Abstract
C15H14MnN3O8, monoclinic, P21/m (no. 11), a = 7.3212(3) Å, b = 11.9120(4) Å, c = 9.3666(3) Å, β = 94.345(3)∘, V = 814.51(5) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0242, wR ref (F 2) = 0.0685, T = 293 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Brown block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.86 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.0°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 7,031, 1,522, 0.021 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 1,421 |
| N(param)refined: | 132 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX 2 , 3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn1 | 0.26380 (4) | 0.250000 | 0.46946 (3) | 0.02215 (13) |
| O1 | 0.1708 (2) | −0.06988 (10) | 0.38543 (13) | 0.0431 (3) |
| O2 | 0.30818 (18) | −0.04675 (9) | 0.66941 (13) | 0.0380 (3) |
| O3 | 0.21269 (15) | 0.11342 (9) | 0.35656 (11) | 0.0275 (3) |
| O4 | 0.5314 (2) | 0.250000 | 0.3865 (2) | 0.0392 (4) |
| H4 | 0.572798 | 0.185999 | 0.388825 | 0.047* |
| O5 | −0.0527 (2) | 0.250000 | 0.46708 (18) | 0.0282 (4) |
| H5 | −0.086772 | 0.192855 | 0.506037 | 0.034* |
| N1 | 0.30644 (18) | 0.14421 (10) | 0.62461 (13) | 0.0248 (3) |
| N2 | 0.9139 (3) | 0.250000 | 0.1591 (2) | 0.0507 (7) |
| H2A | 0.921109 | 0.250000 | 0.261353 | 0.061* |
| C1 | 0.2854 (2) | 0.03577 (13) | 0.59122 (17) | 0.0253 (3) |
| C3 | 0.3463 (2) | 0.19070 (13) | 0.76276 (16) | 0.0257 (3) |
| C2 | 0.2179 (2) | 0.02225 (13) | 0.43096 (17) | 0.0266 (4) |
| C4 | 0.3769 (3) | 0.13240 (15) | 0.89073 (18) | 0.0358 (4) |
| H9 | 0.379781 | 0.054347 | 0.891038 | 0.043* |
| C5 | 0.4033 (3) | 0.19177 (17) | 1.01826 (18) | 0.0419 (5) |
| H10 | 0.421129 | 0.153087 | 1.104436 | 0.050* |
| C6 | 0.8746 (3) | 0.1507 (2) | −0.0546 (2) | 0.0575 (6) |
| H13 | 0.865528 | 0.082831 | −0.103657 | 0.069* |
| C7 | 0.9021 (3) | 0.1523 (2) | 0.0913 (2) | 0.0554 (6) |
| H14 | 0.912569 | 0.085422 | 0.142493 | 0.067* |
| C8 | 0.8606 (5) | 0.250000 | −0.1276 (3) | 0.0558 (8) |
| H15 | 0.841447 | 0.250000 | −0.226920 | 0.067* |
1 Source of materials
The opba ligand {opbaH4 = 2,2′-(1,2-phenylenebis(azanediyl))bis(2-oxoacetic acid)} and Me4N[Mn(opba)(H2O)2] was prepared by following the reported literature methods. 4 , 5 A solution of pyridine hydrochloride (11.6 mg, 0.1 mmol) in methanol (5 mL) was added dropwise under stirring to a methanolic solution (10 mL) of Me4N[Mn(opba)(H2O)2] (41.3 mg g, 0.1 mmol). The formed solution was stirred for about 30 min and then filtered off to evaporate in air at room temperature. X-ray quality block brown crystals appeared after a few days, which were collected and air-dried. Yield: 26.1 mg (62.3 %).
2 Experimental details
Coordinates of hydrogen atoms were refined with constraints or restraints. Their U iso values were set to 1.2U eq of the parent atoms.
