Abstract
C45H47N13O4, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 10.242(6) Å, b = 14.766(15) Å, c = 15.503(8) Å, α = 70.91(2)°, β = 88.052(16)°, γ = 74.13(3)°, V = 2127(3) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0411, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1059, T = 120(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.33 × 0.29 × 0.21 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) 0.09 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θ max, completeness: |
Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω
25.4°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 52751, 7782, 0.050 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 6364 |
| N(param)refined: | 567 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 , 4 Diamond 5 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.1229 (2) | 0.57380 (16) | 0.89109 (14) | 0.0480 (5) |
| H1 | 0.1185 | 0.5069 | 0.9170 | 0.058* |
| C2 | 0.0670 (2) | 0.63972 (16) | 0.93716 (14) | 0.0463 (5) |
| H2 | 0.0255 | 0.6187 | 0.9932 | 0.056* |
| C3 | 0.0731 (2) | 0.73690 (15) | 0.89974 (13) | 0.0409 (5) |
| H3A | 0.0351 | 0.7843 | 0.9294 | 0.049* |
| C4 | 0.13507 (18) | 0.76437 (14) | 0.81866 (13) | 0.0344 (4) |
| H4A | 0.1407 | 0.8309 | 0.7918 | 0.041* |
| C5 | 0.18915 (17) | 0.69335 (13) | 0.77670 (12) | 0.0286 (4) |
| C6 | 0.26186 (16) | 0.71486 (12) | 0.69186 (11) | 0.0271 (4) |
| H6 | 0.2786 | 0.6692 | 0.6588 | 0.032* |
| C7 | 0.37492 (16) | 0.81085 (11) | 0.58017 (11) | 0.0241 (3) |
| C8 | 0.47468 (16) | 0.86042 (12) | 0.57503 (11) | 0.0259 (4) |
| H8A | 0.4911 | 0.8811 | 0.6246 | 0.031* |
| C9 | 0.54994 (16) | 0.87982 (11) | 0.49854 (11) | 0.0253 (4) |
| H9 | 0.6200 | 0.9111 | 0.4973 | 0.030* |
| C10 | 0.52385 (16) | 0.85388 (11) | 0.42338 (11) | 0.0242 (3) |
| C11 | 0.42126 (16) | 0.80661 (12) | 0.42711 (11) | 0.0257 (4) |
| H11A | 0.4010 | 0.7898 | 0.3760 | 0.031* |
| C12 | 0.34909 (16) | 0.78423 (12) | 0.50502 (11) | 0.0256 (4) |
| H12A | 0.2815 | 0.7505 | 0.5074 | 0.031* |
| C13 | 0.63265 (15) | 0.83286 (11) | 0.28296 (11) | 0.0231 (3) |
| C14 | 0.74692 (16) | 0.83580 (12) | 0.13970 (11) | 0.0254 (4) |
| H14A | 0.7114 | 0.8892 | 0.0809 | 0.030* |
| H14B | 0.7054 | 0.7811 | 0.1454 | 0.030* |
| C15 | 0.89992 (16) | 0.79658 (12) | 0.13731 (10) | 0.0244 (3) |
| H15A | 0.9203 | 0.7812 | 0.0799 | 0.029* |
| H15B | 0.9423 | 0.8496 | 0.1365 | 0.029* |
| C16 | 0.3423 (2) | 0.24864 (14) | 1.05648 (12) | 0.0372 (4) |
| H16 | 0.2784 | 0.2106 | 1.0693 | 0.045* |
| C17 | 0.4215 (2) | 0.24448 (16) | 1.12856 (13) | 0.0415 (5) |
| H17 | 0.4151 | 0.2024 | 1.1889 | 0.050* |
| C18 | 0.5101 (2) | 0.30298 (18) | 1.11089 (13) | 0.0471 (5) |
| H18 | 0.5629 | 0.3043 | 1.1595 | 0.057* |
| C19 | 0.52137 (19) | 0.35978 (15) | 1.02157 (13) | 0.0380 (4) |
| H19 | 0.5819 | 0.4005 | 1.0077 | 0.046* |
