Abstract
2(C13H12N3O)+, 2(C7H4.5O2.5)−, 2(H2O), orthorhombic, Pbca (no. 61), a = 8.2775(5) Å, b = 12.6054(9) Å, c = 35.082(2) Å, V = 3,660.5(4) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt (F) = 0.0663, wRref (F 2) = 0.1864, T = 173 K.
1 Source of materials
To synthesize the title compound, 0.23 g (167 mmol) isonicotinic acid hydrazide and 0.23 g (166 mmol) salicylic acid were weight out in a Dram vial and dissolved in 3 mL benzaldehyde. The vial was closed tightly and reacted at 333 K, and stirred at 300 rpm for 24 h. The solution was allowed to slowly evaporate at ambient temperatures between 298 and 300 K. Colourless needles were formed at the bottom of the vial after six weeks (Tables 1 and 2).
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless needles |
| Size: | 0.42 × 0.27 × 0.03 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.10 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 Venture Photon, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.7°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 28,159, 3,482, 0.083 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 2,434 |
| N(param)refined: | 267 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 WinGX/ORTEP, 4 , 5 PLATON 6 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.6866 (3) | 0.5026 (3) | 0.53410 (7) | 0.0470 (7) |
| C2 | 0.6477 (5) | 0.3974 (3) | 0.53390 (9) | 0.0669 (10) |
| H2 | 0.684206 | 0.351752 | 0.514132 | 0.08* |
| C3 | 0.5527 (5) | 0.3591 (4) | 0.56373 (12) | 0.0899 (15) |
| H3 | 0.522484 | 0.286376 | 0.5638 | 0.108* |
| C4 | 0.5434 (6) | 0.5200 (6) | 0.59176 (12) | 0.113 (2) |
| H4 | 0.508254 | 0.563934 | 0.61215 | 0.135* |
| C5 | 0.6326 (5) | 0.5640 (4) | 0.56407 (9) | 0.0748 (11) |
| H5 | 0.658724 | 0.63735 | 0.565084 | 0.09* |
| C6 | 0.7850 (3) | 0.5570 (2) | 0.50425 (7) | 0.0433 (7) |
| C7 | 0.9367 (3) | 0.4959 (2) | 0.41461 (8) | 0.0437 (7) |
| H7 | 0.895479 | 0.425757 | 0.412776 | 0.052* |
| C8 | 1.0349 (3) | 0.5387 (2) | 0.38367 (7) | 0.0448 (7) |
| C9 | 1.0739 (4) | 0.4727 (3) | 0.35318 (8) | 0.0598 (9) |
| H9 | 1.034625 | 0.401912 | 0.352506 | 0.072* |
| C10 | 1.1702 (4) | 0.5104 (4) | 0.32380 (10) | 0.0762 (12) |
| H10 | 1.196917 | 0.465278 | 0.30305 | 0.091* |
| C11 | 1.2265 (4) | 0.6119 (4) | 0.32461 (10) | 0.0784 (13) |
| H11 | 1.292833 | 0.637168 | 0.304462 | 0.094* |
| C12 | 1.1876 (4) | 0.6785 (3) | 0.35458 (10) | 0.0699 (10) |
| H12 | 1.226805 | 0.749376 | 0.354901 | 0.084* |
| C13 | 1.0912 (4) | 0.6418 (3) | 0.38424 (8) | 0.0531 (8) |
| H13 | 1.064151 | 0.687461 | 0.404813 | 0.064* |
| C14 | 0.1871 (3) | 0.2487 (2) | 0.68575 (7) | 0.0424 (6) |
| C15 | 0.1297 (4) | 0.3125 (3) | 0.71500 (9) | 0.0520 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0320 (4) | 0.2677 (3) | 0.74297 (9) | 0.0638 (10) |
| H16 | −0.008676 | 0.31095 | 0.762954 | 0.077* |
| C17 | −0.0060 (4) | 0.1629 (3) | 0.74210 (9) | 0.0691 (10) |
| H17 | −0.074024 | 0.133686 | 0.76121 | 0.083* |
| C18 | 0.0541 (4) | 0.0986 (3) | 0.71351 (10) | 0.0668 (9) |
| H18 | 0.029703 | 0.024977 | 0.713283 | 0.08* |
| C19 | 0.1492 (4) | 0.1418 (2) | 0.68541 (8) | 0.0505 (7) |
| H19 | 0.189336 | 0.097864 | 0.665554 | 0.061* |
