Abstract
C36H58Cl2CuN12, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 8.1490(8) Å, b = 17.0301(15) Å, c = 16.8649(14) Å, β = 101.629(3)°, Z = 2, V = 2292.4(4) Å3, Rgt(F) = 0.0419, wRref(F2) = 0.1121, T = 298(2) K.
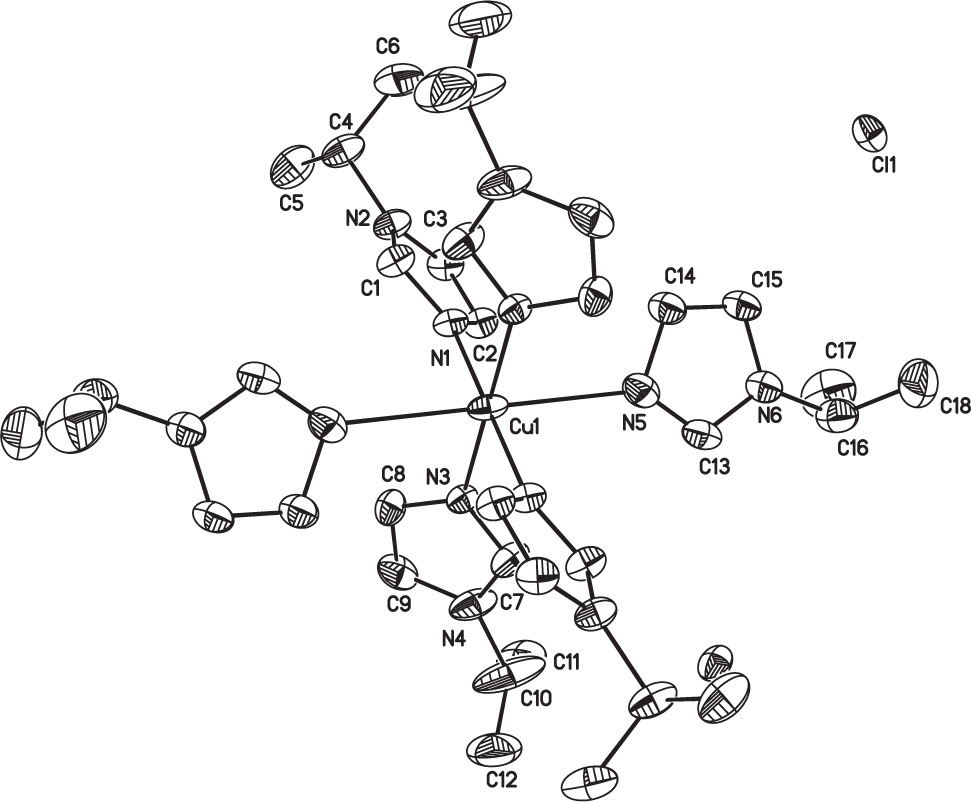
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Blue block |
| Size: | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.63 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker SMART APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 11331, 4033, 0.033 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2846 |
| N(param)refined: | 237 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1 | 1.000000 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.04109(17) |
| N1 | 1.1122(3) | 0.40773(12) | 0.45637(13) | 0.0382(5) |
| N2 | 1.2519(3) | 0.29984(13) | 0.44242(14) | 0.0471(6) |
| N3 | 1.1256(3) | 0.57126(12) | 0.43537(13) | 0.0379(5) |
| N4 | 1.1845(4) | 0.66314(15) | 0.35461(18) | 0.0675(8) |
| N5 | 0.7534(3) | 0.48437(14) | 0.37788(16) | 0.0541(6) |
| N6 | 0.5542(3) | 0.47905(14) | 0.26673(15) | 0.0524(6) |
| Cl1 | 0.32382(9) | 0.23645(4) | 0.19130(5) | 0.0532(2) |
| C1 | 1.1986(4) | 0.34863(16) | 0.49401(17) | 0.0458(7) |
| H1 | 1.220101 | 0.341630 | 0.549838 | 0.055* |
| C2 | 1.1121(4) | 0.39567(16) | 0.37589(16) | 0.0430(7) |
| H2 | 1.060561 | 0.428227 | 0.333924 | 0.052* |
| C3 | 1.1975(4) | 0.32984(17) | 0.36664(17) | 0.0479(7) |
| H3 | 1.215909 | 0.308926 | 0.318234 | 0.057* |
| C4 | 1.3401(4) | 0.22448(17) | 0.4658(2) | 0.0628(9) |
| H4 | 1.368161 | 0.222248 | 0.525018 | 0.075* |
| C5 | 1.4997(5) | 0.2206(2) | 0.4357(3) | 0.0882(13) |
| H5A | 1.475583 | 0.222169 | 0.377590 | 0.132* |
| H5B | 1.557150 | 0.172660 | 0.453732 | 0.132* |
| H5C | 1.569132 | 0.264530 | 0.456348 | 0.132* |
| C6 | 1.2233(6) | 0.1580(2) | 0.4369(4) | 0.126(2) |
| H6A | 1.196200 | 0.157973 | 0.378804 | 0.188* |
| H6B | 1.122609 | 0.164196 | 0.457590 | 0.188* |
| H6C | 1.276170 | 0.109256 | 0.455789 | 0.188* |
| C7 | 1.0658(4) | 0.62744(18) | 0.38461(19) | 0.0553(8) |
| H7 | 0.952967 | 0.640757 | 0.371147 | 0.066* |
| C8 | 1.2944(4) | 0.57080(18) | 0.43694(18) | 0.0499(7) |
| H8 | 1.371361 | 0.536461 | 0.467047 | 0.060* |
| C9 | 1.3312(4) | 0.62759(19) | 0.3883(2) | 0.0618(9) |
| H9 | 1.437019 | 0.640234 | 0.379357 | 0.074* |
| C10 | 1.1586(8) | 0.7298(2) | 0.2958(3) | 0.128(2) |
| H10 | 1.036138 | 0.726878 | 0.281302 | 0.154* |
| C11 | 1.1902(6) | 0.7117(3) | 0.2199(3) | 0.1009(15) |
| H11A | 1.223458 | 0.750948 | 0.188120 | 0.121* |
| H11B | 1.178097 | 0.660355 | 0.200823 | 0.121* |
| C12 | 1.1694(7) | 0.8027(2) | 0.3353(3) | 0.1176(19) |
