]. Nevertheless, these efficient yet intrusive methods may not be suitable for every patient due to their limited applicability dependent on particular clinical traits, as well as the potential for severe complications like reperfusion injury and bleeding [2,3]. Efforts to reduce infarct size and enhance prognosis through pharmacotherapy (such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) in the absence of reperfusion are mainly ineffective, primarily due to non-specific drug delivery, adverse effects, and the brief duration of action of certain drugs [1–4]. As a result, numerous patients undergoing this method continue to develop heart failure and cardiac hypertrophy [1,2]. The atherosclerotic plaques rupture and growth, leading to thrombosis, are the primary factors contributing to acute myocardial infarction [4]. Presently, the interventions accessible for atherosclerosis, such as statins, can lower the acute myocardial infarction risk. However, the impact of these interventions differs among individuals, resulting in notable residual risks [5–8]. Certain chemotherapies, like methotrexate and docetaxel, appear to exhibit advantageous outcomes in atherosclerosis [9–11]. Nevertheless, the drugs administration systemically is restricted due to their unfavorable efficacies. The need for safer and more effective prevention and treatments methods for myocardial infarction is on the rise [12].
Nanotechnology is instrumental in the progress of contemporary treatment alternatives [13,14]. It facilitates the creation and tailoring of materials possessing exceptional properties and attributes, spanning from 1 to 100 nm in size [13]. Currently, a diverse range of nanoparticles are produced through chemical or physical methods. Nevertheless, the utilization of hazardous chemicals and the subsequent environmental damage have given rise to multiple apprehensions [14–16]. Nanoparticles are receiving increased attention due to their importance in biology and potential uses in medicine. Nevertheless, the traditional chemical techniques utilized in their creation frequently introduce harmful reactive materials, making the produced nanoparticles unsuitable for medical applications. The adoption of environmentally friendly methods in nanoparticle production has been extensively acknowledged in several scientific studies [14–16], solidifying its status as a key research focus. Plant extracts have shown great potential as an alternative method for producing metal oxide NPs compared to traditional approaches. The versatility of NPs in fields like medicine, industry, and agriculture is extensive, highlighting their importance across various sectors [17–19]. Researchers have recently been drawn to the unique efficacies and diverse applications of nanoparticles. These minuscule particles have proven to be helpful in a wide array of areas including biological markers, optoelectronic catalysts, medical treatments, and pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, the use of plants to synthesize nanoparticles on a larger scale presents additional benefits, such as the capacity to reduce and absorb metal ions [16–19].
Numerous therapeutic optimized approaches have been extensively investigated, among them being the utilization of nanoparticles. These minute particles at the nanoscale have found significant application in managing both tumors and neural disorders [16–20]. Nanoparticles facilitate the transportation of therapeutic substances to specific locations with precise spatial and temporal accuracy, improve tissue engineering procedures efficiency, and control the activities of transplants like stem cells [16–19]. Utilizing nanoparticles enhances the efficacy of treatments and reduces the negative impacts of conventional or innovative therapies, enhancing the probability of their successful implementation in clinical environments. Nevertheless, studies on NPs in this area are still in the early stages [13–15].
Zinc nanoparticles (ZnNPs) are noteworthy because of their chemical and physical properties. Additionally, ZnNPs have gained traction in biological uses thanks to their minimal toxicity levels. ZnNPs play a beneficial role in biomedicine, specifically in combating fungal infections, bacterial infections, cancer, and diabetes [21–23]. Furthermore, ZnNPs exhibited anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hypolipidemic characteristics [24,25]. Zinc has a main role in maintaining the function and structure of cell membranes, defending against pathogens, enhancing brain function, promoting tissue development, and supporting immunity [26,27]. Additionally, ZnNPs are utilized in the present for their capacity to load drugs, ability to release drugs in a controlled manner, and targeted delivery capabilities [28]. Furthermore, zinc plays essential roles in the formation and operation of various antioxidant enzymes and distinct metallothioneins [29]. In the cardiovascular diseases development, including ischemic cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, and coronary heart disease, the fluctuation in Zn homeostasis plays a significant role, potentially contributing to cardiovascular diseases mortality [30].
In this study, the main objective is to create eco-friendly ZnNPs using curcumin. The author conducted a thorough analysis of the ZnNPs by employing microscopic imaging, diffraction, and spectroscopic techniques to gain insights into their size, shape, and structure. Additionally, the author assessed the therapeutic effects of these ZnNPs in the myocardial infarction treatment.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Preparation of curcumin
To obtain curcumin from turmeric, the initial step involved cutting the turmeric rhizomes into small pieces (0.5–1 cm) and washing them with water. Subsequently, curcumin was extracted from the turmeric pieces (10 g) using a Soxhlet apparatus. A solvent extract of 100 mL of water: ethanol (1:1) was utilized for this purpose. Following a 4 h extraction period, the extract was cooled down before being employed in nanoparticles synthesis.
2.2 Green formulation of ZnNPs
To create the 0.04 M zinc nitrate stock solution, the curcumin (50 mL) was combined with the zinc nitrate stock solution (20 mL) and incubated for 180 min at 25°C. A noteworthy change in color was subsequently reported. The ZnNPs biosynthesis was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), X-Ray diffraction analysis (XRD), fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) [13–15].
2.3 Chemical characterization of ZnNPs
UV-Vis analysis was conducted to check the nanoparticles absorbance value within the 200–600 nm range. The biogenic ZnNPs surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was recorded using the UV-Vis spectrophotometer.
FE-SEM was utilized for the examination of the structure and makeup of ZnNPs. The ZnNPs size distribution was depicted in a histogram through imageJ software.
The identification of the various functional groups accountable for the stabilization and reduction of the formulated ZnNPs was accomplished through FT-IR analysis, utilizing the Cary 630 FTIR model from Tokyo, Japan. It was conducted using the KBr technique.
The XRD has verified that the synthesized NPs are ZnNPs. Following the synthesis of ZnNPs, the samples underwent centrifugation in preparation for the XRD analysis. The X-ray analysis involved adjusting the angle every 3.4 s for a total of three steps, with each step lasting 34 s.
TEM analysis was employed to investigate the structure of ZnNPs using a JEOL model JEM-1010 from Tokyo, Japan.
The Shimadzu DX-700HS machine was utilized to conduct an EDX analysis to identify the elements.
The Zetasizer nano-array was employed to determine the zeta potential. The measurements were conducted at dispersion angles of 90 and 25°C.
2.4 In vivo experimental design
During this experimental investigation, a total of 75 male BALB/c mice weighing between 38 and 40 g were utilized. The mice was housed in a controlled setting with a temperature maintained between 20 and 24°C. It is important to highlight that all procedures conducted in this study adhered to ethical guidelines concerning the use of laboratory animals.
Myocardial infarction + ZnNPs (10 µg/kg).
Myocardial infarction + ZnNPs (40 µg/kg).
Myocardial infarction + curcumin.
Myocardial infarction group.
Control group.
After the mice were accustomed to their surroundings, myocardial infarction was triggered in the mice by injecting isoproterenol (85 mg/kg) dissolved in normal saline (1 mg/mL) subcutaneously for 2 consecutive days with a 24 h gap, following the procedure described in the earlier research. (The next day, four animals exhibited shedding, leading to their immediate replacement.) The standard protocols were utilized to establish the induction of myocardial infarction. Following that, a group of mice were anesthetized 48 h after the occurrence of myocardial infarction, and samples of heart tissue from their left ventricle were examined using hematoxylin–eosin histochemical techniques. The identification of white areas indicated necrotic damage caused by the heart attack [31].
After the final administration of isoproterenol, the mice underwent anesthesia. The researchers then assessed the presence of ST-segment depression or elevation in the animals. On the fifth day, the mice were euthanized to analyze the immunological and biochemical factors. ELISA kits were used to determine the expression levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the homogenized left ventricular heart tissues supernatant. The myocardial cellular damage extent was determined by examining the levels of serum troponin and creatinine kinase isoenzyme. Additionally, an ELISA assay was utilized to measure the levels of serum creatinine kinase isoenzyme and troponin [31].
The Qiasol kit (Qiagen) was used to extract the RNA from the examined heart, following the instructions provided. The concentration of the isolated RNA was assessed using a nanodrop spectrophotometer. The optical absorption of the samples was quantified at a wavelength of 280 nm, with the concentration being calculated according to the dilution factor in µL/ng. Next, a 1 ng/µL RNA solution was prepared for cDNA synthesis. To achieve this, 10 µL of a cDNA synthesis kit was mixed with 10 µL of RNA. The mixture was subsequently placed in a thermocycler and incubated at 25°C for 10 min, followed by 60°C for 50 min. Finally, the resulting cDNA was stored for qPCR analysis at −20°C. The gene replication rate was investigated through the performance of PCR. The control gene utilized in this research was the beta-actin gene. The temperature program for amplifying the PPAR/GAPDH gene, including PPAR-γ/NF-κB/IκB-α/IKKα/β, PPAR-γ, and β-actin, consisted of a series of steps. These steps included primary denaturation for 4 min at 94°C, followed by secondary denaturation at 94°C for 1 min. The temperature was initially set at 55°C for 1 min for the binding process, followed by primary synthesis for 1 min at 52°C. This cycle was repeated 40 times, covering steps 2–4, and concluded with the final synthesis for 18 min at 52°C. Subsequently, the obtained graphs were analyzed to determine changes in gene expression through ΔΔCT analysis, based on the CT variance among the different intervention groups [14,31] (Table 1).
