Abstract
C27H26N9O10Pr, monoclinic, P21/c, a = 13.2280(12) Å, b = 5.5628(5) Å, c = 41.140(3) Å, β = 105.109(2)°, V = 2922.6(4) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt (F) = 0.0426, wRref (F 2) = 0.0803, T = 298.15 K.
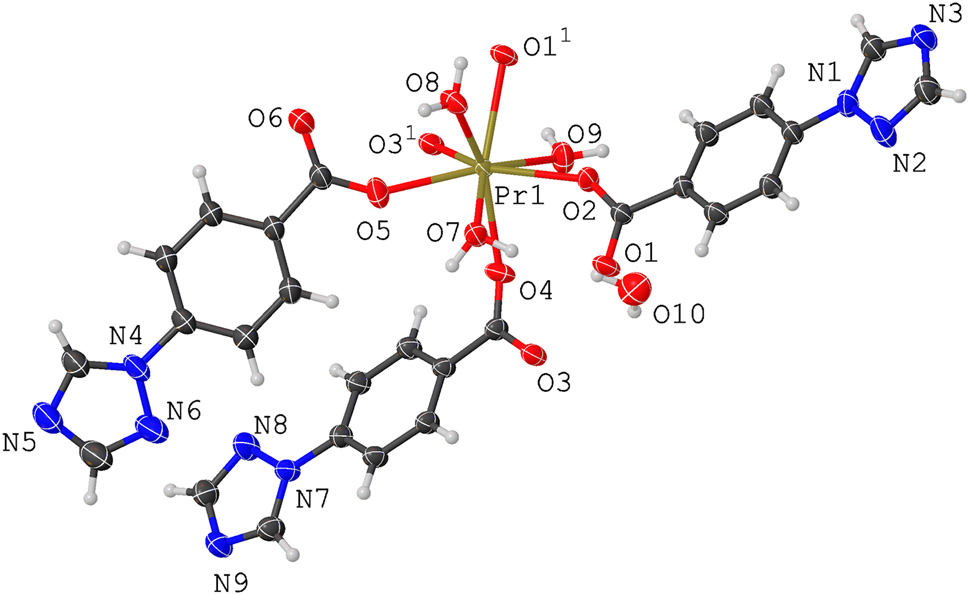
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless plate |
| Size: | 0.28 × 0.21 × 0.13 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.74 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker SMART CCD 6000, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.3°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 14,265, 5339, 0.051 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 4110 |
| N(param)refined: | 436 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], OLEX2 [2], SHELX [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1.2889 (4) | −0.2360 (11) | 0.27171 (15) | 0.0424 (12) |
| H1 | 1.338578 | −0.351155 | 0.270342 | 0.051* |
| C2 | 1.2109 (4) | 0.0914 (10) | 0.26737 (13) | 0.0373 (10) |
| H2 | 1.190663 | 0.250573 | 0.262798 | 0.045* |
| C3 | 1.0689 (4) | −0.0345 (9) | 0.29417 (12) | 0.0295 (9) |
| C4 | 1.0127 (4) | 0.1791 (10) | 0.28720 (13) | 0.0318 (9) |
| H4 | 1.032384 | 0.298230 | 0.274208 | 0.038* |
| C5 | 0.9266 (4) | 0.2099 (9) | 0.30013 (13) | 0.0303 (9) |
| H5 | 0.889056 | 0.352904 | 0.295959 | 0.036* |
| C6 | 0.8954 (4) | 0.0339 (9) | 0.31898 (12) | 0.0263 (9) |
| C7 | 0.9503 (4) | −0.1802 (9) | 0.32431 (13) | 0.0305 (9) |
| H7 | 0.928635 | −0.303008 | 0.336288 | 0.037* |
| C8 | 1.0375 (4) | −0.2134 (9) | 0.31194 (13) | 0.0304 (9) |
| H8 | 1.074359 | −0.357476 | 0.315788 | 0.036* |
| C9 | 0.8065 (4) | 0.0782 (10) | 0.33473 (12) | 0.0261 (9) |
| C10 | −0.0046 (4) | 0.2237 (10) | 0.40425 (14) | 0.0397 (12) |
| H10 | −0.055004 | 0.327807 | 0.408309 | 0.048* |
| C11 | 0.0791 (4) | −0.0914 (10) | 0.40230 (13) | 0.0365 (10) |
| H11 | 0.101178 | −0.250738 | 0.403678 | 0.044* |
| C12 | 0.2169 (4) | 0.0841 (9) | 0.37810 (13) | 0.0291 (8) |
| C13 | 0.2806 (4) | −0.1172 (9) | 0.38370 (13) | 0.0296 (9) |
| H13 | 0.265389 | −0.247623 | 0.395748 | 0.036* |
| C14 | 0.3680 (4) | −0.1193 (8) | 0.37087 (13) | 0.0282 (9) |
