Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
-
Lai-Jun Zhang
, Wen-Fang Weng
Abstract
C28H26CdN4O10, triclinic,
A part of the molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
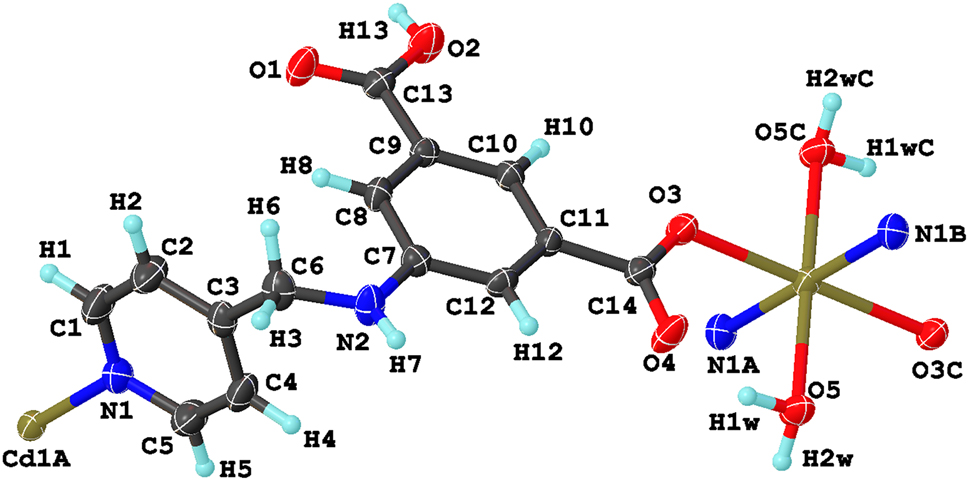
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless plate |
| Size: | 0.42 × 0.29 × 0.13 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.89 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | APEX2, omega |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 3529, 2318, 0.017 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl) gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2228 |
| N(param)refined: | 196 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 , 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.8514 (5) | 0.2559 (3) | 1.4358 (3) | 0.0419 (8) |
| H1 | 0.9513 | 0.2806 | 1.4795 | 0.050* |
| C2 | 0.9338 (5) | 0.1501 (3) | 1.3902 (3) | 0.0404 (7) |
| H2 | 1.0862 | 0.1057 | 1.4031 | 0.049* |
| C3 | 0.7904 (5) | 0.1100 (3) | 1.3256 (2) | 0.0287 (6) |
| C4 | 0.5684 (5) | 0.1820 (3) | 1.3091 (3) | 0.0368 (7) |
| H4 | 0.4651 | 0.1594 | 1.2657 | 0.044* |
| C5 | 0.4991 (5) | 0.2868 (3) | 1.3565 (3) | 0.0382 (7) |
| H5 | 0.3485 | 0.3342 | 1.3434 | 0.046* |
| C6 | 0.8707 (5) | −0.0073 (3) | 1.2751 (2) | 0.0326 (6) |
| H6 | 1.0406 | −0.0191 | 1.2678 | 0.039* |
| C7 | 0.8460 (4) | 0.1228 (3) | 1.0647 (2) | 0.0244 (6) |
| C8 | 1.0193 (4) | 0.2042 (3) | 1.0678 (2) | 0.0263 (6) |
| H8 | 1.0959 | 0.1849 | 1.1365 | 0.032* |
| C9 | 1.0780 (4) | 0.3132 (3) | 0.9694 (2) | 0.0230 (5) |
| C10 | 0.9663 (4) | 0.3445 (3) | 0.8658 (2) | 0.0247 (6) |
| H10 | 1.0050 | 0.4187 | 0.8005 | 0.030* |
| C11 | 0.7949 (4) | 0.2631 (3) | 0.8608 (2) | 0.0225 (5) |
| C12 | 0.7385 (4) | 0.1544 (3) | 0.9592 (2) | 0.0251 (6) |
| H12 | 0.6248 | 0.1005 | 0.9549 | 0.030* |
| C13 | 1.2613 (4) | 0.3961 (3) | 0.9810 (2) | 0.0268 (6) |
| C14 | 0.6641 (4) | 0.2959 (3) | 0.7513 (2) | 0.0261 (6) |
| Cd1 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.02479 (10) |
| H1w | 0.2765 | 0.3122 | 0.6591 | 0.050* |
| H2w | 0.0670 | 0.3913 | 0.6201 | 0.050* |
| H3 | 0.8222 | −0.0941 | 1.3292 | 0.039* |
| H7 | 0.6903 | −0.0374 | 1.1562 | 0.038* |
| H13 | 1.3999 | 0.5406 | 0.8981 | 0.059* |
| N1 | 0.6364 (4) | 0.3244 (2) | 1.42049 (19) | 0.0322 (5) |
| N2 | 0.7798 (4) | 0.0172 (2) | 1.16294 (19) | 0.0318 (5) |
| O1 | 1.3491 (3) | 0.3733 (2) | 1.07464 (17) | 0.0378 (5) |
| O2 | 1.3181 (3) | 0.4938 (2) | 0.88512 (17) | 0.0392 (5) |
| O3 | 0.7277 (3) | 0.39361 (19) | 0.66116 (15) | 0.0296 (4) |
| O4 | 0.5020 (3) | 0.2267 (2) | 0.75398 (17) | 0.0390 (5) |
| O5 | 0.1994 (3) | 0.36707 (19) | 0.58998 (16) | 0.0333 (4) |
