Abstract
C36H26N6O16Yb2, triclinic,
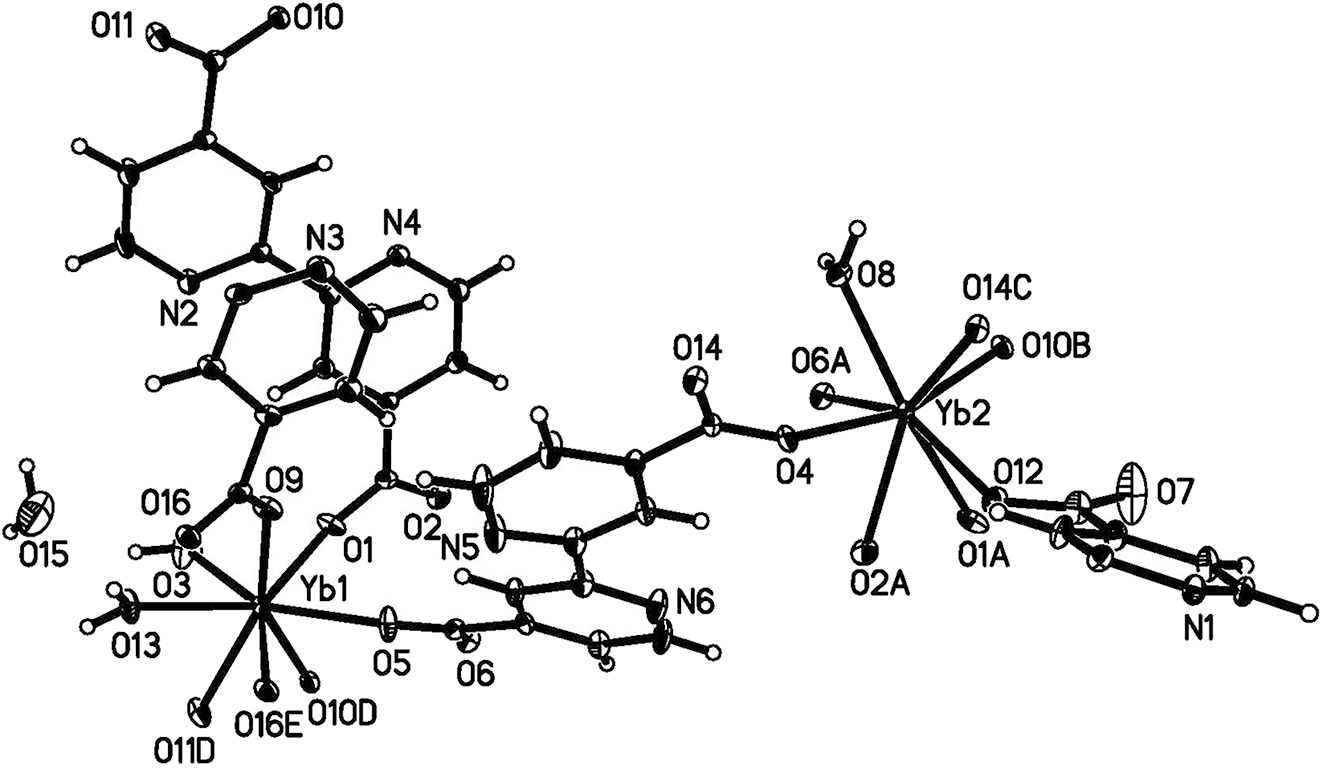
A part of the molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.19 × 0.18 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 5.14 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 28.4°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 26,819, 7,969, 0.043 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 6,913 |
| N(param)refined: | 547 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 34 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yb1 | 0.39387 (2) | 0.83407 (2) | 0.36524 (2) | 0.01324 (5) |
| Yb2 | −0.20611 (2) | 0.36514 (2) | 0.88971 (2) | 0.01646 (5) |
| O1 | −0.3433 (3) | 0.3780 (2) | 0.7482 (2) | 0.0297 (7) |
| O2 | −0.3998 (3) | 0.3477 (2) | 0.5874 (2) | 0.0280 (7) |
| O3 | −0.3981 (3) | 0.3573 (3) | 0.9160 (2) | 0.0500 (10) |
| H3A | −0.407438 | 0.360905 | 0.974050 | 0.075* |
| H3B | −0.460853 | 0.307063 | 0.882111 | 0.075* |
| O4 | 0.4402 (2) | 0.8629 (2) | 0.52661 (19) | 0.0212 (6) |
| O5 | −0.1004 (3) | 0.3635 (3) | 0.7723 (2) | 0.0306 (7) |
| O6 | −0.1967 (2) | 0.2439 (2) | 0.6343 (2) | 0.0217 (6) |
| O7 | 0.5991 (3) | 0.7861 (4) | 0.2037 (3) | 0.0704 (14) |
| O8 | 0.2921 (2) | 0.9808 (2) | 0.3956 (2) | 0.0222 (6) |
| H8A | 0.213803 | 0.956274 | 0.372306 | 0.033* |
| H8B | 0.305293 | 1.046184 | 0.382026 | 0.033* |
| O9 | −0.1422 (3) | 0.5525 (2) | 0.8976 (2) | 0.0289 (7) |
| O10 | −0.2969 (2) | 1.1659 (2) | 0.80136 (19) | 0.0201 (6) |
| O11 | −0.2384 (3) | 1.1979 (2) | 0.9623 (2) | 0.0314 (7) |
| O12 | 0.5827 (2) | 0.8078 (2) | 0.3563 (2) | 0.0259 (7) |
| O13 | −0.1737 (3) | 0.4302 (3) | 1.0591 (2) | 0.0321 (7) |
| H13A | −0.125488 | 0.491814 | 1.090910 | 0.048* |
| H13B | −0.200348 | 0.395944 | 1.102569 | 0.048* |
| O14 | 0.4892 (2) | 0.9989 (2) | 0.6544 (2) | 0.0217 (6) |
| O16 | −0.0015 (2) | 0.6250 (2) | 1.0399 (2) | 0.0238 (7) |
| N1 | 1.0404 (3) | 0.9518 (3) | 0.3897 (2) | 0.0215 (8) |
| N2 | −0.3752 (4) | 0.7737 (3) | 0.8986 (3) | 0.0327 (9) |
| N3 | −0.0002 (4) | 0.9642 (3) | 0.8731 (3) | 0.0337 (9) |
| N4 | −0.3424 (3) | 0.7689 (3) | 0.6514 (2) | 0.0224 (8) |
