Abstract
C12H22N4O12, triclinic,
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.50 × 0.37 × 0.25 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.14 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 Advance, 0.5° ω scans |
| θ max, completeness: | 38.6°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 30,177, 4,931, 0.026 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 4,428 |
| N(param)refined: | 137 |
| Programs: | Bruker 1 , SHELX 2 , 4 , Mercury 3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1A | 0.69907 (7) | 0.85381 (5) | 0.39941 (5) | 0.01125 (7) |
| O2A | 0.51197 (7) | 0.64261 (6) | 0.15892 (5) | 0.01292 (8) |
| H5A | 0.4279 (19) | 0.6904 (16) | 0.0841 (14) | 0.019* |
| O3A | 0.73968 (7) | 0.69650 (7) | −0.03058 (5) | 0.01443 (8) |
| N1A | 0.55260 (7) | 0.84048 (6) | 0.69811 (5) | 0.00983 (8) |
| H1A | 0.484619 | 0.819361 | 0.790034 | 0.015* |
| H2A | 0.464275 | 0.903542 | 0.633218 | 0.015* |
| H3A | 0.651114 | 0.902291 | 0.717911 | 0.015* |
| N2A | 0.79888 (7) | 0.56010 (6) | 0.37172 (5) | 0.00914 (7) |
| H4A | 0.812079 | 0.456353 | 0.416655 | 0.011* |
| C1A | 0.64619 (9) | 0.67246 (7) | 0.62226 (6) | 0.01024 (8) |
| H11A | 0.546072 | 0.593209 | 0.623768 | 0.012* |
| H12A | 0.763036 | 0.615284 | 0.680798 | 0.012* |
| C2A | 0.71728 (8) | 0.70464 (6) | 0.45413 (6) | 0.00779 (8) |
| C3A | 0.86521 (8) | 0.57538 (7) | 0.20843 (6) | 0.00978 (8) |
| H31A | 0.934470 | 0.458231 | 0.169757 | 0.012* |
| H32A | 0.966443 | 0.653716 | 0.201202 | 0.012* |
| C4A | 0.69795 (8) | 0.64535 (7) | 0.10085 (6) | 0.00902 (8) |
| O1B | 0.09505 (6) | 1.01529 (6) | 0.25256 (5) | 0.01028 (7) |
| O2B | 0.26898 (6) | 0.77560 (6) | −0.05380 (5) | 0.01128 (7) |
| C2B | 0.12142 (8) | 0.89921 (7) | −0.02392 (6) | 0.00799 (8) |
| C1B | 0.04255 (8) | 1.00681 (7) | 0.11446 (6) | 0.00768 (8) |
| O1W | 0.81913 (7) | 0.21149 (6) | 0.47676 (5) | 0.01323 (8) |
| H1W | 0.8997 (19) | 0.1431 (16) | 0.4106 (14) | 0.020* |
| H2W | 0.8297 (19) | 0.1579 (16) | 0.5672 (14) | 0.020* |
1 Source of materials
Glycylglycine (Gly–Gly) and 3,4-dihydroxy-3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione (squaric acid) were purchased from Alfa Aesar chemicals and used without further purification. Crystals of the title salt were prepared by completely dissolving separately, in hot water, 1.0 g of squaric acid and 2.3 g of Gly–Gly, in a 1:2 molecular ratio. After complete dissolution the parts were mixed together. The solution was left to crystallize at room temperature by slow evaporation over a period of several weeks.
2 Experimental details
Singel crystal data collection, cell refinement, data reduction and structure solution was executed with APEX2 1 and structure refinement with SHELXT. 2 The illustration was prepared by Mercury 3 while material for publication was prepared by SHELXL. 4 Coordinates were refined for hydroxyl and water H atoms, other H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry and treated as riding atoms, allowing free rotation for the amino group.
3 Comment
Squaric acid is a planar hydrogen-bonded molecular compound belonging to the class of antiferroelectric crystals at room temperature.
