Abstract
C18H16O2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 5.6512(4) Å, b = 4.7795(3) Å, c = 22.9999(15) Å, β = 95.385(6)∘, V = 618.48(7) Å3, Z = 2, R gt(F) = 0.0545, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1712, T = 293(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.16 × 0.15 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 0.72 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 71.5°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured , N(hkl)unique, R int: | 2,125, 1,161, 0.023 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 942 |
| N(param)refined: | 123 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO,
1
Olex2,
2
SHELX
3
,
4
Diamond 5 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.4312 (4) | 0.4733 (4) | 0.47514 (9) | 0.0263 (5) |
| C2 | 0.2264 (4) | 0.2649 (5) | 0.46823 (9) | 0.0292 (6) |
| H2A | 0.110 (4) | 0.302 (5) | 0.4964 (11) | 0.026 (6)* |
| H2B | 0.291 (5) | 0.067 (6) | 0.4790 (12) | 0.041 (8)* |
| C3 | 0.1151 (4) | 0.2861 (5) | 0.40442 (10) | 0.0309 (6) |
| H3A | 0.114 (5) | 0.116 (7) | 0.3833 (13) | 0.041 (8)* |
| H3B | −0.052 (6) | 0.344 (7) | 0.4034 (13) | 0.054 (9)* |
| C4 | 0.2408 (4) | 0.5955 (5) | 0.32000 (9) | 0.0290 (6) |
| C5 | 0.3968 (4) | 0.7927 (5) | 0.30191 (10) | 0.0333 (6) |
| H5 | 0.375 (6) | 0.863 (7) | 0.2619 (15) | 0.054 (9)* |
| C6 | 0.5774 (5) | 0.8963 (5) | 0.34129 (10) | 0.0364 (6) |
| H6 | 0.699 (6) | 1.046 (7) | 0.3283 (14) | 0.057 (10)* |
| C7 | 0.6036 (4) | 0.8059 (5) | 0.39876 (10) | 0.0327 (6) |
| H7 | 0.734 (5) | 0.881 (7) | 0.4266 (13) | 0.043 (8)* |
| C8 | 0.4476 (4) | 0.6016 (4) | 0.41710 (9) | 0.0261 (5) |
| C9 | 0.2658 (4) | 0.4987 (5) | 0.37713 (9) | 0.0275 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0551 (3) | 0.4890 (4) | 0.28252 (7) | 0.0382 (5) |
| H1 | 0.005 (7) | 0.617 (10) | 0.2565 (19) | 0.087 (14)* |
1 Source of material
The title compound was synthesized by McMurry coupling reaction referring to the literature. 6 , 7 , 8 Firstly, TiCl4 (1.4 mL, 12.0 mmol) was slowly added to a stirred suspension of zinc powder (1.569 g, 24 mmol) in dry THF (50 mL) under a N 2 atmosphere. The solution was stirred at reflux for 1.5 h. Then, a THF solution (5 mL) of 1.1 mL pyridine and of 4-hydroxy-1-indanone (0.45 g, 3.0 mmol) was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred at 80 °C for 1 h, treated with a saturated aqueous solution of potassium carbonate, and extracted with CH2Cl2. The volume of the combined extracts was reduced to 30 mL and the precipitate was filtered off and dissolved in methanol. The crystals of the title compound were obtained by evaporation of the methanol solution at room temperature within 3 days. M.p. 234 °C–236 °C 1 H NMR (400 MHz, MeOD) 7.11 (dt, J = 15.6, 7.6 Hz, 4H), 6.64 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 3.15 ?C 3.09 (m, 4H), 2.99 (dd, J = 8.4, 4.4 Hz, 4H). Elemental Anal. Calcd. (%) for C11H8O4(204.18): C, 64.71; H, 3.95. Found (%): C, 63.59; H, 4.08.
2 Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were added in their geometrically theoretical positions. The U iso values of all hydrogen atoms were set to 1.2 U eq(C).
