Abstract
C36H34N6O12S2Ni2, monoclinic, C2/c (no. 15), a = 29.642(4) Å, b = 6.2241(4) Å, c = 21.667(2) Å, β = 108.592(13)°, V = 3788.9(7) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0907, wRref(F2) = 0.1605, T = 293(2) K.
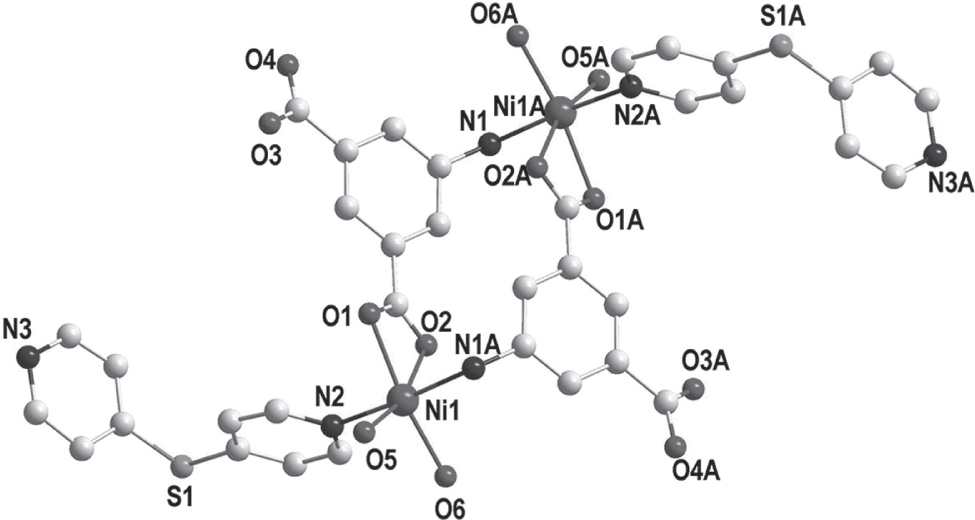
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Green block |
| Size: | 0.29 × 0.25 × 0.25 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.18 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 15078, 4181, 0.092 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2929 |
| N(param)refined: | 264 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni1 | 0.57627(3) | 0.10138(9) | 0.63307(3) | 0.0212(2) |
| S1 | 0.80599(7) | 0.2223(3) | 0.67242(11) | 0.0652(6) |
| O1 | 0.57280(13) | 0.4063(5) | 0.58585(17) | 0.0249(9) |
| O2 | 0.56661(13) | 0.1019(5) | 0.53238(16) | 0.0256(9) |
| O3 | 0.56631(19) | 0.0982(6) | 0.3055(2) | 0.0575(15) |
| O4 | 0.56615(16) | 0.4049(5) | 0.25372(18) | 0.0378(11) |
| O5 | 0.58060(15) | −0.2178(5) | 0.65261(17) | 0.0334(11) |
| H5A | 0.5627 | −0.2885 | 0.6198 | 0.050* |
| H5B | 0.5685 | −0.2438 | 0.6830 | 0.050* |
| O6 | 0.58464(14) | 0.1826(5) | 0.72697(17) | 0.0308(10) |
| H6A | 0.5697 | 0.0925 | 0.7445 | 0.046* |
| H6B | 0.5706 | 0.3046 | 0.7286 | 0.046* |
| N1 | 0.64940(17) | 0.1213(7) | 0.6505(2) | 0.0286(11) |
| N2 | 0.8313(3) | −0.2014(14) | 0.5131(4) | 0.087(2) |
| N3 | 0.49946(15) | 0.9199(6) | 0.3904(2) | 0.0233(10) |
| H3A | 0.5057 | 0.9903 | 0.3583 | 0.028* |
| H3B | 0.5106 | 0.9992 | 0.4262 | 0.028* |
| C1 | 0.55905(19) | 0.4234(7) | 0.4704(2) | 0.0195(12) |
| C2 | 0.5677(2) | 0.3199(7) | 0.4182(3) | 0.0218(12) |
| H2 | 0.5818 | 0.1846 | 0.4243 | 0.026* |
| C3 | 0.55574(19) | 0.4151(7) | 0.3580(3) | 0.0214(12) |
| C4 | 0.53403(19) | 0.6184(7) | 0.3488(3) | 0.0228(12) |
| H4 | 0.5254 | 0.6834 | 0.3080 | 0.027* |
| C5 | 0.52547(19) | 0.7222(7) | 0.4007(3) | 0.0184(12) |
| C6 | 0.53922(19) | 0.6278(7) | 0.4617(3) | 0.0232(13) |
| H6 | 0.5352 | 0.7014 | 0.4969 | 0.028* |
| C7 | 0.56724(19) | 0.3064(8) | 0.5330(2) | 0.0193(12) |
| C8 | 0.5637(2) | 0.2998(8) | 0.3014(3) | 0.0281(14) |
| C9 | 0.6754(2) | 0.2795(10) | 0.6852(3) | 0.0412(17) |
| H9 | 0.6608 | 0.3733 | 0.7064 | 0.049* |
| C10 | 0.7227(2) | 0.3138(10) | 0.6919(3) | 0.0454(18) |
| H10 | 0.7392 | 0.4281 | 0.7166 | 0.055* |
| C11 | 0.7452(2) | 0.1738(9) | 0.6610(3) | 0.0376(15) |
| C12 | 0.7185(2) | 0.0119(10) | 0.6247(3) | 0.0481(18) |
