Abstract
C17H16OS, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 5.4605(12) Å, b = 19.767(4) Å, c = 13.357(4) Å, β = 92.834(3)°, V = 1,439.9(6) Å3, Z = 4, R gt(F) = 0.0398, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1144, T = 296(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size | 0.31 × 0.26 × 0.23 mm |
| Wavelength: | MoKα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.21 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.0°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 7,262, 2,541, 0.018 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ (I obs), 2,147 |
| N(param)refined: | 175 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 WinGX/ORTEP 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.5988 (3) | 0.35369 (8) | 0.95850 (12) | 0.0469 (4) |
| C2 | 0.5455 (3) | 0.31101 (9) | 0.87880 (14) | 0.0607 (5) |
| H2 | 0.642271 | 0.272932 | 0.870230 | 0.073* |
| C3 | 0.3509 (4) | 0.32377 (11) | 0.81143 (15) | 0.0717 (6) |
| H3 | 0.318389 | 0.294341 | 0.758096 | 0.086* |
| C4 | 0.2065 (4) | 0.37912 (10) | 0.82255 (15) | 0.0697 (5) |
| H4 | 0.074617 | 0.387250 | 0.777397 | 0.084* |
| C5 | 0.2560 (4) | 0.42262 (10) | 0.90027 (17) | 0.0750 (6) |
| H5 | 0.158807 | 0.460766 | 0.907646 | 0.090* |
| C6 | 0.4503 (4) | 0.41012 (9) | 0.96810 (15) | 0.0641 (5) |
| H6 | 0.482029 | 0.439981 | 1.020963 | 0.077* |
| C7 | 0.8027 (3) | 0.34223 (8) | 1.03630 (12) | 0.0508 (4) |
| C8 | 0.9408 (3) | 0.27906 (8) | 1.03330 (12) | 0.0502 (4) |
| H8 | 0.888419 | 0.246969 | 0.986031 | 0.060* |
| C9 | 1.1368 (3) | 0.26365 (8) | 1.09323 (12) | 0.0510 (4) |
| C10 | 1.1306 (3) | 0.13821 (8) | 0.99565 (13) | 0.0532 (4) |
| C11 | 0.9234 (3) | 0.10373 (9) | 1.02104 (15) | 0.0615 (5) |
| H11 | 0.865498 | 0.108228 | 1.085016 | 0.074* |
| C12 | 0.8021 (4) | 0.06261 (10) | 0.95175 (16) | 0.0687 (5) |
| H12 | 0.661127 | 0.040166 | 0.969655 | 0.082* |
| C13 | 0.8836 (4) | 0.05377 (9) | 0.85660 (15) | 0.0632 (5) |
| C14 | 1.0906 (4) | 0.08811 (10) | 0.83221 (15) | 0.0682 (5) |
| H14 | 1.149352 | 0.083047 | 0.768468 | 0.082* |
| C15 | 1.2132 (3) | 0.12995 (10) | 0.90025 (14) | 0.0652 (5) |
| H15 | 1.352751 | 0.152853 | 0.881825 | 0.078* |
| C16 | 0.7489 (5) | 0.00794 (12) | 0.78190 (19) | 0.0974 (8) |
| H16A | 0.661491 | 0.034889 | 0.732163 | 0.146* |
| H16B | 0.635077 | −0.019731 | 0.816040 | 0.146* |
| H16C | 0.864623 | −0.020447 | 0.750045 | 0.146* |
| C17 | 1.2511 (4) | 0.30737 (10) | 1.17439 (14) | 0.0655 (5) |
| H17A | 1.297136 | 0.350015 | 1.146504 | 0.098* |
| H17B | 1.394106 | 0.285312 | 1.203590 | 0.098* |
| H17C | 1.135417 | 0.314800 | 1.225082 | 0.098* |
| O1 | 0.8440 (3) | 0.38557 (7) | 1.10038 (10) | 0.0750 (4) |
| S1 | 1.29935 (9) | 0.18752 (3) | 1.08569 (4) | 0.0691 (2) |
1 Source of material
All chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used as received without further purification. An oven-dried flask was charged with 1-phenylbuta-2,3-dien-1-one (0.2 mmol), p-toluenethiol (0.2 mmol) and CH3CN (2 mL). Then, after the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 3.5 h, the mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated in vacuum, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate) to afford the pure title product. Finally, crystals were obtained by slow evaporation from petroleum ether (b.p.: 60–90 °C) solution at room temperature.