1 Source of materials
5-[(Pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino]isophthalic acid (C14H12N2O4, H2L) was synthesized following the literature reported by us. 4 Both the analytical-grade N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and cadmium chloride hemipentahydrate (CdCl2·2.5H2O) were commercially available and were utilized without further purification. The title compound was solvo/hydrothermally synthesized using the following procedure. 0.2 mmol (0.0544 g) of H2L, 1 ml of DMF, 5 ml of distilled water and 0.2 mmol (0.457 g) of CdCl2·2.5H2O were added to a 15 ml Teflon reaction vessel and then sonicated for 10 min, resulting in a white suspension liquid. The Teflon-lined stainless steel reaction vessel was sealed and heated at 110 °C for 136 h. Upon cooling to room temperature, a large amount of colorless rod crystals were obtained with a yield of 73 % based on CdCl2·2.5H2O after being isolated by filtration, washed with the N,N-dimethylformamide/water mixture and dried at room temperature.
2 Experimental details
The structure was solved by Direct Methods by SHELXT program and refined by SHELXL program. All H-atoms bound to the C atoms were positioned with idealized geometry and refined isotropically with U iso(H) = 1.2 times U eq(C) using a riding model with C–H = 0.93 Å for aromatic H atoms and C–H = 0.97 Å for methylene H atoms. The H-atoms (H1w, H2w, H13, and H7) from O and N atoms were positioned with Q peaks and refined isotropically with U iso(H) = 1.5 times U eq(O) or U iso(H) = 1.2 times U eq(N).
3 Comment
At present, the use of diverse polydentate ligands containing rich N/O coordinating atoms is preferred in the design and synthesis of metal coordination polymers including metal-organic frameworks because they generally can provide multiple coordination sites and exhibit various coordination geometries. 5 , 6 , 7 In the past two decades, as a flexible organic polydentate ligand, 5-[(pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino]isophthalic acid (H2L) has been selected to synthesize many interesting metal coordination polymers with some fascinating structural architecture. 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 The Cd(II) atom as the coordination center is a usual choice in the construction of metal coordination polymers, however, these reported metal coordination polymers based on H2L-related ligand, including our previously reported Cd–MOF [Cd(L)]·(DMF)(H2O), 12 are three-dimensional in the crystal structure. Herein, we obtained the first example of one-dimensional Cd(II) coordination polymer when using H2L as organic ligand through a solvo/hydrothermal method.
