Abstract
C20H24N2O2, monoclinic, P21 (no. 4), a = 8.0021(9) Å, b = 5.9588(7) Å, c = 18.7274(19) Å, β = 93.546(7)°, V = 891.27(17) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0408, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1208, T = 300 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.23 × 0.22 × 0.21 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 0.62 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 68.3°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 7,510, 2,770, 0.041 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 2,292 |
| N(param)refined: | 218 |
| Programs: | Olex2, 1 SHELX 2 , 3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.2339 (3) | 0.4615 (6) | 0.09447 (14) | 0.0683 (8) |
| H1 | 0.281723 | 0.324781 | 0.108242 | 0.082* |
| C2 | 0.3086 (4) | 0.5949 (9) | 0.04465 (17) | 0.0890 (11) |
| H2 | 0.407239 | 0.547196 | 0.025666 | 0.107* |
| C3 | 0.2398 (4) | 0.7941 (7) | 0.02325 (16) | 0.0849 (11) |
| H3 | 0.290095 | 0.881266 | −0.010591 | 0.102* |
| C4 | 0.0973 (4) | 0.8647 (7) | 0.05164 (15) | 0.0784 (9) |
| H4 | 0.049878 | 1.001178 | 0.037272 | 0.094* |
| C5 | 0.0218 (4) | 0.7356 (6) | 0.10173 (14) | 0.0655 (8) |
| H5 | −0.075535 | 0.786963 | 0.121017 | 0.079* |
| C6 | 0.0884 (3) | 0.5322 (5) | 0.12351 (12) | 0.0525 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0021 (3) | 0.3866 (5) | 0.17591 (12) | 0.0552 (7) |
| H7A | −0.098953 | 0.461656 | 0.189169 | 0.066* |
| H7B | −0.030690 | 0.246659 | 0.152607 | 0.066* |
| C8 | 0.1475 (3) | 0.5400 (5) | 0.28145 (12) | 0.0558 (7) |
| H8A | 0.044884 | 0.610385 | 0.295029 | 0.067* |
| H8B | 0.204349 | 0.644421 | 0.251474 | 0.067* |
| C9 | 0.2582 (3) | 0.4896 (5) | 0.34794 (13) | 0.0606 (7) |
| H9A | 0.362961 | 0.425160 | 0.334403 | 0.073* |
| H9B | 0.283304 | 0.627819 | 0.373783 | 0.073* |
| C10 | 0.1214 (3) | 0.1310 (5) | 0.35537 (13) | 0.0558 (6) |
| H10A | 0.055511 | 0.038775 | 0.385768 | 0.067* |
| H10B | 0.219030 | 0.045201 | 0.343691 | 0.067* |
| C11 | 0.0179 (3) | 0.1866 (5) | 0.28711 (12) | 0.0537 (6) |
| H11A | −0.009801 | 0.048942 | 0.261396 | 0.064* |
| H11B | −0.085945 | 0.257022 | 0.299132 | 0.064* |
| C12 | 0.2285 (3) | 0.3200 (5) | 0.46605 (12) | 0.0465 (5) |
| C13 | 0.3301 (3) | 0.4845 (6) | 0.49972 (13) | 0.0610 (7) |
| H13 | 0.368937 | 0.601828 | 0.472506 | 0.073* |
| C14 | 0.3746(3) | 0.4780(6) | 0.57195(13) | 0.0610(7) |
| H14 | 0.440465 | 0.592379 | 0.592437 | 0.073* |
| C15 | 0.3233(3) | 0.3051(5) | 0.61451(12) | 0.0520(6) |
| C16 | 0.2251(3) | 0.1401(5) | 0.58155(13) | 0.0630(8) |
| H16 | 0.189499 | 0.020901 | 0.608852 | 0.076* |
