Abstract
Online education resources are more and more abundant, which brings some challenges to learners’ personalized selection. How to provide personalized recommendation services from massive resources according to the needs of learners has gradually become the focus of scholars’ research. Therefore, this article improves the traditional collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm and constructs a personalized recommendation model of an online learning platform based on a long-term memory network and collaborative filtering. First, the stack noise reduction autoencoder combined with auxiliary information is used to extract the user potential vector, and the project potential vector is extracted by using the short-duration memory network and the attention mechanism. Then, the double attribute scoring matrix is used to divide the attributes, and the backpropagation network is used to predict the scores. Through the experimental analysis, the hit rate and recall rate of the model constructed by the research institute are 0.7548 and 0.7247, respectively, and the cumulative gain of normalized loss and running time are 0.3385 and 2.72 s, respectively. This model can effectively make up for the defects of the traditional algorithm caused by cold start and sparse score data and provide more effective and high-quality learning resource recommendations for students.
1 Introduction
Online education based on networks is different from traditional classroom education. Educators not only need to impart knowledge and supervise learning, but also need to provide online teaching resources and environment for learners. Learners need to think independently, take the initiative to explore, and have higher requirements for their conscious initiative [1]. With the continuous development of online education, the number and scale of learning resources have exploded, so that ordinary learners may face difficulties in choosing learning resources [2]. The implementation of a personalized recommendation function for learning resources can help learners obtain more targeted learning resources, help them improve their learning level, and solve the problems of poor personalized traditional education and uneven distribution of educational resources [3]. Although the traditional recommendation algorithm (RA) has realized effective recommendation, there are still some problems such as sparse score data and cold start. These problems further lead to the unsatisfactory recommendation quality of existing RAs [4]. In recent years, the combination of traditional recommendation algorithms and deep learning has gradually attracted the attention of scholars, but there are still many aspects to be explored in the optimization and improvement of recommendation algorithms [5]. At present, traditional recommendation algorithms suffer from issues such as user cold start and sparse data, and the recommendation effect is not ideal enough. With the application of deep learning algorithms, they have gradually been widely applied in the field of recommendation models. However, commonly used convolutional neural networks lack the ability to extract textual contextual information and key information. However, graph neural networks (GNNs) typically require complex preprocessing and feature extraction of graph structures, which may be difficult to implement in some cases. These limitations require further exploration and improvement. In order to achieve higher quality teaching resource recommendation, a new learning resource recommendation model is constructed by using long short term memory (LSTM) and a collaborative filtering algorithm. Compared with existing research, the model designed by the research institute has stronger interpretability and scalability, which can effectively capture the potential features of users and items and improve the accuracy and diversity of recommendations. The research contributions are as follows: proposing a personalized recommendation method for online learning platforms based on LSTM and collaborative filtering, effectively solving the problems of cold start and data sparsity in traditional recommendation algorithms. The use of a stacked denoising autoencoder combined with auxiliary information to extract potential vectors of users and projects has improved the accuracy and diversity of recommendations – Use a dual-attribute rating matrix for attribute partitioning and use a backpropagation network for rating prediction. The research is divided into three parts. The first part is the literature review. First, the research status at home and abroad in the research field is analyzed, and the work to be done is preliminarily planned. The second part is the method part, which introduces the technology needed to study the construction model and the corresponding improvement methods. The third part is the performance analysis part, which analyzes the performance and application effect of the model in detail. The graphical abstract diagram of the study is shown in Figure 1.

Graphical abstract diagram.
2 Related works
In recent years, the scale of online education has been further developed as more and more users choose to study online. Wang et al. sent emails to 42 dental schools in mainland China to investigate the current situation of online medical undergraduate education during the COVID-19 epidemic. According to statistics, 97% of respondents have opened online courses, and 74% choose it as their main teaching method [6]. In order to understand what factors affect students’ willingness to learn online, Maheshwari used structural equation modeling (SEM) to analyze the data of 145 respondents. The results showed that institutional support and perceived enjoyment (satisfaction) directly influenced students’ willingness to take online courses in the future. This study provides a more theoretical basis for the development of online education [7]. Kang and Zhang conducted a case study of forum-based online teaching in order to increase students’ learning engagement and motivation and minimize students’ procrastination and plagiarism. The results show that this online teaching system effectively improves students’ learning engagement and motivation [8]. The explosive growth of teaching resources in quantity and scale makes ordinary learners face difficulty in choosing learning resources. The recommendation system can solve this problem well. Aiming at the low efficiency and low accuracy of the college English distance learning resource recommendation method, Yin proposed a new teaching resource recommendation method based on massively open online course (MOOC) teaching mode. It uses the interest feedback model to optimize the recommendation algorithm, and experimental results show that it can effectively improve the recommendation efficiency and accuracy [9]. Wang integrated the attention mechanism into the learning resource RA and proposed a deep collaborative learning resource recommendation model based on the attention mechanism. This model is constructed to provide a solid technical foundation for intelligent English education [10]. To overcome the low efficiency and high recommendation error of traditional public English MOOC teaching resource recommendation method, Wei proposed a new method of public English MOOC teaching resource recommendation based on data partition. The hierarchical clustering algorithm is used to preprocess the public MOOC teaching resources. According to the preprocessing results, the data fast algorithm and the resource data are iteratively divided. According to the findings, it has higher recommendation accuracy than conventional methods [11].
In recent years, the combination of traditional RA and deep learning has gradually attracted the attention of researchers. Nassar et al. proposed a multi-criteria collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm by combining deep neural network and matrix decomposition to solve the problem that most of the current recommendation systems based on deep learning use traditional recommendation systems with a single rating. According to the findings, it outperforms several most advanced methods in different data sets and performance evaluation indicators [4]. Aljunid and Doddaghatta proposed a multi-model deep learning approach to solve the limited learning ability and sparse data of traditional collaborative filtering technology, which integrates user and project functions to build a hybrid recommendation system and improve it. Compared with existing methods, this method can improve the prediction accuracy by 42% [12]. Bobadilla et al. proposed a deep learn-based algorithm (DeepUnHide) to extract the linear relationship between hidden factors and demographic information. This method applies deep learning to the collaborative filtering recommendation system to extract user-related information and then obtain corresponding features [13]. Liang et al. aim to improve the service quality of the information IoT system, optimize the existing physical space, and increase security. Based on artificial intelligence technology, a security system filtering service RA with integrated content similarity is proposed. By predicting the rating information of the service, it is recommended to users [14]. Yao and Zhao studied the news recommendation algorithm based on knowledge graph and graph neural network (GNN) considering edge computing, aiming at the problem of poor recommendation effect of current news information. First, a knowledge graph is used to extract knowledge, and then GNN is used to train the extracted features to complete news recommendations. Compared with the two baselines, the recommendation accuracy of this method is improved by 9.94% [15]. Tai et al. propose a new recommendation approach to address the problem that existing session-based recommendation systems are unable to capture correlations between interactions. In this method, a location-aware importance extraction module is proposed, and combined with comparative learning, additional knowledge is discovered by using the intrinsic dependence relationship to enhance the ability of information extraction [16].
Machine learning is widely used, and it has gradually become the key research direction of scholars. The relevant literature on machine learning applications in the existing studies is shown in Table 1.
Introduction of related works
| Serial number | Title | Research contents |
|---|---|---|
| [17] | Predicting cervical cancer biopsy results using demographic and epidemiological parameters: a custom stacked ensemble machine learning approach. | Chadaga et al. used a customized stacked ensemble machine learning method to predict the probability and risk of infection in order to find a more accurate and cost-effective diagnostic method for cervical cancer. For feature selection, analysis of variance, mutual information, and Pearson correlation techniques are used. Through experimental analysis, it is known that the average accuracy of this method has reached over 95%. |
| [18] | Deep learning-based detection of monkeypox virus using skin lesion images. | Nayak et al. found an existing method for diagnosing monkeypox using ordinary cameras that capture skin images of people infected with monkeypox. It tested data sets on five pre-trained deep neural networks, and the results showed that ResNet18 had the highest accuracy at more than 98%. |
| [19] | A machine learning and explainable artificial intelligence triage-prediction system for COVID-19. | To effectively prevent severe symptoms caused by the novel coronavirus, Khanna et al. used heterogeneous machine learning and deep learning algorithms to predict the severity of the novel coronavirus, taking into account clinical indicators, vital signs, and other key factors. The experiment shows that this method produces an 83% recall rate. |
Based on the above literature content, it can be seen that the online education resource recommendation system can help students choose more suitable and interesting resources in the learning process. However, the traditional recommendation algorithm has some problems, such as the cold start of users and sparse data, and the recommendation effect is not ideal. The existing deep learning algorithms commonly used in the field of recommendation models include convolutional neural networks, contrast learning, GNNs, etc. However, convolutional neural networks lack the ability to extract text context information and key information. To this end, the method of adding auxiliary information and using LSTM to construct a feature extraction model is studied. However, the comparative learning method can effectively capture the potential characteristics of users and items in the recommendation system and improve the accuracy and diversity of the recommendation. However, it requires a large amount of annotation data, which is difficult to obtain in most recommendation systems. For this purpose, the study uses unsupervised learning and does not rely on labeled data. The GNN method uses graph structure to represent user–item interaction and can effectively capture complex relationships and patterns between users and items. However, it usually requires complex preprocessing and feature extraction of the graph structure, which may be difficult to implement in some cases. In contrast, the proposed model uses a simple collaborative filtering method as the basis, which has stronger interpretability and scalability. Therefore, the collaborative filtering recommendation model combined with LSTM is proposed to better adapt to the ever-changing and developing environment of online education resources. Therefore, based on the traditional algorithm, a collaborative filtering recommendation model based on LSTM is constructed. It aims to realize more accurate resource recommendations and form a more complete and convenient personalized learning platform.
