Abstract
C15H22N2O2, monoclinic, P21 (no. 4), a = 8.4853(2) Å, b = 19.5759(4) Å, c = 9.0640(2) Å, β = 106.845(2)°, V = 1441.00(6) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.00374, wR ref (F 2) = 0.0991, T = 150 K.
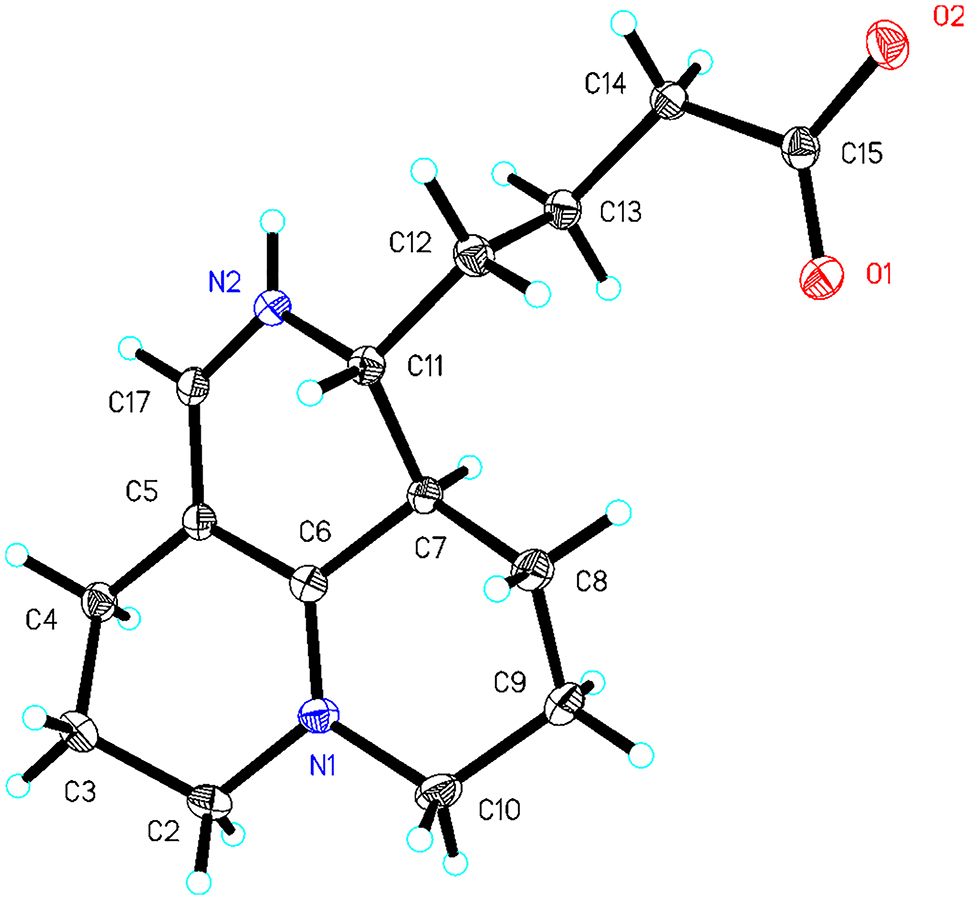
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.12 × 0.11 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) 0.73 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θ max, completeness: |
SuperNova, ω
74.0°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 13135, 5610, 0.034 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 5461 |
| N(param)refined: | 367 |
| Programs: | Olex2, 1 SHELX 2 , 3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.0677 (2) | 0.64406 (9) | 0.4676 (2) | 0.0312 (4) |
| O2 | −0.0398 (2) | 0.54071 (10) | 0.3946 (2) | 0.0325 (4) |
| N1 | 0.2342 (2) | 0.88293 (10) | 1.0100 (2) | 0.0250 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0937 (3) | 0.68675 (10) | 1.0753 (2) | 0.0253 (4) |
| H2 | 0.080730 | 0.642775 | 1.088276 | 0.030* |
| C2 | 0.2620 (3) | 0.93510 (12) | 1.1325 (3) | 0.0284 (5) |
| H2A | 0.201969 | 0.977264 | 1.088893 | 0.034* |
| H2B | 0.380828 | 0.946217 | 1.168477 | 0.034* |
| C3 | 0.2061 (3) | 0.91228 (13) | 1.2692 (3) | 0.0302 (5) |
| H3A | 0.084373 | 0.913547 | 1.241358 | 0.036* |
| H3B | 0.249871 | 0.944057 | 1.356499 | 0.036* |
| C4 | 0.2662 (3) | 0.84011 (12) | 1.3181 (3) | 0.0273 (5) |
| H4A | 0.387929 | 0.839547 | 1.357058 | 0.033* |
| H4B | 0.221542 | 0.824367 | 1.401708 | 0.033* |
| C5 | 0.2091 (3) | 0.79350 (12) | 1.1809 (3) | 0.0227 (4) |
| C6 | 0.2021 (3) | 0.81839 (12) | 1.0334 (3) | 0.0221 (4) |
| C7 | 0.1687 (3) | 0.76709 (12) | 0.9019 (3) | 0.0228 (4) |
| H7 | 0.272091 | 0.740381 | 0.913726 | 0.027* |
| C8 | 0.1234 (3) | 0.80092 (13) | 0.7436 (3) | 0.0312 (5) |
| H8A | 0.124652 | 0.766616 | 0.663669 | 0.037* |
| H8B | 0.011184 | 0.820487 | 0.719391 | 0.037* |
| C9 | 0.2471 (4) | 0.85701 (14) | 0.7445 (3) | 0.0357 (6) |
| H9A | 0.359563 | 0.837566 | 0.771992 | 0.043* |
| H9B | 0.223177 | 0.877524 | 0.640453 | 0.043* |
| C10 | 0.2374 (4) | 0.91131 (13) | 0.8601 (3) | 0.0349 (6) |
| H10A | 0.333400 | 0.942130 | 0.876549 | 0.042* |
| H10B | 0.136731 | 0.938913 | 0.817096 | 0.042* |
| C11 | 0.0367 (3) | 0.71732 (12) | 0.9208 (3) | 0.0238 (5) |
| H11 | −0.064506 | 0.744516 | 0.915694 | 0.029* |
| C12 | −0.0116 (3) | 0.66129 (13) | 0.7994 (3) | 0.0268 (5) |
| H12A | −0.060624 | 0.683013 | 0.697835 | 0.032* |
| H12B | −0.097998 | 0.632781 | 0.822312 | 0.032* |
| C13 | 0.1278 (3) | 0.61467 (12) | 0.7872 (3) | 0.0261 (5) |
| H13A | 0.176239 | 0.591787 | 0.887508 | 0.031* |
| H13B | 0.215004 | 0.642584 | 0.764062 | 0.031* |
| C14 | 0.0691 (3) | 0.56065 (12) | 0.6621 (3) | 0.0273 (5) |
| H14A | −0.030474 | 0.538626 | 0.676404 | 0.033* |
| H14B | 0.155336 | 0.525083 | 0.677879 | 0.033* |
| C15 | 0.0285 (3) | 0.58544 (12) | 0.4953 (3) | 0.0246 (5) |
| C17 | 0.1647 (3) | 0.72619 (12) | 1.1945 (3) | 0.0240 (5) |
| H17 | 0.186370 | 0.707345 | 1.294986 | 0.029* |