2 Experimental details
All H-atoms bonded to C atoms were placed geometrically and refined using a riding model with common isotropic displacement factors U iso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5 U eq (parent C-atom).
3 Comment
Vinyl sulfides play an important role as versatile intermediates in organic chemistry and coordination chemistry, and they also are vital core structures for many natural products and biologically active compounds. 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 Due to the molecular structure of a compound determining its properties, considerable interest has been inclined toward the development of structures for access to vinyl sulfides. 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 Therefore, we have crystallized the title compound and report its crystal structure in this context.
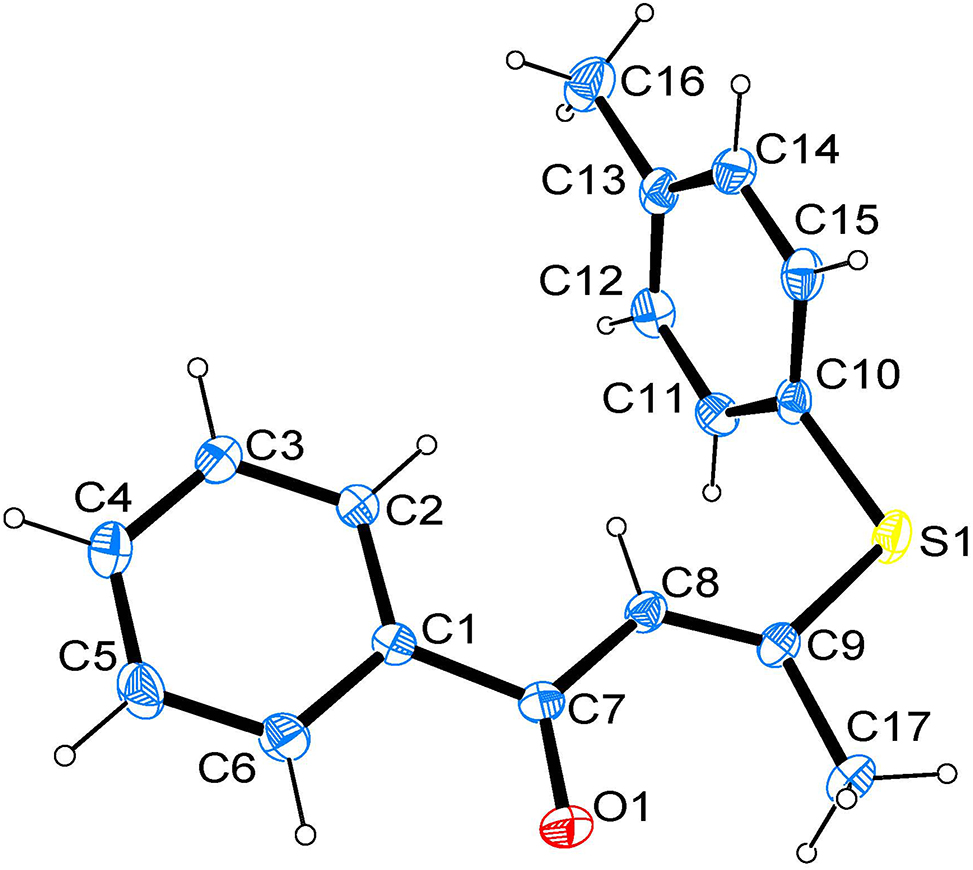
In the molecular structure (Figure), the dihedral angle between the almost planar vinylthio group (S1/C17/C7–C9) and the benzoyl group (O1/C1–C7) is 8.1°. The C(10)–S(1)–C(9)–C(8) and C(10)–S(1)–C(9)–C(17) torsion angles are – 5.54(18)° and 179.97(12)°. The bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges. 14 The thioether bond distances are 1.7526(18) Å for S(1)–C(9) and 1.7708(18) Å for S(1)–C(10), respectively, and the C(3)–S(1)–C(6) bond angle is 105.28(8)°. The bond lengths of C(8)–C(9), C(7)–C(8) and O(1)–C(7) are 1.340(2), 1.460(2) and 1.224(2) Å, respectively. The title compound forms a 2D structure by C–H⋯π and C–H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Funding source: Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2024JJ5057
Funding source: Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project of Hunan Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: CX20240978
Funding source: College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Hengyang Normal University
Award Identifier / Grant number: S202410546045
Funding source: Scientific Research Projects of Education Department of Hunan Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 23B0669
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2024JJ5057), Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project of Hunan Province (No. CX20240978), College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Hengyang Normal University (No. S202410546045), and Scientific Research Projects of Education Department of Hunan Province (No. 23B0669).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space–Group and Crystal–Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and Ortep for Windows: An Update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Search in Google Scholar