3 Construction of a learning resource recommendation model of an online learning platform based on LSTM and collaborative filtering
In order to facilitate learners to query and recommend learning content in a wide range, deep neural networks are used to optimize traditional collaborative filtering algorithms, and a new learning resource recommendation model is constructed. This section introduces the technology used in the construction of the model and the improvement methods.
3.1 Feature extraction and data preprocessing based on LSTM
The study selected historical interaction data of MOOC online learning platform learners from 2015 to 2020 as the dataset to prepare for subsequent research content. Compared with the data stored by the platform, such as learner registration information and the submitted explicit score, learners’ implicit score information needs to be mined and processed by the Web logs and the historical records left by learners when they browse the system [20–22]. Learners’ implicit rating information can be obtained from clickstream data, and static clickstream data can be obtained from server Web logs. Since the data structure of log files is complex and prone to redundancy and loss, it is necessary to preprocess Web logs and transform them into accurate data that can be analyzed for learning behavior. The specific process of acquiring dynamic clickstream data and preprocessing Web log data is shown in Figure 2.
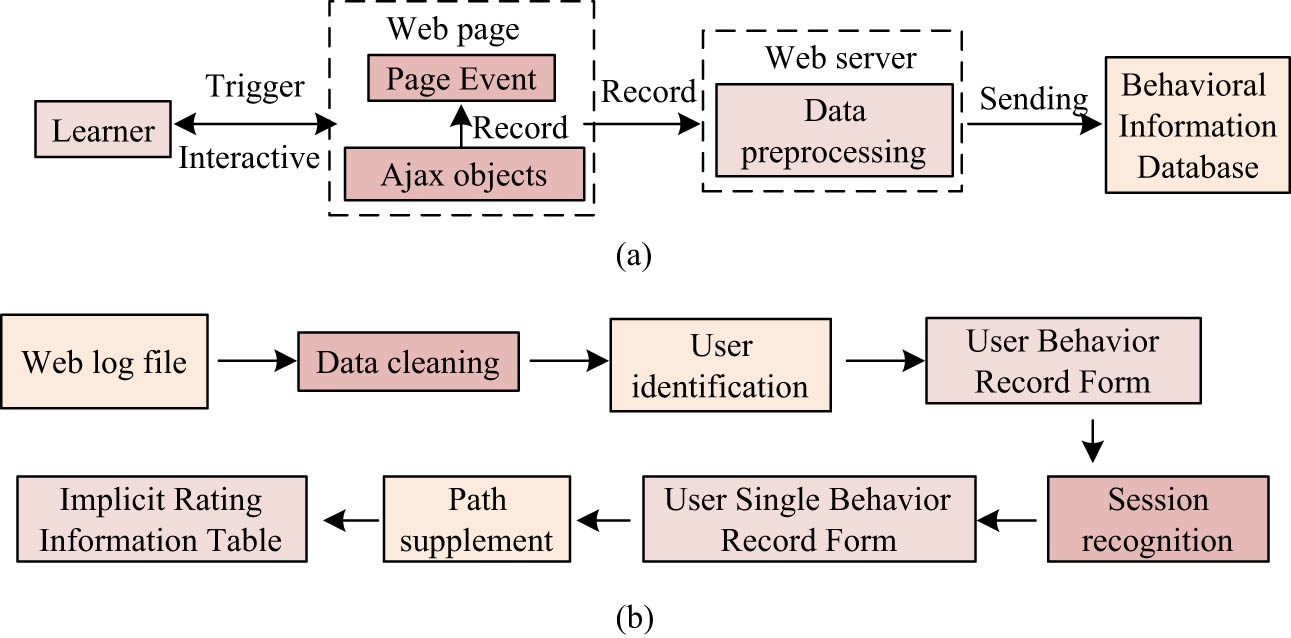
Dynamic click stream data acquisition and Web log data preprocessing process: (a) dynamic click stream data acquisition process and (b) Web log data preprocessing process.
The traditional feature extraction method contains a lot of noise information without keywords and ignores the context and order of words, so it cannot capture the sequence information. To solve this problem, the recommendation model is constructed by combining the overlapping noise reduction autoencoder (aSDAE) of auxiliary information and LSTM based on the attention mechanism. First, score data and auxiliary information of users are used as input of aSDAE to extract potential vectors of users. Then, the auxiliary information of the project is preprocessed using the WordVec word vector tool and then input into the LSTM network layer for feature extraction. After the LSTM layer, the attention mechanism is introduced to extract deeper features, highlight the key information of the project, and output the potential vector of the project. Auxiliary information includes the user’s age, gender, etc., and supporting information for a project includes the type of project, comment information, and so on. The conditional distribution of the score, the user’s present vector, and the project’s potential vector is shown in the following equation:
In equation (1),
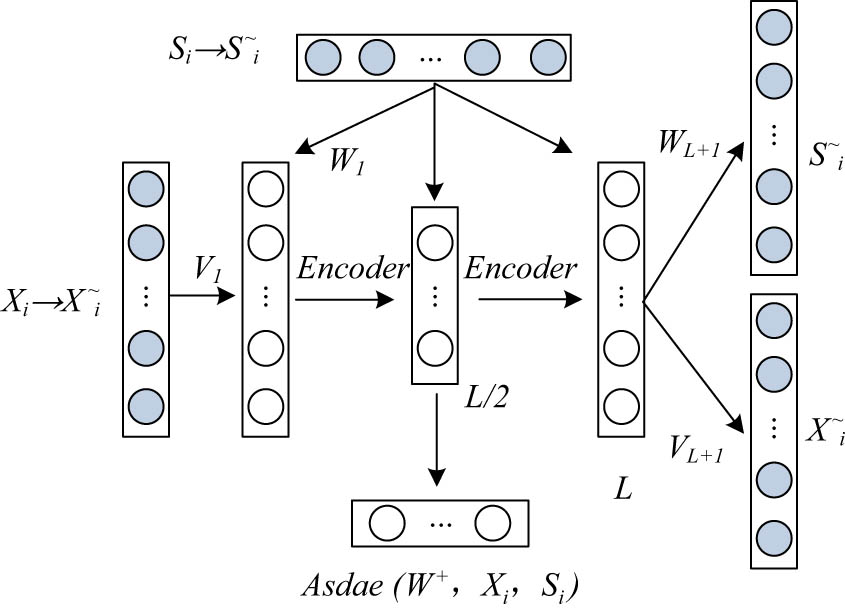
Structure of additional stacked noise reduction autoencoder.
Research integrates auxiliary information into user input for generating potential vectors of users. For each hidden layer of the aSDAE model, the hidden representation of the first layer is shown in the following equation:
In equation (2),
In equation (3),
In equation (4), W
+ is the weight and bias and
In equation (5),
In equation (6),
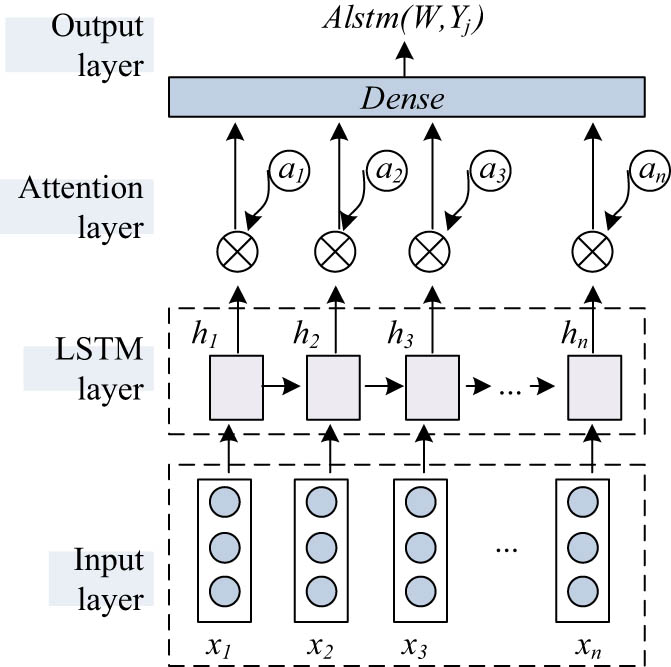
Framework of LSTM attention.
In the input layer, the Skip-Gram model in Word2vec is used for pre-training, and then the document is converted into the corresponding pre-trained word vector and used as the input of the next layer. The LSTM network accepts the output of the previous layer as input to that layer. LSTM outputs the corresponding hidden layer state of the pre-trained word vector at different times. The hidden layer state is entered into the next layer network as a sentence feature vector. In this way, contextual information of word and sentence sequences can be learned. The feature extraction of text information is shown in the following equation:
In equation (7),
In equation (8), W
w is the weight coefficient,
In equation (9),
3.2 Learning resource recommendation based on double attribute scoring matrix and collaborative filtering
To solve the problems caused by sparse data and cold start, a learning resource RA based on a double attribute scoring matrix and collaborative filtering is proposed. In the recommendation system, items have their own characteristics and attributes, and users will choose different items according to their liking for certain attributes of the items [23,24]. Based on this, you can convert a user’s preference for a project property into a user’s preference for a project property. In this article, converting the scoring matrix into a double attribute scoring matrix can realize the cluster analysis of users and items. On this basis, the modified similarity measurement method is used to calculate the similarity of users, and back-propagation neural network (BPNN) is used to construct the user attribute preference model. After training to a certain precision, the unscored items with known attributes are predicted to reduce the coefficient of the frequency division matrix. Finally, the fuzzy preference of user attributes to project attributes is used to generate a valid number of recommendations for new projects or new users in the case of cold start. The process of learning resource recommendation algorithm based on a dual-attribute scoring matrix and collaborative filtering is shown in Figure 5.