| N5 | 0.2319 (3) | 0.6854 (3) | 0.7716 (3) | 0.0345 (10) |
| N6 | 0.1716 (3) | 0.4843 (3) | 0.5539 (3) | 0.0316 (9) |
| C1 | −0.2823 (4) | 1.1295 (3) | 0.8844 (3) | 0.0201 (9) |
| C2 | −0.0168 (5) | 0.8719 (4) | 0.8087 (4) | 0.0412 (13) |
| H2 | −0.011184 | 0.881718 | 0.743844 | 0.049* |
| C3 | 0.8388 (4) | 0.9229 (4) | 0.4214 (3) | 0.0250 (10) |
| H3 | 0.788922 | 0.933519 | 0.465330 | 0.030* |
| C4 | −0.3690 (3) | 0.4139 (3) | 0.6663 (3) | 0.0197 (9) |
| C5 | −0.3486 (4) | 0.6952 (4) | 0.5742 (3) | 0.0247 (10) |
| H5 | −0.345743 | 0.723275 | 0.514028 | 0.030* |
| C6 | −0.1112 (3) | 0.3245 (3) | 0.6851 (3) | 0.0184 (9) |
| C7 | −0.3589 (4) | 0.5803 (3) | 0.5756 (3) | 0.0228 (9) |
| H7 | −0.362887 | 0.531481 | 0.518112 | 0.027* |
| C8 | 0.4348 (3) | 0.9008 (3) | 0.6105 (3) | 0.0148 (8) |
| C9 | −0.3451 (4) | 0.8125 (3) | 0.8192 (3) | 0.0211 (9) |
| C10 | −0.0644 (4) | 0.6331 (3) | 0.9560 (3) | 0.0209 (9) |
| C11 | −0.3499 (4) | 0.7266 (3) | 0.7352 (3) | 0.0201 (9) |
| C12 | −0.0464 (4) | 0.7471 (3) | 0.9246 (3) | 0.0213 (9) |
| C13 | 0.9671 (4) | 0.9676 (3) | 0.4507 (3) | 0.0214 (9) |
| C14 | −0.0120 (3) | 0.3773 (3) | 0.6378 (3) | 0.0171 (9) |
| C15 | 0.3568 (4) | 0.8646 (4) | 0.7585 (3) | 0.0312 (11) |
| H15 | 0.396871 | 0.940439 | 0.787395 | 0.037* |
| C16 | −0.3632 (3) | 0.5380 (3) | 0.6629 (3) | 0.0184 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0952 (4) | 0.3833 (4) | 0.5130 (3) | 0.0341 (12) |
| H17 | 0.106008 | 0.347787 | 0.454043 | 0.041* |
| C18 | −0.3146 (4) | 1.0059 (3) | 0.8899 (3) | 0.0220 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0019 (4) | 0.3277 (4) | 0.5512 (3) | 0.0243 (10) |
| H19 | −0.051118 | 0.257218 | 0.518428 | 0.029* |
| C20 | −0.0415 (4) | 0.7635 (4) | 0.8310 (3) | 0.0313 (11) |
| H20 | −0.055159 | 0.700516 | 0.781866 | 0.038* |
| C21 | 0.2925 (5) | 0.7922 (4) | 0.8090 (4) | 0.0445 (14) |
| H21 | 0.291247 | 0.819810 | 0.873665 | 0.053* |
| C22 | 0.6434 (4) | 0.8145 (4) | 0.2926 (3) | 0.0298 (11) |
| C23 | −0.0086 (4) | 0.9477 (3) | 0.9647 (3) | 0.0232 (10) |
| C24 | 0.3621 (3) | 0.8248 (3) | 0.6651 (3) | 0.0198 (9) |
