Abstract
C24H38CdN4O4P2S4, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 12.2264(1) Å, b = 10.8805(1) Å, c = 12.9590(1) Å, β = 108.172(1)°, V = 1637.95(3) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0183, wRref(F2) = 0.0468, T = 100(2) K.
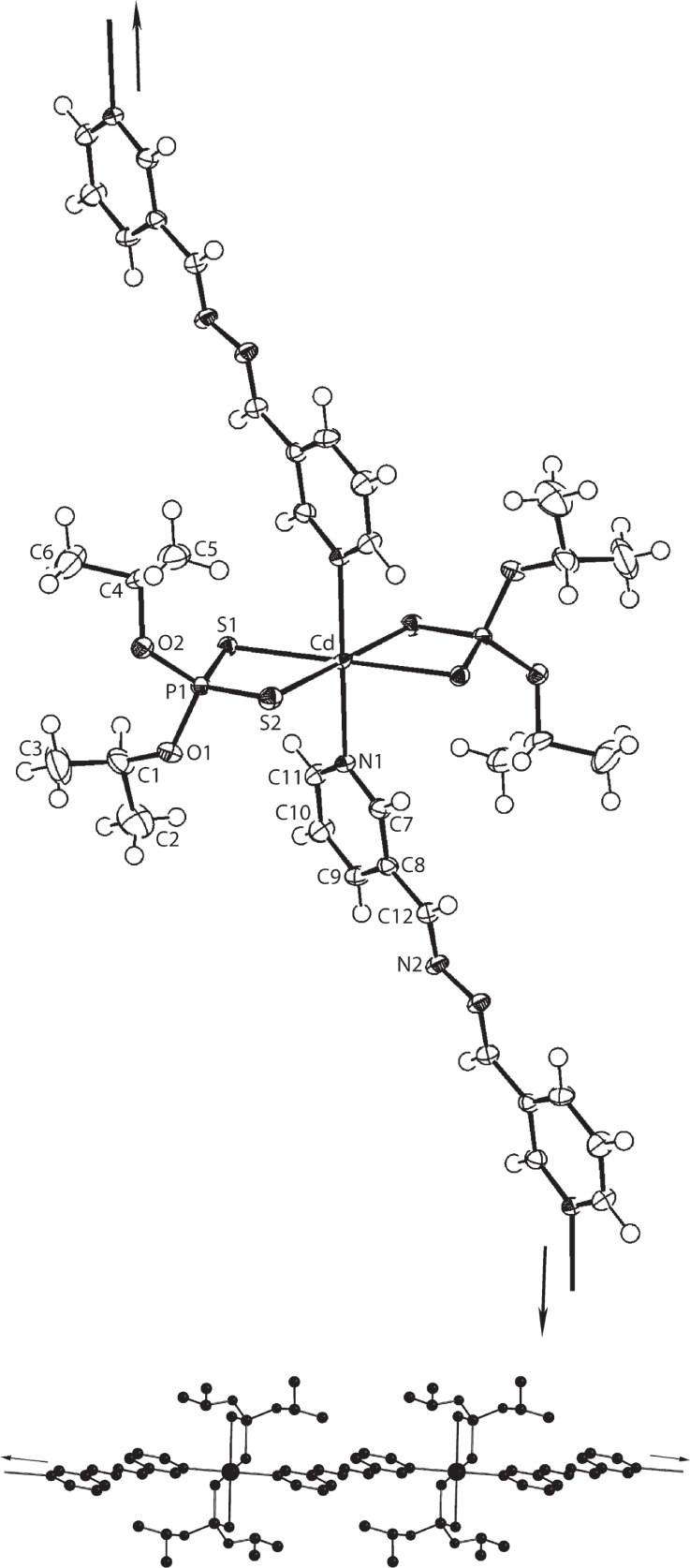
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow plate |
| Size: | 0.13 × 0.08 × 0.03 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 8.94 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 67.1°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 20310, 2925, 0.027 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2812 |
| N(param)refined: | 182 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.01180(6) |
| S1 | 0.69732(3) | 0.43408(4) | 0.46778(3) | 0.01209(9) |
| S2 | 0.56960(3) | 0.71056(4) | 0.42854(3) | 0.01499(10) |
| P1 | 0.69306(3) | 0.60475(4) | 0.40785(3) | 0.01118(10) |
| O1 | 0.67671(10) | 0.60406(11) | 0.28177(9) | 0.0159(3) |
| O2 | 0.81785(9) | 0.66439(11) | 0.45351(9) | 0.0149(2) |
| N1 | 0.39584(11) | 0.43433(14) | 0.31914(10) | 0.0127(3) |
| N2 | 0.05064(12) | 0.46461(14) | 0.01847(11) | 0.0141(3) |
| C1 | 0.74818(17) | 0.5275(2) | 0.23550(15) | 0.0238(4) |
| H1 | 0.785854 | 0.461264 | 0.288120 | 0.029* |
| C2 | 0.6692(2) | 0.4708(2) | 0.13343(18) | 0.0369(5) |
| H2A | 0.608986 | 0.423730 | 0.150917 | 0.055* |
| H2B | 0.713476 | 0.416033 | 0.101442 | 0.055* |
| H2C | 0.633747 | 0.535907 | 0.081476 | 0.055* |
| C3 | 0.8387(2) | 0.6081(3) | 0.2140(2) | 0.0561(8) |
| H3A | 0.801431 | 0.674617 | 0.164499 | 0.084* |
| H3B | 0.886090 | 0.559034 | 0.180837 | 0.084* |
| H3C | 0.887469 | 0.643109 | 0.282563 | 0.084* |
| C4 | 0.88713(14) | 0.66523(18) | 0.56840(13) | 0.0194(4) |
| H4 | 0.879395 | 0.584297 | 0.602022 | 0.023* |
| C5 | 0.85025(17) | 0.7655(2) | 0.62818(15) | 0.0284(5) |
| H5A | 0.858669 | 0.844867 | 0.595719 | 0.043* |
| H5B | 0.898277 | 0.764436 | 0.704478 | 0.043* |
| H5C | 0.769497 | 0.753254 | 0.623740 | 0.043* |
| C6 | 1.01057(16) | 0.6814(2) | 0.56736(18) | 0.0339(5) |
| H6A | 1.031905 | 0.611637 | 0.529750 | 0.051* |
| H6B | 1.062453 | 0.685079 | 0.642170 | 0.051* |
| H6C | 1.016738 | 0.757740 | 0.529477 | 0.051* |
| C7 | 0.29587(15) | 0.48664(16) | 0.26350(13) | 0.0137(4) |
| H7 | 0.270844 | 0.556636 | 0.293778 | 0.016* |
| C8 | 0.22667(13) | 0.44330(16) | 0.16321(12) | 0.0123(3) |