| H14 | 0.409553 | −0.256432 | 0.373580 | 0.034* |
| C15 | 0.3947 (3) | 0.0763 (9) | 0.35421 (12) | 0.0249 (9) |
| C16 | 0.3286 (4) | 0.2749 (9) | 0.34849 (13) | 0.0296 (9) |
| H16 | 0.344451 | 0.406806 | 0.336831 | 0.036* |
| C17 | 0.2394 (4) | 0.2773 (9) | 0.36007 (13) | 0.0301 (8) |
| H17 | 0.194498 | 0.408858 | 0.355712 | 0.036* |
| C18 | 0.4951 (4) | 0.0743 (10) | 0.34392 (12) | 0.0262 (9) |
| C19 | 0.1400 (5) | 0.2677 (13) | 0.50104 (17) | 0.0619 (13) |
| H19 | 0.088881 | 0.151928 | 0.500450 | 0.074* |
| C20 | 0.2391 (4) | 0.5537 (12) | 0.51736 (14) | 0.0471 (10) |
| H20 | 0.275507 | 0.680830 | 0.529789 | 0.056* |
| C21 | 0.3358 (4) | 0.5366 (11) | 0.47282 (13) | 0.0386 (9) |
| C22 | 0.3665 (4) | 0.3818 (10) | 0.45126 (13) | 0.0374 (9) |
| H22 | 0.333842 | 0.233493 | 0.446132 | 0.045* |
| C23 | 0.4472 (4) | 0.4488 (10) | 0.43710 (13) | 0.0355 (9) |
| H23 | 0.468603 | 0.343404 | 0.422657 | 0.043* |
| C24 | 0.4957 (4) | 0.6687 (10) | 0.44417 (13) | 0.0333 (9) |
| C25 | 0.4616 (4) | 0.8225 (10) | 0.46556 (13) | 0.0382 (10) |
| H25 | 0.493393 | 0.972128 | 0.470380 | 0.046* |
| C26 | 0.3823 (4) | 0.7607 (10) | 0.47989 (14) | 0.0397 (9) |
| H26 | 0.360288 | 0.867185 | 0.494061 | 0.048* |
| C27 | 0.5785 (4) | 0.7538 (10) | 0.42801 (14) | 0.0337 (10) |
| N1 | 1.1601 (3) | −0.0668 (8) | 0.28205 (10) | 0.0339 (10) |
| N2 | 1.2105 (4) | −0.2832 (9) | 0.28479 (12) | 0.0447 (13) |
| N3 | 1.2927 (4) | −0.0075 (8) | 0.26031 (13) | 0.0481 (14) |
| N4 | 0.2573 (3) | 0.4679 (9) | 0.48903 (11) | 0.0456 (11) |
| N5 | 0.1632 (4) | 0.4347 (11) | 0.52531 (13) | 0.0574 (12) |
| N6 | 0.1936 (4) | 0.2751 (11) | 0.47780 (14) | 0.0649 (13) |
| N7 | 0.1275 (3) | 0.0899 (7) | 0.39120 (10) | 0.0293 (10) |
| N8 | 0.0726 (3) | 0.2979 (8) | 0.39129 (12) | 0.0417 (12) |
| N9 | −0.0042 (3) | −0.0131 (8) | 0.41102 (12) | 0.0442 (13) |
| O1 | 0.7716 (3) | −0.0958 (6) | 0.34764 (9) | 0.0356 (9) |
| O2 | 0.7762 (3) | 0.2935 (6) | 0.33534 (8) | 0.0312 (9) |
| O3 | 0.5393 (3) | −0.1237 (6) | 0.34317 (9) | 0.0327 (9) |
| O4 | 0.5300 (2) | 0.2743 (6) | 0.33683 (9) | 0.0342 (9) |
| O5 | 0.5998 (3) | 0.6152 (7) | 0.40617 (9) | 0.0389 (10) |
| O6 | 0.6198 (3) | 0.9533 (7) | 0.43624 (10) | 0.0498 (10) |