| C25 | 0.1550 (4) | 0.5325 (3) | 0.6371 (3) | 0.0238 (10) |
| C26 | 0.2997 (3) | 0.7140 (3) | 0.6249 (3) | 0.0196 (9) |
| H26 | 0.302121 | 0.683691 | 0.561295 | 0.024* |
| C27 | 0.0657 (4) | 0.4815 (3) | 0.6815 (3) | 0.0222 (9) |
| H27 | 0.057700 | 0.517563 | 0.741300 | 0.027* |
| C28 | −0.0294 (4) | 0.8422 (3) | 0.9930 (3) | 0.0257 (10) |
| H28 | −0.032131 | 0.834101 | 1.058708 | 0.031* |
| C29 | 0.8589 (4) | 0.8491 (4) | 0.2653 (3) | 0.0269 (10) |
| H29 | 0.824196 | 0.809806 | 0.200431 | 0.032* |
| C30 | −0.3593 (3) | 0.6132 (3) | 0.7434 (3) | 0.0214 (9) |
| H30 | −0.363202 | 0.586950 | 0.804156 | 0.026* |
| C31 | 0.9860 (4) | 0.8942 (4) | 0.3004 (3) | 0.0244 (10) |
| H31 | 1.037667 | 0.883407 | 0.257989 | 0.029* |
| C32 | −0.3136 (4) | 0.9278 (3) | 0.8138 (3) | 0.0211 (9) |
| H32 | −0.291314 | 0.952754 | 0.757207 | 0.025* |
| C33 | −0.3721 (5) | 0.8510 (4) | 0.9732 (3) | 0.0432 (13) |
| H33 | −0.391467 | 0.824542 | 1.030194 | 0.052* |
| C34 | 0.7838 (4) | 0.8632 (4) | 0.3285 (3) | 0.0236 (10) |
| C35 | −0.3431 (5) | 0.9651 (4) | 0.9726 (3) | 0.0380 (12) |
| H35 | −0.342295 | 1.016006 | 1.027856 | 0.046* |
| C36 | 0.2339 (4) | 0.6487 (4) | 0.6796 (3) | 0.0242 (10) |
| O15 | −0.4598 (5) | 0.4209 (4) | 1.0785 (4) | 0.0941 (17) |
| H15A | −0.510080 | 0.370121 | 1.096450 | 0.141* |
| H15B | −0.495080 | 0.476151 | 1.074100 | 0.141* |
1 Source of materials
A mixture of Yb(NO3)3·5H2O (0.0452 g, 0.1 mmol) and 2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid (0.0366 g, 0.15 mmol) was dissolved in 8 mL of deionized water. The mixture was sealed in a 25 mL Teflon-lined steel autoclave after ultrasound treatment for 15 min and heated at 140 °C for 72 h. The mixture was cooled to room temperature at a rate of 3 °C/h, and colorless block crystals were isolated by filtration, washed with distilled water and dried in air.
2 Experimental details
CrysAlisPro 1.171.39.46 (Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, 2018). 1 Empirical absorption correction using spherical harmonics, implemented in SCALE3 ABSPACK scaling algorithm.