| C17 | 0.1780 (3) | 0.1461 (5) | 0.50973 (14) | 0.0605 (7) |
| H17 | 0.111138 | 0.031811 | 0.489820 | 0.073* |
| C18 | 0.3705 (3) | 0.2914 (5) | 0.69206 (13) | 0.0588 (7) |
| C19 | 0.5317 (3) | 0.4551 (7) | 0.78971 (13) | 0.0687 (8) |
| H19A | 0.643144 | 0.518911 | 0.796007 | 0.082* |
| H19B | 0.535932 | 0.303394 | 0.808528 | 0.082* |
| C20 | 0.4138 (4) | 0.5908 (8) | 0.82984 (17) | 0.0885 (11) |
| H20A | 0.406809 | 0.739571 | 0.810174 | 0.133* |
| H20B | 0.453280 | 0.598593 | 0.879244 | 0.133* |
| H20C | 0.305068 | 0.522326 | 0.826101 | 0.133* |
| N1 | 0.1070 (2) | 0.3364 (4) | 0.24113 (10) | 0.0503 (5) |
| N2 | 0.1751 (2) | 0.3332 (3) | 0.39408 (10) | 0.0504 (5) |
| O1 | 0.3198 (3) | 0.1503 (5) | 0.73111 (11) | 0.0947 (9) |
| O2 | 0.4799 (2) | 0.4492 (4) | 0.71423 (9) | 0.0695 (6) |
1 Source of material
Ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate was prepared by the direct reaction between 1-benzylpiperazine hydrochloride and ethyl 4-fluorobenzoate. In detail, a solution of ethyl 4-fluorobenzoate (17.51 g, 0.104 mol) and 1-benzylpiperazine hydrochloride (44.3 g, 0.209 mol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (100 ml) was stirred and refluxed at 433 K for 16 h. The reaction mixture was allowed to reach room temperature and poured into 750 ml stirring water. The solid part was filtered off, washed with water, dried for 15 h at 32 K in vacuo, recrystallized with 150 ml isopropanol, filtered off, washed with isopropanol and dried for 48 h at 323 K in vacuo, producing 23.5 g of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate in 69.7 % yield.
2 Experimental details
Single crystals of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate were cultured in a mixed solvent of dichloromethane and methol (20:1, v/v) for 3 days. Using Olex2, 1 the structure was solved with the ShelXT 2 structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL 3 refinement package. All hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
3 Comment
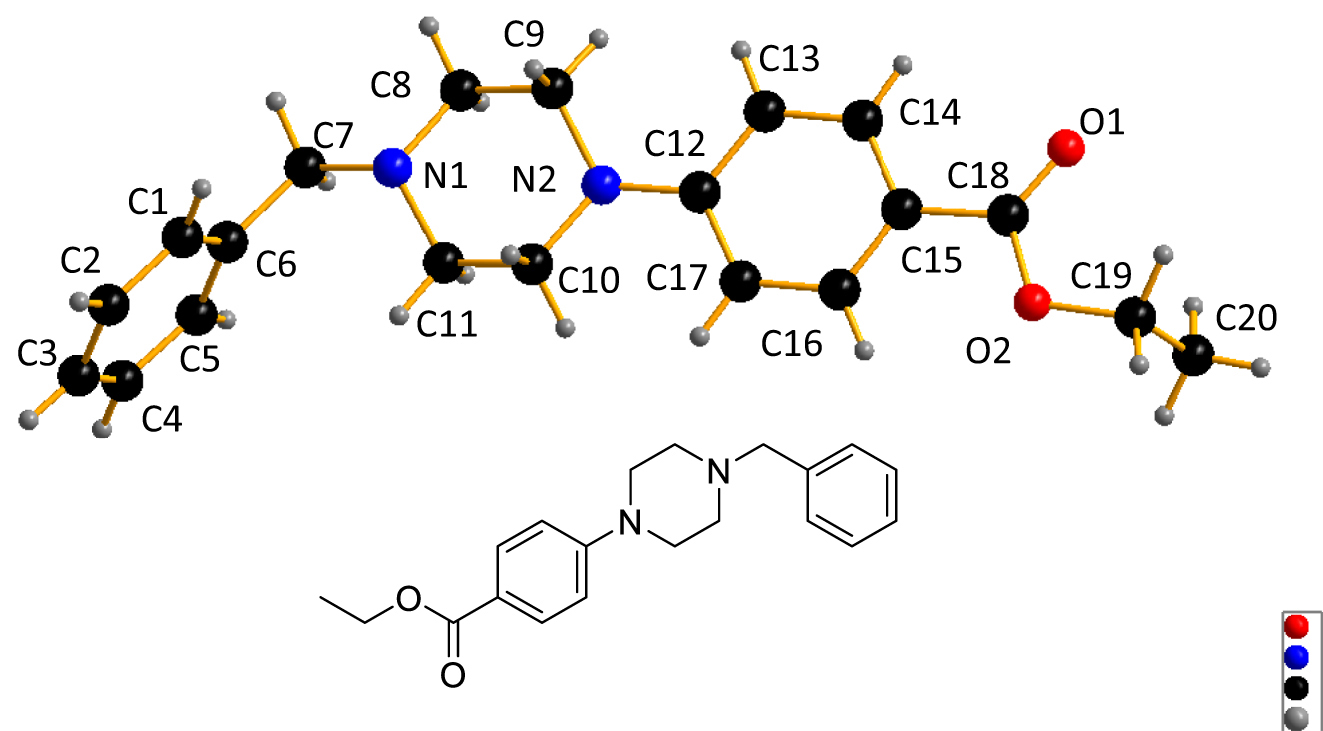
Ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate is a key inermediate for the synthesis of diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) inhibitors, in particular a DGAT1 inhibitor. 4 DGAT is a microsomal enzyme that can be classified into four types based on structural and localization differences: DGAT1, DGAT2, bifunctional enzyme (wax ester synthase, WS/DGAT), and cytosolic DGAT (CytoDGAT). 5 Piperidine or piperazine derivatives exhibiting inhibitory activity against DGAT, particularly DGAT1. 