| C20 | 0.44196 (17) | 0.35580 (13) | 0.95284 (12) | 0.0290 (4) |
| C21 | 0.45851 (17) | 0.40499 (13) | 0.85516 (12) | 0.0303 (4) |
| H21 | 0.4000 | 0.4029 | 0.8100 | 0.036* |
| C22 | 0.57436 (16) | 0.48457 (12) | 0.73628 (11) | 0.0273 (4) |
| C23 | 0.61822 (18) | 0.57036 (13) | 0.70348 (12) | 0.0310 (4) |
| H23 | 0.6231 | 0.6071 | 0.7428 | 0.037* |
| C24 | 0.65458 (17) | 0.60251 (12) | 0.61459 (12) | 0.0295 (4) |
| H24 | 0.6805 | 0.6627 | 0.5924 | 0.035* |
| C25 | 0.65363 (16) | 0.54762 (12) | 0.55702 (11) | 0.0253 (4) |
| C26 | 0.61028 (16) | 0.46152 (12) | 0.58894 (11) | 0.0262 (4) |
| H26 | 0.6089 | 0.4237 | 0.5500 | 0.031* |
| C27 | 0.56915 (16) | 0.43083 (12) | 0.67754 (11) | 0.0271 (4) |
| H27 | 0.5373 | 0.3731 | 0.6984 | 0.033* |
| C28 | 0.79690 (17) | 0.52882 (12) | 0.42935 (11) | 0.0275 (4) |
| C29 | 0.93707 (17) | 0.53848 (12) | 0.29665 (11) | 0.0272 (4) |
| H29A | 0.9317 | 0.4763 | 0.2876 | 0.033* |
| H29B | 1.0214 | 0.5233 | 0.3343 | 0.033* |
| C30 | 0.93950 (17) | 0.61702 (12) | 0.20476 (11) | 0.0251 (4) |
| H30A | 1.0130 | 0.5889 | 0.1699 | 0.030* |
| H30B | 0.8521 | 0.6349 | 0.1694 | 0.030* |
| C31 | 0.8287 (2) | 1.07287 (14) | 0.97354 (13) | 0.0376 (4) |
| H31 | 0.8962 | 1.0826 | 1.0074 | 0.045* |
| C32 | 0.6957 (2) | 1.10197 (14) | 0.99386 (14) | 0.0391 (4) |
| H32 | 0.6717 | 1.1328 | 1.0394 | 0.047* |
| C33 | 0.5976 (2) | 1.08547 (15) | 0.94679 (15) | 0.0448 (5) |
| H33 | 0.5046 | 1.1047 | 0.9595 | 0.054* |
| C34 | 0.63602 (19) | 1.04073 (14) | 0.88102 (13) | 0.0380 (4) |
| H34 | 0.5705 | 1.0273 | 0.8486 | 0.046* |
| C35 | 0.77240 (18) | 1.01576 (12) | 0.86316 (12) | 0.0295 (4) |
| C36 | 0.82269 (19) | 0.97185 (13) | 0.79089 (12) | 0.0329 (4) |
| H36 | 0.9039 | 0.9821 | 0.7631 | 0.039* |
| C37 | 0.81548 (17) | 0.88400 (13) | 0.69330 (12) | 0.0297 (4) |
| C38 | 0.85181 (19) | 0.94384 (13) | 0.61197 (12) | 0.0331 (4) |
| H38 | 0.8391 | 1.0126 | 0.6028 | 0.040* |
| C39 | 0.90614 (19) | 0.90572 (13) | 0.54384 (12) | 0.0327 (4) |
| H39 | 0.9285 | 0.9484 | 0.4883 | 0.039* |
| C40 | 0.92789 (16) | 0.80457 (12) | 0.55697 (12) | 0.0269 (4) |
| C41 | 0.88951 (17) | 0.74470 (12) | 0.63807 (12) | 0.0301 (4) |
| H41 | 0.9025 | 0.6759 | 0.6475 | 0.036* |
| C42 | 0.83304 (17) | 0.78349 (13) | 0.70487 (12) | 0.0314 (4) |
| H42 | 0.8060 | 0.7416 | 0.7590 | 0.038* |
| C43 | 1.02303 (17) | 0.80029 (12) | 0.40722 (11) | 0.0267 (4) |
| C44 | 1.13525 (18) | 0.76380 (12) | 0.27554 (11) | 0.0288 (4) |
| H44A | 1.2328 | 0.7615 | 0.2728 | 0.035* |
| H44B | 1.0815 | 0.8332 | 0.2431 | 0.035* |
| C45 | 1.10698 (16) | 0.69522 (12) | 0.22837 (11) | 0.0250 (4) |
| H45A | 1.1476 | 0.7087 | 0.1682 | 0.030* |
| H45B | 1.1516 | 0.6252 | 0.2655 | 0.030* |
| N1 | 0.18307 (16) | 0.59884 (11) | 0.81175 (11) | 0.0375 (4) |
| N2 | 0.30294 (13) | 0.79322 (10) | 0.66151 (9) | 0.0256 (3) |
| N3 | 0.59786 (14) | 0.88215 (10) | 0.34524 (9) | 0.0275 (3) |
