Abstract
C14H11Cl3N2O, orthorhombic, P212121 (no. 19), a = 8.3600(4) Å, b = 12.0085(8) Å, c = 14.3665(6) Å, V = 1442.27(13) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt (F) = 0.0460, wRref (F 2) = 0.0944, T = 293 K.
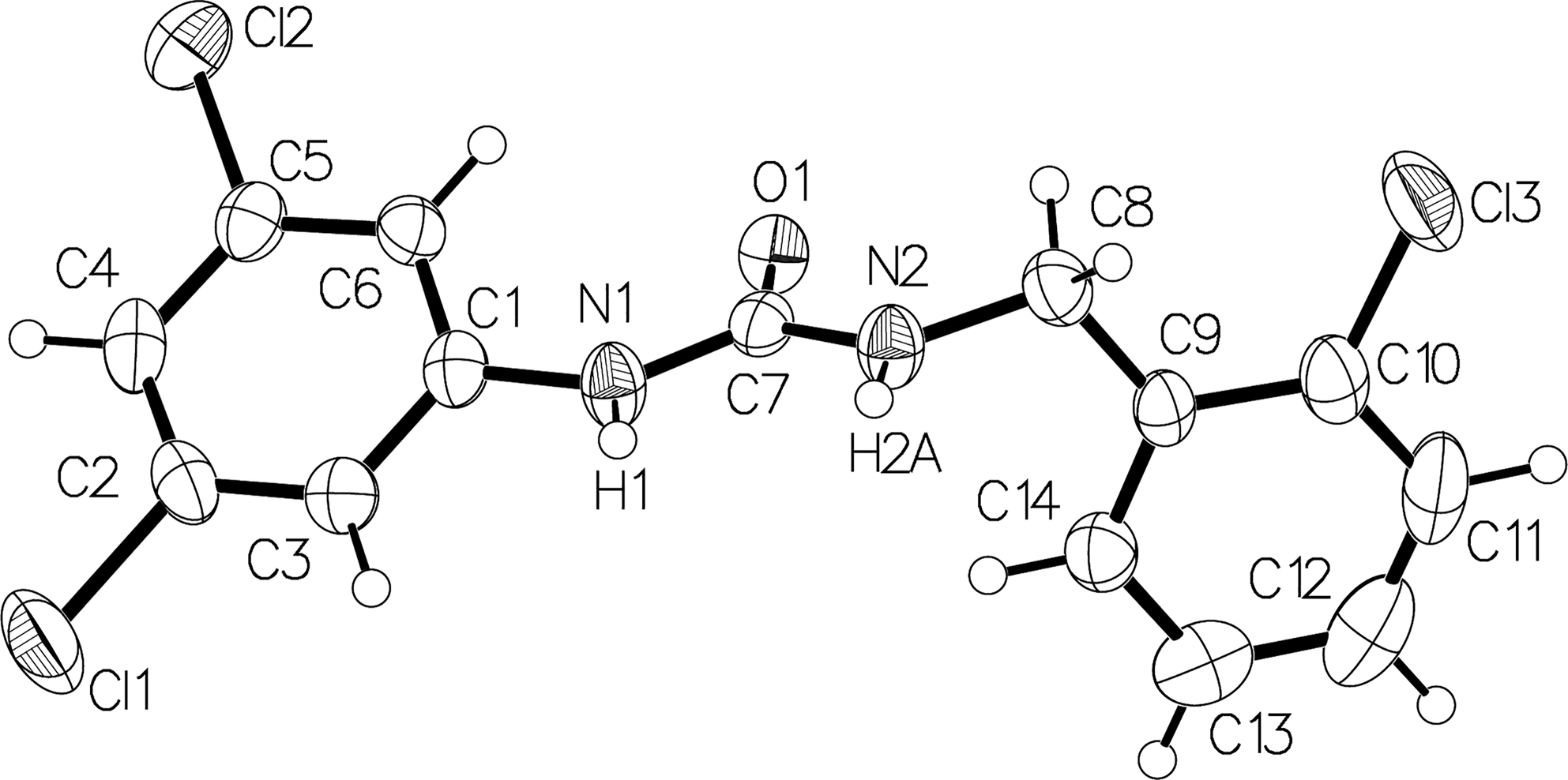
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.26 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.63 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 29.4°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 4927, 3047, 0.022 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2492 |
| N(param)refined: | 181 |
| Programs: | CrysAlis pro [1], SHELX [2, 3], Olex2 [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.4442 (4) | 0.6117 (3) | 0.3845 (2) | 0.0315 (8) |
| C2 | 0.4787 (4) | 0.6263 (3) | 0.2910 (3) | 0.0361 (9) |
| H2 | 0.540130 | 0.686415 | 0.271430 | 0.043* |
| C3 | 0.4210 (4) | 0.5507 (4) | 0.2276 (2) | 0.0398 (9) |
| C4 | 0.3314 (4) | 0.4589 (3) | 0.2538 (3) | 0.0424 (9) |
| H4 | 0.292799 | 0.408309 | 0.210297 | 0.051* |
| C5 | 0.3021 (4) | 0.4463 (3) | 0.3477 (2) | 0.0365 (8) |
| C6 | 0.3555 (4) | 0.5210 (3) | 0.4139 (2) | 0.0345 (8) |
| H6 | 0.332361 | 0.510622 | 0.476584 | 0.041* |
| C7 | 0.4461 (4) | 0.7219 (3) | 0.5305 (2) | 0.0292 (8) |
| C8 | 0.4978 (4) | 0.8333 (3) | 0.6707 (2) | 0.0377 (9) |
| H8A | 0.595255 | 0.845309 | 0.705951 | 0.045* |
| H8B | 0.435791 | 0.777121 | 0.703027 | 0.045* |
| C9 | 0.4038 (4) | 0.9400 (3) | 0.6695 (2) | 0.0326 (8) |
| C10 | 0.3756 (4) | 0.9994 (4) | 0.7512 (3) | 0.0450 (10) |
| C11 | 0.2898 (5) | 1.0976 (4) | 0.7520 (4) | 0.0615 (13) |