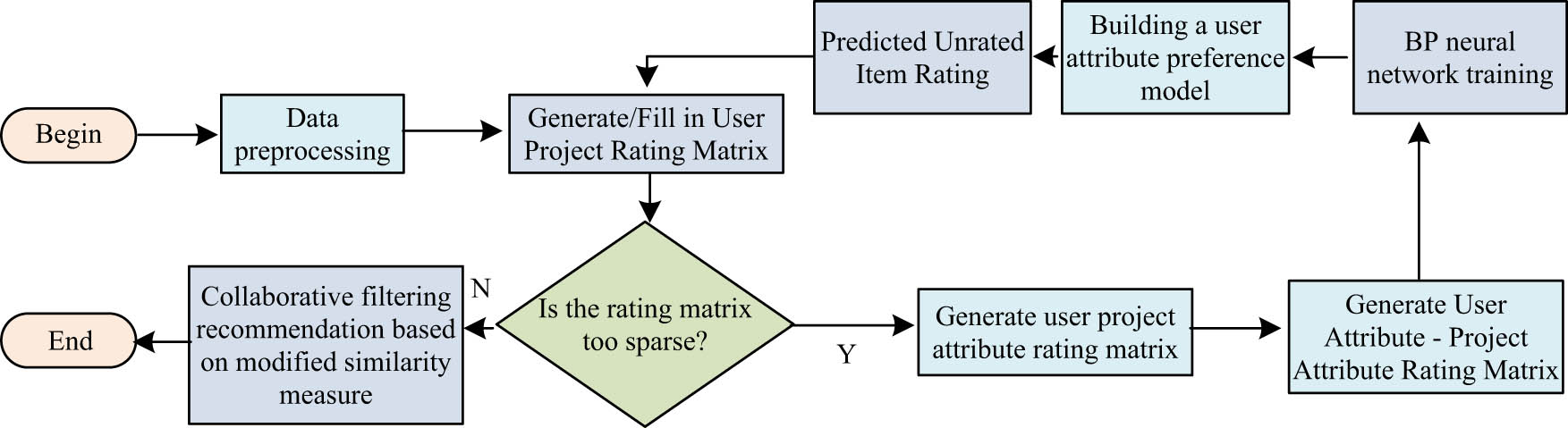
Process of learning resource recommendation algorithm based on dual-attribute scoring matrix and collaborative filtering.
First, the scoring matrix of user attributes and project attributes is constructed. Each project has characteristics that can represent its general attributes, and the characteristics of users can also be described by their attributes. All the features of the project are represented by a set, and then an item is represented by a vector composed of the features of the project. The details are shown in the following equation:
In equation (10),
In equation (11),
Similarly, with the project attribute, if the user has the attribute feature, it is 1; otherwise, the value is 0. The double attribute scoring matrix is obtained by mapping the user attribute features to the established user–item attribute scoring matrix. In traditional recommendation, two users cannot calculate similarity due to the lack of common scoring items. This article proposes a modified similarity measurement method. This method combines Pearson similarity with attribute similarity to measure user similarity. The calculation method is shown in the following equation:
In equation (13),
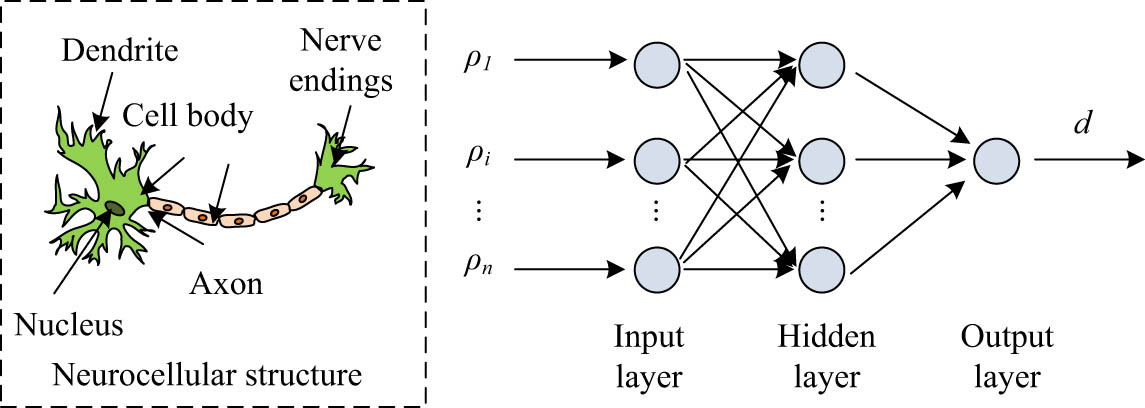
Structure of the user preference model.
The model is trained and learned according to the two-attribute scoring matrix to simulate the preference of user attributes to item attributes. After the preference model is trained to a certain precision, the score is predicted and the matrix is filled to reduce the coefficient of the scoring matrix. The degree to which the preference model prefers an attribute is a function on the closed interval [0, 1], representing the degree of preference from most hated to most liked. Preference can be expressed as shown in the following equation:
In equation (14),
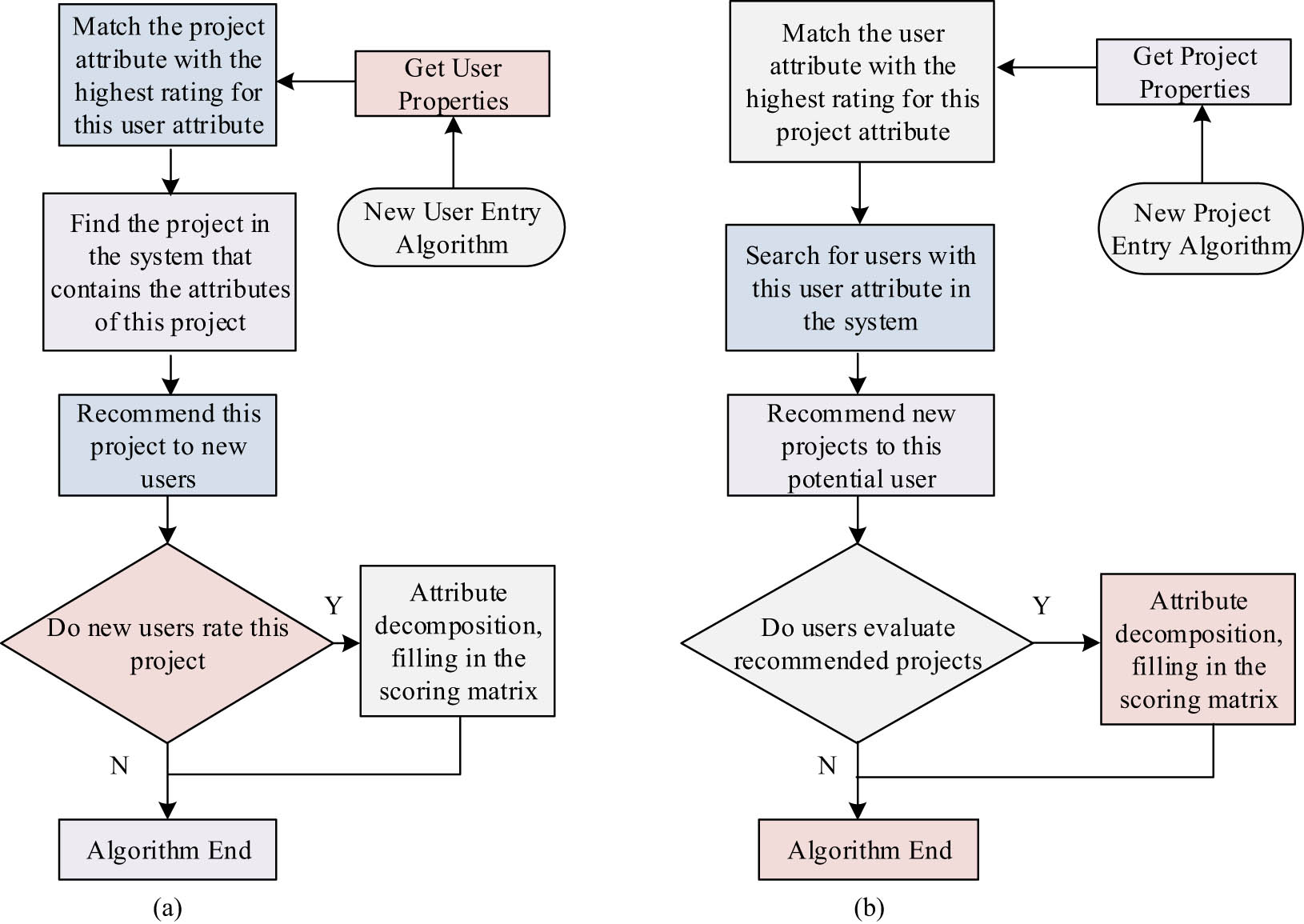
New user and new project recommendation algorithm based on the dual-attribute scoring matrix: (a) new user recommendation and (b) new project recommendation.