| H3 | 0.6241 | 0.9364 | 0.3356 | 0.033* |
| N4 | 0.70468 (14) | 0.87530 (10) | 0.21420 (9) | 0.0256 (3) |
| H4 | 0.7268 | 0.9287 | 0.2145 | 0.031* |
| N5 | 0.35014 (15) | 0.30280 (11) | 0.96983 (10) | 0.0336 (3) |
| N6 | 0.54983 (15) | 0.45011 (11) | 0.83051 (10) | 0.0305 (3) |
| N7 | 0.69215 (14) | 0.58263 (10) | 0.46540 (9) | 0.0300 (3) |
| H7 | 0.6460 | 0.6423 | 0.4299 | 0.036* |
| N8 | 0.81914 (14) | 0.57647 (10) | 0.34294 (9) | 0.0296 (3) |
| H8 | 0.7599 | 0.6333 | 0.3128 | 0.036* |
| N9 | 0.86900 (15) | 1.03132 (12) | 0.90843 (11) | 0.0365 (4) |
| N10 | 0.76015 (15) | 0.92080 (11) | 0.76502 (10) | 0.0325 (3) |
| N11 | 0.98874 (15) | 0.75750 (10) | 0.49445 (10) | 0.0302 (3) |
| H11 | 1.0073 | 0.6920 | 0.5138 | 0.036* |
| N12 | 1.10057 (15) | 0.73460 (10) | 0.37031 (9) | 0.0302 (3) |
| H12 | 1.1313 | 0.6717 | 0.4049 | 0.036* |
| N13 | 0.96127 (13) | 0.70735 (9) | 0.21468 (9) | 0.0216 (3) |
| O1 | 0.60037 (11) | 0.75569 (8) | 0.28979 (7) | 0.0256 (3) |
| O2 | 0.86489 (14) | 0.44333 (9) | 0.47375 (8) | 0.0397 (3) |
| O3 | 0.98820 (13) | 0.89132 (8) | 0.36622 (8) | 0.0342 (3) |
| O4 | 0.75066 (14) | 0.02647 (10) | 0.28975 (9) | 0.0341 (3) |
| H4B | 0.735 (2) | 0.0799 (18) | 0.3028 (15) | 0.057 (7)* |
| H4C | 0.831 (3) | −0.016 (2) | 0.3181 (17) | 0.074 (8)* |
1 Source of material
The target compound was synthesized in three synthetic steps. Fistly, a solution of tris(2-aminoethyl) amine (0.7 g, 4.79 mmol) in 15 mL of THF was added dropwise to a solution of p-nitroisocyanate(2.15 g, 13.10 mmol) in THF (15 mL). After refluxing under intensive stirring for 4 h, the precipitate was filtered off and washed several times with THF and diethyl ether and then dried in vacuum to yield analytically pure 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris (ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-nitrophenyl)urea) (La) as a yellow solid. Secondly, hydrazine monohydrate (11 mL) was added dropwise to the suspension of La and Pd/C 10 % (0.2 g, cat.) in ethanol (70 mL). After refluxing under stirring for 12 h, the solid was filtered off via suction filtration and dissolved in DMF (10 mL) and filtered through Celite to remove Pd/C. The DMF solution was poured in water (150 mL), and the precipitate thus obtained was filtered off, washed several times with ethanol and diethyl ether and dried to give analytically pure 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-aminophenyl)urea) (Lb) as a white solid. Lastly, 2-pyridylaldehyde was added to a solution of Lb in 5 mL of DMSO stirring at room temperature for 12 h. Subsequently, the precipitate was filtered, and washed several times with acetonitrile and diethyl ether, and dried over vacuum to get the target compound (L) as a yellow solid (0.48 g, 0.59 mmol, 80 %). At room temperature, yellow block crystals of L were obtained by ether diffusion method.
