Abstract
Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O, cubic, Fd3̄m (no. 227), a = 17.487(2) Å, V = 5347.7(18) Å3, Z = 8, Rgt (F) = 0.0236, wRref (F 2) = 0.0552, T = 296(2) K.
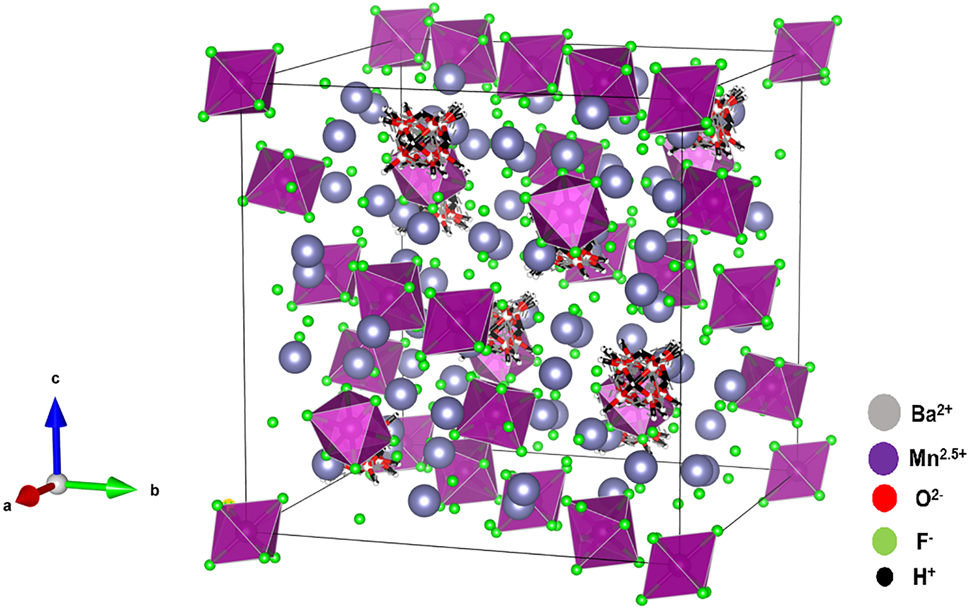
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Purple block |
| Size: | 0.05 × 0.03 × 0.02 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 15.5 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 28.6°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 7734, 370, 0.046 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 344 |
| N(param)refined: | 33 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 , 4 VESTA3 5 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba1 | 0.03947 (2) | 0.21053 (2) | 0.03947 (2) | 0.0184 (2) |
| Ba2 | 0.125000 | 0.125000 | −0.17998 (4) | 0.02194 (19) |
| Mn1 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.0158 (5) |
| F1 | 0.07252 (18) | −0.0377 (3) | 0.07252 (18) | 0.0279 (10) |
| F2 | 0.125000 | 0.125000 | 0.125000 | 0.019 (3) |
| F3 | 0.0221 (2) | 0.3569 (3) | 0.0221 (2) | 0.0308 (11) |
| O1a | −0.0897 (11) | 0.4103 (11) | −0.0897 (11) | 0.028 (6) |
| O2b | −0.0914 (14) | 0.3414 (14) | −0.0914 (14) | 0.028 (6) |
| H1Aa | −0.0592 (11) | 0.4408 (11) | −0.0592 (11) | 0.042* |
| H1Bc | −0.125000 | 0.375000 | −0.067 (4) | 0.042* |
| H2Ad | −0.055 (3) | 0.325 (8) | −0.055 (3) | 0.042* |
| H2Bc | −0.125000 | 0.375000 | −0.065 (3) | 0.042* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.257(18), bOccupancy: 0.243(18), cOccupancy: 0.162(12), dOccupancy: 0.086(6).
1 Source of materials
BaF2 (Alfa Asear, 99 %), MnF3 (Alfa Asear, 98 %) and CF3COOH (Alfa Aesar, 99 %) were used without any further purification. Crystals of Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O were obtained by hydrothermal method using a diluted CF3COOH solution. 6 0.8766 g of BaF2 (5.00 mmol), 0.1119 g of MnF3 (1.00 mmol), 3 ml of CF3COOH (39 mmol), and 5 ml of H2O were combined in a 23-mL Teflon-lined stainless autoclave. The autoclave was subsequently closed, gradually heated to 230 °C, held for 24 h, and cooled slowly to room temperature at a rate of 6 ° C/h. The mother liquor was decanted from the products, and products were recovered by filteration and washed with distilled water and ethanol. Purple colored block shaped crystals of Ba10 Mn2 F25·2H2O were isolated by hand sorting.
2 Experimental details
An purple colored block shaped crystal (0.02 × 0.03 × 0.05 mm3) was selected for single-crystal data collection. The structure was solved by Direct Methods with SHELXS 2 and further refined with the SHELXL program. 3 The oxygen-bound H atoms were located on a difference Fourier map and refined with distances O–H = 0.95 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5U eq(O).
