Abstract
C25H37Br2N2O3P, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 9.827(5) Å, b = 14.441(8) Å, c = 10.175(6) Å, β = 103.573(16)°, V = 1403.6(13) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt (F) = 0.0530, wRref (F 2) = 0.1105, T = 296 K.
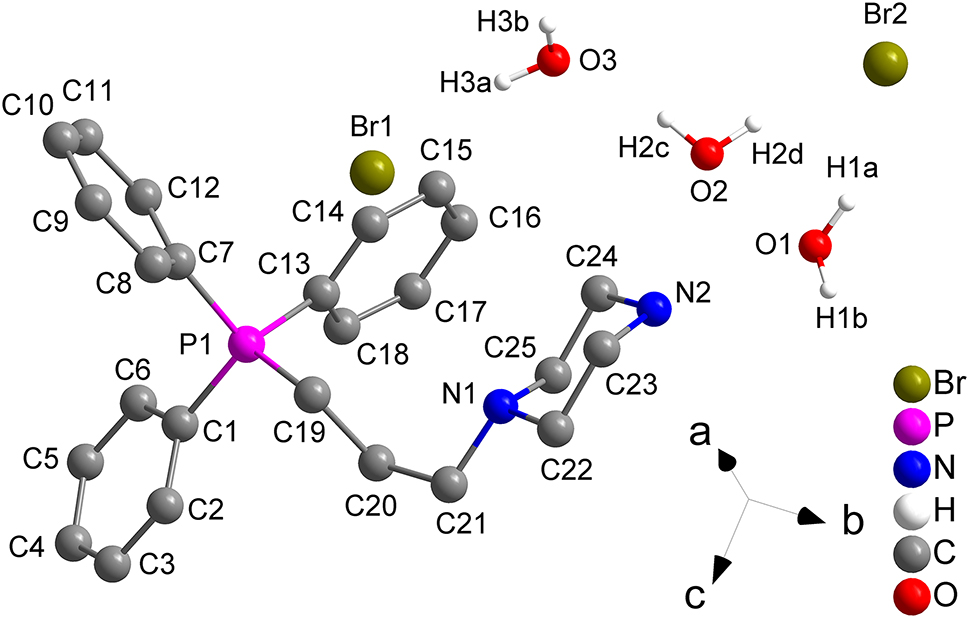
The title crystal structure is shown in the figure (hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity). Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless needle |
| Size: | 0.14 × 0.08 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.97 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 27.5°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 31977, 6437, 0.169 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3,263 |
| N(param)refined: | 307 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 , 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br1 | 0.19266 (10) | 0.36596 (7) | 0.49004 (10) | 0.0675 (3) |
| Br2 | −0.01656 (10) | 0.81477 (6) | 0.01222 (10) | 0.0658 (3) |
| P1 | 0.4777 (2) | 0.42056 (15) | 0.9153 (2) | 0.0372 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0917 (7) | 0.5851 (5) | 0.7322 (8) | 0.0430 (18) |
| N2 | −0.0080 (9) | 0.6728 (6) | 0.4793 (8) | 0.064 (2) |
| H2A | −0.038746 | 0.728065 | 0.498293 | 0.076* |
| H2B | −0.020904 | 0.668571 | 0.389992 | 0.076* |
| C1 | 0.5538 (8) | 0.4141 (6) | 1.0932 (8) | 0.0384 (19) |
| C2 | 0.4699 (9) | 0.4027 (5) | 1.1851 (9) | 0.044 (2) |
| H2 | 0.373048 | 0.400224 | 1.154795 | 0.053* |
| C3 | 0.5302 (10) | 0.3953 (6) | 1.3191 (9) | 0.054 (3) |
| H3 | 0.474137 | 0.388274 | 1.380492 | 0.065* |
| C4 | 0.6723 (10) | 0.3979 (5) | 1.3647 (10) | 0.057 (3) |
| H4 | 0.711624 | 0.393377 | 1.456999 | 0.069* |
| C5 | 0.7586 (9) | 0.4073 (6) | 1.2764 (10) | 0.056 (2) |
| H5 | 0.855363 | 0.408632 | 1.307831 | 0.067* |
| C6 | 0.6976 (8) | 0.4145 (6) | 1.1409 (9) | 0.050 (2) |
| H6 | 0.754330 | 0.419823 | 1.079876 | 0.060* |
| C7 | 0.5072 (8) | 0.3133 (6) | 0.8379 (7) | 0.0404 (19) |
| C8 | 0.4037 (10) | 0.2454 (6) | 0.8106 (9) | 0.051 (2) |
| H8 | 0.315348 | 0.256489 | 0.825517 | 0.061* |
| C9 | 0.4356 (12) | 0.1602 (6) | 0.7603 (9) | 0.060 (3) |
| H9 | 0.368867 | 0.113367 | 0.742783 | 0.072* |
| C10 | 0.5657 (14) | 0.1459 (7) | 0.7368 (10) | 0.066 (3) |
| H10 | 0.585447 | 0.089261 | 0.701931 | 0.079* |
| C11 | 0.6650 (12) | 0.2111 (8) | 0.7628 (11) | 0.073 (3) |
| H11 | 0.753035 | 0.199236 | 0.747627 | 0.088* |
| C12 | 0.6366 (9) | 0.2959 (7) | 0.8120 (10) | 0.063 (3) |
| H12 | 0.705053 | 0.341686 | 0.827979 | 0.075* |
| C13 | 0.5520 (8) | 0.5116 (6) | 0.8374 (9) | 0.039 (2) |
| C14 | 0.5125 (10) | 0.5180 (7) | 0.6982 (10) | 0.060 (3) |
| H14 | 0.459371 | 0.470780 | 0.649022 | 0.072* |
| C15 | 0.5499 (12) | 0.5918 (9) | 0.6317 (12) | 0.075 (3) |
| H15 | 0.525079 | 0.593458 | 0.537759 | 0.090* |
| C16 | 0.6233 (12) | 0.6635 (8) | 0.7013 (13) | 0.067 (3) |
| H16 | 0.645011 | 0.714817 | 0.654974 | 0.080* |
| C17 | 0.6652 (11) | 0.6602 (7) | 0.8396 (13) | 0.069 (3) |
| H17 | 0.716066 | 0.708777 | 0.887384 | 0.082* |
| C18 | 0.6305 (10) | 0.5825 (6) | 0.9086 (10) | 0.055 (3) |
| H18 | 0.660451 | 0.578959 | 1.002218 | 0.066* |
| C19 | 0.2956 (7) | 0.4467 (5) | 0.8845 (8) | 0.041 (2) |
| H19A | 0.255912 | 0.446550 | 0.787709 | 0.049* |
| H19B | 0.249164 | 0.398576 | 0.924199 | 0.049* |