3 Comment
Since the discovery of the first molecular-based magnets exhibiting a spontaneous magnetization below a critical temperature T c and by the perspectives offered by this new class of compounds, molecular magnetic material have attracted intense attention from the beginning of this century. 6 , 7 Due to its large spin state (S = 2) as well as the usually negative magnetic anisotropy, the six-coordinated octahedral high-spin d 4 MnIII ion, which has an orbitally degenerate 5E g ground electronic term that is split by the Jahn–Teller effect into 5A1g and 5B1g orbital singlet low-lying states, have been widely used to prepare molecule magnetism complexes with interesting magnetic properties. 8 , 9 , 10 Here, we report the structure of a new 1,2-phenylenebis(oxamato) (opba) based Mn(III) complex.
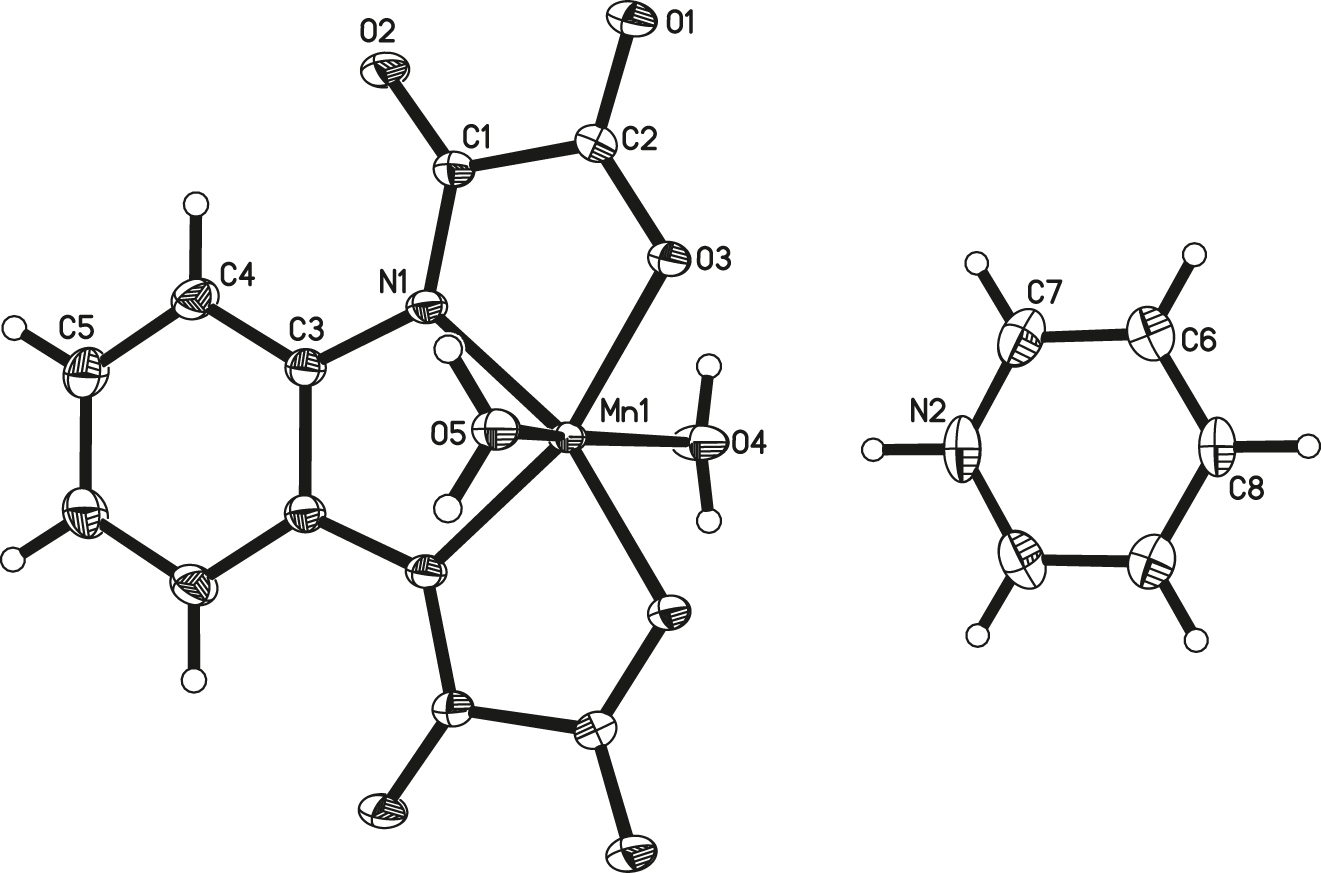
As demonstrated in figure, the title manganese complex [Mn(opba)(H2O)2][C6H6N] contains two independent units in the asymmetric unit cell, is comprised by one [Mn(obpa)(H2O)2]− anion and one pyridinium. The cation and the anion are located on a mirror plane (see the figure). The planar opba ligand adopts a tetradentate coordination mode forming three five-membered chelate rings around the manganese(III) ion. This pattern of 5-5-5 fused chelate rings imposes a severe distortion of the equatorial metal environment. The coordination sphere for the Mn atom in the title complex can be described as a distorted octahedral, in which four equatorial positions are occupied by two amidate nitrogen and two carboxylate oxygen atoms from the opba ligand, while the axial positions are occupied by two O atoms of the water molecules. The averaged Mn–N/Oequatorial bond lengths in the title complex are 1.9312(13) and 1.9615(11) Å, respectively, obviously shorter than the distance between Mn atom and the O axial atom with the values 2.1663(18) and 2.3193(17) Å, clearly indicating the elongation octahedron surrounding the Mn(III) ion, typically accounting for the well-known Jahn–Teller effect. The axial bond angle O4–Mn1–O5 158.55(8)∘ departs significantly from linear configuration. The intermolecular N–H⋯O hydrogen bond interactions can be found between the pyridinium cation and the anion. Additionally, under the help of the intermoleular O–H⋯O hydrogen bond interactions between the coordinated water molecules, the ion-pair complex can be linked into 2D supramolecular network structure.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Doctoral Research Foundation of Weifang University (2021BS07).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT–Plus, XPREP; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2004.