Abstract
C8H6ClIO2, orthorhombic, Pbcn (no. 60), a = 13.3204(7) Å, b = 7.2517(4) Å, c = 18.5627(9) Å, V = 1793.07(16) Å3, Z = 8, Rgt(F) = 0.0195, wRref(F2) = 0.0483, T = 173 K.
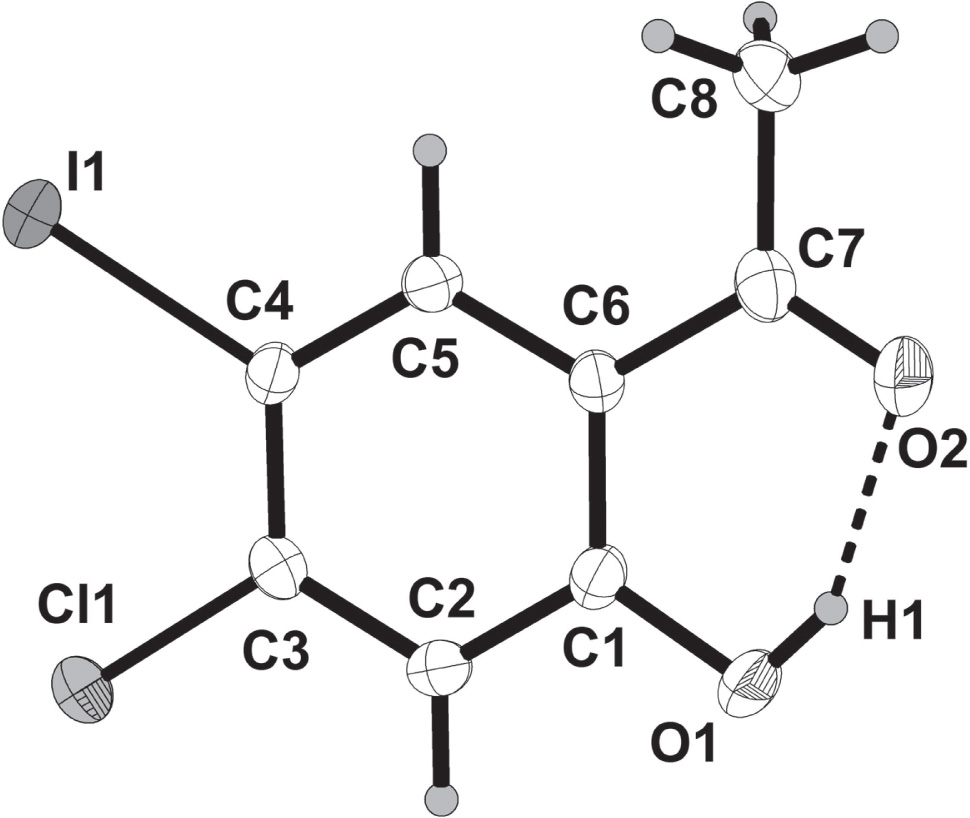
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless rod |
| Size: | 0.46 × 0.07 × 0.07 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 3.82 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 Venture Photon, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 65860, 2158, 0.034 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1983 |
| N(param)refined: | 114 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], ORTEP-3 [2], SHELX [3], PLATON [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.84530(17) | 0.7014(3) | 0.45147(12) | 0.0189(4) |
| C2 | 0.85496(17) | 0.7681(3) | 0.38144(12) | 0.0195(4) |
| H2 | 0.91971 | 0.789074 | 0.361603 | 0.023* |
| C3 | 0.77010(17) | 0.8037(3) | 0.34086(11) | 0.0176(4) |
| C4 | 0.67405(16) | 0.7787(3) | 0.36951(11) | 0.0173(4) |
| C5 | 0.66486(17) | 0.7165(3) | 0.43956(11) | 0.0182(4) |
| H5 | 0.599781 | 0.701392 | 0.459642 | 0.022* |
| C6 | 0.74932(18) | 0.6752(3) | 0.48176(11) | 0.0177(4) |
| C7 | 0.73909(18) | 0.6015(3) | 0.55591(12) | 0.0223(5) |
| C8 | 0.6372(2) | 0.5819(4) | 0.58930(13) | 0.0292(5) |
| H8A | 0.643305 | 0.518815 | 0.635786 | 0.044* |
| H8B | 0.593875 | 0.509677 | 0.55729 | 0.044* |
| H8C | 0.60782 | 0.704337 | 0.596653 | 0.044* |
| O1 | 0.93070(13) | 0.6652(3) | 0.48769(10) | 0.0275(4) |
| O2 | 0.81425(14) | 0.5555(3) | 0.58975(9) | 0.0295(4) |
| Cl1 | 0.78693(4) | 0.87837(8) | 0.25322(3) | 0.02311(12) |
| I1 | 0.54310(2) | 0.82672(2) | 0.31056(2) | 0.02499(6) |
| H1 | 0.912(3) | 0.626(5) | 0.528(2) | 0.056(11)* |
Source of material
The preparation and analytical data for the title compound have been described before [5]. A stirred mixture of a 4-chloro-2-hydroxyacetophenone (5.00 g, 29.3 mmol) and p-toluenesulfonic acid (12.04 g, 35.1 mmol) in acetonitrile (200 mL) at 0 °C was treated with N-iodosuccinimide (5.17 g, 29.3 mmol) over 5 min. The mixture was allowed to stir at room temperature for 14 h, and then quenched with an ice-cold saturated aqueous solution of sodium thiosulphate. The precipitate was filtered and recrystallized to afford the title compound as a solid (7.39 g, 85%), mp. 143–145 °C. Single crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of a ethanol solution of the title compound at room temperature.
Experimental details
