Finite element analysis and retrofit of the existing reinforced concrete columns in Iraqi schools by using CFRP as confining technique
-
Douread Raheem Hassen
, Mustafa Salman Shubber
Abstract
There are many studies about the use of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) to strengthen concrete members such as columns, beams, and slabs. The effectiveness of these strengthening techniques has been proved by enhancing the mechanical properties of concrete structures. So, CFRP has been used to strengthen and repair existing concrete structures in Iraq. For example, in Al-Mosul city, the strengthening and repairing system is done for concrete members such as beams, columns, and slabs using the Near Surface Mounted or confinement technique. Therefore, the research aim is to use CFRP for maintenance as an alternative material to strengthen and repair concrete members in Iraqi schools. This article employs methods to enhance and repairing of some of concrete columns at Al-Abeer school in Najaf city by using modern materials as an alternative method of maintenance. In addition, finite element analysis was carried out using Abaqus software to verify the effectiveness of strengthening. The reinforced concrete (RC) column strengthened by using fiber-reinforced polymer as a confining technique increased compressive strength by about 91% compared to the control column. In addition, the value of strains increased to nearly 100% in the longitudinal direction with the stability of the value of the lateral strains, despite the occurrence of a significant increase in the compressive strength capacity. So, the values of vertical displacement at stress 4 MPa were 22.3 mm for the strengthened RC column and 5 mm for the control RC column. Thus, the strengthened RC column increases the values of compressive strength with a decrease in displacement to approximately 22%. Four years ago, the strength of the school building was assessed, thus the success of the strengthening.
1 Introduction
In the last century and more than 40 years ago, fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) was tried to strengthen and/or repair infrastructures such as bridges [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. This is due to the fact that FRP is lightweight, has high tensile strength, is highly durable (correction-resistant), has good fatigue resistance, is resistant to chemical attack, and is highly versatile [8,9]. The tensile strength of FRP is around six times that of steel bars. Lately, the strengthening and repair of steel bridges by using FRP have been applied and developed worldwide [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17].
In the mid-1980s, fully or partially wrapped columns with carbon FRP (CFRP) sheets were known applications and accepted for the strengthening and repair of concrete and steel structures in Japan [18]. This paper reviews the features of strengthening and repairing by using the Near Surface Mounted technique for concrete columns and slabs with CFRP sheets in Iraq. Many studies have been conducted in different ways to strengthen and repair concrete members, some of which were for the retrofitting of reinforced concrete (RC) columns using CFRP wrapping.
They found that CFRP jacketing reinforces and increases the ultimate load and ductility if it is used to strengthen the hollow concrete sections [19]. Some researchers made models of square-shaped RC columns, wrapped them with CFRP, and studied their effect on increasing the shear load [20,21,22]. It was found that the scheme of failure did not change exclusively, except that the buckling occurred after the column was subjected to greater stress than in the prior. In addition, the CFRP provided an improvement by increasing the bearing of the column (high load capacity) by no less than 15%, and it was also noted that there was an increase in the ductility [23]. Richard and Cheyrezy [24] produced an ultrahigh strength ductile concrete based on improving uniformity by removing coarse aggregate, improving microstructure by post-set heat treatment, and increasing tensile strength by inserting small, straight, high-tensile microfiber. RPC200 and RPC800 were two types of concrete designed with remarkable mechanical properties. Strengthening the RC columns in the longitudinal and transverse directions is very easy when wrapping the column with CFRP material for different column shapes, like circular, square, rectangular, and others [25]. Moreover, research on the effect of wrapping columns with CFRP material is still limited [26]. As previously mentioned, the study of the behavior of columns after confining with CFRP is very important because this technique has a significant impact on increasing the compressive strength of RC columns, and the confinement technique using CFRP has been used since approximately 18 years ago [27].
The behavior of RC columns that are strengthened by confining technique varies according to the design of the column in a structure that is normal or subject to seismic loads [28,29]. The main objective of strengthening the columns using the confining technique is to increase the resistance to compression, especially when the column needs to be re-designed due to an increase in live loads or the addition of new elements to the concrete structure (a change in the use of buildings) [30]. Utilizing the method of confinement with CFRP offers numerous benefits in terms of ease of implementation, speed in processing, a relatively acceptable cost and does not require many labors [31]. Iraq is one of the countries that are most vulnerable to fires resulting from wars in the world. Due to these fires, many structures were damaged entirely and some partially damaged. Many of these partially damaged structures were RC structures [32]. Most of the Iraqi population and the companies executing the projects do not have sufficient information and experience to use modern technologies in the treatment of concrete structures, as many of them are compelled to demolish buildings or use primitive methods to treat the damaged facilities, which leads to a large financial loss in the end. These structures could have been spared if correct retrofitting procedures had been used. In order to increase the capacity of such structures, a variety of strengthening/retrofitting procedures can be used. FRP is one of the newest materials for retrofitting that has several advantages and is utilized worldwide. FRP materials have been widely used in jacketing to improve shear and flexural strength and have proven to be quite successful [33]. Many studies on RPC have been conducted in recent years to analyze its features and behavior. The following are some of the projects that were completed: the main objective of this research is to evaluate the effectiveness of using CFRP material through the confinement technique, as scientific quantifiable evaluation of the different properties of structures strengthened by using CFRP is still insignificant in Iraq.
2 Significance of study
The importance of the research is the implementation of the reinforcement technique using FRP for the constructed building (school Iraqi) that was exposed to collapse as a result of rusting of some RC columns. A numerical study was done using finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate the strengthening before practical implementation. Then, the practical strengthening was carried out on the RC columns using two layers of FRP. The follow-up of the constructed building was more than 5 years without any observation being recorded, indicating the success of the strengthening process. It is worth noting that the cost of rehabilitating the RC columns is approximately $2,000, but the demolition and rebuilding of the concrete structure exceeds $30,000.
3 Experimental program
The experimental work consists of four-square RC columns with a full-scale cross-section of about 0.6 m by 0.4 m and 5 m in height. These columns were wrapped in CFRP sheets according to the Hand lay-up system (Figure 1), a typical wrap system.
![Figure 1
Strengthening of RC columns by FRP sheet in Sweden, photo by Täljsten [34].](/document/doi/10.1515/eng-2022-0461/asset/graphic/j_eng-2022-0461_fig_001.jpg)
Strengthening of RC columns by FRP sheet in Sweden, photo by Täljsten [34].
The same technique was also used in Al-Mosul city of Iraq in 2017. Figure 2 shows the steps involved in repairing and strengthening these columns. First, the damaged concrete is removed, and the column is cleaned of dust. Then, special cement materials were used to repair the affected areas. Finally, epoxy was added to perfect the bond between FRP sheets around RC columns.
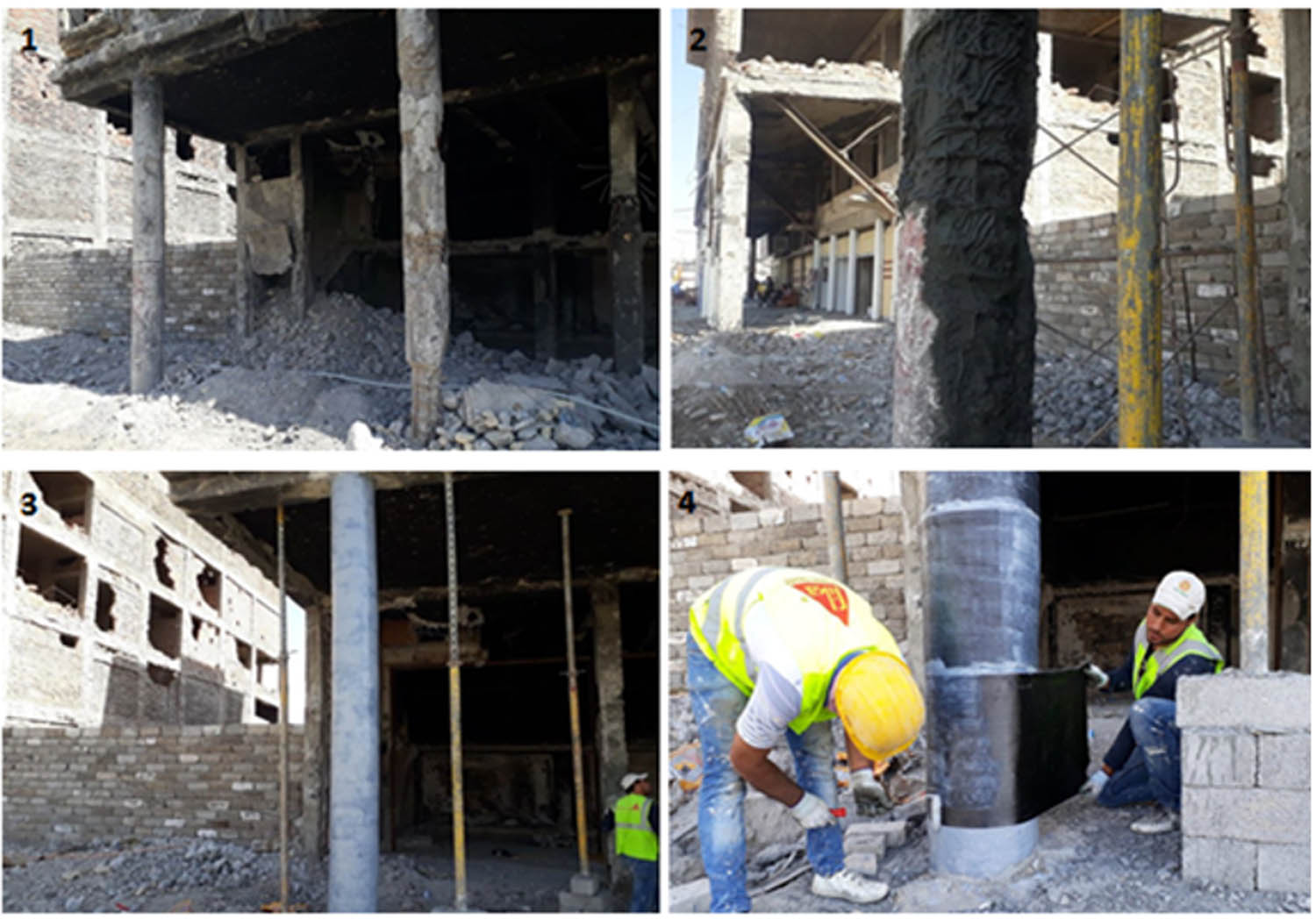

Steps involved in repairing and strengthening RC columns in Al-Mosul city.
