Abstract
C19H20MoN2O6S, orthorhombic, Pbca (no. 61), a = 13.4060(1) Å, b = 16.5112(1) Å, c = 17.6357(1) Å, V = 3903.65(4) Å3, Z = 8, Rgt(F) = 0.0217, wRref(F2) = 0.0602, T = 100(2) K.
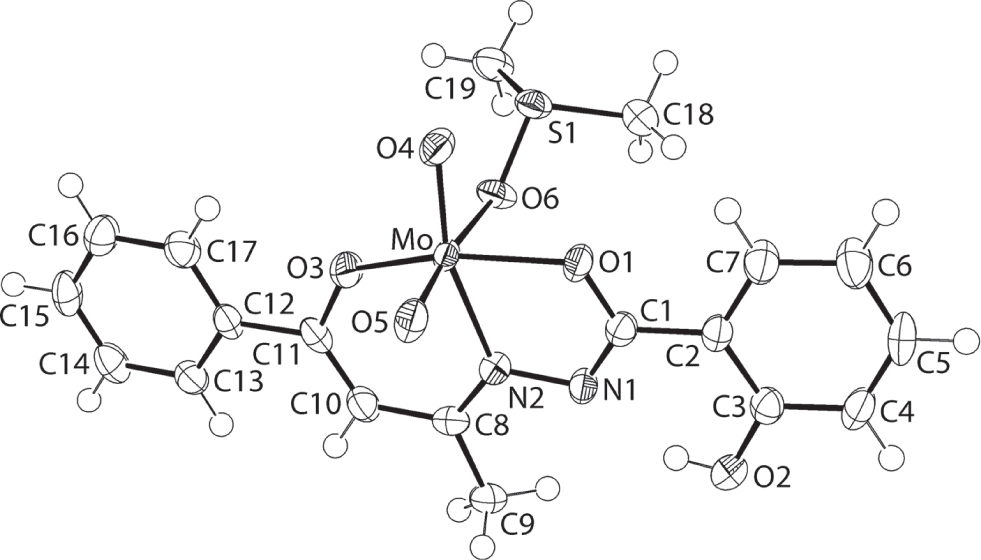
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow prism |
| Size: | 0.12 × 0.09 × 0.08 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 6.86 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker SMART APEX, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 67.1°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 87956, 3477, 0.037 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3445 |
| N(param)refined: | 268 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo | 0.70272(2) | 0.64889(2) | 0.40616(2) | 0.01495(7) |
| S1 | 0.49306(4) | 0.75913(3) | 0.37860(3) | 0.01992(12) |
| O1 | 0.67746(11) | 0.64719(8) | 0.29435(8) | 0.0207(3) |
| O2 | 0.59180(12) | 0.43933(9) | 0.17240(8) | 0.0257(3) |
| H2O | 0.595(2) | 0.4485(17) | 0.2200(6) | 0.039* |
| O3 | 0.66410(11) | 0.61787(8) | 0.50864(8) | 0.0232(3) |
| O4 | 0.71491(11) | 0.75179(9) | 0.41181(8) | 0.0224(3) |
| O5 | 0.82090(12) | 0.61232(10) | 0.40666(7) | 0.0238(3) |
| O6 | 0.53144(11) | 0.67586(9) | 0.40306(8) | 0.0216(3) |
| N1 | 0.61907(12) | 0.51610(10) | 0.30067(9) | 0.0187(3) |
| N2 | 0.63576(12) | 0.52886(10) | 0.37796(9) | 0.0186(3) |
| C1 | 0.64235(14) | 0.58034(12) | 0.26234(11) | 0.0177(4) |
| C2 | 0.62973(14) | 0.58199(12) | 0.17992(11) | 0.0180(4) |
| C3 | 0.60663(14) | 0.51170(12) | 0.13812(11) | 0.0197(4) |
| C4 | 0.60024(15) | 0.51606(13) | 0.05935(12) | 0.0245(4) |
| H4 | 0.5869 | 0.4685 | 0.0308 | 0.029* |
| C5 | 0.61325(16) | 0.58913(15) | 0.02273(12) | 0.0281(5) |
| H5 | 0.6089 | 0.5913 | −0.0310 | 0.034* |
| C6 | 0.63257(18) | 0.65948(14) | 0.06317(13) | 0.0300(5) |
| H6 | 0.6395 | 0.7099 | 0.0377 | 0.036* |
| C7 | 0.64158(17) | 0.65506(13) | 0.14116(12) | 0.0253(5) |