Intensity data was determined on a Bruker Venture D8 Photon CMOS diffractometer with graphite-monochromated MoKα1 (λ 0.71073 Å) radiation at 173 K using an Oxford Cryostream 600 cooler. Data reduction was carried out using the program SAINT+, version 6.02 [1] and empirical absorption corrections were made using SADABS [1]. The structure was solved in the WinGX [2] Suite of programs, using intrinsic phasing through SHELXT [3] and refined using full-matrix least-squares/difference Fourier techniques using SHELXL [3]. All C bound H hydrogen atoms were placed at idealized positions and refined as riding atoms with isotropic parameters 1.2 times those of their parent atoms. The O-bound hydrogen atom were located in the difference fourier map and their coordinates and an isotropic thermal parameter allowed to refine freely. Diagrams and publication material were generated using ORTEP-3 [2], and PLATON [4].
Comment
Phenyl methyl ketones (acetophenones) are a class of aromatic compounds produced by plants in response to stress or as protection reaction against parasites or herbivors [6]. Halogenated 2-hydroxyacetophenones are important intermediates in the synthesis of polysubstituted and polycyclic flavonoid derivatives. The reactions of 2-hydroxoacetophenones with the Vilsmeier-Haack reagent, for example, afford chromone-3-carbaldehyde derivatives with potential anti-inflammatory activity [7] and inhibitory effect against protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B [8], thymidine phosphorylase [9], carbonic anhydrase [10], and metallo-β-lactamase [11]. Claisen-Schmidt aldol condensation of the 2-hydroxyacetophenones with substituted benzaldehydes, on the other hand, furnishes chalcone derivatives with a wide range of biological properties [12]. The presence of the ortho-hydroxy-trans-α,β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety facilitates acid or base mediated cycloisomerization into the corresponding flavanones or oxidative cyclization to afford flavones, isoflavones and flavonol derivatives [13]. We have previously reported the synthesis and in vitro inhibitory effect of a series of 4-halogeno-2-hydroxy-5-iodochalcones and their 7-halogeno substituted 2-aryl-3-hydroxy-6-iodo-4H-chromen-4-one derivatives against acetylcholinesterase (AChE), butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and β-secretase (BACE1) activities [5]. The 4-halogeno-2-hydroxy-5-iodochalcones were, in turn, prepared via a Claisen-Schmidt aldol condensation of the 4-halogeno substituted 2-hydroxy-4-iodoacetophenones with benzaldehyde derivatives. Aryl and heteroaryl iodides in radioiodinated form are routinely used in single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging for the clinical diagnosis of disease and drug development [14]. Moreover, the reactivity of the carbon–iodine bond allows facile oxidative addition and subsequent application as organometallic reagents in cross-coupling reactions.