| C20 | 0.2662 (9) | 0.5413 (6) | 0.9428 (9) | 0.049 (2) |
| H20A | 0.278723 | 0.535935 | 1.039905 | 0.059* |
| H20B | 0.332973 | 0.586481 | 0.925570 | 0.059* |
| C21 | 0.1185 (9) | 0.5750 (7) | 0.8806 (9) | 0.051 (2) |
| H21A | 0.051886 | 0.531419 | 0.902264 | 0.061* |
| H21B | 0.104162 | 0.634267 | 0.920102 | 0.061* |
| C22 | −0.0563 (9) | 0.5988 (6) | 0.6792 (9) | 0.054 (2) |
| H22A | −0.084557 | 0.657150 | 0.711907 | 0.065* |
| H22B | −0.107984 | 0.549495 | 0.710266 | 0.065* |
| C23 | −0.0894 (10) | 0.5995 (7) | 0.5276 (11) | 0.065 (3) |
| H23A | −0.066802 | 0.539787 | 0.494776 | 0.078* |
| H23B | −0.188722 | 0.610570 | 0.492597 | 0.078* |
| C24 | 0.1450 (10) | 0.6646 (8) | 0.5442 (10) | 0.070 (3) |
| H24A | 0.182150 | 0.608999 | 0.512020 | 0.084* |
| H24B | 0.194493 | 0.717422 | 0.519465 | 0.084* |
| C25 | 0.1672 (10) | 0.6604 (7) | 0.6938 (9) | 0.060 (3) |
| H25A | 0.266229 | 0.653038 | 0.734615 | 0.072* |
| H25B | 0.136233 | 0.717873 | 0.726569 | 0.072* |
| O1 | 0.0706 (6) | 0.8579 (6) | 0.3464 (7) | 0.0782 (19) |
| H1A | 0.052879 | 0.865671 | 0.261241 | 0.117* |
| H1B | −0.004244 | 0.864170 | 0.373695 | 0.117* |
| O2 | −0.0628 (9) | 0.6361 (5) | 0.2056 (8) | 0.076 (2) |
| H2C | 0.001246 | 0.597788 | 0.199973 | 0.114* |
| H2D | −0.067489 | 0.672421 | 0.138957 | 0.114* |
| O3 | 0.1075 (9) | 0.4838 (5) | 0.2082 (8) | 0.087 (2) |
| H3A | 0.139578 | 0.449608 | 0.276308 | 0.130* |
| H3B | 0.072832 | 0.446156 | 0.144997 | 0.130* |
1 Source of materials
(3-Bromopropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide (0.1292 mol, 60 g) and anhydrous piperazine (0.0646 mol. 5.567 g) were suspended in anhydrous ethanol (40 g). The suspension liquid was stirred at 60 °C for 20 h. After the reaction, the temperature was lowered to 0 °C and filtered to obtain white solid. The white solid was heated with anhydrous ethanol (13.3 g) to 75 °C for 10 min, then cooled to 15 °C to filter, dry wet products to solid 10.2 g. The title crystals were obtained by slow evaporation from mixed solvent (methanol: 2-ethoxyethanol = 2: 1, v/v) at room temperature.
2 Experimental details
Absorption corrections were used by using multi-scan program. 1 The structure was solved with SHELX. 3 , 4 Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions. Hydrogen atoms were constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
3 Comment
As a widely used mechanical material, high-strength fiber composite materials can be effectively used in electronic devices, aerospace, security protection and national defense military fields. Various phenylphosphine derivatives participate in the preparation of high-strength fiber composite materials, especially in mechanical materials. The layered cerium phenylphosphonate (CeHPP) was prepared by reflux method, and the composite with aluminum diethylphosphonate (ADP) can effectively prepare flame retardant carbon fiber reinforced polyamide 6 (PA6/CF) composite. 5 Triphenylphosphine as a catalyst provides a feasible method for the preparation of thermoplastic epoxy resin and its fiber reinforced composites with good mechanical properties. 6 The addition of triphenylphosphine derivatives and other auxiliary materials can effectively enhance the properties of fiber reinforced polymers, where composites containing up to 76 wt% basalt fiber can be realized. 7
