Abstract
Road toll tax contributes significantly in the economic development of any nation. In developing countries, the toll tax collection is carried out either manually or electronically. However, both approaches suffer from various challenges, including prolonged waiting times, lack of transparency, high operational costs, and concerns regarding data security and privacy. This research aims to address these challenges using a blockchain-based system. The proposed system employs advanced image processing techniques, specifically “You Only Look Once” version 5 (YOLOv5), to accurately capture and store vehicles’ registration numbers in a local server situated at toll plazas. Subsequently, the vehicle identification, along with the driver’s credentials, is transmitted to an application server, where an Ethereum smart contract verifies the information and automatically deducts the toll charges from the driver’s account. The results from this study indicate that the proposed system effectively reduces vehicle waiting time and facilitates uninterrupted vehicular movement. Additionally, the system ensures transaction transparency, safeguards the security and privacy of vehicle details, facilitates non-stop payments, rendering unnecessary cash payments or radio-frequency identification scanning at toll booths, and incorporates a decentralized architectural framework to enhance security and mitigate potential system failures.
1 Introduction
The transport sector is a key contributor to the economic and social development of any country. Efficient transportation methods are closely linked to a nation’s economic performance [1], with a strong correlation between the distance traveled and Gross National Product [2]. Every day, more and more automobiles are added to the road for passengers and freight transportation. The vehicles must wait a considerable period of time to pay the toll tax amount (TA) at toll plazas, resulting in high traffic congestion [3]. Hence, this accelerates the need for an automated toll collecting system to minimize road congestion and thereby decrease waiting times and vehicle fuel consumption.
In developing countries, road tolls are collected using one of the two methods: manual or electronic. In the manual method of toll collection, a toll collector collects the toll fee in cash from the vehicle driver, and the receipt is issued to the driver. The manual toll collection approach has several issues. For instance, vehicles have to wait for a very long time in the queue in order to pay the toll fee, and the problem turns severe during peak hours [3]. Moreover, the manual toll collection also lacks transparency and trust between the stakeholders as no record is maintained that how many and which vehicles have crossed the toll plaza [4]. Further, the absence of records also makes it difficult to track and trace unregistered and stolen vehicles. Finally, the approach incurs high operational costs as two persons are required at each toll gate. One for dealing the cash with driver and the other for opening and closing of the gate.
In electronic toll tax collection (ETC), a toll fee is collected by deducting an amount from a prepaid radio-frequency identification (RFID) passive tag. The tag, installed on the wind shield of a vehicle, usually carries the basic information such as driver data, vehicle id, and available balance in the user account [5,6]. A tag reader installed on the toll gate reads and routes the tag data to a host computer. This host computer is connected to a central server through the internet, and data validation is done on the server side [7]. The one obvious advantage of this approach is that the driver does not need to stop the vehicle at the toll plaza; consequently, it ensures smooth traffic flow. Further, it reduces the high operational costs and efforts incurred in manual toll collection. In addition to this, a record of passing by vehicles is maintained in the central database that can be used to track the vehicles. Despite the advantages of the RFID approach, the system has its unique challenges. One of these is reading a noisy tag. It means that the tag reader may face glitches or failures while reading tags. The process results in the wastage of time, thus annoying drivers in the queue. Also, many a times tags have insufficient balance, hence, driver has to pay the toll fee in cash. Interoperability is another issue [8] as contractors use different RFID standards. Hence, a vehicle must carry multiple RFID tags for speed passage through the toll gate. Due to the openness of radio waves and readability of tag information from a short distance (10 cm to 30 m), the RFID approach suffers from major security and privacy threats. For instance, tags are vulnerable to tempering [2], cloning, and traceability (Figure 1). Therefore, attackers can gain access and subsequently use the information for malicious purposes.
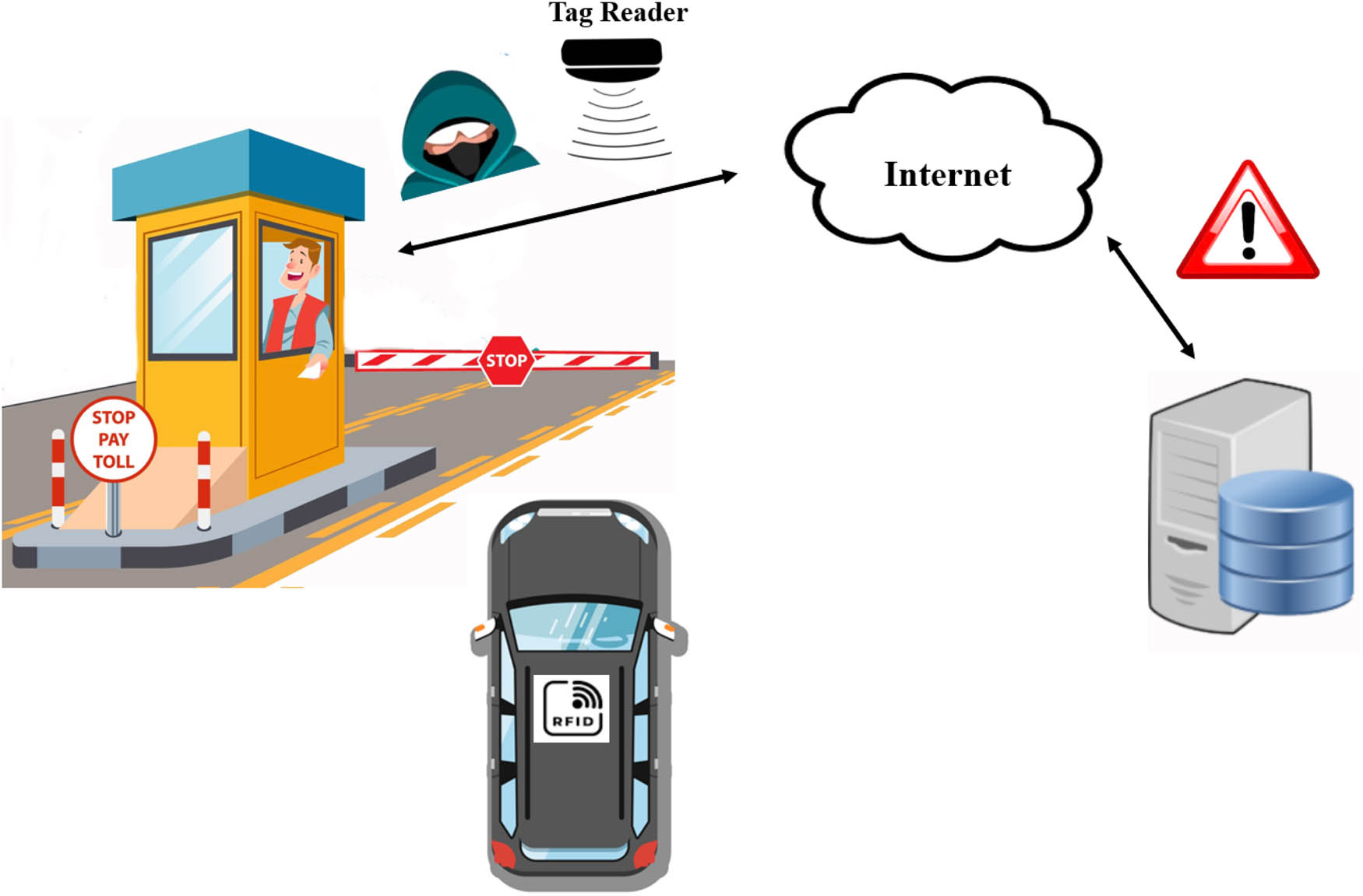
Existing RFID system working with flaws.
The blockchain technology has the capacity to address these problems in a decentralized manner [9]. In such systems, security is often considered to be robust and resilient due to several inherent characteristics of such systems. For example, they rely on consensus mechanisms and provide transparency, as the entire transaction history or state of the system is visible to all participants [10]. In this study, we proposed a blockchain-driven system that automatically collects the toll tax at toll plazas in an efficient manner. The proposed system uses image processing technique, i.e., YOLOv5 [11], to read the vehicles, registration number, which is subsequently stored at toll plazas’ local storage/server. The vehicle id along with driver’s credentials are sent to the application server. Ethereum smart contract authenticates the vehicle data and collects toll charges automatically from the driver’s digital wallet. The results show that the proposed system reduces vehicle waiting time in the toll queue and hence saves on fuel consumption. By regulating the flow of vehicles through toll collection points, authorities can prevent congestion and ensure a smoother traffic experience on highways and expressways [12]. The major contributions of this proposed smart toll collection system over the existing RFID based systems are listed as follows:
An automated toll collection framework: We develop a novel framework that provides the transparency of the transacted data as well as security and privacy of the vehicle details.