Small model systems with intramolecular and/or intermolecular hydrogen bonds such as the 2-hydroxyacetophenones are often employed to study these interactions in the solid state [15]. Hydrogen bond formation causes changes in the distances between atoms and the rearrangement of electron densities on the groups involved in the interaction and therefore chemical reactivity especially if the reaction centres are directly involved in the hydrogen bonding [16]. Likewise, halogen bonding and halogen-halogen interactions continue to attract considerable attention in medicinal chemistry, chemical biology, supramolecular chemistry and crystal engineering [17], [18], [19], [20]. Our continued interest in hydrogen and halogen bonding [21], [22] prompted us to study the structure of the 4-substituted 2-hydroxy-5-iodoacetophenones in the solid state by single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) method.
Single crystals of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethanone (4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodoacetophenone) suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of ethanol. The crystallographic numbering in the above figure has been used in the context of the X-ray analysis and differs with the systematic numbering for these compounds. Single crystal XRD analysis confirmed the existence of one molecule in the asymmetric unit (cf. the figure) with intramolecular hydrogen bond involving the hydroxyl group (donor) and the oxygen atom (acceptor) of the carbonyl group with hydrogen bond distance, d(O(1)–H(1)⋯O(2) = 1.81 Å. Due to involvement in hydrogen bonding, the carbonyl C=O bond is longer 1.228 Å as compared to a typical acetophenone (1.216 Å) [23]. The molecules exist in the crystal lattice as stacked in anti-parallel chains, each chain held together by a combination of aromatic-aromatic stacking interactions, and intra- and intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonding interactions. Apart from the differences in C—I and C—Cl bond lengths 2.088 Å and 1.729 Å, respectively, PLATON analysis [24] revealed the involvement of chlorine atom as an electron density acceptor in contact with the carbonyl oxygen (3.09 Å). Such halogen bond interaction is not observed with iodine atom though it has the largest σ-hole among the halogen atoms [17], [20]. The I⋯Cl contacts of about 3.63 Å are essentially close packing van der Waals interactions that connect the two parallel layers together in eight-membered rings. The molecules are involved in aromatic-aromatic stacking interactions, which are known to maintain a favourable geometry between aromatic units [25]. Aromatic-aromatic stacking interactions and halogen contacts are responsible for the supramolecular arrangements of the title structure. These observations should be valuable for rational drug design and helpful in understanding interactions of halogenated ligands with proteins.
Acknowledgements
The author thanks the University of South Africa and the National Research Foundation (GUN: 118554) for financial assistance. Ms MM Maluleka is gratefully acknowledged for the design and proof-reading of the manuscript. The X-ray data was acquired by Prof A. Lemmerer of the University of the Witwatersrand using the single-crystal diffractometer acquired through the NRF National Equipment Programme (UID: 78572).
