Magnetite–poly-1H pyrrole dendritic nanocomposite seeded on poly-1H pyrrole: A promising photocathode for green hydrogen generation from sanitation water without using external sacrificing agent
Abstract
The Fe3O4 magnetite–poly-1H pyrrole dendritic nanocomposite seeded on additional poly-1H pyrrole film, denoted as Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP, is synthesized by oxidative polymerization utilizing (Fe(NO3)3·5H2O for the pyrrole monomer. The resulting nanocomposite exhibits a notable bandgap of 1.97 eV and demonstrates broad optical absorption up to 625 nm. The structure of each particle consists of numerous smaller internal particles, which are composed of nanofibers of approximately 2.0 nm in length and porous structures of around 5.0 nm. These porous structures cluster together to form a larger configuration, with an overall diameter of ∼230 nm and a length of approximately 300 nm, giving the composite a nano-cactus-like appearance. The fabricated Fe3O4–P1HP/P1HP photocathode is inserted into a three-electrode cell to facilitate green hydrogen production from sanitation water without the need for any external sacrificial agent. The performance of H2 gas generation is assessed by measuring the photocurrent density (J ph) under light, which serves as an indicator of the efficiency of hydrogen production. The J ph value reaches −0.23 mA/cm² under light conditions. The highest J ph values of −0.164 and −0.158 mA/cm² are observed at wavelengths of 340 and 440 nm, respectively. However, as the wavelength reaches 540 nm, the J ph value decreases to −0.134 mA/cm² and drops to its lowest point of −0.128 mA/cm² at 730 nm, which is comparable to the dark current (J o). The fabricated photocathode demonstrates a promising hydrogen generation rate of 90 µmol/h cm², reflecting its potential for commercial applications. The combination of this impressive hydrogen production rate, along with the photocathode’s cost-effectiveness and straightforward fabrication process, suggests that this technology could be commercially viable for converting sanitation water into hydrogen gas.
1 Introduction
The pursuit of renewable energy sources that are both cost-effective and efficient represents a significant challenge for researchers today. This challenge is driven by the need to create solutions that not only provide sustainable energy but also contribute to an eco-friendly and green chemistry environment [1,2,3]. By advancing renewable energy technologies, researchers aim to lessen our reliance on fossil fuels, which have become increasingly problematic in recent years due to their detrimental effects on the environment. Fossil fuels, once the cornerstone of global energy production, have now become a focal point of concern due to their association with pollution, climate change, and other environmental issues. The extraction, processing, and burning of these fuels release harmful greenhouse gases and other pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and environmental degradation. As a result, the urgent need to shift towards renewable energy sources has become a priority for the scientific community. Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and bioenergy offer the promise of a cleaner, more sustainable future. However, the transition to these energy sources is not without its challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the cost associated with developing and implementing these technologies on a large scale. Researchers are tasked with finding ways to make renewable energy more affordable and accessible without compromising on efficiency and effectiveness [2,4].
Hydrogen is recognized as a clean fuel of the future, primarily because it produces zero carbon emissions, which positions sustainable H2 generation as a crucial priority in the energy sector. Among the numerous technologies available for H2 production, photoelectrochemical (PEC) technology stands out due to its innovative approach to water splitting. This method involves the use of various materials with photoresponsive properties, which harness light energy to drive the chemical reactions needed for hydrogen production. The process is enhanced by the presence of additional electrolytes in the reaction medium, which play a critical role in facilitating the movement of ions. These electrolytes ensure that the necessary charge transfer occurs efficiently, supporting the overall reaction process. The use of PEC technology in hydrogen production offers a promising pathway toward sustainable energy, as it leverages abundant solar energy and water, both of which are renewable resources. However, achieving high efficiency in this process requires the careful selection and optimization of materials with suitable photoresponsive properties. These materials must not only effectively absorb sunlight but also exhibit the necessary chemical stability and catalytic activity to drive the water-splitting reaction over extended periods. Through the advancement of PEC technology and the improvement of materials utilized in this process, researchers are working toward establishing a dependable and sustainable method for large-scale hydrogen generation. This strategy supports the larger objective of decreasing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing the environmental effects of energy production, ultimately aiding the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future [3,5,6].
Among various photocatalytic metal oxides studied, Wang et al. [7] demonstrated that CuO nanowires are beneficial for light detection in the IR domain. However, they observed a small photocurrent (20 µA) under high application conditions. In addition, ferric oxide has gained particular interest due to its relative abundance, non-toxicity, and affordability. Recent studies have highlighted the potential of nanoscale ferric oxides [8]. Fe3O4 is particularly notable for its advantageous properties, such as a 2.1 eV band gap [9], non-toxicity, low cost, and strong chemical stability in aqueous solutions. Furthermore, Fe3O4 has various uses in industries, including cement production, water splitting, gas detection, solar energy conversion, lithium-ion battery manufacturing, water purification, and pigmentation. These versatile uses have led to increased interest in the production of iron oxide nanoparticles for these fields [10].
The efficiency of Fe₃O₄ (magnetite) in hydrogen (H₂) production can be significantly enhanced by forming composites with other materials. The synergistic interactions between these combined materials are particularly promising, as they can generate hot electrons that actively engage in the reaction with nearby solutions, thereby boosting hydrogen production [11,12]. Additionally, the direct interaction between the morphology and optical properties of the composite materials plays a crucial role in this process. Porous nanomaterials are especially well suited for such photocatalytic applications due to their unique structure, which offers a high surface area and excellent light absorption capabilities. These characteristics allow for better light harvesting and more efficient charge separation, which are essential for maximizing the photocatalytic activity of Fe₃O₄ composites.
Conducting polymers has some achievements in this area, in which the tunable photophysical properties of P1HP, such as its photothermal conversion ability and Fenton catalysis ability, also enable emerging applications in cancer therapy, including tumor ablation and immune activation [13]. Despite previous studies significantly enhancing materials for H2 gas generation, several challenges remain. These include issues such as limited production yield, the need for advanced preparation techniques, and the use of highly acidic or basic electrolytes, which can cause rapid and severe corrosion of the electrodes used for H2 gas generation [14,15]. Therefore, it is essential to explore other technologies and conduct further studies to address these technical challenges.
Herein, the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode has been meticulously fabricated and thoroughly analyzed to assess its morphology, chemical composition, electrical properties, and optical behavior. This photocathode has demonstrated exceptional performance in hydrogen gas generation, as evidenced by the J ph measurements conducted under both general light conditions and various monochromatic light exposures. The study also includes an evaluation of chopped light, which highlights the sensitivity and reproducibility of the fabricated photocathode.
The hydrogen gas production rate was calculated using sanitation water as the electrolyte, notably without the addition of any external sacrificial agents. The Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode stands out for its efficient hydrogen generation capabilities coupled with cost-effectiveness, positioning it as a promising material. Its unique structural characteristics and robust performance under light conditions indicate that this technology could significantly contribute to sustainable energy solutions, particularly in converting sanitation water into hydrogen gas. The potential for scaling and industrial implementation further enhances the photocathode’s appeal, suggesting that the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode could have great behavior in the future of green hydrogen production. As a valuable advancement in this field, it combines innovative design with practical advantages, offering a pathway toward more sustainable and economically viable hydrogen generation processes.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and characterization techniques
The following chemicals were used in this study: ferric nitrate pentahydrate (Fe(NO3)3·5H2O, 99.9%, Pio-Chem Co, Egypt), ammonium persulfate (NH4)2S2O8·5H2O, 99.9%, Pio-Chem Co, Egypt), pyrrole (Across Co., 99.9%, USA), and HCl (36%, Merck, Germany). The sanitation water is supported by the company water (Beni-Suef city, Egypt, thrice treated).
Characterization techniques involved the use of various instruments for chemical analysis. These include the AXIS-NOVA for XPS, the Bruker for FTIR, and the Pro for XRD. To observe 3D and 2D morphologies, Zeiss and Jole devices were utilized for SEM and TEM, respectively. Optical properties were assessed using an Elmer Perkin device.
2.2 Fabrication of Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode
The fabrication of the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode involves two key steps. Initially, a P1HP seeding layer is created on a glass substrate. This P1HP layer is formed by oxidizing pyrrole using (NH4)2S2O8 in an acidic medium, with the monomer, oxidant, and acid mixed in a ratio of 1:2.5:10. In the subsequent step, the Fe3O4-P1HP layer is deposited using a similar oxidation process, but this time with the inclusion of both (NH4)2S2O8 and iron nitrate nonahydrate (Fe(NO3)3·5H2O maintaining the same ratio. These reagents not only facilitate the oxidation of pyrrole but also contribute to the formation of the Fe3O4-P1HP composite. The reaction is carried out in an acidic medium (0.5 M HCl), which significantly improves the morphology of the resulting polymer composite. Figure 1 shows an illustration of the deposition conditions.

The fabrication and the applications of the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode inside a three-electrode cell for H2 gas generation from sanitation water.
