Abstract
C20H17N3O7Zn, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 10.4368(3) Å, b = 15.1527(5) Å, c = 12.9007(3) Å, β = 101.900(3)°, V = 1996.36(10) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0410, wRref(F2) = 0.0898, T = 293(2) K.
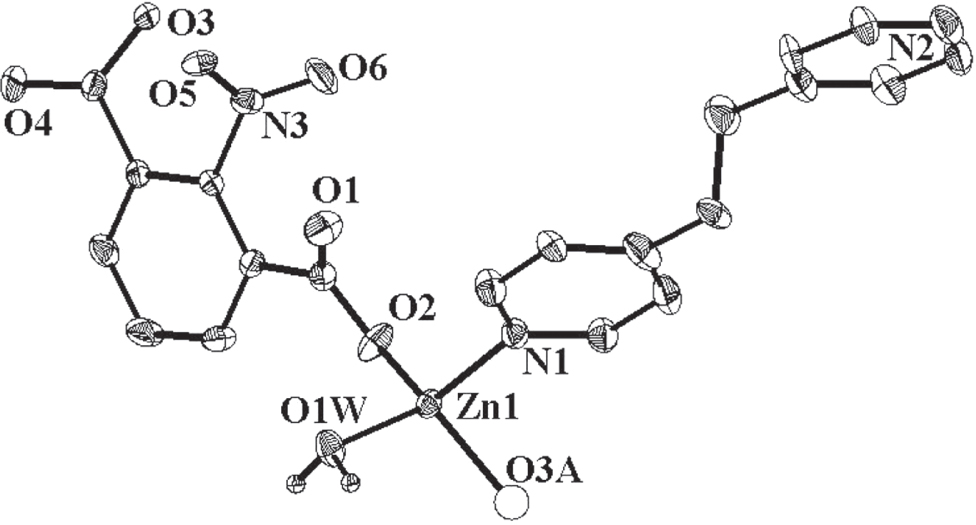
A part of the molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.36 × 0.33 × 0.27 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.28 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 20317, 4466, 0.038 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3729 |
| N(param)refined: | 281 |
| Programs: | Olex2 [1], SHELX [2], [3], CrysAlisPRO [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1 | 0.89979(3) | 0.38717(2) | 0.56375(2) | 0.02860(10) |
| O1 | 0.68499(19) | 0.35737(14) | 0.69036(15) | 0.0485(5) |
| O1W | 0.94251(19) | 0.49672(12) | 0.64465(13) | 0.0412(5) |
| H1WA | 0.9667 | 0.5373 | 0.6053 | 0.062* |
| H1WB | 1.0114 | 0.4891 | 0.6944 | 0.062* |
| O2 | 0.8708(2) | 0.29882(13) | 0.66243(15) | 0.0465(5) |
| O3 | 0.53519(17) | 0.14114(12) | 0.98166(13) | 0.0347(4) |
| O4 | 0.6547(2) | 0.19044(16) | 1.13325(14) | 0.0574(6) |
| O5 | 0.5052(2) | 0.30051(15) | 0.85146(19) | 0.0579(6) |
| O6 | 0.5387(2) | 0.19727(15) | 0.74532(15) | 0.0556(6) |
| N1 | 0.7530(2) | 0.41113(14) | 0.43740(16) | 0.0322(5) |
| N2 | 0.1051(3) | 0.48538(18) | −0.16684(18) | 0.0522(7) |
| N3 | 0.5746(2) | 0.24749(15) | 0.81933(17) | 0.0342(5) |
| C1 | 0.7818(3) | 0.31110(16) | 0.71605(19) | 0.0312(6) |
| C2 | 0.8100(2) | 0.26564(16) | 0.82256(18) | 0.0268(5) |
| C3 | 0.9390(2) | 0.25657(18) | 0.8762(2) | 0.0382(6) |
| H3 | 1.0065 | 0.2699 | 0.8416 | 0.046* |
| C4 | 0.9687(3) | 0.2281(2) | 0.9800(2) | 0.0458(7) |
| H4 | 1.0556 | 0.2233 | 1.0152 | 0.055* |
| C5 | 0.8700(3) | 0.20672(18) | 1.0313(2) | 0.0384(6) |
| H5 | 0.8909 | 0.1896 | 1.1020 | 0.046* |
| C6 | 0.7393(2) | 0.21026(16) | 0.97938(18) | 0.0281(5) |
| C7 | 0.7129(2) | 0.24070(15) | 0.87552(17) | 0.0249(5) |
| C8 | 0.6368(3) | 0.18000(17) | 1.03781(19) | 0.0323(6) |
| C9 | 0.6605(3) | 0.4719(2) | 0.4366(2) | 0.0462(7) |
| H9 | 0.6587 | 0.5023 | 0.4989 | 0.055* |
| C10 | 0.5673(3) | 0.4917(2) | 0.3470(3) | 0.0573(9) |
| H10 | 0.5041 | 0.5345 | 0.3497 | 0.069* |
| C11 | 0.5683(3) | 0.4478(2) | 0.2538(2) | 0.0526(8) |
| C12 | 0.6595(3) | 0.3822(2) | 0.2559(2) | 0.0519(8) |
| H12 | 0.6601 | 0.3488 | 0.1956 | 0.062* |
| C13 | 0.7498(3) | 0.36622(19) | 0.3474(2) | 0.0413(7) |
| H13 | 0.8116 | 0.3221 | 0.3470 | 0.050* |
| C14 | 0.4741(4) | 0.4708(3) | 0.1501(3) | 0.0744(12) |
| H14A | 0.4699 | 0.5345 | 0.1424 | 0.089* |
| H14B | 0.5084 | 0.4471 | 0.0914 | 0.089* |
| C15 | 0.3409(3) | 0.4364(2) | 0.1443(2) | 0.0573(9) |
| H15A | 0.3018 | 0.4649 | 0.1975 | 0.069* |
| H15B | 0.3448 | 0.3735 | 0.1584 | 0.069* |
| C16 | 0.2575(3) | 0.4536(2) | 0.0346(2) | 0.0467(7) |
| C17 | 0.2602(3) | 0.3977(2) | −0.0491(2) | 0.0525(8) |
| H17 | 0.3136 | 0.3480 | −0.0394 | 0.063* |
| C18 | 0.1835(3) | 0.4155(2) | −0.1475(2) | 0.0533(8) |
| H18 | 0.1868 | 0.3768 | −0.2029 | 0.064* |
| C19 | 0.1050(4) | 0.5395(2) | −0.0874(3) | 0.0664(10) |
| H19 | 0.0516 | 0.5892 | −0.0995 | 0.080* |
| C20 | 0.1792(4) | 0.5269(2) | 0.0126(3) | 0.0679(11) |
| H20 | 0.1765 | 0.5682 | 0.0655 | 0.081* |
Source of material
