Abstract
C24H15N4O9Sm, monoclinic, P21/n, a = 6.780(2) Å, b = 27.939(8) Å, c = 11.546(4) Å, β = 101.630(4)°, V = 2142.1(12) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0221, wRref(F2) = 0.0587, T = 296(2) K.
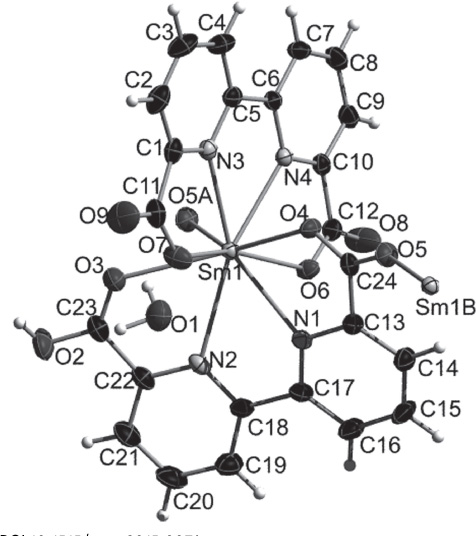
The crystal structure is shown in the figure, Tables 1–3 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Source of material
A mixture of Sm(NO3)3·6H2O (0.1 mmol, 44 mg), 2,2′-bipyridinyl-6,6′-dicarboxylic acid, (0.1 mmol, 24 mg) was dissolved in 8 mL H2O. Then the solution was heated in a 25 mL Teflon-lined autoclave under autogenous pressure at 443 K for four days. After cooling to room temperature colourless block shaped crystals were collected.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless, block, size 0.25×0.38×0.47 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 28.11 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | CCD area detector, φ and ω scans |
| 2θmax: | 50° |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique: | 10789, 3758 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3532 |
| N(param)refined: | 344 |
| Programs: | SHELX [9] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | Site | x | y | z | Uiso |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H(1W) | 4e | 0.6101 | 0.1147 | 0.7417 | 0.061 |
| H(2W) | 4e | 0.6228 | 0.1407 | 0.6425 | 0.061 |
| H(2) | 4e | 1.4042 | 0.0829 | 0.5677 | 0.064 |
| H(2A) | 4e | 0.7787 | 0.2796 | 0.5612 | 0.040 |
| H(3) | 4e | 0.7556 | 0.3433 | 0.4311 | 0.044 |
| H(4) | 4e | 0.7488 | 0.3290 | 0.2334 | 0.038 |
| H(7) | 4e | 0.7842 | 0.3102 | 0.0519 | 0.033 |
| H(8) | 4e | 0.7847 | 0.2837 | −0.1368 | 0.036 |
| H(9) | 4e | 0.7748 | 0.2019 | −0.1756 | 0.031 |
| H(14) | 4e | 0.0816 | 0.0614 | 0.0857 | 0.035 |
| H(15) | 4e | 0.1757 | −0.0163 | 0.0492 | 0.044 |
| H(16) | 4e | 0.4976 | −0.0419 | 0.1300 | 0.039 |
| H(19) | 4e | 0.7886 | −0.0642 | 0.2362 | 0.043 |
| H(20) | 4e | 1.1026 | −0.0819 | 0.3459 | 0.049 |
| H(21) | 4e | 1.2991 | −0.0206 | 0.4448 | 0.043 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | Site | x | y | z | U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sm(1) | 4e | 0.81656(2) | 0.133295(6) | 0.26401(1) | 0.0153(1) | 0.0154(1) | 0.0186(1) | 0.00105(6) | 0.00314(7) | 0.00051(6) |
| N(1) | 4e | 0.5436(4) | 0.0659(1) | 0.2258(2) | 0.018(1) | 0.019(2) | 0.022(2) | 0.002(1) | 0.006(1) | 0.000(1) |
| N(2) | 4e | 0.9194(4) | 0.0429(1) | 0.3166(3) | 0.021(2) | 0.023(2) | 0.024(2) | 0.007(1) | 0.006(1) | 0.004(1) |
| N(3) | 4e | 0.7985(4) | 0.2204(1) | 0.3252(2) | 0.016(1) | 0.021(2) | 0.023(2) | −0.000(1) | 0.002(1) | −0.001(1) |
| N(4) | 4e | 0.7802(4) | 0.1969(1) | 0.1030(2) | 0.014(1) | 0.017(2) | 0.021(2) | 0.001(1) | 0.002(1) | 0.000(1) |
| O(1) | 4e | 0.5348(4) | 0.1218(1) | 0.6666(3) | 0.038(2) | 0.047(2) | 0.035(2) | −0.001(1) | 0.005(1) | −0.002(1) |
| O(2) | 4e | 1.3768(4) | 0.0624(1) | 0.5160(3) | 0.030(2) | 0.046(2) | 0.043(2) | 0.013(1) | −0.011(1) | −0.005(1) |
| O(3) | 4e | 1.1437(4) | 0.11408(9) | 0.4272(2) | 0.031(2) | 0.029(2) | 0.034(2) | 0.003(1) | −0.003(1) | 0.001(1) |