2 Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with C–H = 0.96 Å (methyl), U iso (H) = 1.5 U eq (C), C–H = 0.98 Å (methine), U iso (H) = 1.2 U eq (C), C–H = 0.93 Å (aromatic and alkenyl), U iso (H) = 1.2 U eq (C), and O–H = 0.82 Å (hydroxyl), U iso (H) = 1.5 U eq (O).
3 Comment
Over the past few decades, tripodal urea derivatives have been proved to be a class of excellent anion receptors since the tripodal framework offers a greater opportunity for the spatially adaptive encapsulation of anions with size- and shape-complementarity than linear receptors. 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 Such receptors typically contain three or six urea units, which can effectively bind with anions through multiple hydrogen bonds, making them valuable in various applications including anion extraction, 8 , 9 anion recognition 10 , 11 , 12 and transmembrane transport. 13 In this study, a novel imine-pyridine-functionalized tripodal tris(urea) receptor was prepared and its structure confirmed by single crystal X-ray diffraction.
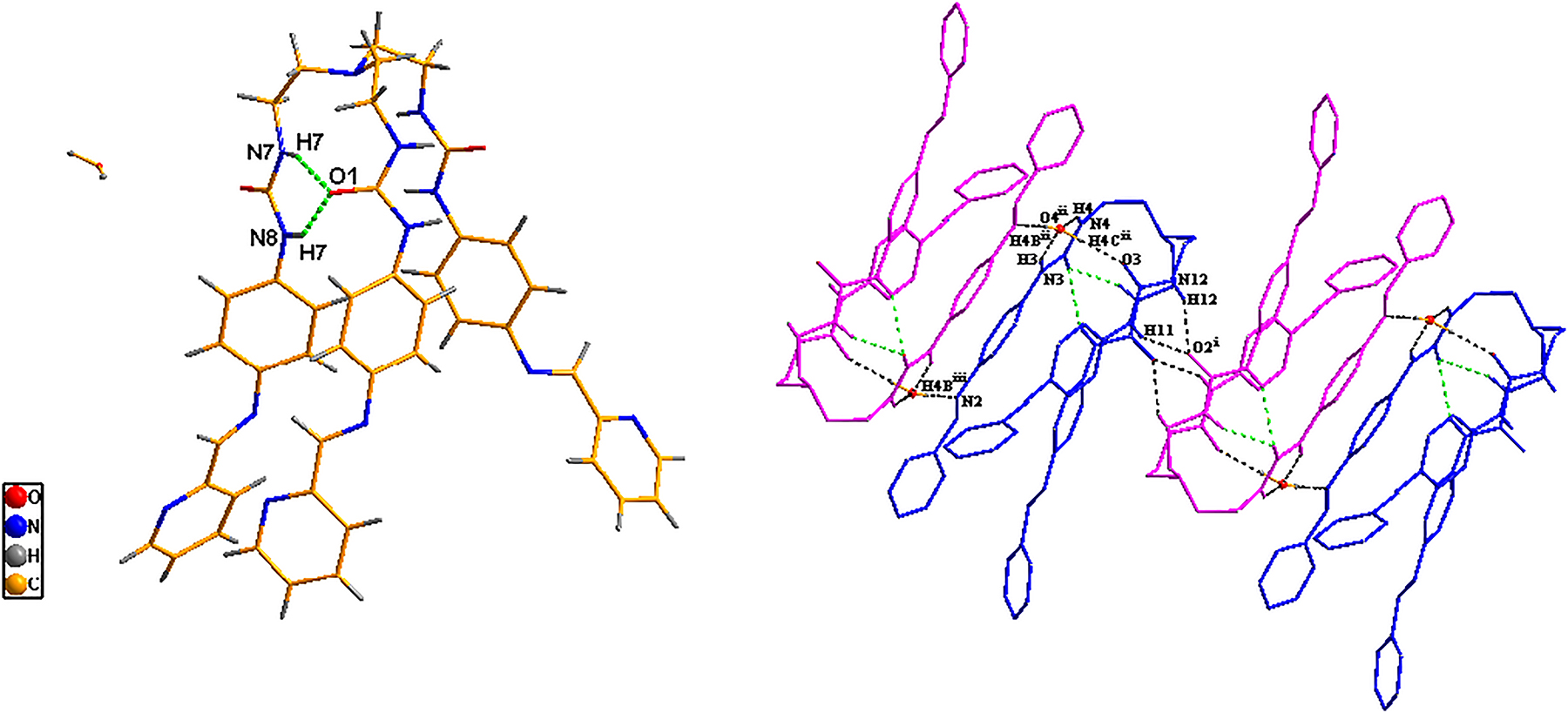
The asymmetric structural unit contains one title molecule (see left part of the figure) and one lattice water molecule. In the tripodal structure, NH groups on two urea units point towards the outside of the cavity, while NH groups on the other urea unit point towards the inside of the cavity. The two urea groups pointing in the same direction form two intramolecular hydrogen bonds of N7–H7···O1(dN7···O1 = 3.020 Å, 148.49°), and N8–H8···O1(dN8···O2 = 2.854 Å, 159.04°). Moreover, there are six intermolecular hydrogen bonds formed by three urea units and the water molecule. Among them, O4 atom from lattice water takes part in four intermolecular hydrogen bonds with three urea units, viz. N3 ii – H3 ii ···O4, N4 ii – H4 ii ···O4, O4–H4C···O3 ii and O4–H4B···N2 iii (symmetry code: (ii) x, y + 1, z; (iii) −x + 2, −y + 1, −z + 1). Meanwhile, O2 atom from one urea unit takes part in two intermolecular hydrogen bonds with another urea unit from the adjacent molecule, viz. N11 i – H11 i ···O2 and N12 i – H12 i ···O2 (symmetry code: (i) −x + 2, −y + 1, −z + 1). The distance of N7···O1 is in the range of 2.702–2.984 Å and the angle of the intermolecular hydrogen bonds is in the range of 148.91–177.43°. The intermolecular hydrogen bonds contribute to the formation of a one-dimensional chain in the crystal structure (right part of the structure).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: The work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (22003055) and Nanhu Scholars Program for Young Scholars of the Xinyang Normal University.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND; Crystal Impact GbR: Bonn Germany, 2006.Search in Google Scholar
