Abstract
C18H16Cl2N2O2S, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 10.915(2) Å, b = 11.801(2) Å, c = 14.059(3) Å, β = 90.10(3)°, V = 1810.9(6) Å3, Z = 4, R gt(F) = 0.0585, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1532, T = 293(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | MoKα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.49 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: ω | Nonius CAD4, |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.4°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 3510, 3327, 0.033 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 2,220 |
| N(param)refined: | 228 |
| Programs: | Olex2 1 , 2 , SHELX 3 , 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.2797 (3) | 0.4196 (3) | 0.5263 (3) | 0.0412 (9) |
| C2 | 0.3957 (4) | 0.3872 (4) | 0.5548 (3) | 0.0577 (11) |
| H2A | 0.432971 | 0.422219 | 0.606539 | 0.069* |
| C3 | 0.4562 (4) | 0.3023 (4) | 0.5056 (3) | 0.0564 (11) |
| H3 | 0.535068 | 0.281639 | 0.523770 | 0.068* |
| C4 | 0.4010 (3) | 0.2483 (3) | 0.4306 (2) | 0.0353 (8) |
| C5 | 0.2858 (3) | 0.2823 (3) | 0.4023 (2) | 0.0379 (8) |
| H5 | 0.248467 | 0.247017 | 0.350696 | 0.045* |
| C6 | 0.2251 (3) | 0.3679 (3) | 0.4494 (3) | 0.0402 (8) |
| H6 | 0.147675 | 0.390555 | 0.429345 | 0.048* |
| C7 | 0.0893 (4) | 0.4580 (4) | 0.6547 (3) | 0.0700 (14) |
| H7A | 0.044050 | 0.512065 | 0.691562 | 0.105* |
| H7B | 0.127611 | 0.404170 | 0.696456 | 0.105* |
| H7C | 0.034656 | 0.419075 | 0.612252 | 0.105* |
| C8 | 0.4649 (3) | 0.1545 (3) | 0.3784 (2) | 0.0358 (8) |
| C9 | 0.5669 (3) | 0.1809 (3) | 0.3237 (3) | 0.0438 (9) |
| H9 | 0.597259 | 0.254547 | 0.322226 | 0.053* |
| C10 | 0.6221 (3) | 0.0967 (3) | 0.2718 (3) | 0.0430 (9) |
| C11 | 0.5792 (3) | −0.0126 (3) | 0.2768 (3) | 0.0468 (10) |
| H11 | 0.618598 | −0.068697 | 0.241834 | 0.056* |
| C12 | 0.4261 (3) | 0.0411 (3) | 0.3799 (2) | 0.0363 (8) |
| C13 | 0.3186 (3) | −0.0022 (3) | 0.4339 (2) | 0.0360 (8) |
| C14 | 0.2762 (3) | 0.0436 (3) | 0.5180 (2) | 0.0383 (8) |
| H14 | 0.314408 | 0.107376 | 0.543205 | 0.046* |
| C15 | 0.1215 (3) | −0.0962 (3) | 0.5344 (3) | 0.0414 (9) |
| C16 | 0.1598 (4) | −0.1437 (3) | 0.4502 (3) | 0.0468 (9) |
| H16 | 0.120262 | −0.207787 | 0.426789 | 0.056* |
| C17 | 0.2558 (3) | −0.0976 (3) | 0.4002 (3) | 0.0460 (9) |
| H17 | 0.279525 | −0.130426 | 0.342979 | 0.055* |
| C18 | 0.0198 (4) | −0.1403 (3) | 0.5945 (3) | 0.0580 (11) |
| H18A | 0.052597 | −0.189730 | 0.642447 | 0.087* |
| H18B | −0.036943 | −0.181525 | 0.555413 | 0.087* |
| H18C | −0.021674 | −0.078065 | 0.624364 | 0.087* |
| Cl1 | 0.74754 (11) | 0.12534 (10) | 0.19970 (9) | 0.0747 (4) |
| Cl2 | 0.09593 (10) | 0.16098 (9) | 0.70782 (7) | 0.0562 (3) |
| N1 | 0.4834 (3) | −0.0407 (2) | 0.3299 (2) | 0.0444 (8) |
| N2 | 0.1807 (3) | −0.0026 (2) | 0.5640 (2) | 0.0415 (7) |
| H2 | 0.155975 | 0.029646 | 0.615321 | 0.050* |
| O1 | 0.1395 (4) | 0.5983 (3) | 0.5223 (2) | 0.0870 (12) |
| O2 | 0.2851 (3) | 0.5788 (3) | 0.6535 (3) | 0.1014 (14) |
| S1 | 0.20075 (10) | 0.52766 (8) | 0.58930 (7) | 0.0506 (3) |
1 Source of material
1.1 Experimental details
Single-crystal diffraction data were collected on a Nonius CAD4 with a MoKα X-ray source (λ = 0.71073 Å). The crystal structures were solved by using Olex2. 1 , 2 The model was solved with the ShelXT 3 structure solution program and further refinement with the ShelXL 4 refinement package. Hydrogen atoms on carbon atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions. All carbon bound hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically. The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with the d(C–H) = 0.96 Å (methyl) and d(C–H) = 0.93 Å (aromatic). And U iso(H) = 1.2 times U iso(C) and U iso(H) = 1.5 times U iso(O), respectively.