| C20 | 0.2852 (4) | 0.2927 (3) | 0.65401 (10) | 0.0653 (10) |
| N1 | 0.5027 (4) | 0.4214 (5) | 0.59222 (10) | 0.1094 (18) |
| H1 | 0.443286 | 0.395616 | 0.610853 | 0.131* |
| N2 | 0.8141 (3) | 0.50176 (18) | 0.47205 (6) | 0.0404 (5) |
| N3 | 0.9055 (3) | 0.55147 (18) | 0.44407 (6) | 0.0413 (5) |
| O1 | 0.8334 (3) | 0.64760 (16) | 0.50919 (6) | 0.0609 (6) |
| O2 | 0.3379 (3) | 0.3871 (2) | 0.65791 (8) | 0.0797 (8) |
| O1W | 0.1945 (3) | 0.20372 (18) | 0.55182 (8) | 0.0625 (7) |
| O3 | 0.3152 (3) | 0.2389 (2) | 0.62522 (7) | 0.0840 (9) |
| O4a | 0.1610 (6) | 0.4098 (4) | 0.72475 (14) | 0.0653 (12) |
| H4Aa | 0.220417 | 0.437932 | 0.70818 | 0.098* |
| H2A | 0.775 (4) | 0.432 (3) | 0.4672 (8) | 0.052 (8)* |
| H1WA | 0.164 (7) | 0.261 (4) | 0.5405 (14) | 0.119 (18)* |
| H1WB | 0.234 (8) | 0.237 (5) | 0.577 (2) | 0.19 (3)* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.5.
2 Experimental details
The C-bound hydrogen atoms were located in the difference map, then positioned geometrically. They were then allowed to ride on their respective parent atoms with thermal displacement parameters 1.2 times of the parent C atom. The coordinates and isotropic displacement parameters of the two N-bound and O-bound H atoms, namely H1 and H4A, were constrained to their parent atoms using the riding model approximation appropriate for their respective geometries. The other O and N-bound hydrogen atoms were allowed to refine freely. Diagrams and publication material were generated using ORTEP-3, 4 WinGX 5 and PLATON. 6
3 Comment
Isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), commonly known as isoniazid is an anti-mycobacterial agent that is primarily used as a tuberculostatic drug and remains the first choice in the treatment of latent tuberculosis (TB). 7 Isoniazid has a simple structure and contains two essential components, namely the hydrazide group and a pyridine ring, both which are required for anti-mycobacterial activity. 8 This drug is commonly used to treat pulmonary and extra pulmonary TB infections and is also utilized as a chemoprophylaxis therapy to prevent or delay the appearance of microbial resistance. 9 Many derivatives of the compound isoniazid have been synthesized over the years to counteract resistance of the mycobacterium species. These include the design of new compound derivatives such as isonicotinoylhydrazone with an intention to improve pharma-toxicological profiles of the drug towards the organism. 10 However, in most cases they demonstrate low solubility. In such instances, it is more suitable to use a multicomponent form such as a co-crystal or salt as these tend to be more soluble than the crystal form of an active pharmaceutical ingredient. 11 Co-crystallization or ionization of these derivatives is also likely to increase bioavailability of the drug. 12 The use of benzaldehyde as a solvent is commonly avoided as it is known to autoxidize at room temperatures to form benzoic acid. 13 Although this reaction is known to be instigated by a catalyst, it can also occur spontaneously over a long period of time. 14 However, in this case, benzaldehyde was used as very slow evaporation was desired.