| O(4) | 4e | 0.4632(3) | 0.15854(8) | 0.2283(2) | 0.016(1) | 0.018(1) | 0.037(1) | −0.000(1) | 0.004(1) | −0.000(1) |
| O(5) | 4e | 0.1340(4) | 0.14418(9) | 0.1990(2) | 0.017(1) | 0.029(1) | 0.038(2) | 0.005(1) | 0.006(1) | −0.001(1) |
| O(6) | 4e | 0.7548(4) | 0.10380(9) | 0.0665(2) | 0.030(1) | 0.021(1) | 0.022(1) | −0.003(1) | 0.007(1) | −0.002(1) |
| O(7) | 4e | 0.7649(5) | 0.1452(1) | 0.4577(2) | 0.050(2) | 0.028(1) | 0.024(1) | 0.007(1) | 0.013(1) | 0.002(1) |
| O(8) | 4e | 0.7763(6) | 0.1117(1) | −0.1207(3) | 0.110(3) | 0.031(2) | 0.024(2) | −0.001(2) | 0.015(2) | −0.005(1) |
| O(9) | 4e | 0.7688(6) | 0.1902(1) | 0.6154(2) | 0.081(2) | 0.052(2) | 0.022(2) | −0.009(2) | 0.016(2) | −0.006(1) |
| C(1) | 4e | 0.7884(5) | 0.2288(1) | 0.4377(3) | 0.017(2) | 0.033(2) | 0.023(2) | −0.001(2) | 0.003(1) | −0.005(2) |
| C(2) | 4e | 0.7773(6) | 0.2745(2) | 0.4815(4) | 0.029(2) | 0.040(2) | 0.032(2) | −0.006(2) | 0.009(2) | −0.015(2) |
| C(3) | 4e | 0.7640(6) | 0.3121(2) | 0.4042(4) | 0.039(2) | 0.025(2) | 0.049(3) | −0.006(2) | 0.015(2) | −0.014(2) |
| C(4) | 4e | 0.7630(6) | 0.3038(1) | 0.2869(4) | 0.033(2) | 0.019(2) | 0.044(2) | −0.003(2) | 0.012(2) | −0.003(2) |
| C(5) | 4e | 0.7834(5) | 0.2573(1) | 0.2491(3) | 0.015(2) | 0.022(2) | 0.030(2) | −0.001(1) | 0.003(1) | 0.001(1) |
| C(6) | 4e | 0.7838(5) | 0.2442(1) | 0.1256(3) | 0.016(2) | 0.019(2) | 0.026(2) | 0.001(1) | 0.001(1) | 0.001(1) |
| C(7) | 4e | 0.7835(5) | 0.2776(1) | 0.0357(3) | 0.025(2) | 0.019(2) | 0.037(2) | −0.001(1) | 0.005(2) | 0.005(2) |
| C(8) | 4e | 0.7822(6) | 0.2618(1) | −0.0764(3) | 0.027(2) | 0.034(2) | 0.028(2) | −0.001(2) | 0.004(2) | 0.012(2) |
| C(9) | 4e | 0.7771(5) | 0.2132(1) | −0.0996(3) | 0.025(2) | 0.032(2) | 0.021(2) | −0.002(2) | 0.002(2) | 0.006(2) |
| C(10) | 4e | 0.7754(5) | 0.1820(1) | −0.0071(3) | 0.016(2) | 0.025(2) | 0.021(2) | 0.000(1) | 0.002(1) | 0.002(1) |
| C(11) | 4e | 0.7757(6) | 0.1847(2) | 0.5109(3) | 0.025(2) | 0.040(2) | 0.021(2) | 0.004(2) | 0.002(2) | −0.003(2) |
| C(12) | 4e | 0.7677(6) | 0.1282(1) | −0.0231(3) | 0.028(2) | 0.024(2) | 0.020(2) | −0.001(1) | 0.002(2) | −0.002(2) |
| C(13) | 4e | 0.3553(5) | 0.0803(1) | 0.1806(3) | 0.018(2) | 0.022(2) | 0.021(2) | 0.000(1) | 0.007(1) | 0.000(1) |
| C(14) | 4e | 0.2117(6) | 0.0506(1) | 0.1151(3) | 0.021(2) | 0.027(2) | 0.037(2) | 0.000(2) | 0.002(2) | −0.004(2) |
| C(15) | 4e | 0.2673(6) | 0.0045(1) | 0.0946(4) | 0.030(2) | 0.025(2) | 0.051(3) | −0.008(2) | 0.000(2) | −0.012(2) |
| C(16) | 4e | 0.4591(6) | −0.0106(1) | 0.1420(4) | 0.031(2) | 0.021(2) | 0.045(2) | −0.002(2) | 0.007(2) | −0.007(2) |
| C(17) | 4e | 0.5943(5) | 0.0207(1) | 0.2073(3) | 0.022(2) | 0.021(2) | 0.026(2) | 0.001(1) | 0.010(2) | 0.003(1) |
| C(18) | 4e | 0.8023(5) | 0.0069(1) | 0.2658(3) | 0.025(2) | 0.018(2) | 0.030(2) | 0.003(1) | 0.007(2) | 0.001(1) |
| C(19) | 4e | 0.8699(6) | −0.0399(1) | 0.2748(4) | 0.031(2) | 0.024(2) | 0.052(3) | 0.003(2) | 0.007(2) | −0.003(2) |
| C(20) | 4e | 1.0560(7) | −0.0505(2) | 0.3402(4) | 0.040(2) | 0.025(2) | 0.058(3) | 0.016(2) | 0.011(2) | 0.007(2) |