| H11 | 0.271136 | 1.134634 | 0.807874 | 0.074* |
| C12 | 0.2324 (5) | 1.1403 (4) | 0.6703 (4) | 0.0656 (14) |
| H12 | 0.176199 | 1.207092 | 0.670272 | 0.079* |
| C13 | 0.2578 (5) | 1.0847 (4) | 0.5885 (3) | 0.0574 (12) |
| H13 | 0.218513 | 1.113586 | 0.533000 | 0.069* |
| C14 | 0.3423 (4) | 0.9849 (3) | 0.5884 (3) | 0.0408 (9) |
| H14 | 0.357759 | 0.947533 | 0.532476 | 0.049* |
| Cl1 | 0.46236 (15) | 0.56963 (12) | 0.11033 (7) | 0.0693 (4) |
| Cl2 | 0.19757 (14) | 0.32855 (9) | 0.38288 (8) | 0.0596 (3) |
| Cl3 | 0.45331 (16) | 0.94840 (12) | 0.85574 (7) | 0.0698 (4) |
| N1 | 0.5093 (3) | 0.6892 (3) | 0.4472 (2) | 0.0370 (8) |
| H1 | 0.598534 | 0.719357 | 0.431414 | 0.044* |
| N2 | 0.5402 (3) | 0.7909 (2) | 0.5797 (2) | 0.0369 (7) |
| H2A | 0.630185 | 0.810793 | 0.555855 | 0.044* |
| O1 | 0.3121 (2) | 0.6907 (2) | 0.55759 (16) | 0.0337 (6) |
Source of materials
In a typical process, 1,3-dichloro-5-isocyanatobenzene (188 mg 1 mmol) was dissolved in 10 mL dichloromethane under vigorous stirring for 20 min. Then, 2-chlorobenzylamine (142 mg, 1 mmol) was added to the resultant mixture, which was further stirred for 24 h at room temperature. After the natural volatilization of the dichloromethane solvent, the white powder product of the title compound was obtained. Fifty milligram of the obtained white powder product was dissolved in 5 mL ethanol/trichloromethane (v/v = 1:1) followed by a 5 min ultrasonic dispersion at room temperature. Subsequently, after slow volatilization of partial solvent at room temperature, colorless single-crystal products were obtained.