3 Comment
Manganese fluoride materials have been extensively studied due to their intriguing magnetic, electric, multiferroic, and optical properties. 7 , 8 A search in the Inorganic Structure Database (ICSD, web version 5.1.0) 9 revealed only four barium manganese fluoride compounds: BaMnF4 6 , BaMnF5 10 , BaMnF5(H2O), 11 and Ba5Mn3F19 12 . Additionally, mixed valence manganese fluorides are relatively rare, and their crystal structures have not been fully investigated due to the challenges in preparation and controlling the oxidation state of manganese. To date, only a few examples have been reported, including CsMn2F6 13 , K4Mn3F12 14 , Mn3F8·12H2O, 15 Mn2F5 16 , and Mn3F8 16 . The crystal structure of Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O belongs to the cubic Fd3̄m (no. 227) space group with lattice parameter a = 17.487(2) Å. This structure is characterized by a zero-dimensional arrangement consisting of isolated Mn(1)F6 octahedra, Ba(1)F10 polyhedra, and Ba(2)F8(H2O)2 polyhedra. The Mn(1) atom is coordinated by six fluorine atoms, forming an octahedral geometry, with Mn–F bond distances of 1.911(4) Å. The Ba(1) atom is coordinated by ten fluorine atoms in a bicapped square antiprismatic geometry, with Ba–F bond distances range between 2.5905(8) and 2.825(3) Å. The Ba(2) atom is coordinated by eight fluorine atoms and two oxygen atoms of water molecules forming a distorted bicapped square antiprismatic geometry. The Ba–F bond distances range between 2.724(2) and 2.847(5) Å, while the Ba–O bond distances range between 2.927(10) and 2.942(13) Å.
Funding source: ACS PRF (American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund)
Award Identifier / Grant number: ACS PRF # 65115-UNI3
Funding source: National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the Ministry of Education
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2022R111A3063132
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: S.W.K thanks the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the Ministry of Education (2022R111A3063132). H.Y.C also thanks to ACS PRF (American Chemical Society Peterolium Fund, #65115-UNI3)
References
1. Bruker SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Hübschle, C. B.; Sheldrick, G. M.; Dittrich, B. ShelXle: a Qt Graphical User Interface for SHELXL. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1281–1284; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889811043202.Search in Google Scholar
5. Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for Three-Dimensional Visualization of Crystal, Volumetric and Morphology Data. J. Appl. Crytallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889811038970.Search in Google Scholar
6. Kim, S. W.; Chang, H. Y.; Halasyamani, P. S. Selective Pure-phase Synthesis of the Multiferroic BaMF4 (M=Mg, Mn, Co, Ni, and Zn) Family. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17684–17685; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja108965s.Search in Google Scholar
7. Hagenmuller, P. INORGANIC SOLID FLUORIDES: Chemistry and Physics; Academic Press, INC.: New York, 1985.Search in Google Scholar
8. Leblanc, M.; Maisonneuve, V.; Tressaud, A. Crystal Chemistry and Selected Physical Properties of Inorganic Fluorides and Oxide-Fluorides. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1191–1254; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500173c.Search in Google Scholar
9. Zagorac, D.; Müller, H.; Ruehl, S.; Zagorac, J.; Rehme, S. Recent Developments in the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database: Theoretical Crystal Structure Data and Related Features. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2019, 52, 918–925; https://doi.org/10.1107/s160057671900997x.Search in Google Scholar
10. Bukovec, P.; Hoppe, R. Zur Kenntnis von BaMnF5: Eine Jahn–Teller-verzerrte Variante von BaGaF5. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1984, 509, 138–144; https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.19845090214.Search in Google Scholar
11. Massa, W.; Burck, V. Erdalkali-Fluoromanganate(III): BaMnF5·H2O und SrMnF5·H2O. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1984, 516, 119–126.10.1002/zaac.19845160916Search in Google Scholar
12. Dahlke, P.; Graulich, J.; Welsch, M.; Pebler, J.; Babel, D. Struktur- und magnetochemische Untersuchungen an Ba5 Mn3 F19 und verwandten Verbindungen A5IIM3IIIF19. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2000, 626, 1255–1263; https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1521-3749(200005)626:5<1255::aid-zaac1255>3.3.co;2-a.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3749(200005)626:5<1255::AID-ZAAC1255>3.3.CO;2-ASearch in Google Scholar
13. Klepov, V. V.; Pace, K. A.; Berseneva, A. A.; Felder, J. B.; Morrison, G.; Zhang, Q.; Kirkham, M. J.; Parker, D. S.; Zur Loye, H. C. Chloride Reduction of Mn3+ in Mild Hydrothermal Synthesis of a Charge Ordered Defect Pyrochlore, CsMn2+ Mn3+ F6, a Canted Antiferromagnet with a Hard Ferromagnetic Component. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 11554–11567; https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c04245.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Frezen, G.; Kummer, S.; Massa, W.; Babel, D. Tetragonale Fluorperowskite AM0.75 ?0.25 F3 mit Kationendefizit: K4MnIIMn2IIIF12 und Ba2 Cs2 Cu3 F12. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1987, 553, 75–84.10.1002/zaac.19875531009Search in Google Scholar
15. Molinier, M.; Massa, W. New Fluoromanganate(III) Hydrates: Mn3F812H2O and AgMnF4·4H2O. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1994, 620, 833–838; https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.19946200514.Search in Google Scholar
16. Bandemehr, J.; Zimmerhofer, F.; Ivlev, S. I.; Pietzonka, C.; Eklund, K.; Karttunen, A. J.; Huppertz, H.; Kraus, F. Syntheses and Characterization of the Mixed–Valent Manganese(II/III) Fluorides Mn2F5 and Mn3F8. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 12651–12663; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c01833.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