So, in this research, the same procedure is used to strengthen the RC columns of school buildings in Al-Mosul city. The wet lay-up method was used for the CFRP wrapping of four plain square columns from each specimen [35]. The first step was cleaning the face of the columns to remove damaged concrete and dust. Then, the outer surface was coated by using weberep 331 TX, as shown in Figure 3. Weberep 331 TX is a ready mortar mainly made of sand (reconstituted grain size range), special cement, fibers, and special additives. So, it provides special properties such as non-shrinking, thixotropic, high strength, high adhesion, and compactness. Thus, its closed porosity slows down carbonation [36].
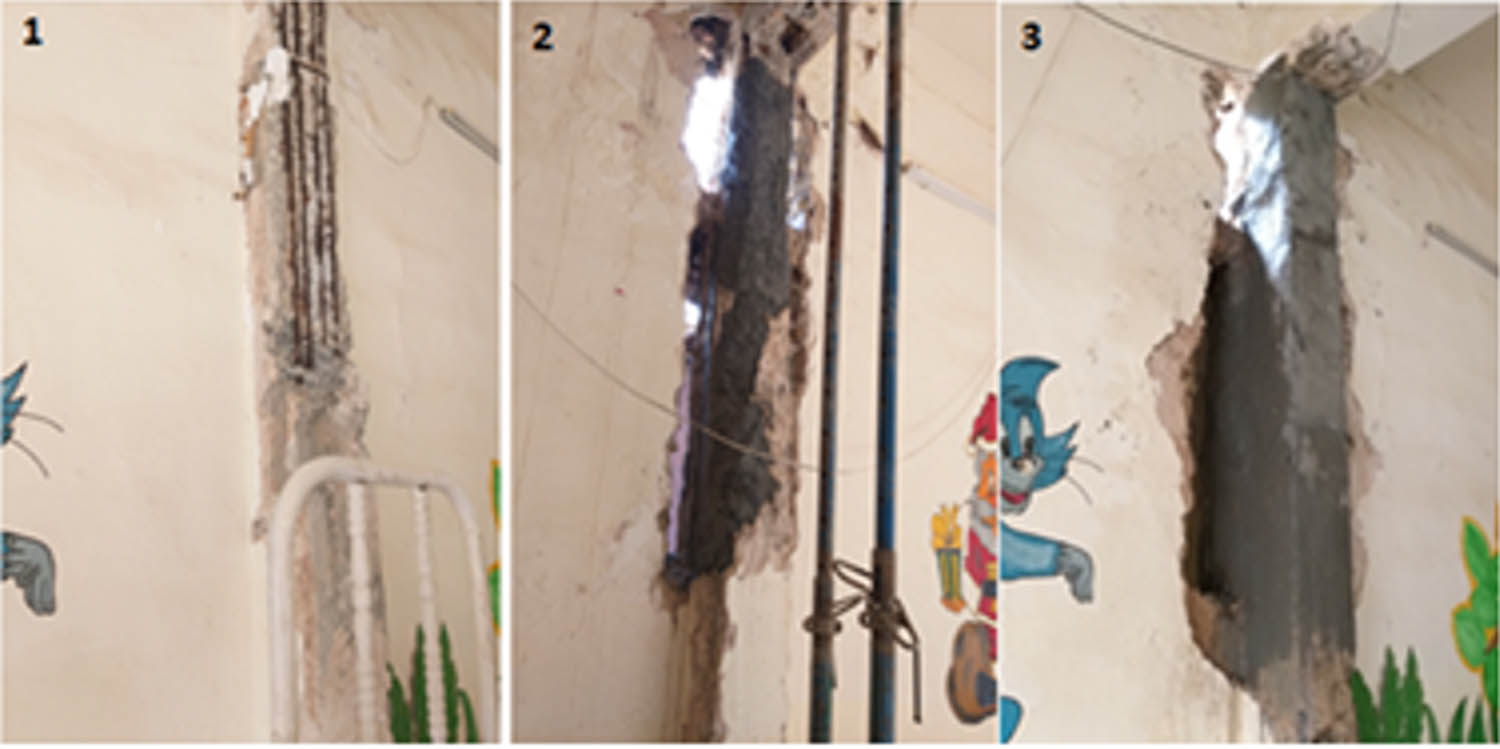

Cleaning and coating concrete surface.
Then, the specimens were sandblasted to provide better adhesion between columns with the CFRP laminates. A thin coat of the Weberep epo 412 Primer was applied, and it was permitted a maximum of 1 h for curing. The primer layer of the column received an application of Weber EPO 412 epoxy at perfect bonding with CFRP laminates. The CFRP laminates were attached to the concrete surface and provided an overlap of not less than 100 mm when the column was wrapped because the normal width of the laminates available in Iraq was 1 m. Then, the column was wrapped with two layers of CFRP laminates interspersed with epoxy, as shown in Figure 4.
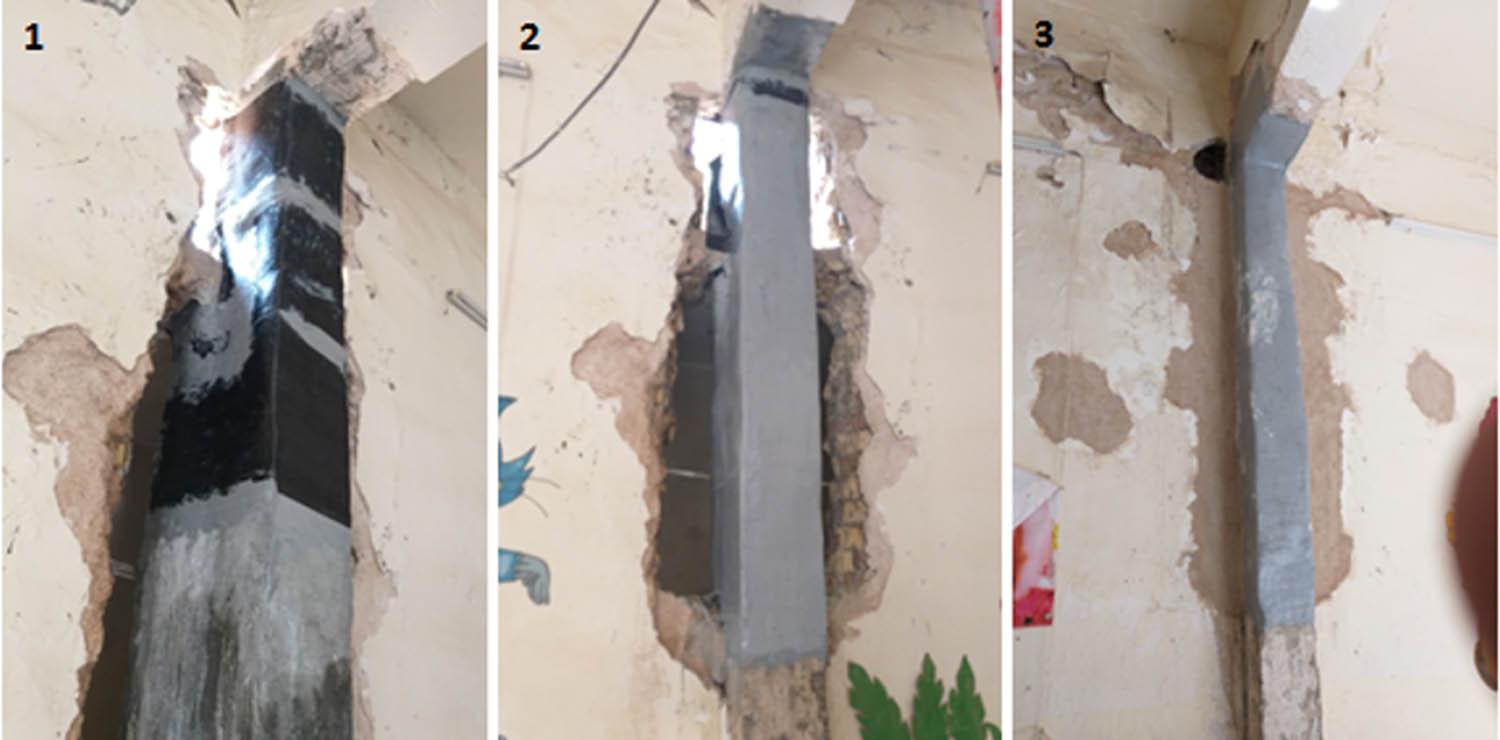

Wrapping columns by using CFRP sheet.