| O1A | 0.2960 (3) | 0.33844 (11) | 0.1245 (2) | 0.0472 (5) |
| O2A | 0.2134 (4) | 0.44442 (12) | 0.1513 (3) | 0.0557 (7) |
| N1A | 0.4754 (3) | 0.10655 (10) | −0.3462 (3) | 0.0285 (4) |
| N2A | 0.2809 (2) | 0.29788 (10) | −0.4760 (2) | 0.0249 (4) |
| H2AA | 0.254774 | 0.341081 | −0.496205 | 0.030* |
| C2A | 0.5439 (4) | 0.06458 (14) | −0.4479 (3) | 0.0368 (6) |
| H2AB | 0.516018 | 0.016033 | −0.437788 | 0.044* |
| H2AC | 0.665415 | 0.068760 | −0.414701 | 0.044* |
| C3A | 0.4784 (4) | 0.08591 (14) | −0.6156 (3) | 0.0370 (6) |
| H3AA | 0.359780 | 0.074700 | −0.654741 | 0.044* |
| H3AB | 0.537190 | 0.060645 | −0.678211 | 0.044* |
| C4A | 0.5031 (3) | 0.16262 (15) | −0.6300 (3) | 0.0331 (5) |
| H4AA | 0.622136 | 0.173228 | −0.602999 | 0.040* |
| H4AB | 0.450926 | 0.177527 | −0.737429 | 0.040* |
| C5A | 0.4265 (3) | 0.19960 (12) | −0.5227 (3) | 0.0248 (5) |
| C6A | 0.4203 (3) | 0.16933 (12) | −0.3843 (3) | 0.0230 (4) |
| C7A | 0.3672 (3) | 0.21316 (12) | −0.2689 (3) | 0.0234 (5) |
| H7A | 0.464891 | 0.240971 | −0.212318 | 0.028* |
| C8A | 0.3144 (3) | 0.17164 (14) | −0.1485 (3) | 0.0313 (5) |
| H8AA | 0.303139 | 0.202139 | −0.064982 | 0.038* |
| H8AB | 0.206226 | 0.150008 | −0.196675 | 0.038* |
| C9A | 0.4423 (4) | 0.11699 (15) | −0.0821 (3) | 0.0368 (6) |
| H9AA | 0.549619 | 0.138795 | −0.031290 | 0.044* |
| H9AB | 0.408731 | 0.090203 | −0.003620 | 0.044* |
| C10A | 0.4600 (4) | 0.06985 (14) | −0.2091 (3) | 0.0366 (6) |
| H10C | 0.558543 | 0.040806 | −0.168267 | 0.044* |
| H10D | 0.362777 | 0.039426 | −0.240138 | 0.044* |
| C11A | 0.2329 (3) | 0.26319 (12) | −0.3523 (3) | 0.0231 (4) |
| H11A | 0.130395 | 0.236452 | −0.400269 | 0.028* |
| C12A | 0.1919 (3) | 0.31801 (13) | −0.2476 (3) | 0.0278 (5) |
| H12C | 0.101107 | 0.346790 | −0.310269 | 0.033* |
| H12D | 0.152132 | 0.295109 | −0.167830 | 0.033* |
| C13A | 0.3365 (3) | 0.36402 (14) | −0.1682 (3) | 0.0324 (6) |
| H13C | 0.380657 | 0.385045 | −0.247381 | 0.039* |
| H13D | 0.424956 | 0.335786 | −0.100272 | 0.039* |
| C14A | 0.2900 (3) | 0.42046 (13) | −0.0726 (3) | 0.0288 (5) |
| H14C | 0.377674 | 0.455573 | −0.050405 | 0.035* |
| H14D | 0.187392 | 0.442392 | −0.135672 | 0.035* |
| C15A | 0.2640 (3) | 0.39783 (13) | 0.0797 (3) | 0.0305 (5) |
| C17A | 0.3626 (3) | 0.26502 (12) | −0.5568 (3) | 0.0247 (5) |
| H17A | 0.379115 | 0.287390 | −0.644186 | 0.030* |
| O3 | 0.0057 (3) | 0.55455 (9) | 0.1139 (2) | 0.0358 (4) |
| H3D | 0.070130 | 0.521348 | 0.113187 | 0.054* |
| H3C | −0.005520 | 0.554018 | 0.204122 | 0.054* |
| O4 | 0.1809 (3) | 0.42944 (10) | 0.4334 (2) | 0.0386 (5) |
| H4C | 0.190543 | 0.433391 | 0.343010 | 0.058* |
| H4D | 0.110787 | 0.459768 | 0.438147 | 0.058* |
1 Source of material
The dried roots of Sophora flavescens (25.0 kg) were sourced from Xi’an, Shanxi Province, China. After three extractions with 95 % ethanol, the combined extracts were concentrated under vacuum to yield 1.6 kg of residue. This was suspended in water, adjusted to pH 4 with HCl, and partitioned with chloroform. The aqueous phase was then adjusted to pH 9 with ammonium hydroxide and re-extracted with chloroform, yielding 464 g of chloroform-soluble fraction. Chromatography on macroporous resin produced several fractions, with the title compound isolated from the EtOH/H2O (10:90) fraction and crystallized from methanol.