Primer sequences of genes studied in this research
| Gene | Sequence | GenBank |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | Forward: CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC | NM_001101 |
| Reverse: AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT | ||
| PPAR-γ | Forward: AGCCTGCGAAAGCCTTTTGGTG | NM_015869 |
| Reverse: GGCTTCACATTCAGCAAACCTGG | ||
| IκB-α | Forward: TCCACTCCATCCTGAAGGCTAC | NM_020529 |
| Reverse: CAAGGACACCAAAAGCTCCACG | ||
| NF-kB p65 | Forward: TGAACCGAAACTCTGGCAGCTG | NM_021975 |
| Reverse: CATCAGCTTGCGAAAAGGAGCC |
2.5 Statistical analysis
The normality of the data was assessed using Minitab-21 in the research. Following this, any data that was not normally distributed was transformed to achieve normality. The data variance analysis was done with SPSS-22, and graphical illustrations were generated using Excel software.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Chemical characterization
The metal–oxygen bond is associated with bands below 700 cm−1 in FT-IR analysis. In Figure 1 of the FT-IR spectrum of ZnNPs, the Zn–O bond is represented by bands at 458 and 523 cm−1. The additional peaks at 1,056, 1,381–1,633, 2,958, and 3,428 correspond to the organic functional groups of curcumin, which serve as the reducing agent during the synthesis process.

FT-IR analysis of ZnNPs green-mediated by curcumin.
EDX assay is the practical method for nanoparticles elemental screening. The EDX diagram and elemental mapping of nanoparticles are reported in Figures 2 and 3. The energy signals at 8.6 and 9 keV are designated for Zn Lα and Zn Kβ, respectively. The presence of signals at 0.52 (O Lα) and 0.27 (for C Lα) confirms the secondary metabolites connection from the extract to the synthetic ZnNPs surface.

EDX analysis of ZnNPs green-mediated by curcumin.

Elemental mapping analysis of ZnNPs green-mediated by curcumin.
One technique utilized to characterize metal nanoparticles involves examining electron microscope (FE-SEM) image, which are useful for analyzing the morphology of the produced NPs. The TEM and FE-SEM images captured from ZnNPs under the specified ideal parameters reveal the production of spherical nanomaterials (Figures 4 and 5). The particles that were generated had a size of 10–60 nm. On average, the nanoparticles that were synthesized had a size between 10 and 30 nm. In terms of their morphology, the nanoparticles exhibited crystalline geometric and uniform shapes. Additionally, due to the lengthy waiting time for analysis, the ZnNPs tended to agglomerate to some extent.
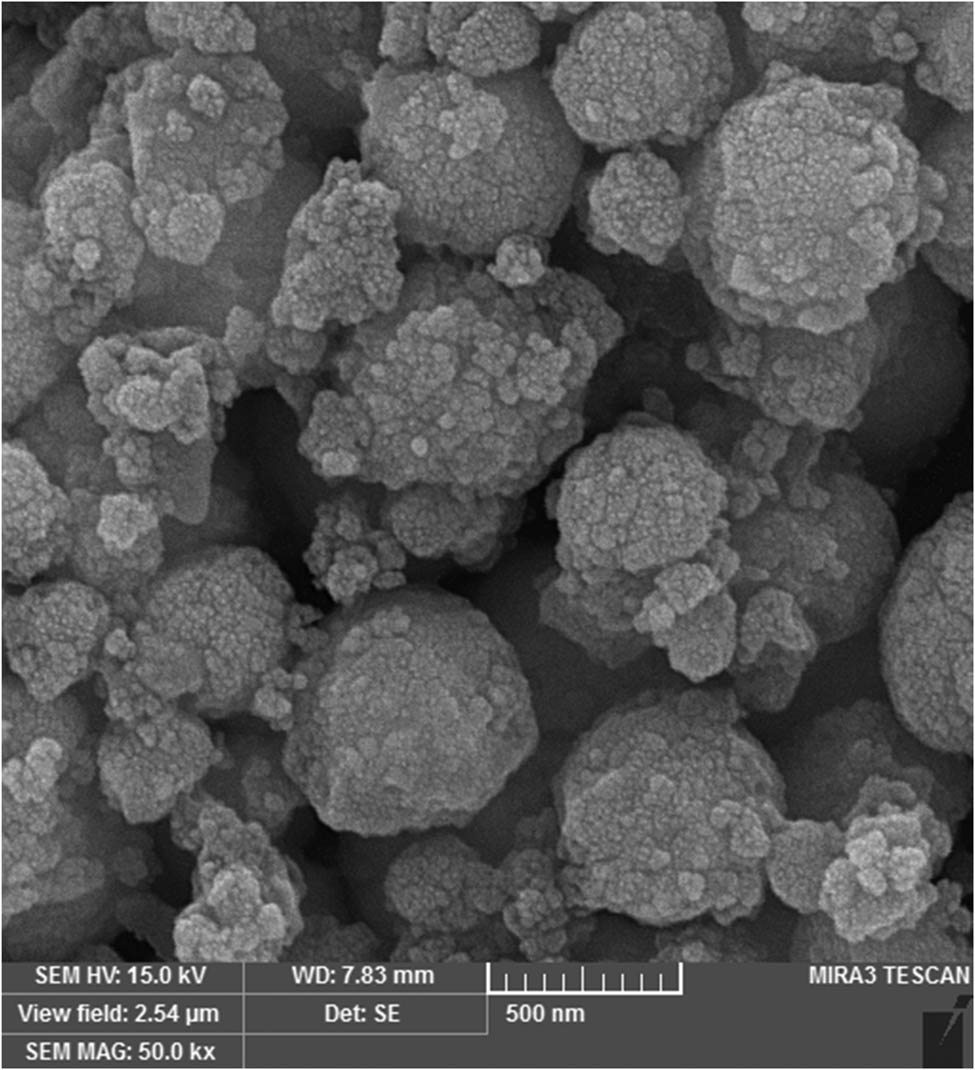

FE-SEM image of ZnNPs green-mediated by curcumin.
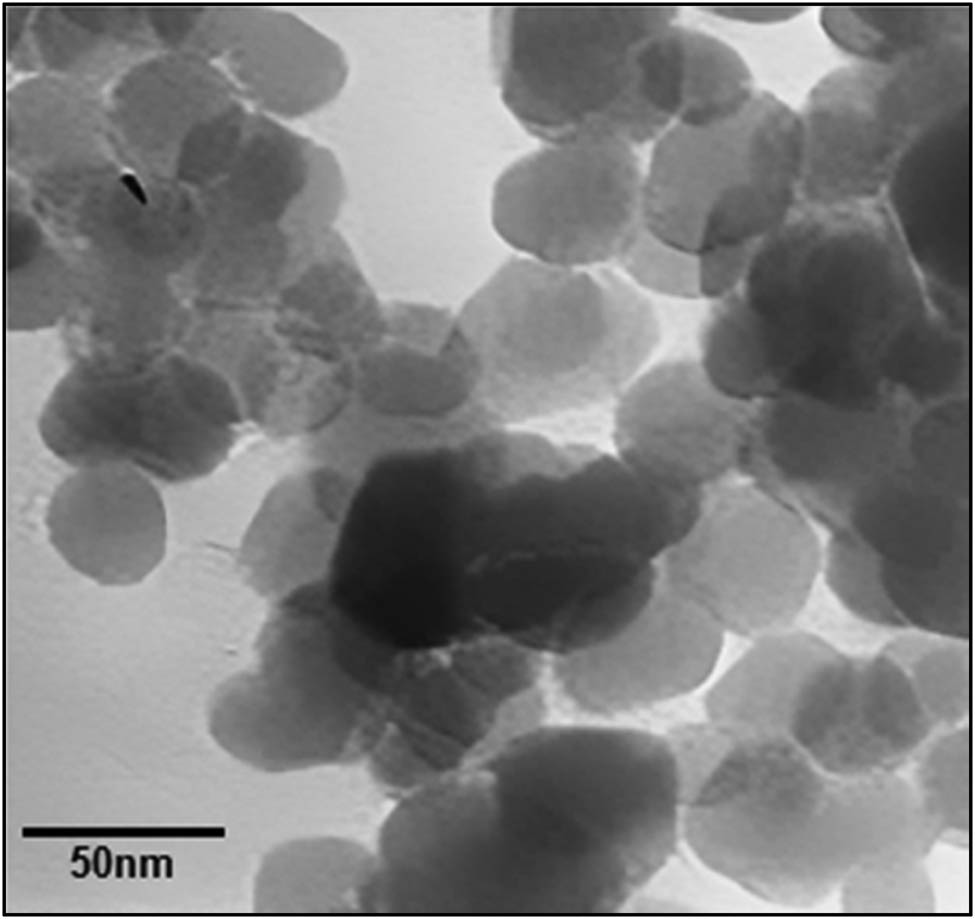
TEM image of ZnNPs green-mediated by curcumin.