2 Comment
Etoricoxib is a specific inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2, employed for the management of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and acute gout attacks. 1 In accordance with the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS), ETR falls under Class II drugs, characterized by low bioavailability. 5 Its poor aqueous solubility, coupled with a pronounced pH-dependency, poses constraints on its clinical utilization. Etoricoxib is an intriguing molecule, devoid of traditional hydrogen bond donors, yet featuring potent electronegativity from its pyridine nitrogen and sulfonyl oxygen atoms. To date, several solid forms, including polymorphs, solvates, cocrystals and salts, have been reported. 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 To explore more solid forms of ETR into a drug candidate, in this paper, a new hydrochloride salt has been explored.
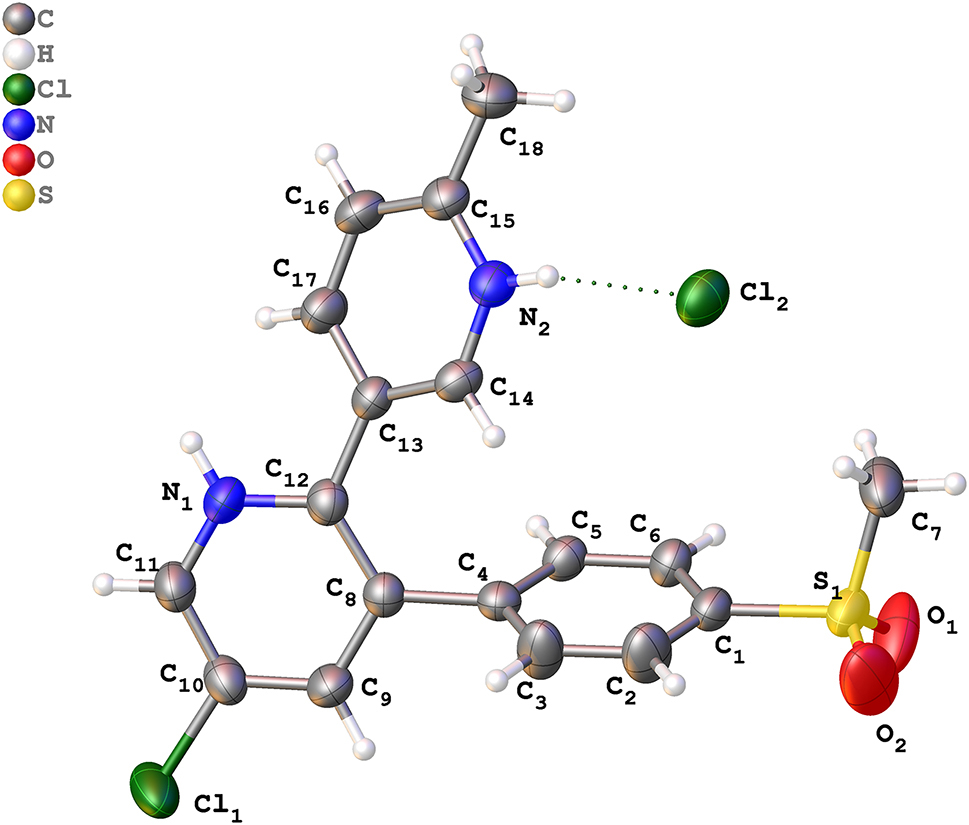
ETR–Bz crystallized in monoclinic, P21/c space group, with four asymmetric units in a unit cell (Z = 4). Each asymmetric unit contains one ETR+ cation and one Cl− anion (Z′ = 1). As expected, intermolecular proton transfer occurs from the chloride, forming charge-assisted hydrogen bond, N2–H2⋯Cl2 (2.127 Å, 158.8°). The intermolecular hydrogen bonding interactions reinforce the robustness and stability of the solid state. The torsion angle [C4–C8–C12–C13] of the pyridine ring of ETR is −0.905°. In general, all bond lengths and angles are in the expected ranges in both molecules.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: New engineering research and reform practice project (2021xgk10); Chuzhou University college students innovation and entrepreneurship training program (No. 2024CXXL021); Anhui University Natural Science Foundation (No. KJ2021B16).
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
2. Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. The Anatomy of a Comprehensive Constrained, Restrained Refinement Program for the Modern Computing Environment – Olex2 Dissected. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 59–75. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. FDA. Waiver of In Vivo Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Immediate–Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms Based on a Biopharmaceutics Classification System; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2002.Search in Google Scholar
6. Dalton, C. R.; Clas, S. D.; Singh, J.; Khougaz, K.; Bilbeisi, R. Investigating the Hydrate Conversion Propensity of Different Etoricoxib Lots. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 56–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.20499.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Grobelny, P.; Mukherjee, A.; Desiraju, G. R. Polymorphs and Hydrates of Etoricoxib, A Selective COX-2 Inhibitor. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 5785–5794. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ce06604a.Search in Google Scholar
8. Sudhir, M.; Geetha, B.; Sravankumar, P.; Ashwini, N. Can We Exchange Water in a Hydrate Structure: A Case Study of Etoricoxib. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 2825–2829. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ce00003g.Search in Google Scholar
9. Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, N.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bao, Y. Structure Analysis and Insight into Hydrogen Bond and van der Waals Interactions of Etoricoxib Cocrystals and Cocrystal Solvate. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1258, 132665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.132665.Search in Google Scholar
10. Ma, Y. H.; Zhu, M. M.; Zhang, C. N.; Tang, X. S.; Zhang, W. G.; Ma, W. J. The Co-Crystal Structure of Etoricoxib-Phthalic Acid (1/1), C18H15ClN2O2S⋅C8H6O4. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 641–643. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0129.Search in Google Scholar
11. Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Fang, W.; Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; Liang, P.; Gao, Z.; Bao, Y. Understanding the Role of Solvent Polarity in the Molecular Self-Assembly Process of Etoricoxib Solvates. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 3650–3662. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.9b01399.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