4 Numerical and result analysis
4.1 Mechanical properties
Theoretical analysis programs have evolved in terms of their ability to predict the mechanical properties of concrete, including cracks and their theoretical appearance over the past decades. The impact parameters of concrete in the Abaqus program, including elastic modulus, Poisson’s ratio, plastic degradation, tensile and compressive stresses, and the ratio of initial compressive yield stress to initial compressive yield stress, are mainly included in the analysis of concrete. As for reinforcing steel, the model used was the metal-plastic model, where it is assumed that steel is a plastic material with perfect elasticity and identical through tensile strength. The modulus of elasticity, Es, and the yield stress, fy, were measured in the experimental study, and the obtained values were Es = 200 GPa, fy = 480 MPa, and the Poisson ratio was assumed to be 0.2. In addition, the used polymer fibers were considered a linear orthodontic material because the composite was unidirectional. The modulus of elasticity of `the CFRP material used in the pilot study was specified by the manufacturer as 170 GPa and the Poisson’s ratio is 0.2. The utilization of the compound foundation, E11 = 225 GPa, E22 = 9.86 GPa, E33 = 9.86 GPa, ν12 = ν13 = 0.1, G12 = 0.1 GPa, G23 = 0.1 GPa, and G13 = 0.1 GPa use for the orthorhombic model.
4.2 Modeling
FEA (ABAQUS software) was used to analyze numerical simulation RC columns strengthened with FRP systems as a three-dimensional finite element [37]. The FEA model of strengthened RC columns improved their behavior in comparison to the non-strengthened control column. The concrete, steel rebar, and CFRP confinement were drawn as shown in Figure 5. Three types of material are used to make a model for concrete columns confined by CFRP, and these materials are defined as presented in Table 1.
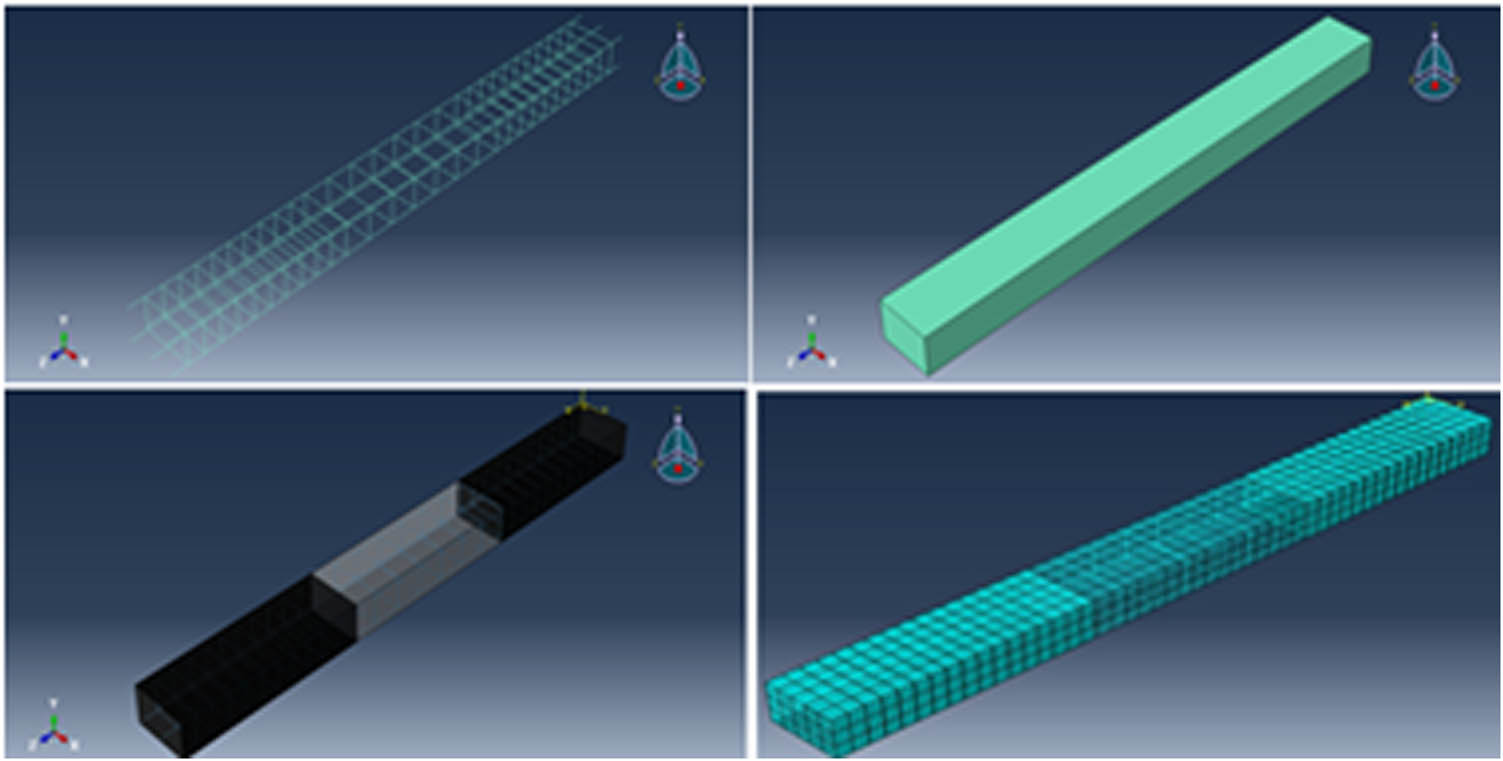
Model and mesh concrete, steel rebar, and CFRP confinement.
Define concrete, steel rebar, and CFRP materials
| Item | Element type | Element no. | Elastic | Isotropic | Hashin damage | Young’s modulus | Poisson’s ratio | Type of analysis | Longitudinal compression strength | Plastic | Yield stress | Plastic strain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete | C3D8R | 750 | Done | Done | — | 31,220 | 0.2 | Dynamic, explicit | — | — | — | — |
| Steel | S4R | 544 | — | Done | — | 200,000 | 0.2 | Dynamic, explicit | — | Done | 280, 370 | 0, 0.1 |
| CFRP | T3D2 | 734 | — | — | Done | — | — | Dynamic, explicit | 1,200 | — | — | — |
The interaction for these materials was done to make a good interaction between the elements, as shown in Figure 6.
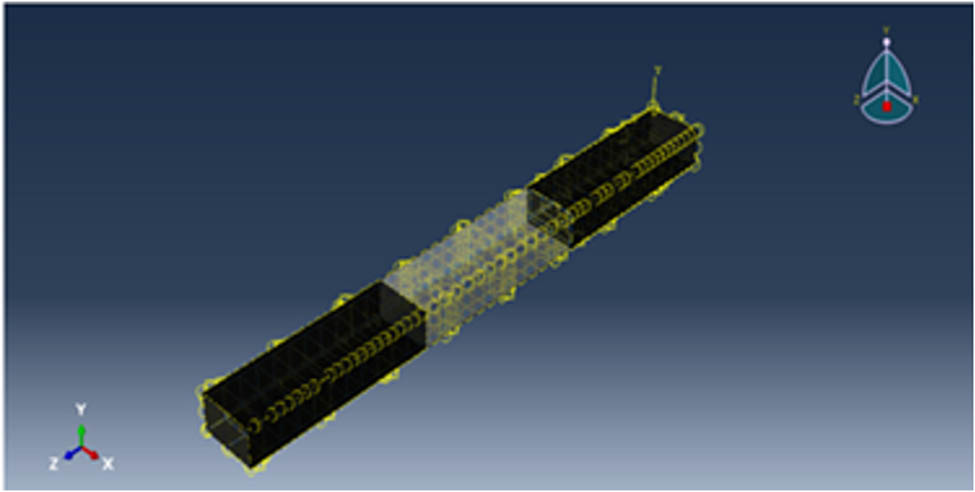
Interaction between the elements.
Two types of support were applied for the column end; one of them was a fix for three dimensions, and a 3 N/mm uniform distribution load was applied at another end. These two supports can be seen in Figure 7.