| C(21) | 4e | 1.1738(6) | −0.0143(2) | 0.3974(4) | 0.029(2) | 0.034(2) | 0.044(2) | 0.015(2) | 0.007(2) | 0.006(2) |
| C(22) | 4e | 1.1003(5) | 0.0320(1) | 0.3826(3) | 0.025(2) | 0.028(2) | 0.024(2) | 0.008(2) | 0.007(2) | 0.005(2) |
| C(23) | 4e | 1.2113(6) | 0.0738(1) | 0.4444(3) | 0.025(2) | 0.034(2) | 0.025(2) | 0.007(2) | 0.004(2) | 0.004(2) |
| C(24) | 4e | 0.3136(5) | 0.1317(1) | 0.2054(3) | 0.017(2) | 0.027(2) | 0.015(2) | 0.001(1) | 0.005(1) | 0.002(1) |
Results and discussion
The metal ion is usually achieved by energy transfer from the bonded ligands, a process termed antenna effect [1] in reference to the naturally occurring phenomenon encountered in green plants [2]. The higher molar absorbance of the organic shell allows a better collection of the incident photons when compared to the free metal ions. This is especially true for lanthanide metal ions, for which the various selection rules make their electronic transitions strongly forbidden with molar absorption coefficients rarely higher than a few M−1·cm−1 [3]. Present-day technology in supramolecular chemistry allows a precise control of the metal coordination spheres and permits a fine-tuning of the energy-transfer processes either in simple devices used as luminescent stains [4] or in more elaborate molecular wires and sensors [5]. The choice of the ligand remains however a crucial point and molecules containing aromatic moieties are usually found to be good sensitisers for LnIII ions [6] but more rarely meet all the above-mentioned criteria [7].
In an effort to bring further understanding to the relationship between the ligand structure and the efficiency of the energy transfer process and, also, to unravel suitable synthons for the design of elaborate compartmental ligands, we have turned our attention to 2,2-bipyridine-6,6-dicarboxylic acid, H2L. Thanks to its aromatic core, combined with a four-site pincer-shaped coordinating pattern, H2L appears as an interesting candidate for use as a light-harvesting moiety for lanthanide complexes.
The asymmetric unit of the title structure contains one Sm(III) ion, and one water molecule and two anionic 2,2′-bipyridinyl-6,6′-dicarboxylato ligands (see the figure) to construct a new coordination polymer. The samarium atom is nine-coordinated by five oxygen atoms (O3, O4, O5a, O6 and O7) and four nitrogen atoms (N1, N2, N3 and N4) from three 2,2′-bipyridinyl-6,6′-dicarboxylato ligands. The Sm—O bond lengths are from 2.356(3) to 2.659(3) Å, and the Sm—N bond lengths are from 2.545(3) to 2.659(3) Å, respectively. The bond angles of O—Sm—O are in the range of 65.24(9)° to 157.95(9)°, the N—Sm—N are in the range of 59.91(9)° to 150.56(9)°. Water molecules and oxygen atoms of the carboxylic groups form hydrogen bonds: O(2)—H(2)…O(1)#1 [O…O = 2.485(4) Å, O–H…O = 161.8°]; O(1)—H(2W)…O(9) [O…O = 2.625(5) Å, O–H…O = 164.5°]; O(1)—H(1W)…O(8)#3 [O…O = 2.678(4) Å, O–H…O = 168.9°]. All the oxygen atoms of the carboxylic groups participate in the hydrogen bonding, contributing to packing stability [8]. Thus these interactions result in the infinite threedimensional architecture.
