Abstract
C20H15FN2O, triclinic, P
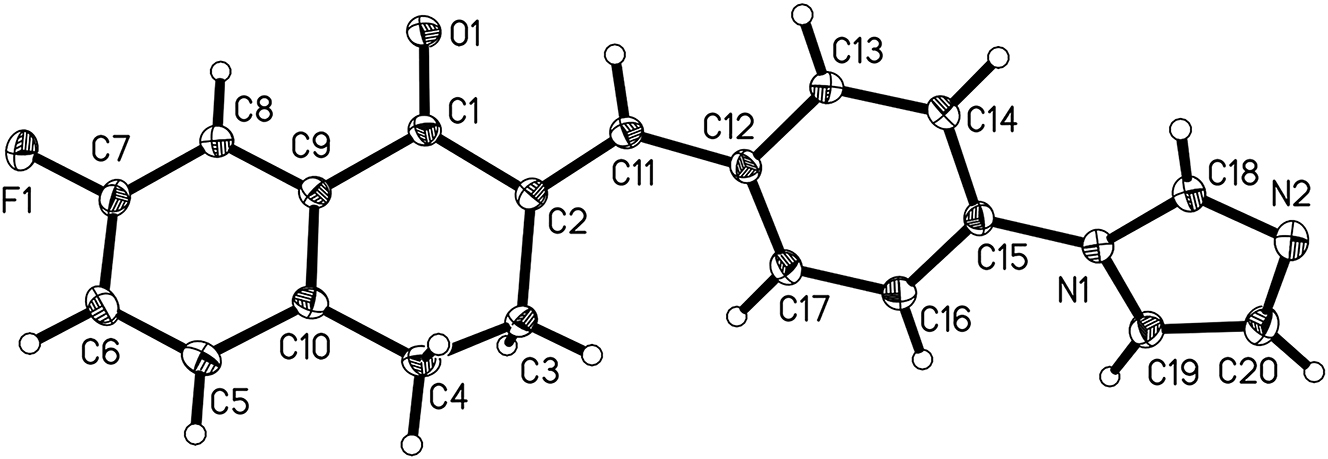
The crystal structure is shown in the Figure. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30 % probability level. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.13 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 0.81 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB AFC12 (RINC), |
| θ max, completeness: | 71.9°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 6,303, 2,770, 0.014 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2,687 |
| N(param)refined: | 218 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO 1 , SHELX 2 , 3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso */U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.82305 (14) | 0.64246 (12) | −0.13061 (12) | 0.0226 (3) |
| C2 | 0.77436 (14) | 0.73780 (12) | −0.02250 (12) | 0.0223 (3) |
| C3 | 0.90416 (15) | 0.83353 (12) | −0.00444 (13) | 0.0255 (3) |
| H3A | 0.870902 | 0.874896 | 0.081287 | 0.031* |
| H3B | 0.911473 | 0.909311 | −0.083435 | 0.031* |
| C4 | 1.07581 (15) | 0.75065 (13) | 0.00353 (13) | 0.0266 (3) |
| H4A | 1.159296 | 0.814850 | 0.007953 | 0.032* |
| H4B | 1.071606 | 0.682666 | 0.089119 | 0.032* |
| C5 | 1.29487 (15) | 0.65281 (13) | −0.17719 (13) | 0.0271 (3) |
| H5 | 1.377630 | 0.682788 | −0.133197 | 0.032* |
| C6 | 1.34109 (15) | 0.58753 (13) | −0.29541 (13) | 0.0286 (3) |
| H6 | 1.453236 | 0.573879 | −0.331600 | 0.034* |
| C7 | 1.21586 (15) | 0.54301 (12) | −0.35851 (13) | 0.0262 (3) |
| C8 | 1.04922 (15) | 0.55929 (12) | −0.30723 (12) | 0.0247 (3) |
| H8 | 0.968042 | 0.526767 | −0.351028 | 0.030* |
| C9 | 1.00428 (14) | 0.62582 (12) | −0.18776 (12) | 0.0218 (3) |
| C10 | 1.12670 (14) | 0.67499 (12) | −0.12191 (12) | 0.0229 (3) |
| C11 | 0.62089 (14) | 0.72668 (12) | 0.05057 (12) | 0.0233 (3) |
| H11 | 0.563242 | 0.655199 | 0.030039 | 0.028* |
| C12 | 0.52927 (14) | 0.80754 (12) | 0.15656 (12) | 0.0227 (3) |
| C13 | 0.39888 (14) | 0.74504 (12) | 0.24790 (12) | 0.0246 (3) |
| H13 | 0.374321 | 0.655116 | 0.238504 | 0.030* |
| C14 | 0.30593 (14) | 0.81330 (13) | 0.35142 (13) | 0.0256 (3) |
| H14 | 0.220059 | 0.769395 | 0.410675 | 0.031* |
| C15 | 0.34086 (14) | 0.94791 (12) | 0.36703 (12) | 0.0219 (3) |
| C16 | 0.46513 (15) | 1.01424 (12) | 0.27461 (13) | 0.0259 (3) |
| H16 | 0.486813 | 1.105295 | 0.282638 | 0.031* |
| C17 | 0.55700 (15) | 0.94529 (13) | 0.17041 (13) | 0.0263 (3) |
| H17 | 0.638856 | 0.991496 | 0.108326 | 0.032* |
| C18 | 0.15526 (14) | 0.95435 (13) | 0.59372 (12) | 0.0250 (3) |
| H18 | 0.140833 | 0.858480 | 0.611856 | 0.030* |
| C19 | 0.23889 (15) | 1.15810 (13) | 0.48889 (13) | 0.0281 (3) |
| H19 | 0.289392 | 1.229127 | 0.425915 | 0.034* |
