Abstract
C17H12O2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 11.0333(13) Å, b = 15.7993(19) Å, c = 7.0619(9) Å, β = 92.302(2)∘, V = 1230.0(3) Å3, Z = 4, R gt(F) = 0.0420, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1081, T = 298 K.
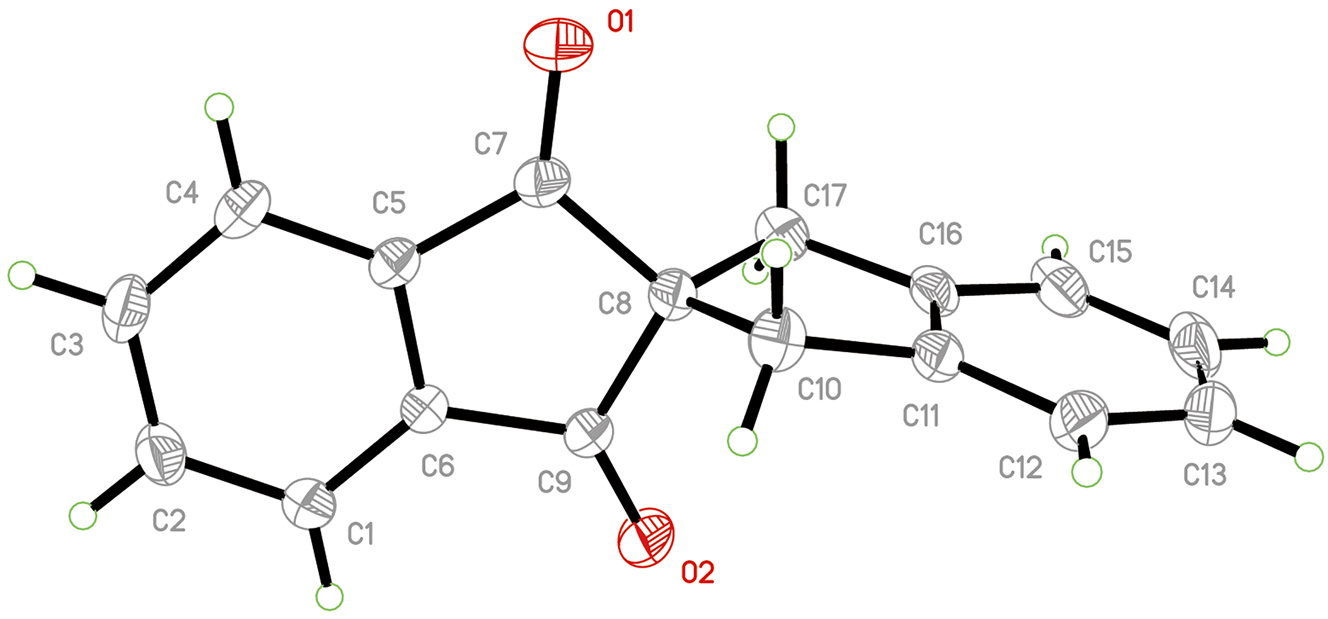
A part of the molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless cube |
| Size: | 0.26 × 0.22 × 0.21 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.09 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker SMART APEX2, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 27.5°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured , N(hkl)unique, R int: | 7285, 2780, 0.026 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2,037 |
| N(param)refined: | 173 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 OLEX2, 2 SHELX 3 , 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.62906 (13) | 0.35645 (9) | 0.8624 (2) | 0.0424 (4) |
| H1 | 0.673358 | 0.405470 | 0.888209 | 0.051* |
| C2 | 0.68129 (14) | 0.27763 (10) | 0.8851 (2) | 0.0499 (4) |
| H2 | 0.762019 | 0.273442 | 0.927252 | 0.060* |
| C3 | 0.61516 (15) | 0.20427 (10) | 0.8461 (2) | 0.0487 (4) |
| H3 | 0.652697 | 0.151872 | 0.861321 | 0.058* |
| C4 | 0.49504 (14) | 0.20786 (8) | 0.7853 (2) | 0.0417 (4) |
| H4 | 0.450825 | 0.158738 | 0.760184 | 0.050* |
| C5 | 0.44216 (12) | 0.28701 (8) | 0.76271 (18) | 0.0336 (3) |
| C6 | 0.50871 (12) | 0.36036 (8) | 0.79994 (18) | 0.0333 (3) |
| C7 | 0.31751 (12) | 0.30919 (9) | 0.6971 (2) | 0.0394 (3) |
| C8 | 0.30486 (12) | 0.40571 (8) | 0.7027 (2) | 0.0376 (3) |
| C9 | 0.43326 (12) | 0.43564 (8) | 0.7580 (2) | 0.0378 (3) |
| C10 | 0.21476 (14) | 0.43489 (9) | 0.8536 (2) | 0.0450 (4) |
| H10A | 0.155896 | 0.390953 | 0.877511 | 0.054* |
| H10B | 0.257508 | 0.449384 | 0.971906 | 0.054* |
| C11 | 0.15425 (12) | 0.51137 (9) | 0.7660 (2) | 0.0400 (3) |
| C12 | 0.08075 (14) | 0.57069 (10) | 0.8498 (3) | 0.0529 (4) |
| H12 | 0.067266 | 0.567986 | 0.978858 | 0.063* |
| C13 | 0.02785 (15) | 0.63384 (11) | 0.7392 (3) | 0.0656 (6) |
| H13 | −0.021631 | 0.673839 | 0.794158 | 0.079* |
| C14 | 0.04781 (15) | 0.63797 (10) | 0.5487 (4) | 0.0662 (6) |
| H14 | 0.011214 | 0.680578 | 0.475762 | 0.079* |
| C15 | 0.12184 (13) | 0.57941 (10) | 0.4638 (3) | 0.0536 (4) |
| H15 | 0.135333 | 0.582581 | 0.334890 | 0.064* |
| C16 | 0.17539 (11) | 0.51610 (9) | 0.5740 (2) | 0.0397 (3) |
| C17 | 0.25703 (13) | 0.44554 (10) | 0.5137 (2) | 0.0426 (4) |
| H17A | 0.323319 | 0.467347 | 0.441801 | 0.051* |
| H17B | 0.212164 | 0.404334 | 0.436939 | 0.051* |
| O1 | 0.23814 (10) | 0.26026 (7) | 0.64641 (19) | 0.0636 (4) |
| O2 | 0.46702 (10) | 0.50840 (6) | 0.76245 (19) | 0.0617 (4) |
1 Source of materials
The synthesis of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione (SPIN) primarily referred to the literature of J. Wilbuer and coworkers. 5 Reagents were purchased from Macklin Inc. and used as received without further purification. An amount of 0.5 g SPIN (2.0 mmol) was added to a 15 mL glass tube with a mixed solution of methanol and dichloromethane (10 mL, 1:1, v/v). After several days, cube-shaped crystals were obtained, washed with anhydrous methanol, dried in air, yield 46 % (based on SPIN).