References
1. Sabbatini, N.; Guardigli, M.; Lehn, J.-M.: Luminescent lanthanide complexes as photochemical supramolecular devices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 123 (1993) 201–228.10.1016/0010-8545(93)85056-ASearch in Google Scholar
2. Witt, H. T.: Examples for the Cooperation of Photons, Excitons, Electrons, Electric Fields and Protons in the Photosynthesis Membrane. New J. Chem. 11 (1987) 91–101.Search in Google Scholar
3. Bünzli, J.-C. G.: Lanthanide probes in life, chemical and earth science: Theory and Practice, J.-C. G. Bunzli and G. R. Choppin, eds., Elsevier Scientific Publishers, B.V., Amsterdam, 1989.Search in Google Scholar
4. Piguet, C.; Bunzli, J.-C. G., Mono- and polymetallic lanthanide-containing functional assemblies: a field between tradition and novelty. Chem. Soc. Rev. 28 (1999) 347–358.10.1039/a804240cSearch in Google Scholar
5. Ziessel, R. F.: Photoinduced energy or electron transfer in supramolecular systems: Applications to molecular wires and light-harvesting sensors. J. Chem. Educ. 74 (1997) 673–679.10.1021/ed074p673Search in Google Scholar
6. Balzani, V.; Scandola, F.: Supramolecular Photochemistry, 1991, Ellis Horwood Ltd, Chichester, England.Search in Google Scholar
7. lhabiri, M.; Scopelliti, R.; Bünzli, J.-C. G.; Piguet, C.: Lanthanide Helicates Self-Assembled in Water: A New Class of Highly Stable and Luminescent Dimetallic Carboxylates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121 (1999) 10747–10762.10.1021/ja991854qSearch in Google Scholar
8. Feng, X.; Xie, C.-Z.; Wang, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Ma, L.-F., Synthesis and Crystal Structures of Ternary Copper(II) Complex Containing Salicylaldehyde Schiff Base and 4,4′-Bipyridine. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 38 (2008) 619–624.10.1007/s10870-008-9358-2Search in Google Scholar
9. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2016 Li Zhang et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of rac-4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-3-methylbutanoic acid, C5H7O2F3
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H14O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(2-(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutanamido)thiazol-4-yl)acetate, C18H21ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (4E,11E,31E,38E)-1,4,12,15,18,26,31,39-Octaaza-7,21,24-trihydroxy-penta-cyclo[13·13·13·16,10·120,24·133,37]tetratetraconta-4,6(44),7,9,11,18,20(43),21,23,25,31,33(42),34,36,38-pentadecaene, C36H42N8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ5-4-(3,5-dicarboxylato-κ3O1:O2:O3-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O5,O7:O8)(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)dicobalt(II)] C24H16N3O11Co2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-acetamido-benzoato-κ2O:O′)triphenyltin(IV)], C27H23NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido(2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(((1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methylylidene))diphenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)iron(III), C20H20ClFeN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(4-tert-butyl)phenyl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C18H17CIO
- Crystal structure of trans-1,2-bis(pyridinium-4-yl)ethylene–2-carboxy-4-methylbenzoate (1/2), C30H26N2O8
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-ethylenediamine-tetraacetatolead(II)zinc(II)]
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazono)methyl)-4-nitrophenol — triethylamine (2/1), C32H33N11O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis-(μ2-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C26H24N2O12Cd
- Crystal structure of 2-(ethoxycarbonyl)-2-(2-nitro-1-phenylethyl)-3-oxopyrrolidinium chloride, C15H19N2O5Cl
- Crystal structure of 4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfinyl)pyridine, C11H10N2OS
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diethoxy-1,4-bis[2-(quinoline)ethenyl]benzene, C32H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua(μ2-1,1′-biphenyl-4,4′-diylbis(1H-imidazole)-κ2N:N′)tetrakis(3-carboxy-5-ethylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)dizinc(II), C54H50N8O18Zn2
- Crystal structure of a poly[bis(3,4,5,6-tetrachlorophthalato)neodym(III)potassium(I)] — 4,4′-bipyridine — water (1/1/5.5)
- The second polymorph of triethylammonium 2,4,6-trisulfanylidene-1,3,5-triazinan-1-ide, C9H18N4S3
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-diamino-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid dihydrate, C14H16N2O6
- Crystal structure of the catena-poly[bis(1H-imidazole-κN)-(μ2-furan-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ2O1:O4)manganese(II)]monohydrate, C12H12MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of (acetylacetonato-κ2O:O′)bis-((1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one)-κ2C,N)iridium(III), C33H27IrN2O6
- Crystal structure of 1-benzyl-3-(4-methylpyridin-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C16H16F6N3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, C15H23N3O7
- Crystal structure of 4-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl] benzenesulfonamide, C21H18FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of 2,4-dichlorobenzene anhydride, C14H6Cl4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetato-κ2O,O′)bis(pyridine-κN)nickel(II), C26H24N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-nitro-2-(((3-(tetrahydro-8λ4-[1,3,2]oxazaborolo[2,3-b][1,3,2]oxaborol-8-yl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenol – water (1/2), C17H18BN3O5·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 5-(4-carboxyphenoxy)-nicotinic acid, C13H9NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexaaquabis(μ2-3-nitrophthalate-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-1,4-bis(4-pyridylmethyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)dimanganese(II)] dihydrate, C32H42Mn2N6O20