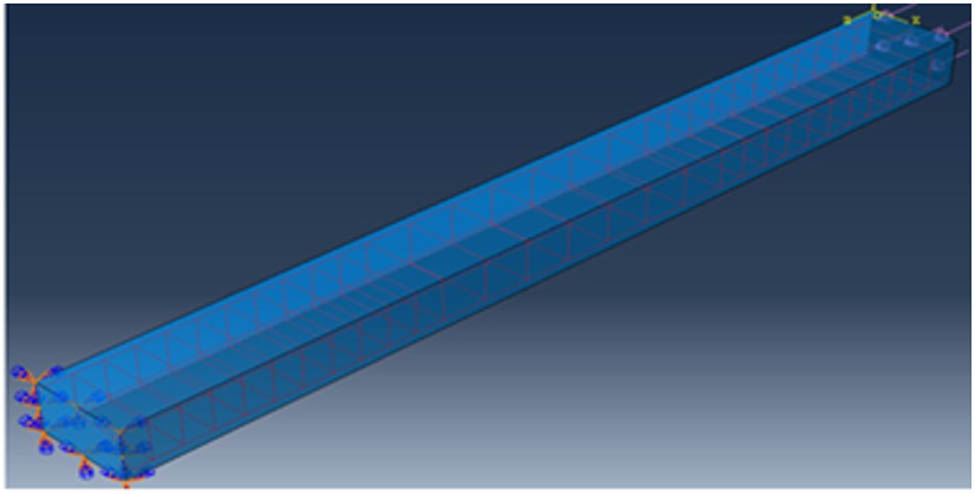
Loading and fixing of supports.
In the next stage, the model was meshed with 0.5 mm for all materials. Finally, the job was made to analyze this model. This job was divided into two steps according to the type of load, support, and displacement. For the control specimen, the stress at the load point was very high and reached 1.4E01, as shown in Figure 8.
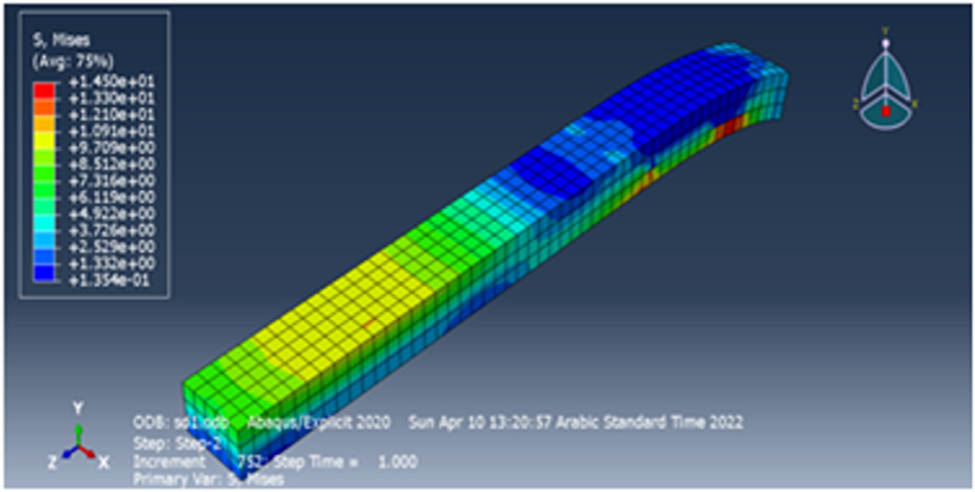
The stress of the control column.
4.3 Performance of rehabilitation method
The displacements of steel rebar and concrete were 3.168 × 102 and 8.797, respectively. Figure 9 shows the displacement for each material in the control column.
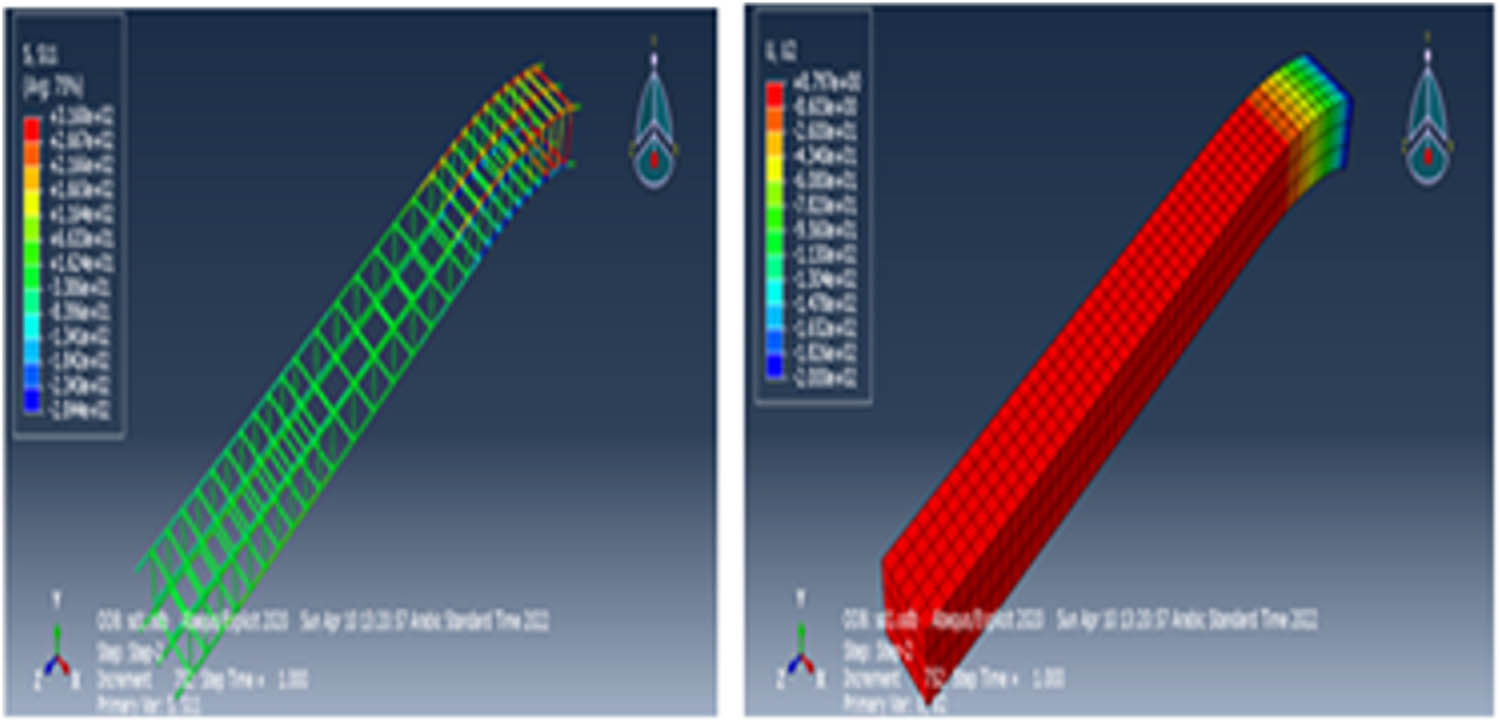
The displacement for each material in the control column.
For the confined column using CFRP material, the stress for this specimen was 9.344, as shown in Figure 10.
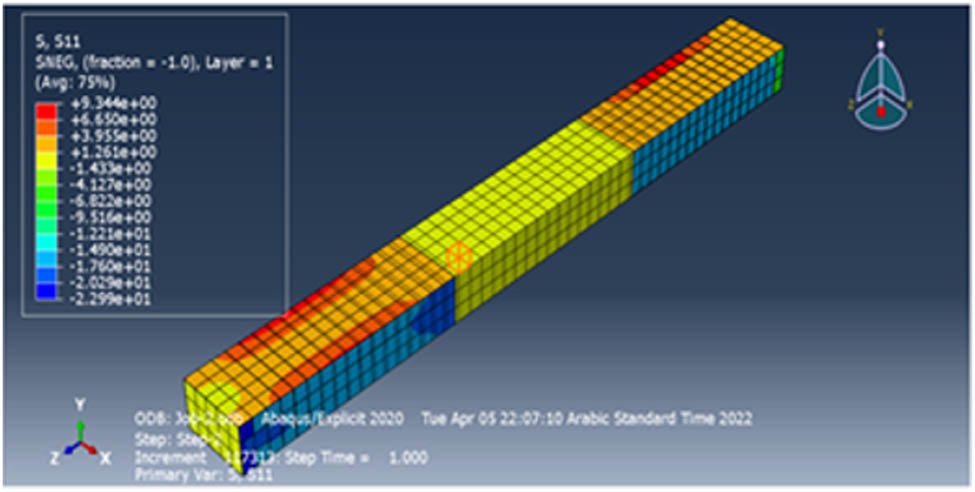
The stress of the strengthened column.
In addition, the maximum displacement for a confined column can be seen in Figure 11.

The displacement for each material in the strengthened column.