Non-stop payment: The proposed system does not require the vehicle to stop at the booth for cash payment or RFID scanning.
Decentralized system: As compared to existing systems, it is a decentralized system with lost cost, saves time, and reduces fuel consumption.
The article is organized into six sections. Section 2 overviews the background and related works. The proposed approach is in Section 3 followed by experimental design and results in Section 4. Section 5 presents the limitations of this work. This study concludes in Section 6 with future directions.
2 Literature review
Blockchain technology has taken its roots in many application areas such as energy trading, healthcare, intelligent transportation, vehicular networks, and smart toll collection [13]. The decentralized architecture of blockchain offers the advantages like secure data storage and payment in a transparent manner. In this regard, Galande et al. [1] show that the manual toll collection process results in long queues of vehicles at toll plazas and more fuel consumption by vehicles. They proposed a global positioning system (GPS)-based electronic toll collection system to address the issues in manual toll collection. GPS technology helps us to determine the vehicle coordinates for toll charges calculation. The solution requires that vehicle drivers possess a GPS-enabled cell phone for toll payment. However, the proposed solution depends upon the GPS service availability in the vicinity of the toll plaza that is often absent or suffer from weak signal strength on the highways.
Comparison of the existing systems
| Reference | Easy to use | App | Technique | Smart contract |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiao et al. [14] | — | N | Blockchain | Y |
| Cai et al. [15] | — | Y | Blockchain | N |
| Dayana et al. [16] | Y | N | Electronic | N |
| Deng et al. [17] | — | N | Blockchain | N |
| Ying et al. [18] | — | Y | Blockchain | N |
| Laghari et al. [3] | N | N | RFID | N |
| Rashid and Abbas [19] | N | N | RFID | N |
| Das et al. [12] | Y | N | Blockchain, OCR | Y |
| Sahoo et al. [20] | N | N | Ethereum, GPS | Y |
| Soner et al. [21] | Y | N | Blockchain, OCR | Y |
| Tanveer and Javaid [22] | — | N | Ethereum | Y |
| Zhang et al. [23] | — | N | Blockchain | N |
| Das et al. [24] | — | N | Blockchain | N |
| Das et al. [25] | Y | N | Blockchain | Y |
| Banerjee et al. [10] | — | N | Blockchain | N |
| Banerjee et al. [26] | Y | N | Blockchain | Y |
| Proposed | Y | Y | Blockchain, OCR | Y |
Previous studies [3,19] proposed an RFID-based toll deduction system to overcome the traffic congestion problem at toll booths, reducing the operating cost and saving the toll payment time. The vehicles carry RFID tags that contain the vehicle data and owner information. The proposed system scans the RFID tag placed on the vehicle and compares the credentials with the central database to charge the toll amount. The toll tax is automatically deducted from the driver’s account and a notification is sent to the driver. Vehicle owners must top up the account to cross the toll plaza. However, the system suffers limitations such as data privacy, data immutability, and transparency due to its centralized nature.
Sathya et al. addressed the traffic congestion problem at the toll gate by introducing the pre-paid tax approach. In the proposed scheme, the driver must register himself at the portal. Once registered, stored credentials can be used to pay the toll amount in advance using UPI. The transaction is saved in the database against the driver. At the toll plaza gate, cameras are used to read the vehicle number plate and subsequently use the vehicle registration number to verify the toll payment in the database. However, the advance payment causes inconvenience to the user. Further, image recognition during peak times may suffer latency causing long queues of vehicles.
Das et al. [12] argued that the intelligent transportation management system for toll collection ensures confidentiality, availability, immutability, privacy and security, transparency, reduced crossing time, less traffic congestion, and less fuel consumption.
Xiao et al. [14] developed a blockchain-driven toll tax payment system. They collect the toll amount in the heterogeneous environment. The proposed public edge-sharing system design was helpful in validating the test bed for the experiments. The smart contract supports the system for record maintenance of an agreement and splitting the payment. However, the system only operates starting and ending of payment using a decentralized node, while the rest of the transactions are performed on-off between participants.
Cai et al. [15] developed a decentralized application based on blockchain for toll payment collection. Dayana et al. [16] implemented toll gate automation with a predefined route based on blockchain. Deng and Gao [17] proposed a blockchain-based toll management system where a payment scheme is used for the transactions.
Ying et al. [18] used the autonomous build platform using blockchain technology for secure communication. Their system uses the platoon payment at each toll collection. Sahoo et al. [20] used GPS to track vehicle movement. They used Eutheriam smart contracts to carry out business logic. Their results show that every transaction between vehicle owners and the authorities is traceable, immutable, transparent, and trustworthy. However, the proposed solution is costly as it involves real-time vehicle tracking. The approach is also not feasible because the user must confirm his starting location and ending location that is not available in many cases.
Soner et al. [21] proposed the toll management system uses smart contracts to enhance parties’ agreements and QR codes for payments. This system offers trust, security, and ease of use. After user verification, it is added to the blockchain and, hence, then it is able to make a transaction. In this system, the generated QR code of the user is scanned by the QR code scanner and the user’s details are displayed on the beneficiary’s account. The user then enters the route details and confirms the entire payment of toll in a single transaction.
Tanveer and Javaid [22] proposed the use of smart contracts for the payment of toll fees. The RFID system installed at the roadside can read the vehicle details and subsequently execute a smart contract to deduct the toll fee from user’s bank account. However, the involvement of a third party (e.g., bank) for toll payment incurs additional costs, e.g., transaction fee charges.
Zhang et al. focused on the security of announcement messages in Internet of Vehicles (IoV). They proposed a blockchain-based data sharing system where IoV is divided into multiple regions. The communications are distributed on a parent blockchain and an auxiliary blockchain for each region. The parent blockchain is controlled by all the system’s entities, while each auxiliary blockchain is maintained by the entities in an area and utilized to boost the throughput of the parent blockchain.
Das et al. [24] suggested blockchain applications, challenges, and opportunities for intelligent transportation system. They also proposed a blockchain-based security management framework for smart cities as one of many applications [25]. Banerjee et al. [10] provided an overview of the fundamental principles and practical applications of digital twins (DTs) and blockchain in the field of transportation. They explored use cases such as autonomous vehicles, smart logistics, and mobility as a service. They also proposed a sustainable safety management framework [26] for connected vehicles through the integration of blockchain. They introduced an AI-enabled vehicle smart device (AVSD) designed for vehicular communications. The AVSD has the capability to lower energy consumption by reducing computational costs in vehicular communications. The system employs smart contracts to automatically identify vehicles and establish secure communication channels among vehicles and emergency service stations, such as hospitals, police stations, and fire stations.
The above literature highlights the fact that ETC systems based on RFID technology cause traffic congestion at the toll plazas. Also, these suffer from the problems such as data integrity, data security, privacy, fuel consumption, and transparency of the transacted data over the internet. It can also be observed that (Table 1) most of the studies have not used blockchain technology and are difficult to use with lack of an application. Therefore, it triggers a need for a system that is easy to use, secure, and automated.
3 Proposed methodology
In a traditional tollbooth system, each vehicle waits at the booth for payment processing that puts each subsequent vehicle on hold, causing traffic congestion. In this section, we propose a blockchain-driven solution for a cashless, fast, and track-able scheme that divides the tollbooth operation into multiple processes. The proposed system consists of the following components:
Vehicle registration on blockchain,
Vehicle identification unit,
Tollbooth local server (TLS), and
Blockchain network.
3.1 Vehicle registration on blockchain
In the proposed system, the vehicles are registered through a registration portal. The vehicle owner’s metamask account is created with vehicle details such as vehicle number plate, vehicle type, owner citizenship no, owner name, and contact number (Figure 2). This information is saved on the blockchain as registration details, and every vehicle is identified through a number plate. After successful registration, the system recognizes the vehicle for the toll tax collection process, as shown in Figure 3. The algorithm for vehicle registration on the blockchain network is given in Algorithm 1.
