Abstract
C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 18.3690(6) Å, b = 3.8010(1) Å, c = 21.5232(7) Å, β = 108.867(1)∘, V = 1422.02(8) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0340, wR ref (F 2) = 0.0959, T = 173 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.38 × 0.24 × 0.13 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.11 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 28.0°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured , N(hkl)unique, R int: | 64276, 3409, 0.052 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3,194 |
| N(param)refined: | 234 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 ORTEP, 4 WinGX, 5 PLATON 6 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.67077 (5) | 0.4839 (3) | 0.52327 (5) | 0.0220 (2) |
| C2 | 0.64854 (5) | 0.3871 (3) | 0.58163 (5) | 0.0215 (2) |
| C3 | 0.69557 (6) | 0.4382 (3) | 0.64611 (5) | 0.0259 (2) |
| H3C | 0.745701 | 0.533785 | 0.65502 | 0.031* |
| C4 | 0.66878 (7) | 0.3486 (3) | 0.69729 (5) | 0.0317 (2) |
| H4A | 0.700354 | 0.387623 | 0.741369 | 0.038* |
| C5 | 0.59646 (7) | 0.2029 (3) | 0.68470 (6) | 0.0351 (3) |
| H5 | 0.578847 | 0.139029 | 0.720076 | 0.042* |
| C6 | 0.54983 (7) | 0.1501 (3) | 0.62075 (7) | 0.0354 (3) |
| H6 | 0.500146 | 0.050023 | 0.612111 | 0.043* |
| N1 | 0.73497 (5) | 0.6721 (2) | 0.53332 (4) | 0.02459 (19) |
| H1 | 0.7645 (8) | 0.737 (4) | 0.5720 (7) | 0.03* |
| N2 | 0.75807 (5) | 0.7979 (3) | 0.48085 (4) | 0.02526 (19) |
| O1 | 0.63121 (5) | 0.3933 (2) | 0.46747 (4) | 0.0358 (2) |
| C7 | 0.57550 (6) | 0.2429 (3) | 0.56932 (6) | 0.0292 (2) |
| H7 | 0.543162 | 0.20826 | 0.525346 | 0.035* |
| C8 | 0.62663 (5) | 0.2308 (3) | 0.31247 (5) | 0.0231 (2) |
| C9 | 0.59276 (5) | 0.1998 (3) | 0.23993 (5) | 0.02112 (19) |
| C10 | 0.63734 (5) | 0.0515 (3) | 0.20534 (5) | 0.0227 (2) |
| H10 | 0.688242 | −0.024467 | 0.22824 | 0.027* |
| C11 | 0.60787 (5) | 0.0135 (3) | 0.13737 (5) | 0.0226 (2) |
| C12 | 0.53323 (6) | 0.1313 (3) | 0.10492 (5) | 0.0238 (2) |
| H12 | 0.512502 | 0.109934 | 0.058529 | 0.029* |
| C13 | 0.48881 (5) | 0.2795 (3) | 0.13957 (5) | 0.0219 (2) |
| C14 | 0.51800 (5) | 0.3132 (3) | 0.20753 (5) | 0.0215 (2) |
| H14 | 0.487512 | 0.411739 | 0.23136 | 0.026* |
| C15 | 0.40987 (6) | 0.4131 (3) | 0.10450 (5) | 0.0244 (2) |
| N3 | 0.65209 (5) | −0.1260 (3) | 0.10164 (5) | 0.0287 (2) |
| O2 | 0.68833 (4) | 0.1043 (2) | 0.34397 (4) | 0.03175 (19) |
| O3 | 0.58273 (4) | 0.4088 (2) | 0.33915 (4) | 0.03042 (19) |
| H3 | 0.6050 (9) | 0.414 (4) | 0.3824 (9) | 0.046* |
| O4 | 0.39040 (5) | 0.3872 (3) | 0.03990 (4) | 0.0378 (2) |
| O5 | 0.36787 (4) | 0.5381 (2) | 0.13213 (4) | 0.03225 (19) |
| H3A | 0.6925 (10) | −0.244 (4) | 0.1253 (8) | 0.044 (4)* |
| H3B | 0.6236 (10) | −0.231 (5) | 0.0637 (9) | 0.049 (4)* |
| H2A | 0.7175 (9) | 0.918 (4) | 0.4520 (7) | 0.035 (4)* |
| H2B | 0.7696 (9) | 0.614 (4) | 0.4586 (8) | 0.045 (4)* |
| H4 | 0.3381 (11) | 0.491 (5) | 0.0177 (9) | 0.064 (5)* |
1 Source of materials
Benzhydrazide and 5-amino-isophthalic acid were both purchased commercially and not purified any further. An amount of 0.0214 g of benzhydrazide (0.157 mmol) and 0.0132 g 5-aminoisophthalic acid (0.0728 mmol) were added to a vial and dissolved in 3 ml of AP-grade methanol. The mixture was stirred and heated to 100 °C for 1 min, and then placed in the fridge (8 °C) overnight. The solution was then allowed to slowly evaporate at room temperature with cap being left slightly open. Yellow block crystals formed after three days.