2.3 Photocathode for the hydrogen generation photoelectrochemically
Hydrogen generation is accomplished through the electrochemical splitting of sanitation water using a Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP thin film deposited on a glass substrate. The process involves measuring the current density electrochemically with a CHI608E device, where the fabricated photocathode acts as the working electrode. Hydrogen production is evaluated via linear sweep voltammetry, comparing the generated J ph to the initial J o. The sanitation water used has a pH of 7.4, and its composition is detailed in Table 1. This method of converting environmentally harmful waste into hydrogen gas marks a significant advancement in waste-to-energy technology. The splitting reaction is conducted photoelectrochemically under a halide lamp (vacuum tube) that provides high-quality white light. The light can be filtered to generate specific monochromatic wavelengths, including 730, 540, 440, and 340 nm, by using various optical filters. These filters, circular and manufactured by Andover Corporation (model AM 106004, USA), allow only the desired wavelengths to pass through. The energy of the incident light is assessed in relation to the bandgap of the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP thin film photocathode. The hydrogen gas production is estimated by Faraday’s law of electrolysis, as outlined in equation (1) [16]:
Chemical constitution of the electrolyte (sanitation water) [17]
| Material or element | Concentration (µg/l) |
|---|---|
| Ni3+ | 0.01 |
| F− | 0.001 |
| Hg2+ | 0.005 |
| Mn2+ | 0.001 |
| Phenols | 0.015 |
| Ba3+ | 0.002 |
| NH3 | 0.005 |
| Cd3+ | 0.05 |
| Al3+ | 0.003 |
| As3+ | 0.05 |
| Cr3+ | 0.001 |
| Co2+ | 0.002 |
| Pb2+ | 0.005 |
| Zn2+ | 0.005 |
| Cu2+ | 0.00015 |
| Industrial washing | 0.05 |
| Fe3+ | 0.0015 |
| Coli groups | 4.0 × 0.1 cm3 |
| Ag+ | 0.01 |
| Pesticides | 0.02 |
| CN−1 | 0.01 |
| Other cations | 0.01 |
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Fe3O4-P1HP physicochemical characterization
The chemical characterization of Fe3O4-P1HP nanomaterials is conducted using various analytical tools, including FTIR spectroscopy, to identify the functional groups associated with the composite. The estimated vibration mode associated with the N–H group in P1HP is observed at 33,408 cm−1, while the P1HP ring groups are identified at 1,551, 1,409, 1,313, 1,188, and 1,036 and 908 cm−1, corresponding to the internal functional groups C–C, C═C, C–N, C–H, and out-of-plane bonds, respectively. The vibration modes of the composite show significant changes in P1HP upon the incorporation of Fe3O4. This incorporation substantially affects the bonds within the composite, altering both bond rotation and bond length. These alterations are evident through shifts in the positions of the bonds, as illustrated in Figure 2(a) and Table 2. The redshift observed in the bond positions indicates the impact of the Fe3O4 groups, with the bands associated with this oxide appearing at 789 and 625 cm−1. These bands exhibit strong intensity compared to the pristine P1HP, highlighting the significant effect of Fe3O4 insertion on the composite structure.

Chemical analyses of the Fe3O4-P1HP nanocomposite in comparison to P1HP: (a) FTIR, (b) XRD, (c) and (d) XPS survey, and Fe element, respectively. Optical analysis: (e) absorbance and (f) bandgap estimation.
Summary of estimated bonds from Figure 2(a) for the composite formation
| Group and its value (cm−1) | Functional group | |
|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4-P1HP | P1HP | |
| 3,433 | 3,408 | N–H [18] |
| 1,631, 1,548, 1,399, 1,305, 1,187, 1,047, and 921 | 1,551, 1,409, 1,313, 1,188, 1,036, and 908 | P1HP ring [19] |
| 789 and 625 | — | Fe–O |
The evaluation of the crystalline structure of the fabricated P1HP and Fe3O4/P1HP nanocomposite is illustrated in Figure 2(b). This analysis shows promising crystalline characteristics, particularly with regard to the peaks associated with Fe3O4, which are not present in the pristine P1HP due to its amorphous nature. The composite displays peaks at 16.7°, 29.6°, 34.9°, 36.1°, 41.4°, 56.4°, 54.8°, and 63.8°, corresponding to the growth directions of (111), (220), (311), (222), (400), (422), (511), and (440) planes, respectively [20]. These crystalline features indicate the successful incorporation of Fe3O4 into the composite.
The crystalline size of the nanocomposite is estimated using the Scherrer equation (equation (2)) [21,22], based on the peak observed at 2θ = 29.6°. The resulting crystalline size is calculated to be 53 nm. This fine crystalline size, combined with the favorable crystalline properties, suggests that the Fe3O4/P1HP nanocomposite is highly effective for optical applications. Specifically, the composite’s ability to respond to light and utilize photon energy to generate hot electrons is particularly advantageous. These hot electrons can be harnessed for the generation of H2 gas from wastewater, showcasing the composite’s potential in energy conversion and environmental applications:
To further emphasize the chemical characteristics of the fabricated Fe3O4/P1HP nanocomposite, XPS analyses are presented in Figure 2(c). These analyses illustrate the significant elemental oxidation behavior of both the organic and inorganic components within the composite. Specifically, the carbon and nitrogen elements are estimated at 285.2 and 401 eV, respectively. Oxygen (O), associated with the elements that form the inorganic structure through its connection with iron, is detected at 532 eV.
The XPS analysis also provides detailed information on the oxidation states of iron within the Fe3O4 material, highlighting the presence of both Fe2+ and Fe3+ states. This is clearly shown in Figure 2(d), where the peaks corresponding to Fe2+ are identified at 711.2 and 724.5 eV for the Fe2p3/2 and Fe2p1/2 orbitals, respectively. In contrast, the peaks for Fe3+ are observed at slightly higher binding energies, with Fe2p3/2 and Fe2p1/2 orbitals at 714.5 and 727.8 eV, respectively [20]. The combination of these oxidation states confirms the formation of the Fe3O4 structure within the P1HP polymer network, contributing to the overall integrity and functionality of the Fe3O4/P1HP nanocomposite. This well-defined Fe3O4 structure embedded in the P1HP polymer is crucial for its enhanced optical properties. The nanocomposite exhibits significant photon absorption capabilities, making it highly effective for applications in renewable energy sources. The interaction of Fe3O4 with the P1HP matrix not only stabilizes the composite structure but also enhances its ability to harness photon energy efficiently. This property is particularly advantageous for generating hot electrons, for hydrogen production from wastewater.
The optical properties of the synthesized Fe3O4-P1HP nanocomposite, in comparison to P1HP, are depicted in Figure 2(e). The analysis shows significant changes in absorbance, marked by various peaks that reflect its responsiveness to incident photons. The Fe3O4-P1HP composite exhibits a broad absorbance spectrum extending up to 625 nm, reflecting its improved optical properties. Within this range, two distinct peaks are observed, corresponding to the two components of the composite: P1HP shows a UV peak, while Fe3O4 displays a visible peak. Beyond 625 nm, the composite’s absorbance decreases, attributed to lower absorption values in the near-IR region. In contrast, P1HP exhibits an absorbance peak limited to 390 nm. Both materials share a common mechanism for these peaks, involving electron transfer and collection in the conduction band. However, the composite shows superior optical properties due to the larger absorbance regions, resulting in a higher quantity of collected electrons.
To highlight this difference, the bandgap values of both materials were estimated. The Fe3O4-P1HP composite has a bandgap of approximately 1.97 eV, whereas P1HP has a bandgap of 3.2 eV. These values were determined using the Tauc equation (equations (3) and (4)) [23,24], based on the absorbance coefficient (α):
This comparison underscores the significant enhancement in the optical behavior of the Fe3O4-P1HP composite, making it more effective in photon absorption and related applications.
The synthesized Fe3O4-P1HP nanocomposite exhibits impressive morphology characterized by a highly porous nanostructure resembling a nano-cactus, as shown in Figure 3(a). This composite features excellent particle distribution, with porous regions between molecules contributing to its unique structure [25,26]. Each particle comprises numerous smaller internal particles, as depicted in Figure 3(b), which consist of nanofibers approximately 2.0 nm in length and porous structures around 5.0 nm. These porous structures aggregate to form a larger shape with an overall diameter of about 230 nm and a length of about 300 nm, resembling a nano-cactus. This morphology is advantageous for photon absorbance, as photons are trapped within the structure, allowing photon energy to be efficiently transferred to the particles. This process is conducive to the formation of hot electrons, which are then collected in the conducting band of the material [27,28].

The morphological estimation of the Fe3O4-P1HP composite: (a) and (b) SEM at various magnifications, and (c) TEM. (d) SEM of the P1HP pristine polymer.
This morphological feature is further confirmed through TEM analysis, as illustrated in Figure 3(c). The porous structure, evident in the TEM image, underscores the superior behavior of the Fe3O4-P1HP nanocomposite. The variation in color from faint to dark in the TEM images highlights the distinction between the organic P1HP and the inorganic Fe3O4 components, indicating a strong interface in the composite formation. The nanopores and nanoparticles are consistently around 5.0 nm in size.
Conversely, P1HP itself possesses notable features related to the formation of porous structured particles with a semi-circular shape. These particles exhibit unique porosity and size characteristics. This remarkable morphology contributes to the development of the Fe3O4-P1HP composite with its distinctive nano-cactus structure.