| H7 | 0.6562 | 0.7029 | 0.1690 | 0.030* |
| C8 | 0.61799(15) | 0.46797(12) | 0.42312(12) | 0.0191(4) |
| C9 | 0.58919(16) | 0.38593(12) | 0.39468(12) | 0.0219(4) |
| H9A | 0.5511 | 0.3916 | 0.3476 | 0.033* |
| H9B | 0.5482 | 0.3585 | 0.4328 | 0.033* |
| H9C | 0.6495 | 0.3540 | 0.3850 | 0.033* |
| C10 | 0.62743(15) | 0.47795(12) | 0.50377(11) | 0.0216(4) |
| H10 | 0.6185 | 0.4305 | 0.5335 | 0.026* |
| C11 | 0.64755(14) | 0.54709(12) | 0.54262(11) | 0.0189(4) |
| C12 | 0.64907(14) | 0.55244(12) | 0.62672(11) | 0.0183(4) |
| C13 | 0.62411(15) | 0.48592(12) | 0.67207(12) | 0.0224(4) |
| H13 | 0.6060 | 0.4360 | 0.6492 | 0.027* |
| C14 | 0.62576(16) | 0.49289(13) | 0.75058(12) | 0.0256(4) |
| H14 | 0.6096 | 0.4473 | 0.7811 | 0.031* |
| C15 | 0.65078(16) | 0.56556(14) | 0.78473(11) | 0.0256(5) |
| H15 | 0.6520 | 0.5697 | 0.8385 | 0.031* |
| C16 | 0.67404(17) | 0.63220(14) | 0.74047(12) | 0.0252(4) |
| H16 | 0.6905 | 0.6824 | 0.7636 | 0.030* |
| C17 | 0.67317(16) | 0.62514(13) | 0.66205(12) | 0.0227(4) |
| H17 | 0.6894 | 0.6709 | 0.6319 | 0.027* |
| C18 | 0.42329(19) | 0.74120(14) | 0.29391(12) | 0.0318(5) |
| H18A | 0.4684 | 0.7230 | 0.2536 | 0.048* |
| H18B | 0.3902 | 0.7914 | 0.2782 | 0.048* |
| H18C | 0.3730 | 0.6994 | 0.3035 | 0.048* |
| C19 | 0.39214(16) | 0.77829(13) | 0.44150(12) | 0.0260(4) |
| H19A | 0.3472 | 0.7315 | 0.4420 | 0.039* |
| H19B | 0.3556 | 0.8264 | 0.4245 | 0.039* |
| H19C | 0.4180 | 0.7876 | 0.4927 | 0.039* |
Source of material
All chemicals and solvents were used as purchased without further purification. The melting point was determined using a Mel-temp II digital melting point apparatus and was uncorrected. The IR spectrum was obtained on a Bruker Vertex 70v FTIR Spectrometer in the scan range 4000–400 cm−1. The 1H NMR spectrum was recorded at room temperature in CDCl3 solution on a Bruker Ascend 400 MHz NMR spectrometer with chemical shifts relative to tetramethylsilane.