The mixture of plant extract and zinc nitrate salt was combined and left to incubate for 180 min. Throughout this period, a noticeable alteration in color occurred within the reaction mixture. The initial yellow-orange hue of the solution transformed into a deep brown shade, thereby approving the phytosynthesis occurrence in the ZnNPs production. The color change was a consequence of the nanoparticles’ exhibited SPR activity [22,25]. The color intensity is dictated by the electrons quantity liberated during the conversion of NO3 to NO2, leading to the Zn++ reduction to metallic ions [24,25]. The research the author conducted was backed by the results from previous studies [22,25], which mirrored the findings regarding the visual alteration of the solution’s color. Further investigation into the reaction solution color change was conducted by analyzing the ZnNPs UV-Vis spectrum. An absorption peak at 282 nm was reported in the ZnNPs, which was attributed to the free electrons excitation of the metal during the nanoparticles formation (Figure 6). Nevertheless, the absorption peak absence was observed in the plant extract within this particular range. Typically, these spectra offer valuable insights into the characteristics and development of colloidal ZnNPs. An absorption peak between 200 and 300 nm is a distinctive attribute of ZnNPs [25–29].
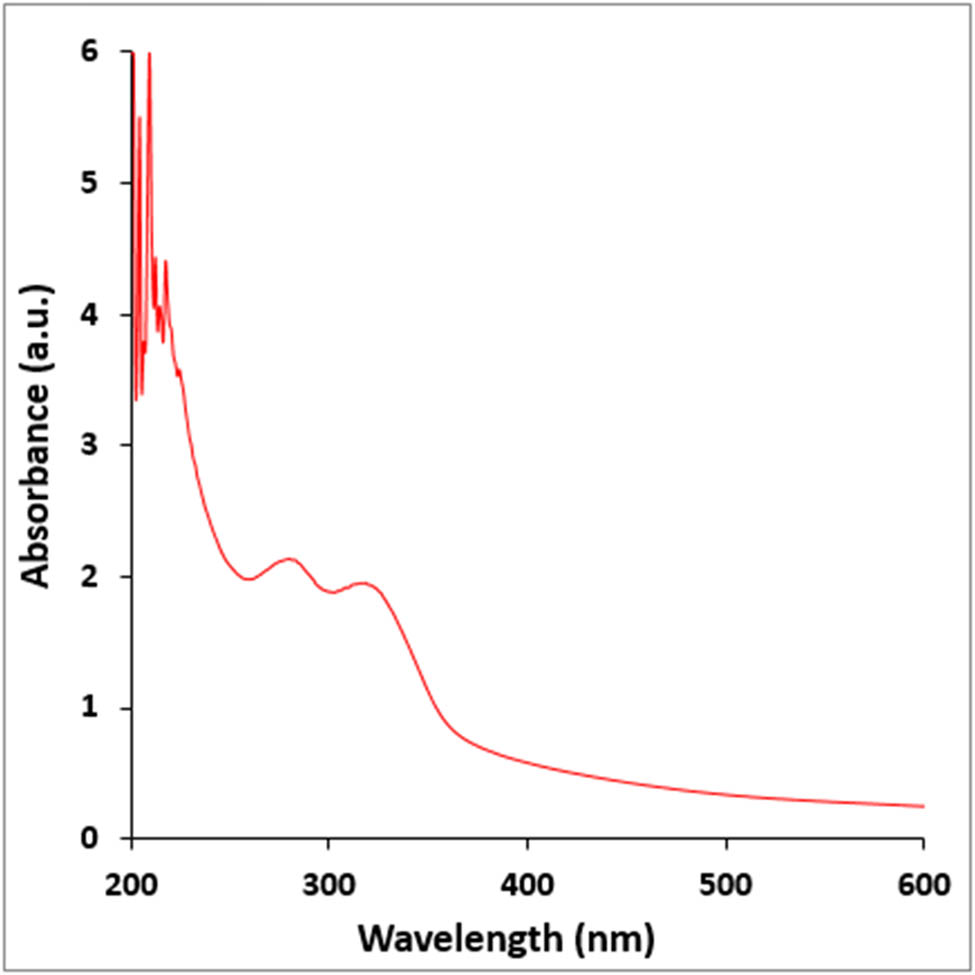
UV-Vis analysis of ZnNPs green-mediated by curcumin.
ZnO colloidal particles exhibit a neutral charge at their isoelectric point (pI). When the pH is below the pI of ZnO, the particles acquire a positive charge, which hinders their aggregation and leads to the formation of a stable suspension. Likewise, when the pH exceeds the pI of ZnO, the particles become negatively charged on the surface, resulting in similar observations. Figure 7 illustrates the standard relationship between pH and the zeta potential of ZnO suspension. The zeta potential becomes positive in acidic conditions. The isoelectric point (pI) is approximately at pH 9.9. The surface area is intricately linked to the size and morphology of the particles [32].

Zeta potential values of ZnNPs green-mediated by curcumin at several pH values (at 25°C).
Figure 8 displays the XRD diffraction diagrams of ZnNPs, indicating the successful crystallization of the nanoparticles. The results have been compared to the ICDD PDF card no. 01-080-3002 for validation. The peaks observed at 2θ angles of 67.98, 62.86, 56.62, 47.59, 36.15, 34.48, and 31.82 correspond to the crystal planes of (112), (103), (110), (102), (101), (002), and (100). The crystal size of ZnNPs was determined to be 19.52 nm using Scherer’s equation.

XRD analysis of ZnNPs green-mediated by curcumin.
3.2 Cardioprotective effects of ZnNPs green-mediated by curcumin
A recent investigation involved the administration of isoproterenol to mice to induce myocardial infarction. Elevated doses of isoproterenol quickly increase the myocardial load, resulting in myocardial dysfunction. The changes in morphology and pathophysiology induced by isoproterenol in mice closely mirror those seen in human myocardial infarction. Increased free radicals production during myocardial infarction leads to heightened activity of the MAPK signaling pathway, which includes three subfamilies: p38, JNK, and ERK. Activation of this pathway boosts κB-NF, leading to an increase in inflammatory cytokines production and ultimately causing damage to the myocardium [33]. Extensive studies have been done on the ERK signaling pathway, which is crucial in regulating cellular death, growth, and survival, along with the immune response linked to inflammation [34]. Despite the association of p38 MAPK and JNK with apoptosis, the importance of ERK lies in its role in promoting cell survival and minimizing the chances of myocardial infarction [35]. Numerous research reported the involvement of κB-NF and MAPK pathways in myocardial hypertrophy, heart failure, and blood pressure regulation. Several research findings have indicated that the inhibition of MAPK can lead to the 2-Nrf activation, which plays a critical role in regulating the expression of antioxidant and detoxification enzymes during the second step [34–36].
The study introduced an eco-friendly formulation of ZnNPs synthesized using curcumin. Different spectroscopic methods were utilized to analyze the ZnNPs, and their potential in treating myocardial infarction was explored.
The present study examined the protective properties of nanoparticles derived from curcumin in preventing myocardial damage. This was done by creating a myocardial infarction model in mice using isoproterenol. Additionally, the research evaluated the expression levels of PPAR-γ/NF-κB/IκB-α/IKKα/β, and PPAR-γ or MAPK signaling pathway in the experimental groups to gain insight into the treatment’s mechanism (Figure 9). The green-synthesized curcumin ZnNPs resulted in a decrease in the levels of p-IKKα/β/IKKα/β, p-IkBα/IkBα, and p-NF-kβ p65/NF-kβ p65, along with a decline in PPAR/GAPDH. Additionally, the curcumin-derived ZnNPs produced through green synthesis showed a notable decrease (P ≤ 0.05) in the mRNA levels of IL6, TNFα, and IL1β, as well as the presence of CD68+ cells, in comparison to the control group (Figure 10). The mice involved in the study displayed a model of myocardial infarction induced by isoproterenol. This was supported by the significant accumulation of collagen and extensive damage to the myocardial tissue. Additionally, the expression of MAPK was found to be increased, providing further validation of the model’s effectiveness. Recent research has proposed that various signaling pathways, including the proteins within the MAPK pathway, change in response to myocardial damage caused by isoproterenol [37]. Recent studies have shown that isoproterenol is effective in boosting MAPK levels. The MAPK pathway plays a key role in controlling gene expression related to apoptosis, such as Bax and Bcl-2. These genes are essential components of the apoptotic signaling pathway and become active in response to external signals within the cell. Additionally, myocardial infarction triggers the inflammatory cytokines secretion and increases the activity of MAPK P38 [38]. Curcumin-synthesized nanoparticles show great promise in treating myocardial damage caused by isoproterenol intake. The nanoparticles possess antioxidant properties that, in conjunction with their compounds, have a significant effect on inhibiting 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl free radicals. Boosting the immune system by increasing antioxidant levels undoubtedly protects individuals from chronic diseases. As stated by Martinez et al., antioxidants can reduce the likelihood of heart failure by affecting MAPK and κB-NF signaling pathways [39]. Therefore, the potential influence of curcumin-derived nanoparticles on reducing MAPK expression may be due to their antioxidative traits.

Effect of ZnNPs on several genes (fold change).