3.2 Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode for the green hydrogen study
The study focuses on green hydrogen production through photoelectrochemistry, using a specially fabricated Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode as the primary electrode within a three-electrode cell. This cell employs sanitation water as the electrolyte, with the aim of converting this water into green hydrogen gas. The use of sanitation water offers significant advantages due to its harmful nature and enrichment with heavy metals, which promote the electrolysis reaction necessary for H2 gas formation. The process of H2 gas generation occurs in several steps, beginning with the formation of OH radicals. These radicals attack additional H2O molecules, facilitating the production of H2 gas. The reaction is driven by hot electrons generated on the surface of the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode when exposed to light. These electrons are produced in high density and are subsequently transferred to H2O via a reduction reaction.
The impact of light on the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode’s performance is assessed through linear sweep voltammetry (Figure 4(a)) and chopped light measurements (Figure 4(b)). Figure 4(a) shows the effect of photon incidence in activating hot electrons from the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP surface, resulting in an increased production of H2 gas. This is evidenced by the photocurrent density reaching −0.23 mA/cm², a significant improvement relative to the J o of −0.128 mA/cm². This indicates that photons greatly enhance the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode’s efficiency, as both Fe3O4 and P1HP are photocatalytic materials enriched with hot electrons. These electrons are transferred from P1HP to Fe3O4, generating a strong electric field that initiates and drives the water-splitting reaction. The observed J ph value highlights the promising potential of this approach for effectively splitting harmful sanitation water. Additionally, using sanitation water makes this a cost-effective process, especially when combined with the low-cost materials and techniques used, including the glass substrate for the thin-film deposition of the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode.
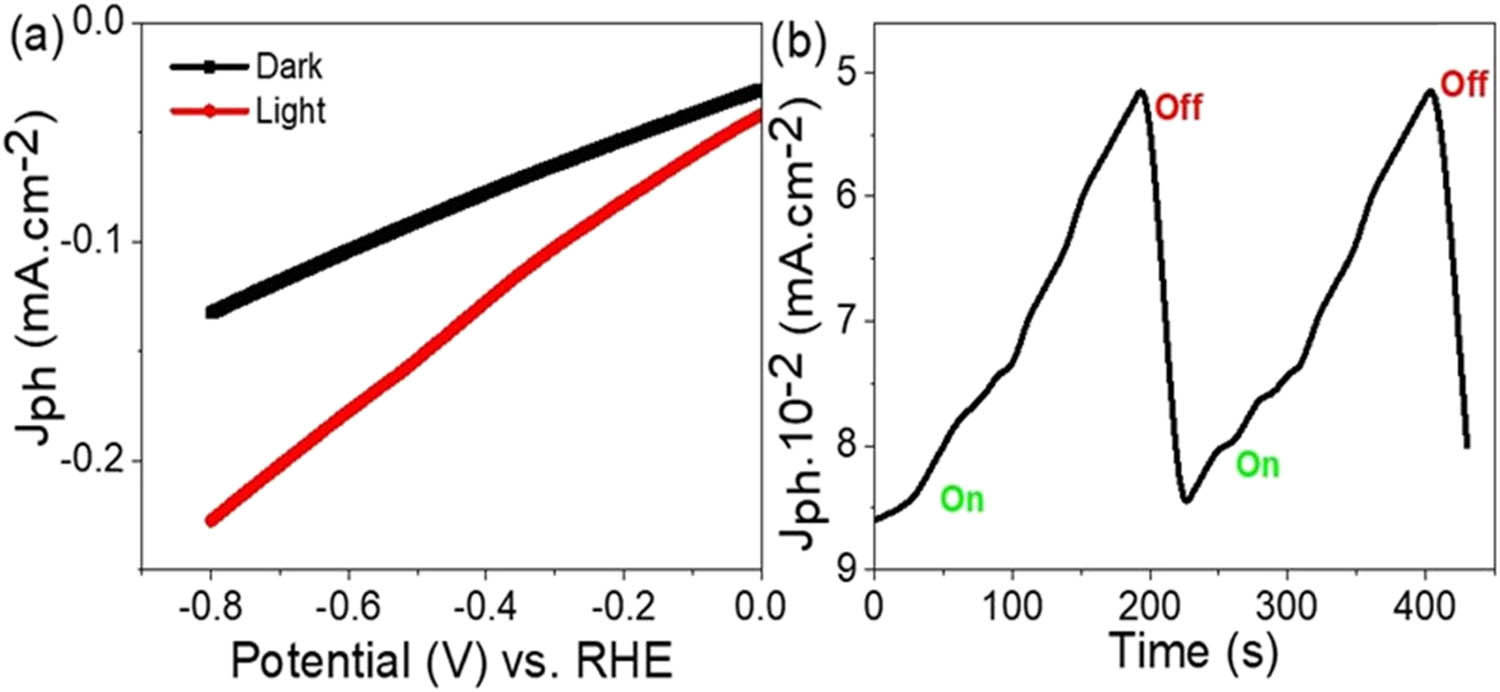
PEC testing of green H2 gas production using the fabricated Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode with wastewater as the electrolyte: (a) linear sweep voltammetry analysis showing the relationship between potential and current density, and (b) study under chopped light illumination.
The sensitivity and reproducibility of the photocathode are further validated through the chopped light current measurements shown in Figure 4(b). The consistent J ph and J o relative to alternating light and dark conditions indicate the excellent stability of this photocathode. This stability is attributed to the P1HP material, which coats the Fe3O4 layer and acts as a protective barrier, enhancing the photocathode’s resistance to corrosion. The overall results demonstrate that the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode not only achieves efficient hydrogen generation but also maintains high stability and reproducibility, making it a viable option for green hydrogen production from sanitation water.
The sensitivity of the fabricated Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode was investigated by analyzing its response under varying light wavelengths and frequencies, achieved using a series of optical filters that selectively pass the desired wavelengths (as shown in Figure 5(a)). The study reveals that the photocurrent density increases with the photon energy, indicating a strong correlation between photon energy and the photocathode’s performance [29–31]. The maximum J ph values were observed at 340 and 440 nm, with corresponding values of −0.164 and −0.158 mA/cm², respectively. However, at 540 nm, the J ph value decreased to −0.134 mA/cm² and reached its lowest point of −0.128 mA/cm² at 730 nm, a value that is essentially equivalent to J o. This indicates that photons at 730 nm have no significant impact on the photocathode’s performance.

The influence of monochromatic light on the PEC testing of green H2 gas production using the fabricated Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode with wastewater as the electrolyte: (a) testing with optical filters at different wavelengths ranging from 340 to 730 nm, and (b) the resulting J ph values under these various optical filters at −0.8 V.
The variation in J ph values across different wavelengths highlights the photocathode’s differing responsiveness to photons of various energies, underscoring the sensitivity of the fabricated Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode. Figure 5(b) estimates the data obtained from the analysis, offering a clear comparison of the photocathode’s response to different wavelengths.
To better understand the effect of photon energies on the fabricated photocathode, the photon energies at specific wavelengths (340, 440, and 540 nm) are compared with the bandgap energy of the material, which is 1.97 eV. According to equation (5), the photon energies at 340, 440, and 540 nm are 3.6, 2.8, and 2.3 eV, respectively, all of which exceed the bandgap energy. As a result, these photons are capable of exciting electrons into the conduction band, causing the generation of hot electrons and a corresponding increase in the J ph values.
However, the photon energy at 730 nm is 1.7 eV, which is lower than the bandgap energy. Because this energy is insufficient to promote electrons to the conduction band, it fails to generate hot electrons, resulting in a J ph value that closely matches J o. This lack of response at 730 nm further emphasizes the relationship between the photon energy and photocathode’s ability to generate a photocurrent [31,32]:
The amount of H2 gas generated was calculated using equation (1), as depicted in Figure 6. The results show a significant production of H2 gas, measured at 0.09 mmol/cm² h. This impressive value highlights the potential of the fabricated Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode for industrial applications in commercial hydrogen synthesis. In addition to the high yield, the photocathode offers technical advantages such as cost-effectiveness and the use of sanitation water as an electrolyte. These factors make the fabricated photocathode a promising and superior option relative to previous studies, as shown in Table 3.

The estimated green H2 produced moles using the fabricated Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode with sanitation water as the electrolyte.
Comparison of the generated H2 gas through the fabricated Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode relative to other previous studies
| Photoelectrode | J ph (mA/cm2) | Electrolyte |
|---|---|---|
| Polypyrrole/graphene oxide [33] | 0.1 | Sewage water |
| Polypyrrole/NiO [34] | 0.11 | Sewage water |
| Poly-3-methyl aniline/graphene oxide [35] | 0.09 | Sewage water |
| Cr2S3-Cr2O3/poly-2-aminobenzene-1-thiol [18] | 0.017 | Sewage water |
| Poly-O-aminothiophenol/intercalated iodide composite [16] | 0.12 | Red Sea water |
| Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP (this work) | 0.16 | Sewage water |
4 Conclusions
The Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode is constructed by the oxidation of pyrrole in the presence of Fe(NO3)3, which is carried out on a thin seeding film of P1HP. The resulting Fe3O4-P1HP composite features porous structures that cluster together, forming a larger configuration with an overall diameter of ∼230 nm and a length of ∼300 nm. This structure, with dendritic formations of about 2.0 nm on the surface, gives the composite a unique nano-cactus-like appearance.
The Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode demonstrates strong performance in H2 gas generation, as indicated by the photocurrent density (J ph) measurements. Under light conditions, the J ph value reaches −0.23 mA/cm². When exposed to monochromatic wavelengths, the photocathode achieves its highest J ph values at 340 and 440 nm, recording −0.164 and −0.158 mA/cm², respectively. However, as the wavelength reaches 540 nm, the J ph value declines to −0.134 mA/cm², eventually reaching its lowest point of −0.128 mA/cm² at 730 nm, which is comparable to J o. This variation in J ph values across different wavelengths reflects the photocathode’s sensitivity to photon energies and its efficiency in generating hydrogen.
The fabricated photocathode exhibits a promising hydrogen generation rate of 90 µmol/h cm², showcasing its potential for industrial applications. The high hydrogen production rate, combined with the cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication, indicates that this photocathode could be commercially viable for converting sanitation water into hydrogen gas. Its impressive performance, along with the economic and practical benefits, positions the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode as a strong contender for future large-scale H2 production.
In summary, the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode offers a combination of efficient hydrogen generation and cost-effectiveness, making it a promising material for commercial applications. The unique structure and high performance under light conditions suggest that this technology could play a significant role in sustainable energy solutions, particularly in the conversion of sanitation water into hydrogen gas. With its potential for scalability and industrial use, the Fe3O4-P1HP/P1HP photocathode represents a valuable advancement in green hydrogen production.
Acknowledgments
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2024R186), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
-
Funding information: This research was financially supported by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project (number PNURSP2024R186), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
-
Author contributions: Maha Abdallah Alnuwaiser: writing, funding, and ordering the work. Mohamed Rabia and Asmaa M Elsayed: conducting experiments and writing.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflict of interest.
-
Ethical approval: This study does not include any human or animal studies.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
[1] Rabia M, Aldosari E, Geneidy AHA. Exceptionally crystalline nature of CrO3-Cr2O3/Ppy nanocomposite as a prospective photoelectrode for efficient green hydrogen generation in the context of environmentally friendly water-splitting reactions using sanitized water. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. 2024;43:e14455. 10.1002/EP.14455.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Giovanniello MA, Cybulsky AN, Schittekatte T, Mallapragada DS. The influence of additionality and time-matching requirements on the emissions from grid-connected hydrogen production. Nat Energy. 2024;2024:1–11. 10.1038/s41560-023-01435-0.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Constantinou P, Stock TJZ, Tseng L-T, Kazazis D, Muntwiler M, Vaz CAF, et al. EUV-induced hydrogen desorption as a step towards large-scale silicon quantum device patterning. Nat Commun. 2024;15:1–13. 10.1038/s41467-024-44790-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Tsao CW, Narra S, Kao JC, Lin YC, Chen CY, Chin YC, et al. Dual-plasmonic Au@Cu7S4 Yolk@shell nanocrystals for photocatalytic hydrogen production across visible to near infrared spectral region. Nat Commun. 2024;15:1–13. 10.1038/s41467-023-44664-3.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Purvis G, Šiller L, Crosskey A, Vincent J, Wills C, Sheriff J, et al. Generation of long-chain fatty acids by hydrogen-driven bicarbonate reduction in ancient alkaline hydrothermal vents. Commun Earth Environ. 2024;5:1–9. 10.1038/s43247-023-01196-4.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Barber J. Hydrogen derived from water as a sustainable solar fuel: Learning from biology. Sustain Energy Fuels. 2018;2:927–35.10.1039/C8SE00002FSearch in Google Scholar
[7] Wang M, Wan L, Luo J. Promoting CO2 electroreduction on CuO nanowires with a hydrophobic nafion overlayer. Nanoscale. 2021;13:3588–93. 10.1039/D0NR08369K.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Zhang Y, Wan J, Zhang C, Cao X. MoS2 and Fe2O3 Co-modify g-C3N4 to improve the performance of photocatalytic hydrogen production. Sci Rep. 2022;12:1–12. 10.1038/s41598-022-07126-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Momeni MM, Ghayeb Y, Mohammadi F. Solar water splitting for hydrogen production with Fe2O3 nanotubes prepared by anodizing method: Effect of anodizing time on performance of Fe2O3 nanotube arrays. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 2015;26:685–92. 10.1007/S10854-014-2450-9/FIGURES/11.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Alkallas FH, Ben Gouider Trabelsi A, Alrebdi TA, Ahmed AM, Rabia M. Development of a highly efficient optoelectronic device based on CuFeO2/CuO/Cu composite nanomaterials. Materials. 2022;15:6857. 10.3390/MA15196857.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Lin YF, Chen JL, Xu CY, Chung TW. One-pot synthesis of paramagnetic iron(III) hydroxide nanoplates and ferrimagnetic magnetite nanoparticles for the removal of arsenic ions. Chem Eng J. 2014;250:409–15. 10.1016/j.cej.2014.04.029.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Elsayed AM, Rabia M, Shaban M, Aly AH, Ahmed AM. Preparation of hexagonal nanoporous Al2O3/TiO2/TiN as a novel photodetector with high efficiency. Sci Rep. 2021;11:1–12. 10.1038/s41598-021-96200-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Blackwood D, Josowicz M. Work function and spectroscopic studies of interactions between conducting polymers and organic vapors. J Phys Chem. 1991;95:493–502. 10.1021/J100154A086/ASSET/J100154A086.FP.png_V03.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Rabia M, Mohamed HSH, Shaban M, Taha S. Preparation of polyaniline/PbS core-shell nano/microcomposite and its application for photocatalytic H2 electrogeneration from H2O. Sci Rep. 2018;8:1–11. 10.1038/s41598-018-19326-w.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Shaban M, Rabia M, El-Sayed AMA, Ahmed A, Sayed S. Photocatalytic properties of PbS/graphene oxide/polyaniline electrode for hydrogen generation. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1–13. 10.1038/s41598-017-14582-8.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Rabia M, Aldosari E, Geneidy AHA. Highly flexible poly-O-aminothiophenol/intercalated iodide composite with highly morphological properties for green hydrogen generation from Red Sea water. Phys Scr. 2024;99:045001. 10.1088/1402-4896/AD2BC5.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Hadia NMA, Abdelazeez AAA, Alzaid M, Shaban M, Mohamed SH, Hoex B, et al. Converting sewage water into H2 fuel gas using Cu/CuO nanoporous photocatalytic electrodes. Materials. 2022;15:1489. 10.3390/MA15041489.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Rabia M, Elsayed AM, Alnuwaiser MA. Cr2S3-Cr2O3/poly-2-aminobenzene-1-thiol as a highly photocatalytic material for green hydrogen generation from sewage water. Micromachines. 2023;14:1567. 10.3390/MI14081567.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Sayyah SM, Shaban M, Rabia M. A high-sensitivity potentiometric mercuric ion sensor based on m-toluidine films. IEEE Sens J. 2016;16:1541–8. 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2505313.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Ai Q, Yuan Z, Huang R, Yang C, Jiang G, Xiong J, et al. One-pot co-precipitation synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles embedded in 3D carbonaceous matrix as anode for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Sci. 2019;54:4212–24. 10.1007/s10853-018-3141-3.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Burton AW, Ong K, Rea T, Chan IY. On the estimation of average crystallite size of zeolites from the Scherrer equation: A critical evaluation of its application to zeolites with one-dimensional pore systems. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009;117:75–90. 10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2008.06.010.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Lim DJ, Marks NA, Rowles MR. Universal Scherrer equation for graphene fragments. Carbon. 2020;162:475–80. 10.1016/J.CARBON.2020.02.064.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Haryński Ł, Olejnik A, Grochowska K, Siuzdak K. A facile method for tauc exponent and corresponding electronic transitions determination in semiconductors directly from UV–Vis spectroscopy data. Opt Mater. 2022;127:112205. 10.1016/J.OPTMAT.2022.112205.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Aziz SB, Nofal MM, Ghareeb HO, Dannoun EMA, Hussen SA, Hadi JM, et al. Characteristics of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) based composites integrated with green synthesized Al3+-metal complex: Structural, optical, and localized density of state analysis. Polymers. 2021;13:1316. 10.3390/POLYM13081316.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Alnuwaiser MA, Rabia M. Hollow mushroom nanomaterials for potentiometric sensing of Pb 2+ ions in water via the intercalation of iodide ions into the polypyrrole matrix. Open Chemistry. 2024;22:20240217.10.1515/chem-2024-0217Search in Google Scholar