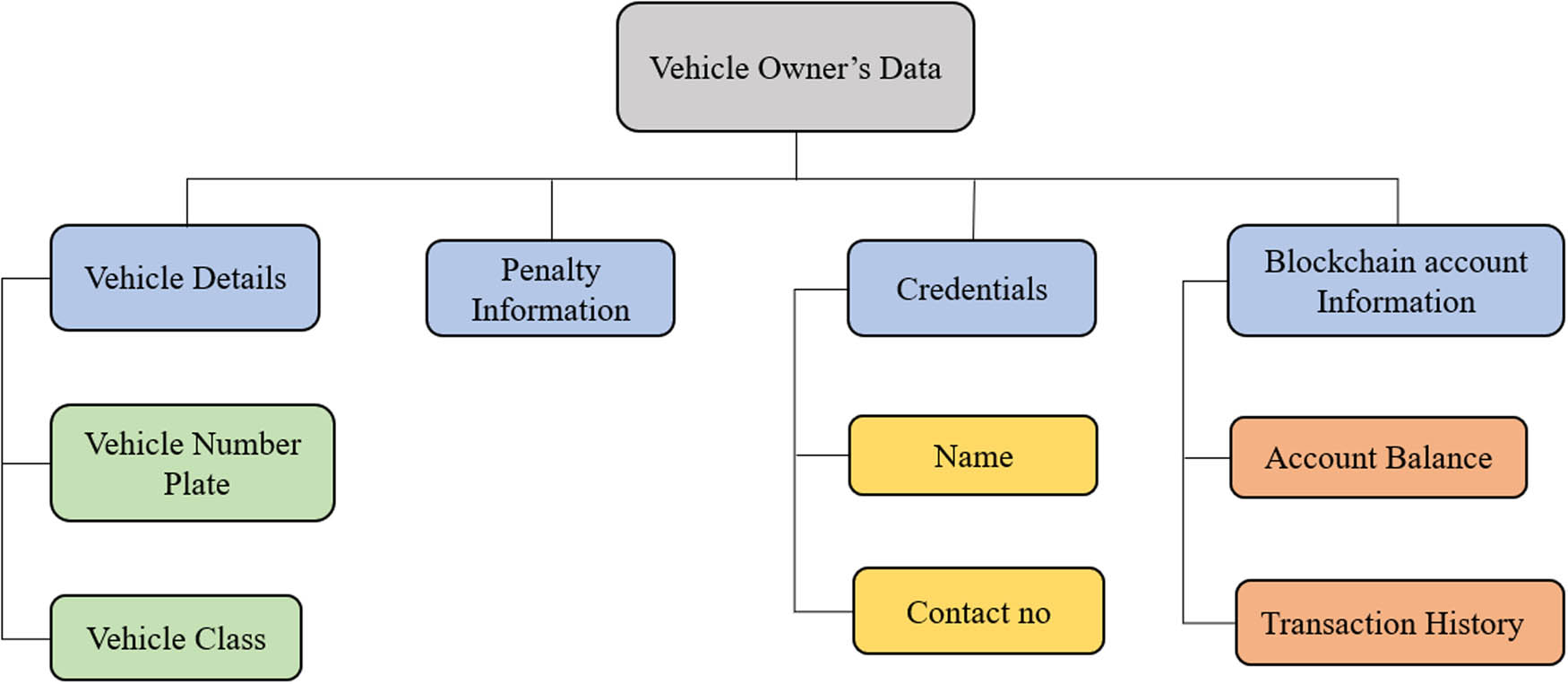
Data access through vehicle owner’s details on blockchain.
Workflow of the proposed model.
| Algorithm 1. Vehicle registration |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| post
|
|
|
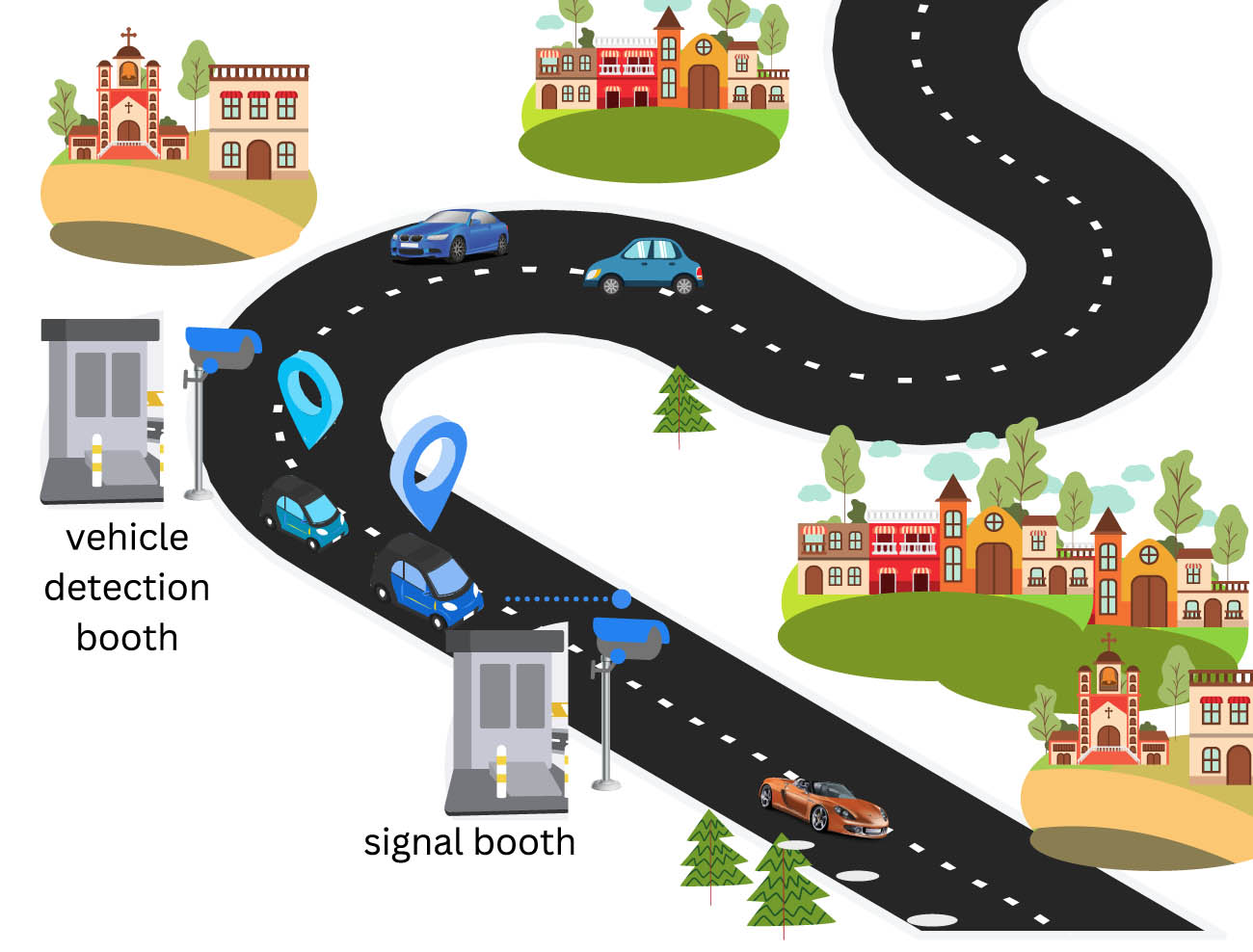
3.2 Vehicle identification unit
The vehicle identification unit consists of two processing points to recognize the vehicle, i.e., detection point and signal point. The detection point is deployed at 100 m before the exit point so that each entering vehicle is identified. This point plays an important role in determining the vehicle information, clearance, and toll tax exemption. When a vehicle passes the detection point, the installed camera captures the number plate of the vehicle and process it to determine the vehicle number. Then, this information is sent to the TLS detection queue. The algorithm for vehicle initial detection is given in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2. Initial detection |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The signal point is deployed at the exit of the tollbooth. It informs the tollbooth server that the vehicle has been exited from the tollbooth and direct the TLS to perform the transaction.
3.3 TLS
TLS is responsible for the toll tax collection process. The server is guarded by a firewall and works in coordination with detection points. It continuously monitors the detection queue and subsequently fetches the vehicle information when a vehicle number plate is detected by the detection point. To calculate the toll tax of a vehicle, it needs the vehicle details from the blockchain such as vehicle type, fine, and tax exemption. In general, blockchain query is a slow process. To address this issue, TLS maintains a local cache of the vehicle’s information to speed up the query process (Figure 4). The cache contains the copy of frequently passing by vehicles, and each entry is synchronized to keep it up to date. As soon as a toolbooth or law enforcement agency changes vehicle clearance status, the information is passed to all tollbooths so that they can update their local cache. So, every query to get vehicle information is checked against the cache. In case of a cache miss, TLS fetches the information from blockchain. The algorithm for vehicle processing at TLS is given in Algorithm 3.