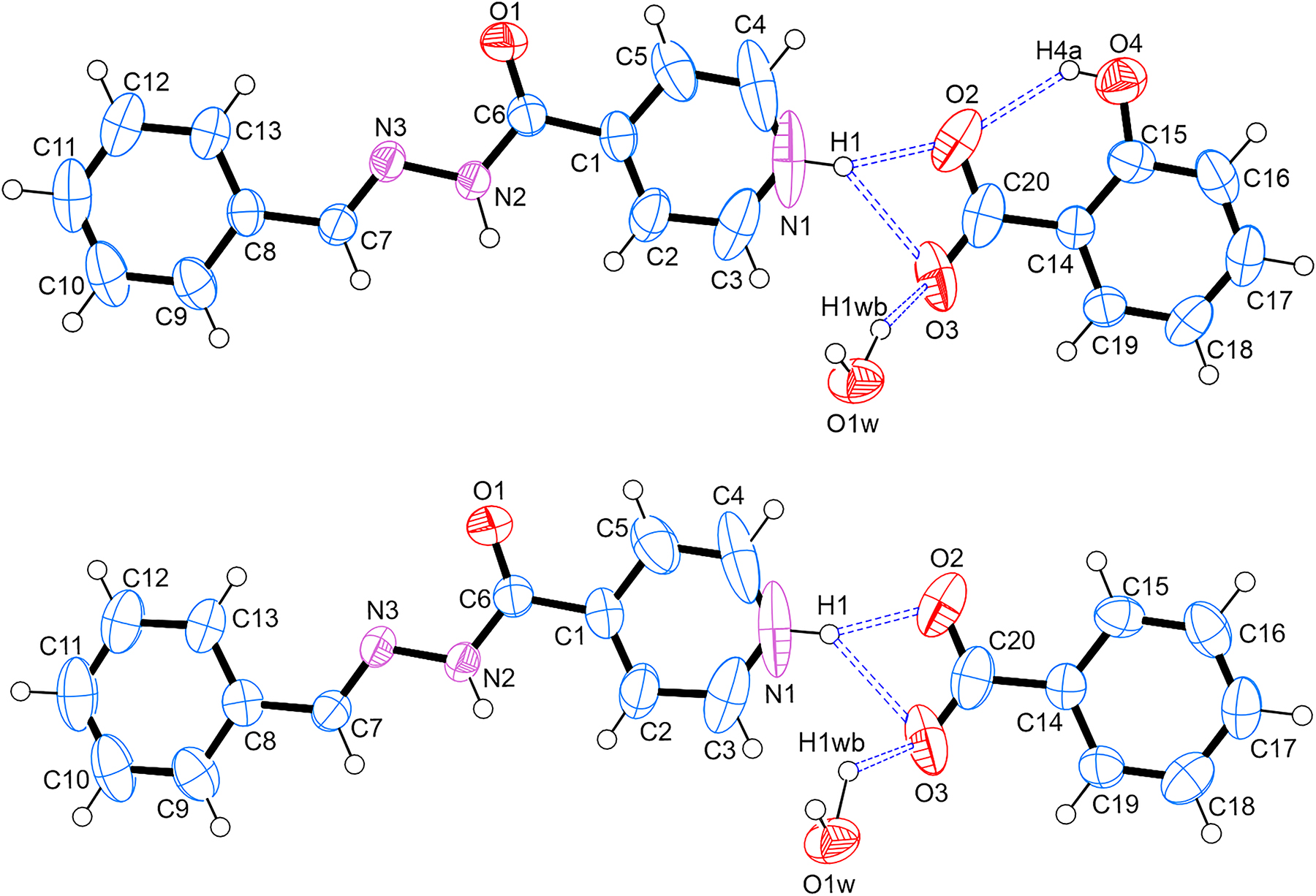
The crystal structure of the title structure crystallised in the orthorhombic Pbca space group and the asymmetric unit contains one molecule of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium, one molecule of water, and two anions, namely 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate with 50:50 occupancy (see the Figure). The benzoate anion is produced in situ via the autoxidation of the benzaldehyde solvent. In the asymmetric unit, the H1 atom of the carbohydrazide moiety is bonded via bifurcated hydrogen bonds to the two oxygen atoms of the carboxylate functional group of the 2-hydroxybenzoate or the benzoate anion, respectively. The O3 oxygen on the anion is also bifurcated and hydrogen bonded to both H1 as described above as well as to the H1wb atom on the water molecule. Each water molecule in the unit cell is connected to two carbohydrazide moieties. The first carbohydrazide moiety is hydrogen bonded to the water through the N2–H2⋯O1 hydrogen bond. The second carbohydrazide moiety has a bifurcated hydrogen bond between H1wa on the water molecule and O1 and N3 on the moiety. Furthermore, the second hydrogen atom on the water molecule, H1wb, is bonded to the O3 atom on the 2-hydroxybenzoate or benzoate molecule respectively. The salt is therefore stabilised by the water molecule in the crystal. The packing of the crystal contains an anticlockwise twofold screw rotation along the b-axis, resulting in a three-dimensional (3D) network in the crystal structure.
