Abstract
C20H13NiN3O7; triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 8.329(7) Å, b = 8.726(8) Å, c = 13.300(12) Å, α = 85.948(14)°, β = 75.509(14)°, γ = 72.258(13)°, V = 891.3(13) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0373, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1007, T = 296(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.26 × 0.21 × 0.17 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.14 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.0°, 98 % |
| N(hkl)measured , N(hkl)unique, R int: | 4,471, 3,086, 0.024 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2,704 |
| N(param)refined: | 276 |
| Programs: | Olex2, 1 , 2 Bruker, 3 SHELX 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni1 | 0.95599 (5) | −0.04474 (4) | 0.68080 (3) | 0.02280 (14) |
| O1W | 1.1042 (3) | 0.0582 (3) | 0.56520 (17) | 0.0297 (5) |
| O1 | 0.7538 (3) | 0.0856 (2) | 0.62287 (15) | 0.0292 (5) |
| O2 | 0.5819 (3) | 0.1976 (3) | 0.76952 (16) | 0.0447 (6) |
| O3 | 0.2933 (3) | 0.5092 (3) | 0.81915 (16) | 0.0391 (5) |
| O4 | 0.5335 (3) | 0.5403 (3) | 0.73304 (18) | 0.0464 (6) |
| O5 | 0.0209 (3) | 0.7437 (2) | 0.59075 (15) | 0.0280 (5) |
| O6 | 0.1887 (3) | 0.7683 (2) | 0.68602 (16) | 0.0315 (5) |
| N1 | 0.9477 (3) | 0.1088 (3) | 0.79041 (18) | 0.0263 (5) |
| N2 | 0.8221 (3) | −0.1379 (3) | 0.80752 (18) | 0.0258 (5) |
| N3 | 0.4057 (3) | 0.5000 (3) | 0.74070 (19) | 0.0278 (6) |
| C1 | 0.6184 (4) | 0.1820 (3) | 0.6768 (2) | 0.0252 (6) |
| C3 | 0.4743 (2) | 0.21391 (16) | 0.53001 (14) | 0.0281 (6) |
| H3 | 0.545099 | 0.111530 | 0.507299 | 0.034* |
| C4 | 0.3502 (2) | 0.2995 (2) | 0.47746 (12) | 0.0313 (7) |
| H4 | 0.337929 | 0.254318 | 0.419582 | 0.038* |
| C5 | 0.2444 (2) | 0.4525 (2) | 0.51141 (14) | 0.0301 (7) |
| H5 | 0.161368 | 0.509727 | 0.476245 | 0.036* |
| C6 | 0.2628 (2) | 0.51997 (16) | 0.59791 (13) | 0.0230 (6) |
| C7 | 0.3869 (2) | 0.43442 (19) | 0.65047 (11) | 0.0214 (6) |
| C2 | 0.4927 (2) | 0.28139 (18) | 0.61652 (13) | 0.0223 (6) |
| C8 | 0.1521 (4) | 0.6878 (3) | 0.6272 (2) | 0.0240 (6) |
| C9 | 1.0095 (4) | 0.2319 (4) | 0.7790 (3) | 0.0347 (7) |
| H9 | 1.068355 | 0.254237 | 0.713191 | 0.042* |
| C10 | 0.9904 (5) | 0.3295 (4) | 0.8609 (3) | 0.0410 (8) |