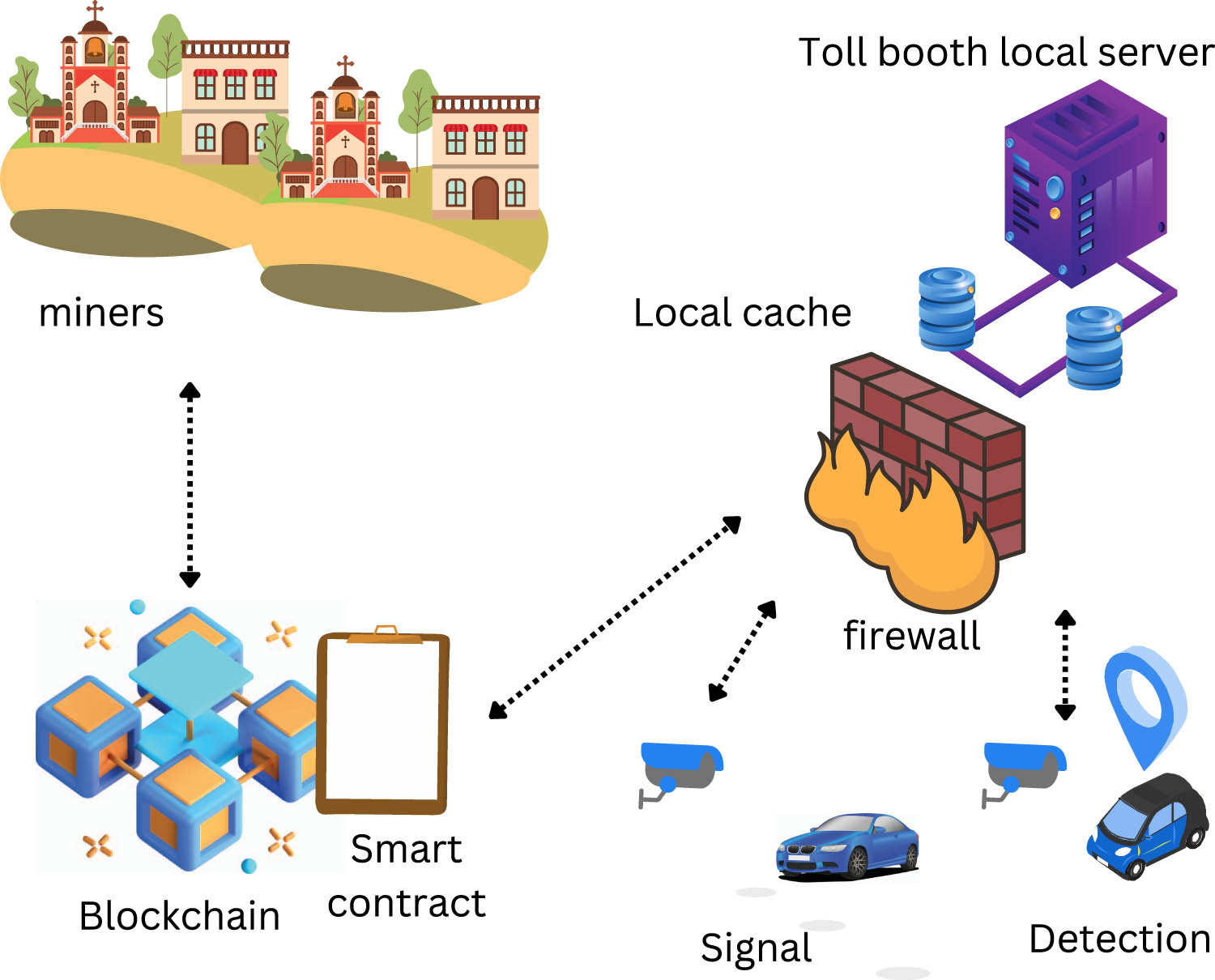
TLS and blockchain integration.
| Algorithm 3. Processing entry list at TLS |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For each vehicle in the detection queue, the TLS server looks for a clearance flag to look for any malicious vehicle and a category flag to look for the vehicle toll exemption. If the vehicle is malicious, then, the server informs the nearest police station with the captured image of the vehicle. It helps the law enforcement agencies to streamline their operations about vehicle theft and malicious activities. After performing the clearance check, the vehicle number plate, along with vehicle type and TA for that vehicle category, is put into the entry list at TLS. The entry list contains information about the vehicles that have entered the tollbooth range, and toll tax from these vehicles is collected. The algorithm for processing transaction queue at TLS is given in Algorithm 4.
| Algorithm 4. Processing transaction queue at TLS |
|---|
|
|
| while true do |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| else |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| end while |
3.4 Blockchain network
After TLS receives confirmation of the vehicle exit from the signal point, it takes that vehicle information from the entry list and prepares the transaction to perform on the blockchain. The transaction processing on the blockchain requires determining hashes, which is a time-taking process, and it is not feasible for a real-time system like toll tax collection. It is not easy to pay a lot of gas fees to perform the transaction on a priority basis; thus, TLS maintains a local transaction queue. Hence, the prepared transaction is put in the transaction queue. A separate process takes the transaction queue, determines the vehicle balance, and by relying on the trust of vehicle, it performs the transaction on the blockchain. If the vehicle owner has not enough balance, then, a penalty is charged and the vehicle is marked as defaulter.
4 Experimental analysis
4.1 Experimental setup
For experimentation, we simulated the vehicle entry and exit using the Python programming language. The local tollbooth server application is also written in Python to handle the vehicle queue, and the MySQL database is used for the local cache. Smart contracts code is written and experimented with solidity language using Remix that is a web-based platform. Then, we deployed that smart contract at Infura, which is blockchain as a service platform. To interact with Infura (BaaS), we used the Web3 library of Python for the sake of performing transactions. The applications for detection, signal processing, and local toolbooth server are deployed on Intel Corei7 systems, each having 8 GB of RAM. We connected these systems using 1 Gbps LAN and provided the internet connection of 8 Mbps with TLS to connect with a blockchain network.
4.2 Results and discussion
This section illustrates the experimental results of the incorporated smart contract for a secure, reliable, and fast toll tax transaction system. The smart contract reduces the risk of errors associated with manual toll collection, ensures that transactions are executed according to predefined rules, and ensures that all stakeholders, including authorities and users, have access to a tamper-resistant and transparent record of toll transactions. The results show that the blockchain integration enables the toll tax payment system transparent, trustworthy, fast, and secure. The metamask account was created to deploy and perform transactions on blockchain. In real, government is the owner of the data and deploys the smart contract to take the ownership. For the experimental purpose, we deployed the contract from a metamask account to act as government department. The result of smart contract deployment is shown in Figure 5.
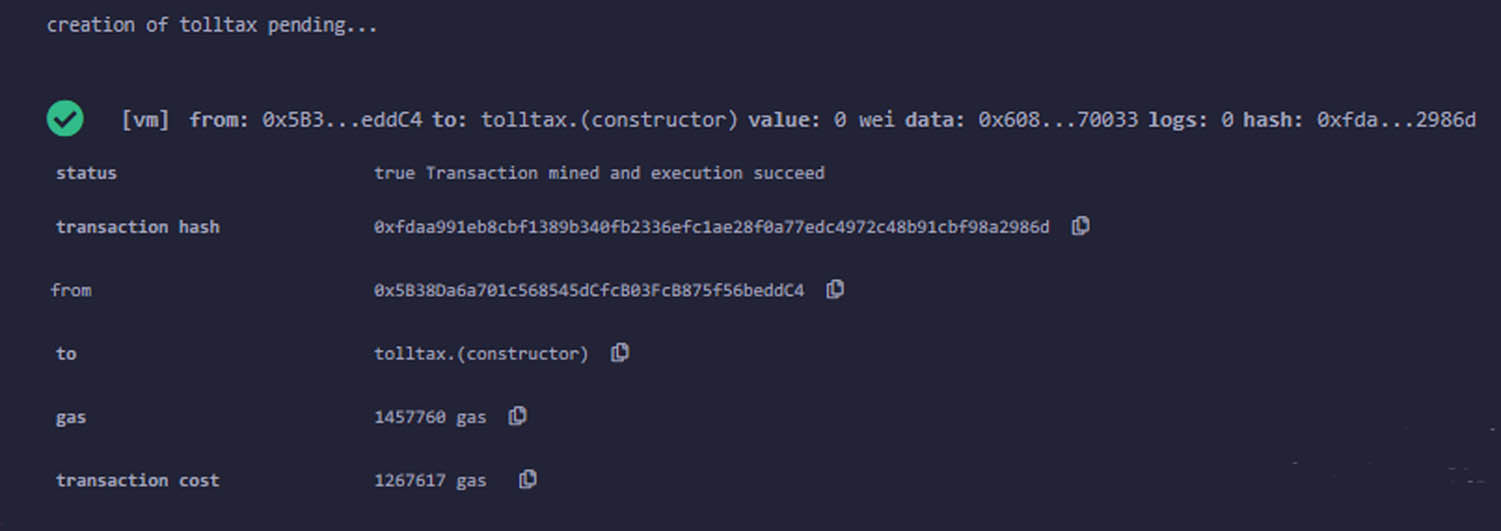
Smart contract has been deployed successfully.