| C9 | 0.26435(14) | 0.34128(17) | 0.11888(13) | 0.0157(4) |
| H9 | 0.219390 | 0.309253 | 0.050633 | 0.019* |
| C10 | 0.36786(15) | 0.28734(18) | 0.17539(14) | 0.0187(4) |
| H10 | 0.395498 | 0.217828 | 0.146720 | 0.022* |
| C11 | 0.43099(14) | 0.33687(17) | 0.27531(13) | 0.0161(4) |
| H11 | 0.502267 | 0.299663 | 0.314042 | 0.019* |
| C12 | 0.11717(15) | 0.50510(15) | 0.10886(14) | 0.0140(4) |
| H12 | 0.095577 | 0.575692 | 0.141063 | 0.017* |
Source of material
The Cd[S2P(OiPr)2]2 precursor was prepared in high yield from the in situ reaction of Cd(NO3)2 ⋅ 4 H2O (Acros Organic; 15.42 g, 0.05 mol), iPrOH (Merck; 16.05 mL, 0.21 mol), P2S5 (Sigma-Aldrich; 11.11 g, 0.05 mol) and 50% w/w NaOH solution (Merck; 8.80 mL, 0.11 mol). 1,2-Bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine was prepared in high yield from the reaction (reflux) of 3-picolylamine (Aldrich; 2.03 mL, 0.02 mol) and hydrazinium hydroxide (Merck; 0.49 mL, 0.01 mol) in ethanol solution (Merck; 5 mL). The title compound was obtained by mixing a suspension of Cd[S2P(OiPr)2]2 (0.50 g, 0.93 mmol) and 1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine (0.20 g, 0.95 mmol) in dimethylformamide (Merck; 5 mL), followed by stirring for 30 min at 373 K. The solution was filtered and the filtrate transferred to a vial containing acetonitrile (Merck; 1 mL). Yellow crystals formed after one day. Yield: 0.50 g, (71.8%, based on Cd[S2P(OiPr)2]2). M. pt. (Stuart SMP 30 Melting point apparatus): 453.5–454.9 K. Elem. Anal. [Leco TruSpec Micro CHN Elemental Analyser]: Calc. for C24H38CdN4O4P2S4: C, 38.47; H, 5.11; N, 7.48%. Found: C, 38.87; H, 5.47; N, 7.77%. IR (Bruker Vertex 70 V equipped with Platinum ATR from 400 to 80 cm−1): 1178(w) ν(C—O); 968(s) ν(P—O); 657(s) ν(P—S); 384(w) ν(Cd—N); 278(m) ν(Cd—S).
Experimental details
The H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C).
Comment
A recent review describes the diverse structural chemistry of the zinc-triad 1,1-dithiolates with bipyridyl-type molecules [5]. Early systematic studies of the zinc(II) [6], [7] and cadmium(II) [8] dithiophosphates [−S2P(OR)2] were motivated by evaluating the control of coordination polymer formation and, when one-dimensional coordination polymers did form, the topology of the resulting chain. This is nicely illustrated in the 1:1 adducts formed between Cd[S2P(OR)2]2 