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Fettouhi, M.; Ouahab, L.; Boukhari, A.; Cador, O.; Mathonière, C.; Kahn, O. New Metal Oxamates as Precursors of Low-Dimensional Heterobimetallics. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 4932–4937; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic960174a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Barroso, S.; Blay, G.; Fernandez, I.; Pedro, J. R.; Ruiz-Garcia, R.; Pardo, E.; Lloret, F.; Munoz, M. C. Chemistry and Reactivity of Mononuclear Manganese Oxamate Complexes: Oxidative Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage of Vic-Diols by Dioxygen Andaldehydes Catalyzed by a Trans- Dipyridine Manganese(III) Complex with a Tetradentate O-Phenylenedioxamate Ligand. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2006, 243, 214–220; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2005.08.027.Search in Google Scholar
6. Miyasaka, H.; Saitoh, A.; Abe, S. Magnetic Assemblies Based on Mn(III) Salen Analogues. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 2622–2664; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.028.Search in Google Scholar
7. Feng, M.; Ruan, Z. Y.; Chen, Y. C.; Tong, M. L. Physical Stimulus and Chemical Modulations of Bistable Molecular Magnetic Materials. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 13702–13718; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cc04202a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Zhang, D. P.; Lan, W. L.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, Q. Y.; Bian, Y. Z.; Jiang, J. Z. Manganese(III) Porphyrin-Based Magnetic Materials. Topics Curr. Chem. 2019, 377, 18–60; https://doi.org/10.1007/s41061-019-0244-5.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Bernot, K.; Luzon, J.; Sessoli, R.; Vindigni, A.; Thion, J.; Richeter, S.; Leclercq, D.; Larionova, J.; van der Lee, A. The Canted Antiferromagnetic Approach to Single-Chain Magnets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1619–1627; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0751734.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Vallejo, J.; Pascual-Alvarez, A.; Cano, J.; Castro, I.; Julve, M.; Lloret, F.; Giovanni De Munno, J. K.; Armentano, D.; Wernsdorfer, W.; Ruiz-García, R.; Pardo, E. Field-Induced Hysteresis and Quantum Tunneling of the Magnetization in a Mononuclear Manganese(III) Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 14075–14079; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201308047.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