| H12 | 0.7321 | −0.0827 | 0.6026 | 0.058* |
| C13 | 0.6716(2) | −0.0120(9) | 0.6206(3) | 0.0408(17) |
| H13 | 0.6544 | −0.1251 | 0.5960 | 0.049* |
| C14 | 0.8157(2) | 0.0551(11) | 0.6104(4) | 0.0466(18) |
| C15 | 0.8058(3) | 0.1311(12) | 0.5483(4) | 0.059(2) |
| H15 | 0.7936 | 0.2687 | 0.5375 | 0.070* |
| C16 | 0.8143(3) | 0.0006(16) | 0.5025(4) | 0.077(3) |
| H16 | 0.8077 | 0.0556 | 0.4607 | 0.093* |
| C17 | 0.8410(3) | −0.2613(12) | 0.5739(5) | 0.071(3) |
| H17 | 0.8541 | −0.3975 | 0.5844 | 0.085* |
| C18 | 0.8339(3) | −0.1423(11) | 0.6247(4) | 0.062(2) |
| H18 | 0.8415 | −0.1979 | 0.6667 | 0.074* |
Source of material
5-Aminoisophthalic acid (AIPH2) (0.02 g, 0.1 mmol), 4,4′-dipyridylsulfide (dps; 0.02 g, 0.1 mmol) and nickel(II) acetate tetrahydrate (0.03 g, 0.1 mmol) were added to water (7 mL) in a Teflon-lined stainless steel reactor with a small amount of a base. The mixture was heated at 393 K for 3 d, and then slowly cooled down to room temperature. Green crystals of the title compound were obtained.
Experimental details
The hydrogen atoms were placed at calculated positions with the SHELX program (AFIX options: 43 and 147).
Comment
The rational design of metal–organic complexes has received remarkable attention and has developed rapidly due to their fascinating potential applications in functional materials, [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11]. All aspects of this research hotspot have been deeply discussed by some recent reviews, which show that the diverse structures of such materials are always dependent on many factors, such as substituent and number of coordination sites provided by organic ligands, ligand to metal salt ratio, template, metal ion, pH value, and counteranion [12]. In recent years, one of our interests focuses on the coordination assembly based on bis(pyridine) ligands and aromatic polycarboxylic acids ligands. In 4,4′-dipyridylsulfide ligand, two pyridine rings can keep different dihedral angles around the sulphur atom in the process of forming a complex. On the other hand, the aromatic polycarboxylic acids can form complexes with metal ions in flexible way, which can enhance stability of the complex [13]. As a continuation of our previous investigation, in this study we reacted 5-aminoisophthalic acid with Ni2+ ions, then employed 4,4′-dipyridylsulfide ligand as an auxiliary ligand, which features di-nuclear structure.