and trans-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)propane (bpp). When R = iPr, a linear one-dimensional chain was characterized in the solid-state, i.e. {Cd[S2P(O-iPr)2]2(bpp)}n, but when the steric bulk of R is increased to cyclohexyl (Cy), only binuclear species could be isolated, i.e. {Cd[S2P(OCy)2]2(bpp)}2 with bpp coordinating in a bidentate, bridging mode [8]. It was in this context the title compound, {Cd[S2P(O-iPr)2]2(3-PyAld)}n (I) was originally characterized by crystallographic methods [9]; 3-PyAld is 3-pyridylaldazine, i.e. 3-NC5H4C(H)=N—N=C(H)C5H4N-3. While the original connectivity was determined unambiguously as a one-dimensional coordination polymer with a step-ladder topology, disorder was noted in the structure. Herein, a low temperature (100 K) redetermination of (I) is described in which the disorder is no longer apparent and, with the aid of Cu Kα radiation, a better resolution data set was achieved with the result that significantly improved standard uncertainty values are evident. The new data will enable a better comparison of geometric parameters with related structures in the literature.
The asymmetric unit of (I) comprises half a Cd[S2P(O-iPr)2]2 entity as, the cadmium atom lies on a centre of inversion, and half a 3-PyAld molecule, being disposed about a centre of inversion, as indicated in the figure (70% probability displacement ellipsoids; the unlabelled atoms of “Cd[S2P(O-iPr)2]2” are related by the symmetry operation (i) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z, and those for the 3-PyAld molecule are related by (ii) −x, 1 − y, −z). The cadmium(II) atom is octahedrally coordinated within a trans-N2S4 donor set defined by two chelating dithiophosphate ligands and two nitrogen atoms derived from symmetry related pyridyl-nitrogen atoms. The Cd—S1 [2.6715(4) Å] and Cd—S2 [2.7059(4) Å] bond lengths differ by less that 0.04 Å, a result consistent with a symmetric mode of coordination of the dithiophosphato ligand. The small disparity in the P1—S1 [2.0073(6) Å] and P1—S2 [1.9820(6) Å] bond lengths also reflects this observation. Nevertheless, the longer P1—S1 bond involves the more tighly bound S1 atom. The Cd—N1 bond length is 2.4008(13) Å. The greatest distortion from the regular octahedral geometry is manifested in the acute S1—P1—S2 chelate angle of 77.18(1)°.