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene-2,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O, O′:/O′′,O′′′)bis-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N, N′)dicadmium(II) hydrate
- Crystal structure of (R)-1-(1-(6-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)ethyl)-3-phenylthiourea
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidiazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-4,4′-(1,2-phenylenebis(oxy)dibenzoato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)nickel(II)], C34H26O6N4Ni
- Crystal structure of 3′,4′,5-trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone, C17H14O7
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-chlorido-bis[N-sec-butyl,N-n-propyl-carbamodithioato κ2S,S′]-tin(IV), C20H41ClN2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ4-4,4′-(1,2-phenylenebis(oxy))dibenzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)bis(μ3-4,4′-(1,2-phenylenebis(oxy))dibenzoato–κ3O:O′:O′′)(μ2-1-(4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzyl)-1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′)tetracobalt(II)], C94H62O24N4Co4
- Crystal structure of catenapoly[diaqua-(μ24,4′-bipyridine)-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoate)-κO)nickel(II)] ethanol monosolvate, C28H30F4N2O8Ni
- Crystal structure of 2-(9H-fluoren-9-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H11N3S
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C18H16N2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaquabis(μ2-3-carboxybenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-1:2κ2O:O′)-(μ2-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)-benzene-1:1′κ2N:N′)dizinc(II)], [Zn2(C26H26N4)(C9H4O6)2(H2O)2]
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(phenoxyacetato-κ2O,O′)-zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- Crystal structure of 4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-6-pyrimidinylferrocene, C17H14FeN4
- Crystal structure of [2-(4-methoxyphenyl)pyrazine-κ2C,N) chlorido[N,N′-bis-(2,6-diisopropyl-phenyl)imidazol-2-ylidene-κC)] palladium(II), C38H45ClN4OPd
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-acetyl-2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-5,6-dichloro-isoindole-1,3-dione, C18H13Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridin-1-ium 3,3′,5′-tricarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylate, (C26H18N2O8)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-μ2-4,4′-biphenyl-4,4′-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′-bis(5-carboxy-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboxylato-κO)nickel(II)] dihydrate, C40H40N4O12Ni
- Crystal structure of poly-[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′−μ3-thiophene-2,3-di-carboxylato-κ4O,O′, O′′:O′′′ -cadmium(II)]
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamanganese(II) bis(3-carboxythiophene-2-carboxylate) C12H18MnO14S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)benzoic acid, C14H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)acrylonitrile)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[2,2′-bipyridinyl-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridinyl-6′-carboxyl-6-carboxylato-κ5N,N′,O,O′:O′′)samarium(III)] monohydrate, C24H13N4O8Sm · H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-4-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)benzoato)-κ2N:O)copper(II)] dihydrate, C28H22N8O6Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-k2N:N′)-zinc(II)] fumarate tetrahydrate, C14H26N2O12Zn
- Crystal structure of triaqua-(1,10-phenanthroline)-(dihydrogen-3,3′,3′′-(2,4,6-trioxo-1,3,5-triazinane-1,3,5-triyl)tripropanoato) cobalt(II)dihydrogen-3,3′,3′′-(2,4,6-trioxo-1,3,5-triazinane-1,3,5-triyl)tripropanoate, C72H82Co2N16O42
- Crystal structure of poly[dibromido-(μ2–4,4′-bis-(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)lead(II)], C22H16N2PbBr2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)-cobalt(II)]dihydrate, C26H24N2O12Co
- Crystal structure of 5-(4-pyridyl)pyrimidine–4,4′-bipyridine–1,3,5-benzenetriol–water (1:1:1:1), C25H23N5O4
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-4-((4-hydroxyphenyl)imino)naphthalen-1(4H)-one monohydrate, C16H11NO3 · 0.5H2O
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzamide, C14H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methanone, C15H14O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)5′-([2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridin]-4′-yl)-[1,1′:3′,1′′-terphenyl]-4,4′′-dicarboxylato]zinc(II), C39H31Cl2N3O6Zn
- Crystal structure of bis[4-(3-carboxy-6-fluoro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium] benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate (C20H18F2N3O3)2(C8H4O4), C48H40F4N6O10
- Crystal structure of (2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-(4-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C14H12O4
- Crystal structure of photochromic 1-(2-methyl-5-phenyl-3-thienyl-2-[2-methyl-5-(4-ethoxylphenyl)-3-thienyl] 3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H22F6OS2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaquabis(μ2-biphenyl-2,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)tris(μ2-1,1′-biphenyl-4,4′-diylbis(1H-imidazole)-κ2N:N′)dicobalt(II)] monohydrat, C82H64N12O11Co2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4-difluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12N2O2F2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-μ2-aqua-κ2O:O)bis(μ5-oxalato-1:2κ2O1; 1κ1O2; 3:4:5κ3O3; 3κ1O4)(μ4-oxalato-1:2κ2O1; 2:3κ2O2; 3:4κ2O3; 4:1κ2O4)dizinc(II)disodium(I)]
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hexachloridotantalate(V), C8H20Cl6NTa
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((2-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H8Br2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 6-chloro-2,4-diphenylquinoline
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1,10-phenanthrolin-5-yl)imino)methyl)-5-methylphenol monohydrate, C20H15N3O·H2O