We registered 10,000 vehicles on the blockchain and manually put 200 vehicles information in the local cache.
4.2.1 Detection point delay
We generated a total of 500 vehicles in the simulation using Python application at a regular interval of 1 s, for measuring the delay at the detection point. The vehicles were generated in such a way that first 80 of the vehicle information is found from the local cache, and the rest of the vehicle information is distributed in such a way that 90% of the vehicle information need to be accessed from the blockchain. The simulation was started and the result of simulation is presented in Figure 6.
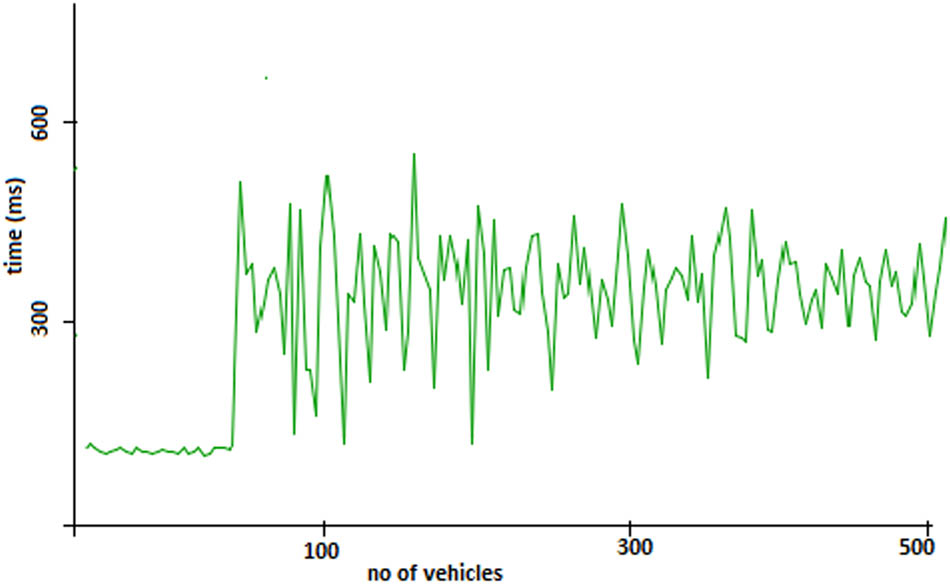
Vehicle processing at the detection point.
The detection point system booted fully at 7 s and started processing vehicles. First, 80 vehicles are processed by detection point quickly as the information was present in the local cache, and the detection point did not fetch their information from the blockchain. From 80 vehicles to on-wards, a mixed number of requests were received, the upper edge of the graph line shows that information was fetched from the blockchain, while the lower edge shows that the information was fetched from the local cache that increased the identification time.
4.2.2 Gas consumption
We run the system to process 1,000 vehicles to find out the gas consumption for the payments. The vehicle payment information varies, i.e., some vehicles are not cleared, few are penalized; hence, the transaction size is different. Therefore, the gas fee is different for each transaction. Figure 7 shows the gas consumption for processing transactions of 1,000 vehicles.
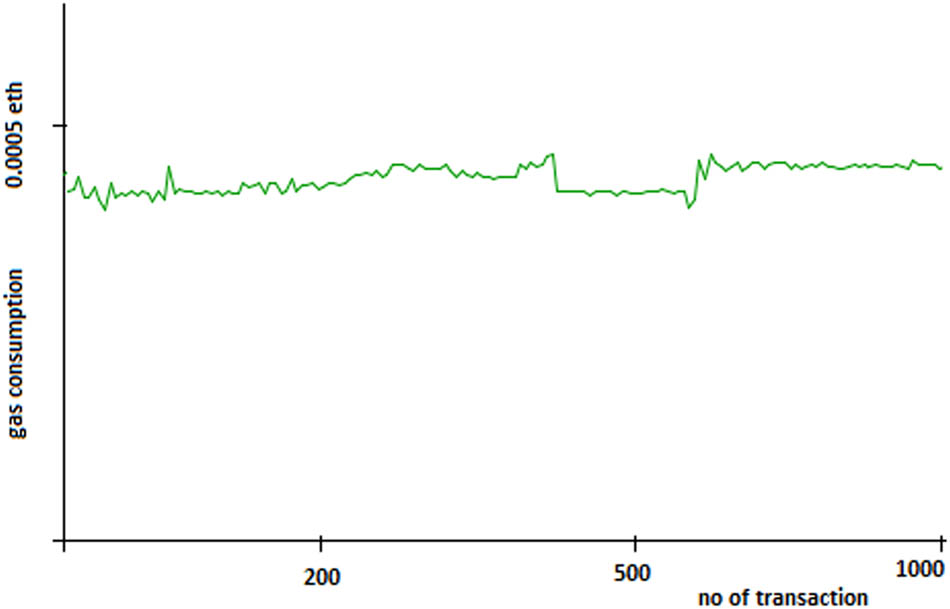
Gas consumption of posted transactions.
4.2.3 Transaction processing time
To measure the transaction processing time, we generated 1,000 vehicles to enter the detection point using simulation. The vehicles are generated in such a way that 10% of the vehicles have insufficient wallet balance, and 5% of the vehicles are tax exempted. After the vehicles are processed from the detection point, their information is saved in the list. The signal point processed that list finally to perform payment transactions at the exit. Upon the vehicle exit, the signal point removed that vehicle information from the list, prepared the transaction according to the algorithm, and put that prepared transaction information in queue. That queue is processed to perform transactions on the local blockchain, and the results are shown in Figure 8.
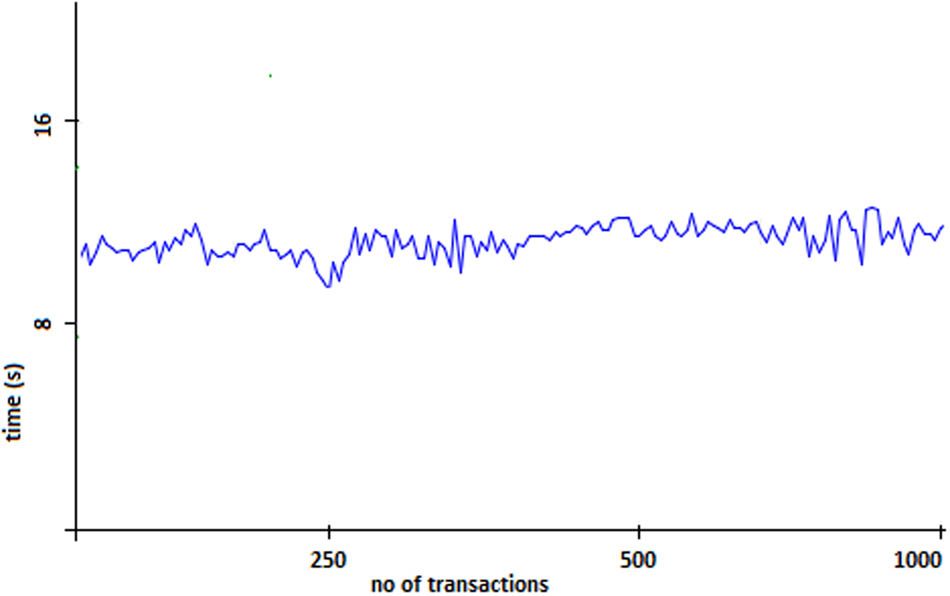
Posting the vehicle transactions on the blockchain.
In this system, the vehicle passes the toll plaza at a threshold speed, with a 30 km/h maximum speed. As a result, passing vehicle through the toll plaza saves more time. The green line in Figure 9 shows that the number of vehicles served fully through an automated blockchain-based system, and the blue line shows the time taken to fully serve the vehicles using the manual system. The results clearly show that the automated system performs better than the manual system.