Experimental details
The structure was solved with the ShelXT [2] program and refined with the ShelXL [3] software package in Olex2 [4]. All hydrogen atoms were placed in idealized positions and refined as riding atoms. Their Uiso values were set to 1.2 Ueq of the parent atoms.
Comment
The urea derivatives frequently crystallize into structures through the self-assembly of intermolecular hydrogen bonds between urea groups, which is a crucial crystal design element [5]. Additionally, diphenylurea has conformational polymorphism because of the low rotation energy around the central amide bond. On the one hand, the one-dimensional chains were formed via self-assembly of N–H⋯O hydrogen bonds in the diphenylurea derivative structures. For instance, 1,3-diphenylurea [6] and 1,3-bis (m–X-phenyl) urea [7], where X = chlorine, bromine, iodine, or methyl, exhibited one-dimensional urea chains. On the other hand, some intermolecular hydrogen bonds were observed in 1,3-bis (m-nitrophenyl) urea [8, 9], leading to various polymorphs and hydrates. Due to the vital application prospect in drug development and the interesting crystal structures, there are many crystal structures of diphenylurea derivatives reported [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16].
Three Cl atoms replaced three H atoms in the two phenyl groups of the title compound (see the figure). The bond length of these three C–Cl bonds is 1.747 (5) Å of the C10–Cl3 bond, 1.737 (4) Å of the C5–Cl2 bond, and 1.735 (4) Å of C3–Cl1 bond, respectively. The dihedral angles of C13–C11–C10–Cl3, C2–C6–C5–Cl2, and C1–C4–C3–Cl1 are 178.6 (3)°, 177.2 (3)°, and 179.9 (4)° respectively, which are all close to 180°, indicating these Cl groups are almost in the same plane of the corresponding phenyl group. These parameters agree with the literature [17, 18]. The dihedral angle of the chlorophenyl plane and the urea group plane is 88.8°, and the dihedral angle of the dichlorophenyl plane and the urea group plane is 32.5°. These torsions of these two phenyl groups are more evident than that of 1,3-diphenylurea without Cl substitute with dihedral angles of 37.1° and 43.8° [19].
The hydrogen bonds N1–H1⋯O1 and N2–H2A⋯O1 connect molecules forming a chain structure. The bond angles of N1–H1⋯O1 and N2–H2A⋯O1 are 159.7(3)° and 152.3(2)°, and the bond length are 2.093 (2) and 2.229 (3) Å, respectively. Compared with the hydrogen bond of diphenylurea, bond angles of 157(3)° and 148(3)°, bond lengths of 1.954 (19) Å and 2.12(2)Å, the hydrogen bonds of the title compound are little longer, indicating that the hydrogen bonds between urea groups may be weakened after chlorine substitution.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: None declared.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlispro; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
5. Capacci-Daniel, C. A., Mohammadi, C., Urbelis, J. H., Heyrana, K., Khatri, N. M., Solomos, M. A., Swift, J. A. Structural diversity in 1,3-bis(m-cyanophenyl)urea. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 2373–2379; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5b00168.Search in Google Scholar
6. Dannecker, J. K., Rust, H. Crystal structure of N,N- diphenylurea. Cryst. Struct. Commun. 1979, 8, 429–432.Search in Google Scholar
7. Capacci-Daniel, C., Dehghan, S., Wurster, V. M., Basile, J. A., Hiremath, R., Sarjeant, A. A., Swift, J. A. Halogen/methyl exchange in a series of isostructural 1,3-bis (m-dihalophenyl) ureas. CrystEngComm 2008, 10, 1875–1880; https://doi.org/10.1039/b812138a.Search in Google Scholar
8. Rafilovich, M., Bernstein, J., Harris, R. K., Apperley, D. C., Karamertzanis, P. G., Price, S. L. Groth’s original concomitant polymorphs revisited. Cryst. Growth Des. 2005, 5, 2197–2209; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg050151j.Search in Google Scholar
9. Hiremath, R., Basile, J. A., Varney, S. W., Swift, J. A. Controlling molecular crystal polymorphism with self-assembled monolayer templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 18321–18327; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0565119.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Koshti, V. S., Thorat, S. H., Gote, R. P., Chikkali, S. H., Gonnade, R. G. The impact of modular substitution on crystal packing: the tale of two ureas. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 7078–7094; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ce01324d.Search in Google Scholar