The Schiff base ligand was synthesised from the reaction of benzoylacetone (Sigma Aldrich) and 2-hydroxybenzhydrazide (Fluka) in a 1:1 molar ratio. Bis(acetylacetonato)dioxomolybdenum(VI) (Sigma Aldrich, 0.33 g, 1 mmol) and the prepared Schiff base were dissolved in methanol (30 mL) and the mixture was refluxed for 2 h. After filtration, the filtrate was evaporated slowly until yellow crystals were formed. The crystals were filtered, washed with a minimum amount of methanol and air-dried in vacuo over P4O10. Yield: 0.20 g (40%). M.pt: 469–471 K. IR (cm−1) 1612 (m) ν(C—N), 1599 (s) ν(C—N), 1548 (s) ν(C—O), 1368 (m) ν(C—O), 1260 (m) ν(C—O), 1085 (m) ν(C—O), 1034 (m) ν(S—O), 931 (m) ν(Mo—O), 900 (m) ν(Mo—O). 1H NMR (CDCl3, ppm): δ 2.46 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.67 (s, 6H, CH3), 6.12 (s, 1H, CH), 6.88 (d, 1H, J = 7.10 Hz, Ph—H), 6.91 (d, 1H, J = 8.10 Hz, Ph—H), 7.35–7.44 (m, 5H, Ph—H), 7.83 (d, 1H, J = 7.85 Hz, Ph—H), 7.84 (d, 1H, J = 7.90 Hz, Ph—H), 11.48 (s, 1H, OH).
Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–0.98 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C). The O-bound H-atom was also geometrically placed (O—H = 0.84 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O).
Comment
The study of di-oxido-molybdenum complexes with di-anionic tridentate ligands is particularly significant as the coordination environment of the [MoO2]2+ core is known to be crucial as an open active site for catalytic oxidation processes [5], [6]. In this work, the synthesis and crystal structure analysis of the title complex, Mo(=O)2(L)(O=SMe2), (I), where H2L is 2-hydroxy-N-[(2Z)-4-hydroxy-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl] benzenecarbohydrazonic acid, with a slight modification of the Schiff base ligand employed in earlier reported work [7], is described in continuation of on-going studies in this area [7], [8], [9].
The mononuclear title complex in (I) is shown in the figure (70% probability displacement ellipsoids). The Mo(VI) centre is complexed by O1, O3 and imine-N2 atoms, derived from the tridentate Schiff base di-anion, the oxido-O4 and O5 atoms as well as the O6 atom of the dimethylsulphoxide ligand [10]. This results in a N2O4 donor set that defines an approximate octahedral geometry in which the oxido groups are cis to each other, and where the three donor atoms of the L2− anion occupy meridional positions. The O1—Mo—O3 angle [149.93(6)°] deviates significantly from linearity, which is due mainly to the acute angles subtended by the five-[O1—Mo—N2 = 72.54(6)°] and six-membered [O3—Mo—N2 = 82.32(6)°] chelate rings owing to the tridentate mode of coordination of the Schiff base di-anion. Each of the five- and six-membered chleate rings adopts an envelope configuration with the Mo atoms being the flap atom. In the smaller chelate ring, the Mo flap atom lies 0.106(3) Å out of the plane defined by the four remaining atoms (r.m.s. deviation = 0.0014 Å). In the larger chelate ring, the envelope configuration is significantly more pronounced with the Mo atom lying 0.446(3) Å out of the least-squares plane defined by the five remaining atoms of the chelate ring (r.m.s. deviation = 0.0158 Å). The dihedral angle formed between the least-squares planes through the chelate rings is 9.37(5)°. The dihedral angles between the five-membered chelate ring and the pendent hydroxyphenyl ring is 10.94(6)°, between the six-membered ring and adjacent phenyl ring is 2.45(6)°, and between the hydroxyphenyl and phenyl rings is 7.58(6)°. Thus, to a first approximation, the Schiff base ligand is planar. An intramolecular loop – S(6) graph set – is evident owing to the formation of a hydroxy-O—H⋯N(imine) hydrogen bond [O2—H2O⋯N1: H2O⋯N1 = 1.837(19) Å, O2⋯N1 = 2.619(2) Å with angle at H2O = 151(3)°].