[26] Han T, Wei Y, Jin X, Jiu H, Zhang L, Sun Y, et al. Hydrothermal self-assembly of α-Fe2O3 nanorings@graphene aerogel composites for enhanced Li storage performance. J Mater Sci. 2019;54:7119–30. 10.1007/S10853-019-03371-5/FIGURES/9.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Kwon JH, Choi KC. Highly reliable and stretchable OLEDs based on facile patterning method: Toward stretchable organic optoelectronic devices. npj Flex Electron. 2024;8. 10.1038/s41528-024-00303-5.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Cai X, Suess RJ, Drew HD, Murphy TE, Yan J, Fuhrer MS. Pulsed near-IR photoresponse in a Bi-metal contacted graphene photodetector. Sci Rep. 2015;5:1–7. 10.1038/srep14803.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Jia Z, Qin S, Meng L, Ma Q, Angunawela I, Zhang J, et al. High performance tandem organic solar cells via a strongly infrared-absorbing narrow bandgap acceptor. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1–10. 10.1038/s41467-020-20431-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Rabia M, Shaban M, Adel A, Abdel‐Khaliek AA. Effect of plasmonic Au nanoparticles on the photoactivity of polyaniline/indium tin oxide electrodes for water splitting. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. 2019;38:13171. 10.1002/ep.13171.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Ibrahim AM, Abdel-wahab MS, Elfayoumi MAK, Tawfik WZ. Highly efficient sputtered Ni-doped Cu2O photoelectrodes for solar hydrogen generation from water-splitting. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2023;48:1863–76. 10.1016/J.IJHYDENE.2022.10.089.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Chen Q-Y, Zhang K, Liu J-S, Wang Y-H. Hydrogen and electricity production in a light-assisted microbial photoelectrochemical cell with CaFe2O4 photocathode. J Photonics Energy. 2017;7:026501. 10.1117/1.JPE.7.026501.Search in Google Scholar
[33] Hamid MMA, Alruqi M, Elsayed AM, Atta MM, Hanafi HA, Rabia M. Testing the photo-electrocatalytic hydrogen production of polypyrrole quantum dot by combining with graphene oxide sheets on glass slide. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 2023;34:1–11. 10.1007/S10854-023-10229-9/METRICS.Search in Google Scholar
[34] Atta A, Negm H, Abdeltwab E, Rabia M, Abdelhamied MM. Facile fabrication of polypyrrole/NiOx core-shell nanocomposites for hydrogen production from wastewater. Polym Adv Technol. 2023;34(5):1633–41. 10.1002/PAT.5997.Search in Google Scholar
[35] Helmy A, Rabia M, Shaban M, Ashraf AM, Ahmed S, Ahmed AM. Graphite/rolled graphene oxide/carbon nanotube photoelectrode for water splitting of exhaust car solution. Int J Energy Res. 2020;44:7687–97. 10.1002/er.5501.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Porous silicon nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and their antifungal activity
- Biochar from de-oiled Chlorella vulgaris and its adsorption on antibiotics
- Phytochemicals profiling, in vitro and in vivo antidiabetic activity, and in silico studies on Ajuga iva (L.) Schreb.: A comprehensive approach
- Synthesis, characterization, in silico and in vitro studies of novel glycoconjugates as potential antibacterial, antifungal, and antileishmanial agents
- Sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by potato starch: Its performance in the treatment of esophageal cancer
- Computational study of ADME-Tox prediction of selected phytochemicals from Punica granatum peels
- Phytochemical analysis, in vitro antioxidant and antifungal activities of extracts and essential oil derived from Artemisia herba-alba Asso
- Two triazole-based coordination polymers: Synthesis and crystal structure characterization
- Phytochemical and physicochemical studies of different apple varieties grown in Morocco
- Synthesis of multi-template molecularly imprinted polymers (MT-MIPs) for isolating ethyl para-methoxycinnamate and ethyl cinnamate from Kaempferia galanga L., extract with methacrylic acid as functional monomer
- Nutraceutical potential of Mesembryanthemum forsskaolii Hochst. ex Bioss.: Insights into its nutritional composition, phytochemical contents, and antioxidant activity
- Evaluation of influence of Butea monosperma floral extract on inflammatory biomarkers
- Cannabis sativa L. essential oil: Chemical composition, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial properties, and acute toxicity: In vitro, in vivo, and in silico study
- The effect of gamma radiation on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural conversion in water and dimethyl sulfoxide
- Hollow mushroom nanomaterials for potentiometric sensing of Pb2+ ions in water via the intercalation of iodide ions into the polypyrrole matrix
- Determination of essential oil and chemical composition of St. John’s Wort
- Computational design and in vitro assay of lantadene-based novel inhibitors of NS3 protease of dengue virus
- Anti-parasitic activity and computational studies on a novel labdane diterpene from the roots of Vachellia nilotica
- Microbial dynamics and dehydrogenase activity in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) rhizospheres: Impacts on growth and soil health across different soil types
- Correlation between in vitro anti-urease activity and in silico molecular modeling approach of novel imidazopyridine–oxadiazole hybrids derivatives
- Spatial mapping of indoor air quality in a light metro system using the geographic information system method
- Iron indices and hemogram in renal anemia and the improvement with Tribulus terrestris green-formulated silver nanoparticles applied on rat model
- Integrated track of nano-informatics coupling with the enrichment concept in developing a novel nanoparticle targeting ERK protein in Naegleria fowleri
- Cytotoxic and phytochemical screening of Solanum lycopersicum–Daucus carota hydro-ethanolic extract and in silico evaluation of its lycopene content as anticancer agent
- Protective activities of silver nanoparticles containing Panax japonicus on apoptotic, inflammatory, and oxidative alterations in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity
- pH-based colorimetric detection of monofunctional aldehydes in liquid and gas phases
- Investigating the effect of resveratrol on apoptosis and regulation of gene expression of Caco-2 cells: Unravelling potential implications for colorectal cancer treatment
- Metformin inhibits knee osteoarthritis induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats: S100A8/9 and S100A12 as players and therapeutic targets
- Effect of silver nanoparticles formulated by Silybum marianum on menopausal urinary incontinence in ovariectomized rats
- Synthesis of new analogs of N-substituted(benzoylamino)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridines
- Response of yield and quality of Japonica rice to different gradients of moisture deficit at grain-filling stage in cold regions
- Preparation of an inclusion complex of nickel-based β-cyclodextrin: Characterization and accelerating the osteoarthritis articular cartilage repair
- Empagliflozin-loaded nanomicelles responsive to reactive oxygen species for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury protection
- Preparation and pharmacodynamic evaluation of sodium aescinate solid lipid nanoparticles
- Assessment of potentially toxic elements and health risks of agricultural soil in Southwest Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Theoretical investigation of hydrogen-rich fuel production through ammonia decomposition
- Biosynthesis and screening of cobalt nanoparticles using citrus species for antimicrobial activity
- Investigating the interplay of genetic variations, MCP-1 polymorphism, and docking with phytochemical inhibitors for combatting dengue virus pathogenicity through in silico analysis
- Ultrasound induced biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles embedded into chitosan polymers: Investigation of its anti-cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma effects
- Copper oxide nanoparticles-mediated Heliotropium bacciferum leaf extract: Antifungal activity and molecular docking assays against strawberry pathogens
- Sprouted wheat flour for improving physical, chemical, rheological, microbial load, and quality properties of fino bread
- Comparative toxicity assessment of fisetin-aided artificial intelligence-assisted drug design targeting epibulbar dermoid through phytochemicals
- Acute toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity of bis-thiourea derivatives
- Anti-diabetic activity-guided isolation of α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory terpenes from Capsella bursa-pastoris Linn.