11. Chutia, R., Das, G. Hydrogen and halogen bonding in a concerted act of anion recognition: F-induced atmospheric CO2 uptake by an iodophenyl functionalized simple urea receptor. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 15628–15637; https://doi.org/10.1039/c4dt00940a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Kirby, I. L., Pitak, M. B., Wenzel, M., Wilson, C., Sparkes, H. A., Coles, S. J., Gale, P. A. Systematic structural analysis of a series of anion receptor complexes. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 9003–9010; https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ce41503a.Search in Google Scholar
13. Lin, Q., Zhang, Y.-M., Wei, T.-B., Wang, H. N,N′–Bis(4- bromophenyl)urea. Acta Crystallogr. 2004, E60, o696–o698; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536804005495.Search in Google Scholar
14. Bentley, K. W., Proano, D., Wolf, C. Chirality imprinting and direct asymmetric reaction screening using a stereodynamic Brønsted/Lewis acid receptor. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12539; https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12539.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
15. George, S., Nangia, A., Lam, C.-K., Mak, T. C. W., Nicoud, J.-F. Crystal engineering of urea α-network via I … O2N synthon and design of SHG active crystal N-4-iodophenyl-N′-4′- nitrophenylurea. Chem. Commun. 2004, 40, 1202–1203; https://doi.org/10.1039/b402050b.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
16. Boiocchi, M., Del Boca, L., Gómez, D. E., Fabbrizzi, L., Licchelli, M., Monzani, E. Nature of urea-fluoride interaction: incipient and definitive proton transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 16507–16514; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja045936c.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
17. Yan, X.-C., Wang, H.-B., Liu, Z.-Q. [3-(2–Chlorophenyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]methanol. Acta Crystallogr. 2006, E62, o3007–o3008; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536806018952.Search in Google Scholar
18. Stepakov, A. V., Kinzhalov, M. A., Boitsov, V. M., Stepakova, L. V., Starova, G. L., Vyazmin, S. Y., Grinenko, E. V. A new approach to the synthesis of 4-(N-aryl)carbamoylmethyl-4,5-dihydropyridazin- 3(2H)-ones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 3146–3149; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2011.04.038.Search in Google Scholar
19. Huth, S. L., Threlfall, T. L., Hursthouse, M. B. Crystal Structure Report Archive; University of Southampton: Southampton, 2008; p. 681.Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of phenyl(3,3-dichloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-2-one)methanone, C7H4Cl2N2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 2-1,4-diaminobutane-N:N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride, C8H28Cl2CoN4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (4aR,7S)-7-hydroxy-7-isopropyl-1,1-dimethyldecahydro-2H,6H-8a,4a-(epoxymethano)phenanthren-12-one, C20H32O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)urea, C14H11Cl3N2O
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium-1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate – 1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine – water (1/1/1), C17H37N9O3S2
- Tetrabutylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate—1,2,4-thiadiazole-3,5-diamine— water (1/1/1), C21H45N9O3S2
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Cl2MnN5O4
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3 N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1 O-erbium(III) chloride – dimethylformamide – water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr
- Crystal structure of (diaqua-bis(phenanthroline-K 2 N,N′)-tetrakis(m 2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-K 4 O,O:O′:O″;K 2 O:O′)dierbium (III) phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Er2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H17F3O3
- The crystal structure of 4–(4,4,5,5–tetramethyl–1,3,2–dioxaborolan–2–yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3
- The crystal structure of catena–poly[aqua(1-naphthoato-κ 2 O,O′)-(μ-1-naphthoato-κ 4 O:O,O′:O′)lead(II)], C22H16O5Pb
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(pyren-1-yl)butyl-4-nitrobenzoate, C27H21NO4
- Crystal structure of cyclo-(bis(µ2-3,3′-(1H-imidazole-3-ium-1,3-diyl)dipropionato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O″′)-dinitrato-κ2 O,O′-tetraoxido-diuranium(VI) C18H22N6O18U2