Based on the above content, LSTM attention and aSDAE models are used to extract potential feature vectors in the dataset, and then a collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on the dual-attribute scoring matrix is proposed. Therefore, a learning resource recommendation model of an online learning platform based on LSTM and collaborative filtering is constructed.
4 Performance analysis of learning resource recommendation model based on deep neural network and collaborative filtering
4.1 Effect analysis of feature extraction based on LSTM
The interactive data of learners’ course history from 2015 to 2020 on the MOOC learning platform were selected as the experimental data. The sparsity of the dataset is 90%. This is a typical coefficient matrix that can verify the algorithm in solving the sparse problem of fractional matrices. PyCharm 2017.1 and Matlab_R2017b were used to implement data preprocessing and RAs. To test the effect of the algorithm’s attribute vector extraction, the proposed recommendation algorithm based on LSTM attention and collaborative filtering (Method 1), the feature extraction algorithm using convolutional neural network (Method 2), the feature extraction algorithm using aSDAE (Method 3), the recommendation algorithm based on fusion stack noise reduction autoencoder and convolutional neural network (Method 4), and the latent vector are not carried out. The extracted recommendation algorithm (Method 5) was compared. Recall was introduced as an evaluation index. The data set is divided into two data sets with different sparsity, and the performance of different methods in the same environment is discussed. This is shown in Figure 8.
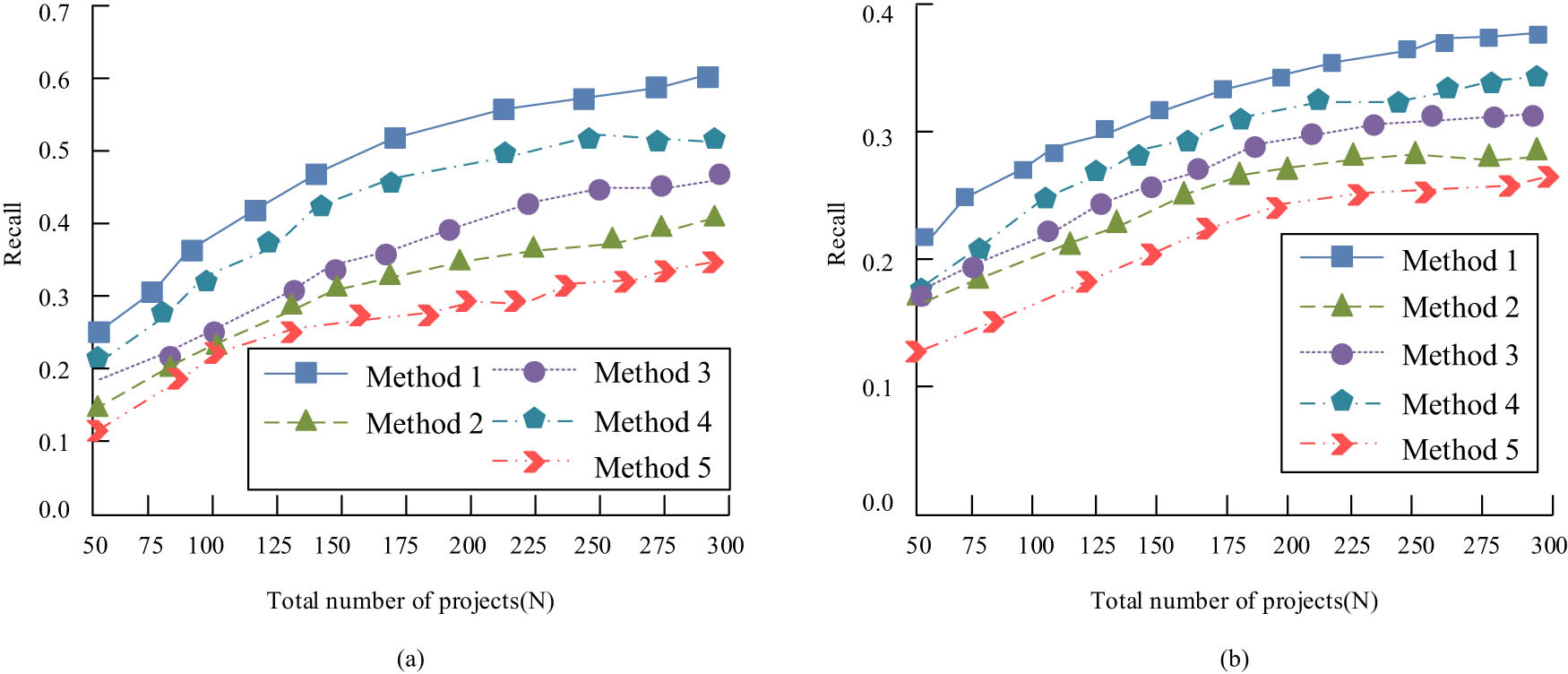
Recall rate changes of different methods in two sparse datasets: (a) sparsity = 58% and (b) sparsity = 88%.
In Figure 8, with the increase of N in the two data sets, several algorithms all show an upward trend. However, Method 5 is the least effective. This is because Method 5 ignores the role of auxiliary information, so the recommendation effect is not good. The recall value of Method 1 is always higher than that of Method 3, which indicates that the combination of models can better extract auxiliary information and learn more effective potential factors. In addition, the attention mechanism is used in Method 1 to extract important words based on different weights to achieve different attention to text information. This shows that the attention mechanism can highlight key information during model training, thus improving model recommendation performance.
To further verify the effect of potential attribute extraction, the root-mean-square error (RMSE) of several models under different iterations of the dataset was observed. Under four different data sets, the impact of the number of iterations on the method RMSE is shown in Figure 9.
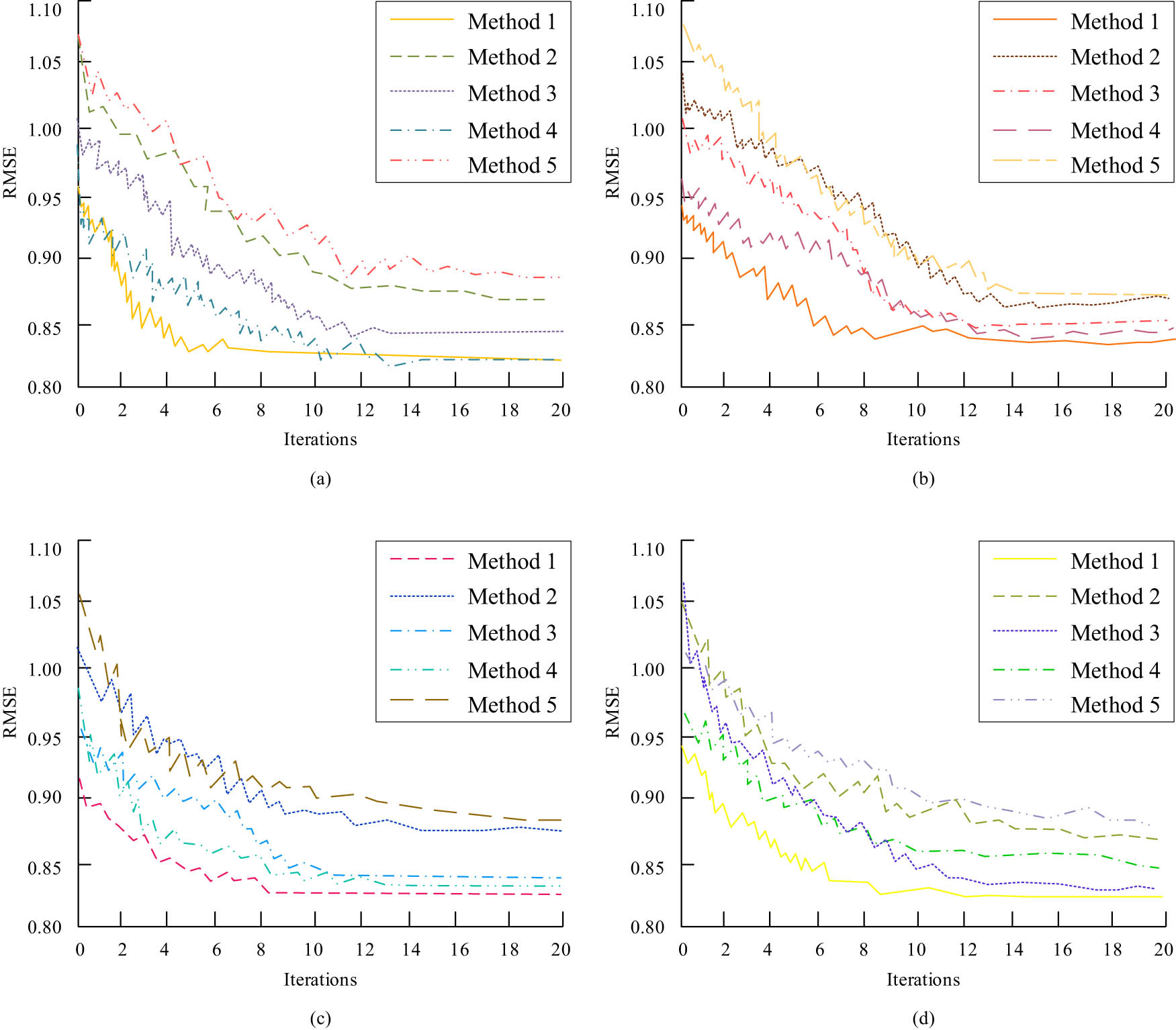
Impact of iteration times on RMSE of each method: (a) Dataset 1, (b) Dataset 2, (c) Dataset 3, and (d) Dataset 4.