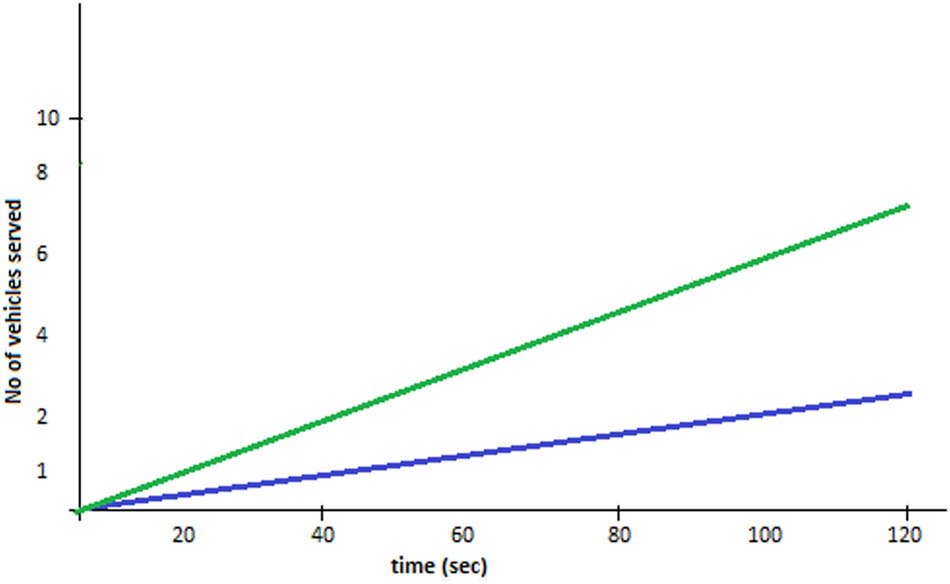
Comparative analysis of the number of vehicles served through a tollgate using the proposed system.
5 Threats to validity
This study helps to the automation of the road toll tax system in an efficient and transparent manner, considering data security and privacy issues. However, this work has some limitations. First, the proposed system needs to be evaluated in a real environment. Second, the gas fee value can be a constraint. Third, with the rising number of transactions, the processing and validation time of the blockchain network for those transactions may become strained.
6 Conclusion
This research presents a blockchain-based automated toll collection system as a promising solution to the challenges faced by traditional toll collection methods in developing countries. It reduces operational costs, saves time, and enhances efficiency compared to existing RFID-based systems. By combining image processing, blockchain, and smart contracts, the system offers improved efficiency, transparency, and convenience for both drivers and toll operators.
The proposed system leverages image processing technology, YOLOv5 algorithm, to read and store vehicles’ information at the toll plaza local server. Subsequently, the vehicle and driver’s credentials are transmitted to a remote server, where the Ethereum smart contract verifies the information and automatically deducts the toll charges from the account wallet. The system eliminates the need for cash payments or RFID scanning at toll booths, thus ensuring a smooth fast toll collection process. Further, the decentralized nature of the system makes it robust against potential failures in a centralized system. The introduction of blockchain technology adds an additional layer of security and trust, mitigating issues related to data tampering, cloning, and traceability.
Future research can focus on scalability, and further enhancing the security aspects of the system to ensure its successful implementation in real-world scenarios.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: Shahid Islam contributed to design and development of this study. Natasha Nigar worked on the proposed methodology and wrote the original draft. Sunday Adeola Ajagbe analysed the results and contributed in draft writing, whereas Matthew O. Adigun reviewed the article.
-
Conflict of interest: We all authors do not have any conflict of interest with anyone.
-
Data availability statement: Data are available on request.
References
[1] Galande S, Oswal S, Gidde V, Ranaware N, Bandgar SB. Automated toll cash collection system for road transportation. Int J Comput Sci Mobile Comput. 2015;4(2):216–24. Search in Google Scholar
[2] Yang R. Research on the correlation between freight transportation and national economic development. In: E3S Web of Conferences. vol. 253. EDP Sciences; 2021. p. 01008. 10.1051/e3sconf/202125301008Search in Google Scholar
[3] Laghari AA, Memon MS, Pathan AS. RFID based toll deduction system. IJ Inform Technol Comput Sci. 2012;4:40–6. 10.5815/ijitcs.2012.04.06Search in Google Scholar
[4] Khoso AK. Mobile phone toll tax payment on national highways & motorways in Pakistan. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences; 2015. Search in Google Scholar
[5] Chen J, Wang Q, Peng W, Xu H, Li X, Xu W. Disparity-based multiscale fusion network for transportation detection. IEEE Trans Intell Transport Syst. 2022;23(10):18855–63. 10.1109/TITS.2022.3161977Search in Google Scholar
[6] Kumar TA, Rajmohan R, Pavithra M, Ajagbe SA, Hodhod R, Gaber T. Automatic face mask detection system in public transportation in smart cities using IoT and deep learning. Electronics. 2022;11(6):904. 10.3390/electronics11060904Search in Google Scholar
[7] Suresh AC, Rao MS, Sridhar D, Annapurna GS. Online Toll Gate Payment System using RFID & IoT. India: Blue Eyes Intelligence Engineering and Sciences Publication (BEIESP); 2019.10.35940/ijrte.D4382.118419Search in Google Scholar
[8] Das D, Banerjee S, Biswas U. Design of a secure blockchain-based toll-tax collection system. In: Micro-electronics and telecommunication engineering. Singapore: Springer Nature; 2022. p. 183–91. 10.1007/978-981-16-8721-1_18Search in Google Scholar
[9] Qu Z, Zhang Z, Liu B, Tiwari P, Ning X, Muhammad K. Quantum detectable Byzantine agreement for distributed data trust management in blockchain. Inform Sci. 2023;637:118909. 10.1016/j.ins.2023.03.134Search in Google Scholar
[10] Banerjee S, Das D, Chatterjee P, Ghosh U. Blockchain-enabled digital twin technology for next-generation transportation systems. In: 2023 IEEE 26th International Symposium on Real-Time Distributed Computing (ISORC). IEEE; 2023. p. 224–9. 10.1109/ISORC58943.2023.00040Search in Google Scholar
[11] Nigar N, Muhammad Faisal H, Kashif Shahzad M, Islam S, Oki O. An offline image auditing system for legacy meter reading systems in developing countries: a machine learning approach. J Electric Comput Eng. 2022;2022:4543530. 10.1155/2022/4543530Search in Google Scholar
[12] Das D, Banerjee S, Chatterjee P, Biswas M, Biswas U, Alnumay W. Design and development of an intelligent transportation management system using blockchain and smart contracts. Cluster Comput. 2022;25(3):1899–913. 10.1007/s10586-022-03536-zSearch in Google Scholar
[13] Sharma V, Awasthi LK. Divergent applications of blockchain security: a survey. In:2021 2nd International Conference on Secure Cyber Computing and Communications (ICSCCC). IEEE; 2021. p. 212–7. 10.1109/ICSCCC51823.2021.9478094Search in Google Scholar
[14] Xiao B, Fan X, Gao S, Cai W. EdgeToll: a blockchain-based toll collection system for public sharing of heterogeneous edges. In: IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS). IEEE; 2019. p. 1–6. 10.1109/INFOCOMWKSHPS47286.2019.9093792Search in Google Scholar
[15] Cai W, Wang Z, Ernst JB, Hong Z, Feng C, Leung VC. Decentralized applications: the blockchain-empowered software system. IEEE Access. 2018;6:53019–33. 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2870644Search in Google Scholar
[16] Dayana B, Krishnan C, Patrick VCS, Venkateswaran N. Tracking and monitoring of vehicles and a stable and secure tolltax payment methodology based on blockchain enabled cryptocurrency E-wallets. Int J Eng Adv Technol. 2019;8(4):685–90. Search in Google Scholar
[17] Deng X, Gao T. Electronic payment schemes based on blockchain in VANETs. IEEE Access. 2020;8:38296–303. 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974964Search in Google Scholar
[18] Ying Z, Yi L, Ma M. BEHT: blockchain-based efficient highway toll paradigm for opportunistic autonomous vehicle platoon. Wireless Commun Mobile Comput. 2020;2020:8868656. 10.1155/2020/8868656Search in Google Scholar
[19] Rashid F, Abbas G. RFID based toll booth management system using Internet of things. Int J Integrated Eng. 2021;13(1):7–18. Search in Google Scholar
[20] Sahoo SS, Menon AR, Chaurasiya VK. Secure blockchain model for vehicles toll collection by GPS tracking: A case study of India. In: 2022 IEEE India Council International Subsections Conference (INDISCON). IEEE; 2022. p. 1–6. 10.1109/INDISCON54605.2022.9862921Search in Google Scholar
[21] Soner S, Litoriya R, Pandey P. Making toll charges collection efficient and trustless: a blockchain-based approach. In: 2021 3rd International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication Control and Networking (ICAC3N). IEEE; 2021. p. 1533–8. 10.1109/ICAC3N53548.2021.9725447Search in Google Scholar
[22] Tanveer H, Javaid N. Using Ethereum blockchain technology for road toll collection on highways. Pakistan: COMSATS University Islamabad; 2019. Search in Google Scholar
[23] Zhang L, Luo M, Li J, Au MH, Choo KKR, Chen T, et al. Blockchain based secure data sharing system for Internet of vehicles: A position paper. Vehicular Commun. 2019;16:85–93. 10.1016/j.vehcom.2019.03.003Search in Google Scholar
[24] Das D, Banerjee S, Chatterjee P, Ghosh U, Biswas U. Blockchain for intelligent transportation systems: applications, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023;10(21):18961–70. 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3277923Search in Google Scholar
[25] Das D, Banerjee S, Chakraborty R, Dasgupta K, Chatterjee P, Ghosh U. A blockchain-based security management framework for cyber-physical systems. In: 2023 IEEE/ACM 23rd International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing Workshops (CCGridW). IEEE; 2023. p. 39–44. 10.1109/CCGridW59191.2023.00021Search in Google Scholar
[26] Banerjee S, Das D, Chatterjee P, Blakely B, Ghosh U. A blockchain-enabled sustainable safety management framework for connected vehicles. IEEE Tran Intell Transport Syst. 2023;1–11. Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- A study on intelligent translation of English sentences by a semantic feature extractor
- Detecting surface defects of heritage buildings based on deep learning
- Combining bag of visual words-based features with CNN in image classification
- Online addiction analysis and identification of students by applying gd-LSTM algorithm to educational behaviour data
- Improving multilayer perceptron neural network using two enhanced moth-flame optimizers to forecast iron ore prices
- Sentiment analysis model for cryptocurrency tweets using different deep learning techniques
- Periodic analysis of scenic spot passenger flow based on combination neural network prediction model
- Analysis of short-term wind speed variation, trends and prediction: A case study of Tamil Nadu, India
- Cloud computing-based framework for heart disease classification using quantum machine learning approach
- Research on teaching quality evaluation of higher vocational architecture majors based on enterprise platform with spherical fuzzy MAGDM
- Detection of sickle cell disease using deep neural networks and explainable artificial intelligence
- Interval-valued T-spherical fuzzy extended power aggregation operators and their application in multi-criteria decision-making