- The crystal structure of catena-[nitrato-κ 2 O,O′-(μ 3-3-iodobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O:O′:O″,O‴)-(2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine-κ 3 N,N′,N″)lanthanum(III)], C23H14IN4O7La
- Redetermination of crystal structure of [bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ 3 N,Nʹ,Nʺ]chloridopalladium(II) chloride monohydrate
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-[bis(m2-4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k2O:O')-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1O)-praseodymium (III) monohydrate], C27H26N9O10Pr
- Crystal structure of trans-diaqua-bis(methyl methylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2 N,N′) nickel(II) iodide semihydrate, C6H22N6O2NiS2I2·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluoro-4-methyl-5-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thio)phenyl)isoindolin-1-one, C17H13F4NOS
- The crystal structure of di-μ-1-naphthylacetato-κ 3 O,O′:O;κ 3 O:O,O′-bis[(1-naphthylacetato-κ 2 O,O′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ 2 N,N′)lead(II)] monohydrate, C68H54N4O9Pb2
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium guanidinium 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate monohydrate, C27H44N4O7S
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) terephthalate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (1/2/4) C18H40N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-morpholinobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H20FNO2
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ 3-5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 3 O,O,O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis-(4-pyridyl)-propane-κ 2 N,N′)-dizinc(II))] – 5-bromobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [2/1], C37H29Br3N2O14Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3-phenylene bis(4-methylbenzenesulfonate), C20H17BrO6S2
- Crystal structure of europium dichromium icosaaluminum, EuCr2Al20
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-di((E)-benzylidene) isophthalohydrazide dihydrate, C 22 H 22 N 4 O 4
- Crystal structure of 7α,11α-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-pyridin-3-ylmethylidene]benzohydrazide, C13H10ClN3O
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-(1-(2-((E)-4-isopropylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene) chroman-2,4-dione, C21H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of E-7-fluoro-2-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H12F4O
- Crystal structure of bis(6-aminopyridine-2-carboxylato–k2O,N)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-k1 O)zinc(II), C18H24N6O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-methyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thione, C25H31F3N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrapropylammonium bicarbonate–1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/2/1), C30H72N10O7S2
- Crystal structure of tris(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)iron(II) triiodide – dichloromethane (2/1), C61H50Cl2Fe2I12N12
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-3-[2-(1,3,3-trimethyl-1,3-dihydro-indol-2-ylidene)-ethylideneamino]-but-2-enedinitrile, C17H17N5
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19ClN2O
- Crystal structure of potassium bis(pentaselenido-κ 2 Se 1,Se 5)palladate(II), K2[Pd(Se5)2]
- The crystal structure of 5,10-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-5,10-dihydro-[1,2,3,4]tetrathiocino[5,6-b:8, 7-b′]diindole, C22H22N2O2S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-iodophenyl)-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione, C8H4INS3
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O:O′}-bis{μ2-(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ3 O,O′:O)- bis{(4-acetyl-phenoxy)acetato-κ2 O,O′}-bis(phenanthrolin-κ2 N,N′)didysprosium(III) tetrahydrate, C84H78N4O28Dy2
- Crystal structure of Eu2Pd3.37(1)Zn13.63(1)
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4-(methoxy-carbonyl)phenyl 2-chloro-4-fluorobenzoate, C16H12ClFO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-dicyanamide-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-vinylpyridine-κN)-copper(II)], C18H14CuN8
- The crystal structure of iguratimod-dimethylformamide (1/1), C17H14N2O6S·C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-bromo-2-formylphenoxy)zinc(II), C14H12Br2O6Zn
- The crystal structure of tetra(1-ethylimidazole-κ 1 N)-[μ 4-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 4 O, N, O′, N′]-trioxido-divanadium, C25H33N10O7V2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2