References
1. Bruker. APEX-3 and SAINT+. Version 6.02 (Includes XPREP and SADABS). Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2016).Search in Google Scholar
2. Farrugia, L. J.: ORTEP-3 for Windows – a version of ORTEP-III with a graphical user interface (GUI). J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889897003117Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Spek, A. L.: Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D65 (2009) 148–15510.1107/S090744490804362XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Mphahlele, M. J.; Agbo, E. N.; Gildenhys, S.: Synthesis and evaluation of the 4-substituted 2-hydroxy-5-iodochalcones and their 7-substituted 6-iodoflavonol derivatives for inhibitory effect on cholinesterases and β-secretase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (2018) 4112–4135.10.3390/ijms19124112Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Tocco, G.; Eloh, K.; Onnis, V.; Sasanelli, N.; Caboni, P.: Haloacetophenones as newly potent nematicides against Meloidogyne incognita. Ind. Crop. Prod. 110 (2017) 94–102.10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.06.003Search in Google Scholar
7. Khan, K. M.; Ambreen, N.; Mughal, U. R.; Jalil, S.; Perveen, S.; Choudhary, M. I.: 3-Formylchromones: potential anti-inflammatory agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45 (2010) 4058–4064.10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.05.065Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Shim, Y. S.; Kim, K. C.; Lee, K. A.; Shrestha, S.; Lee, K. H.; Kim, C. K.; Cho, H.: Formylchromone derivatives as irreversible and selective inhibitors of human protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. kinetic and modeling studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13 (2005) 1325–1332.10.1016/j.bmc.2004.11.006Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Khan, K. M.; Ambreen, N.; Hussain, S.; Perveen, S.; Choudhary, M. I.: Schiff bases of 3-formylchromone as thymidine phosphorylase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 (2009) 2983–2988.10.1016/j.bmc.2009.03.020Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Ekinci, D.; Al-Rashida, M.; Abbas, G.; Senturk, M.; Supuran, C. T.: Chromone containing sulfonamides as potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 27 (2012) 744–747.10.3109/14756366.2011.614607Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Christopeit, T.; Albert, A.; Leiros, H. K.: Discovery of a novel covalent non-β-lactam inhibitor of the metallo-β-lactamase NDM-1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 24 (2016) 2947–2953.10.1016/j.bmc.2016.04.064Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Chavan, B. B.; Gadekar, A. S.; Mehta1, P. P.; Vawhal1, P. K.; Kolsure1, A. K.; Chabukswar, A. R.: Synthesis and medicinal significance of chalcones – a review. Asian J. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 6 (2016) 1–7.Search in Google Scholar
13. Kumar, S.; Pandey, A. K.: Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: an overview. Sci. World J. 2013 (2013) 162–750.10.1155/2013/162750Search in Google Scholar
14. Pimlott, S. L.; Sutherland, A.: Molecular tracers for the PET and SPECT imaging of disease. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40 (2011) 149–162.10.1039/B922628CSearch in Google Scholar
15. Saikat, K. S.; Dipak, H. K.; Monika, M.; Tanusree, K.: Synthesis, structural elucidation and DFT studies of ortho-hydroxy acetophenones. J. Mol. Struct. 936 (2009) 277–282.10.1016/j.molstruc.2009.08.013Search in Google Scholar
16. Hadzi, D.; Kidric, J.; Koller, J.; Mavrij, J.: The role of hydrogen bonding in drug-receptor interactions. J. Mol. Struct. 237 (1990) 139–150.10.1016/0022-2860(90)80136-8Search in Google Scholar
17. Scholfield, M. R.; Zanden, C. M.; Carter, M.; Ho, P. S.: Halogen bonding (X-bonding): a biological perspective. Protein Sci. 22 (2013) 139–152.10.1002/pro.2201Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
18. Wilcken, R.; Zimmermann, M. O.; Lange, A.; Joerger, A. C.; Boeckler, F. M.: Principles and applications of halogen bonding in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology J. Med. Chem. 56 (2013) 1363–1388.10.1021/jm3012068Search in Google Scholar PubMed
19. Persch, E.; Dumele, O.; Diederich, F.: Molecular recognition in chemical and biological systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54 (2015) 3290–3327.10.1002/anie.201408487Search in Google Scholar PubMed
20. Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G.: The halogen bond. Chem. Rev. 116 (2016) 2478–2601.10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00484Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
21. Mphahlele, M. J.; Maluleka, M. M.; Ramasami, P.; Rhyman, L.; Mampa, R. M.: Spectroscopic, DFT and XRD studies of hydrogen bonds in N-unsubstituted 2-aminobenzamides. Molecules 22 (2017) 83–96.10.3390/molecules22010083Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
22. Mphahlele, M. J.: Crystal structure and hydrogen bonding study of the 3-trifluoroacetyloxime substituted 7-acetamido-2-aryl-5-bromoindoles. Crystals 8 (2018) 274–284.10.3390/cryst8070274Search in Google Scholar
23. Yaninmoto, Y.; Kabayashi, H.; Nagakura, S.; Saito, Y.: The crystal structure of acetophenone at 154 K. Acta Crystallogr. B29 (1973) 1822–1826.10.1107/S0567740873005583Search in Google Scholar