- Characterization of neighborhood operators based on neighborhood relationships
- Real-time pose estimation and motion tracking for motion performance using deep learning models
- QoS prediction using EMD-BiLSTM for II-IoT-secure communication systems
- A novel framework for single-valued neutrosophic MADM and applications to English-blended teaching quality evaluation
- An intelligent error correction model for English grammar with hybrid attention mechanism and RNN algorithm
- Prediction mechanism of depression tendency among college students under computer intelligent systems
- Research on grammatical error correction algorithm in English translation via deep learning
- Microblog sentiment analysis method using BTCBMA model in Spark big data environment
- Application and research of English composition tangent model based on unsupervised semantic space
- 1D-CNN: Classification of normal delivery and cesarean section types using cardiotocography time-series signals
- Real-time segmentation of short videos under VR technology in dynamic scenes
- Application of emotion recognition technology in psychological counseling for college students
- Classical music recommendation algorithm on art market audience expansion under deep learning
- A robust segmentation method combined with classification algorithms for field-based diagnosis of maize plant phytosanitary state
- Integration effect of artificial intelligence and traditional animation creation technology
- Artificial intelligence-driven education evaluation and scoring: Comparative exploration of machine learning algorithms
- Intelligent multiple-attributes decision support for classroom teaching quality evaluation in dance aesthetic education based on the GRA and information entropy
- A study on the application of multidimensional feature fusion attention mechanism based on sight detection and emotion recognition in online teaching
- Blockchain-enabled intelligent toll management system
- A multi-weapon detection using ensembled learning
- Deep and hand-crafted features based on Weierstrass elliptic function for MRI brain tumor classification
- Design of geometric flower pattern for clothing based on deep learning and interactive genetic algorithm
- Mathematical media art protection and paper-cut animation design under blockchain technology
- Deep reinforcement learning enhances artistic creativity: The case study of program art students integrating computer deep learning
- Transition from machine intelligence to knowledge intelligence: A multi-agent simulation approach to technology transfer
- Research on the TF–IDF algorithm combined with semantics for automatic extraction of keywords from network news texts
- Enhanced Jaya optimization for improving multilayer perceptron neural network in urban air quality prediction
- Design of visual symbol-aided system based on wireless network sensor and embedded system
- Construction of a mental health risk model for college students with long and short-term memory networks and early warning indicators
- Personalized resource recommendation method of student online learning platform based on LSTM and collaborative filtering
- Employment management system for universities based on improved decision tree
- English grammar intelligent error correction technology based on the n-gram language model
- Speech recognition and intelligent translation under multimodal human–computer interaction system
- Enhancing data security using Laplacian of Gaussian and Chacha20 encryption algorithm
- Construction of GCNN-based intelligent recommendation model for answering teachers in online learning system
- Neural network big data fusion in remote sensing image processing technology
- Research on the construction and reform path of online and offline mixed English teaching model in the internet era
- Real-time semantic segmentation based on BiSeNetV2 for wild road
- Online English writing teaching method that enhances teacher–student interaction
- Construction of a painting image classification model based on AI stroke feature extraction
- Big data analysis technology in regional economic market planning and enterprise market value prediction
- Location strategy for logistics distribution centers utilizing improved whale optimization algorithm
- Research on agricultural environmental monitoring Internet of Things based on edge computing and deep learning
- The application of curriculum recommendation algorithm in the driving mechanism of industry–teaching integration in colleges and universities under the background of education reform
- Application of online teaching-based classroom behavior capture and analysis system in student management
- Evaluation of online teaching quality in colleges and universities based on digital monitoring technology
- Face detection method based on improved YOLO-v4 network and attention mechanism
- Study on the current situation and influencing factors of corn import trade in China – based on the trade gravity model
- Research on business English grammar detection system based on LSTM model
- Multi-source auxiliary information tourist attraction and route recommendation algorithm based on graph attention network
- Multi-attribute perceptual fuzzy information decision-making technology in investment risk assessment of green finance Projects
- Research on image compression technology based on improved SPIHT compression algorithm for power grid data
- Optimal design of linear and nonlinear PID controllers for speed control of an electric vehicle
- Traditional landscape painting and art image restoration methods based on structural information guidance
- Traceability and analysis method for measurement laboratory testing data based on intelligent Internet of Things and deep belief network
- A speech-based convolutional neural network for human body posture classification
- The role of the O2O blended teaching model in improving the teaching effectiveness of physical education classes
- Genetic algorithm-assisted fuzzy clustering framework to solve resource-constrained project problems
- Behavior recognition algorithm based on a dual-stream residual convolutional neural network
- Ensemble learning and deep learning-based defect detection in power generation plants
- Optimal design of neural network-based fuzzy predictive control model for recommending educational resources in the context of information technology
- An artificial intelligence-enabled consumables tracking system for medical laboratories
- Utilization of deep learning in ideological and political education
- Detection of abnormal tourist behavior in scenic spots based on optimized Gaussian model for background modeling
- RGB-to-hyperspectral conversion for accessible melanoma detection: A CNN-based approach
- Optimization of the road bump and pothole detection technology using convolutional neural network
- Comparative analysis of impact of classification algorithms on security and performance bug reports
- Cross-dataset micro-expression identification based on facial ROIs contribution quantification
- Demystifying multiple sclerosis diagnosis using interpretable and understandable artificial intelligence
- Unifying optimization forces: Harnessing the fine-structure constant in an electromagnetic-gravity optimization framework
- E-commerce big data processing based on an improved RBF model
- Analysis of youth sports physical health data based on cloud computing and gait awareness
- CCLCap-AE-AVSS: Cycle consistency loss based capsule autoencoders for audio–visual speech synthesis
- An efficient node selection algorithm in the context of IoT-based vehicular ad hoc network for emergency service
- Computer aided diagnoses for detecting the severity of Keratoconus
- Improved rapidly exploring random tree using salp swarm algorithm
- Network security framework for Internet of medical things applications: A survey
- Predicting DoS and DDoS attacks in network security scenarios using a hybrid deep learning model
- Enhancing 5G communication in business networks with an innovative secured narrowband IoT framework
- Quokka swarm optimization: A new nature-inspired metaheuristic optimization algorithm
- Digital forensics architecture for real-time automated evidence collection and centralization: Leveraging security lake and modern data architecture
- Image modeling algorithm for environment design based on augmented and virtual reality technologies
- Enhancing IoT device security: CNN-SVM hybrid approach for real-time detection of DoS and DDoS attacks
- High-resolution image processing and entity recognition algorithm based on artificial intelligence
- Review Articles
- Transformative insights: Image-based breast cancer detection and severity assessment through advanced AI techniques
- Network and cybersecurity applications of defense in adversarial attacks: A state-of-the-art using machine learning and deep learning methods
- Applications of integrating artificial intelligence and big data: A comprehensive analysis
- A systematic review of symbiotic organisms search algorithm for data clustering and predictive analysis
- Modelling Bitcoin networks in terms of anonymity and privacy in the metaverse application within Industry 5.0: Comprehensive taxonomy, unsolved issues and suggested solution
- Systematic literature review on intrusion detection systems: Research trends, algorithms, methods, datasets, and limitations
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- A study on intelligent translation of English sentences by a semantic feature extractor
- Detecting surface defects of heritage buildings based on deep learning
- Combining bag of visual words-based features with CNN in image classification
- Online addiction analysis and identification of students by applying gd-LSTM algorithm to educational behaviour data
- Improving multilayer perceptron neural network using two enhanced moth-flame optimizers to forecast iron ore prices
- Sentiment analysis model for cryptocurrency tweets using different deep learning techniques