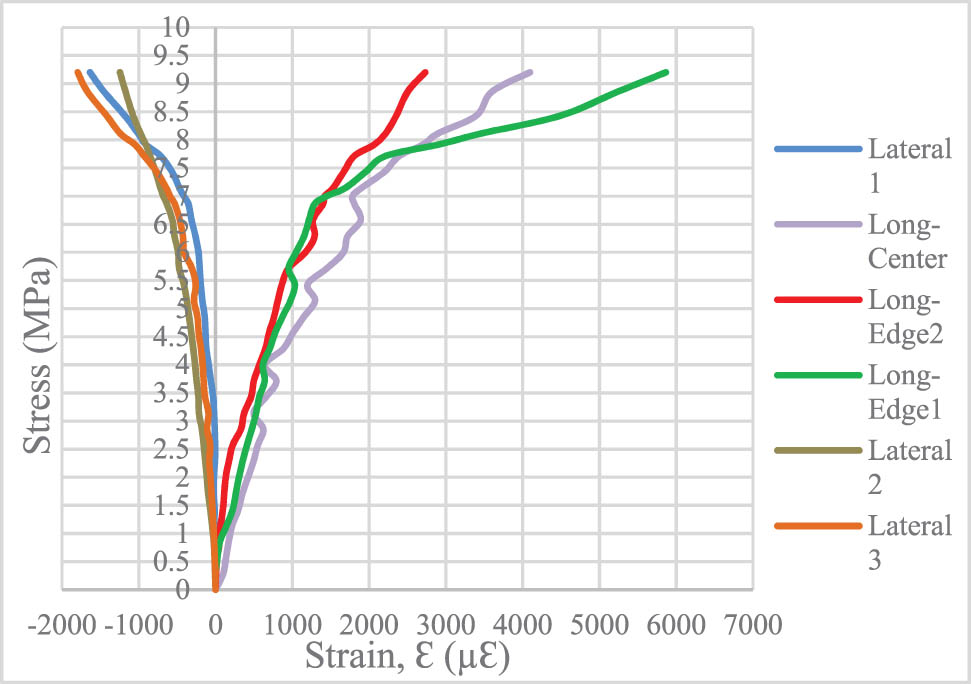
On the other hand, the longitudinal and lateral strains were calculated according to the points shown in Figure 12, where it was found that the highest value of the stress of the control column (RC column) reached 4.2 MPa, and the highest value of the strain was 0.0018, 0.001, 0.0015, and 0.0018 in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, as shown in Figure 13.

Strain results of the different nodes locations.

The stress–strain profile of the control column.
Moreover, it was noted that the RC column using the confining technique gave an increase in compressive strength of about 91% compared to the control column. In addition, the value of strains increased to nearly 100% in the longitudinal direction with the stability of the value of the lateral strains, despite the occurrence of a significant increase in the compressive strength capacity. It was also noted that the shape of the curve between stress and strain has changed for the reinforced column and become almost linear, as shown in Figure 14.
The stress–strain profile of a strengthened column.
In this article, the effect of confining on the vertical displacements in the concrete column was studied. From observing the results of strengthening using 0.5 mm CFRP columns, it was recorded an increase in the amount of compressive strength and a decrease in displacement to approximately 22%, as the amount of vertical displacement at stress 4 MPa was 22.3 and 5 mm for the strengthened and control columns, respectively, as shown in Figure 15. Similarly, the effectiveness of wraps according to different thicknesses of CFRP is shown in Figure 15. On the other hand, the variable readings of load–displacement results for 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2 mm thickness of CFRP wraps recorded by Abaqus software are shown in Figure 16.
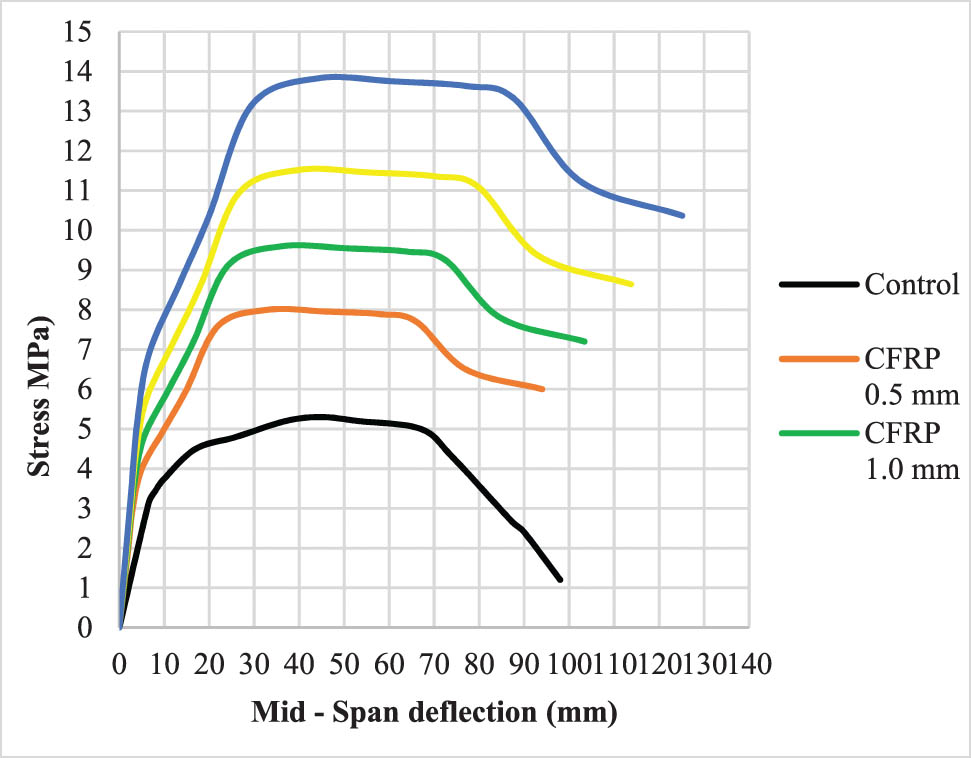
The displacement of CFRP and the control column profile.
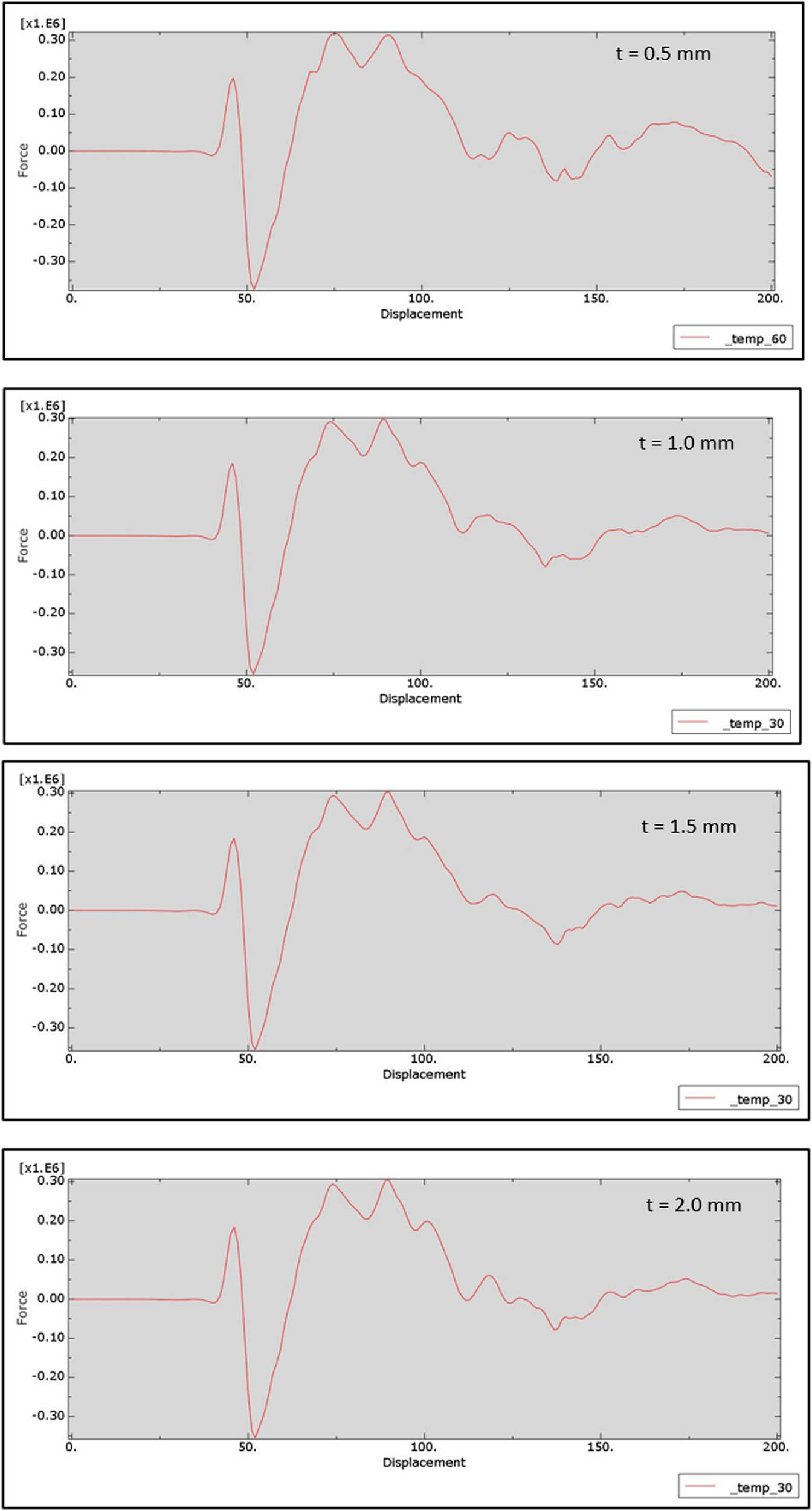
Load–displacement readings of CFRP.