| C20 | 0.14064 (16) | 1.17197 (13) | 0.61159 (13) | 0.0305 (3) |
| H20 | 0.112239 | 1.256746 | 0.646644 | 0.037* |
| F1 | 1.26047 (9) | 0.48216 (8) | −0.47745 (8) | 0.0357 (2) |
| N1 | 0.24878 (12) | 1.01667 (10) | 0.47639 (10) | 0.0229 (2) |
| N2 | 0.08820 (13) | 1.04393 (11) | 0.67778 (11) | 0.0295 (3) |
| O1 | 0.72062 (10) | 0.58009 (10) | −0.17490 (9) | 0.0320 (2) |
1 Source of material
Synthesis method based on literature in Ref. 4: in a 250 mL spherical backside flask, imidazole (10.88 g, 0.16 mol) and potassium carbonate (27.64 g, 0.2 mol) were reacted with N,N-dimethylformamide (10.0 mL) at 353 K for 4 h. The p-fluorobenzaldehyde (2.48 g, 0.02 mol) is added and the temperature is raised to 393 K for reflux. Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC, dichloromethane:methyl alcohol = 15:1, v:v) was used for detection. After the response, the yellow intermediate was purified by extraction, vacuum distillation and silica gel column (dichloromethane:methyl alcohol = 30:1, v:v). Using 25 % sodium hydroxide (2.0 mL) as catalyst, the intermediate (1.70 g, 10.00 mmol) and 7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthhalen-1(2H)-one (2.30 g, 10.00 mmol) were dissolved in methanol (5.0 mL) and stirred at room temperature for 1 h. Filtered and the filter cake dissolved in methylene chloride, the crude product was obtained by vacuum distillation and recrystallized at 293 K to obtain yellow crystals (dichloromethane:methyl alcohol = 1:1, v:v).
2 Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d (C–H) = 0.97 Å (methylene), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.93 Å (aromatic), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C).
3 Comment
It has been established that 3,4-dihydronaphthalene-1(2H)-one derivatives act as a,b-unsaturated ketones having proper anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory things to do. 4 , 5 It frequently inhibits the activation of NF-κB transcription factors in vivo to exert therapeutic effects. 6 In order to similarly discover molecules with higher therapeutic effects, we selected to introduce an imidazole ring at the C15 position, it can no longer solely enhance the water solubility of molecules via intramolecular hydrogen bonding, and it additionally has incredible contributions in antibacterial and anti-inflammatory aspects. 7 In this study, p-fluorobenzaldehyde and imidazole reacted to acquire 4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzaldehyde intermediate. Then, the intermediate reacts with 7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one to obtain the title compound through the Claisen–Schmidt reaction.
