Abstract
C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4, orthorhombic, Pbca (no. 61), a = 13.9593(2) Å, b = 11.1227(2) Å, c = 21.6656(3) Å, V = 3363.91(9) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0252, wRref(F2) = 0.0642, T = 100(2) K.
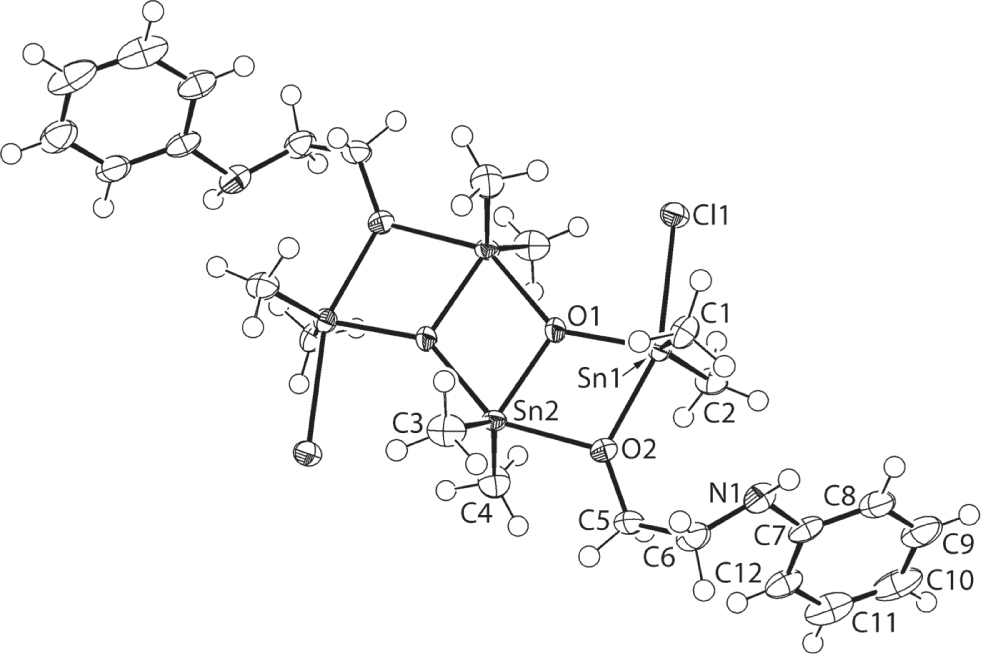
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| Size: | 0.16 × 0.12 × 0.06 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 25.0 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 67.1°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 21693, 3006, 0.042 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2840 |
| N(param)refined: | 170 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sn1 | 0.53720(2) | 0.28294(2) | 0.47533(2) | 0.01347(9) |
| Sn2 | 0.46391(2) | 0.01011(2) | 0.42686(2) | 0.01254(9) |
| Cl1 | 0.59652(6) | 0.30565(8) | 0.58783(4) | 0.01838(18) |
| O1 | 0.51453(17) | 0.1109(2) | 0.49898(11) | 0.0165(5) |
| O2 | 0.47623(17) | 0.1953(2) | 0.39460(12) | 0.0180(5) |
| N1 | 0.5083(2) | 0.4455(3) | 0.34412(15) | 0.0203(7) |
| H1N | 0.480(3) | 0.510(2) | 0.360(2) | 0.024* |
| C1 | 0.4119(2) | 0.3840(3) | 0.49237(18) | 0.0188(7) |
| H1A | 0.3558 | 0.3315 | 0.4893 | 0.028* |
| H1B | 0.4068 | 0.4487 | 0.4618 | 0.028* |
| H1C | 0.4151 | 0.4188 | 0.5339 | 0.028* |
| C2 | 0.6758(2) | 0.3090(4) | 0.43797(17) | 0.0200(8) |
| H2A | 0.6890 | 0.2463 | 0.4074 | 0.030* |
| H2B | 0.7234 | 0.3047 | 0.4711 | 0.030* |
| H2C | 0.6791 | 0.3881 | 0.4181 | 0.030* |
| C3 | 0.3131(3) | 0.0038(4) | 0.42892(19) | 0.0243(9) |
| H3A | 0.2906 | 0.0202 | 0.4709 | 0.036* |
| H3B | 0.2914 | −0.0762 | 0.4161 | 0.036* |
| H3C | 0.2871 | 0.0645 | 0.4007 | 0.036* |
| C4 | 0.5720(3) | −0.0579(4) | 0.36759(19) | 0.0238(8) |
| H4A | 0.6352 | −0.0416 | 0.3855 | 0.036* |
| H4B | 0.5673 | −0.0187 | 0.3272 | 0.036* |
| H4C | 0.5637 | −0.1449 | 0.3626 | 0.036* |
| C5 | 0.4829(3) | 0.2247(3) | 0.33104(18) | 0.0216(8) |
| H5A | 0.4448 | 0.1666 | 0.3067 | 0.026* |
| H5B | 0.5505 | 0.2183 | 0.3176 | 0.026* |
| C6 | 0.4466(3) | 0.3514(4) | 0.31875(18) | 0.0232(8) |
| H6A | 0.4410 | 0.3632 | 0.2736 | 0.028* |
| H6B | 0.3818 | 0.3598 | 0.3368 | 0.028* |
| C7 | 0.5856(3) | 0.4890(3) | 0.30925(18) | 0.0200(8) |
| C8 | 0.6262(3) | 0.6010(4) | 0.32490(18) | 0.0255(8) |
| H8 | 0.5995 | 0.6463 | 0.3579 | 0.031* |
| C9 | 0.7039(3) | 0.6458(4) | 0.2931(2) | 0.0334(10) |
| H9 | 0.7300 | 0.7218 | 0.3040 | 0.040* |
| C10 | 0.7444(3) | 0.5798(5) | 0.2449(2) | 0.0373(11) |
| H10 | 0.7984 | 0.6098 | 0.2231 | 0.045* |
| C11 | 0.7046(3) | 0.4702(5) | 0.2294(2) | 0.0342(11) |
| H11 | 0.7320 | 0.4246 | 0.1968 | 0.041* |
| C12 | 0.6259(3) | 0.4255(4) | 0.26014(18) | 0.0248(8) |
| H12 | 0.5988 | 0.3509 | 0.2478 | 0.030* |
Source of material
All chemicals and solvents were used as purchased without purification. The melting point of the compound was measured on a Mel-Temp II digital melting point apparatus and was uncorrected. The IR spectrum was recorded on a Perkin-Elmer RX1 spectrophotometer in the range 4000 to 400 cm−1.