All reagents used in the synthesis were of analytical grade and used as purchased without further purification. The mixtures of 2-nitroisophthalic acid (nipc) (0.1 mmol, 21.1 mg), Zn(OAC)2 ⋅ 2H2O (0.1 mmol, 22.0 mg), 1,2-bi(4-pyridyl)ethane (bpa) (0.1 mmol, 18.4 mg) and H2O (6.0 mL) was placed in a 23 mL Teflon liner stainless steel reactor. The vessel was heated to 393 K for 4 days, and then slowly cooled to room temperature. Colorless crystals were obtained, and further crystals were filtered off, washed with mother liquid, and dried under ambient conditions. Yield 46%.
Experimental details
A suitable crystal was selected and mounted on a SuperNova, Single source at offset/far, EosS2 diffractometer. Using Olex2 [1], the structure was solved with the ShelXT [2] structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL [3] refinement package. All hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions with a riding model.
Comment
A coordination polymer is generally formed by self-assembly through coordination bonds between ligands and central metal ions or clusters to produce one-, two-, or three-dimensional metal-organic coordination network [5], [6], [7]. Porous coordination polymers (PCPs) are of great interest due to their potential applications in guest exchange and separation, gas storage, and selective catalysis, etc [8], [9], [10]. For many years, it has been demonstrated that intermolecular weak interactions including H-bonds, π–π interactions, and even van der Waals forces are able to create stable molecular networks in crystalline solids that are reproducible, thermally stable, and resilient upon undergoing dynamic processes [11], [12]. Our work focuses on the design and synthesis of functional PCPs based on multitopic organic ligands. We select 2-nitroisophthalate (nipc) as the assembly ligand, considering its following characteristics: (a) it is a bent ligand with the two carboxylate groups located at appropriate angles (approximately 120°), which may allow it to connect metal ions to generate 1D helical chains; (b) the nitro and carboxylate groups of the ligand can act as hydrogen-bond donors. In addition, the dipyridyl-type pillar ligands, such as 4,4′-bipyridine (bpy), 1,2-bi(4-pyridyl)ethane (bpa), 1,2-di(4-pyridyl)-ethylene(dpe), 1,3-di(4-pyridyl)propane (bpp), and trans-1-(2-pyridyl)-2-(4-pyridyl)ethylene (ppe), are known to be ideal connectors for the propagation of coordination networks and can provide a synergistic coordination together with carboxylate ligands [13], [14], [15]. To the best of our knowledge, coordination polymers constructed from the nipc ligand are rather rare.
The asymmetric unit contains one Zn(II) atom, one bpa molecule, one nipc dianion and one coordinated H2O. Each Zn(II) ion is four coordinated by three oxygen atoms from two carboxylate groups of nipc and one coordinated water (Zn—O: 1.9138(18) Å – 1.9797(17) Å), and one nitrogen atom of the bpa ligand (Zn—N: 2.026(2) Å), displaying a highly distorted tetrahedral coordination environment. Each nipc anion through a bis(monodentate) coordinated mode bridges adjacent Zn(II) atoms to yield an undulating helical chain along the [111] direction, with bpa ligands as free lateral arms; in contrast to a similar 2D network containing analogous ligands [16]. The paralleled chains are connected by H-bonds between H2O molecule and carboxylate oxygen atom of nipc ligand [O(1W)-H(1WA)⋯O(3); d(O1⋯O3) = 2.767(2) Å; degree (H—O⋯O3) = 161.6°] forming a open layered motif. Two adjacent layer blocks are connected by H-bonds between H2O molecule and pyridine N atoms of bpa molecules [O(1W)-H(1WB)⋯N(2); d(O1⋯N2) = 2.668(3) Å; degree (H—O⋯N2) = 155.5°] producing its 3D supramolecular network.