2 Experimental details
C-bound hydrogen atoms were located in the difference map then positioned geometrically and were allowed to ride on their respective parent atoms with thermal displacement parameters 1.2 times of the parent C atom. The coordinates and isotropic displacement parameters of the N-bound and O-bound H atoms involved in hydrogen bonding interactions were allowed to refine freely. Diagrams and publication material were generated using ORTEP-3, 4 WinGX 5 and PLATON. 6
3 Comment
Benzhydrazide also known as benzohydrazide and its derivatives have become popular due to their biological properties, such as anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-cancer and anti-tubercular activity. 7 Benzhydrazide in its pure form crystallizes in the P21/n space group. 8
5-aminoisophthalic acid, a dicarboxylic acid with an amino group is used a lot in the metal organic frameworks of co-ordination chemistry, 9 but is also used in co-crystal engineering. 10 The 5-aminoisophthalic acid can react with a number of aldehydes to form Schiff bases, due to the amino group, by removing water molecules. 11 5–Aminoisophthalic acid in its pure form crystallizes in the Pbcn space group. 12
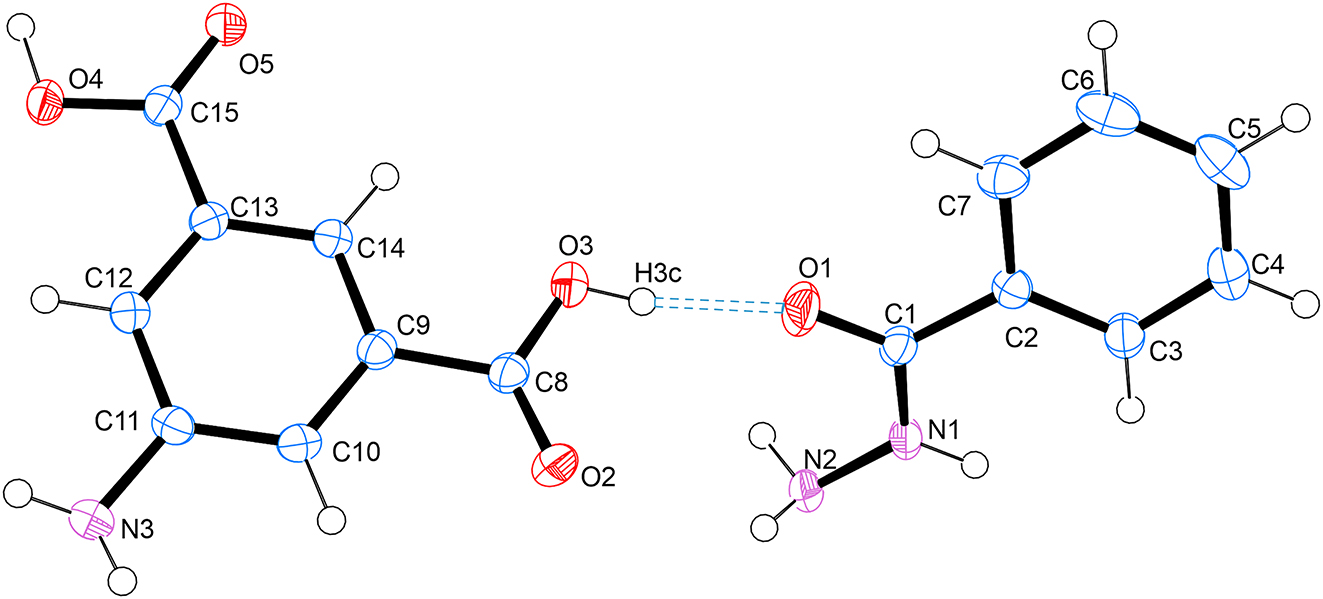
The benzhydrazide⋅5-aminoisophthalic acid asymmetric unit contains one molecule of benzhydrazide and one molecule of 5-aminoisophthalic acid (see the figure). There is a single hydrogen bond between the two molecules making a discrete hydrogen bond via O1⃛H3c–O3.