| O7 | 0.7178 (3) | 0.2043 (6) | 0.39729 (9) | 0.0360 (9) |
| H7A | 0.664551 | 0.155846 | 0.403412 | 0.054* |
| H7B | 0.733424 | 0.087091 | 0.386223 | 0.054* |
| O8 | 0.8248 (3) | 0.6583 (7) | 0.40586 (8) | 0.0357 (9) |
| H8A | 0.830941 | 0.634587 | 0.426694 | 0.054* |
| H8B | 0.871877 | 0.761406 | 0.405417 | 0.054* |
| O9 | 0.6196 (3) | 0.6184 (7) | 0.29602 (9) | 0.0405 (10) |
| H9A | 0.597624 | 0.761949 | 0.291242 | 0.061* |
| H9B | 0.649 (4) | 0.582 (9) | 0.2803 (11) | 0.08 (2)* |
| O10 | 0.5584 (3) | 0.0738 (8) | 0.27251 (10) | 0.0521 (11) |
| H10A | 0.496423 | 0.058755 | 0.259994 | 0.078* |
| H10B | 0.552237 | 0.167802 | 0.288111 | 0.078* |
| Pr1 | 0.66827 (2) | 0.56140 (5) | 0.35920 (2) | 0.02277 (9) |
1 Source of materials
The 4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid (Htba) was obtained from Jinan Henghua Technology Co., Ltd. Other chemicals were obtained from Shanghai Aladdin Bio–Chem Technology Co., LTD. Pr2O3 (0.0240 g, 0.1 mmol), Htba (0.0189 g, 0.1 mmol), distilled H2O (10 mL) and five drops of concentrated HCl were mixed in a 20 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel reactor and heated to 140 °C for 72 h. The reactor was cooled to room temperature slowly. Clear light colourless plate crystals of the title complex were obtained, yielding 51% (based on the ligand).
2 Experimental details
The crystal structure was solved by SHELXT program with intrinsic phasing and refined by SHELXT program. All the H-atoms were generated geometrically with isotropic thermal factors. The H-atoms (H9A and H9B) of the free water were restrained. The bond lengths of O9–H9A and O9–H9B were fixed to 0.85 Å with command DFIX and the distance of H9A–H9B was fixed to 1.344 Å with command DANG.
3 Comment
As a rigid carboxylate ligand containing triazole heterocycle, 4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid (Htba), has been applied to build metal complexes with various ions [5], [6], [7], [8]. However, to the best of our knowledge, only limited lanthanide metal (Nd3+/Sm3+/Tb3+) complexes were reported [9, 10]. To enrich the Ln-series of the structure based on Htba ligand, the title 1D Pr(III)-complex was synthesized.