- GC–MS analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 metabolites and its computational analysis on familial pulmonary fibrosis hub genes
- Green formulation of copper nanoparticles by Pistacia khinjuk leaf aqueous extract: Introducing a novel chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of prostate cancer
- Improved photocatalytic properties of WO3 nanoparticles for Malachite green dye degradation under visible light irradiation: An effect of La doping
- One-pot synthesis of a network of Mn2O3–MnO2–poly(m-methylaniline) composite nanorods on a polypyrrole film presents a promising and efficient optoelectronic and solar cell device
- Groundwater quality and health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride in Al Qaseem area, Saudi Arabia
- A comparative study of the antifungal efficacy and phytochemical composition of date palm leaflet extracts
- Processing of alcohol pomelo beverage (Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck) using saccharomyces yeast: Optimization, physicochemical quality, and sensory characteristics
- Specialized compounds of four Cameroonian spices: Isolation, characterization, and in silico evaluation as prospective SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Identification of a novel drug target in Porphyromonas gingivalis by a computational genome analysis approach
- Physico-chemical properties and durability of a fly-ash-based geopolymer
- FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitory potentials of some phytochemicals from anti-leukemic plants using computational chemical methodologies
- Wild Thymus zygis L. ssp. gracilis and Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh.: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of essential oils
- 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, ADMET, simulation dynamic, and retrosynthesis studies on new styrylquinolines derivatives against breast cancer
- Deciphering the influenza neuraminidase inhibitory potential of naturally occurring biflavonoids: An in silico approach
- Determination of heavy elements in agricultural regions, Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis and characterization of antioxidant-enriched Moringa oil-based edible oleogel
- Ameliorative effects of thistle and thyme honeys on cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity in mice
- Study of phytochemical compound and antipyretic activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. fractions
- Investigating the adsorption mechanism of zinc chloride-modified porous carbon for sulfadiazine removal from water
- Performance repair of building materials using alumina and silica composite nanomaterials with electrodynamic properties
- Effects of nanoparticles on the activity and resistance genes of anaerobic digestion enzymes in livestock and poultry manure containing the antibiotic tetracycline
- Effect of copper nanoparticles green-synthesized using Ocimum basilicum against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice lung infection model
- Cardioprotective effects of nanoparticles green formulated by Spinacia oleracea extract on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in mice by the determination of PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway
- Anti-OTC antibody-conjugated fluorescent magnetic/silica and fluorescent hybrid silica nanoparticles for oxytetracycline detection
- Curcumin conjugated zinc nanoparticles for the treatment of myocardial infarction
- Identification and in silico screening of natural phloroglucinols as potential PI3Kα inhibitors: A computational approach for drug discovery
- Exploring the phytochemical profile and antioxidant evaluation: Molecular docking and ADMET analysis of main compounds from three Solanum species in Saudi Arabia
- Unveiling the molecular composition and biological properties of essential oil derived from the leaves of wild Mentha aquatica L.: A comprehensive in vitro and in silico exploration
- Analysis of bioactive compounds present in Boerhavia elegans seeds by GC-MS
- Homology modeling and molecular docking study of corticotrophin-releasing hormone: An approach to treat stress-related diseases
- LncRNA MIR17HG alleviates heart failure via targeting MIR17HG/miR-153-3p/SIRT1 axis in in vitro model
- Development and validation of a stability indicating UPLC-DAD method coupled with MS-TQD for ramipril and thymoquinone in bioactive SNEDDS with in silico toxicity analysis of ramipril degradation products
- Biosynthesis of Ag/Cu nanocomposite mediated by Curcuma longa: Evaluation of its antibacterial properties against oral pathogens
- Development of AMBER-compliant transferable force field parameters for polytetrafluoroethylene
- Treatment of gestational diabetes by Acroptilon repens leaf aqueous extract green-formulated iron nanoparticles in rats
- Development and characterization of new ecological adsorbents based on cardoon wastes: Application to brilliant green adsorption
- A fast, sensitive, greener, and stability-indicating HPLC method for the standardization and quantitative determination of chlorhexidine acetate in commercial products
- Assessment of Se, As, Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb content status in Ankang tea plantations of China
- Effect of transition metal chloride (ZnCl2) on low-temperature pyrolysis of high ash bituminous coal
- Evaluating polyphenol and ascorbic acid contents, tannin removal ability, and physical properties during hydrolysis and convective hot-air drying of cashew apple powder
- Development and characterization of functional low-fat frozen dairy dessert enhanced with dried lemongrass powder
- Scrutinizing the effect of additive and synergistic antibiotics against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Preparation, characterization, and determination of the therapeutic effects of copper nanoparticles green-formulated by Pistacia atlantica in diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction in rat
- Antioxidant and antidiabetic potentials of methoxy-substituted Schiff bases using in vitro, in vivo, and molecular simulation approaches
- Anti-melanoma cancer activity and chemical profile of the essential oil of Seseli yunnanense Franch
- Molecular docking analysis of subtilisin-like alkaline serine protease (SLASP) and laccase with natural biopolymers
- Overcoming methicillin resistance by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Computational evaluation of napthyridine and oxadiazoles compounds for potential dual inhibition of PBP-2a and FemA proteins
- Exploring novel antitubercular agents: Innovative design of 2,3-diaryl-quinoxalines targeting DprE1 for effective tuberculosis treatment
- Drimia maritima flowers as a source of biologically potent components: Optimization of bioactive compound extractions, isolation, UPLC–ESI–MS/MS, and pharmacological properties
- Estimating molecular properties, drug-likeness, cardiotoxic risk, liability profile, and molecular docking study to characterize binding process of key phyto-compounds against serotonin 5-HT2A receptor
- Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin-based microgels for enhancing solubility of Terbinafine: An in-vitro and in-vivo toxicological evaluation
- Phyto-mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of cationic and anionic dyes
- Monosodium glutamate induces hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis hyperactivation, glucocorticoid receptors down-regulation, and systemic inflammatory response in young male rats: Impact on miR-155 and miR-218
- Quality control analyses of selected honey samples from Serbia based on their mineral and flavonoid profiles, and the invertase activity
- Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus niruri leaf extract: Assessment of antimicrobial activity, effectiveness on tropical neglected mosquito vector control, and biocompatibility using a fibroblast cell line model
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles containing Cichorium intybus to treat the sepsis-induced DNA damage in the liver of Wistar albino rats
- Quality changes of durian pulp (Durio ziberhinus Murr.) in cold storage
- Study on recrystallization process of nitroguanidine by directly adding cold water to control temperature
- Determination of heavy metals and health risk assessment in drinking water in Bukayriyah City, Saudi Arabia
- Larvicidal properties of essential oils of three Artemisia species against the chemically insecticide-resistant Nile fever vector Culex pipiens (L.) (Diptera: Culicidae): In vitro and in silico studies
- Design, synthesis, characterization, and theoretical calculations, along with in silico and in vitro antimicrobial proprieties of new isoxazole-amide conjugates
- The impact of drying and extraction methods on total lipid, fatty acid profile, and cytotoxicity of Tenebrio molitor larvae
- A zinc oxide–tin oxide–nerolidol hybrid nanomaterial: Efficacy against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Research on technological process for production of muskmelon juice (Cucumis melo L.)
- Physicochemical components, antioxidant activity, and predictive models for quality of soursop tea (Annona muricata L.) during heat pump drying
- Characterization and application of Fe1−xCoxFe2O4 nanoparticles in Direct Red 79 adsorption
- Torilis arvensis ethanolic extract: Phytochemical analysis, antifungal efficacy, and cytotoxicity properties
- Magnetite–poly-1H pyrrole dendritic nanocomposite seeded on poly-1H pyrrole: A promising photocathode for green hydrogen generation from sanitation water without using external sacrificing agent
- HPLC and GC–MS analyses of phytochemical compounds in Haloxylon salicornicum extract: Antibacterial and antifungal activity assessment of phytopathogens
- Efficient and stable to coking catalysts of ethanol steam reforming comprised of Ni + Ru loaded on MgAl2O4 + LnFe0.7Ni0.3O3 (Ln = La, Pr) nanocomposites prepared via cost-effective procedure with Pluronic P123 copolymer
- Nitrogen and boron co-doped carbon dots probe for selectively detecting Hg2+ in water samples and the detection mechanism
- Heavy metals in road dust from typical old industrial areas of Wuhan: Seasonal distribution and bioaccessibility-based health risk assessment
- Phytochemical profiling and bioactivity evaluation of CBD- and THC-enriched Cannabis sativa extracts: In vitro and in silico investigation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
- Investigating dye adsorption: The role of surface-modified montmorillonite nanoclay in kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics
- Antimicrobial activity, induction of ROS generation in HepG2 liver cancer cells, and chemical composition of Pterospermum heterophyllum
- Study on the performance of nanoparticle-modified PVDF membrane in delaying membrane aging
- Impact of cholesterol in encapsulated vitamin E acetate within cocoliposomes
- Review Articles
- Structural aspects of Pt(η3-X1N1X2)(PL) (X1,2 = O, C, or Se) and Pt(η3-N1N2X1)(PL) (X1 = C, S, or Se) derivatives
- Biosurfactants in biocorrosion and corrosion mitigation of metals: An overview
- Stimulus-responsive MOF–hydrogel composites: Classification, preparation, characterization, and their advancement in medical treatments
- Electrochemical dissolution of titanium under alternating current polarization to obtain its dioxide
- Special Issue on Recent Trends in Green Chemistry
- Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of Vitex agnus-castus L.
- Phytochemical study, antioxidant activity, and dermoprotective activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.)
- Exploitation of mangliculous marine fungi, Amarenographium solium, for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against multiple drug-resistant bacteria
- Study of the phytotoxicity of margines on Pistia stratiotes L.