Effect of ZnNPs on the inflammatory cytokines mRNA levels (a), inflammatory cytokines quantitative analysis (b) pg/mg and CD68+ cell.
The latest research revealed that the ZnNPs synthesized using curcumin led to a reduction in cardiac troponin-1, cTn-T, ST segment deviation in MI mice, as well as the heart wet weight/body weight ratio (Figures 11 and 12).

Effect of ZnNPs on the concentrations of cardiac troponin-1 (ng/mL) and cTn-T (pg/mL) and MI mice ST segment deviation (mV).

Effect of ZnNPs on heart wet weight/body weight ratio (mg/g).
4 Conclusion
The author has effectively developed a cutting-edge drug for cardioprotection using ZnNPs combined with curcumin. This groundbreaking therapy is designed to combat isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in mice, with a particular emphasis on the PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway. The range of 400–700 cm−1 showed vibrational bands for Zn–O bonds, as indicated by the FT-IR spectroscopy. Furthermore, the FE-SEM image exhibited a spherical morphology. ZnNPs have demonstrated the ability to reduce the pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in the hearts of mice with myocardial infarction. Moreover, they have been discovered to effectively suppress the myocardial injury marker levels, decrease mortality rates, and enhance ventricular wall infarction. The beneficial impacts of ZnNPs may be attributed to the normalization of gene expression associated with PPAR-γ/NF-κB/IκB-α/IKKα/β, and PPAR-γ phosphorylation.
-
Funding information: Author states no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: Lijuan Tan: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, writing – original draft, and writing – review & editing.
-
Conflict of interest: There is no any conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
-
Ethical approval: The experiments were performed according to the ethical guidelines of the International Association for the Study of Humans.
References
[1] Reed GW, Rossi JE, Cannon CP. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 2017;389(10065):197–210.10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30677-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Marín-Juez R, El-Sammak H, Helker CSM, Kamezaki A, Mullapuli ST, Bibli SI, et al. Coronary revascularization during heart regeneration is regulated by epicardial and endocardial cues and forms a scaffold for cardiomyocyte repopulation. Dev Cell. 2019;51(4):503–15.e4.10.1016/j.devcel.2019.10.019Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Rentrop KP, Feit F. Reperfusion therapy for acute myocardial infarction: concepts and controversies from inception to acceptance. Am Heart J. 2015;170(5):971–80.10.1016/j.ahj.2015.08.005Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Arbab-Zadeh A, Nakano M, Virmani R, Fuster V. Acute coronary events. Circulation. 2012;125(9):1147–56.10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.047431Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Ekroos K, Jänis M, Tarasov K, Hurme R, Laaksonen R. Lipidomics: a tool for studies of atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2010;12(4):273–81.10.1007/s11883-010-0110-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Young DR, Hivert MF, Alhassan S, Camhi SM, Ferguson JF, Katzmarzyk PT, et al. Sedentary behavior and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: a science advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;134(13):e262–79.10.1161/CIR.0000000000000440Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Gorabi AM, Kiaie N, Reiner Ž, Carbone F, Montecucco F, Sahebkar A. The therapeutic potential of nanoparticles to reduce inflammation in atherosclerosis. Biomolecules. 2019;9(9):2545.10.3390/biom9090416Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Ou LC, Zhong S, Ou JS, Tian JW. Application of targeted therapy strategies with nanomedicine delivery for atherosclerosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021;42(1):10–7.10.1038/s41401-020-0436-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Cervadoro A, Palomba R, Vergaro G, Cecchi R, Menichetti L, Decuzzi P, et al. Targeting inflammation with nanosized drug delivery platforms in cardiovascular diseases: immune cell modulation in atherosclerosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018;6:177.10.3389/fbioe.2018.00177Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Bulgarelli A, Martins Dias AA, Caramelli B, Maranhão RC. Treatment with methotrexate inhibits atherogenesis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012;59(4):308–14.10.1097/FJC.0b013e318241c385Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Meneghini BC, Tavares ER, Guido MC, Tavoni TM, Stefani HA, Kalil-Filho R, et al. Lipid core nanoparticles as vehicle for docetaxel reduces atherosclerotic lesion, inflammation, cell death and proliferation in an atherosclerosis rabbit model. Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;115:46–54.10.1016/j.vph.2019.02.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Zhang J, Zu Y, Dhanasekara CS, Li J, Wu D, Fan Z, et al. Detection and treatment of atherosclerosis using nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017;9(1):e1412.10.1002/wnan.1412Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Dai W, Li Y, Liu X, Wang N, Luo P, Kong L. Protective effects of Nigella sativa L. seeds aqueous extract-based silver nanoparticles on sepsis-induced damages in rats. Inorg Chem Commun. 2024;166:112594.10.1016/j.inoche.2024.112594Search in Google Scholar
[14] Zhang D, Wang L, Tian L, Chen W, El-kott AF, Negm S, et al. Bio-inspired deposition of gold nanoparticles onto the surface of kaolin for in vitro management of human ovarian cancer and modulation of the inflammatory response in adenomyosis-induced mice in vivo via the MAPK signaling pathway. J Sci: Adv Mater Devices. 2024;9(2):100714.10.1016/j.jsamd.2024.100714Search in Google Scholar
[15] Guo Y, Shahriari M, Eltantawy W, El-kott AF, AlShehri MA, Ibrahim EH. Ultrasound assisted synthesis of starch-green tea extract composite and its therapeutic effects on adenomyosis by following the MAPK/ERK signaling and pro-inflammatory pathways in mice. J Polym Environ. 2024;1–10.10.1007/s10924-024-03271-zSearch in Google Scholar
[16] Bakir EM, Younis NS, Mohamed ME, El Semary NA. Cyanobacteria as nanogold factories: chemical and anti-myocardial infarction properties of gold nanoparticles synthesized by lyngbya majuscula. Mar Drugs. 2018;16:217.10.3390/md16060217Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Danila D, Johnson E, Kee P. CT imaging of myocardial scars with collagen-targeting gold nanoparticles. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2013;9:1067–76.10.1016/j.nano.2013.03.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Shen Y, Gong S, Li J, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zheng H, et al. Co-loading antioxidant N-acetylcysteine attenuates cytotoxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles in hypoxia/reoxygenation cardiomyocytes. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:6103–15.10.2147/IJN.S209820Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Merinopoulos I, Gunawardena T, Stirrat C, Cameron D, Eccleshall SC, Dweck MR, et al. Diagnostic applications of ultrasmall superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide for imaging myocardial and vascular inflammation. JACC: Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021;14:1249–64.10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.06.038Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Zheng H, You J, Yao X, Lu Q, Guo W, Shen Y. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles promote ferroptosis of ischemic cardiomyocytes. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24:11030–3.10.1111/jcmm.15722Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Siddiqui SA, Or Rashid MM, Uddin MG, Robel FN, Hossain MS, Haque MA, et al. Biological efficacy of zinc oxide nanoparticles against diabetes: a preliminary study conducted in mice. Biosci Rep 40. 2020;40:BSR20193972.10.1042/BSR20193972Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Bashandy SA, Ahmed-Farid OA, Abdelmottaleb-Moussa S, Omara EA, Abdel Jaleel GA, Ibrahim FA. Efficacy of zinc oxide nanoparticles on hepatocellular carcinoma-induced biochemical and trace element alterations in rats. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2021;11:108–17.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Jain D, Shivani, Bhojiya AA, Singh H, Daima HK, Singh M, et al. Microbial fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of their antimicrobial and photocatalytic properties. Front Chem. 2020;8:778.10.3389/fchem.2020.00778Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Ahmed RF, Nasr M, Abd Elbaset M, Hessin AF, Ahmed-Farid O, Shaffie NM, et al. Combating hematopoietic and hepatocellular abnormalities resulting from administration of cisplatin: role of liver targeted glycyrrhetinic acid nanoliposomes loaded with amino acids. Pharm Dev Technol. 2022;27:925–941. 10.1080/10837450.2022.2129687 Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] El-Bahr SM, Shousha S, Albokhadaim I, Shehab A, Khattab W, Ahmed-Farid O, et al. Impact of dietary zinc oxide nanoparticles on selected serum biomarkers, lipid peroxidation and tissue gene expression of antioxidant enzymes and cytokines in Japanese quail. BMC Vet Res. 2020;16:349.10.1186/s12917-020-02482-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] MacKenzie S, Bergdahl A. Zinc homeostasis in diabetes mellitus and vascular complications. Biomedicines. 