| H10 | 1.034616 | 0.416733 | 0.850140 | 0.049* |
| C11 | 0.9069 (4) | 0.2967 (4) | 0.9568 (3) | 0.0388 (8) |
| H11 | 0.892751 | 0.362072 | 1.012564 | 0.047* |
| C12 | 0.8418 (4) | 0.1655 (4) | 0.9726 (2) | 0.0317 (7) |
| C13 | 0.8648 (4) | 0.0764 (3) | 0.8855 (2) | 0.0257 (6) |
| C14 | 0.7987 (4) | −0.0576 (3) | 0.8954 (2) | 0.0259 (6) |
| C15 | 0.7144 (4) | −0.0999 (4) | 0.9917 (2) | 0.0302 (7) |
| C16 | 0.6963 (4) | −0.0083 (4) | 1.0798 (2) | 0.0369 (8) |
| H16 | 0.641573 | −0.036882 | 1.145096 | 0.044* |
| C17 | 0.7567 (4) | 0.1187 (4) | 1.0705 (2) | 0.0380 (8) |
| H17 | 0.742526 | 0.177407 | 1.129479 | 0.046* |
| C18 | 0.6521 (4) | −0.2316 (4) | 0.9960 (2) | 0.0364 (7) |
| H18 | 0.595430 | −0.264764 | 1.059241 | 0.044* |
| C19 | 0.6744 (4) | −0.3109 (4) | 0.9077 (3) | 0.0373 (8) |
| H19 | 0.632163 | −0.398426 | 0.909445 | 0.045* |
| C20 | 0.7602 (4) | −0.2610 (3) | 0.8150 (2) | 0.0313 (7) |
| H20 | 0.775125 | −0.317093 | 0.754791 | 0.038* |
| H1WA | 1.050 (5) | 0.131 (4) | 0.540 (3) | 0.036 (10)* |
| H1WB | 1.165 (5) | −0.006 (5) | 0.517 (3) | 0.046 (11)* |
1 Source of materials
An aqueous solution (20 mL) containing Ni(NO3)2·6H2O (116.4 mg, 0.4 mmol) was added to the ethanol/water (v:v = 2:1) solution (30 mL) of 1,10-phenanthroline (59.4 mg, 0.3 mmol) and 2-nitroisophthalic acid (nipaH2; 84.5 mg, 0.4 mmol) under stirring at room temperature, followed by adjusting pH to about 8.5 with NH3·H2O solution (1.0 mol/L). After continuing to stir for 0.5 h, the mixture was transferred into a Teflon-lined steel autoclave and reacted at 150 °C for 48 h, and then cooled to room temperature naturally. The yellow crystalline product of the title compound was collected by filtration, washed with water and ethanol, and dried in air (yield: 57 %, based on Ni).
2 Experimental details
The hydrogen atoms were located from the difference Fourier map and allowed to ride on their parent atoms with U iso(H) = 1.2 U eq(C).
3 Comment