The dithiocarbamate salt, K[S2CN(Ph)CH2CH2OH], was prepared in situ (methanol) from the reaction of CS2 (Merck, 0.25 mmol) with 2-anilinoethanol (Merck, 0.25 mmol) and KOH (0.03 mL; 50% w/v); CS2 was added dropwise into the methanolic solution (10 mL). The resulting mixture solution was kept at 273 K for 0.5 h. Dimethyltin dichloride (0.25 mmol, 0.05 g) in methanol (10 mL) was added to the prepared salt. The resulting mixture was stirred and refluxed for 2 h. The filtrate was evaporated slowly until a white precipitate was formed. The precipitate was recrystallised from methanol and dimethylformamide. The title molecule was isolated as a side-product obtained from the slow evaporation of the solvent. Yield: 0.02 g (16%). M.pt: >573 K. IR (cm−1) 467 (w) ν(Sn—O), 1487 (m) ν(C—N), 1018 (s) ν(C—O).
Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C). The N-bound H-atom was located in a difference Fourier map but was refined with a distance restraint of N—H = 0.88 ± 0.01 Å, and with Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(N).
Comment
Diorganotin dichloride molecules are well-known to be subject to hydrolysis [5], [6] and it was in this context the crystals of the title tetra-tin oxido-cluster {[(Me2SnCl)(Me2Sn)(OCH2CH2N(H)Ph)]O}2, (I), was isolated. The difficulties associated with hydrolysis notwithstanding, recent work has highlighted the potential anti-tumour activity of related tetra-tin oxido clusters [7], [8], a well-documented attribute of organotin compounds [9]. Herein, the crystal and molecular structures of (I) are described.
The molecular structure of (I) is shown in the figure (70% displacement ellipsoids; unlabelled atoms are related by the symmetry operation (i) 1 − x, −y, 1 − z); the entire molecule is generated by the application of a crystallographic centre of inversion. The molecule is constructed about a central Sn2O2 core, containing endocyclic Sn2 atoms. The μ3-O1 oxido atom of the core also binds to an exocyclic Sn1 atom. Further links between the Sn1 and Sn2 atoms are provided by a μ2-O2 alkoxide atom. The coordination geometry for the Sn1 atom is completed by two methyl groups and a chloride atom [Sn1—Cl1 = 2.5866(9) Å], while that of the Sn2 atom is completed by two methyl substituents. Within the core, the Sn2—O1, O1i bond lengths of 2.049(2) and 2.118(2) Å, respectively, and the O1—Sn2—O1i = 73.76(10)° and Sn2—O1—Sn2i = 106.24(10)° bond angles indicate the core has the shape of a distorted rhombus. The Sn1—O2 [2.176(3) Å] and Sn2—O2 [2.181(3) Å] bond lengths indicate the μ2-O(alkoxide) bridge is symmetric. Each of the penta-coordinate geometries is highly distorted. For the Sn1 atom, the donor set is defined by C2ClO2 atoms with the widest angle defined by the Cl1 and O2 atoms [Cl1–Sn1—O2 = 157.89(7)°] whereas for the Sn2 atom, the widest angle in the C2O3 geometry is defined by the O2 and O1i atoms [O2—Sn2—O1i = 146.31(9)°]. The next widest angles are subtended by the tin-bound methyl substituents [C1—Sn1—C2 = 138.66(15)° and C3—Sn2—C4 = 135.40(16)°]. The value of τ is a parameter that quantifies five-coordinate geometries, equalling 0.0 for an ideal square-pyramidal coordination geometry and 1.0 for an ideal trigonal-bipyramid [10]. In (I), τ = 0.32 for the Sn1 atom and τ = 0.18 for the Sn2 atom, each indicative of tendancies towards a square-pyramidal coordination geometry. The sequence of three edge-shared Sn2O2 rhombi have the shape of a kinked ladder.