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21571093
Funding statement: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21571093).
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H.: OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program J. Appl. Crystallogr. 42 (2009) 339–341.10.1107/S0021889808042726Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Agilent Technologies: CrysAlisPRO Software system. Version 1.171.35.15. Agilent Technologies UK Ltd, Oxford, UK (2011).Suche in Google Scholar
5. Liu, G. Z.; Wang, J. G.; Wang, L. Y.: Divalent metal coordination polymers assembled from dual linkers-semirigid carboxyphenylpropionate and dipyridyl type molecule. CrystEngComm 14 (2012) 951–960.10.1039/C1CE05760JSuche in Google Scholar
6. Li, Z. H.; Li, Z. Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y. Y.; Zhao, B. T.: Auxiliary ligands mediated one- and two-dimensional Cd(II) coordination polymers incorporating methyl-3- hydroxy-5-carboxy-2-thiophenecarboxylate ligand. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 37 (2018) 617–623.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Xin, L. Y.; Liu, G. Z.; Ma, L. F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Y.: Structural diversity and fluorescence regulation of three ZnII coordination polymers assembled from mixed ligands tectons. Aust. J. Chem. 68 (2015) 758–765.10.1071/CH14347Suche in Google Scholar
8. Zheng, D. D.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Kurmoo, M.; Zeng, M. H.: A porous metal-organic framework [Zn2(bdc)(L-lac)] as a coating material for capillary columns of gas chromatography. Inorg. Chem. 56 (2017) 11043–11049.10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b01413Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, N. N.; Han, M. L.; Yang, G. P.; Ma, L. F.: Porous Zn(II)-based metal-organic frameworks decorated with carboxylate groups exhibiting high gas adsorption and separation of organic dyes. Cryst. Growth Des. 18 (2018) 7114–7121.10.1021/acs.cgd.8b01290Suche in Google Scholar
10. Xue, L. P.; Li, Z. H.; Zhang, T.; Cui, J. J.; Gao, Y.; Yao, J. X.: Construction of two Zn(II)/Cd(II) multifunctional coordination polymers with mixed ligands for catalytic and sensing properties. New J. Chem. 42 (2018) 14203–14209.10.1039/C8NJ02055HSuche in Google Scholar
11. Li, X. L.; Liu, G. Z.; Xin, L. Y.; Wang, L. Y.: A novel metal-organic framework displaying reversibly shrinking and expanding pore modulation. CrystEngComm 14 (2012) 5757–5760.10.1039/c2ce25715gSuche in Google Scholar
12. Shekurov, R.; Miluykov, V.; Kataeva, O.; Krivolapov, D.; Sinyashin, O.; Gerasimova, T.; Katsyuba, S.; Kovalenko, V.; Krupskaya, Y.; Kataev, V.; Buchner, B.; Senkovska, I.: Reversible water-induced structural and magnetic transformations and selective water adsorption properties of poly(manganese 1,1′- ferrocenediyl-bis(H-phosphinate)). Cryst. Growth Des. 16 (2016) 5084–5090.10.1021/acs.cgd.6b00681Suche in Google Scholar
13. Xin, L. Y.; Liu, G. Z.; Li, X. L.; Wang, L. Y.; Structural diversity for a series of metal(II) complexes based on flexible 1,2-phenylenediacetate and dipyridyl-type coligand. Cryst. Growth Des. 12 (2012) 147–157.10.1021/cg200903kSuche in Google Scholar
14. Wang, Y. F.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y. C.; Zhao, J. S.; Zhang, S. C.: Synthesis, characterization and crystal structures of 2D Co(II)/Zn(II)-coordination polymers containing 3-(pyridin-4-yl)-5-(pyrazin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole and benzenetetracarboxylate co-ligands. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 44 (2014) 25–28.10.1016/j.inoche.2014.02.043Suche in Google Scholar
15. Li, Y. P.; Ju, F. Y.; Li, G. L.; Xin, L. Y.; Li, X. L.; Liu, G. Z.: Syntheses, structures, and properties of two Zn(II)/Ag(I) complexes assembled from tetracarboxylic acids and N-donor ligands. Koord. Khim. 44 (2018) 214–219.10.1134/S1070328418030028Suche in Google Scholar
16. Adalikwu, S. A.; Mothika, V. S.; Hazra, A.; Maji, T. K.: Polar functional groups anchored to a 2D MOF template for the stabilization of Pd(0) nps for the catalytic C–C coupling reaction. Dalton Trans. 48 (2019) 7117–7121.10.1039/C8DT04766ASuche in Google Scholar PubMed
©2019 Guang-Zhen Liu et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n
Artikel in diesem Heft
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n