The lower view of the figure highlights the resultant coordination polymer after the application of translational symmetry. The topology of the linear chain is that of a step-ladder, as noted for the {Zn[S2P(O-iPr)2]2(3-PyAld)}n analogue [10], indeed, the structures are isostructural. A step-ladder topology was also found in {Cd[S2P(OCy)2]2(3-PyAld)}n, isolated as a chloroform solvate [11], but in the recently determined {Zn[S2P(OEt)2]2(3-PyAld)}n derivative, a twisted topology was noted [12].
In the crystal, the chain is aligned along the [1 0 1] direction. The only directional links between chains are of the type pyridyl-C—H⋯S [C9—H9⋯S1iii: H9⋯S1iii = 2.84 Å, C9⋯S1iii = 3.5329(18) Å with angle at H9 = 131° for (iii) −1/2 + x, 1/2 − y, −1/2 + z] and as these occur laterally, the result is a supramolecular layer. Layers stack without directional interactions between them.
Acknowledgements
Sunway University Sdn Bhd is thanked for financial support of this work through Grant no. STR-RCTR-RCCM-001-2019.
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction: CrysAlisPRO. Rigaku Corporation, Oxford, UK (2018).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
5. Tiekink, E. R. T.: Perplexing coordination behaviour of potentially bridging bipyridyl-type ligands in the coordination chemistry of zinc and cadmium 1,1-dithiolate compounds. Crystals 8 (2018) 18.10.3390/cryst8010018Search in Google Scholar
6. Lai, C. S.; Liu, S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Steric control over polymer formation and topology in adducts of zinc dithiophosphates formed with bridging bipyridine ligands. CrystEngComm 6 (2004) 221–226.10.1039/b407335eSearch in Google Scholar
7. Chen, D.; Lai, C. S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Supramolecular aggregation in diimine adducts of zinc(II) dithiophosphates: controlling the formation of monomeric, dimeric, polymeric (zig-zag and helical), and 2-D motifs. CrystEngComm 8 (2006) 51–58.10.1039/B513393ASearch in Google Scholar
8. Lai, C. S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Engineering polymers with variable topology – bipyridine adducts of cadmium dithiophosphates. CrystEngComm 6 (2004) 593–605.10.1039/b414847aSearch in Google Scholar
9. Lai, C. S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Polymeric topologies in cadmium(II) dithiophosphate adducts of the isomeric n-pyridinealdazines, n = 2, 3 and 4. Z. Kristallogr. CM 221 (2006) 288–293.10.1524/zkri.2006.221.4.288Search in Google Scholar
10. Avila, V.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: catena-Poly[[bis(O,O′-diisopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)zinc(II)]-μ-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′]. Acta Crystallogr. E62 (2006) m3530–m3531.10.1107/S160053680605001XSearch in Google Scholar
11. Lai, C. S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Delineating the principles controlling polymer formation and topology in zinc(II)- and cadmium(II)-dithiophosphate adducts of diimine-type ligands. J. Mol. Struct. 796 (2006) 114–118.10.1016/j.molstruc.2006.03.036Search in Google Scholar
12. Tan, Y. S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)zinc(II)], {C20H30N4O4P2S4Zn}n. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0621.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0621Search in Google Scholar
©2019 Yee Seng Tan et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n