5 Conclusion
This study implemented a dual reinforcement approach for square-shaped RC columns were carried out, that it was studying the effect of static loads on these columns had low compressive strength. From these results, it can be concluded that the FRP jackets can increase the strength and ductility of the columns. The efficiency of FRP jackets increased the axial capacity of columns. The value of vertical displacement at stress 4 MPa was 22.3 and 5 mm for the strengthened and control columns, respectively. The strengthened RC column recorded an increase in the values of compressive strength with a decrease in displacement to approximately 22%. Through the results obtained, an increase in the bearing values of the RC columns of the applied loading leads to a decrease in the vertical and lateral displacements as a result of these strengthening. The strengthened RC column using FRP increased compressive strength by nearly 91% compared to the control column. Despite the occurrence of a significant increase in the compressive capacity, the value of strains increased to nearly 100% in the longitudinal direction, while the value of lateral strains remained stable. In addition, the absence of the need to evacuate the building during the treatment of columns, beams, and others in concrete facilities is one of the important advantages of using the confinement technique by CFRP. In general, FRP jackets have proven to be highly effective in strengthening, maintaining, and rehabilitating RC buildings in Iraqi schools.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to extend their thanks to the Fourth Dimension Contracting Company for their support, guidance, and expertise that greatly assisted the research, especially in preparing the research materials and laboratory.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: Most datasets generated and analyzed in this study are included in this submitted manuscript. The other datasets are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author with the attached information.
References
[1] Jain R, Lee L, editors. Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) composites for infrastructure applications: Focusing on innovation, technology implementation and sustainability. Springer Science & Business Media; 2012.10.1007/978-94-007-2357-3Search in Google Scholar
[2] Miyamoto A, Kawamura K, Nakamura H. Bridge management system and maintenance optimization for existing bridges. Comput‐Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng. 2000;15(1):45–55.10.1111/0885-9507.00170Search in Google Scholar
[3] Wu Z, Wang X, Iwashita K. State-of-the-art of advanced FRP applications in civil infrastructure in Japan. Compos Polycon. 2007;37:1–17.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Uktamovich SB, Yuldashevich SA, Rahmonqulovich AM, Uralbayevich DU. Review of strengthening reinforced concrete beams using CFRP laminate. Eur Sci Rev. 2016;9–10:213–5.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Täljsten B. Strengthening concrete beams for shear with CFRP sheets. Constr Build Mater. 2003;17(1):15–26.10.1016/S0950-0618(02)00088-0Search in Google Scholar
[6] Sen R, Liby L, Mullins G. Strengthening steel bridge sections using CFRP laminates. Compos Part B: Eng. 2001;32(4):309–22.10.1016/S1359-8368(01)00006-3Search in Google Scholar
[7] Fukuyama H, Sugano S. Japanese seismic rehabilitation of concrete buildings after the Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake. Cem Concr Compos. 2000;22(1):59–79.10.1016/S0958-9465(99)00042-6Search in Google Scholar
[8] Naser MZ, Hawileh RA, Abdalla JA. Fiber-reinforced polymer composites in strengthening reinforced concrete structures: A critical review. Eng Struct. 2019 Nov;198:109542.10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109542Search in Google Scholar
[9] Sim J, Park C. Characteristics of basalt fiber as a strengthening material for concrete structures. Compos Part B: Eng. 2005;36(504–512):6–7.10.1016/j.compositesb.2005.02.002Search in Google Scholar
[10] Mortazavi AA, Jalal M. Investigation of CFRP- and GFRP-confined concrete cylinders under monotonic and cyclic loading. Sci Eng Compos Mater. 2014;21(4):607–14.10.1515/secm-2013-0213Search in Google Scholar
[11] Köroğlu MA. Artificial neural network for predicting the flexural bond strength of FRP bars in concrete. Sci Eng Compos Mater. 2019;26(1):12–29.10.1515/secm-2017-0155Search in Google Scholar
[12] Shakil UA, Hassan SBA. Behavior and properties of tin slag polyester polymer concrete confined with FRP composites under compression. J Mech Behav Mater. 2020;29(1):44–56.10.1515/jmbm-2020-0005Search in Google Scholar
[13] Nascimbene R. Numerical model of a reinforced concrete building: Earthquake analysis and experimental validation. Period Polytech Civ Eng. 2015;59(4):521–30.10.3311/PPci.8247Search in Google Scholar
[14] Pavese A, Lanese I, Nascimbene R. Seismic vulnerability assessment of an infilled reinforced concrete frame structure designed for gravity loads. J Earthq Eng. 2017;21(2):267–89.10.1080/13632469.2016.1172372Search in Google Scholar
[15] Abdulrazzaq Azeez A, Jamaluddin N, Abd Rahman N, Hassen DR, Attiyah AN. Experimental and analytical study of PVC confined concrete cylinders. J Eng Appl Sci. 2018;13(8):2145–51.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Abdulrazzaq Azeez A. Behavior of concrete-filled PVC tube columns under axial load. Doctoral dissertation. Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia; 2018.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Meier U. Strengthening of structures using carbon fibre/epoxy composites. Constr Build Mater. 1995;9(6):341–51.10.1016/0950-0618(95)00071-2Search in Google Scholar
[18] Chajes MJ, Thomson Jr TA, Januszka TF, Finch Jr WW. Flexural strengthening of concrete beams using externally bonded composite materials. Constr Build Mater. 1994;8(3):191–201.10.1016/S0950-0618(09)90034-4Search in Google Scholar
[19] Nanni A. North American design guidelines for concrete reinforcement and strengthening using FRP: Principles, applications and unresolved issues. Constr Build Mater. 2003;17(6–7):439–46.10.1016/S0950-0618(03)00042-4Search in Google Scholar
[20] Lignola GP, Prota A, Manfredi G, Cosenza E. Non-linear modeling of RC rectangular hollow piers confined with CFRP. Compos Struct. 2009;88(1):56–64.10.1016/j.compstruct.2008.10.001Search in Google Scholar
[21] Lignola GP, Prota A, Manfredi G, Cosenza E. Deformability of RC hollow columns confined with CFRP. ACI Struct J. 2007;104(5):629–37.10.14359/18865Search in Google Scholar
[22] Sheikh MN, Vivier A, Legeron F. Seismic vulnerability of hollow core concrete bridge piers. CONSEC’07 Tours. France; 2007.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Prota A, Manfredi G, Cosenza E. Ultimate behavior of axially loaded RC wall-like columns confined with GFRP. Compos: Part B. 2006;37:670–8. Elsevier.10.1016/j.compositesb.2006.01.005Search in Google Scholar
[24] Richard P, Cheyrezy M. Composition of reactive powder concretes. Cem Concr Res. 1995 Oct;25(7):1501–11.10.1016/0008-8846(95)00144-2Search in Google Scholar
[25] Yoddumrong P, Rodsin K, Katawaethwarag S. Seismic strengthening of low-strength RC concrete columns using low-cost glass fiber reinforced polymers (GFRPs). Case Stud Constr Mater. 2020 Dec;13:e00383.10.1016/j.cscm.2020.e00383Search in Google Scholar
[26] Raval R, Dave U. Behavior of GFRP wrapped RC Columns of different shapes. Procedia Eng. 2013 Jan;51:240–9.10.1016/j.proeng.2013.01.033Search in Google Scholar
[27] Maalej M, Tanwongsval S, Paramasivam P. Modelling of rectangular RC columns strengthened with FRP. Cem Concr Compos. 2003;25:264–5.10.1016/S0958-9465(02)00017-3Search in Google Scholar
[28] Deyanova M, Bellotti D, Nascimbene R, Pampanin S. Performance-based assessment of slender reinforced concrete columns typical of precast industrial buildings. Bull Earthq Eng. 2023;21(1):433–71.10.1007/s10518-022-01542-5Search in Google Scholar
[29] https://www.middleeast.weber/concrete-repair-anchoring-and-grouting/concrete-repair-smoothing/weberep-331-tx.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Kaveh A, Massoudi MS, Massoudi MJ. Efficient finite element analysis using graph-theoretical force method; rectangular plane stress and plane strain serendipity family elements. Period. Polytech.: Civ. Eng., 2014;58(1):3–22.10.3311/PPci.7405Search in Google Scholar
[31] Al-Duaij J, Al-Khaiat H, Fereig S, Awida TA. Behaviour of structural systems in residential buildings due to war damage caused by the Iraqi invasion. Kuwait J Sci Eng. 2000;27(2):279–89.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Qin D, Gao P, Aslam F, Sufian M, Alabduljabbar H. A comprehensive review on fire damage assessment of reinforced concrete structures. Case Stud Constr Mater. 2022;16:e00843.10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00843Search in Google Scholar
[33] Al-Shawaf A. Modelling wet lay-up CFRP–steel bond failures at extreme temperatures using stress-based approach. Int J Adhes Adhes. 2011 Sep;31(6):416–28.10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2011.02.005Search in Google Scholar
[34] Täljsten B. Plate bonding, strengthening of existing concrete structures with epoxy bonded plates of steel or fibre reinforced plastics. Doctoral Thesis. Vol. 1994, No. 152D. Luleå: University of Technology; 1994. p. 308.Search in Google Scholar
[35] Meier U. Composite materials in bridge repair. Appl Compos Mater. 2000 May;7(2):75–94.10.1023/A:1008919824535Search in Google Scholar
[36] Amir EA, AmjadNaseer E, Azam O. Strengthening of existing building column using FRP wrap& GI wire mesh. Contributory Pap. 2013 May;207–12.Search in Google Scholar
[37] Alshimmeri AJ, Jaafar EK, Shihab LA, Al-Maliki HN, Al-Balhawi A, Zhang B. Structural efficiency of non-prismatic hollow reinforced concrete beams retrofitted with CFRP sheets. Buildings. 2022 Feb;12(2):109.10.3390/buildings12020109Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Design optimization of a 4-bar exoskeleton with natural trajectories using unique gait-based synthesis approach