2022;10:139.10.3390/biomedicines10010139Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Kambe T, Tsuji T, Hashimoto A, Itsumura N. The physiological, biochemical, and molecular roles of zinc transporters in zinc homeostasis and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2015;95:749–84.10.1152/physrev.00035.2014Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Huang X, Zheng X, Xu Z, Yi C. ZnO-based nanocarriers for drug delivery application: from passive to smart strategies. Int J Pharm. 2017;534:190–4.10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.10.008Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] DiSilvestro RA. Zinc in relation to diabetes and oxidative disease. J Nutr. 2000;130:1509S–S1511.10.1093/jn/130.5.1509SSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Huang L, Teng T, Bian B, Yao W, Yu X, Wang Z, et al. Zinc levels in left ventricular hypertrophy. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017;176:48–55.10.1007/s12011-016-0808-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Arozal W, Monayo ER, Barinda AJ, Perkasa DP, Soetikno V, Nafrialdi N, et al. Protective effects of silver nanoparticles in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug;9:867497.10.3389/fmed.2022.867497Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Huang HB, Leung DYC, Kwong PCW, Xiong J, Zhang L. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under vacuum ultraviolet irradiation. Catal Today. 2013;201:189–94.10.1016/j.cattod.2012.06.022Search in Google Scholar
[33] Verma VK, Malik S, Narayanan SP, Mutneja E, Sahu AK, Bhatia J, et al. Role of MAPK/NF-κB pathway in cardioprotective effect of Morin in isoproterenol induced myocardial injury in rats. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(1):1139–48.10.1007/s11033-018-04575-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Ren G, Cui Y, Li W, Li F, Han X. Research on cardioprotective effect of irbesartan in rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through MAPK-ERK signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(12):5487–94.Search in Google Scholar
[35] Liu K, Wang F, Wang S, Li W-N, Ye Q. Mangiferin attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via MAPK/Nrf-2/HO-1/NF-κB in vitro and in vivo. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:7285434.10.1155/2019/7285434Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Bao W, Hu E, Tao L, Boyce R, Mirabile R, Thudium DT, et al. Inhibition of Rho-kinase protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;61(3):548–58.10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.12.004Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Fakhri F, Shakeryan S, Fakhri S, Alizadeh A. The effect of 6 weeks of high intensity interval training (HIIT) with nano-curcumin supplementation on factors related to cardiovascular disease in inactive overweight girls. Feyz. 2020;24(2):181–9.10.18502/ijdo.v11i3.2606Search in Google Scholar
[38] Krishnamurthy P, Rajasingh J, Lambers E, Qin G, Losordo DW, Kishore R. IL-10 inhibits inflammation and attenuates left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction via activation of STAT3 and suppression of HuR. Circ Res. 2009;104(2):e9–e18.10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.188243Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Martinez PF, Bonomo C, Guizoni DM, Junior SA, Damatto RL, Cezar MD, et al. Modulation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways by antioxidant therapy in skeletal muscle of heart failure rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(1):371–84.10.1159/000445631Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Porous silicon nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and their antifungal activity
- Biochar from de-oiled Chlorella vulgaris and its adsorption on antibiotics
- Phytochemicals profiling, in vitro and in vivo antidiabetic activity, and in silico studies on Ajuga iva (L.) Schreb.: A comprehensive approach
- Synthesis, characterization, in silico and in vitro studies of novel glycoconjugates as potential antibacterial, antifungal, and antileishmanial agents
- Sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by potato starch: Its performance in the treatment of esophageal cancer
- Computational study of ADME-Tox prediction of selected phytochemicals from Punica granatum peels
- Phytochemical analysis, in vitro antioxidant and antifungal activities of extracts and essential oil derived from Artemisia herba-alba Asso
- Two triazole-based coordination polymers: Synthesis and crystal structure characterization
- Phytochemical and physicochemical studies of different apple varieties grown in Morocco
- Synthesis of multi-template molecularly imprinted polymers (MT-MIPs) for isolating ethyl para-methoxycinnamate and ethyl cinnamate from Kaempferia galanga L., extract with methacrylic acid as functional monomer
- Nutraceutical potential of Mesembryanthemum forsskaolii Hochst. ex Bioss.: Insights into its nutritional composition, phytochemical contents, and antioxidant activity
- Evaluation of influence of Butea monosperma floral extract on inflammatory biomarkers
- Cannabis sativa L. essential oil: Chemical composition, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial properties, and acute toxicity: In vitro, in vivo, and in silico study
- The effect of gamma radiation on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural conversion in water and dimethyl sulfoxide
- Hollow mushroom nanomaterials for potentiometric sensing of Pb2+ ions in water via the intercalation of iodide ions into the polypyrrole matrix
- Determination of essential oil and chemical composition of St. John’s Wort
- Computational design and in vitro assay of lantadene-based novel inhibitors of NS3 protease of dengue virus
- Anti-parasitic activity and computational studies on a novel labdane diterpene from the roots of Vachellia nilotica
- Microbial dynamics and dehydrogenase activity in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) rhizospheres: Impacts on growth and soil health across different soil types
- Correlation between in vitro anti-urease activity and in silico molecular modeling approach of novel imidazopyridine–oxadiazole hybrids derivatives
- Spatial mapping of indoor air quality in a light metro system using the geographic information system method
- Iron indices and hemogram in renal anemia and the improvement with Tribulus terrestris green-formulated silver nanoparticles applied on rat model
- Integrated track of nano-informatics coupling with the enrichment concept in developing a novel nanoparticle targeting ERK protein in Naegleria fowleri
- Cytotoxic and phytochemical screening of Solanum lycopersicum–Daucus carota hydro-ethanolic extract and in silico evaluation of its lycopene content as anticancer agent
- Protective activities of silver nanoparticles containing Panax japonicus on apoptotic, inflammatory, and oxidative alterations in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity
- pH-based colorimetric detection of monofunctional aldehydes in liquid and gas phases
- Investigating the effect of resveratrol on apoptosis and regulation of gene expression of Caco-2 cells: Unravelling potential implications for colorectal cancer treatment
- Metformin inhibits knee osteoarthritis induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats: S100A8/9 and S100A12 as players and therapeutic targets
- Effect of silver nanoparticles formulated by Silybum marianum on menopausal urinary incontinence in ovariectomized rats
- Synthesis of new analogs of N-substituted(benzoylamino)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridines
- Response of yield and quality of Japonica rice to different gradients of moisture deficit at grain-filling stage in cold regions
- Preparation of an inclusion complex of nickel-based β-cyclodextrin: Characterization and accelerating the osteoarthritis articular cartilage repair
- Empagliflozin-loaded nanomicelles responsive to reactive oxygen species for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury protection
- Preparation and pharmacodynamic evaluation of sodium aescinate solid lipid nanoparticles
- Assessment of potentially toxic elements and health risks of agricultural soil in Southwest Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Theoretical investigation of hydrogen-rich fuel production through ammonia decomposition
- Biosynthesis and screening of cobalt nanoparticles using citrus species for antimicrobial activity
- Investigating the interplay of genetic variations, MCP-1 polymorphism, and docking with phytochemical inhibitors for combatting dengue virus pathogenicity through in silico analysis
- Ultrasound induced biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles embedded into chitosan polymers: Investigation of its anti-cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma effects
- Copper oxide nanoparticles-mediated Heliotropium bacciferum leaf extract: Antifungal activity and molecular docking assays against strawberry pathogens
- Sprouted wheat flour for improving physical, chemical, rheological, microbial load, and quality properties of fino bread
- Comparative toxicity assessment of fisetin-aided artificial intelligence-assisted drug design targeting epibulbar dermoid through phytochemicals
- Acute toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity of bis-thiourea derivatives
- Anti-diabetic activity-guided isolation of α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory terpenes from Capsella bursa-pastoris Linn.