Using Olex2, 2 the structure was solved with the ShelXT 3 structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL 4 refinement package.
The carbon bound hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined using a riding model on attached atoms.
3 Comment
In recent years, ytterbium(III) metal-organic frameworks (Yb–MOFs) have attracted considerable attentions due to their structural diversity and potential applications in various fields such as adsorption, catalysis, detection, degradation, etc. 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 . Nitrogen-containing carboxylic acids are widely used as ligands in the synthesis of Yb–MOFs. 5 , 8 , 9 Among these ligands, 2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid (H2BPDC) has garnered considerable interest due to its potential as a bridging ligand and abundant coordination modes. 10 In this study, a new Yb–MOF was constructed using H2BPDC as ligand and water as solvent.
The asymmetric unit contains two Yb(III) ions, three deprotonated BPDC2− ligands (with two different coordination modes), three coordinated water molecules, and one lattice water (see figure). Yb1 and Yb2 are both 8-coordinated. Yb1 coordinates with six oxygen atoms from five deprotonated BPDC2− ligands (O1; O5; O9; O10D, O11D; O16E; D: x, −1 + y, z; E: −x, 1 − y, 2 − z), and two oxygen atoms from coordinated water molecules (O3, O13). Yb2 coordinates with seven oxygen atoms from six deprotonated BPDC2− ligands (O1A, O2A; O4; O6A; O10B; O12; O14C; A: −x, 1 − y, 1 − z; B: −x, 2 − y, 1 − z; C: 1 − x, 2 − y, 1 − z), and one oxygen atom from a water molecule (O8). The bond distances of Yb–O range from 2.198(3) to 2.795(3) Å, which are in agreement with distances found in similar Yb compound. 8 , 9 Yb1 and Yb2 are linked by a bridging BPDC2− ligand, and the title compound was connected into a three-dimensional MOF structure through alternating bridging ligands and Yb(III) centers. 11 The crystal structure of the title compound is further stablized by multiple hydrogen bonds.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22371110), the Program for Science & Technology Innovation Research Team in Universities of Henan Province, China (No. 21IRTSTHN004).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Oxford Diffraction Ltd, CrysAlisPRO, Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Version 1.171.39.6a, England, 2018.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Fan, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Zheng, L.; Cao, Q. e.; Fan, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Zheng, L.; Cao, Q. A Turn-On NIR Fluorescence Sensor for Gossypol Based on Yb-Based Metal-Organic Framework. Talanta 2022, 238, 123030; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123030.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Xie, Y.; Sun, G.; Mandl, G. A.; Maurizio, S. L.; Chen, J.; Capobianco, J. A.; Sun, L. Upconversion Luminescence through Cooperative and Energy–Transfer Mechanisms in Yb3+–Metal–Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. 2023, 135, e202216269; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202216269.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Li, Q.-L.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.-F.; Wang, M.-L.; Zhao, R.-S. In Situ Hydrothermal Growth of Ytterbium-Based Metal–Organic Framework on Stainless Steel Wire for Solid-phase Microextraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Environmental Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1415, 11–19; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.08.036.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Hashemzadeh, A.; Amini, M. M.; Khavasi, H. R.; Ng, S. W. Ligand Preferences in Ytterbium Ions Complexation with Carboxylate-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Coord. Chem. 2017, 70, 3217–3232; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2017.1375098.Search in Google Scholar
9. Dang, S.; Min, X.; Yang, W.; Yi, F. Y.; You, H.; Sun, Z. M. Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks Showing Luminescence in the Visible and Near–Infrared Regions with Potential for Acetone Sensing. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 17172–17179; https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201301346.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Vitiu, B. A.; Croitor, L.; Siminel, A.; Koropchanu, E.; Bourosh, P. A Novel 2D Zinc (II) Coordination Polymer Based on 2, 2′-Bipyridine-4, 4′-dicarboxylic Acid: Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Photoluminescence Property. Chem. J. Mold. 2018, 13, 30–35; https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2017.479.Search in Google Scholar
11. Fan, K.; Bao, S.-S.; Huo, R.; Huang, X.-D.; Liu, Y.-J.; Yu, Z.-W.; Kurmoo, M.; Zheng, L.-M. Luminescent Ir(iii)–Ln(iii) Coordination Polymers Showing Slow Magnetization Relaxation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 4580–4592; https://doi.org/10.1039/c9qi01504c.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