6. Vilar, R. Anion Recognition and Templation in Coordination Chemistry. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 3, 357–367; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.200701017.Search in Google Scholar
7. Zhao, J.; Yang, D.; Yang, X. J.; Wu, B. Anion Coordination Chemistry: From Recognition to Supramolecular Assembly. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 415–444; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2018.01.002.Search in Google Scholar
8. Chen, S. Q.; Yu, S. N.; Zhao, W.; Liang, L.; Gong, Y. Y.; Yuan, L. F.; Tang, J.; Yang, X. J.; Wu, B. Recognition-guided Sulfate Extraction and Transport Using Tripodal Hexaurea Receptors. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 6091–6101; https://doi.org/10.1039/d2qi01991d.Search in Google Scholar
9. Jia, C. D.; Wu, B.; Li, S. G.; Huang, X. J.; Zhao, Q. L.; Li, Q. S.; Yang, X. J. Highly Efficient Extraction of Sulfate Ions with a Tripodal Hexaurea Receptor. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 486–490; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201004461.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Ravikumar, I.; Lakshminarayanan, P. S.; Arunachalam, M.; Suresh, E.; Ghosh, P. Anion Complexation of a Pentafluorophenyl-Substituted Tripodal Urea Receptor in Solution and the Solid State: Selectivity toward Phosphate. Dalton Trans. 2009, 21, 4160–4168; https://doi.org/10.1039/b820322a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Custelcean, R.; Remy, P.; Bonnesen, P. V.; Jiang, D. E.; Moyer, B. A. Sulfate Recognition by Persistent Crystalline Capsules with Rigidified Hydrogen–Bonding Cavities. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 47, 1866–1870; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200704937.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Zhao, J.; Yang, D.; Zhao, Y. X.; Cao, L. P.; Zhang, Z. B.; Yang, X. J.; Wu, B. Phosphate-induced Fluorescence of a Tetraphenylethene-Substituted Tripodal Tris(urea) Receptor. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 7360–7365; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6dt00672h.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Gale, P. A. From Anion Receptors to Transporters. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 216–226; https://doi.org/10.1021/ar100134p.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Zhang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ji, L. G.; Yang, X. J.; Wu, B. Chloride Encapsulation by a Tripodal Tris(4-Pyridylurea) Ligand and Effects of Countercations on the Secondary Coordination Sphere. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 544–551; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg401345z.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3