6 Here, ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate is the main starting material for the synthesis of piperazine derivatives. In the molecules forming the title crystal structure, the key bond lengths and angles are within normal ranges. The C–N bonds are confirmed by the distance of N1–C7, N2–C12. Their lengths are 1.469(3) Å, and 1.391(3) Å, respectively. Additionally, the lengths of C18–O1 and C18–O2 are 1.201(3) Å and 1.334(4) Å, which are consistent with the ester group. The bond angles of C8–N1–C11 and C9–N2–C10 measures 107.78(18) Å and 111.39(19) Å, respectively, which is attributed to the bond angles characteristic of piperazine. These results indicated the structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate.
-
Author contributions: Xue Zeng drafted most parts of the manuscript and conducted the experiments of crystal analysis. Wenwu Zhong and Yuanfang Hou cultured the crystal of compound. Yuanjiao Feng contributed to the analysis of results. All authors agreed to the final version of the manuscript. All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Chongqing Municipal Health Commission Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Project (2022MSXM213). Chongqing Education Commission Natural Science Foundation (KJZD-K202402802).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Qi, J.; Lang, W.; Geisler, J. G.; Wang, P.; Petrounia, I.; Mai, S.; Smith, C.; Askari, H.; Struble, G. T.; Williams, R.; Bhanot, S.; Monia, B. P.; Bayoumy, S.; Grant, E.; Caldwell, G. W.; Todd, M. J.; Liang, Y.; Gaul, M. D.; Demarest, K. T.; Connelly, M. A. The Use of Stable Isotope-Labeled Glycerol and Oleic Acid to Differentiate the Hepatic Functions of DGAT1 and -2. J. Lipid Res., 2012, 53, 1106–1116. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M020156.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Chen, G.; Harwood, J. L.; Lemieux, M. J.; Stone, S. J.; Weselake, R. J. Acyl–CoA: Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase: Properties, Physiological Roles, Metabolic Engineering and Intentional Control. Prog. Lipid Res. 2022, 88, 101181; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101181.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Okuma, C.; Ohta, T.; Tadaki, H.; Ishigure, T.; Sakata, S.; Taniuchi, H.; Sano, R.; Hamada, H.; Kume, S.; Nishiu, J.; Kakutani, M. JTP-103237, a Monoacylglycerol Acyltransferase Inhibitor, Prevents Fatty Liver and Suppresses Both Triglyceride Synthesis and De Novo Lipogenesis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 128, 150–157; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2015.06.007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