- GC–MS analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 metabolites and its computational analysis on familial pulmonary fibrosis hub genes
- Green formulation of copper nanoparticles by Pistacia khinjuk leaf aqueous extract: Introducing a novel chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of prostate cancer
- Improved photocatalytic properties of WO3 nanoparticles for Malachite green dye degradation under visible light irradiation: An effect of La doping
- One-pot synthesis of a network of Mn2O3–MnO2–poly(m-methylaniline) composite nanorods on a polypyrrole film presents a promising and efficient optoelectronic and solar cell device
- Groundwater quality and health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride in Al Qaseem area, Saudi Arabia
- A comparative study of the antifungal efficacy and phytochemical composition of date palm leaflet extracts
- Processing of alcohol pomelo beverage (Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck) using saccharomyces yeast: Optimization, physicochemical quality, and sensory characteristics
- Specialized compounds of four Cameroonian spices: Isolation, characterization, and in silico evaluation as prospective SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Identification of a novel drug target in Porphyromonas gingivalis by a computational genome analysis approach
- Physico-chemical properties and durability of a fly-ash-based geopolymer
- FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitory potentials of some phytochemicals from anti-leukemic plants using computational chemical methodologies
- Wild Thymus zygis L. ssp. gracilis and Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh.: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of essential oils
- 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, ADMET, simulation dynamic, and retrosynthesis studies on new styrylquinolines derivatives against breast cancer
- Deciphering the influenza neuraminidase inhibitory potential of naturally occurring biflavonoids: An in silico approach
- Determination of heavy elements in agricultural regions, Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis and characterization of antioxidant-enriched Moringa oil-based edible oleogel
- Ameliorative effects of thistle and thyme honeys on cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity in mice
- Study of phytochemical compound and antipyretic activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. fractions
- Investigating the adsorption mechanism of zinc chloride-modified porous carbon for sulfadiazine removal from water
- Performance repair of building materials using alumina and silica composite nanomaterials with electrodynamic properties
- Effects of nanoparticles on the activity and resistance genes of anaerobic digestion enzymes in livestock and poultry manure containing the antibiotic tetracycline
- Effect of copper nanoparticles green-synthesized using Ocimum basilicum against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice lung infection model
- Cardioprotective effects of nanoparticles green formulated by Spinacia oleracea extract on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in mice by the determination of PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway
- Anti-OTC antibody-conjugated fluorescent magnetic/silica and fluorescent hybrid silica nanoparticles for oxytetracycline detection
- Curcumin conjugated zinc nanoparticles for the treatment of myocardial infarction
- Identification and in silico screening of natural phloroglucinols as potential PI3Kα inhibitors: A computational approach for drug discovery
- Exploring the phytochemical profile and antioxidant evaluation: Molecular docking and ADMET analysis of main compounds from three Solanum species in Saudi Arabia
- Unveiling the molecular composition and biological properties of essential oil derived from the leaves of wild Mentha aquatica L.: A comprehensive in vitro and in silico exploration
- Analysis of bioactive compounds present in Boerhavia elegans seeds by GC-MS
- Homology modeling and molecular docking study of corticotrophin-releasing hormone: An approach to treat stress-related diseases
- LncRNA MIR17HG alleviates heart failure via targeting MIR17HG/miR-153-3p/SIRT1 axis in in vitro model
- Development and validation of a stability indicating UPLC-DAD method coupled with MS-TQD for ramipril and thymoquinone in bioactive SNEDDS with in silico toxicity analysis of ramipril degradation products
- Biosynthesis of Ag/Cu nanocomposite mediated by Curcuma longa: Evaluation of its antibacterial properties against oral pathogens
- Development of AMBER-compliant transferable force field parameters for polytetrafluoroethylene
- Treatment of gestational diabetes by Acroptilon repens leaf aqueous extract green-formulated iron nanoparticles in rats
- Development and characterization of new ecological adsorbents based on cardoon wastes: Application to brilliant green adsorption
- A fast, sensitive, greener, and stability-indicating HPLC method for the standardization and quantitative determination of chlorhexidine acetate in commercial products
- Assessment of Se, As, Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb content status in Ankang tea plantations of China
- Effect of transition metal chloride (ZnCl2) on low-temperature pyrolysis of high ash bituminous coal
- Evaluating polyphenol and ascorbic acid contents, tannin removal ability, and physical properties during hydrolysis and convective hot-air drying of cashew apple powder
- Development and characterization of functional low-fat frozen dairy dessert enhanced with dried lemongrass powder
- Scrutinizing the effect of additive and synergistic antibiotics against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Preparation, characterization, and determination of the therapeutic effects of copper nanoparticles green-formulated by Pistacia atlantica in diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction in rat
- Antioxidant and antidiabetic potentials of methoxy-substituted Schiff bases using in vitro, in vivo, and molecular simulation approaches
- Anti-melanoma cancer activity and chemical profile of the essential oil of Seseli yunnanense Franch
- Molecular docking analysis of subtilisin-like alkaline serine protease (SLASP) and laccase with natural biopolymers
- Overcoming methicillin resistance by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Computational evaluation of napthyridine and oxadiazoles compounds for potential dual inhibition of PBP-2a and FemA proteins
- Exploring novel antitubercular agents: Innovative design of 2,3-diaryl-quinoxalines targeting DprE1 for effective tuberculosis treatment
- Drimia maritima flowers as a source of biologically potent components: Optimization of bioactive compound extractions, isolation, UPLC–ESI–MS/MS, and pharmacological properties
- Estimating molecular properties, drug-likeness, cardiotoxic risk, liability profile, and molecular docking study to characterize binding process of key phyto-compounds against serotonin 5-HT2A receptor
- Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin-based microgels for enhancing solubility of Terbinafine: An in-vitro and in-vivo toxicological evaluation
- Phyto-mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of cationic and anionic dyes
- Monosodium glutamate induces hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis hyperactivation, glucocorticoid receptors down-regulation, and systemic inflammatory response in young male rats: Impact on miR-155 and miR-218
- Quality control analyses of selected honey samples from Serbia based on their mineral and flavonoid profiles, and the invertase activity
- Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus niruri leaf extract: Assessment of antimicrobial activity, effectiveness on tropical neglected mosquito vector control, and biocompatibility using a fibroblast cell line model
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles containing Cichorium intybus to treat the sepsis-induced DNA damage in the liver of Wistar albino rats
- Quality changes of durian pulp (Durio ziberhinus Murr.) in cold storage
- Study on recrystallization process of nitroguanidine by directly adding cold water to control temperature
- Determination of heavy metals and health risk assessment in drinking water in Bukayriyah City, Saudi Arabia
- Larvicidal properties of essential oils of three Artemisia species against the chemically insecticide-resistant Nile fever vector Culex pipiens (L.) (Diptera: Culicidae): In vitro and in silico studies
- Design, synthesis, characterization, and theoretical calculations, along with in silico and in vitro antimicrobial proprieties of new isoxazole-amide conjugates
- The impact of drying and extraction methods on total lipid, fatty acid profile, and cytotoxicity of Tenebrio molitor larvae
- A zinc oxide–tin oxide–nerolidol hybrid nanomaterial: Efficacy against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Research on technological process for production of muskmelon juice (Cucumis melo L.)
- Physicochemical components, antioxidant activity, and predictive models for quality of soursop tea (Annona muricata L.) during heat pump drying
- Characterization and application of Fe1−xCoxFe2O4 nanoparticles in Direct Red 79 adsorption
- Torilis arvensis ethanolic extract: Phytochemical analysis, antifungal efficacy, and cytotoxicity properties
- Magnetite–poly-1H pyrrole dendritic nanocomposite seeded on poly-1H pyrrole: A promising photocathode for green hydrogen generation from sanitation water without using external sacrificing agent
- HPLC and GC–MS analyses of phytochemical compounds in Haloxylon salicornicum extract: Antibacterial and antifungal activity assessment of phytopathogens
- Efficient and stable to coking catalysts of ethanol steam reforming comprised of Ni + Ru loaded on MgAl2O4 + LnFe0.7Ni0.3O3 (Ln = La, Pr) nanocomposites prepared via cost-effective procedure with Pluronic P123 copolymer
- Nitrogen and boron co-doped carbon dots probe for selectively detecting Hg2+ in water samples and the detection mechanism
- Heavy metals in road dust from typical old industrial areas of Wuhan: Seasonal distribution and bioaccessibility-based health risk assessment
- Phytochemical profiling and bioactivity evaluation of CBD- and THC-enriched Cannabis sativa extracts: In vitro and in silico investigation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
- Investigating dye adsorption: The role of surface-modified montmorillonite nanoclay in kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics
- Antimicrobial activity, induction of ROS generation in HepG2 liver cancer cells, and chemical composition of Pterospermum heterophyllum
- Study on the performance of nanoparticle-modified PVDF membrane in delaying membrane aging
- Impact of cholesterol in encapsulated vitamin E acetate within cocoliposomes
- Review Articles
- Structural aspects of Pt(η3-X1N1X2)(PL) (X1,2 = O, C, or Se) and Pt(η3-N1N2X1)(PL) (X1 = C, S, or Se) derivatives
- Biosurfactants in biocorrosion and corrosion mitigation of metals: An overview
- Stimulus-responsive MOF–hydrogel composites: Classification, preparation, characterization, and their advancement in medical treatments
- Electrochemical dissolution of titanium under alternating current polarization to obtain its dioxide
- Special Issue on Recent Trends in Green Chemistry
- Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of Vitex agnus-castus L.
- Phytochemical study, antioxidant activity, and dermoprotective activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.)
- Exploitation of mangliculous marine fungi, Amarenographium solium, for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against multiple drug-resistant bacteria
- Study of the phytotoxicity of margines on Pistia stratiotes L.