2-nitroisophthalic acid (H2nipa) is a semi-rigid ligand with a curved structure, and its two carboxyl groups are located at an appropriate angle (approximately 120°), which can join metal ions to form one-dimensional helical chains, and its nitro and carboxyl groups can be excellent donors of coordination atoms and hydrogen bonds. 5 , 6 It can exhibit fine binding abilities as a bridge ligand in a variety of coordination modes. H2nipa and its derivatives can form interesting metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with N-donor ligands. 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 The 1,10-phenanthrene (phen) is an important N-donor ligand and has a strong affinity for metals in various oxidation states. 12
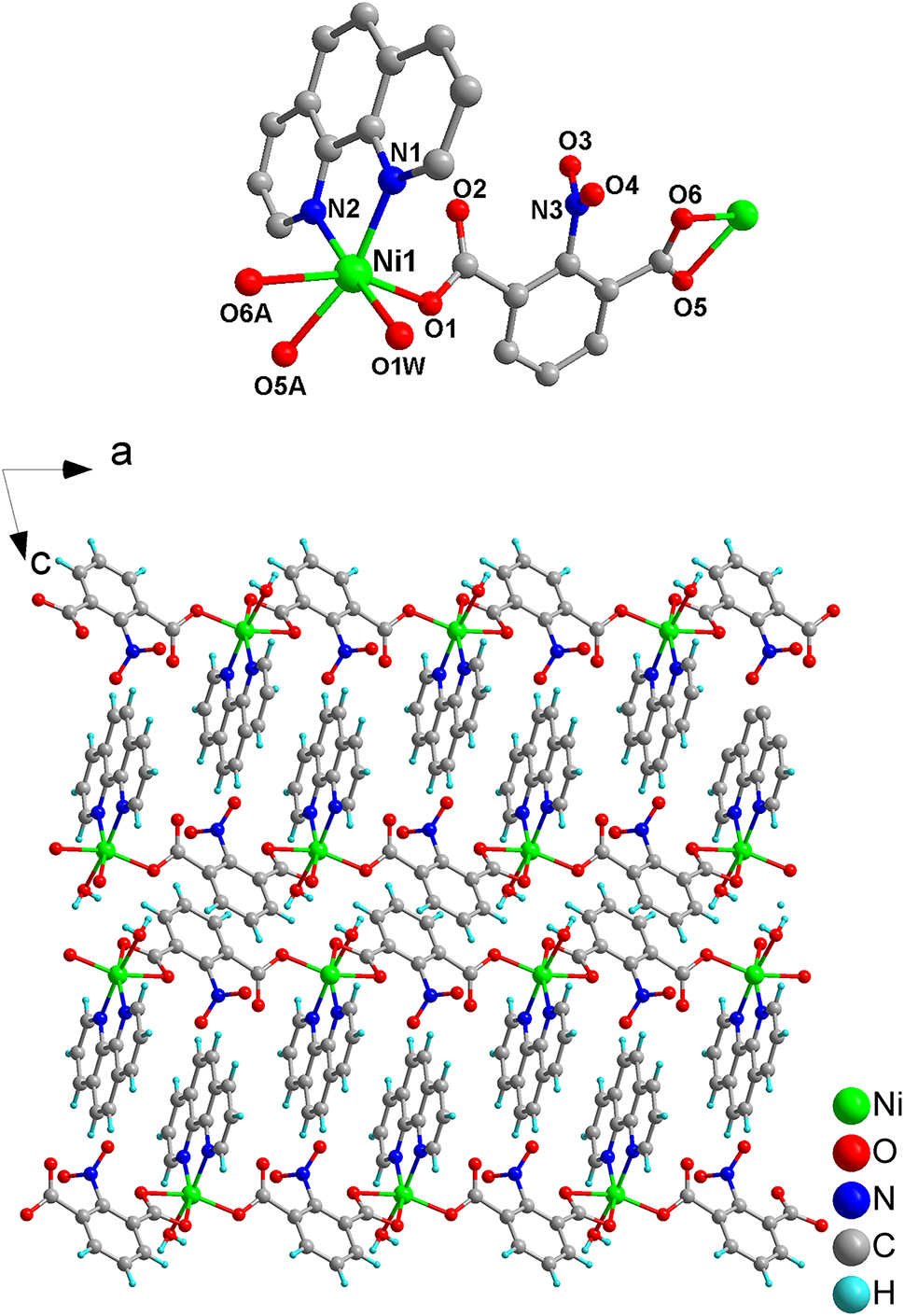
The asymmetric unit of the molecular structure is shown in the upper part of the figure. The title compound crystallizes in the triclinic space group P1̄, and the asymmetric unit contains one Ni2+ ion, one nipa ligand, one phen ligand and one coordinated water molecule. The Ni2+ ion resides in a slightly distorted coordination octahedron, defined by two nitrogen atoms from one phen ligand (Ni–N 2.023–2.0691 Å), one oxygen atom from the coordinated water molecule (Ni–O1W, 2.056 Å), and three μ 2-oxygen atoms (Ni1–O1, 2.021 Å; Ni1–O5A, 2.124 Å and Ni1–O6A, 2.132 Å; symmetry codes: A = x + 1, y − 1, z) from the two carboxyl groups of two H2nipa ligands. The mentioned parameters of bond lengths are within normal range. 13 , 14 , 15 It must be pointed out that in each nipa ligand, one carboxylate group coordinates in a k2 O,O and the other in a k1 O mode monodentate coordination modes, respectively. Each Ni2+ ion is bonded by a chelating carboxyl group in one nipa ligand and a monodentate carboxyl group in another nipa ligand. Each H2nipa ligand connects two Ni2+ centers leading to form a one-dimensional zigzag chain (see lower part of the figure) where all phen ligands are oriented to the same side, respectively.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This project was supported by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2019GXNSFAA185025), the Key Projects of Natural Science Research in Universities of Anhui Province (No. KJ2021A0921), Hefei Normal University 2022 Scientific Research Launch Fund for Introducing High level Talents (No. 2022rcjj26), The Science and Technology Major Project of Fuyang of Anhui Province of China (FK20208018).