In Figure 9, the overall trend of several methods is that the RMSE value of the number of iterations gradually declines and eventually becomes stable. However, it can be seen that too many iterations will also lead to an increase in the RMSE value, which is because too many iterations will lead to overfitting of the method and reduce the recommendation performance. The RMSE value of Method 4 is higher than that of Method 1, which indicates that LSTM and attention layer can quickly highlight key information, extract deep features of text, and converge faster than the maximum pooling layer of the convolutional neural network, which makes the recommendation effect better.
4.2 Recommendation performance analysis based on a double attribute scoring matrix and collaborative filtering
To test the improvement effect of the proposed model on the cold start problem of the traditional recommendation algorithm. The study randomly selected 20 users and zeroed their rating data to simulate the situation of new users entering the recommendation system. The neighbor users are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 14. The user-based Collaborative RA (Ub-CF) and the RA constructed by the research institute (LSTM-CF) are used to recommend new users. The recommended items for new users are compared between the two. At the same time, 10 items are randomly chosen. The score data are cleared to 0. The new project entering the RA is simulated. The potential users recommended by the two algorithms are compared. This is shown in Figure 10.
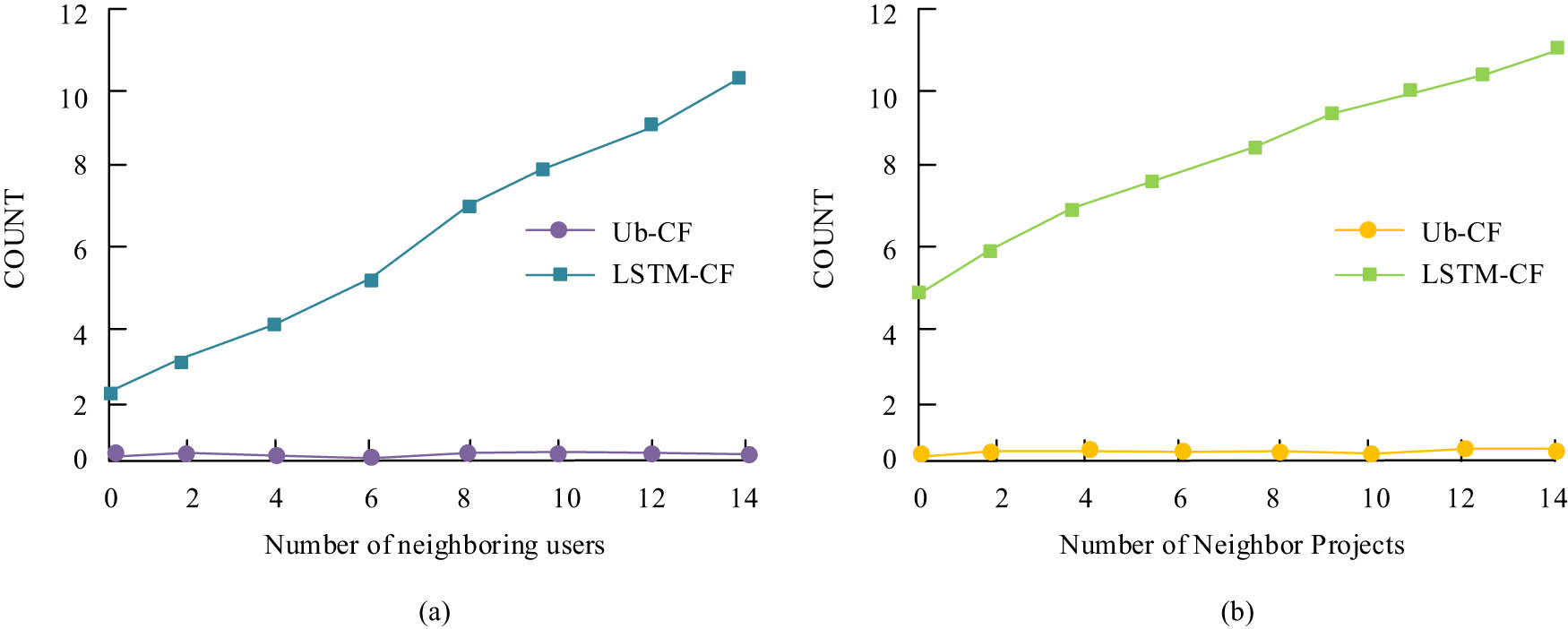
Comparison of the improvement effects of two algorithms for cold start problems: (a) user cold start issue and (b) project cold start issues.
From Figure 10(a), LSTM-CF can provide more items to new users than Ub-CF when new users enter. As the number of neighboring users increase, the recommended items gradually increase. It can alleviate the impact of a cold start on recommendation quality. From Figure 10(b), when a new project enters the system, it can recommend the new project to more users than the collaborative algorithm. With the increase of the neighbor projects, the new project can be recommended to more potential preferred users. The impact of a cold start on recommended quality can be alleviated.
To further verify the performance of the recommended model (Model 1) constructed by the research institute, it is compared with some current research results. The comparison models include a recommendation model based on dual quaternion and collaborative filtering (Model 2), a mobile learning resource recommendation model based on learners’ spatio-temporal characteristics (Model 3), and a hybrid gated neural network recommendation model based on global sampling (Model 4). The four models were compared with the number of recommended courses and the specific changes in recommendation performance. The evaluation indexes selected in this study were hit ratio (HR) and normalized cumulative loss gain (NDGG). The change of the two indicators with the increase in the number of courses is shown in Figure 11.
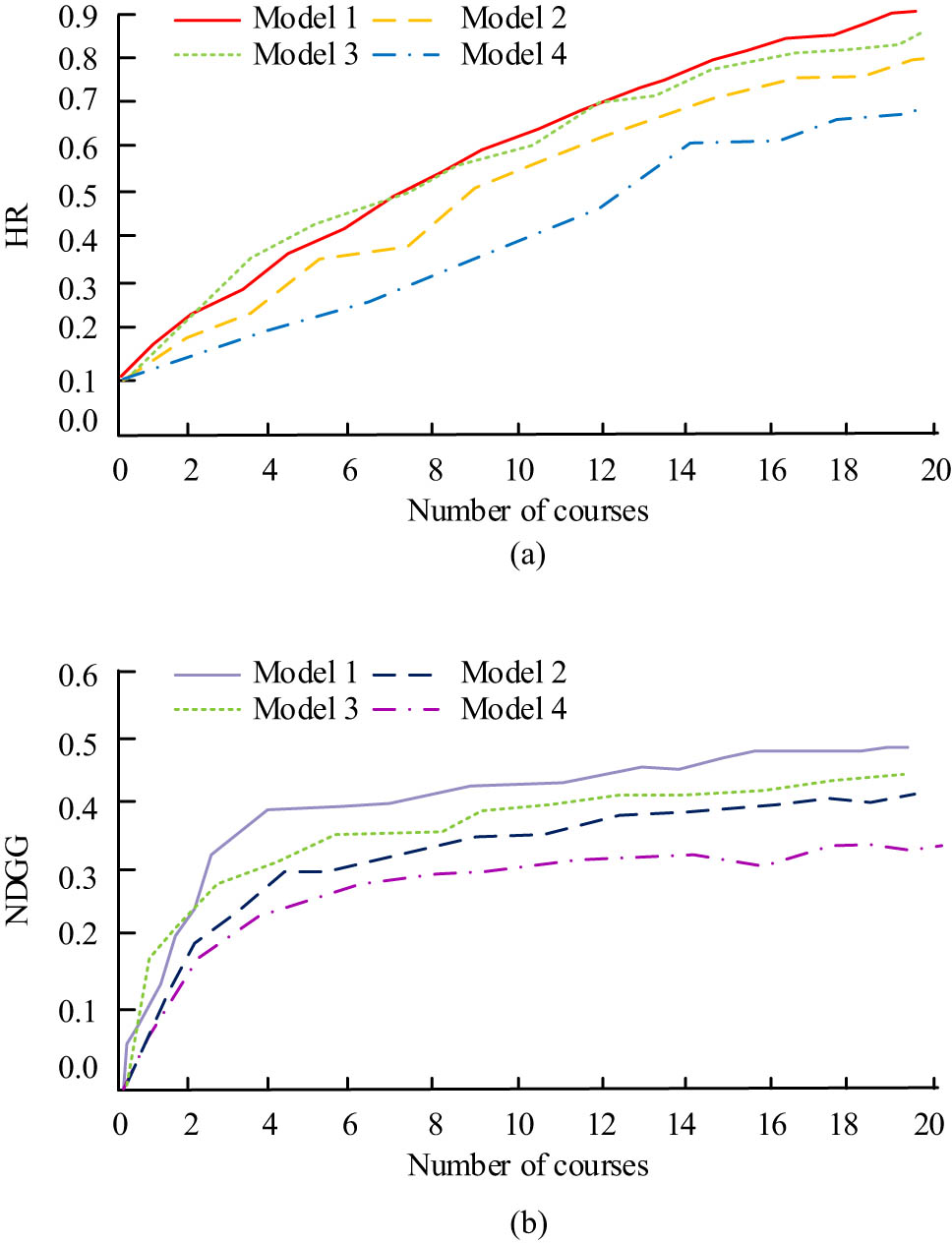
The impact of increasing the number of courses on the HR and NDGG indicators of the model: (a) the impact of the number of recommended courses on the model’s HR indicators and (b) the impact of the number of recommended courses on the model’s NDGG indicators.