2 Experimental details
The crystal structure was determined using the SHELXT program, followed by refinement using the SHELXL program. The refinement process included anisotropic displacement parameters for all non-hydrogen atoms, while the hydrogen atoms were placed in idealized positions with isotropic thermal parameters.
3 Comment
The special stereoelectronic effects of spiro-conjugated compounds make them potentially useful in the fields of optics, dyes, organic conductors, etc. 6 , 7 , 8 At present, there are relatively few reported crystal structures of spiro-conjugated compounds. To better understand the properties of these compounds, it is necessary to synthesize more novel spiro-conjugated compounds and investigate their crystal structures in detail. Therefore, we report the single-crystal structure of the title 2,2′-spirobi[indene] compound. The asymmetric unit contains one SPIN molecule. The C–C bond and C–O bond lengths are in the normal range of 1.373(3) – 1.5320(19) Å and 1.2084(16) – 1.2115(17) Å, compared to the reported structures with similar molecules. 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 The torsion angle of C16–C17–C8–C9 and C9–C8–C17 are 100.642° and 111.992°. The SPIN molecules are linked by the C–H⃛O short contact (C4–H4⃛O21−x, 1/2+y, 1/2−z ). Ultimately, a three-dimensional network was formed, facilitated by π-π stacking interactions, with centroid-centroid distances ranging from 3.6752(5) Å to 3.8876(5) Å. The crystal data for the compound has been deposited to the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC no. 2391002).
Acknowledgements
The correspondence author would like to express her gratitude to Qi Liu for her valuable comments and suggestions about the manuscript.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: None declared.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar
5. Wilbuer, J.; Schnakenburg, G.; Esser, B. Syntheses, Structures and Optoelectronic Properties of Spiroconjugated Cyclic Ketones. Eur. J. Org Chem. 2016, 14, 2404–2412; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201600235.Search in Google Scholar
6. Hashmi, A. S.; Haffner, T.; Rudolph, M.; Rominger, F. Gold Catalysis: Domino Reaction of En-Diynes to Highly Substituted Phenols. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 8195–8201; https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201100305.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Ding, Z.; Hou, A.; Fu, J., Su, H.; Cheng, M.; Lin, B.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y. Gold(I)–Catalyzed Tandem Intramolecular Methoxylation/Double Aldol Condensation Strategy Yielding 2,2′–Spirobi[indene] Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 6777–6782; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.2c02653.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Ivanov, K. S.; Riesebeck, T.; Skolyapova, A.; Liakisheva, I.; Kazantsev, M. S.; Sonina, A. A.; Peshkov, R. Y.; Mostovich, E. A. P2O5–Promoted Cyclization of Di[aryl(hetaryl)methyl] Malonic Acids as a Pathway to Fused Spiro[4.4]nonane-1, 6–Diones. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 2456–2469; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.1c02379.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Wu, T.; Zhou, Q.; Tang, W. Enantioselective Alpha–Carbonylative Arylation for Facile Construction of Chiral Spirocyclic β, β′–Diketones. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 9978–9983; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202101668.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Rahemtulla, B. F.; Clark, H. F.; Smith, M. D. Catalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of C1- and C2 –Symmetric Spirobiindanones through Counterion- Directed Enolate C–Acylation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13180–13183; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201607731.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Petersen, K. B.; Danielsen, J. (+)-2,2′–Spirobi[indan]-1,1′-dione. Acta Crystallogr. 1974, 30, 338–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0567740874002780.Search in Google Scholar
12. Hu, G.; Rømming, C.; Undheim, K. Stereoselective Synthesis of α, α′-Spirane–Bridged Dibenzyl Ligands. Synth. Commun. 2006, 35, 2277–2288.10.1080/00397910500186250Search in Google Scholar
13. Hashmi, A. S. K.; Haffner, T.; Rudolph, M.; Rominger, F. Gold Catalysis: Domino Reaction of En–Diynes to Highly Substituted Phenols. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 8195–8201; https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201100305.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