5
,
6
,
7
,
8
It has the ability to crystallize either as a squarate dianion (
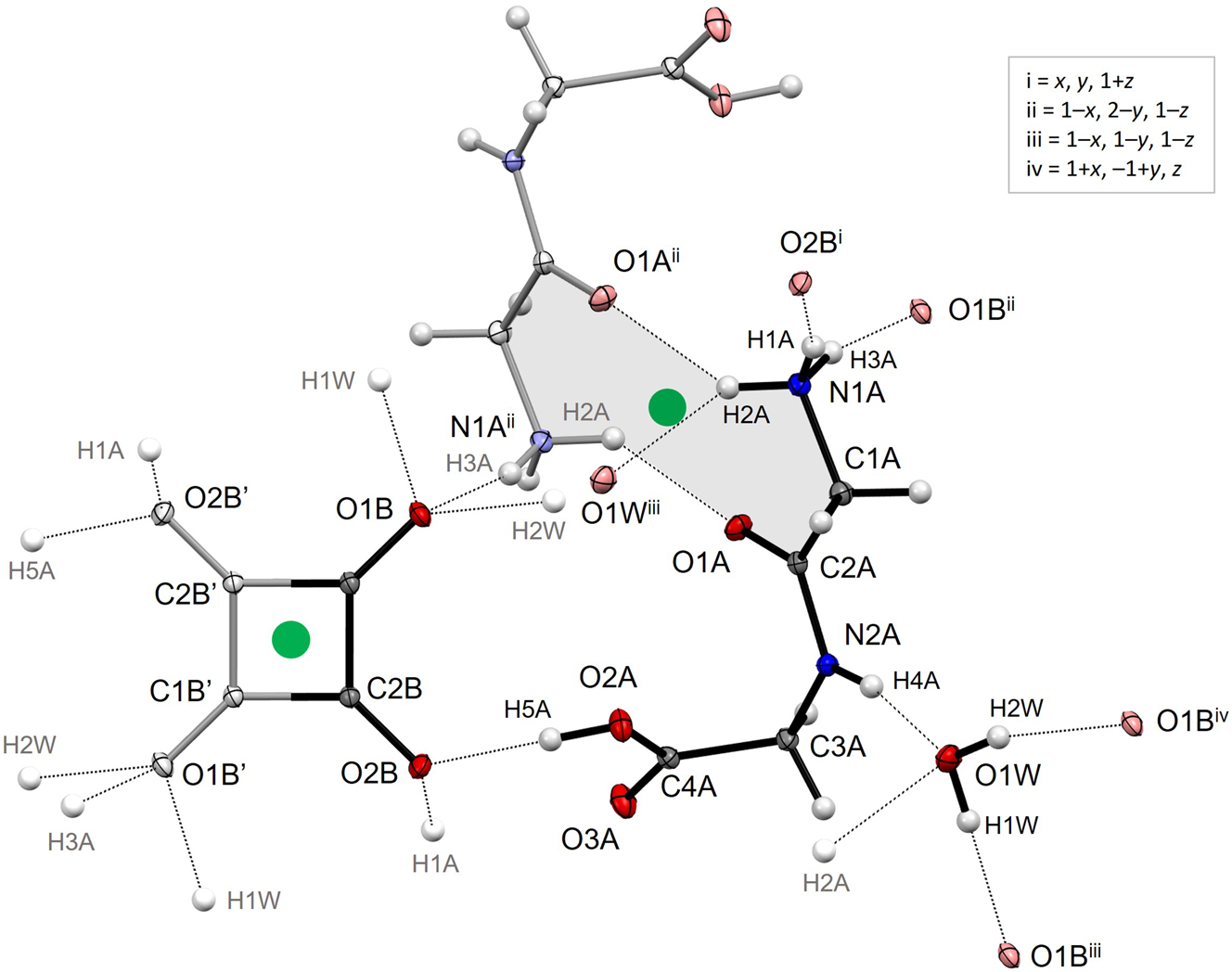
The illustration shows the asymmetric unit (with black bonds), a neighbouring glycylglicinium anion (in pale colours) at 1 – x, 2 – y, 1 – z generated by inversion symmetry, and the second half of the squarate dianion (in pale colours) at –x, 2 – y, –z also generated by inversion. Hydrogen bond acceptor atoms appear in pale colours with symmetry operations indicated, while atom labels for donated H atoms appear in grey without symmetry codes. The pertinent centres-of symmetry at (0.5 1 0.5) and (0 1 0), respectively, have been highlighted as green spheres. The grey shade shows the 10-membered ring system associated with formation of the glycylglycinium dimer, involving two amino⋯carbonyl interactions. Formation of similar dimers has been observed for a handful of zwitterionic dipeptides, but is more common when the C-terminal does not carry a negative charge, in which case it is a less attractive acceptor for the amino H atoms. By comparison, out of the 18 distinct structures in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) 14 containing the glycylglycine cation, five have similar dimers, but only in the 2,6-naphtalenedisulfonate dihydrate 15 are the two partners related by a centre-of-inversion like here.