- Periodic analysis of scenic spot passenger flow based on combination neural network prediction model
- Analysis of short-term wind speed variation, trends and prediction: A case study of Tamil Nadu, India
- Cloud computing-based framework for heart disease classification using quantum machine learning approach
- Research on teaching quality evaluation of higher vocational architecture majors based on enterprise platform with spherical fuzzy MAGDM
- Detection of sickle cell disease using deep neural networks and explainable artificial intelligence
- Interval-valued T-spherical fuzzy extended power aggregation operators and their application in multi-criteria decision-making
- Characterization of neighborhood operators based on neighborhood relationships
- Real-time pose estimation and motion tracking for motion performance using deep learning models
- QoS prediction using EMD-BiLSTM for II-IoT-secure communication systems
- A novel framework for single-valued neutrosophic MADM and applications to English-blended teaching quality evaluation
- An intelligent error correction model for English grammar with hybrid attention mechanism and RNN algorithm
- Prediction mechanism of depression tendency among college students under computer intelligent systems
- Research on grammatical error correction algorithm in English translation via deep learning
- Microblog sentiment analysis method using BTCBMA model in Spark big data environment
- Application and research of English composition tangent model based on unsupervised semantic space
- 1D-CNN: Classification of normal delivery and cesarean section types using cardiotocography time-series signals
- Real-time segmentation of short videos under VR technology in dynamic scenes
- Application of emotion recognition technology in psychological counseling for college students
- Classical music recommendation algorithm on art market audience expansion under deep learning
- A robust segmentation method combined with classification algorithms for field-based diagnosis of maize plant phytosanitary state
- Integration effect of artificial intelligence and traditional animation creation technology
- Artificial intelligence-driven education evaluation and scoring: Comparative exploration of machine learning algorithms
- Intelligent multiple-attributes decision support for classroom teaching quality evaluation in dance aesthetic education based on the GRA and information entropy
- A study on the application of multidimensional feature fusion attention mechanism based on sight detection and emotion recognition in online teaching
- Blockchain-enabled intelligent toll management system
- A multi-weapon detection using ensembled learning
- Deep and hand-crafted features based on Weierstrass elliptic function for MRI brain tumor classification
- Design of geometric flower pattern for clothing based on deep learning and interactive genetic algorithm
- Mathematical media art protection and paper-cut animation design under blockchain technology
- Deep reinforcement learning enhances artistic creativity: The case study of program art students integrating computer deep learning
- Transition from machine intelligence to knowledge intelligence: A multi-agent simulation approach to technology transfer
- Research on the TF–IDF algorithm combined with semantics for automatic extraction of keywords from network news texts
- Enhanced Jaya optimization for improving multilayer perceptron neural network in urban air quality prediction
- Design of visual symbol-aided system based on wireless network sensor and embedded system
- Construction of a mental health risk model for college students with long and short-term memory networks and early warning indicators
- Personalized resource recommendation method of student online learning platform based on LSTM and collaborative filtering
- Employment management system for universities based on improved decision tree
- English grammar intelligent error correction technology based on the n-gram language model
- Speech recognition and intelligent translation under multimodal human–computer interaction system
- Enhancing data security using Laplacian of Gaussian and Chacha20 encryption algorithm
- Construction of GCNN-based intelligent recommendation model for answering teachers in online learning system
- Neural network big data fusion in remote sensing image processing technology
- Research on the construction and reform path of online and offline mixed English teaching model in the internet era
- Real-time semantic segmentation based on BiSeNetV2 for wild road
- Online English writing teaching method that enhances teacher–student interaction
- Construction of a painting image classification model based on AI stroke feature extraction
- Big data analysis technology in regional economic market planning and enterprise market value prediction
- Location strategy for logistics distribution centers utilizing improved whale optimization algorithm
- Research on agricultural environmental monitoring Internet of Things based on edge computing and deep learning
- The application of curriculum recommendation algorithm in the driving mechanism of industry–teaching integration in colleges and universities under the background of education reform
- Application of online teaching-based classroom behavior capture and analysis system in student management
- Evaluation of online teaching quality in colleges and universities based on digital monitoring technology
- Face detection method based on improved YOLO-v4 network and attention mechanism
- Study on the current situation and influencing factors of corn import trade in China – based on the trade gravity model
- Research on business English grammar detection system based on LSTM model
- Multi-source auxiliary information tourist attraction and route recommendation algorithm based on graph attention network
- Multi-attribute perceptual fuzzy information decision-making technology in investment risk assessment of green finance Projects
- Research on image compression technology based on improved SPIHT compression algorithm for power grid data
- Optimal design of linear and nonlinear PID controllers for speed control of an electric vehicle
- Traditional landscape painting and art image restoration methods based on structural information guidance
- Traceability and analysis method for measurement laboratory testing data based on intelligent Internet of Things and deep belief network
- A speech-based convolutional neural network for human body posture classification
- The role of the O2O blended teaching model in improving the teaching effectiveness of physical education classes
- Genetic algorithm-assisted fuzzy clustering framework to solve resource-constrained project problems
- Behavior recognition algorithm based on a dual-stream residual convolutional neural network
- Ensemble learning and deep learning-based defect detection in power generation plants
- Optimal design of neural network-based fuzzy predictive control model for recommending educational resources in the context of information technology
- An artificial intelligence-enabled consumables tracking system for medical laboratories
- Utilization of deep learning in ideological and political education
- Detection of abnormal tourist behavior in scenic spots based on optimized Gaussian model for background modeling
- RGB-to-hyperspectral conversion for accessible melanoma detection: A CNN-based approach
- Optimization of the road bump and pothole detection technology using convolutional neural network
- Comparative analysis of impact of classification algorithms on security and performance bug reports
- Cross-dataset micro-expression identification based on facial ROIs contribution quantification
- Demystifying multiple sclerosis diagnosis using interpretable and understandable artificial intelligence
- Unifying optimization forces: Harnessing the fine-structure constant in an electromagnetic-gravity optimization framework
- E-commerce big data processing based on an improved RBF model
- Analysis of youth sports physical health data based on cloud computing and gait awareness
- CCLCap-AE-AVSS: Cycle consistency loss based capsule autoencoders for audio–visual speech synthesis
- An efficient node selection algorithm in the context of IoT-based vehicular ad hoc network for emergency service
- Computer aided diagnoses for detecting the severity of Keratoconus
- Improved rapidly exploring random tree using salp swarm algorithm
- Network security framework for Internet of medical things applications: A survey
- Predicting DoS and DDoS attacks in network security scenarios using a hybrid deep learning model
- Enhancing 5G communication in business networks with an innovative secured narrowband IoT framework
- Quokka swarm optimization: A new nature-inspired metaheuristic optimization algorithm
- Digital forensics architecture for real-time automated evidence collection and centralization: Leveraging security lake and modern data architecture
- Image modeling algorithm for environment design based on augmented and virtual reality technologies
- Enhancing IoT device security: CNN-SVM hybrid approach for real-time detection of DoS and DDoS attacks
- High-resolution image processing and entity recognition algorithm based on artificial intelligence
- Review Articles
- Transformative insights: Image-based breast cancer detection and severity assessment through advanced AI techniques
- Network and cybersecurity applications of defense in adversarial attacks: A state-of-the-art using machine learning and deep learning methods
- Applications of integrating artificial intelligence and big data: A comprehensive analysis
- A systematic review of symbiotic organisms search algorithm for data clustering and predictive analysis
- Modelling Bitcoin networks in terms of anonymity and privacy in the metaverse application within Industry 5.0: Comprehensive taxonomy, unsolved issues and suggested solution
- Systematic literature review on intrusion detection systems: Research trends, algorithms, methods, datasets, and limitations