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. The Anatomy of a Comprehensive Constrained, Restrained Refinement Program for the Modern Computing Environment – Olex2 Dissected. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 59–75; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Bruker SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
5. Li, S. J.; Li, K.; Li, Y. W. The Crystal Structure of 2-nitroisophthalic acid, C8H5NO6. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 399–400; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0704.Search in Google Scholar
6. Liu, G. Z.; Ma, L. P.; Jia, R. Crystal Structure of the Coordination Polymer catena-poly[(1,2-Di(pyridin-4-Yl)ethane-kN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-Κ2O:O′) zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 87–98; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0510.Search in Google Scholar
7. Wu, R. X.; Bi, C. F.; Zhang, D. M.; Fan, C. B.; Wang, L. L.; Zhu, B.; Liu, W. B.; Li, N. N.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y. H. Highly Selective, Sensitive and Stable Three-Dimensional Luminescent Metal-Organic Framework for Detecting and Removing of the Antibiotic in Aqueous Solution. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105349–105378; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105349.Search in Google Scholar
8. Wu, R. X.; Bi, C. F.; Wang, L. L.; Wang, J. M.; Fan, C. B.; Li, N. N.; Wang, M.; Shao, F.; Chen, G. B.; Fan, Y. H. Five Functional Cd/Zn-Based MOFs Constructed from V-Shaped Tricarboxylate Ligand for Rapidly Selective Adsorption and Efficiently Photocatalytic Degradation of Hazardous Aromatic Dyes. Synthetic Met. 2021, 277, 116786–116800; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2021.116786.Search in Google Scholar
9. Shi, X. M.; Fu, Y. J.; Zhang, Z. C. Crystal Structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitro-isophthalato-k4O:O′:O″:O‴) manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 71–73; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0478.Search in Google Scholar
10. Wu, R. X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. M.; Wang, L. L.; Zhu, B.; Xu, C. G.; Cui, G. N.; Zhang, D. M.; Fan, Y. H. Two Novel Zn (II)-based Metal-Organic Frameworks for Rapidly Selective Adsorption and Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Hazardous Aromatic Dyes in Aqueous Phase. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103665; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2022.103665.Search in Google Scholar
11. Wu, R. X.; Du, X. C.; Wang, J. M.; Wang, L. L.; Xu, C. G.; Luo, R.; Shao, F.; Fan, Y. H.; Zhang, X. The Hierarchical Co(II)-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks as Bifunctional Catalysts for Efficient Water Splitting and Pollutant Degradation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2023, 23, 5498–5508; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.3c00134.Search in Google Scholar
12. Queffélec, C.; Pati, P. B.; Pellegrin, Y. Fifty Shades of Phenanthroline: Synthesis Strategies to Functionalize 1,10-Phenanthroline in All Positions. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 6700–6902; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00543.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Banerjee, A.; Mahata, P.; Natarajan, S. The Use of Liquid–Liquid Interface (Biphasic) for the Preparation of Benzenetricarboxylate Complexes of Cobalt and Nickel. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 3501–3514; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.200800152.Search in Google Scholar
14. Guo, C. Y.; Li, S. H. Synthesis and Crystal Structure of a Ni(II) Complex with 4-Bromoisophthalic Acid and 1,10-phenanthroline. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 2012, 42, 902–904; https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2012.680135.Search in Google Scholar
15. Li, T.; Chen, L.; Shen, S. H.; Wen, C. L.; Liu, S. L. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of a 1D Coordination Polymer [Ni(phth)(phen) (H2O)]n·nH2O. J. Coord. Chem. 2007, 60, 683–689.10.1080/00958970600899856Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