From Figure 11, the HR index and NDGG index values of each model increase with the addition of the courses. The index value of Model 1 is always slightly higher than that of other models. The average HR value of Model 1 is 0.69, and the NDGG value is 0.44. Compared with other models, the performance of Model 1 is significantly better.
To compare the recommendation performance of each model more comprehensively, HR, NDGG, Recall, and running time were introduced as evaluation indexes. When the data sparsity is 90%, the recommendation performance of each model is compared and analyzed. Table 2 displays the analysis results.
Comparison of recommended performance of various models
| Project | HR | NDGG | Recall | Running time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | 0.7548 | 0.3385 | 0.7247 | 2.72 |
| Model 2 | 0.5672 | 0.3004 | 0.6028 | 6.35 |
| Model 3 | 0.6110 | 0.3125 | 0.6854 | 4.81 |
| Model 4 | 0.4897 | 0.2975 | 0.5984 | 6.97 |
From Table 2, the HR index value of Model 1 is 0.7548, the NDGG index is 0.3385, and the Recall value is 0.7247. The values of each evaluation index are higher than those of the other three models. In addition, its running time has reached 2.72 s, which is more than 50% shorter than the other three models. Based on the contents in the table, it can be seen that the model built by the research institute can achieve a relatively ideal recommendation effect, and the running time of the model is shorter than other models.
To test the practical application effect of the model, the model is put into the existing learning platform. After using this recommended model for one semester, a total of 200 students from four classes were surveyed by questionnaire, and their assessment results were counted. Based on this data analysis, the author study the effect of building a model to help students learn. Table 3 displays the details.
Comparison of questionnaire results and final assessment scores for the actual application effect of the model
| Project | Questionnaire rating | Average score of assessment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended Fit | Effectiveness | Personalized rating | Reasonability rating | Before use | After use | |
| Class 1 | 84.15 | 80.72 | 90.15 | 86.47 | 68.14 | 75.44 |
| Class 2 | 86.45 | 80.45 | 90.58 | 86.45 | 70.12 | 72.45 |
| Class 3 | 83.01 | 80.44 | 89.46 | 83.46 | 68.23 | 74.48 |
| Class 4 | 83.24 | 81.46 | 90.12 | 82.78 | 65.04 | 71.98 |
As can be seen from Table 3, after the model constructed by the research institute was put into use, students’ scores for various experiences of the system were all above 80 points. The assessment scores of the students in the four classes have been improved to varying degrees. The average score of Class 1 increased by 7.30 points from 68.14, and that of Class 2 increased by 2.35 points. According to the in-depth investigation on the study of the lowest level of improvement in class 2, two students in class 2 did not participate in learning for nearly half of the semester due to illness and hospitalization. As a result, the model failed to provide personalized services for them, which affected their level of improvement. In addition, the average score of Classes 3 and 4 also increased by 8.23 and 6.94 points, respectively. In general, through the use of the model, most students can get a better learning experience and learning effect. Therefore, from the theoretical verification and practical application effect analysis, the recommendation model constructed by the research can achieve a more ideal recommendation effect, and students can find learning resources suitable for their own learning through the appropriate recommendation system. Through self-study and classroom learning, I have improved to different degrees in the final assessment.
5 Conclusion
With the explosive growth of educational resources in quantity and scale, ordinary learners may face difficulties in choosing learning resources. The resources obtained only through traditional search engines usually have complicated results and poor accuracy. In order to realize higher quality learning resource recommendations, LSTM attention and aSDAE are used to extract potential vectors of users and projects. Then, on the basis of traditional collaborative filtering, a double attribute scoring matrix and BP neural network are used to achieve score prediction. Therefore, a learning resource recommendation model of an online learning platform based on LSTM and collaborative filtering is constructed. According to the experimental analysis, under different sparsity data, the recall rate of Method 1 is higher than that of the other three methods, which is 83% higher than that of Method 5. With the increase in the number of iterations, Method 1 converges fastest and can reach a stable state only after seven iterations. It can be seen that the potential vector extraction method used in this study can effectively improve the recommendation quality of the model. The HR index value of Model 1 is 0.7548, the NDGG index is 0.3385, and the recall value is 0.7247. Its running time is more than 50% shorter than the other three models. After the model built by the research institute was put into use, the students’ scores for various experiences of the system were above 80 points. It can be seen that the research and construction model can achieve better recommendation results and provide more suitable learning channels for students. In the later research, the attributes of learning resources can be analyzed more comprehensively, and the attributes that can better express their needs and characteristics can be found.
6 Discussion
In the above experimental analysis, it can be seen that the recommendation method designed by the research institute and several other methods have significant advantages in the process of attribute vector feature extraction. Method 1 has a significant advantage in performance on different sparsity datasets, and the Recall value has increased by more than 80% compared to Method 5. In the iterative process of several methods, Method 1 converges relatively quickly, with its RMSE value consistently lower than Method 4. This is due to the use of LSTM and attention mechanism in Method 1, which can further highlight key information in the data, extract deep-level features, and achieve fast convergence. In terms of cold start issues, research and design methods can provide recommended content to users in the early stages of startup, and as the number of projects increases, recommend projects to more new users. The HR index value of Model 1 is 0.7548, its NDGG index is 0.3385, and the Recall value is 0.7247. Its running time has been reduced by more than 50% compared to the other three models. This indicates that the model designed by the research institute can achieve high efficiency in resource recommendation, and the recommendation effect is significantly better than other models. After the model constructed by the research institute was put into use, students rated the various experiential feelings of the system above 80 points. This indicates that the research design model has high application value and can further help students learn and improve learning efficiency.
7 Challenges and future directions
Although the current personalized recommendation methods for learning resources have achieved satisfactory results, there is still a need to continuously improve and refine the models in the field of education in the future. Meanwhile, the continuous development of computer technology also indicates that resource recommendation methods need to keep up with the times and make continuous progress. In the future, research needs to achieve the following tasks:
At present, the representation of learner attributes and learning resource attributes is not yet complete and relatively singular. In future research, more comprehensive analysis and mining of more feature attributes are needed for both.
The rating information and auxiliary information in learning resources are relatively sparse, and in future research, more reasonable recommendation frameworks can be found to further improve recommendation accuracy. For example, sequence recommendation is used to establish a recommendation framework.
-
Funding information: Author states no funding involved.
-
Author contribution: The author confirms the sole responsibility for the conception of the study, presented results and manuscript preparation.
-
Conflict of interest: The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
-
Data availability statement: The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
[1] Sari FM, Oktaviani L. Undergraduate students’ views on the use of online learning platform during COVID-19 pandemic. Teknosastik. 2021;19(1):41–7.10.33365/ts.v19i1.896Search in Google Scholar
[2] Lubis AH, Dasopang MD. Online learning during the covid-19 pandemic: How is it implemented in elementary schools. Premiere Educandum: Jurnal Pendidikan Dasar Dan Pembelajaran. 2021;11(1):120–34.10.25273/pe.v11i1.8618Search in Google Scholar
[3] Adedoyin OB, Soykan E. Covid-19 pandemic and online learning: the challenges and opportunities. Interact Learn Environ. 2023;31(2):863–75.10.1080/10494820.2020.1813180Search in Google Scholar
[4] Nassar N, Jafar A, Rahhal Y. Multi-criteria collaborative filtering recommender by fusing deep neural network and matrix factorization. J Big Data. 2020;7(1):1–12.10.1186/s40537-020-00309-6Search in Google Scholar
[5] Yi S, Liu X. Machine learning based customer sentiment analysis for recommending shoppers, shops based on customers’ review. Complex Intell Syst. 2020;6(3):621–34.10.1007/s40747-020-00155-2Search in Google Scholar
[6] Wang K, Zhang L, Ye L. A nationwide survey of online teaching strategies in dental education in China. J Dental Educ. 2021;85(2):128–34.10.1002/jdd.12413Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Maheshwari G. Factors affecting students’ intentions to undertake online learning: an empirical study in Vietnam. Educ Inf Technol. 2021;26(6):6629–49.10.1007/s10639-021-10465-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Kang X, Zhang W. An experimental case study on forum-based online teaching to improve student’s engagement and motivation in higher education. Interact Learn Environ. 2023;31(2):1029–40.10.1080/10494820.2020.1817758Search in Google Scholar
[9] Yin H. The recommendation method for distance learning resources of college English under the MOOC education mode. Int J Contin Eng Educ Life Long Learn. 2022;32(2):265–78.10.1504/IJCEELL.2022.121944Search in Google Scholar
[10] Wang F. IoT for smart English education: AI-based personalised learning resource recommendation algorithm. Int J Computer Appl Technol. 2023;71(3):200–7.10.1504/IJCAT.2023.132093Search in Google Scholar
[11] Wei Z. Recommended methods for teaching resources in public English MOOC based on data chunking. Int J Continuing Eng Educ Life Long Learn. 2023;33(2-3):192–202.10.1504/IJCEELL.2023.129213Search in Google Scholar
[12] Aljunid MF, Doddaghatta HM. Multi‐model deep learning approach for collaborative filtering recommendation system. CAAI Trans Intell Technol. 2020;5(4):268–75.10.1049/trit.2020.0031Search in Google Scholar
[13] Bobadilla J, González-Prieto Á, Ortega F, Lara-Cabrera R. Deep learning feature selection to unhide demographic recommender systems factors. Neural Comput Appl. 2021;33(12):7291–308.10.1007/s00521-020-05494-2Search in Google Scholar
[14] Liang W, Xie S, Cai J, Xu J, Hu Y, Xu Y, et al. Deep neural network security collaborative filtering scheme for service recommendation in intelligent cyber–physical systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021;9(22):22123–32.10.1109/JIOT.2021.3086845Search in Google Scholar