2 Experimental details
Using Olex2, 1 the structure was solved with the ShelXT 2 structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL 3 refinement package.
3 Comment
Matrine-type alkaloids are a class of naturally occurring compounds predominantly found in plants of the Sophora genus. These alkaloids are characterized by their tetracyclic quinolizidine core structure. 4 Recent advancements in pharmacological research have highlighted the diverse biological activities. 5 , 6 Due to their intricate stereostructure and diverse biological activities, matrine-type alkaloids have garnered significant interest as promising targets for both pharmacological studies and synthetic chemistry endeavors.
The title compound was identified as (−)-flavesine H, the enantiomer of the previously reported (+)-flavesine H. 6 It belongs to the matrine-type alkaloids, distinguished by an open-loop ring D. Notably, the single-crystal structure of (+-)-flavesine H has not yet been reported. The C=O bond lengths 1.236(3)–1.277(3) Å, C–N bond lengths 1.314(3)–1.476(3) Å, C=C bond lengths 1.386(3)–1.408(3) Å and C–C bond lengths 1.507(3)–1.547(2) Å, which were derived from the title structure are within normal ranges. 7
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82304320).
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: a Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxtl – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Li, J.; Wei, S.; Marabada, D.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q. Research Progress of Natural Matrine Compounds and Synthetic Matrine Derivatives. Molecules 2023, 28, 5780; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155780.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Zhang, Y. B.; Zhan, L. Q.; Li, G. Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. L.; Ye, W. C.; Wang, G. C. Dimeric Matrine-type Alkaloids from the Roots of Sophora flavescens and their anti–Hepatitis B Virus Activities. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 6273–6280; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.6b00804.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Zhang, Y. B.; Luo, D.; Yang, L.; Cheng, W.; He, L. J.; Kuang, G. K.; Li, M. M.; Li, Y. L.; Wang, G. C. Matrine-type Alkaloids from the Roots of Sophora flavescens and their Antiviral Activities against the Hepatitis B Virus. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2259–2265; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.8b00576.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Li, W. Z.; Xu, L. H.; Liang, C. B.; Wang, H. B. Crystal Structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-Dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 399–400; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0017.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