The asymmetric unit of title complex contains one independent Ni(II) cation, one AIP2− anion, two coordinated H2O and one dps ligand. Each Ni center is six coordinated by two carboxylato O atoms from one AIP2− ligand, two N atoms from one dps ligand and one AIP2− ligand and two water molecules to form a slight distorted octahedral geometry (see the figure). The two carboxylic O atoms of the AIP2− molecule are coordinated with Ni(II) by chelate mode. The Ni—O lengths are in the range of 2.029(4)–2.140(4) Å. The Ni—N lengths are 2.144(5)(Ni-N1A) and 2.080(6) (Ni-N2) Å. Two carboxylate groups of each AIP2− ligand have a dihedral angle of 23.49° and 26.17° toward the plane of the corresponding linking phenyl rings, respectively. The dps ligand shows obvious torsion with a dihedral angle between the two pyridine rings of 80.39°.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by key scientific research projects of higher education of Henan Province (16A150016) and Henan Province Natural Science Foundation (182300410166).
References
1. Oxford Diffraction: CrysAlisPRO. Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England (2006).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Han, M. L.; Duan, Y. P.; Li, D. S.; Xu, G. W.; Wu, Y. P.; Zhao, J.: A series of divalent metal coordination polymers based on isomeric tetracarboxylic acids: Synthesis, structures and magnetic properties. Dalton Trans. 43 (2014) 17519–17527.10.1039/C4DT01946FSearch in Google Scholar
5. Han, Y. F.; Jin, G. X.; Daniliuc, C. G.; Hahn, F. E.: Reversible photochemical modifications in dicarbene-derived metallacycles with coumarin pendants. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54 (2015) 4958–4962.10.1002/anie.201411006Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Yang, X. G.; Ma, L. F.; Yan, D. P.: Facile synthesis of 1D organic–inorganic perovskite micro-belts with high water stability for sensing and photonic applications. Chem. Sci. 10 (2019) 4567–4572.10.1039/C9SC00162JSearch in Google Scholar
7. Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. G.; Lu, X. M.; Yang, C. D.; Fan, N. N.; Yang, Z. T.; Wang, L. Y.; Ma, L. F.: {Zn6} cluster based metal–organic framework with enhanced room-temperature phosphorescence and optoelectronic performances. Inorg. Chem. 58 (2019) 6215–6221.10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b00450Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Yang, X. G.; Zhai, Z. M.; Lu, X. M.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, X. H.; Ma, L. F.: Room temperature phosphorescence of Mn(II) and Zn(II) coordination polymers for photoelectron response applications. Dalton Trans. 48 (2019) 10785–10789.10.1039/C9DT02178GSearch in Google Scholar
9. Liu, X. F.; Zhang, X. Y.; Li, R. F.; Feng, X.: Two neutral copper(I) complexes bearing 2-(4-nitrophenyl) imidazole[4,5-f]-1,10-phenanthroline: synthesis, crystal structure, and luminescence properties. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 37 (2016) 282–286.10.1002/bkcs.10666Search in Google Scholar
10. Wang, H. R.; Meng, W.; Wu, J.; Ding, J.; Hou, H.; Fan, Y.: Crystalline central-metal transformation in metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 307 (2016) 130–146.10.1016/j.ccr.2015.05.009Search in Google Scholar
11. Qin, J. H.; Ma, B.; Liu, X. F.; Lu, H. L.; Dong, X. Y.; Zang, S. Q.; Hou, H.: Ionic liquid directed syntheses of water-stable Eu– and Tb–organic-frameworks for aqueous-phase detection of nitroaromatic explosives. Dalton Trans. 44 (2015) 14594–14603.10.1039/C5DT02054ASearch in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Lee, K. J.; Lee, J. H.; Jeoung, S.; Moon, H. R.: Transformation of metal–organic frameworks/coordination polymers into functional nanostructured materials: experimental approaches based on mechanistic insights. Acc. Chem. Res. 50 (2017) 2684–2692.10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00259Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Yuan, S.; Zhang, W. Y.; Shu, K. X.; Liang, Y. L.; Yan, G. F.: Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[(5-nitroisophthalato)-(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide)cobalt(II)], Co2(H2O)2(C8H3NO6)2(C10H8N2S)2. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 224 (2009) 203–204.10.1524/ncrs.2009.0091Search in Google Scholar
©2019 Xin-Hong Chang et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n