[15] Yao C, Zhao C. Knowledge graph and GNN-based news recommendation algorithm with edge computing support. Int J Distrib Syst Technol (IJDST). 2022;13(2):1–11.10.4018/IJDST.291080Search in Google Scholar
[16] Tai W, Lan T, Wu Z, Wang P, Wang Y, Zhou F. Improving session-based recommendation with contrastive learning. User Model User-Adapted Interact. 2023;33(1):1–42.10.1007/s11257-022-09332-zSearch in Google Scholar
[17] Chadaga K, Prabhu S, Sampathila N, Chadaga R, KS S, Sengupta S. Predicting cervical cancer biopsy results using demographic and epidemiological parameters: A custom stacked ensemble machine learning approach. Cogent Eng. 2022;9(1):2143040.10.1080/23311916.2022.2143040Search in Google Scholar
[18] Nayak T, Chadaga K, Sampathila N, Mayrose H, Gokulkrishnan N, Prabhu S, et al. Deep learning based detection of monkeypox virus using skin lesion images. Med Nov Technol Devices. 2023;18(1):100243.10.1016/j.medntd.2023.100243Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Khanna VV, Chadaga K, Sampathila N, Prabhu S, Chadaga R. A machine learning and explainable artificial intelligence triage-prediction system for COVID-19. Decis Anal J. 2023;6:100246.10.1016/j.dajour.2023.100246Search in Google Scholar
[20] Ouyang F, Zheng L, Jiao P. Artificial intelligence in online higher education: A systematic review of empirical research from 2011 to 2020. Educ Inf Technol. 2022;27(6):7893–925.10.1007/s10639-022-10925-9Search in Google Scholar
[21] Lau EYH, Li JB, Lee K. Online learning and parent satisfaction during COVID-19: Child competence in independent learning as a moderator. Early Educ Dev. 2021;32(6):830–42.10.1080/10409289.2021.1950451Search in Google Scholar
[22] Kim JY, Fienup DM. Increasing access to online learning for students with disabilities during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Spec Educ. 2022;55(4):213–21.10.1177/0022466921998067Search in Google Scholar
[23] Chen Z. Research on internet security situation awareness prediction technology based on improved RBF neural network algorithm. J Comput Cognit Eng. 2022;1(3):103–8.10.47852/bonviewJCCE149145205514Search in Google Scholar
[24] Yazbek HA, Surriya F, Khan SU, Jan N, Marinkovic D. A novel approach to model the economic characteristics of an organization by interval-valued complex pythagorean fuzzy information. J Comput Cognit Eng. 2023;2(1):75–87.10.47852/bonviewJCCE2202249Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- A study on intelligent translation of English sentences by a semantic feature extractor
- Detecting surface defects of heritage buildings based on deep learning
- Combining bag of visual words-based features with CNN in image classification
- Online addiction analysis and identification of students by applying gd-LSTM algorithm to educational behaviour data
- Improving multilayer perceptron neural network using two enhanced moth-flame optimizers to forecast iron ore prices
- Sentiment analysis model for cryptocurrency tweets using different deep learning techniques
- Periodic analysis of scenic spot passenger flow based on combination neural network prediction model
- Analysis of short-term wind speed variation, trends and prediction: A case study of Tamil Nadu, India
- Cloud computing-based framework for heart disease classification using quantum machine learning approach
- Research on teaching quality evaluation of higher vocational architecture majors based on enterprise platform with spherical fuzzy MAGDM
- Detection of sickle cell disease using deep neural networks and explainable artificial intelligence
- Interval-valued T-spherical fuzzy extended power aggregation operators and their application in multi-criteria decision-making
- Characterization of neighborhood operators based on neighborhood relationships
- Real-time pose estimation and motion tracking for motion performance using deep learning models
- QoS prediction using EMD-BiLSTM for II-IoT-secure communication systems
- A novel framework for single-valued neutrosophic MADM and applications to English-blended teaching quality evaluation
- An intelligent error correction model for English grammar with hybrid attention mechanism and RNN algorithm
- Prediction mechanism of depression tendency among college students under computer intelligent systems
- Research on grammatical error correction algorithm in English translation via deep learning
- Microblog sentiment analysis method using BTCBMA model in Spark big data environment
- Application and research of English composition tangent model based on unsupervised semantic space
- 1D-CNN: Classification of normal delivery and cesarean section types using cardiotocography time-series signals
- Real-time segmentation of short videos under VR technology in dynamic scenes
- Application of emotion recognition technology in psychological counseling for college students
- Classical music recommendation algorithm on art market audience expansion under deep learning
- A robust segmentation method combined with classification algorithms for field-based diagnosis of maize plant phytosanitary state
- Integration effect of artificial intelligence and traditional animation creation technology
- Artificial intelligence-driven education evaluation and scoring: Comparative exploration of machine learning algorithms
- Intelligent multiple-attributes decision support for classroom teaching quality evaluation in dance aesthetic education based on the GRA and information entropy
- A study on the application of multidimensional feature fusion attention mechanism based on sight detection and emotion recognition in online teaching
- Blockchain-enabled intelligent toll management system
- A multi-weapon detection using ensembled learning
- Deep and hand-crafted features based on Weierstrass elliptic function for MRI brain tumor classification
- Design of geometric flower pattern for clothing based on deep learning and interactive genetic algorithm
- Mathematical media art protection and paper-cut animation design under blockchain technology
- Deep reinforcement learning enhances artistic creativity: The case study of program art students integrating computer deep learning
- Transition from machine intelligence to knowledge intelligence: A multi-agent simulation approach to technology transfer
- Research on the TF–IDF algorithm combined with semantics for automatic extraction of keywords from network news texts
- Enhanced Jaya optimization for improving multilayer perceptron neural network in urban air quality prediction
- Design of visual symbol-aided system based on wireless network sensor and embedded system
- Construction of a mental health risk model for college students with long and short-term memory networks and early warning indicators
- Personalized resource recommendation method of student online learning platform based on LSTM and collaborative filtering
- Employment management system for universities based on improved decision tree
- English grammar intelligent error correction technology based on the n-gram language model
- Speech recognition and intelligent translation under multimodal human–computer interaction system
- Enhancing data security using Laplacian of Gaussian and Chacha20 encryption algorithm
- Construction of GCNN-based intelligent recommendation model for answering teachers in online learning system
- Neural network big data fusion in remote sensing image processing technology
- Research on the construction and reform path of online and offline mixed English teaching model in the internet era
- Real-time semantic segmentation based on BiSeNetV2 for wild road
- Online English writing teaching method that enhances teacher–student interaction
- Construction of a painting image classification model based on AI stroke feature extraction
- Big data analysis technology in regional economic market planning and enterprise market value prediction
- Location strategy for logistics distribution centers utilizing improved whale optimization algorithm
- Research on agricultural environmental monitoring Internet of Things based on edge computing and deep learning
- The application of curriculum recommendation algorithm in the driving mechanism of industry–teaching integration in colleges and universities under the background of education reform
- Application of online teaching-based classroom behavior capture and analysis system in student management
- Evaluation of online teaching quality in colleges and universities based on digital monitoring technology
- Face detection method based on improved YOLO-v4 network and attention mechanism
- Study on the current situation and influencing factors of corn import trade in China – based on the trade gravity model
- Research on business English grammar detection system based on LSTM model
- Multi-source auxiliary information tourist attraction and route recommendation algorithm based on graph attention network
- Multi-attribute perceptual fuzzy information decision-making technology in investment risk assessment of green finance Projects
- Research on image compression technology based on improved SPIHT compression algorithm for power grid data
- Optimal design of linear and nonlinear PID controllers for speed control of an electric vehicle
- Traditional landscape painting and art image restoration methods based on structural information guidance
- Traceability and analysis method for measurement laboratory testing data based on intelligent Internet of Things and deep belief network
- A speech-based convolutional neural network for human body posture classification
- The role of the O2O blended teaching model in improving the teaching effectiveness of physical education classes
- Genetic algorithm-assisted fuzzy clustering framework to solve resource-constrained project problems
- Behavior recognition algorithm based on a dual-stream residual convolutional neural network
- Ensemble learning and deep learning-based defect detection in power generation plants
- Optimal design of neural network-based fuzzy predictive control model for recommending educational resources in the context of information technology
- An artificial intelligence-enabled consumables tracking system for medical laboratories
- Utilization of deep learning in ideological and political education
- Detection of abnormal tourist behavior in scenic spots based on optimized Gaussian model for background modeling
- RGB-to-hyperspectral conversion for accessible melanoma detection: A CNN-based approach
- Optimization of the road bump and pothole detection technology using convolutional neural network
- Comparative analysis of impact of classification algorithms on security and performance bug reports
- Cross-dataset micro-expression identification based on facial ROIs contribution quantification
- Demystifying multiple sclerosis diagnosis using interpretable and understandable artificial intelligence
- Unifying optimization forces: Harnessing the fine-structure constant in an electromagnetic-gravity optimization framework
- E-commerce big data processing based on an improved RBF model
- Analysis of youth sports physical health data based on cloud computing and gait awareness
- CCLCap-AE-AVSS: Cycle consistency loss based capsule autoencoders for audio–visual speech synthesis
- An efficient node selection algorithm in the context of IoT-based vehicular ad hoc network for emergency service
- Computer aided diagnoses for detecting the severity of Keratoconus
- Improved rapidly exploring random tree using salp swarm algorithm
- Network security framework for Internet of medical things applications: A survey
- Predicting DoS and DDoS attacks in network security scenarios using a hybrid deep learning model
- Enhancing 5G communication in business networks with an innovative secured narrowband IoT framework
- Quokka swarm optimization: A new nature-inspired metaheuristic optimization algorithm
- Digital forensics architecture for real-time automated evidence collection and centralization: Leveraging security lake and modern data architecture