| H12A | 1.283925 | 0.813055 | 0.360281 | 0.176* |
| H12B | 1.102237 | 0.801669 | 0.375968 | 0.176* |
| H12C | 1.129315 | 0.843194 | 0.296642 | 0.176* |
| C13 | 0.6668(4) | 0.52378(18) | 0.3171(2) | 0.0546(8) |
| H13 | 0.681125 | 0.577199 | 0.309319 | 0.065* |
| C14 | 0.6929(4) | 0.40928(18) | 0.36523(19) | 0.0548(8) |
| H14 | 0.730787 | 0.366883 | 0.398701 | 0.066* |
| C15 | 0.5720(4) | 0.40487(17) | 0.29829(19) | 0.0538(8) |
| H15 | 0.512399 | 0.360334 | 0.277572 | 0.065* |
| C16 | 0.4399(5) | 0.5047(2) | 0.1929(2) | 0.0698(10) |
| H16 | 0.448218 | 0.561958 | 0.189938 | 0.084* |
| C17 | 0.4935(7) | 0.4708(3) | 0.1191(2) | 0.1114(17) |
| H17A | 0.607440 | 0.485551 | 0.119501 | 0.167* |
| H17B | 0.422240 | 0.490893 | 0.070985 | 0.167* |
| H17C | 0.484938 | 0.414637 | 0.119878 | 0.167* |
| C18 | 0.2604(5) | 0.4849(3) | 0.1955(3) | 0.1006(15) |
| H18A | 0.245079 | 0.428992 | 0.191610 | 0.151* |
| H18B | 0.187012 | 0.509791 | 0.150907 | 0.151* |
| H18C | 0.235079 | 0.503176 | 0.245469 | 0.151* |
Source of material
In a 25 mL round-bottom flask, N-isopropylimidazole (1.102 g; 10 mmol), and copper(II) chloride dihydrate (0.341 g; 2 mmol), molybdenyl acetylacetonate (0.328 g; 1 mmol) and 15 mL water were added successively. The mixture was heated to 80 °C for 6 h, resulting in a blue solution. The mixture was filtrated and the filtrate stood by slow evaporation for seven days. Crystals of the title complex were obtained.
Yield: 52% (based on Cu element), and elemental analysis: calc. for C36H58Cl2CuN12: C 54.50, H 7.37, N 21.19; found: C 54.55, H 7.24, N 21.24 (PERKIN ELMER MODEL 2400 SERIES II).
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were refined with variable isotropic displacement parameters. Hydrogen atoms were assigned with common isotropic displacement factors Uiso(H) = 1.5 times Ueq (C, methyl) and Uiso(H) = 1.2 times Ueq (C, imidazole and methylene). All the H atoms were refined as riding on their parent atom.
Comment
Copper complexes are a class which have been widely used in gas storage and separation and catalysis [3], [4], [5]. The design of new copper complexes not only expands our understanding of structure and bonding but also extends the range of copper-inspired materials [6], [7]. So far, a variety of organic-inorganic hybrids containing copper complexes have been demonstrated [8]. In addition, as a class of versatile N-ligands, imidazole derivatives can be used not only as a solvent but also as a ligand in the synthesis of metal complexes [9], [10]. However, to the best of our knowledge, examples of imidazole-copper complexes of organic-inorganic hybrids are still rare.