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part III
- Impact of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, development, and antioxidant system of high protein content crop (Lablab purpureus L.) sweet
- Green synthesis, characterization, and application of iron and molybdenum nanoparticles and their composites for enhancing the growth of Solanum lycopersicum
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Olea europaea L. extracted polysaccharides, characterization, and its assessment as an antimicrobial agent against multiple pathogenic microbes
- Photocatalytic treatment of organic dyes using metal oxides and nanocomposites: A quantitative study
- Antifungal, antioxidant, and photocatalytic activities of greenly synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles
- Special Issue on Phytochemical and Pharmacological Scrutinization of Medicinal Plants
- Hepatoprotective effects of safranal on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
- Chemical composition and biological properties of Thymus capitatus plants from Algerian high plains: A comparative and analytical study
- Chemical composition and bioactivities of the methanol root extracts of Saussurea costus
- In vivo protective effects of vitamin C against cyto-genotoxicity induced by Dysphania ambrosioides aqueous extract
- Insights about the deleterious impact of a carbamate pesticide on some metabolic immune and antioxidant functions and a focus on the protective ability of a Saharan shrub and its anti-edematous property
- A comprehensive review uncovering the anticancerous potential of genkwanin (plant-derived compound) in several human carcinomas
- A study to investigate the anticancer potential of carvacrol via targeting Notch signaling in breast cancer
- Assessment of anti-diabetic properties of Ziziphus oenopolia (L.) wild edible fruit extract: In vitro and in silico investigations through molecular docking analysis
- Optimization of polyphenol extraction, phenolic profile by LC-ESI-MS/MS, antioxidant, anti-enzymatic, and cytotoxic activities of Physalis acutifolia
- Phytochemical screening, antioxidant properties, and photo-protective activities of Salvia balansae de Noé ex Coss
- Antihyperglycemic, antiglycation, anti-hypercholesteremic, and toxicity evaluation with gas chromatography mass spectrometry profiling for Aloe armatissima leaves
- Phyto-fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles by using Timur (Zanthoxylum armatum DC) and their effect on wound healing
- Does Erodium trifolium (Cav.) Guitt exhibit medicinal properties? Response elements from phytochemical profiling, enzyme-inhibiting, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities
- Integrative in silico evaluation of the antiviral potential of terpenoids and its metal complexes derived from Homalomena aromatica based on main protease of SARS-CoV-2
- 6-Methoxyflavone improves anxiety, depression, and memory by increasing monoamines in mice brain: HPLC analysis and in silico studies
- Simultaneous extraction and quantification of hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants in Solanum lycopersicum L. varieties marketed in Saudi Arabia
- Biological evaluation of CH3OH and C2H5OH of Berberis vulgaris for in vivo antileishmanial potential against Leishmania tropica in murine models
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Porous silicon nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and their antifungal activity
- Biochar from de-oiled Chlorella vulgaris and its adsorption on antibiotics
- Phytochemicals profiling, in vitro and in vivo antidiabetic activity, and in silico studies on Ajuga iva (L.) Schreb.: A comprehensive approach
- Synthesis, characterization, in silico and in vitro studies of novel glycoconjugates as potential antibacterial, antifungal, and antileishmanial agents
- Sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by potato starch: Its performance in the treatment of esophageal cancer
- Computational study of ADME-Tox prediction of selected phytochemicals from Punica granatum peels
- Phytochemical analysis, in vitro antioxidant and antifungal activities of extracts and essential oil derived from Artemisia herba-alba Asso
- Two triazole-based coordination polymers: Synthesis and crystal structure characterization
- Phytochemical and physicochemical studies of different apple varieties grown in Morocco
- Synthesis of multi-template molecularly imprinted polymers (MT-MIPs) for isolating ethyl para-methoxycinnamate and ethyl cinnamate from Kaempferia galanga L., extract with methacrylic acid as functional monomer
- Nutraceutical potential of Mesembryanthemum forsskaolii Hochst. ex Bioss.: Insights into its nutritional composition, phytochemical contents, and antioxidant activity
- Evaluation of influence of Butea monosperma floral extract on inflammatory biomarkers
- Cannabis sativa L. essential oil: Chemical composition, anti-oxidant, anti-microbial properties, and acute toxicity: In vitro, in vivo, and in silico study
- The effect of gamma radiation on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural conversion in water and dimethyl sulfoxide
- Hollow mushroom nanomaterials for potentiometric sensing of Pb2+ ions in water via the intercalation of iodide ions into the polypyrrole matrix
- Determination of essential oil and chemical composition of St. John’s Wort
- Computational design and in vitro assay of lantadene-based novel inhibitors of NS3 protease of dengue virus
- Anti-parasitic activity and computational studies on a novel labdane diterpene from the roots of Vachellia nilotica
- Microbial dynamics and dehydrogenase activity in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) rhizospheres: Impacts on growth and soil health across different soil types
- Correlation between in vitro anti-urease activity and in silico molecular modeling approach of novel imidazopyridine–oxadiazole hybrids derivatives
- Spatial mapping of indoor air quality in a light metro system using the geographic information system method
- Iron indices and hemogram in renal anemia and the improvement with Tribulus terrestris green-formulated silver nanoparticles applied on rat model
- Integrated track of nano-informatics coupling with the enrichment concept in developing a novel nanoparticle targeting ERK protein in Naegleria fowleri
- Cytotoxic and phytochemical screening of Solanum lycopersicum–Daucus carota hydro-ethanolic extract and in silico evaluation of its lycopene content as anticancer agent
- Protective activities of silver nanoparticles containing Panax japonicus on apoptotic, inflammatory, and oxidative alterations in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity
- pH-based colorimetric detection of monofunctional aldehydes in liquid and gas phases
- Investigating the effect of resveratrol on apoptosis and regulation of gene expression of Caco-2 cells: Unravelling potential implications for colorectal cancer treatment
- Metformin inhibits knee osteoarthritis induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats: S100A8/9 and S100A12 as players and therapeutic targets
- Effect of silver nanoparticles formulated by Silybum marianum on menopausal urinary incontinence in ovariectomized rats
- Synthesis of new analogs of N-substituted(benzoylamino)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridines
- Response of yield and quality of Japonica rice to different gradients of moisture deficit at grain-filling stage in cold regions
- Preparation of an inclusion complex of nickel-based β-cyclodextrin: Characterization and accelerating the osteoarthritis articular cartilage repair
- Empagliflozin-loaded nanomicelles responsive to reactive oxygen species for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury protection
- Preparation and pharmacodynamic evaluation of sodium aescinate solid lipid nanoparticles
- Assessment of potentially toxic elements and health risks of agricultural soil in Southwest Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Theoretical investigation of hydrogen-rich fuel production through ammonia decomposition
- Biosynthesis and screening of cobalt nanoparticles using citrus species for antimicrobial activity
- Investigating the interplay of genetic variations, MCP-1 polymorphism, and docking with phytochemical inhibitors for combatting dengue virus pathogenicity through in silico analysis
- Ultrasound induced biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles embedded into chitosan polymers: Investigation of its anti-cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma effects
- Copper oxide nanoparticles-mediated Heliotropium bacciferum leaf extract: Antifungal activity and molecular docking assays against strawberry pathogens
- Sprouted wheat flour for improving physical, chemical, rheological, microbial load, and quality properties of fino bread
- Comparative toxicity assessment of fisetin-aided artificial intelligence-assisted drug design targeting epibulbar dermoid through phytochemicals
- Acute toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity of bis-thiourea derivatives
- Anti-diabetic activity-guided isolation of α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory terpenes from Capsella bursa-pastoris Linn.
- GC–MS analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 metabolites and its computational analysis on familial pulmonary fibrosis hub genes
- Green formulation of copper nanoparticles by Pistacia khinjuk leaf aqueous extract: Introducing a novel chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of prostate cancer
- Improved photocatalytic properties of WO3 nanoparticles for Malachite green dye degradation under visible light irradiation: An effect of La doping
- One-pot synthesis of a network of Mn2O3–MnO2–poly(m-methylaniline) composite nanorods on a polypyrrole film presents a promising and efficient optoelectronic and solar cell device
- Groundwater quality and health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride in Al Qaseem area, Saudi Arabia
- A comparative study of the antifungal efficacy and phytochemical composition of date palm leaflet extracts
- Processing of alcohol pomelo beverage (Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck) using saccharomyces yeast: Optimization, physicochemical quality, and sensory characteristics
- Specialized compounds of four Cameroonian spices: Isolation, characterization, and in silico evaluation as prospective SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Identification of a novel drug target in Porphyromonas gingivalis by a computational genome analysis approach
- Physico-chemical properties and durability of a fly-ash-based geopolymer
- FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitory potentials of some phytochemicals from anti-leukemic plants using computational chemical methodologies
- Wild Thymus zygis L. ssp. gracilis and Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh.: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of essential oils
- 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, ADMET, simulation dynamic, and retrosynthesis studies on new styrylquinolines derivatives against breast cancer
- Deciphering the influenza neuraminidase inhibitory potential of naturally occurring biflavonoids: An in silico approach
- Determination of heavy elements in agricultural regions, Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis and characterization of antioxidant-enriched Moringa oil-based edible oleogel
- Ameliorative effects of thistle and thyme honeys on cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity in mice
- Study of phytochemical compound and antipyretic activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. fractions
- Investigating the adsorption mechanism of zinc chloride-modified porous carbon for sulfadiazine removal from water
- Performance repair of building materials using alumina and silica composite nanomaterials with electrodynamic properties
- Effects of nanoparticles on the activity and resistance genes of anaerobic digestion enzymes in livestock and poultry manure containing the antibiotic tetracycline
- Effect of copper nanoparticles green-synthesized using Ocimum basilicum against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice lung infection model