5. Fogeron, T.; Retailleau, P.; Chamoreau, L.-M.; Li, Y.; Fontecave, M. Pyranopterin Related Dithiolene Molybdenum Complexes as Homogeneous Catalysts for CO2 Photoreduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 17033–17037; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201809084.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, X.; Tang, Z.; Au, C.-T.; Qiu, R. Nickel–Catalyzed Regioselective Cleavage of Csp2–S Bonds: Method for the Synthesis of Tri- and Tetrasubstituted Alkenes. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 3246–3255; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.6b00203.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Zhao, Y.-M.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.-T.; Xie, M.-H. Cu–Catalyzed Diarylthiolation of Ynones with Aryl Iodides and Elemental Sulfur: An Access to Tetrasubstituted (Z)-1,2–Bis(arylthio)alkenes and Benzo[b] [1,4]dithiines. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 11796–11804; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.2c01575.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Sun, Q.; Xiong, L.; Yin, G. Highly Regio- and Stereoselective Synthesis of Bis-sulfanylSubstituted Conjugated Dienes by Copper–Palladium Cooperative Catalysis. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 628–634; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0qo01256d.Search in Google Scholar
9. Jali, B. R.; Baruah, J. B. Polymorphs and Solvates of 2-(1,4–Dihydro-1,4-Dioxonaphthalen-3-Ylthio)Benzoic Acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 3114–3122; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg300318u.Search in Google Scholar
10. Stephens, F. S. Crystal and Molecular Structure of trans-3-p–Tolylthiocinnamic Acid. J. Chem. Soc. A 1970, 1843–1846; https://doi.org/10.1039/j19700001843.Search in Google Scholar
11. Roche, D.; Métin, J.; Madesclaire, M. (E)-3-(4–Chlorophenyl)-3-Cyclopropyl-2-(Phenylthio)Acrylonitrile. Acta Crystallogr. 1996, C52, 3104–3105; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108270196007172.Search in Google Scholar
12. Yavari, I.; Taheri, Z.; Sheikhi, S.; Halvagar, M. R. A Synthesis of (Arylthio-Ethylidene)Indolin-2-Ones via S-Arylation of Oxoindolin-Ethanethiolates with Aryl Halides. J. Sulfur Chem. 2019, 40, 124–136; https://doi.org/10.1080/17415993.2018.1540701.Search in Google Scholar
13. Kang, G.; Kim, J.; Lim, H.; Kim, T. H. Crystal Structure of Benzobicyclon. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, E52, o1035–o3105; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989015023221.Search in Google Scholar
14. Dong, L.; Guo, Y.-F.; Ma, J.-Y.; Wang, J.-L.; Feng, S.-X.; Huo, H.-K. Crystal Structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-Butyl)Phenyl)Thio)-4-Hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 37–39; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2021-0365.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