The asymmetric unit contains one Pr(III) ion, three deprotonated Htba ligands, three coordinated water molecules and one free water molecule. The Pr(III) ion is eight-coordinated with five carboxyl oxygen atoms (O1+x, 1 + y, +z , O2, O3+x, 1 + y, +z , O4, O5) from five different ligands and three oxygen atoms (O7, O8, O9) from three different coordinated water molecules. It is worth noting that even though the Htba ligand contains two potential N-coordination sites, no nitrogen participated in the self-assembly process with Pr(III) ion. The bond distances of Pr–O are in the regular range of 2.357(3)–2.529(4) Å, similar to the other Pr(III)-complexes with analogical coordination modes [11, 12]. The Htba ligands in the crystal structure adopt two kinds of connection modes: monodentate terminal mode or bidentate bridging mode. Interestingly, two Pr(III) ions, two bidentate bridging Htba ligands and one monodentate terminal Htba ligand formed a Pr2(tba)3 binuclear unit. These units are interconnected and generated a 1D linear structure. The 1D structures are further expended by O—H ⃛ O and N—H ⃛ O hydrogen bonding interactions and the π-π stacking interactions between the benzene rings and heterocyclic rings, centroid-centroid distance range: 3.750(3)–3.814(3) Å, and finally, constituted a 3D network.
Funding source: Undergraduate Teaching Reform Project of Shandong Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: Z2022072
Acknowledgements
Special thanks are given to Dr. Yu-Pei Xia for his kind assistance with the structure discussion of the complex.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by the Undergraduate Teaching Reform Project of Shandong Province (No. Z2022072).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Wang, D.-W., Wang, T., Du, L., Zhou, J., Yan, T., Zhao, Q.-H. Four supramolecular transition metal(II) complexes based on triazole-benzoic acid derivatives: crystal structure, hirshfeld surface analysis, and spectroscopic and thermal properties. Struct. Chem. 2018, 29, 1013–1023; https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-018-1084-6.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Liu, M. M., Bi, Y. L., Dang, Q. Q., Zhang, X. M. Reversible single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformation from a mononuclear complex to a fourfold interpenetrated MOF with selective adsorption of CO2. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 19796–19799; https://doi.org/10.1039/c5dt03570h.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Gao, X., Zhang, C.-L., Fu, A.-Y. Crystal structure of di-μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-bis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)disodium(I), C18H24N6Na2O10. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2018, 233, 965–966; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2017-0225.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Wang, Y.-L., Fu, J.-H., Wei, J.-J., Xu, X., Li, X.-F., Liu, Q.-Y. Noncentrosymmetric organic solid and its zinc coordination polymer with diamonded network prepared from an ionothermal reaction: syntheses, crystal structures, and second-order nonlinear optics properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 4663–4668; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg300889x.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Zhong, J.-X., Zhang, H.-H., Gao, X., Ou, Y.-C., Wu, J.-Z., Cai, Y.-P. Crystal structures and luminescent properties modulated by auxiliary ligands for series of lanthanide coordination polymers with triazole-benzoic acid. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2016, 71, 1–4; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2016.06.024.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Fang, Z.-L., Nie, Q.-X., Zheng, S.-R., Zhong, Y., Xiong, S. Two lanthanide coordination polymers derived from 4-(1H-1,2,4-trizol-1-yl) benzoic acid: synthesis, crystal structures, and fluorescence. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 30, 1503–1510.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Peter, C. J., Cameron, J. K., Lu, W.-M., Brian, W. S., Allan, H. W. Structural systematics of rare earth complexes. XI (‘Maximally’) hydrated rare earth(III) trifluoro- and trichloro-acetates. Aust. J. Chem. 1999, 52, 459–479.10.1071/CH98042Suche in Google Scholar
12. Bone, S. P., Sowerby, D. B., Verma, R. D. Crystal structure of tetrakis-μ-trifluoroacetato-bis[triaqua(trifluoroacetato) praseodymium(III)]. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1978, 1544–1548; https://doi.org/10.1039/dt9780001544.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2