- Crystal structure of tris(3-(2-pyridyl)pyrazole)zinc(II)tetrachlorido zincate(II), C24H21Cl4N9Zn2
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N,N-diethyl-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine, C12H20ClN5
- The crystal structure of 4-allyl-5-benzyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, C12H13N3O
- Crystal structure of diethyl 2-(((2-(pyridin-3-ylthio)phenyl)amino)methylene)malonate, C19H20N2O4S
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(2-(isopropylimino)methyl-5-methylphenolatido-κ2N,O)(pyridine-κN)rhenium(I), C19H19N2O4Re
- Crystal structure of 1,3,6,8-tetrakis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C44H34S4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-(diaqua-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)-(4-methylphthalato-κ2O,O′)-cobalt(II)trihydrate, C21H26CoN2O9
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium fac-tricarbonyl(hexafluoroacetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(nitrato-κO)rhenium(I), C16H21O8N2F6Re
- Crystal structure of 3-(thiophen-2-yl)-5-(p-tolyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxamide
- Crystal structure of bis(1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium) tetrabromidocadmate(II), [C6H11N2]2[CdBr4]
- Crystal structure of N′-(adamantan-2-ylidene)-isonicotinohydrazide, C16H19N3O
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaquabis(4-(pyridin-4-ylsulfonyl)pyridine-κN)cobalt(II) diperchlorate dihydrate, C20H28Cl2CoN4O18S2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(furan-2-yl(p-tolylamino)methylene)-3-methyl-1-p-tolyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C23H21N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-fluorobenzyl)sulfanyl]-4-(2-methylpropyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile, C16H16FN3OS
- Crystal structure of poly[octaaqua-tris(benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)tetralanthanum(III)] hexahydrate, C30H34La4O38
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4,4′-sulfonyldipyridine-κN)zinc(II) diperchlorate dihydrate, C20H28Cl2ZnN4O18S2
- Crystal structure of 4-nitro-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid, a structure with a Z′ = 4, C5H3NO4S
- Crystal structure of dirubidium trimercury(II) tetraselenide, Rb2Hg3Se4
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-chloroanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C19H22ClN3OS
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) 5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate, C2H12N8O8Mg
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-benzene-1,4-diylbis(1H-benzimidazole-κ2N:N′)silver(I)] nitrate, C20H14N5AgO3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-4-chlorophenyl)ethanone, C14H10Cl2O2
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dinitro-1,3,5-oxadiazinane, C3H6N4O5
- Crystal structure of methyl 5-methoxy 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C11H11NO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(((3-acetyl-2-hydroxyphenyl)amino)methylene)naphthalen-2(1H)-one, C19H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-5-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one —dimethylsulfoxide (1:1), C12H12ClNO2S3
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-((4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)methylene)bis(1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione) – diethylamine – dichloromethane (1/1/1) C25H32Cl2F3N5O6
- Crystal structure of 2-(dimethylsulfanylidene)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-oxo-3-phenylpropanamide
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)bis(thiocyanato-κN)platinum(II), C14H8N4PtS2
- Crystal structure of di(μ2-chlorido)bis[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]dipalladium(II), C22H16Cl2N2Pd2
- Crystal structure of trans-dibromidodi(pyridine-κN)palladium(II), PdBr2(C5H5N)2
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of rac-4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-3-methylbutanoic acid, C5H7O2F3
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H14O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(2-(2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutanamido)thiazol-4-yl)acetate, C18H21ClN2O3S
- The crystal structure of (4E,11E,31E,38E)-1,4,12,15,18,26,31,39-Octaaza-7,21,24-trihydroxy-penta-cyclo[13·13·13·16,10·120,24·133,37]tetratetraconta-4,6(44),7,9,11,18,20(43),21,23,25,31,33(42),34,36,38-pentadecaene, C36H42N8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ5-4-(3,5-dicarboxylato-κ3O1:O2:O3-phenoxy)phthalato-κ3O5,O7:O8)(μ2-4-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)dicobalt(II)] C24H16N3O11Co2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-acetamido-benzoato-κ2O:O′)triphenyltin(IV)], C27H23NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido(2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(((1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methylylidene))diphenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)iron(III), C20H20ClFeN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(4-tert-butyl)phenyl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C18H17CIO
- Crystal structure of trans-1,2-bis(pyridinium-4-yl)ethylene–2-carboxy-4-methylbenzoate (1/2), C30H26N2O8
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-ethylenediamine-tetraacetatolead(II)zinc(II)]
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)hydrazono)methyl)-4-nitrophenol — triethylamine (2/1), C32H33N11O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis-(μ2-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C26H24N2O12Cd
- Crystal structure of 2-(ethoxycarbonyl)-2-(2-nitro-1-phenylethyl)-3-oxopyrrolidinium chloride, C15H19N2O5Cl
- Crystal structure of 4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)sulfinyl)pyridine, C11H10N2OS