-
Author contributions: The author has accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) Thuthuka Grant Number 118127 (Dr IB Setshedi) as well as the National Research Foundation (NRF) “Competitive Support for Unrated Researchers” grant Number CSUR23042597072 (Dr. MG Smith).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The author declares no conflict of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX3. SAINT–Plus and XPREP; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2016.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: An Update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Search in Google Scholar
5. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX Suite for Small-Molecule Single-Crystal Crystallography. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 837–838; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889899006020.Search in Google Scholar
6. Spek, A. L. Structure Validation in Chemical Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155; https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Search in Google Scholar
7. Denholm, J. T.; McBryde, E. S.; Einsen, D. P.; Penington, J. S.; Chen, C.; Street, A. C. Effect of Isoniazid Preventive Therapy on Tuberculosis Incidence and Associated Risk Factors Among HIV Infected Adults in Tanzania: a Retrospective Cohort Study. Drug. Healthc. Patient Saf. 2014, 6, 145–149; https://doi.org/10.2147/dhps.s68837.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Jena, L.; Waghmare, P.; Kashikar, S.; Kumar, S.; Harinath, B. C. Computational Approach to Understanding the Mechanism of Action of Isoniazid, an Anti-TB Drug. Int. J. Mycobact. 2014, 3, 276–282; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmyco.2014.08.003.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Mahmoud, B. G.; Khairy, M.; Rashwan, F. A.; Banks, C. E. Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Acetaminophen and Isoniazid (Hepatotoxicity-Related Drugs) Utilizing Bismuth Oxide Nanorod Modified Screen-Printed Electrochemical Sensing Platforms. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2170–2178; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b05130.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Dragostin, I.; Dragostin, O. M.; Samal, S. K.; Dash, S.; Tatia, R.; Dragan, M.; Confederat, L.; Ghiciuc, C. M.; Diculencu, D.; Lupusoru, C. E.; Zamfir, C. L. New Isoniazid Derivatives with Improved Pharmaco-toxicological Profile: Obtaining, Characterization and Biological Evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104974; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2019.104974.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Aitipamula, S.; Banerjee, R.; Bansal, A. K.; Biradha, K.; Cheney, M. L.; Choudhury, A. R.; Desiraju, G. R.; Dikundwar, A. G.; Dubey, R.; Duggirala, N.; Ghogale, P. P.; Ghosh, S.; Goswami, P. K.; Goud, N. R.; Jetti, R. R. K. R.; Karpinski, P.; Kaushik, P.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, V.; Moulton, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Mukherjee, G.; Myerson, A. S.; Puri, V.; Ramanan, A.; Rajamannar, T.; Reddy, C. M.; Rodriguez–Hornedo, N.; Rogers, R. D.; Row, T. N. G.; Sanphui, P.; Shan, N.; Shete, G.; Singh, A.; Sun, C. C.; Swift, J. A.; Thaimattam, R.; Thakur, T. S.; Kumar, T. R.; Thomas, S. P.; Tothadi, S.; Vangala, V. R.; Variankaval, N.; Vishweshwar, P.; Weyna, D. R.; Zaworotko, M. J. Polymorphs, Salts, and Cocrystals: What’s in a Name? Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 2147–2152; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg3002948.Search in Google Scholar
12. Smith, M. G.; Forbes, R. P.; Lemmerer, A. Covalent-assisted Supramolecular Synthesis: Masking of Amides in Co-crystal Synthesis Using Benzophenone Derivatives. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 3813–3821; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5b00462.Search in Google Scholar
13. Meenakshisundaram, S.; Nowicka, E.; Carter, E.; Murphy, D. M.; Knight, D. W.; Bethell, D.; Hutchings, G. J. The Benzaldehyde Oxidation Paradox Explained by the Interception of Peroxy Radical by Benzyl Alcohol. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3332; https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4332.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Setshedi, I. B.; Lemmerer, A.; Smith, M. G.. Co-crystallization of N′-benzylidenepyridine-4-carbohydrazide and Benzoic Acid via Autoxidation of Benzaldehyde. Acta Crystallogr. 2023, E79, 682–685.10.1107/S2056989023005698Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 3-nitrophenol-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (1/1), C12H9N3O3Se
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(hydroxido)-{μ-[2-(hydroxy)-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato]}-{2-hydroxy-5-[(4-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]benzoato}-(1,10-phenanthroline)-diterbium hydrate, C38H27.4N8O12.2Tb
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-3-fluoro-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ3 O:O′:N)cadmium(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C21H17CdF2N7O5
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-N-(pyridin-2-yl)benzamide, C12H11N3O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(pyridin-2-yl)-2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C18H14N4O
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl (R)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18ClFO3
- Crystal structure of [1-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid]-(methylsulfinyl)methane, C15H16N2O6S
- The crystal structure of 2-ethyl-1,1-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole, C16H17N
- The crystal structure of (Z)-5-amino-N ′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)phenyl)imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2 O:O′)-bis[(4′-phenyl-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κ1 N)dicopper(II)], C25H21CuN3O4