The most prominent feature of the molecular packing is the formation of amine-N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds [N1—H1n⋯Cl1ii: H1n⋯Cl1ii = 2.57(3) Å, N1⋯Cl1ii = 3.461(3) Å with angle at H1n = 177(2)° for (ii) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z]. These give rise to a linear supramolecular chain along the b-axis direction. The chains are linked into a supramolecular layer in the bc-plane by weak methylene-C—H⋯π(phenyl) interactions [C5—H5⋯Cg(C7–C12)iii: H5⋯Cg(C7—C12)iii = 2.79 Å, C5⋯Cg(C7—C12)iii = 3.766(4) Å with angle at H5 = 170° for (iii) 1 − x, −1/2 + y, 1/2 − z]. Layers stack along the a-axis without significant directional interactions between them.
Finally, the Hirshfeld surfaces and two-dimensional fingerprint (full and decomposed) plots were calculated on the entire tetra-tin oxido-cluster using Crystal Explorer 17 [11] and standard procedures [12]. This analysis points to the significance of H⋯H contacts which contribute 76.0% of all contacts to the Hirshfeld surface. The only other two contacts registered are C⋯H/H⋯C [12.7%] and Cl⋯H/H⋯Cl [10.9%].
Funding source: Sdn Bhd
Award Identifier / Grant number: STR-RCTR-RCCM-001-2019
Funding statement: Sunway University Sdn Bhd is thanked for financial support of this work through Grant no. STR-RCTR-RCCM-001-2019.
References
1. Agilent Technologies: CrysAlisPRO. Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA (2010).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
5. Dakternieks, D.; Jurkschat, J.; van Dreumel, S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Molecular dynamics within diorganotin systems: solution and solid state studies of new mixed distannoxane dimers [tBu2(Cl)SnOSn(Cl)R2]2. Inorg. Chem. 36 (1997) 2023–2029.10.1021/ic9611608Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Lo, K. M.; Lee, S. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 235 (2019) 175–177.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0562Search in Google Scholar
7. Hong, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, L.; Li, D.; Li, C.: Study of the effect of molecular structure and alkyl groups bound with tin(IV) on their cytotoxicity of organotin(IV) 2-phenyl-4-selenazole carboxylates. RSC Adv. 5 (2015) 102885–102894.10.1039/C5RA18445BSearch in Google Scholar
8. Casas, J. S.; Castiñeiras, A.; Couce, M. D.; Sánchez, A.; Sordo, J.; Vázquez-López, E.: New tin-oxometallates from the hydrolysis of SnEt22+ in the presence of 2,6-lutidine-α2,3-diol and different anions. Chem. Sel. 2 (2017) 1983–1991.10.1002/slct.201601877Search in Google Scholar
9. Gielen, M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Metallotherapeutic drugs and metal-based diagnostic agents: the use of metals in medicine. John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Chichester, England (2005) 421–439.10.1002/0470864052.ch22Search in Google Scholar
10. Addison, A. W.; Rao, T. N.; Reedijk, J.; van Rijn, J.; Verschoor, G. C.: Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen–sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua[1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]- copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans (1984) 1349–1356.10.1039/DT9840001349Search in Google Scholar
11. Turner, M. J.; McKinnon, J. J.; Wolff, S. K.; Grimwood, D. J.; Spackman, P. R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M. A.: Crystal Explorer v17. The University of Western Australia, Australia (2017).Search in Google Scholar
12. Tan, S. L.; Jotani, M. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Utilizing Hirshfeld surface calculations, non-covalent interaction (NCI) plots and the calculation of interaction energies in the analysis of molecular packing. Acta Crystallogr. E75 (2019) 308–318.10.1107/S2056989019001129Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2019 Kong Mun Lo et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n