Each asymmetric unit contains one triphenylphosphonium group, one piperazinium group two bromide anions and three water molecules. The C–C distances are in the range of 1.338(14)–1.544(11) Å. The C–N distances are in the range of 1.422(12)–1.498(11) Å. 8 The C–P distances are in the range of 1.777(8)–1.792(9) Å. 9 The title molecule was assembled into a twisted structure by five hydrogen bonds. First hydrogen bond is O1–H1B–Br1, the distance of O1–H1B bond is 0.85 Å, the distance of H1B–Br1 bond is 2.56 Å, the angle of O1–H1B–Br1 is 166°. 10 Second hydrogen bond is N2–H2A–Br1, the distance of N2–H2A bond is 0.89 Å, the distance of H2A–Br1 bond is 2.52 Å, the angle of N2–H2A–Br1 is 163°. 11 Third hydrogen bond is O3–H3B–Br2, the distance of O3–H3B bond is 0.85 Å, the distance of H3B–Br2 bond is 2.46 Å, the angle of O3–H3B–Br2 is 167°. Fourth hydrogen bond is C19–H19A–N1, the distance of C19–H19A bond is 0.97 Å, the distance of H19A–N1 bond is 2.55 Å, the angle of C19–H19A–N1 is 108°, this hydrogen bond is an intramolecular hydrogen bond. Fifth hydrogen bond is C19–H19B–Br2, the distance of C19–H19B bond is 0.97 Å, the distance of H19B–Br2 bond is 2.79 Å, the angle of C19–H19B–Br2 is 154°.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: None declared.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker SAINT, APEX2; Bruker AXS Inc: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Juan, C.; Wei, F.; Hongqiang, Y.; Yan, X.; Yong, Y.; Bingtao, W.; Juan, L.; Zhengping, F.; Zhenghong, G. Synergistic Flame-Retardancy of Lamellar Cerium Phenylphosphonate and Aluminum Diethylphosphinate towards Suppressing “Candlewick Effect” of Polyamide 6/Carbon Fiber Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54546; https://doi.org/10.1002/app.54546.Search in Google Scholar
6. Chong, C.; Jun, W.; Shuang, Y.; Jingsheng, W.; Xi, C.; Yue, J.; Qiufei, C.; Pengzong, G.; Xiao, W.; Fu, L. Preparation and Properties of Aniline Chain-Extended Thermoplastic Epoxy Resin Using Triphenylphosphine as Catalyst. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 260–269; https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5513.Search in Google Scholar
7. Benjamin, R. K.; Georgios, M.; Mark, S.; Tanja, S.; Iris, E.; Michael, R. B. Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization-Derived Poly(Dicyclopentadiene)/Fiber Composites Using Latent Pre-catalysts. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2024, 309, 2300367; https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.202300367.Search in Google Scholar
8. Maria, V. K.; Konstantin, V. L.; Dmitry, V. D.; Stanislav, I. B.; Mikhail, A. K. Phosphorescent Cyclometalated Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Complexes Derived from Diaminocarbene Precursors. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 5315–5531.10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c03346Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Wen-Long, M.; Cheng-Jie, G.; Zi-Xi, L.; Si-Jie, F.; Chuan-Bin, H.; Jing-Tong, Z.; Shuai, Z.; Zhong-Feng, L.; Hong-Liang, H.; Chun-Bo, D.; Guo, W.; Qiong-Hua, J. Synthesis and Luminescent Properties of Three Excellent Yellow Emissive Cu(I) Complexes Based on the Diphosphine Ligand and the Diimine Ligand. CrystEngComm 2024, 26, 2297–2305; https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ce00206g.Search in Google Scholar