24. Clark, T.; Hennemann, M.; Murray, J. S.; Politzer, P. J.: Halogen bonding: the σ-hole. J. Mol. Model. 13 (2007) 291–296.10.1007/s00894-006-0130-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
25. Martinez, C. R.; Iverson, B. L.: Rethinking the term “p-stacking”. Chem. Sci. 3 (2012) 2191–2201.10.1039/c2sc20045gSearch in Google Scholar
©2019 Malose J. Mphahlele, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n
Articles in the same Issue
- 10.1515/ncrs-2020-frontmatter1
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dicarboxybenzenaminium perchlorate monohydrate, C8H8ClNO9
- The crystal structure of poly[(m4-4-bromoisophthalato-κ4O: O′:O′′:O′′′)zinc(II)], C8H3BrO4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C8H8ClN3O4S
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-methylenebis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C11H18F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H58Cl2CuN12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)], C19H10Cl6CoN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-bromo-6-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-4-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C18H21NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- Crystal structure of Bis(acetato-κ2O,O′)-bis[4-(dimethylamino)pyridine-κN]nickel(II), C18H26N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-chlorophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9Cl2NO
- The co-crystal structure of (17b)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17diol – acetamide (1/1), a Z′ = 4 structure, C20H29NO3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)ureido)benzoic acid, C13H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(9-ethyl-9H-carbazole-3,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(IV)), C24H27N5F12P2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisophthalic acid, C8H5BrO4
- The crystal structure of 13-ethoxycarbonyl-9-methyl-4-chlor-11-thioxo-8-oxa-10,12-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2,4,6-triene, C14H15ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-(diethylamino)benzylidene)amino)-N,N-diphenylaniline, C29H29N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C27H27N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-ethoxy-6-((E)-((3-(((E)-3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-2-hydroxypropyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C21H26N2O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-tetrakis(μ2-2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κ2O:O′)dinickel(II)], C19H10Cl6N3NiO6
- Crystal structure of hexakis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-diazido-κ1N-tetrakis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tetrazinc(II), C48H32N32Zn4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)–dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(((4-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H9ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(5-bromo-6-methyl-picolinato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) dihydrate, C14H16Br2N2O7Zn
- Crystal structure of biaqua(2,2′-bipyridine-4,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2N,N′)(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)nickel(II) hydrate, C19H15N3NiO10
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-aminoisophthalato-κ3N:O,O′)-bis(4,4′-dipyridylsulfide-κ1N)dizinc(II), C36H34N6O12S2Ni2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)palladium(II) tetracyanonickelate(II), C14H24N8NiPd
- The crystal structure of 3-benzyl-1-((8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-yl)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C27H24N3OF6P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-iodophenyl)ethan-1-one, C8H6ClIO2
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) bis((E)-4-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)benzenesulfonate), C28H40MgN6O12S2
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[(1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κN)-(μ2-2-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)], C20H17N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-{[tri-aqua-di-sodium bis(2-{[n-butyl(methyl)carbamothioyl]sulfanyl}acetate)]}n, [C16H34N2Na2O7S4]n
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-3-((3-acetyl-5-carboxyphenyl)oxidophosphoryl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2O:O′)bis(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-k2N,N′)zinc(II), C56H46N4O22P2Zn2
- Crystal structure of N′,2-bis((E)-2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothiohydrazide, C15H12Cl2N4O2S
- Crystal structure of 2-[(1E)-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]iminiumyl}methyl]-5-(dodecyloxy)benzen-1-olate, C23H39NO5
- Crystal structure of 12-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzo[f]pyrido[1,2-a]indole-6,11-dione, C23H13NO4
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-chloro-6-(p-tolyl)pyrimidine-κ2C,N)-(triphenylphosphane-κP)palladium(II), C29H23Cl2N2PPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3,4,5,6-tetrabromo-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H14Br8CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibenzyl-dichlorido-(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′)tin(IV)], C24H22Cl2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of benzyl-chlorido-(4-chloro-N-[(2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]benzenecarbohydrazonato)-methanol-tin(IV), C22H20Cl2N2O3Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(3-nitrophthalato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — water (2/3), C20H22N5O10.5Co