- Technical review of supervised machine learning studies and potential implementation to identify herbal plant dataset
- Effect of ECAP die angle and route type on the experimental evolution, crystallographic texture, and mechanical properties of pure magnesium
- Design and characteristics of two-dimensional piezoelectric nanogenerators
- Hybrid and cognitive digital twins for the process industry
- Discharge predicted in compound channels using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS)
- Human factors in aviation: Fatigue management in ramp workers
- LLDPE matrix with LDPE and UV stabilizer additive to evaluate the interface adhesion impact on the thermal and mechanical degradation
- Dislocated time sequences – deep neural network for broken bearing diagnosis
- Estimation method of corrosion current density of RC elements
- A computational iterative design method for bend-twist deformation in composite ship propeller blades for thrusters
- Compressive forces influence on the vibrations of double beams
- Research on dynamical properties of a three-wheeled electric vehicle from the point of view of driving safety
- Risk management based on the best value approach and its application in conditions of the Czech Republic
- Effect of openings on simply supported reinforced concrete skew slabs using finite element method
- Experimental and simulation study on a rooftop vertical-axis wind turbine
- Rehabilitation of overload-damaged reinforced concrete columns using ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete
- Performance of a horizontal well in a bounded anisotropic reservoir: Part II: Performance analysis of well length and reservoir geometry
- Effect of chloride concentration on the corrosion resistance of pure Zn metal in a 0.0626 M H2SO4 solution
- Numerical and experimental analysis of the heat transfer process in a railway disc brake tested on a dynamometer stand
- Design parameters and mechanical efficiency of jet wind turbine under high wind speed conditions
- Architectural modeling of data warehouse and analytic business intelligence for Bedstead manufacturers
- Influence of nano chromium addition on the corrosion and erosion–corrosion behavior of cupronickel 70/30 alloy in seawater
- Evaluating hydraulic parameters in clays based on in situ tests
- Optimization of railway entry and exit transition curves
- Daily load curve prediction for Jordan based on statistical techniques
- Review Articles
- A review of rutting in asphalt concrete pavement
- Powered education based on Metaverse: Pre- and post-COVID comprehensive review
- A review of safety test methods for new car assessment program in Southeast Asian countries
- Communication
- StarCrete: A starch-based biocomposite for off-world construction
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part I
- Analysis and assessment of the human factor as a cause of occurrence of selected railway accidents and incidents
- Testing the way of driving a vehicle in real road conditions
- Research of dynamic phenomena in a model engine stand
- Testing the relationship between the technical condition of motorcycle shock absorbers determined on the diagnostic line and their characteristics
- Retrospective analysis of the data concerning inspections of vehicles with adaptive devices
- Analysis of the operating parameters of electric, hybrid, and conventional vehicles on different types of roads
- Special Issue: 49th KKBN - Part II
- Influence of a thin dielectric layer on resonance frequencies of square SRR metasurface operating in THz band
- Influence of the presence of a nitrided layer on changes in the ultrasonic wave parameters
- Special Issue: ICRTEEC - 2021 - Part III
- Reverse droop control strategy with virtual resistance for low-voltage microgrid with multiple distributed generation sources
- Special Issue: AESMT-2 - Part II
- Waste ceramic as partial replacement for sand in integral waterproof concrete: The durability against sulfate attack of certain properties
- Assessment of Manning coefficient for Dujila Canal, Wasit/-Iraq
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part I
- Modulation and performance of synchronous demodulation for speech signal detection and dialect intelligibility
- Seismic evaluation cylindrical concrete shells
- Investigating the role of different stabilizers of PVCs by using a torque rheometer
- Investigation of high-turbidity tap water problem in Najaf governorate/middle of Iraq
- Experimental and numerical evaluation of tire rubber powder effectiveness for reducing seepage rate in earth dams
- Enhancement of air conditioning system using direct evaporative cooling: Experimental and theoretical investigation
- Assessment for behavior of axially loaded reinforced concrete columns strengthened by different patterns of steel-framed jacket
- Novel graph for an appropriate cross section and length for cantilever RC beams
- Discharge coefficient and energy dissipation on stepped weir
- Numerical study of the fluid flow and heat transfer in a finned heat sink using Ansys Icepak
- Integration of numerical models to simulate 2D hydrodynamic/water quality model of contaminant concentration in Shatt Al-Arab River with WRDB calibration tools
- Study of the behavior of reactive powder concrete RC deep beams by strengthening shear using near-surface mounted CFRP bars
- The nonlinear analysis of reactive powder concrete effectiveness in shear for reinforced concrete deep beams
- Activated carbon from sugarcane as an efficient adsorbent for phenol from petroleum refinery wastewater: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic study
- Structural behavior of concrete filled double-skin PVC tubular columns confined by plain PVC sockets
- Probabilistic derivation of droplet velocity using quadrature method of moments
- A study of characteristics of man-made lightweight aggregate and lightweight concrete made from expanded polystyrene (eps) and cement mortar
- Effect of waste materials on soil properties
- Experimental investigation of electrode wear assessment in the EDM process using image processing technique
- Punching shear of reinforced concrete slabs bonded with reactive powder after exposure to fire
- Deep learning model for intrusion detection system utilizing convolution neural network
- Improvement of CBR of gypsum subgrade soil by cement kiln dust and granulated blast-furnace slag
- Investigation of effect lengths and angles of the control devices below the hydraulic structure
- Finite element analysis for built-up steel beam with extended plate connected by bolts
- Finite element analysis and retrofit of the existing reinforced concrete columns in Iraqi schools by using CFRP as confining technique
- Performing laboratory study of the behavior of reactive powder concrete on the shear of RC deep beams by the drilling core test
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part I
- Depletion zones of groundwater resources in the Southwest Desert of Iraq
- A case study of T-beams with hybrid section shear characteristics of reactive powder concrete
- Feasibility studies and their effects on the success or failure of investment projects. “Najaf governorate as a model”
- Optimizing and coordinating the location of raw material suitable for cement manufacturing in Wasit Governorate, Iraq
- Effect of the 40-PPI copper foam layer height on the solar cooker performance
- Identification and investigation of corrosion behavior of electroless composite coating on steel substrate
- Improvement in the California bearing ratio of subbase soil by recycled asphalt pavement and cement
- Some properties of thermal insulating cement mortar using Ponza aggregate
- Assessment of the impacts of land use/land cover change on water resources in the Diyala River, Iraq
- Effect of varied waste concrete ratios on the mechanical properties of polymer concrete
- Effect of adverse slope on performance of USBR II stilling basin
- Shear capacity of reinforced concrete beams with recycled steel fibers
- Extracting oil from oil shale using internal distillation (in situ retorting)
- Influence of recycling waste hardened mortar and ceramic rubbish on the properties of flowable fill material
- Rehabilitation of reinforced concrete deep beams by near-surface-mounted steel reinforcement
- Impact of waste materials (glass powder and silica fume) on features of high-strength concrete
- Studying pandemic effects and mitigation measures on management of construction projects: Najaf City as a case study
- Design and implementation of a frequency reconfigurable antenna using PIN switch for sub-6 GHz applications
- Average monthly recharge, surface runoff, and actual evapotranspiration estimation using WetSpass-M model in Low Folded Zone, Iraq
- Simple function to find base pressure under triangular and trapezoidal footing with two eccentric loads
- Assessment of ALINEA method performance at different loop detector locations using field data and micro-simulation modeling via AIMSUN
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part I
- Experimental and theoretical investigation of the structural behavior of reinforced glulam wooden members by NSM steel bars and shear reinforcement CFRP sheet
- Improving the fatigue life of composite by using multiwall carbon nanotubes
- A comparative study to solve fractional initial value problems in discrete domain
- Assessing strength properties of stabilized soils using dynamic cone penetrometer test
- Investigating traffic characteristics for merging sections in Iraq
- Enhancement of flexural behavior of hybrid flat slab by using SIFCON
- The main impacts of a managed aquifer recharge using AHP-weighted overlay analysis based on GIS in the eastern Wasit province, Iraq