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part III
- Impact of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, development, and antioxidant system of high protein content crop (Lablab purpureus L.) sweet
- Green synthesis, characterization, and application of iron and molybdenum nanoparticles and their composites for enhancing the growth of Solanum lycopersicum
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Olea europaea L. extracted polysaccharides, characterization, and its assessment as an antimicrobial agent against multiple pathogenic microbes
- Photocatalytic treatment of organic dyes using metal oxides and nanocomposites: A quantitative study
- Antifungal, antioxidant, and photocatalytic activities of greenly synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles
- Special Issue on Phytochemical and Pharmacological Scrutinization of Medicinal Plants
- Hepatoprotective effects of safranal on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
- Chemical composition and biological properties of Thymus capitatus plants from Algerian high plains: A comparative and analytical study
- Chemical composition and bioactivities of the methanol root extracts of Saussurea costus
- In vivo protective effects of vitamin C against cyto-genotoxicity induced by Dysphania ambrosioides aqueous extract
- Insights about the deleterious impact of a carbamate pesticide on some metabolic immune and antioxidant functions and a focus on the protective ability of a Saharan shrub and its anti-edematous property
- A comprehensive review uncovering the anticancerous potential of genkwanin (plant-derived compound) in several human carcinomas
- A study to investigate the anticancer potential of carvacrol via targeting Notch signaling in breast cancer
- Assessment of anti-diabetic properties of Ziziphus oenopolia (L.) wild edible fruit extract: In vitro and in silico investigations through molecular docking analysis
- Optimization of polyphenol extraction, phenolic profile by LC-ESI-MS/MS, antioxidant, anti-enzymatic, and cytotoxic activities of Physalis acutifolia
- Phytochemical screening, antioxidant properties, and photo-protective activities of Salvia balansae de Noé ex Coss
- Antihyperglycemic, antiglycation, anti-hypercholesteremic, and toxicity evaluation with gas chromatography mass spectrometry profiling for Aloe armatissima leaves
- Phyto-fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles by using Timur (Zanthoxylum armatum DC) and their effect on wound healing
- Does Erodium trifolium (Cav.) Guitt exhibit medicinal properties? Response elements from phytochemical profiling, enzyme-inhibiting, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities
- Integrative in silico evaluation of the antiviral potential of terpenoids and its metal complexes derived from Homalomena aromatica based on main protease of SARS-CoV-2
- 6-Methoxyflavone improves anxiety, depression, and memory by increasing monoamines in mice brain: HPLC analysis and in silico studies
- Simultaneous extraction and quantification of hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants in Solanum lycopersicum L. varieties marketed in Saudi Arabia
- Biological evaluation of CH3OH and C2H5OH of Berberis vulgaris for in vivo antileishmanial potential against Leishmania tropica in murine models
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Porous silicon nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and their antifungal activity
- Biochar from de-oiled Chlorella vulgaris and its adsorption on antibiotics
- Phytochemicals profiling, in vitro and in vivo antidiabetic activity, and in silico studies on Ajuga iva (L.) Schreb.: A comprehensive approach
- Synthesis, characterization, in silico and in vitro studies of novel glycoconjugates as potential antibacterial, antifungal, and antileishmanial agents
- Sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by potato starch: Its performance in the treatment of esophageal cancer
- Computational study of ADME-Tox prediction of selected phytochemicals from Punica granatum peels
- Phytochemical analysis, in vitro antioxidant and antifungal activities of extracts and essential oil derived from Artemisia herba-alba Asso
- Two triazole-based coordination polymers: Synthesis and crystal structure characterization
- Phytochemical and physicochemical studies of different apple varieties grown in Morocco
- Synthesis of multi-template molecularly imprinted polymers (MT-MIPs) for isolating ethyl para-methoxycinnamate and ethyl cinnamate from Kaempferia galanga L., extract with methacrylic acid as functional monomer
- Nutraceutical potential of Mesembryanthemum forsskaolii Hochst. ex Bioss.: Insights into its nutritional composition, phytochemical contents, and antioxidant activity
- Evaluation of influence of Butea monosperma floral extract on inflammatory biomarkers
- Cannabis sativa L. essential oil: Chemical composition, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial properties, and acute toxicity: In vitro, in vivo, and in silico study
- The effect of gamma radiation on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural conversion in water and dimethyl sulfoxide
- Hollow mushroom nanomaterials for potentiometric sensing of Pb2+ ions in water via the intercalation of iodide ions into the polypyrrole matrix
- Determination of essential oil and chemical composition of St. John’s Wort
- Computational design and in vitro assay of lantadene-based novel inhibitors of NS3 protease of dengue virus
- Anti-parasitic activity and computational studies on a novel labdane diterpene from the roots of Vachellia nilotica
- Microbial dynamics and dehydrogenase activity in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) rhizospheres: Impacts on growth and soil health across different soil types
- Correlation between in vitro anti-urease activity and in silico molecular modeling approach of novel imidazopyridine–oxadiazole hybrids derivatives
- Spatial mapping of indoor air quality in a light metro system using the geographic information system method
- Iron indices and hemogram in renal anemia and the improvement with Tribulus terrestris green-formulated silver nanoparticles applied on rat model
- Integrated track of nano-informatics coupling with the enrichment concept in developing a novel nanoparticle targeting ERK protein in Naegleria fowleri
- Cytotoxic and phytochemical screening of Solanum lycopersicum–Daucus carota hydro-ethanolic extract and in silico evaluation of its lycopene content as anticancer agent
- Protective activities of silver nanoparticles containing Panax japonicus on apoptotic, inflammatory, and oxidative alterations in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity
- pH-based colorimetric detection of monofunctional aldehydes in liquid and gas phases
- Investigating the effect of resveratrol on apoptosis and regulation of gene expression of Caco-2 cells: Unravelling potential implications for colorectal cancer treatment
- Metformin inhibits knee osteoarthritis induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats: S100A8/9 and S100A12 as players and therapeutic targets
- Effect of silver nanoparticles formulated by Silybum marianum on menopausal urinary incontinence in ovariectomized rats
- Synthesis of new analogs of N-substituted(benzoylamino)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridines
- Response of yield and quality of Japonica rice to different gradients of moisture deficit at grain-filling stage in cold regions
- Preparation of an inclusion complex of nickel-based β-cyclodextrin: Characterization and accelerating the osteoarthritis articular cartilage repair
- Empagliflozin-loaded nanomicelles responsive to reactive oxygen species for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury protection
- Preparation and pharmacodynamic evaluation of sodium aescinate solid lipid nanoparticles
- Assessment of potentially toxic elements and health risks of agricultural soil in Southwest Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Theoretical investigation of hydrogen-rich fuel production through ammonia decomposition
- Biosynthesis and screening of cobalt nanoparticles using citrus species for antimicrobial activity
- Investigating the interplay of genetic variations, MCP-1 polymorphism, and docking with phytochemical inhibitors for combatting dengue virus pathogenicity through in silico analysis
- Ultrasound induced biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles embedded into chitosan polymers: Investigation of its anti-cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma effects
- Copper oxide nanoparticles-mediated Heliotropium bacciferum leaf extract: Antifungal activity and molecular docking assays against strawberry pathogens
- Sprouted wheat flour for improving physical, chemical, rheological, microbial load, and quality properties of fino bread
- Comparative toxicity assessment of fisetin-aided artificial intelligence-assisted drug design targeting epibulbar dermoid through phytochemicals
- Acute toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity of bis-thiourea derivatives
- Anti-diabetic activity-guided isolation of α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory terpenes from Capsella bursa-pastoris Linn.
- GC–MS analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 metabolites and its computational analysis on familial pulmonary fibrosis hub genes
- Green formulation of copper nanoparticles by Pistacia khinjuk leaf aqueous extract: Introducing a novel chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of prostate cancer
- Improved photocatalytic properties of WO3 nanoparticles for Malachite green dye degradation under visible light irradiation: An effect of La doping
- One-pot synthesis of a network of Mn2O3–MnO2–poly(m-methylaniline) composite nanorods on a polypyrrole film presents a promising and efficient optoelectronic and solar cell device
- Groundwater quality and health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride in Al Qaseem area, Saudi Arabia
- A comparative study of the antifungal efficacy and phytochemical composition of date palm leaflet extracts
- Processing of alcohol pomelo beverage (Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck) using saccharomyces yeast: Optimization, physicochemical quality, and sensory characteristics
- Specialized compounds of four Cameroonian spices: Isolation, characterization, and in silico evaluation as prospective SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Identification of a novel drug target in Porphyromonas gingivalis by a computational genome analysis approach
- Physico-chemical properties and durability of a fly-ash-based geopolymer
- FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitory potentials of some phytochemicals from anti-leukemic plants using computational chemical methodologies
- Wild Thymus zygis L. ssp. gracilis and Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh.: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of essential oils
- 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, ADMET, simulation dynamic, and retrosynthesis studies on new styrylquinolines derivatives against breast cancer
- Deciphering the influenza neuraminidase inhibitory potential of naturally occurring biflavonoids: An in silico approach
- Determination of heavy elements in agricultural regions, Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis and characterization of antioxidant-enriched Moringa oil-based edible oleogel
- Ameliorative effects of thistle and thyme honeys on cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity in mice
- Study of phytochemical compound and antipyretic activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. fractions
- Investigating the adsorption mechanism of zinc chloride-modified porous carbon for sulfadiazine removal from water
- Performance repair of building materials using alumina and silica composite nanomaterials with electrodynamic properties
- Effects of nanoparticles on the activity and resistance genes of anaerobic digestion enzymes in livestock and poultry manure containing the antibiotic tetracycline