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diethoxy-1,4-bis[2-(quinoline)ethenyl]benzene, C32H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua(μ2-1,1′-biphenyl-4,4′-diylbis(1H-imidazole)-κ2N:N′)tetrakis(3-carboxy-5-ethylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)dizinc(II), C54H50N8O18Zn2
- Crystal structure of a poly[bis(3,4,5,6-tetrachlorophthalato)neodym(III)potassium(I)] — 4,4′-bipyridine — water (1/1/5.5)
- The second polymorph of triethylammonium 2,4,6-trisulfanylidene-1,3,5-triazinan-1-ide, C9H18N4S3
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-diamino-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid dihydrate, C14H16N2O6
- Crystal structure of the catena-poly[bis(1H-imidazole-κN)-(μ2-furan-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ2O1:O4)manganese(II)]monohydrate, C12H12MnN4O6
- Crystal structure of (acetylacetonato-κ2O:O′)bis-((1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(pyridin-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one)-κ2C,N)iridium(III), C33H27IrN2O6
- Crystal structure of 1-benzyl-3-(4-methylpyridin-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate, C16H16F6N3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, C15H23N3O7
- Crystal structure of 4-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl] benzenesulfonamide, C21H18FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of 2,4-dichlorobenzene anhydride, C14H6Cl4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetato-κ2O,O′)bis(pyridine-κN)nickel(II), C26H24N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-nitro-2-(((3-(tetrahydro-8λ4-[1,3,2]oxazaborolo[2,3-b][1,3,2]oxaborol-8-yl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenol – water (1/2), C17H18BN3O5·2H2O
- Crystal structure of 5-(4-carboxyphenoxy)-nicotinic acid, C13H9NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexaaquabis(μ2-3-nitrophthalate-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-1,4-bis(4-pyridylmethyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)dimanganese(II)] dihydrate, C32H42Mn2N6O20
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene-2,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O, O′:/O′′,O′′′)bis-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N, N′)dicadmium(II) hydrate
- Crystal structure of (R)-1-(1-(6-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)ethyl)-3-phenylthiourea
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidiazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-4,4′-(1,2-phenylenebis(oxy)dibenzoato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)nickel(II)], C34H26O6N4Ni
- Crystal structure of 3′,4′,5-trihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone, C17H14O7
- Crystal structure of n-butyl-chlorido-bis[N-sec-butyl,N-n-propyl-carbamodithioato κ2S,S′]-tin(IV), C20H41ClN2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ4-4,4′-(1,2-phenylenebis(oxy))dibenzoato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)bis(μ3-4,4′-(1,2-phenylenebis(oxy))dibenzoato–κ3O:O′:O′′)(μ2-1-(4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzyl)-1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′)tetracobalt(II)], C94H62O24N4Co4
- Crystal structure of catenapoly[diaqua-(μ24,4′-bipyridine)-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,6-difluorobenzoate)-κO)nickel(II)] ethanol monosolvate, C28H30F4N2O8Ni
- Crystal structure of 2-(9H-fluoren-9-ylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H11N3S
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C18H16N2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaquabis(μ2-3-carboxybenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-1:2κ2O:O′)-(μ2-1,4-bis(2-ethylbenzimidazol-1-ylmethyl)-benzene-1:1′κ2N:N′)dizinc(II)], [Zn2(C26H26N4)(C9H4O6)2(H2O)2]
- Crystal structure of diaquabis(phenoxyacetato-κ2O,O′)-zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- Crystal structure of 4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-6-pyrimidinylferrocene, C17H14FeN4
- Crystal structure of [2-(4-methoxyphenyl)pyrazine-κ2C,N) chlorido[N,N′-bis-(2,6-diisopropyl-phenyl)imidazol-2-ylidene-κC)] palladium(II), C38H45ClN4OPd
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-acetyl-2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-5,6-dichloro-isoindole-1,3-dione, C18H13Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridin-1-ium 3,3′,5′-tricarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylate, (C26H18N2O8)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-μ2-4,4′-biphenyl-4,4′-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′-bis(5-carboxy-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboxylato-κO)nickel(II)] dihydrate, C40H40N4O12Ni
- Crystal structure of poly-[μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′−μ3-thiophene-2,3-di-carboxylato-κ4O,O′, O′′:O′′′ -cadmium(II)]
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamanganese(II) bis(3-carboxythiophene-2-carboxylate) C12H18MnO14S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)benzoic acid, C14H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)acrylonitrile)
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[2,2′-bipyridinyl-6,6′-dicarboxylato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(μ2-2,2′-bipyridinyl-6′-carboxyl-6-carboxylato-κ5N,N′,O,O′:O′′)samarium(III)] monohydrate, C24H13N4O8Sm · H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-4-(3-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)benzoato)-κ2N:O)copper(II)] dihydrate, C28H22N8O6Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-k2N:N′)-zinc(II)] fumarate tetrahydrate, C14H26N2O12Zn
- Crystal structure of triaqua-(1,10-phenanthroline)-(dihydrogen-3,3′,3′′-(2,4,6-trioxo-1,3,5-triazinane-1,3,5-triyl)tripropanoato) cobalt(II)dihydrogen-3,3′,3′′-(2,4,6-trioxo-1,3,5-triazinane-1,3,5-triyl)tripropanoate, C72H82Co2N16O42
- Crystal structure of poly[dibromido-(μ2–4,4′-bis-(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)lead(II)], C22H16N2PbBr2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2O:N)-cobalt(II)]dihydrate, C26H24N2O12Co