Single-crystal structure analysis reveals that there is only a molecule in the asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure (cf. the Figure). Bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges. 8 , 9 , 10 Fluorine atoms with electron withdrawing properties replace the 7 position of 3,4-dihydronaphthalene-1(2H)-one, and the introduction of fluorine can decorate organic undertaking and enhance metabolism. 11 In the C(2) position, a,b-unsaturated ketone was obtained through the Claisen–Schmidt reaction. 8 , 9 , 12 The torsion angle of O(1)=C(1)–C(2)=C(11) is about 15.96(17)°. The bond lengths of O(1)=C(1) and C(2)=C(11) are 1.2274(14) Å and 1.3470(16) Å, respectively. In the C(15) position, there’s an imidazole group substitution. Nitrogen atoms on imidazole groups have lone pair electrons, which are easy to act as hydrogen bond receptors and form hydrogen bond or electrostatic interaction with bioactive molecules. 7 The dihedral angle between 3,4-dihydronaphthalene-1(2H)-one and phenyl group is about 49.2°. The dihedral angle between the phenyl group and the imidazole group is about 16.8°.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Nos. ZR2022MH159 and ZR2023MH190) and Shandong Province Science and Technology-based Small and Medium-sized Enterprises Innovation Capacity Enhancement Project (No. 2023TSGC0870).
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Li, W. X.; Yu, L.; Chi, J. B.; Wang, J. P.; Liu, Y. J.; Wang, C. H.; Zhang, M.; Hou, G. G. Discovery of Anti-Inflammatory Agents from 3, 4-Dihydronaphthalene-1(2h)-One Derivatives by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 268, 116284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116284.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Zhang, X. F.; Luan, M. Z.; Yan, W. B.; Zhao, F. L.; Hou, Y.; Hou, G. G.; Meng, Q. G. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effects of Novel 5, 6-Dihydrobenzo [h]quinazolin-2-Amine Derivatives in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated BV2 Microglial Cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 235, 114322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114322.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Luan, M. Z.; Zhang, X. F.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Q. G.; Hou, G. G. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Fluorine-Substituted Benzo[h]quinazoline-2-Amine Derivatives as NF-Κb Inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 132, 106360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106360.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Chopra, P. N.; Sahu, J. K. Biological Significance of Imidazole-Based Analogues in New Drug Development. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2020, 17, 574–584. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570163816666190320123340.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Li, Y. L.; Meng, Q. G.; Hou, G. G.; Geng, Z. K. Crystal Structure of 2-((2-Fluoro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)(Hydroxy)Methyl)-7-Methoxy-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1((2h))-One, C19H16F4O3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 1157–1159. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0373.Search in Google Scholar
9. Yu, L.; Wang, J.-P.; Wang, M.-D.; Yu, W.-X.; Cui, Y.-T.; Gao, H.-X.; Liu, Y.-J.; Hou, G.-G. Crystal Structure of (E)-6-(4-Ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-Fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(E)-One, C23H25FN2O. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 515–517. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0066.Search in Google Scholar
10. Baddeley, T. C.; Gomes, L. R.; Low, J. N.; Turner, A. B.; Wardell, J. L.; Watson, G. J. R. Structural Studies of (E)-2-(Benzylidene)-1-Tetralone Derivatives: Crystal Structures and Hirshfeld Surface Analysis. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2017, 232, 697–718. https://doi.org/10.1515/zkri-2017-2048.Search in Google Scholar
11. Shah, P.; Westwell, A. D. The Role of Fluorine in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2007, 22, 527–540. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756360701425014.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Luo, H. L.; Li, W. X.; Bai, X. Y.; Meng, Q. G.; Hou, Y. Crystal Structure of (E)-7-Fluoro-2-(4-Morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One, C21H20FNO2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 495–497. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0053.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