- Cardioprotective effects of nanoparticles green formulated by Spinacia oleracea extract on isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in mice by the determination of PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathway
- Anti-OTC antibody-conjugated fluorescent magnetic/silica and fluorescent hybrid silica nanoparticles for oxytetracycline detection
- Curcumin conjugated zinc nanoparticles for the treatment of myocardial infarction
- Identification and in silico screening of natural phloroglucinols as potential PI3Kα inhibitors: A computational approach for drug discovery
- Exploring the phytochemical profile and antioxidant evaluation: Molecular docking and ADMET analysis of main compounds from three Solanum species in Saudi Arabia
- Unveiling the molecular composition and biological properties of essential oil derived from the leaves of wild Mentha aquatica L.: A comprehensive in vitro and in silico exploration
- Analysis of bioactive compounds present in Boerhavia elegans seeds by GC-MS
- Homology modeling and molecular docking study of corticotrophin-releasing hormone: An approach to treat stress-related diseases
- LncRNA MIR17HG alleviates heart failure via targeting MIR17HG/miR-153-3p/SIRT1 axis in in vitro model
- Development and validation of a stability indicating UPLC-DAD method coupled with MS-TQD for ramipril and thymoquinone in bioactive SNEDDS with in silico toxicity analysis of ramipril degradation products
- Biosynthesis of Ag/Cu nanocomposite mediated by Curcuma longa: Evaluation of its antibacterial properties against oral pathogens
- Development of AMBER-compliant transferable force field parameters for polytetrafluoroethylene
- Treatment of gestational diabetes by Acroptilon repens leaf aqueous extract green-formulated iron nanoparticles in rats
- Development and characterization of new ecological adsorbents based on cardoon wastes: Application to brilliant green adsorption
- A fast, sensitive, greener, and stability-indicating HPLC method for the standardization and quantitative determination of chlorhexidine acetate in commercial products
- Assessment of Se, As, Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb content status in Ankang tea plantations of China
- Effect of transition metal chloride (ZnCl2) on low-temperature pyrolysis of high ash bituminous coal
- Evaluating polyphenol and ascorbic acid contents, tannin removal ability, and physical properties during hydrolysis and convective hot-air drying of cashew apple powder
- Development and characterization of functional low-fat frozen dairy dessert enhanced with dried lemongrass powder
- Scrutinizing the effect of additive and synergistic antibiotics against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Preparation, characterization, and determination of the therapeutic effects of copper nanoparticles green-formulated by Pistacia atlantica in diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction in rat
- Antioxidant and antidiabetic potentials of methoxy-substituted Schiff bases using in vitro, in vivo, and molecular simulation approaches
- Anti-melanoma cancer activity and chemical profile of the essential oil of Seseli yunnanense Franch
- Molecular docking analysis of subtilisin-like alkaline serine protease (SLASP) and laccase with natural biopolymers
- Overcoming methicillin resistance by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Computational evaluation of napthyridine and oxadiazoles compounds for potential dual inhibition of PBP-2a and FemA proteins
- Exploring novel antitubercular agents: Innovative design of 2,3-diaryl-quinoxalines targeting DprE1 for effective tuberculosis treatment
- Drimia maritima flowers as a source of biologically potent components: Optimization of bioactive compound extractions, isolation, UPLC–ESI–MS/MS, and pharmacological properties
- Estimating molecular properties, drug-likeness, cardiotoxic risk, liability profile, and molecular docking study to characterize binding process of key phyto-compounds against serotonin 5-HT2A receptor
- Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin-based microgels for enhancing solubility of Terbinafine: An in-vitro and in-vivo toxicological evaluation
- Phyto-mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of cationic and anionic dyes
- Monosodium glutamate induces hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis hyperactivation, glucocorticoid receptors down-regulation, and systemic inflammatory response in young male rats: Impact on miR-155 and miR-218
- Quality control analyses of selected honey samples from Serbia based on their mineral and flavonoid profiles, and the invertase activity
- Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus niruri leaf extract: Assessment of antimicrobial activity, effectiveness on tropical neglected mosquito vector control, and biocompatibility using a fibroblast cell line model
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles containing Cichorium intybus to treat the sepsis-induced DNA damage in the liver of Wistar albino rats
- Quality changes of durian pulp (Durio ziberhinus Murr.) in cold storage
- Study on recrystallization process of nitroguanidine by directly adding cold water to control temperature
- Determination of heavy metals and health risk assessment in drinking water in Bukayriyah City, Saudi Arabia
- Larvicidal properties of essential oils of three Artemisia species against the chemically insecticide-resistant Nile fever vector Culex pipiens (L.) (Diptera: Culicidae): In vitro and in silico studies
- Design, synthesis, characterization, and theoretical calculations, along with in silico and in vitro antimicrobial proprieties of new isoxazole-amide conjugates
- The impact of drying and extraction methods on total lipid, fatty acid profile, and cytotoxicity of Tenebrio molitor larvae
- A zinc oxide–tin oxide–nerolidol hybrid nanomaterial: Efficacy against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Research on technological process for production of muskmelon juice (Cucumis melo L.)
- Physicochemical components, antioxidant activity, and predictive models for quality of soursop tea (Annona muricata L.) during heat pump drying
- Characterization and application of Fe1−xCoxFe2O4 nanoparticles in Direct Red 79 adsorption
- Torilis arvensis ethanolic extract: Phytochemical analysis, antifungal efficacy, and cytotoxicity properties
- Magnetite–poly-1H pyrrole dendritic nanocomposite seeded on poly-1H pyrrole: A promising photocathode for green hydrogen generation from sanitation water without using external sacrificing agent
- HPLC and GC–MS analyses of phytochemical compounds in Haloxylon salicornicum extract: Antibacterial and antifungal activity assessment of phytopathogens
- Efficient and stable to coking catalysts of ethanol steam reforming comprised of Ni + Ru loaded on MgAl2O4 + LnFe0.7Ni0.3O3 (Ln = La, Pr) nanocomposites prepared via cost-effective procedure with Pluronic P123 copolymer
- Nitrogen and boron co-doped carbon dots probe for selectively detecting Hg2+ in water samples and the detection mechanism
- Heavy metals in road dust from typical old industrial areas of Wuhan: Seasonal distribution and bioaccessibility-based health risk assessment
- Phytochemical profiling and bioactivity evaluation of CBD- and THC-enriched Cannabis sativa extracts: In vitro and in silico investigation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
- Investigating dye adsorption: The role of surface-modified montmorillonite nanoclay in kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics
- Antimicrobial activity, induction of ROS generation in HepG2 liver cancer cells, and chemical composition of Pterospermum heterophyllum
- Study on the performance of nanoparticle-modified PVDF membrane in delaying membrane aging
- Impact of cholesterol in encapsulated vitamin E acetate within cocoliposomes
- Review Articles
- Structural aspects of Pt(η3-X1N1X2)(PL) (X1,2 = O, C, or Se) and Pt(η3-N1N2X1)(PL) (X1 = C, S, or Se) derivatives
- Biosurfactants in biocorrosion and corrosion mitigation of metals: An overview
- Stimulus-responsive MOF–hydrogel composites: Classification, preparation, characterization, and their advancement in medical treatments
- Electrochemical dissolution of titanium under alternating current polarization to obtain its dioxide
- Special Issue on Recent Trends in Green Chemistry
- Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of Vitex agnus-castus L.
- Phytochemical study, antioxidant activity, and dermoprotective activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.)
- Exploitation of mangliculous marine fungi, Amarenographium solium, for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their activity against multiple drug-resistant bacteria
- Study of the phytotoxicity of margines on Pistia stratiotes L.
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part III
- Impact of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, development, and antioxidant system of high protein content crop (Lablab purpureus L.) sweet
- Green synthesis, characterization, and application of iron and molybdenum nanoparticles and their composites for enhancing the growth of Solanum lycopersicum
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Olea europaea L. extracted polysaccharides, characterization, and its assessment as an antimicrobial agent against multiple pathogenic microbes
- Photocatalytic treatment of organic dyes using metal oxides and nanocomposites: A quantitative study
- Antifungal, antioxidant, and photocatalytic activities of greenly synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles
- Special Issue on Phytochemical and Pharmacological Scrutinization of Medicinal Plants
- Hepatoprotective effects of safranal on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
- Chemical composition and biological properties of Thymus capitatus plants from Algerian high plains: A comparative and analytical study
- Chemical composition and bioactivities of the methanol root extracts of Saussurea costus
- In vivo protective effects of vitamin C against cyto-genotoxicity induced by Dysphania ambrosioides aqueous extract
- Insights about the deleterious impact of a carbamate pesticide on some metabolic immune and antioxidant functions and a focus on the protective ability of a Saharan shrub and its anti-edematous property
- A comprehensive review uncovering the anticancerous potential of genkwanin (plant-derived compound) in several human carcinomas
- A study to investigate the anticancer potential of carvacrol via targeting Notch signaling in breast cancer
- Assessment of anti-diabetic properties of Ziziphus oenopolia (L.) wild edible fruit extract: In vitro and in silico investigations through molecular docking analysis
- Optimization of polyphenol extraction, phenolic profile by LC-ESI-MS/MS, antioxidant, anti-enzymatic, and cytotoxic activities of Physalis acutifolia
- Phytochemical screening, antioxidant properties, and photo-protective activities of Salvia balansae de Noé ex Coss
- Antihyperglycemic, antiglycation, anti-hypercholesteremic, and toxicity evaluation with gas chromatography mass spectrometry profiling for Aloe armatissima leaves
- Phyto-fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles by using Timur (Zanthoxylum armatum DC) and their effect on wound healing
- Does Erodium trifolium (Cav.) Guitt exhibit medicinal properties? Response elements from phytochemical profiling, enzyme-inhibiting, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities
- Integrative in silico evaluation of the antiviral potential of terpenoids and its metal complexes derived from Homalomena aromatica based on main protease of SARS-CoV-2
- 6-Methoxyflavone improves anxiety, depression, and memory by increasing monoamines in mice brain: HPLC analysis and in silico studies
- Simultaneous extraction and quantification of hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants in Solanum lycopersicum L. varieties marketed in Saudi Arabia
- Biological evaluation of CH3OH and C2H5OH of Berberis vulgaris for in vivo antileishmanial potential against Leishmania tropica in murine models