3 Comment
Stiff-stilbene derivatives, with reversible photo-induced isomerization properties, have been widely studied as molecular force probes, 9 , 10 molecular rotors 11 , 12 and optical switches, 13 , 14 owing to that the structures of (E)- and (Z) isomers were very different and all have high stability. Biindenylidene 6,6′-diol, as an important material for preparing fluorescent probes, plays an important role in the synthesis of supramolecular polymers. 15 , 16 , 17 However, biindenylidene 4,4′-diol is rarely developed as the core of photoprobes, so it is of great significance to study the synthesis and crystal structure of novel stiff-stilbene derivatives with stabilized fluorescence properties.
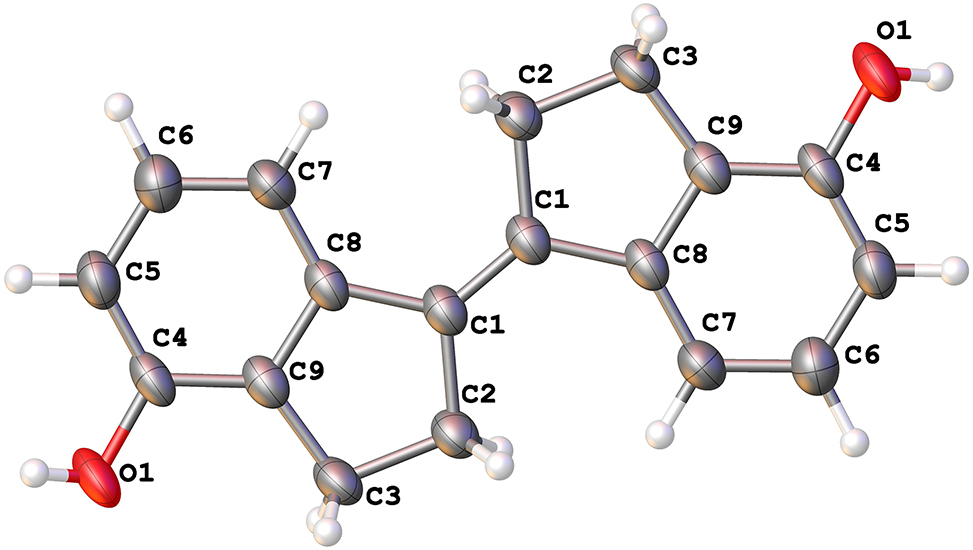
The Ortep diagram is displayed in the Figure. The asymmetric unit contains half of a molecule. Bond lengths and angles are within the expected range and very similar to stilbene derivative given in the literature. 18 The bond angles of C1′–C1–C2 and C1′–C1–C8 are 125.8(3)∘ and 127.5(3)∘. The C(1) = C(1′) olefinic bond adopts the E stereochemistry. 18 The indene ring is approximately planar. 19 The torsion angles of C1′–C1–C8–C9, C1′–C1–C8–C7, C1–C8–C7–C6 and C1–C8–C9–C4 are −177.5(3)∘, −0.2(5)∘, −178.5(2)∘, and 178.10(19)∘, respectively. This enhanced conjugate system is expected to be a good fluorophore, which promotes us to further explore restricted rigid stilbene derivatives to enhance their emission properties.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: National Natural Science Foundation of China (21702051), the Key Project of Henan Educational Committee (22A150041), the Henan Science and Technology Program (232102310364, 242102310575), the Science and Technology Major Projects in Henan Science and Technology Agency (241111311400) and the Young Backbone Teacher Training Objects of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province (2024GGJS154)
References
1. Oxford Diffraction Ltd, CrysAlisPRO, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England, 2006.Search in Google Scholar
2. OlexSys Ltd. Olex2, Chemistry Department; Durham University: UK. DH1 3LE.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of Shelx. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
5. Brandenburg, K. Diamond. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Version 3.0f; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 1998.Search in Google Scholar
6. Wu, Y. -H.; Huang, K.; Chen, S. -F.; Chen, Y. -Z.; Tung, C. -H.; Wu, L. -Z. Stiff-stilbene Derivatives as New Bright Fluorophores with Aggregation-Induced Emission. Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 1194–1197; https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-019-9514-8.Search in Google Scholar
7. Oelgemöller, M.; Frank, R.; Lemmen, P.; Lenoir, D.; Lex, J.; Inoue, Y. Synthesis, Structural Characterization and Photoisomerization of Cyclic Stilbenes. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 4048–4056; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2012.03.038.Search in Google Scholar
8. Wezenberg, S. J.; Feringa, B. L. Photocontrol of Anion Binding Affinity to a Bis-Urea Receptor Derived from Stiff-Stilbene. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 324–327; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03423.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y. -Z.; Niu, L. -Y.; Wu, L. -Z.; Tung, C. -H.; Yang, Q. -Z.; Boulatovc, R. A Light-Driven Molecular Machine Based on Stiff Stilbene. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 7991–7994; https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc04542a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Xu, F.; Sheng, J.; Stindt, C. N.; Crespi, S.; Danowski, W.; Hilbers, M. F.; Buma, W. J.; Feringa, B. L. All-visible-light-driven Stiff-Stilbene Photoswitches. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 6763–6769; https://doi.org/10.1039/d4sc00983e.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Panahi, F.; Mahmoodi, A.; Ghodrati, S.; Abdi, A. A.; Eshghi, F. New White Light-Emitting Halochromic Stilbenes with Remarkable Quantum Yields and Aggregation-Induced Emission. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2385; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-06435-w.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
12. Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Tian, C.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, L.; Cao, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, X.; Niu, C.; Ren, Y. -L.; Yang, L.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y. Highly Reversible Photomodulated Hydrosoluble Stiff-Stilbene Supramolecular Luminophor Induced by Cucurbituril. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109403; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2023.109403.Search in Google Scholar
13. Darugar, V.; Vakili, M.; Heydari, S.; Tahriri, M.; Brandán, S. A.; Castillo, M. V. Molecular Approach of Au – Stilbene – Au and Au – TCAB – Au Molecular Optical Electronic Devices Designed for Organic Light-Sensitive Circuits. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2024, 56, 757; https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-024-06522-4.Search in Google Scholar
14. Lvov, A. G.; Bredihhin, A. Azulene as an Ingredient for Visible-Light- and Stimuli-Responsive Photoswitches. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 4460–4468; https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ob00422k.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Wezenberg, S. J.; Chen, L. –J.; Bos, J. E.; Feringa, B. L.; Howe, E. N. W.; Wu, X.; Siegler, M. A.; Gale, P. A. Photomodulation of Transmembrane Transport and Potential by Stiff-Stilbene Based Bis(thio)ureas. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 331–338; https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c10034.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
16. Lu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Hong, Z.; Liang, P.; Liao, R.; Wang, F. Light-triggered Transformation of Stilbene Supramolecular Polymers: Thermodynamic versus Kinetic Control. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 8585–8588; https://doi.org/10.1039/d4cc01977f.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
17. Weyandt, E.; Leanza, L.; Capelli, R.; Pavan, G. M.; Vantomme, G.; Meijer, E. W. Controlling the Length of Porphyrin Supramolecular Polymers via Coupled Equilibria and Dilution-Induced Supramolecular Polymerization. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 248; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27831-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
18. Saltiel, J.; Mace, J. E.; Watkins, L. P.; Gormin, D. A.; Clark, R. J.; Dmitrenko, O. Biindanylidenes: Role of Central Bond Torsion in Nonvertical Triplet Excitation Transfer to the Stilbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 16158–16159; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja038087m.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
19. Xiong, Z. -Q.; Yang, L.; Xiao, S. -Z.; Yang, C. -Y.; Nie, X. -L. Crystal Structure of 3-Acetyl-6-Hydroxy-2H-Chromen-2-One Monohydrate. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 635–637; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0113.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