The molecular structure of the title complex is shown in the figure. The title complex contains six N-isopropylimidazole ligands, one copper cation and two free chlorine anions. The copper cation adopts a distorted octahedron geometry and is located on an inversion center. The four short Cu—N distances in the equatorial plane; Cu—N(1) is 2.029(2) Å and the Cu—N(3) is 2.039(2) Å, are comparable to inner sphere Cu—N distances found in the hexakis (N-methylimidazole) copper(II) salicylate complexes [11]. The two long distances Cu—N(5) and Cu—N(5A) in the complex are 2.585(3) Å, which are similar with those reported for hexakis(1-(4-cyanophenyl)imidazole-N3)-copper(II) diperchlorate [12]. The bond angles around the copper(II) ion are N(1)—Cu(1)—N(3) (89.95(8)°), N(1)—Cu(1)—N(5) (94.22(8)°), N(3)—Cu(1)—N(5) (91.45(8)°), which are similar with those of bis(4,5-dicyano-1H-imidazol-1-yl)-tetrakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole)copper(II) [13] and a more complex material [14].
Funding source: Research on Experimental Technology of Liaocheng University
Award Identifier / Grant number: 38622170214
Funding statement: We gratefully acknowledge support by the Research on Experimental Technology of Liaocheng University (38622170214).
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2004).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar
3. Jia, X. F.; Peng, P.; Cui, J.; Xin, N. N.; Huang, X. Q.: Four N,O-bidentate-chelated ligand-tunable copper(II) complexes: synthesis, structural characterization and exceptional catalytic properties for Chan-Lam coupling reactions. Asian J. Org. Chem. 7 (2018) 1093–1100.10.1002/ajoc.201800153Suche in Google Scholar
4. Dasireddy, V. D. B. C.; Likozar, B.: The role of copper oxidation state in Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts in CO2 hydrogenation and methanol productivity. Renewable Energy 140 (2019) 452–460.10.1016/j.renene.2019.03.073Suche in Google Scholar
5. Chen, Y. F.; Huang, X.; Feng, X.; Li, J. K.; Huang, Y. Y.; Zhao, J. S.; Guo, Y. X.; Dong, X. M.; Han, R. D.; Qi, P. F.; Han, Y. Z.; Li, H. W.; Hu, C. W.; Wang, B.: Facile fabrication of magnetically recyclable metal-organic framework nanocomposites for highly efficient and selective catalytic oxidation of benzylic C—H bonds. Chem. Commun. 50 (2014) 8374–8377.10.1039/C4CC03728FSuche in Google Scholar
6. Jiang, X. Y.; Rong, N. X.; Qian, R.; Qiu, T. T.; Yao, Q. X.; Huang, X. Q.: Two copper complexes based on pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid as heterogeneous catalysts for highly selective oxidation of alkylbenzenes. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 37 (2018) 329–337.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Abbaszadeh, M.; Hejazi, P.: Metal affinity immobilization of cellulase on Fe3O4 nanoparticles with copper as ligand for biocatalytic applications. Food Chem. 290 (2019) 47–55.10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.117Suche in Google Scholar
8. Chen, Y. F.; Huang, X. Q.; Zhang, S. H.; Li, S. Q.; Cao, S. J.; Pei, X. K.; Zhou, J. W.; Feng, X.; Wang, B.: Shaping of metal-organic frameworks: from fluid to shaped bodies and robust foams. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 (2016) 10810–10813.10.1021/jacs.6b06959Suche in Google Scholar
9. Chen, B.; Huang, X.; Wang, b.; Lin, Z.; Hu, J.; Chi, Y.; Hu, C.: Three new imidazole-functionalized hexanuclear oxidovanadium clusters with exceptional catalytic oxidation properties for alcohols. Chem. Eur. J. 19 (2013) 4408–4413.10.1002/chem.201203854Suche in Google Scholar
10. Hog, M.; Schneider, M.; Studer, G.; Baüerle, M.; Föhrenbacher, S. A.; Scherer, H.; Krossing, I.: An investigation of the symmetric and asymmetric cleavage products in the system aluminum trihalide/1-butylimidazole. Chem. Eur. J. 23 (2017) 11054–11066.10.1002/chem.201701553Suche in Google Scholar
11. Abuhijleh, L.; Woods, C.: Synthesis, crystal structure and superoxide dismutase mimetic activity of hexakis (N-methylimidazole) copper(II) salicylate. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 5 (2002) 269–273.10.1016/S1387-7003(02)00379-9Suche in Google Scholar
12. Singh, A. K.; Yadav, M.; Kumar, P.; Singh, S. K.; Sunkari, S.; Pandey, D. S.: Novel structures based on 1-(4-cyanophenyl)-imidazole resulting from weak bonding interactions. J. Mol. Struct. 935 (2009) 1–7.10.1016/j.molstruc.2009.06.031Suche in Google Scholar
13. Kelley, S. P.; Nuss, J. S.; Rogers, R. D.: Nonstoichiometric, protic azolium azolate ionic liquids provide unique environments for N-donor coordination chemistry. Chem. Eur. J. 21 (2015) 17196–17199.10.1002/chem.201503914Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Çetinkaya, F.; Kürkçüoǧlu, G. S.; Yeşilel, O. Z.; Hökelek, T.; Dal, H.: One-dimensional cyano-bridged heterometallic (Cu/Ni and Cu/Pd) complexes with 1-ethylimidazole. Polyhedron 47 (2012) 126–133.10.1016/j.poly.2012.08.041Suche in Google Scholar
©2019 Miao Cheng et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n
Artikel in diesem Heft
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n