In the crystal of (I), C—H⋯O interactions connect complexes into a three-dimensional architecture. Thus, hydroxyphenyl, phenyl- and imine-methyl-C—H⋯O(oxo) [C6—H6⋯O4i: H6⋯O4i = 2.52 Å, C6⋯O4i = 3.239(3) Å with angle at H6 = 132°; C14—H14⋯O5ii: H14⋯O5ii = 2.60 Å, C14⋯O5ii = 3.333(3) Å with angle at H14 = 135° and C9—H9c⋯O4iii: H9c⋯O4iii = 2.53 Å, C9⋯O4iii = 3.449(3) Å with angle at H9c = 157° for symmetry operations (i) x, 3/2 − y, −1/2 + z, (ii) 3/2 − x, 1 − y, 1/2 + z and (iii) 3/2 − x, −1/2 + y, z] interactions lead to the formation of a supramolecular layer in the bc-plane. The coordinated dimethylsulphoxide groups protrude to either side of the layer and inter-digitate with neighbouring layers with the connections between them being of the type dimethylsulphoxide-C—H⋯O(oxide) [C18—H18b⋯.O1iv: H18b⋯.O1iv = 2.60 Å, C18⋯.O1iv = 3.331(3) Å with angle at H18b = 131° for (iv) 1 − x, 1/2 + z, 1/2 − z].
Further analysis of the molecular packing was conducted with Crystal Explorer 17 [11] to calculate the Hirshfeld surfaces of (I) along with the full and delineated two-dimensional fingerprint plots following literature precedents [12]. This analysis showed, reflecting the formation of many C—H⋯O contacts in the crystal, that O⋯H/H⋯O contacts amounted to 30.7% of all contacts on the calculated Hirshfeld surface, approaching the 41.3% contributed by H⋯H contacts. The C⋯H/H⋯C contacts to the surface, at 15.7%, were also prominent with smaller but, notable C⋯C [4.8%], N⋯H/H⋯N [2.1%], O⋯C/C⋯O [1.6%] and N⋯C/N⋯C [1.4%] contacts. However, these occur at separations greater than the sum of the respective van der Waals radii.
Acknowledgements
Sunway University Sdn Bhd is thanked for financial support of this work through Grant no. STR-RCTR-RCCM-001-2019.
References
1. Bruker. SADABS, APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2008).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
5. Holm, R. H.; Kennepohl, P.; Solomon, E. I.: Structural and functional aspects of metal sites in biology. Chem. Rev. 96 (1996) 2239–2314.10.1021/cr9500390Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Brito, J. A.; Gómez, M.; Muller, G.; Teruel, H.; Clinet, J.-C.; Duñach, E.; Maestro, M. A.: Structural studies of mono- and dimetallic MoVI complexes – a new mechanistic contribution in catalytic olefin epoxidation provided by oxazoline ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2004 (2004) 4278–4285.10.1002/ejic.200400331Search in Google Scholar
7. Ngan, N. K.; Lo, K. M.; Wong, R. C. S.: Synthesis, structure studies and electrochemistry of molybdenum(VI) Schiff base complexes in the presence of different donor solvent molecules. Polyhedron 30 (2011) 2922–2932.10.1016/j.poly.2011.08.038Search in Google Scholar
8. Ngan, N. K.; Lo, K. M.; Wong, R. C. S.: Dinuclear and polynuclear dioxomolybdenum(VI) Schiff base complexes: synthesis, structural elucidation, spectroscopic characterization, electrochemistry and catalytic property. Polyhedron 33 (2012) 235–251.10.1016/j.poly.2011.11.057Search in Google Scholar
9. Lo, K. M.; Lee, S. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 235 (2019) 189–191.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0566Search in Google Scholar
10. Biswal, D.; Pramanik, N. R.; Chakrabarti, S.; Drew, M. G. B.; Sarkar, B.; Maurya, M. R.; Mukherjee, S. K.; Chowdhury, P.: New polymeric, dimeric and mononuclear dioxidomolybdenum(VI) complexes with an ONO donor ligand: crystal structures, DFT calculations, catalytic performance and protein binding study of the ligand. New J. Chem. 41 (2017) 4116–4137.10.1039/C7NJ00136CSearch in Google Scholar
11. Turner, M. J.; Mckinnon, J. J.; Wolff, S. K.; Grimwood, D. J.; Spackman, P. R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M. A.: Crystal Explorer v17. The University of Western Australia, Australia (2017).Search in Google Scholar
12. Tan, S. L.; Jotani, M. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Utilizing Hirshfeld surface calculations, non-covalent interaction (NCI) plots and the calculation of interaction energies in the analysis of molecular packing. Acta Crystallogr. E75 (2019) 308–318.10.1107/S2056989019001129Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2019 Kong Mun Lo et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n