The asymmetric unit consists of one half of a Cd(II), one HL − anion, and one coordinated water molecule. Each Cd(II) atom is six-coordinated with two pyridine nitrogen atoms from two HL − ligands and four oxygen atoms from another two HL − ligands and two coordinated water molecules, which results in a slightly distorted octahedral geometric configuration {CdO4N2}. The Cd–N and Cd–O lengths are in the ranges of 2.317(2) Å and 2.3182(19)–2.3193(19) Å, respectively. These bond distances are in agreement with these previously reported cadmium coordination polymers. 13 In the title compound, the HL − ligand serves as a μ 2-bridge linking two adjacent Cd(II) atoms with its pyridine nitrogen atom and one carboxylate oxygen atom, where the dihedral angle between benzene ring and pyridine ring is 116.57°. Pairs of HL − ligands connect symmetry-related Cd(II) atoms through monodentate carboxylate O and pyridine N atoms with the Cd⋯Cd separation of 12.160(10) Å to form one-dimensional loop-like chain. An infinite three-dimensional supramolecular structure in the title compound was further formed from the one-dimensional loop-like chains and stabilized through hydrogen bonding and π–π stacking interactions. The distance between the benzene rings of two adjacent HL − ligands is 3.3599(12)–3.4205(12) Å, indicating the presence of π–π stacking interactions. Rich hydrogen bonding interactions include an intramolecular hydrogen bond (O5–H1w⋯O4) and intermolecular hydrogen bondings (O5–H2w⋯O3A, N2–H7⋯O4B, O2–H13⋯O1C).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Shangrao Normal University (No. 2024-CX-10) and the Science and Technology Research Project of the Education Department of Jiangxi Province (No. 201708).
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2004.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
5. Zhang, L. J.; Qi, L.; Chen, X. Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, L. J.; Ding, W. L.; Li, D.-L.; Yuan, G.-C.; Tong, J.-Z.; Chen, F.-Y.; Huang, H.-J.; Wang, Y.-H. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Photophysical Properties of Two Reduced Schiff Bases Derived from 5-Aminoisophthalic Acid. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2019, 49, 260–266; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10870-018-0761-z.Search in Google Scholar
6. Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Li, D.; Yuan, G.; Li, Y.; Wan, S.; Xiao, H.; Chen, F.; Zou, R. A 2D Pillared-Bilayer Iron-based Metal–Organic Framework: Syntheses, Crystal Structure, UV-Light Photocatalytic and Heterogeneous Fenton-like Catalytic Activities. Transition Met. Chem. 2023, 48, 47–54; https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-023-00522-1.Search in Google Scholar
7. Chen, X.-Y., Yao, X.-T., Cui, Y., Chen, M.-S. Crystal Structure of Poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-bromoisophthalato-κ3O,O′: O″)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N: N′) Dicadmium(II)] Dihydrate. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024; 239, 825–827.10.1515/ncrs-2024-0123Search in Google Scholar
8. Das, M. C.; Bharadwaj, P. K. A Porous Coordination Polymer Exhibiting Reversible Single-Crystal to Single-Crystal Substitution Reactions at Mn(II) Centers by Nitrile Guest Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10942–10949; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9006035.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Das, M. C.; Bharadwaj, P. K. Effect of Bulkiness on Reversible Substitution Reaction at MnII Center with Concomitant Movement of the Lattice DMF: Observation through Single-Crystal to Single-Crystal Fashion. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 5070–5077; https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200903129.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Karmakar, A.; Martins, L. M. D. R. S.; Hazra, S.; Silva, M. F. C. G.; Pombeiro, A. J. L. Metal–Organic Frameworks with Pyridyl-Based Isophthalic Acid and Their Catalytic Applications in Microwave Assisted Peroxidative Oxidation of Alcohols and Henry Reaction. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1837–1849; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5b01178.Search in Google Scholar
11. You, L. X.; Xie, S.; Xia, C. C.; Wang, J.; Xiong, G.; He, Y.; Dragutan, I.; Dragutan, V.; Fedin, V. P.; Sun, Y.-G. Unprecedented Homochiral 3D Lanthanide Coordination Polymers with Triple-Stranded Helical Architecture Constructed from a Rigid Achiral Aryldicarboxylate Ligand. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 1758–1763; https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ce01242c.Search in Google Scholar
12. Yuan, G. C.; Zhang, L. J.; Li, D. L.; Huang, D.; Chen, F. Y.; Huang, H. J.; Wang, Y. H. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Optical Properties of a Three-Dimensional Cadmium Complex Based on 5-{(pyridin-4-Yl-Methyl)amino} Isophthalic Acid. Chem. World 2017 (12), 736–740.Search in Google Scholar
13. Zhou, A.-M.; Wei, H.; Gao, W.; Liu, J.-P.; Zhang, X.-M. Two 2D Multiresponsive Luminescence Coordination Polymers for Selective Sensing of Fe3+, CrVI Anions and TNP in Aqueous Medium. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 5185–5194; https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ce01045a.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