With regard to packing, each benzhydrazide molecule is hydrogen bonded to four 5-aminoisophthalic acid molecules via O1⃛H3c–O3, O2⃛H2a–N2, N3⃛H2b–N2, N2⃛H4a–O4 and O5⃛H1–N1. Each aminoterephthalic acid is hydrogen bonded to four benzhydrazide molecules and two aminoterephthalic acid molecules.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) “Competitive Support for Unrated Researchers” grant Number CSUR23042597072 (Dr MG Smith) and the University of South Africa (Ms JMM Bourletidis How).
References
1. Bruker Apex3. Saint–Plus and Xprep; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2016.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Shelxt , Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxtl – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Ortep-3, Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and Ortep for Windows: an Update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Search in Google Scholar
5. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX Suite for Small-Molecule Single-Crystal Crystallography. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 837–838; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889899006020.Search in Google Scholar
6. Spek, A. L. Structure Validation in Chemical Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155; https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Search in Google Scholar
7. Kumari, D.; Bansal, H.; Kumari, D.; Benzohydrazides, C. As Potential Bio-Active Agents. Pharm. Innov. 2018, 7, 543–550.Search in Google Scholar
8. Kallel, A.; Amor, B. H.; Svoboda, I.; Fuess, H. Crystal Structure of Benzhydrazide, NH2NHCO(C6H5). Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 1992, 198, 137–138; https://doi.org/10.1524/zkri.1992.198.1-2.137.Search in Google Scholar
9. Wang, H. N.; Meng, X.; Qin, C.; Wang, X. L.; Yang, G. S.; Su, Z. M. A Series of Pillar-Layer Metal–Organic Frameworks Based on 5-aminoisophthalic Acid and 4,4′-bipyridine. J. Chem. Soc. 2011, 41, 1047–1053; https://doi.org/10.1039/c1dt11304f.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Mcguire, S. C.; Travis, S. C.; Tuohey, D. W.; Deering, T. J.; Martin, B.; Cox, J. M.; Benedict, J. B. Crystal Structure of the Co-crystal of 5-Amino-Isophthalic Acid and 1,2-Bis(pyridin-4-Yl)ethene. Acta Crystallogr. 2016, E72, 639–642; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989016005259.Search in Google Scholar
11. Zhang, L. J.; Qi, L.; Chen, X. Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, L. J.; Ding, W. L.; Li, D. L.; Yuan, G. C.; Tong, J. Z.; Chen, F. Y.; Huang, H. J.; Wang, Y. H. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Photophysical Properties of Two Reduced Schiff Bases Derived from 5–Aminoisophthalic Acid. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2019, 49, 260–266; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10870-018-0761-z.Search in Google Scholar
12. Fujii, K.; Sakon, A.; Sekine, A.; Uekusa, H. Reversible Color Switching of an Organic Crystal Induced by Organic Solvent Vapors. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 4305–4308; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg2010437.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