10. Petra, G.; Cezarina, C. M.; Thorsten, W.; Uwe, M. A Trigonal Coordination of Au(I) Phosphane Complexes Stabilized by O–H–X (X = Cl−, Br−, I−) Interactions. Monatsh. Chem. 2021, 152, 1201–1207; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-021-02843-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Wafa, A.; Abderrahim, K.; Michael, K.; Lukas, B.; Anna, K.; Carsten, S.; Mohamed, L. E.; Azaiez, B. A. Synthesis, Crystal Structures and Hirshfeld Analyses of Phosphonothioamidates (EtO)2 P(=O)C(=S)N(H)R (R = Cy, Bz) and Their Coordination on CuI and HgX2 (X = Br, I). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2022, 197, 1238–1247; https://doi.org/10.1080/10426507.2021.1927032.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1,3-dioxide — acetic acid (1/2) C7H14N6O6
- Crystal structure of the dinuclear mercury(II) complex bis(μ2-bromido)-dibromido-bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-ethyl-5-methyl-imidazol)-κ1 N} dimercury(II), C26H30N10Hg2Br4
- Crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-pentakis(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2 O:O)tetraytterbium(III)] hydrate, C36H26N6O16Yb2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(μ 2-nitroisophthalato-κ 3 O,O′:O″)nickel(II)], C20H13NiN3O7
- Crystal structure of 72,73,75,76-tetrafluoro-25,44-dimethyl-31,33,36,38-tetraoxo-31,32,33,36,37,38-hexahydro-3(2,7)-benzo[lmn][3,8]phenanthrolina-1,5(4,1)-dipyridin-1-iuma-2,4(1,2),7(1,4)-tribenzenacyclooctaphane-11,51-diium hexafluoridophosphate, [C46H28F4N4O4][PF6]2, a dicationic cyclophane
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzylidene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H15FN2O
- The salt crystal structure of etoricoxib hydrochloride, C18H16Cl2N2O2S
- The structure of t-butyl 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, C37H43FN2O5
- The crystal structure of (μ4-oxo)-tri(μ4-2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-bis(olato)-κ5 O,O′:N:N′:O″)tetrazinc(II) – methylformamide (1/1), C33H25N7O8Zn4
- The co-crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzophenone–salicylhydrazide(1/1), C20H17ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal composed of benzhydrazide and 5-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4⋅C7H8N2O
- The cocrystal structure of praziquantel-hesperetin (1/1), C35H38N2O8
- Crystal structure of new barium manganese fluorides dihydrates, Ba10Mn2F25·2H2O
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(3-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propanoate-κ2O:N)-bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N, N′)dicopper(II)]dinitrate, C42H36Cu2N12O10
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-phenylaminopyridazine-κ2N,N′)-bis(2-(p-toluene)pyridinyl-κ2C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate –dichloromethane (1/1), C45H37Cl2F6IrN7P
- The crystal structure of 2-(2′-carboxybenzyl)benzoic acid, C15H12O5
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[(E)-N′,N″-bis((2E,3E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)-2-((E)-3-(hydroxyimino)butan-2-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide-κ 4 N 4]cobalt(II), C13H22N9O3Cl2Co