- Crystal structure of 5-(4-pyridyl)pyrimidine–4,4′-bipyridine–1,3,5-benzenetriol–water (1:1:1:1), C25H23N5O4
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-4-((4-hydroxyphenyl)imino)naphthalen-1(4H)-one monohydrate, C16H11NO3 · 0.5H2O
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)benzamide, C14H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methanone, C15H14O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)5′-([2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridin]-4′-yl)-[1,1′:3′,1′′-terphenyl]-4,4′′-dicarboxylato]zinc(II), C39H31Cl2N3O6Zn
- Crystal structure of bis[4-(3-carboxy-6-fluoro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium] benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate (C20H18F2N3O3)2(C8H4O4), C48H40F4N6O10
- Crystal structure of (2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-(4-methoxyphenyl)methanone, C14H12O4
- Crystal structure of photochromic 1-(2-methyl-5-phenyl-3-thienyl-2-[2-methyl-5-(4-ethoxylphenyl)-3-thienyl] 3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluoro-cyclopent-1-ene, C29H22F6OS2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaquabis(μ2-biphenyl-2,4′-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)tris(μ2-1,1′-biphenyl-4,4′-diylbis(1H-imidazole)-κ2N:N′)dicobalt(II)] monohydrat, C82H64N12O11Co2
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4-difluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12N2O2F2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-μ2-aqua-κ2O:O)bis(μ5-oxalato-1:2κ2O1; 1κ1O2; 3:4:5κ3O3; 3κ1O4)(μ4-oxalato-1:2κ2O1; 2:3κ2O2; 3:4κ2O3; 4:1κ2O4)dizinc(II)disodium(I)]
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hexachloridotantalate(V), C8H20Cl6NTa
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((2-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C13H8Br2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 6-chloro-2,4-diphenylquinoline
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1,10-phenanthrolin-5-yl)imino)methyl)-5-methylphenol monohydrate, C20H15N3O·H2O
- Crystal structure of tris(3-(2-pyridyl)pyrazole)zinc(II)tetrachlorido zincate(II), C24H21Cl4N9Zn2
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N,N-diethyl-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine, C12H20ClN5
- The crystal structure of 4-allyl-5-benzyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, C12H13N3O
- Crystal structure of diethyl 2-(((2-(pyridin-3-ylthio)phenyl)amino)methylene)malonate, C19H20N2O4S
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(2-(isopropylimino)methyl-5-methylphenolatido-κ2N,O)(pyridine-κN)rhenium(I), C19H19N2O4Re
- Crystal structure of 1,3,6,8-tetrakis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C44H34S4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-(diaqua-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)-(4-methylphthalato-κ2O,O′)-cobalt(II)trihydrate, C21H26CoN2O9
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium fac-tricarbonyl(hexafluoroacetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(nitrato-κO)rhenium(I), C16H21O8N2F6Re
- Crystal structure of 3-(thiophen-2-yl)-5-(p-tolyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carboxamide
- Crystal structure of bis(1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium) tetrabromidocadmate(II), [C6H11N2]2[CdBr4]
- Crystal structure of N′-(adamantan-2-ylidene)-isonicotinohydrazide, C16H19N3O
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaquabis(4-(pyridin-4-ylsulfonyl)pyridine-κN)cobalt(II) diperchlorate dihydrate, C20H28Cl2CoN4O18S2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(furan-2-yl(p-tolylamino)methylene)-3-methyl-1-p-tolyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C23H21N3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-[(4-fluorobenzyl)sulfanyl]-4-(2-methylpropyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile, C16H16FN3OS
- Crystal structure of poly[octaaqua-tris(benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)tetralanthanum(III)] hexahydrate, C30H34La4O38
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4,4′-sulfonyldipyridine-κN)zinc(II) diperchlorate dihydrate, C20H28Cl2ZnN4O18S2
- Crystal structure of 4-nitro-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid, a structure with a Z′ = 4, C5H3NO4S
- Crystal structure of dirubidium trimercury(II) tetraselenide, Rb2Hg3Se4
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-chloroanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C19H22ClN3OS
- Crystal structure of hexaaquamagnesium(II) 5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate, C2H12N8O8Mg
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-benzene-1,4-diylbis(1H-benzimidazole-κ2N:N′)silver(I)] nitrate, C20H14N5AgO3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-4-chlorophenyl)ethanone, C14H10Cl2O2
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dinitro-1,3,5-oxadiazinane, C3H6N4O5
- Crystal structure of methyl 5-methoxy 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C11H11NO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(((3-acetyl-2-hydroxyphenyl)amino)methylene)naphthalen-2(1H)-one, C19H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-5-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one —dimethylsulfoxide (1:1), C12H12ClNO2S3
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-((4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)methylene)bis(1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione) – diethylamine – dichloromethane (1/1/1) C25H32Cl2F3N5O6
- Crystal structure of 2-(dimethylsulfanylidene)-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-oxo-3-phenylpropanamide
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)bis(thiocyanato-κN)platinum(II), C14H8N4PtS2
- Crystal structure of di(μ2-chlorido)bis[2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2N,C1]dipalladium(II), C22H16Cl2N2Pd2
- Crystal structure of trans-dibromidodi(pyridine-κN)palladium(II), PdBr2(C5H5N)2