- Crystal structure of (3R,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol, C30H52O3
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-(4-carboxyphenyl)ureido)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C26H24Cl2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 8-hydroxy-2-methylquinolin-1-ium chloride dihydrate, C10H14ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (dibenzyl sulphoxide-κO)dibromido-bis(4-bromobenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C28H26Br4OSSn
- Crystal structure of bromido-tri(4-chlorophenyl-κ1C)-(ethanol-κ1O)tin(IV) — 4,4′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine (2/1), C52H48Br2Cl6N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-butyl-6-(ethylamino)-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-dione, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-chloro-N-[(2-oxido-5-chlorophenyl)methylidene] benzene-carbohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)bis(2-fluorobenzyl)tin(IV), C28H20Cl2F2N2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-(4-fluorobenzyl-κC)-(N′-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazidato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C26H22ClFN2O5Sn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tri(4-chlorophenyl)-(μ2-hydroxido)tin(IV)] – 2-propanol (1/1), C21H21Cl3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of bromido-dimethyl-4-tolyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C27H28BrOPSn
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonio)ethane-1-sulfonate, C6H15NO5S
- Crystal structure of bis[triaqua-(μ2-1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethylene-κ2N:N′)-(4-sulfonatobenzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C13H15NO8SZn
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-(3-hydroxy-7-methylene-2,3-dihydro-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-2-yl)propan-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol – a marmesin derivative, C20H24O10
- Crystal structure of octa(4-chlorobenzyl)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-methanolato)-bis(μ3-oxo)-tetratin(IV), C58H54Cl10O4Sn4
- Crystal structure of iodido-triphenyl-(triphenylphosphine oxide)tin(IV), C36H30IOPSn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-benzyl-1-oxo-N-phenethyl-1H-[1,4]oxazino [4,3-b]indazole-3-carboxamide, C26H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{(N-[(5-chloro-2-oxidophenyl)methylidene]-2-hydroxybenzenecarbohydrazonato)-dioxo-molybdenum(VI)}(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine), C38H26Cl2Mo2N6O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-octamethyl-bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-(phenylamino)ethanolato-κ2O:O)tetratin(IV), C24H44Cl2N2O4Sn4
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(2-(imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium)ethoxy)ethyl)-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-4-ium bis(hexafluorophosphate) — acetonitrile (1/1), C18H20ON4F12P2
- Crystal structure of cyclo[tetra(μ2-cyanido)-tetracyanido-bis(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)dinickel(II)dipalladium(II)] hexahydrate, C24H52N16Ni2O6Pd2
- Crystal structure of (dimethyl sulfoxide)-dioxido-[2-hydroxy-N′-(4-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)benzohydrazidato κ3N,O,O′]molybdenum(VI), C19H20MoN2O6S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(ethanolamine-κ2N,O)copper(II), C14H25CuNO5
- Crystal structure of chlorido-diphenyl-(isopropyl(propyl)carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C19H24ClNS2Sn
- The crystal structure of bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane monohydrate, C7H10N4O
- The crystal structure of bis(4-nitroimidazole-1-1yl)methane, C7H6N6O4
- Crystal structure of di(naphthalen-2-yl)sulfane, C20H14S
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-bromo-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C11H7BrO4
- Crystal structure of N′2,N′6-bis((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridine-2,6-dicarbohydrazide — methanol (1/2), C21H25N9O4
- The crystal structure of 3-nitro-4-(p-tolylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C16H12N2O4
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis((4-methoxyphenyl)ethynyl)benzene, C24H18O2
- Crystal structure of a low-temperature (100 K) polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)], C18H28N2O4P2S4Zn
- The pseudosymmetric low temperature polymorph of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κN,N′)-bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-κS)-cadmium(II)], {C18H28CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of 3-iodophthalic acid, C8H5IO4
- The crystal structure of tert-butyl (tert-butoxy(oxo)methyl)(5-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)carbamate, C16H21BrFNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ3N,O:O)-tetrakis(5,7-dichloroquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)bis(methanol-κ1O)dieuropium(III) — toluene (1/1), C63H39Cl12Eu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-4-methoxybenzohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II), C16H18N4O2Cl2Cd
- A redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-isopropyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C24H38CdN4O4P2S4}n