- Crystal structure of poly(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ 3 O,O′:O′)-(methanol-κO)cadmium(II), C11H10O5S2Cd
- The crystal structure of dichloridobis[4′-(p-methoxylphenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-κN] zinc(II), C44H34Cl2N6O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-carboxyethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- Crystal structure of 1,1′,1″-(nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(3-(4-(((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)urea), C45H47N13O4
- Crystal structure of a (E)-4-bromo-N-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxybenzylidene) benzenaminium acetate ─ 4-bromoaniline (1/1)
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(iminobis(methylene))bis(benzimidazolium) bis(p-toluenesulfonate), C30H31N5O6S2
- The crystal structure of alogliptinium meta-chlorobenzoate
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl 2-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19BrO3
- The hydrated double salt structure of (E)-4-(2-benzylidenehydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium cation with 2-hydroxybenzoate and benzoate anions
- Crystal structure of (R)(R)-5-chloro-3-((S,1E,3E)-3,5-dimethyl-hepta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-7-methyl-6,8-dioxo-2,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-yl acetate, C21H24ClNO4
- The crystal structure of bis(3-oxo-1,3-diphenylprop-1-en-1-olato-κ 2 O:O′)-bis(1,4-dioxane-κ 1 O)nickel(II), C38H38O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ1 N)(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κ2 O,O′) cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C12H14N2O7Cd
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-phenyl-5-(((1-(2,4,6-tribromophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)thio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridine, C22H14Br3N7S
- The crystal structure of N-benzylquinoline-2-carbothioamide, C17H14N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(3-isopropylphenyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride dihydrate, C28H30N2⋅2Cl⋅2H2O
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(cyanophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O4
- Crystal structure of (4R,10S)-6-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-4,10-dimethyl-1,2,3,5-hexahydro-6,10-epoxyazulen-9-one, C15H22O3
- The crystal structure of (E)-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)aminophenyl)arsonic acid, C14H14AsNO5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 2-2-aminoisophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″:O″′)-(N-methylpyrrolidone κ1O)-dioxido-uranium(VI)], C13H14N2O7U
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal isonicotinamide · terephthalic acid, C8H6O4·2(C6H6N2O)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolylthio)but-2-en-1-one, C17H16OS
- The crystal structure of 4,5-bis((Z)-chloro(hydroxyimino)methyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)ethane-1,2-dione. C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C16H12ClFO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (3-(dimethoxymethyl)-5-methoxy-1H-indol-1-yl)(5-fluoro-2-iodophenyl)methanone, C19H17FINO4
- Crystal structure of tetrachlorido-bis(1-[(1H-triazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ2 N:N′)dicopper, C36H32Cu2N24Cl4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2,3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-1-yl)anilin, C30H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one–N,N-dimethylformamide(1/1), C18H17NO5
- The crystal structure of bis(μ 2-biphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylato)-diaqua-bis(nitrato)-bis(2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine)dineodymium(III), C46H32I2N8Nd2O16
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N ′-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)benzohydrazide, C20H16ClN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6,8-dimethoxy-4-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one, C23H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-((3-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-6-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-4(5H)-yl) methyl)-4-fluorobenzonitrile benzoate monohydrate, C24H27FN6O4
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylato-κ 3 N,O,O)copper(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cu
- Crystal structure of (((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κ 2 N,O)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ 2 N,N′)cobalt(II) tetrahydrate, C32H30ClCoN5O8S
- Crystal structure of (((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-β-alaninato-κO)bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N, N′)copper(II) 3-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C35H29CuN7O11S2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenoxybenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C27H24O4
- 6-(2′,3′-Dihydroxy-3′-methylbutyl)-7-methoxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-en-1″-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-4′-onato-κ3N)palladium(II) methanol solvate
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of (1E,3E,5E)-1,6-bis(4-(pentyloxy)phenyl)hexa-1,3,5-triene, C28H36O2
- The crystal structure of tris(2-bromo-4-methylphenyl)amine, C21H18Br3N
- The crystal structure of 3-(2,5-dimethylanilino)-1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione, C21H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl (μ2-indole-2-carboxylato κ2 O:O′)tris(triphenylarsine-κAs)dirhodium(I) acetone solvate, C68H56As3NO5Rh2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-formylphenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C14H11ClO4S
- Crystal structure of 4-iodobenzyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanoate, C21H19IO3