Squarate dianions occur in 84 unique metal-free entries in the CSD, 13 in Sohncke space groups, 3 in non-centrosymmetric non-Sohncke space groups and 68 in centrosymmetric space groups. In the latter, the squarate is, like here, located on a centre-of-inversion in 73.5 % of the structures. If only contacts with H⋯O distances shorter than 2.4 Å are included, the number of hydrogen atoms accepted by squarate in the present structure, 10, is also the maximum number encountered in the CSD. Illustrations of the hydrogen bonding pattern are provided as Supplementary Material.
To check for phase transitions, diffraction data were also collected at room temperature, 294 K (CCDC 2391122). The best possible overlay of the refined structures at 105 and 294 K gives a root-mean-square deviation of just 0.028 Å, indicating no major changes with shifting temperature.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: National funds (OE) through Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (framework contract under the Decree-Law 57/2016, Law 57/2017) and FEDER (European Fund for Regional Development)-COMPETE-QREN-EU (ref. UID/FIS/04650/2013 and UID/FIS/04650/2019).
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT+ and SADABS; Bruker AXS, Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2016.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Macrae, C. F.; Sovago, I.; Cottrell, S. J.; Galek, P. T. A.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Platings, M.; Shields, G. P.; Stevens, J. S.; Towler, M.; Wood, P. A. Mercury 4.0: From Visualization to Analysis, Design and Prediction. J. Appl. Cryst. 2020, 53, 226–235; https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576719014092.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Semmingsen, D. The Crystal Structure of Squaric Acid. Acta Chem. Scand. 1973, 27, 3961–3972; https://doi.org/10.3891/acta.chem.scand.26–0143.10.3891/acta.chem.scand.27-3961Search in Google Scholar
6. Schwartz, L. M.; Howard, L. O. Aqueous Dissociation of Squaric Acid. J. Phys. Chem. 1970, 74, 4374–4377; https://doi.org/10.1021/j100719a013.Search in Google Scholar
7. Semmingsen, D.; Hollander, F. J.; Koetzle, T. F. A Neutron Diffraction Study of Squaric Acid (3,4-Dihydroxy-3-Cyclobutene-1,2-Dione). J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 66, 4405–4412; https://doi.org/10.1063/1.433745.Search in Google Scholar
8. Horiuchi, S.; Kumai, R.; Ishibashi, S. Strong Polarization Switching with Low-Energy Loss in Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Antiferroelectrics. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 425–432; https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC03859C.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Gilli, G.; Bertolasi, V.; Gilli, P.; Ferretti, V. Associations of Squaric Acid and its Anions as Multiform Building Blocks of Hydrogen-Bonded Molecular Crystals. Acta Crystallogr. 2001, B57, 859–865; https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108768101014963.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Kolev, T.; Spiteller, M.; Sheldrick, W. S.; Mayer-Figge, H. l-argininamidium Bis(hydrogensquarate). Acta Crystallogr. 2006, C62, o299–o300; https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108270106012108.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Yadav, H.; Sinha, N.; Goel, S.; Singh, B.; Bdikin, I.; Saini, A.; Gopalaiah, K.; Kumar, B. Growth, Crystal Structure, Hirshfeld Surface, Optical, Piezoelectric, Dielectric and Mechanical Properties of Bis(l-asparaginium hydrogensquarate) Single Crystal. Acta Crystallogr. 2017, B73, 347–359; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052520617002906.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Koleva, B. B.; Kolev, T. M.; Spiteller, M. Spectroscopic and Structural Elucidation of Alanyl-Containing Dipeptides and their Hydrogensquarates. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 877, 79–88; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2007.07.017.Search in Google Scholar
13. Pepinsky, R.; Vedam, K.; Hoshino, S.; Okaya, Y. Ferroelectricity in Di-Glycine Nitrate (NH2CH2COOH)2·HNO3. Phys. Rev. 1958, 111, 430–432; https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.111.430.Search in Google Scholar
14. Groom, C. R.; Bruno, I. J.; Lightfoot, M. P.; Ward, S. C. The Cambridge Structural Database. Acta Crystallogr. 2016, B72, 171–173; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052520616003954.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
15. Sudbeck, E. A.; Etter, M. C.; Gleason, W. B. Growth of High-Quality Crystals Containing Peptides: Arenesulfonate Salts of l-alanyl-l-alanine, Glycylglycine, and l-leucyl-l-alanine. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 1192–1199; https://doi.org/10.1021/cm00044a017.Search in Google Scholar
Supplementary Material
This article contains supplementary material (https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0416).
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