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Design optimization of a 4-bar exoskeleton with natural trajectories using unique gait-based synthesis approach
- Technical review of supervised machine learning studies and potential implementation to identify herbal plant dataset
- Effect of ECAP die angle and route type on the experimental evolution, crystallographic texture, and mechanical properties of pure magnesium
- Design and characteristics of two-dimensional piezoelectric nanogenerators
- Hybrid and cognitive digital twins for the process industry
- Discharge predicted in compound channels using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS)
- Human factors in aviation: Fatigue management in ramp workers
- LLDPE matrix with LDPE and UV stabilizer additive to evaluate the interface adhesion impact on the thermal and mechanical degradation
- Dislocated time sequences – deep neural network for broken bearing diagnosis
- Estimation method of corrosion current density of RC elements
- A computational iterative design method for bend-twist deformation in composite ship propeller blades for thrusters
- Compressive forces influence on the vibrations of double beams
- Research on dynamical properties of a three-wheeled electric vehicle from the point of view of driving safety
- Risk management based on the best value approach and its application in conditions of the Czech Republic
- Effect of openings on simply supported reinforced concrete skew slabs using finite element method
- Experimental and simulation study on a rooftop vertical-axis wind turbine
- Rehabilitation of overload-damaged reinforced concrete columns using ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete
- Performance of a horizontal well in a bounded anisotropic reservoir: Part II: Performance analysis of well length and reservoir geometry
- Effect of chloride concentration on the corrosion resistance of pure Zn metal in a 0.0626 M H2SO4 solution
- Numerical and experimental analysis of the heat transfer process in a railway disc brake tested on a dynamometer stand
- Design parameters and mechanical efficiency of jet wind turbine under high wind speed conditions
- Architectural modeling of data warehouse and analytic business intelligence for Bedstead manufacturers
- Influence of nano chromium addition on the corrosion and erosion–corrosion behavior of cupronickel 70/30 alloy in seawater
- Evaluating hydraulic parameters in clays based on in situ tests
- Optimization of railway entry and exit transition curves
- Daily load curve prediction for Jordan based on statistical techniques
- Review Articles
- A review of rutting in asphalt concrete pavement
- Powered education based on Metaverse: Pre- and post-COVID comprehensive review
- A review of safety test methods for new car assessment program in Southeast Asian countries
- Communication
- StarCrete: A starch-based biocomposite for off-world construction
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part I
- Analysis and assessment of the human factor as a cause of occurrence of selected railway accidents and incidents
- Testing the way of driving a vehicle in real road conditions
- Research of dynamic phenomena in a model engine stand
- Testing the relationship between the technical condition of motorcycle shock absorbers determined on the diagnostic line and their characteristics
- Retrospective analysis of the data concerning inspections of vehicles with adaptive devices
- Analysis of the operating parameters of electric, hybrid, and conventional vehicles on different types of roads
- Special Issue: 49th KKBN - Part II
- Influence of a thin dielectric layer on resonance frequencies of square SRR metasurface operating in THz band
- Influence of the presence of a nitrided layer on changes in the ultrasonic wave parameters
- Special Issue: ICRTEEC - 2021 - Part III
- Reverse droop control strategy with virtual resistance for low-voltage microgrid with multiple distributed generation sources
- Special Issue: AESMT-2 - Part II
- Waste ceramic as partial replacement for sand in integral waterproof concrete: The durability against sulfate attack of certain properties
- Assessment of Manning coefficient for Dujila Canal, Wasit/-Iraq
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part I
- Modulation and performance of synchronous demodulation for speech signal detection and dialect intelligibility
- Seismic evaluation cylindrical concrete shells
- Investigating the role of different stabilizers of PVCs by using a torque rheometer
- Investigation of high-turbidity tap water problem in Najaf governorate/middle of Iraq
- Experimental and numerical evaluation of tire rubber powder effectiveness for reducing seepage rate in earth dams
- Enhancement of air conditioning system using direct evaporative cooling: Experimental and theoretical investigation
- Assessment for behavior of axially loaded reinforced concrete columns strengthened by different patterns of steel-framed jacket
- Novel graph for an appropriate cross section and length for cantilever RC beams
- Discharge coefficient and energy dissipation on stepped weir
- Numerical study of the fluid flow and heat transfer in a finned heat sink using Ansys Icepak
- Integration of numerical models to simulate 2D hydrodynamic/water quality model of contaminant concentration in Shatt Al-Arab River with WRDB calibration tools
- Study of the behavior of reactive powder concrete RC deep beams by strengthening shear using near-surface mounted CFRP bars
- The nonlinear analysis of reactive powder concrete effectiveness in shear for reinforced concrete deep beams
- Activated carbon from sugarcane as an efficient adsorbent for phenol from petroleum refinery wastewater: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic study
- Structural behavior of concrete filled double-skin PVC tubular columns confined by plain PVC sockets
- Probabilistic derivation of droplet velocity using quadrature method of moments
- A study of characteristics of man-made lightweight aggregate and lightweight concrete made from expanded polystyrene (eps) and cement mortar
- Effect of waste materials on soil properties
- Experimental investigation of electrode wear assessment in the EDM process using image processing technique
- Punching shear of reinforced concrete slabs bonded with reactive powder after exposure to fire
- Deep learning model for intrusion detection system utilizing convolution neural network
- Improvement of CBR of gypsum subgrade soil by cement kiln dust and granulated blast-furnace slag
- Investigation of effect lengths and angles of the control devices below the hydraulic structure
- Finite element analysis for built-up steel beam with extended plate connected by bolts
- Finite element analysis and retrofit of the existing reinforced concrete columns in Iraqi schools by using CFRP as confining technique
- Performing laboratory study of the behavior of reactive powder concrete on the shear of RC deep beams by the drilling core test
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part I
- Depletion zones of groundwater resources in the Southwest Desert of Iraq
- A case study of T-beams with hybrid section shear characteristics of reactive powder concrete
- Feasibility studies and their effects on the success or failure of investment projects. “Najaf governorate as a model”
- Optimizing and coordinating the location of raw material suitable for cement manufacturing in Wasit Governorate, Iraq
- Effect of the 40-PPI copper foam layer height on the solar cooker performance
- Identification and investigation of corrosion behavior of electroless composite coating on steel substrate
- Improvement in the California bearing ratio of subbase soil by recycled asphalt pavement and cement
- Some properties of thermal insulating cement mortar using Ponza aggregate
- Assessment of the impacts of land use/land cover change on water resources in the Diyala River, Iraq
- Effect of varied waste concrete ratios on the mechanical properties of polymer concrete
- Effect of adverse slope on performance of USBR II stilling basin
- Shear capacity of reinforced concrete beams with recycled steel fibers
- Extracting oil from oil shale using internal distillation (in situ retorting)
- Influence of recycling waste hardened mortar and ceramic rubbish on the properties of flowable fill material
- Rehabilitation of reinforced concrete deep beams by near-surface-mounted steel reinforcement
- Impact of waste materials (glass powder and silica fume) on features of high-strength concrete
- Studying pandemic effects and mitigation measures on management of construction projects: Najaf City as a case study
- Design and implementation of a frequency reconfigurable antenna using PIN switch for sub-6 GHz applications
- Average monthly recharge, surface runoff, and actual evapotranspiration estimation using WetSpass-M model in Low Folded Zone, Iraq
- Simple function to find base pressure under triangular and trapezoidal footing with two eccentric loads
- Assessment of ALINEA method performance at different loop detector locations using field data and micro-simulation modeling via AIMSUN
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part I
- Experimental and theoretical investigation of the structural behavior of reinforced glulam wooden members by NSM steel bars and shear reinforcement CFRP sheet
- Improving the fatigue life of composite by using multiwall carbon nanotubes
- A comparative study to solve fractional initial value problems in discrete domain
- Assessing strength properties of stabilized soils using dynamic cone penetrometer test
- Investigating traffic characteristics for merging sections in Iraq
- Enhancement of flexural behavior of hybrid flat slab by using SIFCON
- The main impacts of a managed aquifer recharge using AHP-weighted overlay analysis based on GIS in the eastern Wasit province, Iraq