- Crystal structure of (−)-flavesine H, C15H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C22H22O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ 2 O,O)iridium(I), C7H4IrNO4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-(triphenylphosphonio)propyl)piperazin-1-ium dibromide trihydrate, C25H37Br2N2O3P
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dihydroxybenzofuran-3-carboxylate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 14-(R)-(2′-cyano-phenoxy)-3,19-diacetyl andrographolide, C31H37NO7
- The twinned crystal structure of 10-(4-methyl benzoate)-2,8-diethyl-5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-di-pyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f] [1,3,2]diazaborinin-4-ium-5-uide, C25H29BF2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (9H-thioxanthen-9- ylidene)hydrazine monohydrate, C13H11N2SO0.5
- The crystal structure of pyridinium diaqua-{1,2-phenylenebis((carboxylatocarbonyl)amido-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C15H14MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active high entropy phase Tb0.82Sm0.18Ni0.83Co0.17Mg
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[5-methyl-1-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ 2 N,O)]manganese(II), C14H16MnN10O6
- Crystal structures of diiodido-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one-cadmium(II)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C14H18O7
- Crystal structure of isoxazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-amine, C6H5N3O
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-1-isobutyl-1H-imidazo, C14H14ClN3
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,2,2,2-hexakis(2-methyl-2-phenylpropyl)distannane,C60H78Sn2
- The crystal structure of (2,7-dimethoxynaphthalene-1,8-diyl)bis((3-nitrophenyl)methanone), C26H18N2O8
- Crystal structure of diaqua-tetra((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)zinc(II) dinitrate dihydrate, C60H76Cl8N14O14Zn
- The crystal structure of diphenyl bis(2-((diphenoxyphosphoryl)amino)ethyl)phosphoramidate monohydrate C40H42N3O10P3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bis(dibromomethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl, C14H10Br4
- Crystal structure of CaPtZn
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, C7H3ClF3NO2
- The crystal structure of (3′-(2-bromophenyl)-2-phenyl-[2,2′-bioxiran]-3-yl)(phenyl)methanone, C92H68O12Br4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)benzoate, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(selenocyanato-κ1 N)-bis(methanol)-bis((1E,2E)-1,2-bis (1-(pyridin-4-yl)ethylidene)-hydrazine)iron(II) methanol solvate, C34H44FeN10O4Se2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(5-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C26H21BrN2O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 1′,3′-dihydro-2,2′-spirobi[indene]-1,3-dione, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biindenylidene]-4,4′-diol, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of di-glycylglycinium squarate dihydrate, C12H22N4O12, at 105 K
- Crystal structure of {[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]triphenylphosphonium}dibromocopper(I), [C25H21FP]+[CuBr2]−
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-((pyridin-4-yl-methyl)amino)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 2 N:O)cadmium(II)], C28H26CdN4O10