- Effect of copper nanoparticles green-synthesized using Ocimum basilicum against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice lung infection model
- Cardioprotective effects of nanoparticles green formulated by Spinacia oleracea extract on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in mice by the determination of PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway
- Anti-OTC antibody-conjugated fluorescent magnetic/silica and fluorescent hybrid silica nanoparticles for oxytetracycline detection
- Curcumin conjugated zinc nanoparticles for the treatment of myocardial infarction
- Identification and in silico screening of natural phloroglucinols as potential PI3Kα inhibitors: A computational approach for drug discovery
- Exploring the phytochemical profile and antioxidant evaluation: Molecular docking and ADMET analysis of main compounds from three Solanum species in Saudi Arabia
- Unveiling the molecular composition and biological properties of essential oil derived from the leaves of wild Mentha aquatica L.: A comprehensive in vitro and in silico exploration
- Analysis of bioactive compounds present in Boerhavia elegans seeds by GC-MS
- Homology modeling and molecular docking study of corticotrophin-releasing hormone: An approach to treat stress-related diseases
- LncRNA MIR17HG alleviates heart failure via targeting MIR17HG/miR-153-3p/SIRT1 axis in in vitro model
- Development and validation of a stability indicating UPLC-DAD method coupled with MS-TQD for ramipril and thymoquinone in bioactive SNEDDS with in silico toxicity analysis of ramipril degradation products
- Biosynthesis of Ag/Cu nanocomposite mediated by Curcuma longa: Evaluation of its antibacterial properties against oral pathogens
- Development of AMBER-compliant transferable force field parameters for polytetrafluoroethylene
- Treatment of gestational diabetes by Acroptilon repens leaf aqueous extract green-formulated iron nanoparticles in rats
- Development and characterization of new ecological adsorbents based on cardoon wastes: Application to brilliant green adsorption
- A fast, sensitive, greener, and stability-indicating HPLC method for the standardization and quantitative determination of chlorhexidine acetate in commercial products
- Assessment of Se, As, Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb content status in Ankang tea plantations of China
- Effect of transition metal chloride (ZnCl2) on low-temperature pyrolysis of high ash bituminous coal
- Evaluating polyphenol and ascorbic acid contents, tannin removal ability, and physical properties during hydrolysis and convective hot-air drying of cashew apple powder
- Development and characterization of functional low-fat frozen dairy dessert enhanced with dried lemongrass powder
- Scrutinizing the effect of additive and synergistic antibiotics against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Preparation, characterization, and determination of the therapeutic effects of copper nanoparticles green-formulated by Pistacia atlantica in diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction in rat
- Antioxidant and antidiabetic potentials of methoxy-substituted Schiff bases using in vitro, in vivo, and molecular simulation approaches
- Anti-melanoma cancer activity and chemical profile of the essential oil of Seseli yunnanense Franch
- Molecular docking analysis of subtilisin-like alkaline serine protease (SLASP) and laccase with natural biopolymers
- Overcoming methicillin resistance by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Computational evaluation of napthyridine and oxadiazoles compounds for potential dual inhibition of PBP-2a and FemA proteins
- Exploring novel antitubercular agents: Innovative design of 2,3-diaryl-quinoxalines targeting DprE1 for effective tuberculosis treatment
- Drimia maritima flowers as a source of biologically potent components: Optimization of bioactive compound extractions, isolation, UPLC–ESI–MS/MS, and pharmacological properties
- Estimating molecular properties, drug-likeness, cardiotoxic risk, liability profile, and molecular docking study to characterize binding process of key phyto-compounds against serotonin 5-HT2A receptor
- Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin-based microgels for enhancing solubility of Terbinafine: An in-vitro and in-vivo toxicological evaluation
- Phyto-mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of cationic and anionic dyes
- Monosodium glutamate induces hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis hyperactivation, glucocorticoid receptors down-regulation, and systemic inflammatory response in young male rats: Impact on miR-155 and miR-218
- Quality control analyses of selected honey samples from Serbia based on their mineral and flavonoid profiles, and the invertase activity
- Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus niruri leaf extract: Assessment of antimicrobial activity, effectiveness on tropical neglected mosquito vector control, and biocompatibility using a fibroblast cell line model
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles containing Cichorium intybus to treat the sepsis-induced DNA damage in the liver of Wistar albino rats
- Quality changes of durian pulp (Durio ziberhinus Murr.) in cold storage
- Study on recrystallization process of nitroguanidine by directly adding cold water to control temperature
- Determination of heavy metals and health risk assessment in drinking water in Bukayriyah City, Saudi Arabia
- Larvicidal properties of essential oils of three Artemisia species against the chemically insecticide-resistant Nile fever vector Culex pipiens (L.) (Diptera: Culicidae): In vitro and in silico studies
- Design, synthesis, characterization, and theoretical calculations, along with in silico and in vitro antimicrobial proprieties of new isoxazole-amide conjugates
- The impact of drying and extraction methods on total lipid, fatty acid profile, and cytotoxicity of Tenebrio molitor larvae
- A zinc oxide–tin oxide–nerolidol hybrid nanomaterial: Efficacy against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Research on technological process for production of muskmelon juice (Cucumis melo L.)
- Physicochemical components, antioxidant activity, and predictive models for quality of soursop tea (Annona muricata L.) during heat pump drying
- Characterization and application of Fe1−xCoxFe2O4 nanoparticles in Direct Red 79 adsorption
- Torilis arvensis ethanolic extract: Phytochemical analysis, antifungal efficacy, and cytotoxicity properties
- Magnetite–poly-1H pyrrole dendritic nanocomposite seeded on poly-1H pyrrole: A promising photocathode for green hydrogen generation from sanitation water without using external sacrificing agent
- HPLC and GC–MS analyses of phytochemical compounds in Haloxylon salicornicum extract: Antibacterial and antifungal activity assessment of phytopathogens
- Efficient and stable to coking catalysts of ethanol steam reforming comprised of Ni + Ru loaded on MgAl2O4 + LnFe0.7Ni0.3O3 (Ln = La, Pr) nanocomposites prepared via cost-effective procedure with Pluronic P123 copolymer
- Nitrogen and boron co-doped carbon dots probe for selectively detecting Hg2+ in water samples and the detection mechanism
- Heavy metals in road dust from typical old industrial areas of Wuhan: Seasonal distribution and bioaccessibility-based health risk assessment
- Phytochemical profiling and bioactivity evaluation of CBD- and THC-enriched Cannabis sativa extracts: In vitro and in silico investigation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
- Investigating dye adsorption: The role of surface-modified montmorillonite nanoclay in kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics
- Antimicrobial activity, induction of ROS generation in HepG2 liver cancer cells, and chemical composition of Pterospermum heterophyllum
- Study on the performance of nanoparticle-modified PVDF membrane in delaying membrane aging
- Impact of cholesterol in encapsulated vitamin E acetate within cocoliposomes
- Review Articles
- Structural aspects of Pt(η3-X1N1X2)(PL) (X1,2 = O, C, or Se) and Pt(η3-N1N2X1)(PL) (X1 = C, S, or Se) derivatives
- Biosurfactants in biocorrosion and corrosion mitigation of metals: An overview
- Stimulus-responsive MOF–hydrogel composites: Classification, preparation, characterization, and their advancement in medical treatments
- Electrochemical dissolution of titanium under alternating current polarization to obtain its dioxide
- Special Issue on Recent Trends in Green Chemistry
- Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of Vitex agnus-castus L.
- Phytochemical study, antioxidant activity, and dermoprotective activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.)
- Exploitation of mangliculous marine fungi, Amarenographium solium, for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against multiple drug-resistant bacteria
- Study of the phytotoxicity of margines on Pistia stratiotes L.
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part III
- Impact of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, development, and antioxidant system of high protein content crop (Lablab purpureus L.) sweet
- Green synthesis, characterization, and application of iron and molybdenum nanoparticles and their composites for enhancing the growth of Solanum lycopersicum
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Olea europaea L. extracted polysaccharides, characterization, and its assessment as an antimicrobial agent against multiple pathogenic microbes
- Photocatalytic treatment of organic dyes using metal oxides and nanocomposites: A quantitative study
- Antifungal, antioxidant, and photocatalytic activities of greenly synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles
- Special Issue on Phytochemical and Pharmacological Scrutinization of Medicinal Plants
- Hepatoprotective effects of safranal on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
- Chemical composition and biological properties of Thymus capitatus plants from Algerian high plains: A comparative and analytical study
- Chemical composition and bioactivities of the methanol root extracts of Saussurea costus
- In vivo protective effects of vitamin C against cyto-genotoxicity induced by Dysphania ambrosioides aqueous extract
- Insights about the deleterious impact of a carbamate pesticide on some metabolic immune and antioxidant functions and a focus on the protective ability of a Saharan shrub and its anti-edematous property
- A comprehensive review uncovering the anticancerous potential of genkwanin (plant-derived compound) in several human carcinomas
- A study to investigate the anticancer potential of carvacrol via targeting Notch signaling in breast cancer
- Assessment of anti-diabetic properties of Ziziphus oenopolia (L.) wild edible fruit extract: In vitro and in silico investigations through molecular docking analysis
- Optimization of polyphenol extraction, phenolic profile by LC-ESI-MS/MS, antioxidant, anti-enzymatic, and cytotoxic activities of Physalis acutifolia
- Phytochemical screening, antioxidant properties, and photo-protective activities of Salvia balansae de Noé ex Coss
- Antihyperglycemic, antiglycation, anti-hypercholesteremic, and toxicity evaluation with gas chromatography mass spectrometry profiling for Aloe armatissima leaves
- Phyto-fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles by using Timur (Zanthoxylum armatum DC) and their effect on wound healing
- Does Erodium trifolium (Cav.) Guitt exhibit medicinal properties? Response elements from phytochemical profiling, enzyme-inhibiting, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities
- Integrative in silico evaluation of the antiviral potential of terpenoids and its metal complexes derived from Homalomena aromatica based on main protease of SARS-CoV-2
- 6-Methoxyflavone improves anxiety, depression, and memory by increasing monoamines in mice brain: HPLC analysis and in silico studies
- Simultaneous extraction and quantification of hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants in Solanum lycopersicum L. varieties marketed in Saudi Arabia
- Biological evaluation of CH3OH and C2H5OH of Berberis vulgaris for in vivo antileishmanial potential against Leishmania tropica in murine models