- Image modeling algorithm for environment design based on augmented and virtual reality technologies
- Enhancing IoT device security: CNN-SVM hybrid approach for real-time detection of DoS and DDoS attacks
- High-resolution image processing and entity recognition algorithm based on artificial intelligence
- Review Articles
- Transformative insights: Image-based breast cancer detection and severity assessment through advanced AI techniques
- Network and cybersecurity applications of defense in adversarial attacks: A state-of-the-art using machine learning and deep learning methods
- Applications of integrating artificial intelligence and big data: A comprehensive analysis
- A systematic review of symbiotic organisms search algorithm for data clustering and predictive analysis
- Modelling Bitcoin networks in terms of anonymity and privacy in the metaverse application within Industry 5.0: Comprehensive taxonomy, unsolved issues and suggested solution
- Systematic literature review on intrusion detection systems: Research trends, algorithms, methods, datasets, and limitations
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- A study on intelligent translation of English sentences by a semantic feature extractor
- Detecting surface defects of heritage buildings based on deep learning
- Combining bag of visual words-based features with CNN in image classification
- Online addiction analysis and identification of students by applying gd-LSTM algorithm to educational behaviour data
- Improving multilayer perceptron neural network using two enhanced moth-flame optimizers to forecast iron ore prices
- Sentiment analysis model for cryptocurrency tweets using different deep learning techniques
- Periodic analysis of scenic spot passenger flow based on combination neural network prediction model
- Analysis of short-term wind speed variation, trends and prediction: A case study of Tamil Nadu, India
- Cloud computing-based framework for heart disease classification using quantum machine learning approach
- Research on teaching quality evaluation of higher vocational architecture majors based on enterprise platform with spherical fuzzy MAGDM
- Detection of sickle cell disease using deep neural networks and explainable artificial intelligence
- Interval-valued T-spherical fuzzy extended power aggregation operators and their application in multi-criteria decision-making
- Characterization of neighborhood operators based on neighborhood relationships
- Real-time pose estimation and motion tracking for motion performance using deep learning models
- QoS prediction using EMD-BiLSTM for II-IoT-secure communication systems
- A novel framework for single-valued neutrosophic MADM and applications to English-blended teaching quality evaluation
- An intelligent error correction model for English grammar with hybrid attention mechanism and RNN algorithm
- Prediction mechanism of depression tendency among college students under computer intelligent systems
- Research on grammatical error correction algorithm in English translation via deep learning
- Microblog sentiment analysis method using BTCBMA model in Spark big data environment
- Application and research of English composition tangent model based on unsupervised semantic space
- 1D-CNN: Classification of normal delivery and cesarean section types using cardiotocography time-series signals
- Real-time segmentation of short videos under VR technology in dynamic scenes
- Application of emotion recognition technology in psychological counseling for college students
- Classical music recommendation algorithm on art market audience expansion under deep learning
- A robust segmentation method combined with classification algorithms for field-based diagnosis of maize plant phytosanitary state
- Integration effect of artificial intelligence and traditional animation creation technology
- Artificial intelligence-driven education evaluation and scoring: Comparative exploration of machine learning algorithms
- Intelligent multiple-attributes decision support for classroom teaching quality evaluation in dance aesthetic education based on the GRA and information entropy
- A study on the application of multidimensional feature fusion attention mechanism based on sight detection and emotion recognition in online teaching
- Blockchain-enabled intelligent toll management system
- A multi-weapon detection using ensembled learning
- Deep and hand-crafted features based on Weierstrass elliptic function for MRI brain tumor classification
- Design of geometric flower pattern for clothing based on deep learning and interactive genetic algorithm
- Mathematical media art protection and paper-cut animation design under blockchain technology
- Deep reinforcement learning enhances artistic creativity: The case study of program art students integrating computer deep learning
- Transition from machine intelligence to knowledge intelligence: A multi-agent simulation approach to technology transfer
- Research on the TF–IDF algorithm combined with semantics for automatic extraction of keywords from network news texts
- Enhanced Jaya optimization for improving multilayer perceptron neural network in urban air quality prediction
- Design of visual symbol-aided system based on wireless network sensor and embedded system
- Construction of a mental health risk model for college students with long and short-term memory networks and early warning indicators
- Personalized resource recommendation method of student online learning platform based on LSTM and collaborative filtering
- Employment management system for universities based on improved decision tree
- English grammar intelligent error correction technology based on the n-gram language model
- Speech recognition and intelligent translation under multimodal human–computer interaction system
- Enhancing data security using Laplacian of Gaussian and Chacha20 encryption algorithm
- Construction of GCNN-based intelligent recommendation model for answering teachers in online learning system
- Neural network big data fusion in remote sensing image processing technology
- Research on the construction and reform path of online and offline mixed English teaching model in the internet era
- Real-time semantic segmentation based on BiSeNetV2 for wild road
- Online English writing teaching method that enhances teacher–student interaction
- Construction of a painting image classification model based on AI stroke feature extraction
- Big data analysis technology in regional economic market planning and enterprise market value prediction
- Location strategy for logistics distribution centers utilizing improved whale optimization algorithm
- Research on agricultural environmental monitoring Internet of Things based on edge computing and deep learning
- The application of curriculum recommendation algorithm in the driving mechanism of industry–teaching integration in colleges and universities under the background of education reform
- Application of online teaching-based classroom behavior capture and analysis system in student management
- Evaluation of online teaching quality in colleges and universities based on digital monitoring technology
- Face detection method based on improved YOLO-v4 network and attention mechanism
- Study on the current situation and influencing factors of corn import trade in China – based on the trade gravity model
- Research on business English grammar detection system based on LSTM model
- Multi-source auxiliary information tourist attraction and route recommendation algorithm based on graph attention network
- Multi-attribute perceptual fuzzy information decision-making technology in investment risk assessment of green finance Projects
- Research on image compression technology based on improved SPIHT compression algorithm for power grid data
- Optimal design of linear and nonlinear PID controllers for speed control of an electric vehicle
- Traditional landscape painting and art image restoration methods based on structural information guidance
- Traceability and analysis method for measurement laboratory testing data based on intelligent Internet of Things and deep belief network
- A speech-based convolutional neural network for human body posture classification
- The role of the O2O blended teaching model in improving the teaching effectiveness of physical education classes
- Genetic algorithm-assisted fuzzy clustering framework to solve resource-constrained project problems
- Behavior recognition algorithm based on a dual-stream residual convolutional neural network
- Ensemble learning and deep learning-based defect detection in power generation plants
- Optimal design of neural network-based fuzzy predictive control model for recommending educational resources in the context of information technology
- An artificial intelligence-enabled consumables tracking system for medical laboratories
- Utilization of deep learning in ideological and political education
- Detection of abnormal tourist behavior in scenic spots based on optimized Gaussian model for background modeling
- RGB-to-hyperspectral conversion for accessible melanoma detection: A CNN-based approach
- Optimization of the road bump and pothole detection technology using convolutional neural network
- Comparative analysis of impact of classification algorithms on security and performance bug reports
- Cross-dataset micro-expression identification based on facial ROIs contribution quantification
- Demystifying multiple sclerosis diagnosis using interpretable and understandable artificial intelligence
- Unifying optimization forces: Harnessing the fine-structure constant in an electromagnetic-gravity optimization framework
- E-commerce big data processing based on an improved RBF model
- Analysis of youth sports physical health data based on cloud computing and gait awareness
- CCLCap-AE-AVSS: Cycle consistency loss based capsule autoencoders for audio–visual speech synthesis
- An efficient node selection algorithm in the context of IoT-based vehicular ad hoc network for emergency service
- Computer aided diagnoses for detecting the severity of Keratoconus
- Improved rapidly exploring random tree using salp swarm algorithm
- Network security framework for Internet of medical things applications: A survey
- Predicting DoS and DDoS attacks in network security scenarios using a hybrid deep learning model
- Enhancing 5G communication in business networks with an innovative secured narrowband IoT framework
- Quokka swarm optimization: A new nature-inspired metaheuristic optimization algorithm
- Digital forensics architecture for real-time automated evidence collection and centralization: Leveraging security lake and modern data architecture
- Image modeling algorithm for environment design based on augmented and virtual reality technologies
- Enhancing IoT device security: CNN-SVM hybrid approach for real-time detection of DoS and DDoS attacks
- High-resolution image processing and entity recognition algorithm based on artificial intelligence
- Review Articles
- Transformative insights: Image-based breast cancer detection and severity assessment through advanced AI techniques
- Network and cybersecurity applications of defense in adversarial attacks: A state-of-the-art using machine learning and deep learning methods
- Applications of integrating artificial intelligence and big data: A comprehensive analysis
- A systematic review of symbiotic organisms search algorithm for data clustering and predictive analysis
- Modelling Bitcoin networks in terms of anonymity and privacy in the metaverse application within Industry 5.0: Comprehensive taxonomy, unsolved issues and suggested solution
- Systematic literature review on intrusion detection systems: Research trends, algorithms, methods, datasets, and limitations


